7. Electrical and Auxiliary systems
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Electricity
A form of energy caused by the movement of electrons.
Transformer> Service Entrance> Meter> panel board
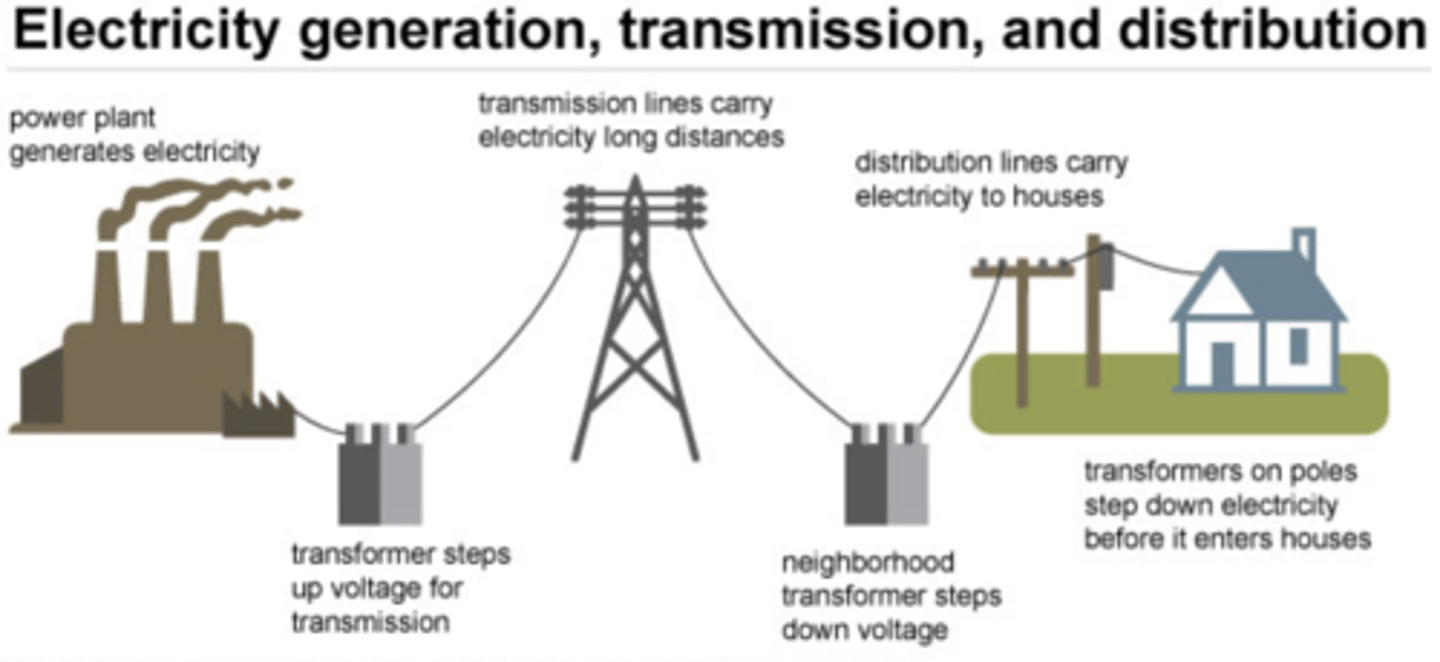
How does Electricity travel from Electric Post to household
Electricity distribution
Circuit
the complete path that an electric current travels along
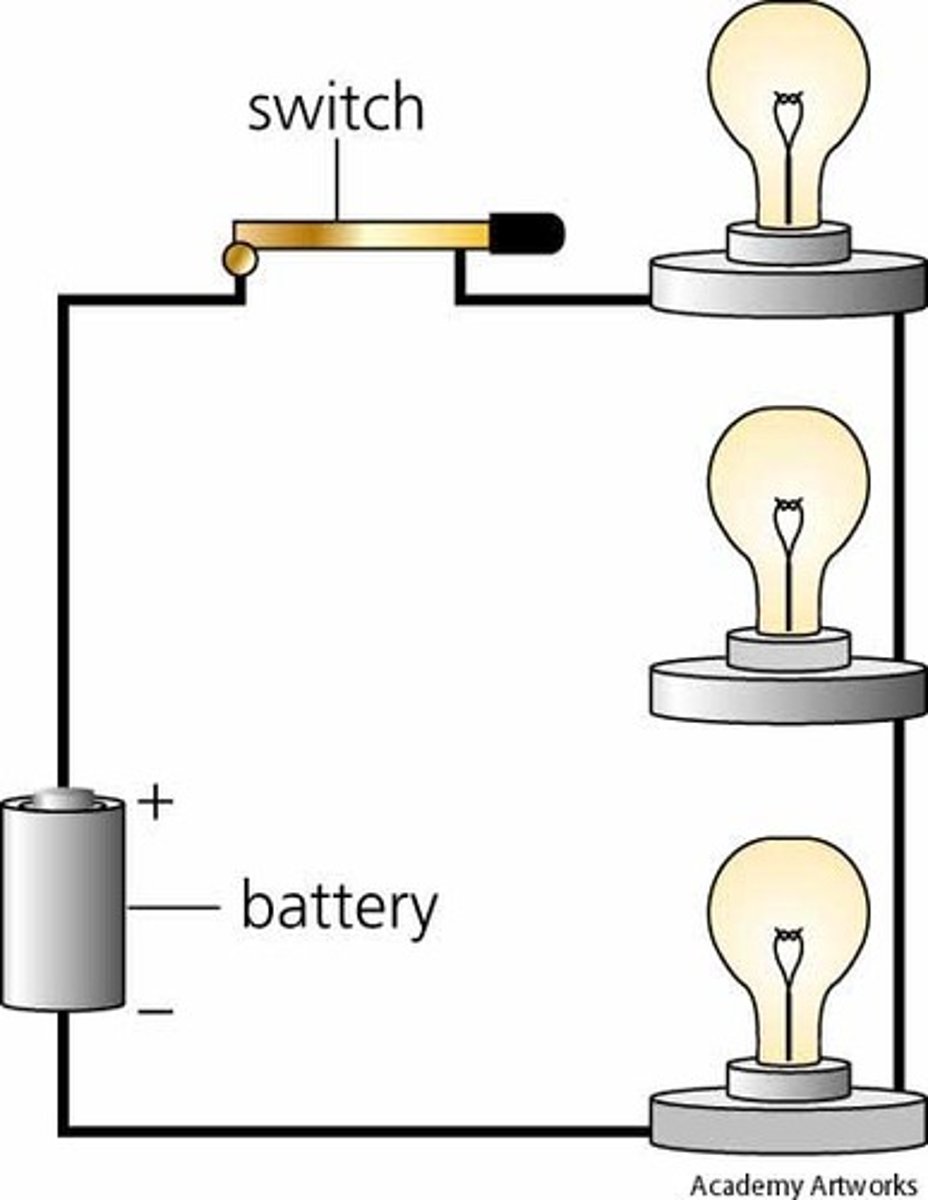
series circuit
An electric circuit with only one path through which charge can flow
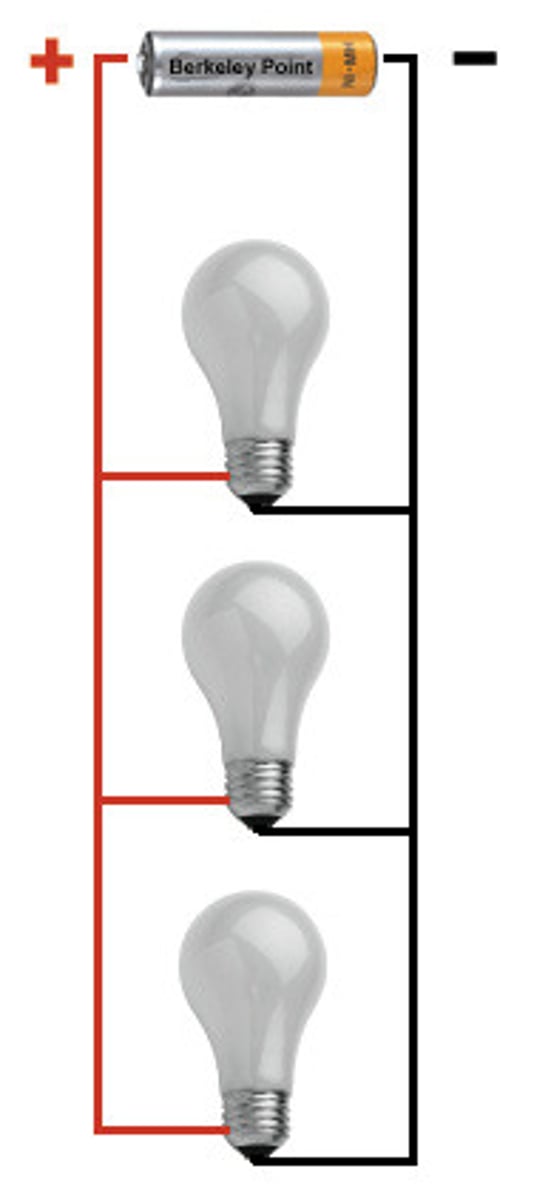
parallel circuit
A closed electrical circuit in which the current is divided into two or more paths and then returns via a common path to complete the circuit.
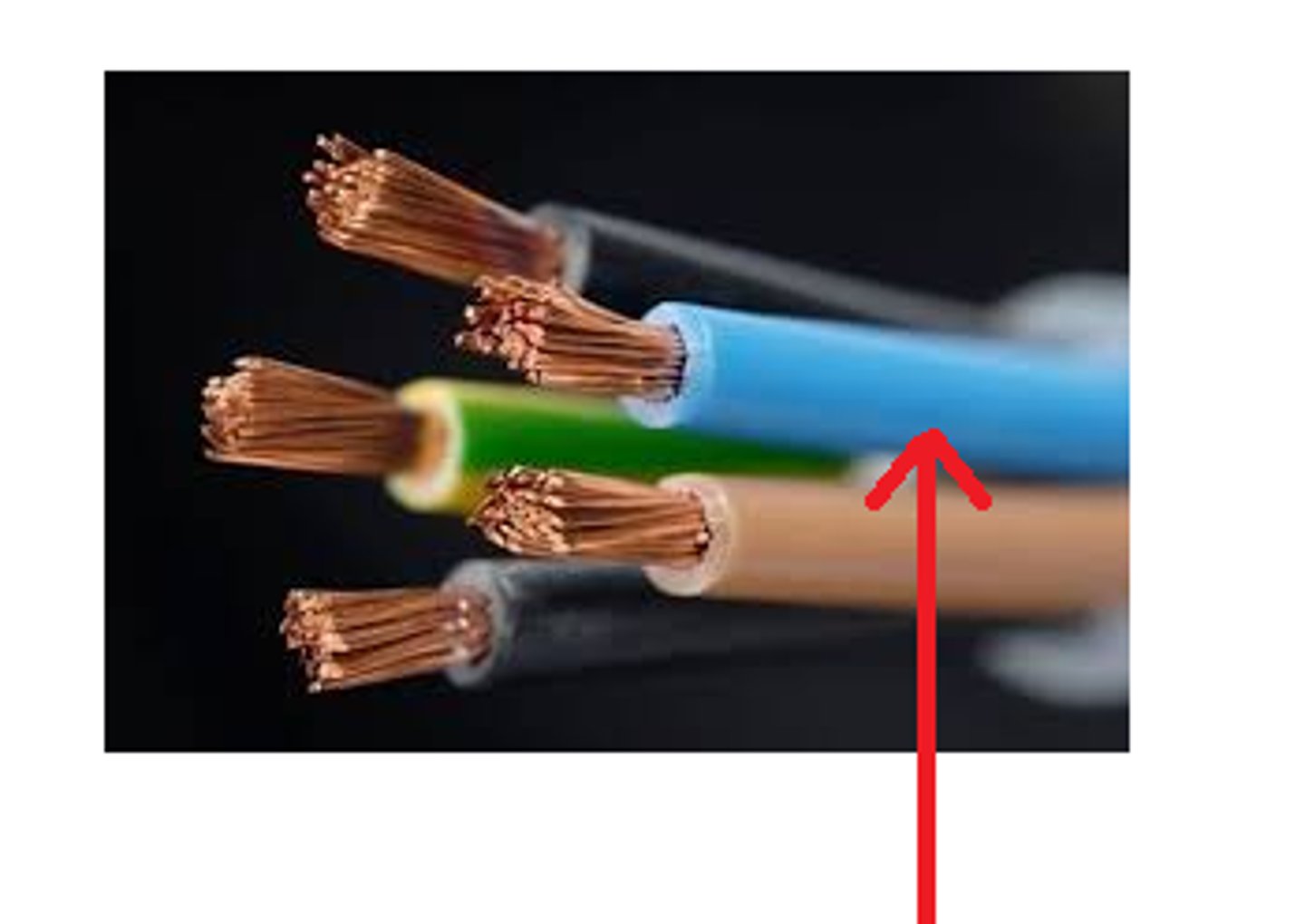
Conductors
materials that allow electric charges to flow through them easily; generally metallic material
Gold, silver and Platinum
best conductors are Precious metals (3)
Copper
Most commonly used conductor
Wires
Small conductor; no. 8 AWG or smaller
Cables
Medium conductor; No. 6 AWG or smaller
Bus bars
Big conductor; used inside large panels; for large amount of power
Cord
insulated stranded wire that conducts electricity; may be SOLID or STRANDED
Insulator
A material that does not allow heat or electrons to move through it easily.
Ampacity
The amount of electric current that can flow through a wire.
thermoplastic
Kind of conductor: abbreviated "T"
Moisture-resistant Thermoplastic
Kind of conductor: abbreviated "TW"
Heat-resistant Thermoplastic
Kind of conductor: abbreviated "THHN"
Moisture and Heat-resistant thermoplastic
Kind of conductor: abbreviated "THW"
Moisture and Heat-resistant Thermoplastic (w/ Nylon coating)
*N stands for nylon
Kind of conductor: abbreviated "TWHN"
Conduits
Roughing ins; Circular raceways used to enclose wires and cables; either made out of metal or PVC plastic
Rigid steel conduits (RSC)
Heavy-wall steel conduits; used outdoors for service entrance
Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC)
Medium thickness conduit. Also threaded.
Electric Metal tubing (EMT)
Thin-wall steel conduits.
Raceways
channels or wiring accessories so designed for holding wires, cables and bus bars that are either made of metal, plastic, or any insulating medium.
Outlets
a point in an electrical circuit from which current may be drawn
Receptacles
The wiring device in which the appliance cord is plugged into.
Switches
Devices for making, breaking or changing conditions in an electrical circuit
2-way switch
directs the flow of current to one of two routes, according to its position
3-way switch
Controls light from 2 locations
4 way switch
Controls light from 3 or more locations
Electrolier
Also called Multi-Circuit switches; controlling mutiple light fixtures
Momentary Contact switches
Switch for doorbells; has a spring so that it will return to its original position as soon as the handle or button is released.
Dimmer switch
rheostat; can increse or decrease the intensity of a light fixture
time controlled switch
Switch that has a precision of low-speed miniature drive motor or a timer
Air switch
A switch in which the interruption of a circuit occurs in air
Key switch
a switch operated only by inserting a key or a card. Also called a card switch. Used in hotels (key card)
Intelligent systems
Switch using touchpad
Float switch
A switch controlled by a conductor floating in a liquid; detect level of liquid in a tank
Mercury switch
An especially quiet switch that opens and closes an electric circuit by shifting a sealed glass tube of mercury so as to uncover or cover the contacts
Overcurrent protection devices
Prevent overheating or burning of a circuit/ devices due to faults like excessive loads or a short circuit
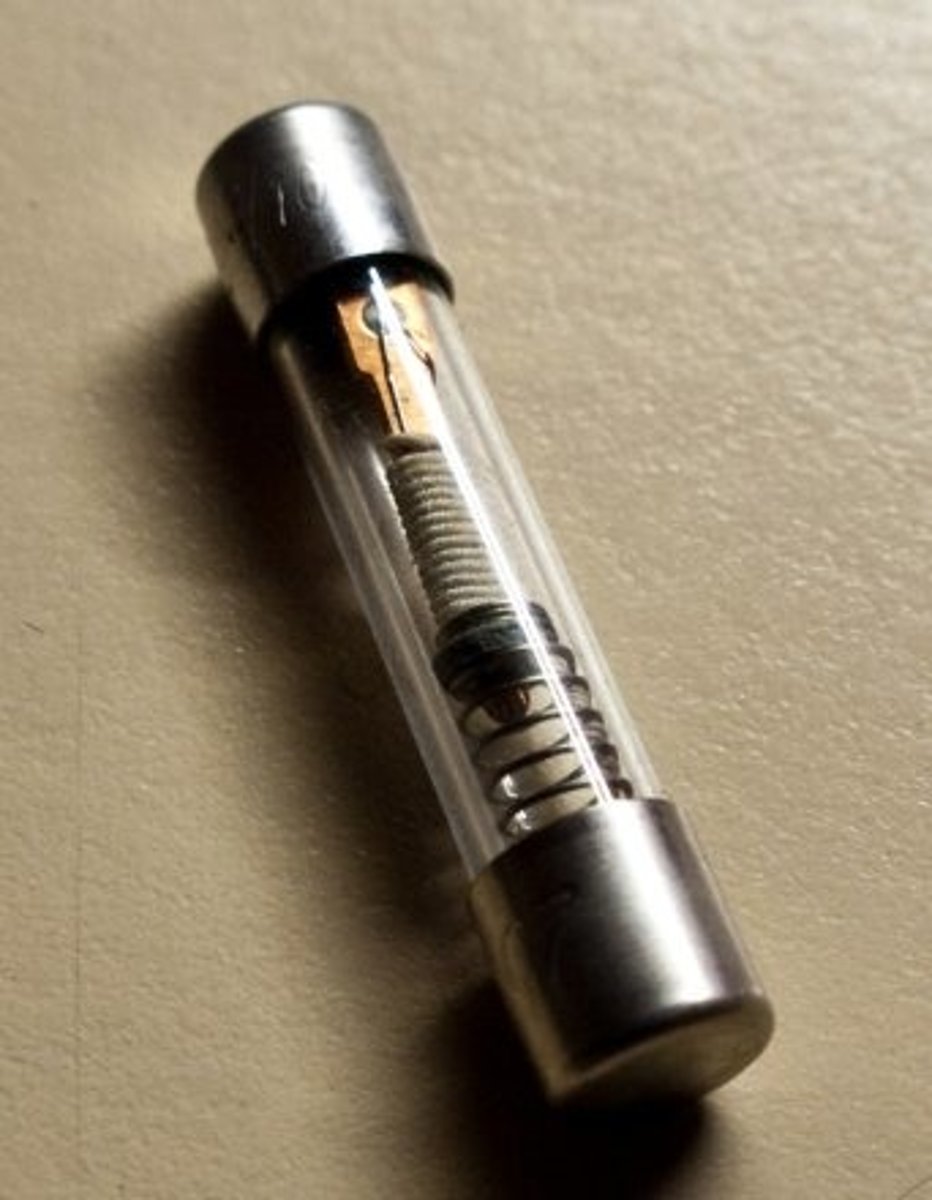
Fuse
A safety device with a thin metal strip that will melt if too much current passes through a circuit

Circuit breaker
A reusable safety switch that breaks the circuit when there is fault in the circuit
GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter)
A special electrical outlet that has a circuit breaker built in which trips due to even small changes in current; normally installed in WET LOCATIONS bathrooms, kitchens, laundry rooms etc.
AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter)
A device intended to provide protection from the effects of arc faults
Switchboards
Provide switching and feeder protection to larger buildings; free standing assemblies of switches, fuses, and circuit breakers

Unit substations
(Transfer Load Centers) an assembly of primary switch-fuse-breaker, step-down transformer, meters, controls, bus bars and secondary switchboard. Used in large facility or COMPLEX of buildings
Electrical Engineers
Has the liability over electrical plans
Electrical symbols

Load schedule
Tabulated form of the electrical layout showing the circuit identities, quantities and Engineer's computation
Auxiliary plans
also known as Extra Low-Voltage Plans/ Layout; showcases CCTV, CATV, smoke detector, telephone, Speakers, Internet, IT server layout and is under the responsibility of ECE or Electronics Communications Engineer
closed circuit television (CCTV)
Video cameras and receivers used for surveillance in areas that require security monitoring.
Community Antenna Television (CATV)
Delivering television programming to consumers via radio frequency signals transmitted through coaxial cables
Fire Detection & Alarm system
Provides audible and visual signals as a result of the operation of manual or automatic fire alarm initiating devices