Biology Year 9 - Unit 1 Cells
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
In 1663 and 1664, Hooke made his microscope and made many scientific findings with it. Hooke coined the term "cell", suggesting a resemblance between plant structures and honeycomb cells.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Cell
The basic and fundamental unit of life, possessing a highly organized structure that carries out vital functions.
Organelles
Smaller structures within a cell that perform specific functions and are varied between different cell types.
Light Microscope
A tool that identifies, observes, and magnifies objects by transmitting light through lenses.
Electron Microscope
A microscope that uses a beam of electrons to provide higher magnifications and resolution for images.
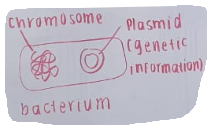
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells that lack a defined nucleus and are typically unicellular organisms.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells that contain a defined nucleus and may form multicellular organisms.
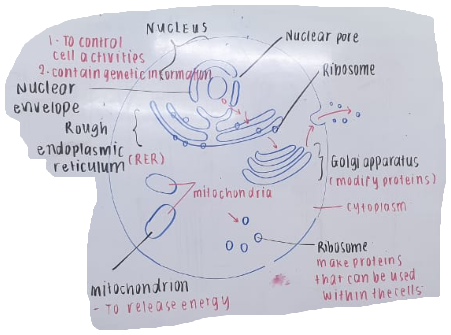
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
A network of membranes involved in the transport and processing of proteins and lipids, with two main types: Rough and Smooth.
Ribosome
Small structures that synthesize proteins, may be free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Golgi Apparatus
An organelle key in the processing, packaging, and transport of proteins and lipids produced in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Mitochondria
Organelles present in eukaryotic cells, responsible for energy generation through cellular respiration.
Chloroplasts
Organelles found in plant cells that contain chlorophyll which carries out photosynthesis.
Vacuoles
Fluid-filled spaces within cells that store nutrients and waste, regulating turgor pressure and osmotic balance.
Cell Wall
A rigid layer surrounding certain types of cells that provides protection and shape. For plant cells, it is made of cellulose.
Ovum
The female sex cell made in the ovaries and released during ovulation.
Sperm Cell
The male sex cell produced in the testes, characterized by a tail for movement and high energy-producing mitochondria.
Red Blood Cell
Cells found in blood that transport oxygen, characterized by their disc shape and lack of a nucleus.
White Blood Cells
Cells of the immune system that help fight infections, capable of changing shape to engulf pathogens.
Levels of Organization
The hierarchical structure of biological organization, from cells to tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms.
Ciliated Cells
Cells equipped with tiny hairs called cilia that aid in moving mucus and dust out of airways.
Magnification
The observed size of an image divided by the actual size of the specimen.
Chitin
The substance the cell wall of fungal cells are made of