AP Macroeconomics: Unit 1 - Module 3: The Production Possibilities Curve Model
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Production Possibilities Curve
The _____ is a model which helps economists think about the trade-offs every economy faces.
efficiency, opportunity cost, economic growth
The production possibilities curve helps us understand three important aspects of the real economy: _____, _____, and _____.
Trade-off
A _____ is when you give something up in order to have something else.
Production Possibilities Curve
A _____ illustrates the trade-offs facing an economy that produces only two goods. It shows the maximum quantity of one good that can be produced for each possible quantity of the other good produced.
feasible, efficient
If a point lies on the curve (A, B, or C), it is _____ and _____.
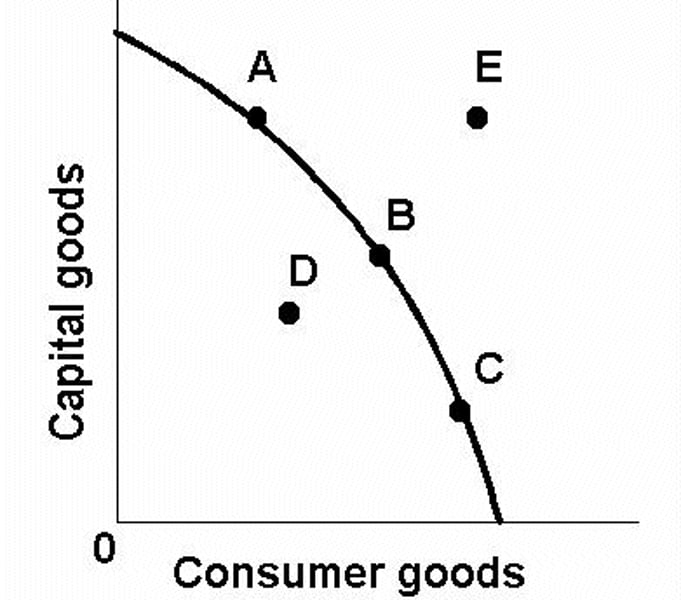
feasible, inefficient
If a point lies inside the curve (D), it is _____ but _____.
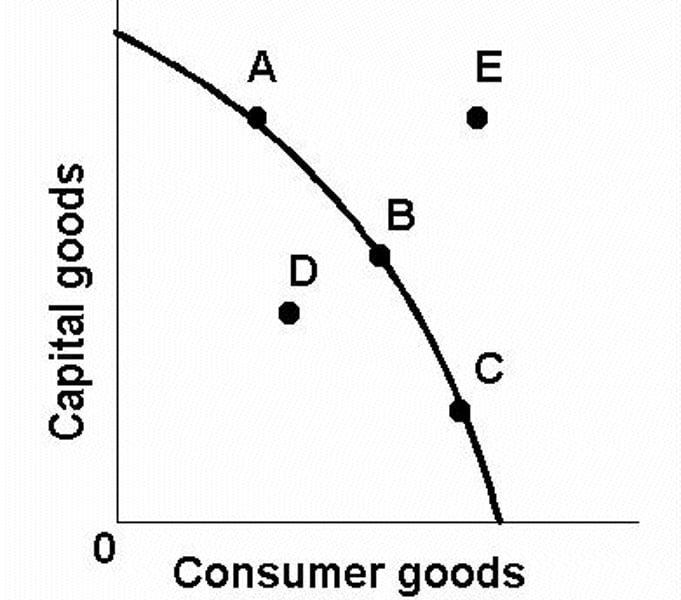
not feasible, inefficient
If a point lies outside the curve (E), it is _____ and _____.
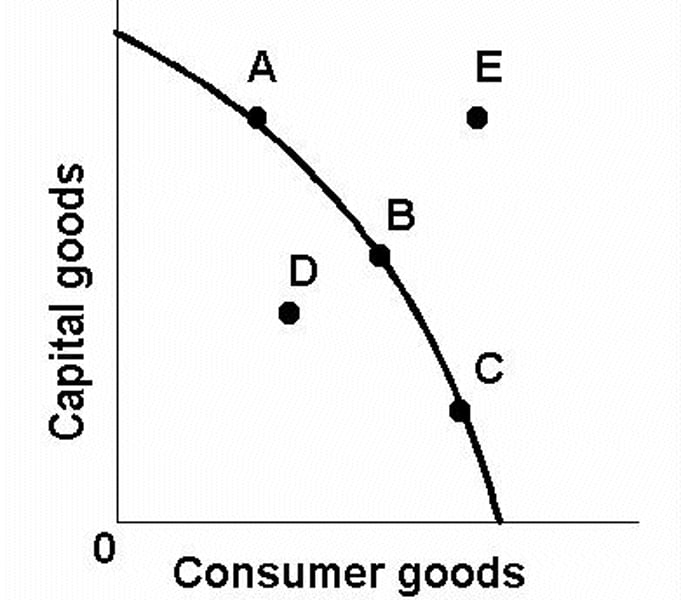
axis
If a point lies on the _____, all resources could be spent dedicated to that point. However, there would not be any resources left to produce the other point lying on the axis.
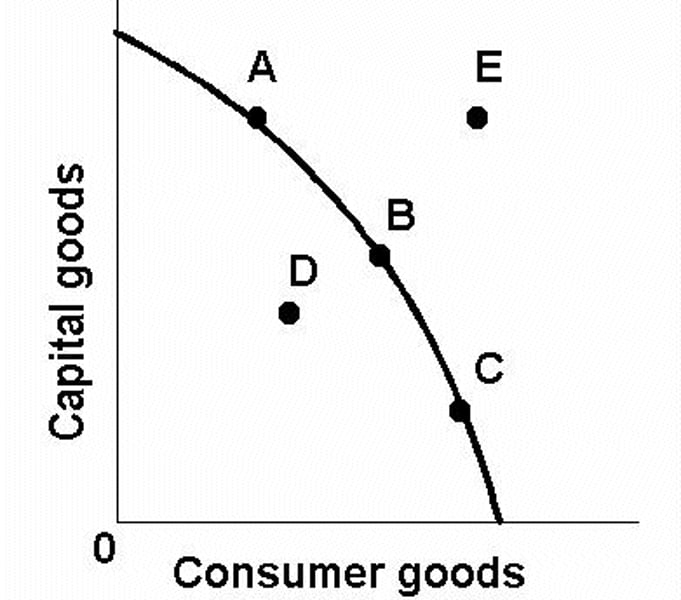
efficient
An economy is _____ if there are no missed opportunities, meaning that there is no way to make some people better off without making other people worse off.
efficiently
When an economy is using all of its resources _____, the only way one person can be made better off is by rearranging the use of resources in such a way that the change makes someone else worse off.
Efficient in Production
An economy is _____ when an economy is producing at a point on its production curve.
Inefficient
An _____ economy is missing the opportunity to produce more of both goods.
produce more output if those people were employed
An example of inefficiency in production occurs when people in an economy are involuntarily unemployed; they want to work but are unable to find jobs. This economy is not efficient in production because it could _____.
employed
The production possibility curve shows the amount that can possibly be produced if all resources are fully _____.
efficient in allocation
Efficiency also requires that the economy allocate its resources so that consumers are as well off as possible. If an economy does this, we say that it is _____.
production, allocation
Efficiency for the economy as a whole requires both efficiency in _____ and efficiency in _____.
production possibilities curve
The _____ is also useful as a reminder that the true cost of any good is not only its price, but also everything else in addition to money that must be given up in order to get that good, the opportunity cost.
opportunity cost
The slope of a straight-line production possibilities curve is equal to the _____, specifically the cost for the good measured on the horizontal axis in terms of the good measured on the vertical axis.
increasing
In reality, opportunity costs are typically _____. Producing a small amount of goods has a smaller opportunity cost because it requires less resources, but producing more goods can give up a considerably large amount of other good output.
production possibilities
Economic growth is the expansion of the economy's _____. The economy can produce more of everything. It is an _____ shift of the production possibilities curve.
Economic growth
What is this shift called?
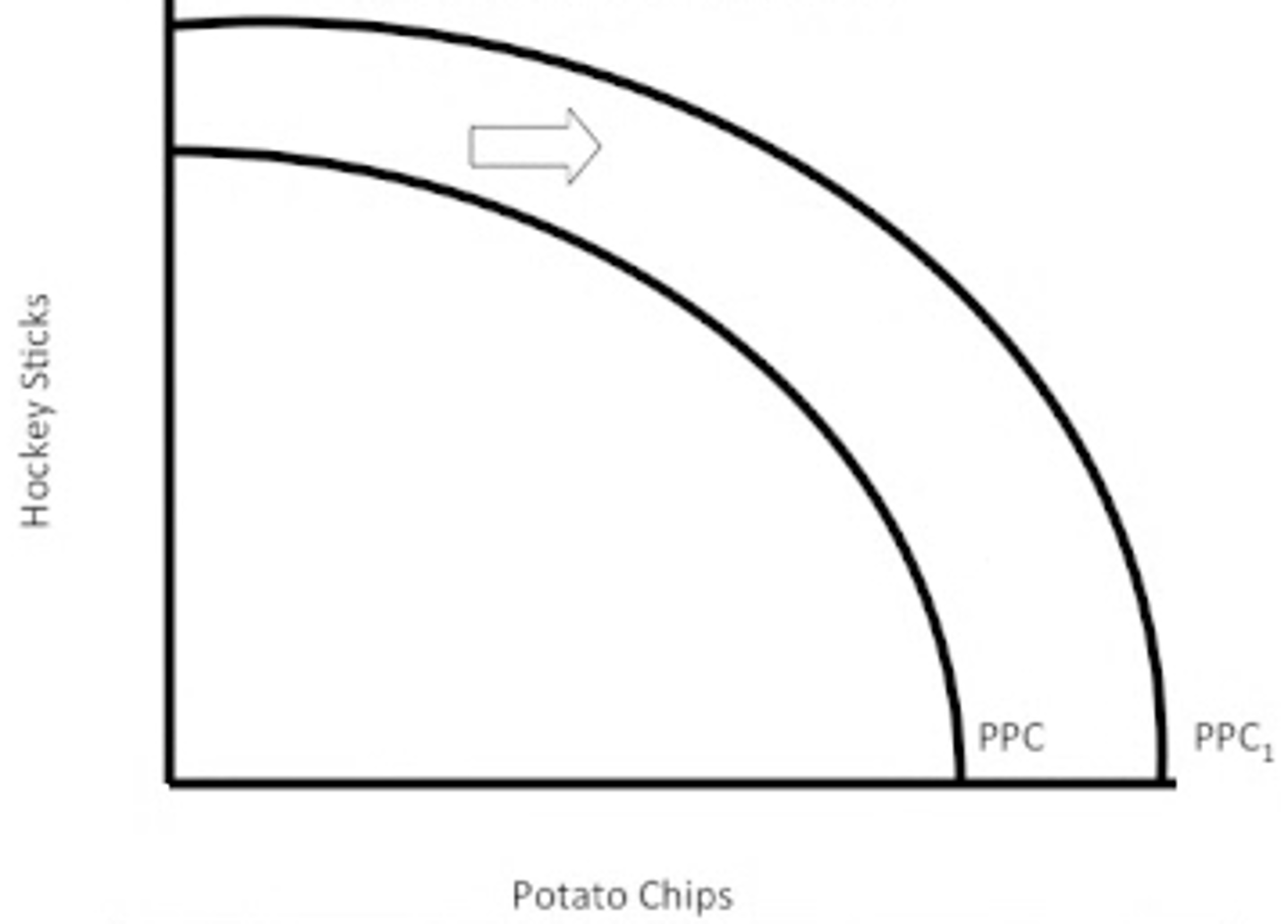
resources, technology
The two general sources of economic growth is an increase in the _____ used to produce goods and services (labor, land, capital, entrepreneurship) and progress in _____.
Technology
_____ is the technical means for the production of goods and services.