Chapter 8 Lipids
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Lipids
hydrophobic/amphipathic
fats/oils/vitamins/hormones/non-protein membrane components
Major purposes of lipids
energy storage
cell membrane development
serving as a component of hormones/vitamins
Major classes of lipids
fatty acids
triacylglycerols
glycerophospholipids
sphingolipids
waxes
isoprene-based lipids
Fatty Acids
long carbon chain + carboxylic acid
commonly found in esterified form with glycerol
saturated or unsaturated
Unsaturated
contains double bonds
classified as omega 3, omega 6, or omega 9
Saturated fatty acids (let me pack saturated acid)
lauric acid 12C
myristic acid 14C
palmitic acid 16C
stearic acid 18C
arachidic acid 20C
Lauric Acid
saturated
12 carbons
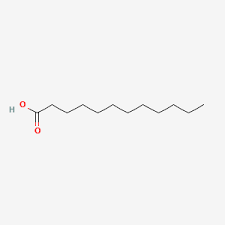
Myristic Acid
saturated
14 carbons
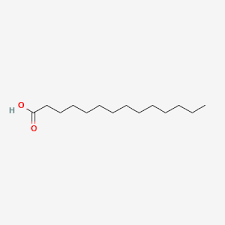
Palmitic Acid
saturated
16 carbons
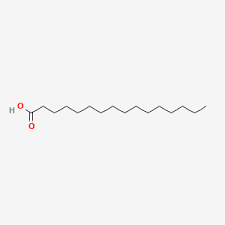
Stearic Acid
saturated
18 carbons
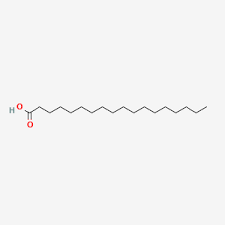
Arachidic Acid
saturated
20 carbons
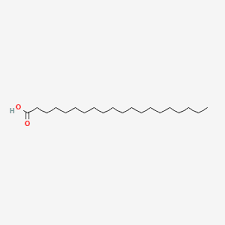
Unsaturated fatty acids (pocket only lean alphas gammas and arachnids)
palmitoleic acid 16:1 omega 7
oleic acid 18:1 omega 9
linoleic acid 18:2 omega 6
alpha-linolenic acid 18:3 omega 3
gamma-linolenic acid 18:3 omega 6
arachidonic acid 20:4 omega 6
Palmitoleic Acid
unsaturated
16:1
omega 7
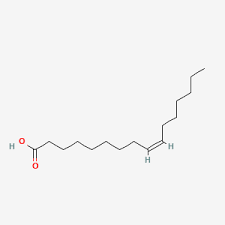
Oleic Acid
Unsaturated
18:1
omega 9
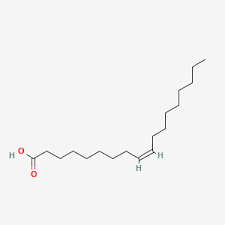
Linoleic Acid
unsaturated
18:2
omega 6
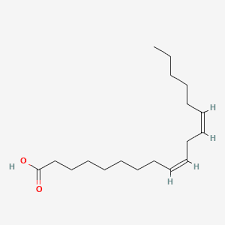
Alpha-Linolenic Acid
unsaturated
18:3
omega 3
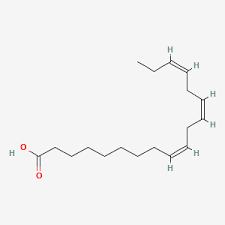
Gamma-Linolenic Acid
Unsaturated
18:3
omega 6
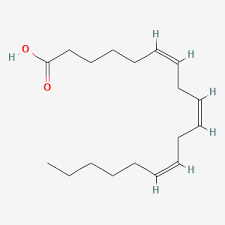
Arachidonic Acid
unsaturated
20:4
omega 6
what configuration are most unsaturated fatty acids in? how does it affect the chain?
cis configuration
causes bend/kink
how does the saturation level affect lipid fluidity?
lower levels of saturation result in higher lipid fluidity and lower melting points
what essential fatty acids are not synthesized by mammals?!
linoleic acid (obtained from diets)
alpha-linolenic acid
why is arachidonic acid important?!
not in plants
synthesized by animals from linoleic acid
can create essential molecules and precursors for hormones
what class of compounds can fatty acid be a precursor for?
essential fatty acids can serve as a precursor for synthesis of eicosanoids ex. prostaglandins that exert hormone-like effects on processes
How are trans fatty acids formed?
Trans fatty acids are formed by some bacteria via double bond migration and isomerization.
ex. found in butter, milk, animal meat
How are processed fats formed?
Formed via partial hydrogenation of polyunsaturated oils
Consequences of diets high in trans/saturated fats
increased risk for heart disease/strokes
high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol
low HDL cholesterol
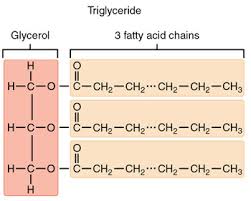
Triacylglycerols (triglyceride)
glycerol esterified with three fatty acids
same fatty acids = simple TAG
different fatty acids = mixed TAG
why are triacylglycerols a major energy source?
rich in highly reduced carbons used in oxidative reactions
hydrophobic nature allows them to aggregate in highly anhydrous forms (high energy density)
Glycerophospholipids
glycerol motif
phosphate group esterified at C3
one of the largest groups of lipid
essential cell membrane component
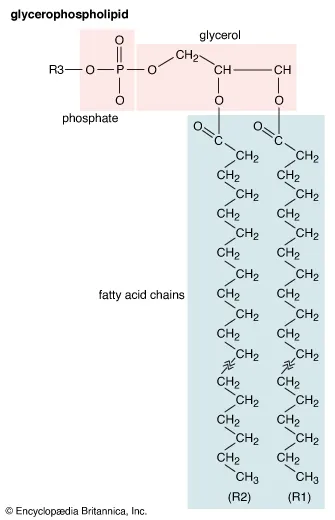
Phosphatidic acid
parent compound
important intermediate in the biosynthesis of the more common glycerophospholipid
-OH group connected to P
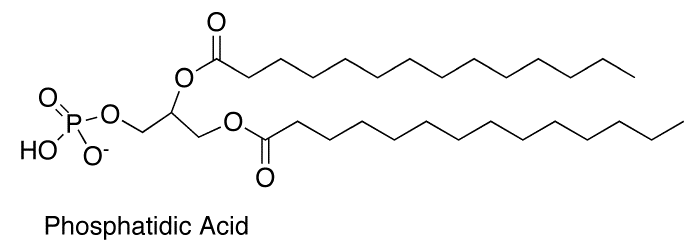
Ether glycerophospholipids
ether linkage at C1 instead of hydroxyl
ex. platelet activating factor (PAF) a signal molecule
Sphingolipids
an 18 carbon amino alcohol (sphingosine) backbone instead of glycerol
a fatty acid is joined via amide linkage
ex. sphingomyelins
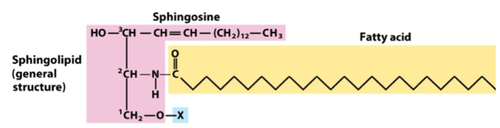
Glycosphingolipids
ceramides with one or more sugars in a glycosidic linkage at the 1-hydroxyl group
Waxes
esters of long-chain alcohols with long-chain fatty acids
insoluble
animal skin and fur, plant leaves, bird feathers are wax-coated
ex. Lanolin is a wool wax used in cosmetics
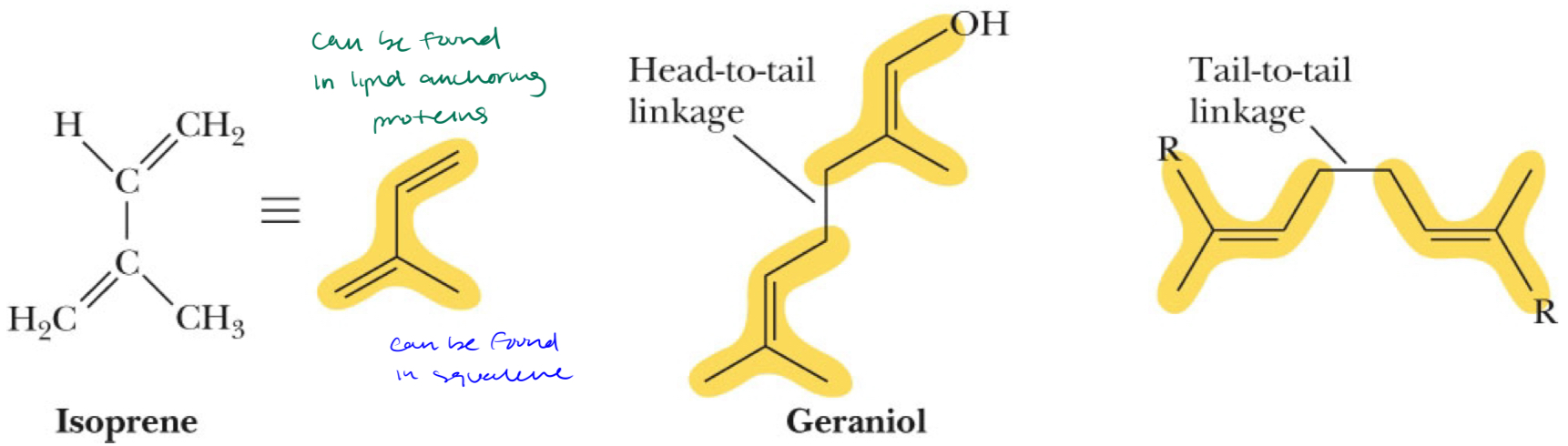
Terpenes
class of lipids formed from combinations of two or more isoprene molecules
head to tail linkage
tail to tail linkage
can be found in lipid anchoring proteins and squalene
Squalene
an important intermediate in cholesterol synthesis
Monoterpenes
consist of two isoprene units
occur in all higher plants i.e. lemons, roses, etc
ex. limonene, citronellal
Sesquiterpenes
consist of three isoprenes
ex. bisabolene
Diterpenes
consist of four isoprene units
ex. phytol
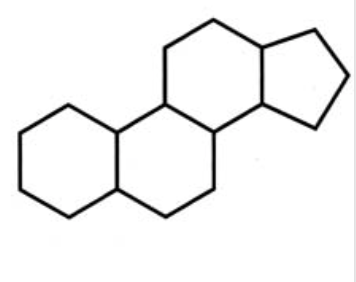
Gonane
a common motif for steroids
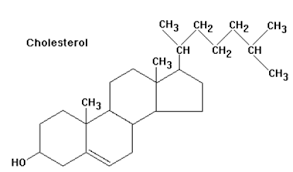
Cholesterol
principle component of animal plasma membranes
weakly polar due to hydroxyl group on C3
amphipathic polar nature allows it to enter membranes and disrupt packaging
How does cholesterol affect the permeability of the plasma membrane?
hydroxyl group interacts with polar headgroups of the membrane
bulky steroid and alkyl chain is embedded in the membrane
reduced permeability to protons and sodium ions
provides stability to cell membrane
Describe the relationship between hormones and receptors using affinity and concentration
Hormones travel through bloodstream to enter cells and bind to highly specific receptor
Hormones have high affinity for their receptors = low concentration of hormone is sufficient
What does Km represent?
michaelis menten constant
[S] when Vmax is ½
What does Kd represent?
enzyme affinity for a substrate/ligand
Low Kd = greater affinity
High Kd = weaker affinity
What does Kcat represent?
Kcat = K2
the number of times the enzyme converts substrate to product per unit of time
What is considered low Kd?
low Kd = greater affinity = low [S] required
100 microMolar or less
What are some hormone families derived from cholesterol in animals?
Androgens
Progestins
Glucocorticoids
What are the bile acids?
cholic acid and deoxycholic acid
significant role in repackaging fatty acids
detergent molecules assisting in breakdown of dietary lipids for oxidation
What is the active form of vitamin D?
1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
Step 1: vitamin D synthesis
substrate: cholesterol precursor
→→→
product: 7-hydroxycholecalciferol
Step 2: vitamin D synthesis
substrate: 7-hydroxycholecalciferol
sun → skin
product: cholecalciferol
Step 3: vitamin D synthesis
substrate: cholecalciferol
25-hydroxylase → liver
product: 25-hydroxycholecalciferol
Step 4: vitamin D synthesis
substrate: 25-hydroxycholecalciferol
1-a-hydroxylase → kidney
product: 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
What are the physiological effects of vitamin D?
hormone involved in mineral metabolism and bone growth
facilitate intestinal absorption of calcium/phosphate/magnesium
What are some disease states of vitamin D?
Rickets - deficiency in babies that results in bone deformities ex. bowed legs
Osteomalacia - deficiency in adults that results in soft/weak bones