Pet Blood Bank Seminar
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Criteria for blood donor dogs (6)
Fit/healthy
1-8 years old
at least 25kg
Relaxed/confident temperment
Born and remained in UK/Ireland whole life
Not on long term medication
List the types of blood products (6)
Fresh/Stored Whole Blood
Packed Red Blood Cells
Fresh Frozen Plasma/ Frozen Plasma
Cryosupernatant
Cryoprecipitate
Platelet concentration
Shelf life of Fresh/Stored Whole Blood and components (6)
Fresh whole blood for 6 hours at room temperature, then stored in fridge for 21 days as stored whole blood
Contents:
Erythrocytes
Haemostatic proteins
Plasma proteins
Immunoglobulins
Antiproteases
Platelets
3 uses of Whole Blood
- haemostatic resuscitation
- haemostatic protein deficiency with blood loss
- Help arrest active haemorrhage in a patient with thrombocytopenia or thrombopathia
Shelf life and component of Packed Red Blood Cells
42-day shelf life
Erythrocytes only
2 uses of Packed Red Blood Cells
anaemia
haemostatic resuscitation (may be combined with fresh frozen plasma)
Shelf life and 4 components of Fresh Frozen Plasma
Stores for 1 year
Contents:
Haemostatic proteins
Antiproteases
Immunoglobulins
Plasma proteins
8 uses of Fresh Frozen Plasma
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Adder bite
Consumptive coagulopathy
Haemophilia (A and B)
von Willebrand’s Factor Deficiency
Angyostrongylus bleeding
Acute haemorrhagic shock
Shelf life and 10 components of frozen plasma and cryosupernatant
FP = 5 years (including one year as fresh frozen plasma)
Cryo - 1 year
8 uses of frozen plasma and cryosupernatant
Haemorrhagic gastroenteritis
Hepatic coagulopathy
Haemophilia B
Hypoproteinaemia
Resuscitative IVFT
Immunoglobulin transfer
Hypoalbuminaemia (cryosupernatant)
Shelf life and 5 components of cryoprecipitate
1 year
Contents = Factor I, VIII, XIII, xWF, fibronectin
3 uses of cryoprecipitate
Von Willebrand’s disease
Haemophilia A
Hypofibrinogenemia
Shelf life and components of Platelet concentrate
3 days
Platelets and some RBC (so typing is reccomonded)
2 uses of platelet concentrate
Uncontrolled/life-threatening haemorrhage due to thrombocytopenia/thrombocytopathia
Prophylactic treatment in patients with hereditary thrombopathia before surgery
What can happen following blood transfusion without typing the blood
Acute Haemolytic Transfusion Reaction due to intra/extravascular cell destruction
What is the most common blood type in dogs
DEA 1
Purpose of crossmatching over blood typing
The number of blood types is not known, so these tests directly determine if there will be a reaction between the donor and recipient
Explain the difference between major and minor cross matching and when would they be used?
Major - check recipient plasma for alloantibodies against donor erythrocytes
Minor - check donor plasma for alloantibodies against recipient erythrocytes. This can be used when using non-cellular products
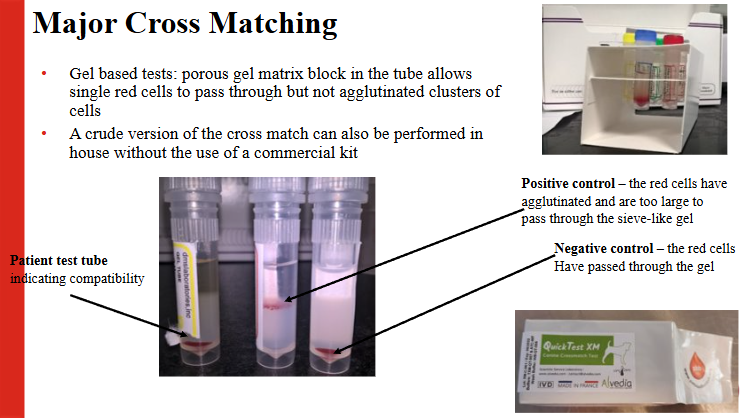
What 2 reactions are seen when cross matching incompatible blood types?
Haemagglutination (clump)
Haemolysis (red plasma)
What are the blood types of cats and their reactivity patterns (4)
A- low amount of weak anti-B antibodies
B - high amount of anti-A antibodies
AB - no antibodies for either A or B antigen
Mik negative/positive