Lecture 8 : Renal Function Tests
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
Clearance Tests
Creatinine
Cystatin C
Beta2-Microlobulin (B2M)
Radionucleotides
Urea
Glomerular Filtration Tests
Clearance Tests
standard tests used to measure the filtering capacity of the glomeruli
Measures rate in milliliters per minute at which kidneys are able to remove a filterable substance from the blood.
must be neither reabsorbed nor secreted by the tubules
Stability in urine during a 24hr collection
Consistency of the plasma level
Availability to the body and tests to analyze
Factors to be considered in selecting a clearance test substance
Exogenous Procedure
Endogenous Procedure
Two categories of clearance tests
Exogenous Procedure
Test that requires an infused substance (foreign to the body)
Endogenous Procedure
Suitable substance is already in the body
Creatinine
Beta2-Microglobulin
Cystatin C
Radioisotopes
Primary substances used in clearance tests
To assess glomerular filtration rate (GFR) using serum creatinine and specific equations.
What is the purpose of estimating kidney function?
Cockcroft-Gault (1973)
MDRD (1999)
CKD-EPI (2009)
CKD-EPI (2021)
What are the four main equations used to estimate kidney function?
Two measurements of 24-hour creatinine excretion per kg (n = 236).
What is the Cockcroft-Gault (1973) study design?
18–92 years old, all white men.
What population was used in the Cockcroft-Gault equation?
CrCl = (140 − age) × weight / (72 × SCr)
Multiply by 0.85 if female
What is the Cockcroft-Gault equation?
Uses weight; needs adjustment for BSA and BMI > 30
What are the limitations of the Cockcroft-Gault formula
Cross-sectional study (n = 1628).
Non-diabetic CKD population, 18–70 years, ~80% white.
What is the MDRD (1999) study design and population?
eGFR = 186.3 × (SCr)^−1.154 × (Age)^−0.203
Multiply by 0.742 if female and 1.21 if Black.
What is the MDRD equation?
Underestimates measured GFR at higher levels.
What is a limitation of the MDRD formula?
Cross-sectional validation (n = 3896), estimation of GFR using creatinine.
What is the CKD-EPI (2009) study design?
31.5% Black, median age 47, mean GFR 67.6
What population was used in CKD-EPI 2009?
eGFR = 141 × min(SCr/k,1)^a × max(SCr/k,1)^−1.209 × 0.993^Age
Multiply by 1.018 if female, 1.159 if Black.
What is the CKD-EPI (2009) equation?
Limited inclusion of elderly, racial, and ethnic minorities.
What are the limitations of CKD-EPI 2009?
Cross-sectional validation (n = 4050), estimation of GFR using creatinine.
What is the CKD-EPI (2021) study design?
14.3% Black, 10 years older on average, with mGFR 9 points higher than 2009 dataset.
What population was used in CKD-EPI 2021?
eGFR = 142 × min(SCr/k,1)^a × max(SCr/k,1)^−1.200 × 0.9938^Age
Multiply by 1.012 if female. (No race variable)
What is the CKD-EPI (2021) equation?
Limited number of Black patients with low GFR; combining creatinine and cystatin C gives more accurate results.
What are the limitations of CKD-EPI 2021?
Strassinger → MDRD-IDMS traceable formula
NKDEP & National Kidney Foundation → CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) Formula
Recommended Formula for Estimating GFR
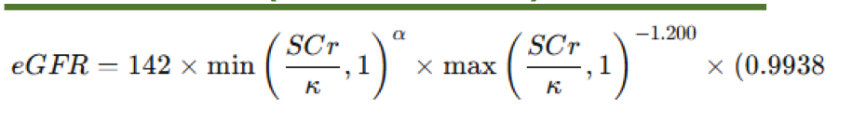
CKD - EPI Formula (2009 - 2021 Update)
Serum Creatinine
What does SCr stand for?
Constant depending on sex
What does K stand for?
0.7
0.9
In CKD - EPI formula , what is the constant for :
females
Males
- 0.329
- 0.411
Alpha 2009 CKD - EPI values
females
Males
- 0.241
- 0. 302
Alpha 2021 CKD - EPI values
females
Males
If SCr/k < 1 → use computed value
If SCr/k > or equal to 1 → assign 1
In CKD - EPI formula, How to determine min?
min (SCr/K , 1)
If SCr/κ > 1 → use computed value
If SCr/κ ≤ 1 → assign 1
In CKD - EPI formula, How to determine max?
max(SCr/κ, 1)
Creatinine
waste product of muscle metabolism
Normally found at a relatively constant level in blood
Creatine phosphokinase
Creatinine is produce by what enzyme ?
phosphocreatine
Whenever the body wants to store energy, creatine accepts the donated phosphate from ATP and forms
_____________.
ATP
Whenever the body needs energy, phosphocreatine can donate back the phosphate group to ADP and form _______.
some creatinine is secreted by the tubules, and secretion increases as blood levels rise, potentially overestimating GFR.
Why is creatinine secretion by the tubules important to consider in kidney function tests?
react chemically during analysis, can falsely elevate creatinine values
What is the effect of plasma chromogens on creatinine testing?
Gentamicin, cephalosporins, and cimetidine
Which medications can inhibit tubular secretion of creatinine and cause falsely high serum levels?
Bacteria break down urinary creatinine, leading to falsely low results.
What happens if urine specimens are kept at room temperature for too long?
Increased meat intake raises creatinine levels in both urine and plasma during a 24-hour collection.
How does diet affect creatinine levels?
muscle mass and supplementation affect creatinine production, leading to inaccurate estimates of GFR
Why is creatinine clearance unreliable in patients with muscle-wasting diseases or athletes?
Incomplete collection causes underestimation of clearance results.
Why is the completeness of a 24-hour urine collection important in creatinine clearance tests?
To ensure accuracy and comparability between individuals of different sizes; correction is especially important in children.
Why should creatinine clearance values be corrected for body surface area (BSA)?
CP = UV and C = UV/P
GFR formula
Milliliters of plasma cleared per minute
mg/dL of plasma creatinine
mg/dL of urine creatinine
urine Volume in mL/min
In GFR formula , what do these stand for?
C
P
U
V

Using urine creatinine of 120 mg/dL (U) , plasma creatinine of 1.0 mg/dL (P) , and urine volume of 1440 mL obtained from a 24-hour specimen (V), calculate the GFR.

Calculate the urine volume (V) for a 2-hour specimen measuring 249 mL.
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rates
Results of newer methods that do not require the collection of timed (24hr) urine specimens
Equations are superior to serum creatinine alone
Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) Formula
Most frequently used formula
MDRD-IDMS-Traceable Formula
recommended by the National Kidney Education Program (NKDEP)
Designed to equal the results that compare to the reference body size of 1.73m²
Not accurate for pediatric patients
Lower than 60mL /min
MDRD-IDMS-Traceable Formula Is most accurate when results are?

MDRD-IDMS-Traceable Formula
Older formula for estimating GFR
What type of formula is the Cockcroft-Gault?
Serum Creatinine (SCr)
What parameter does Cockcroft-Gault use to estimate GFR?
Sex and age
What factors does Cockcroft-Gault formula adjust for?
Variability due to muscle mass differences
What does Cockcroft-Gault formula aim to reduce in GFR estimation?
Disease-related muscle mass changes
Extra-renal elimination
Tubular secretion of creatinine
What factors are not accounted for in the formula?
50 kg + 2.3 kg per inch over 5 ft
How do you calculate Ideal Body Weight (IBW) for males?
45.5 kg + 2.3 kg per inch over 5 ft
How do you calculate Ideal Body Weight (IBW) for females?
Obese, edematous, and chronically ill patients
In which patients does Cockcroft-Gault overestimate GFR?
Ignores disease-related muscle mass, extra-renal elimination, tubular secretion
What are the main weaknesses of Cockcroft-Gault formula?

Schwartz Formula
Used for estimating creatinine clearance for children
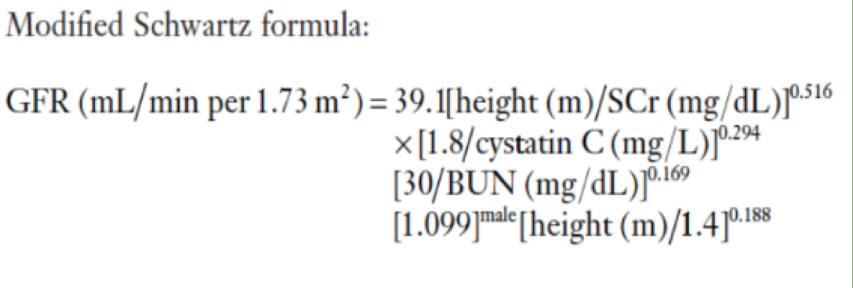
Modified Schwartz Formula
Used to estimate GFR more accurately in children
Requires knowing serum creatinine value, height, BUN , and serum Cystatin C
KDIGO stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
The use of GFR or eGFR Values are interpreted by using?
KDIGO stages of Chronic Kidney Disease, Stage 1
≥90 ml/min/1.73m² (normal or high; with evidence of kidney damage)
KDIGO stages of Chronic Kidney Disease, Stage 2
60–89 ml/min/1.73m² (mild decrease)
KDIGO stages of Chronic Kidney Disease, Stage 3a
45–59 ml/min/1.73m²
(mild to moderate decrease)
KDIGO stages of Chronic Kidney Disease, Stage 3b
30–44 ml/min/1.73m² (moderate to severe decrease)
KDIGO stages of Chronic Kidney Disease, Stage 4
15–29 ml/min/1.73m² (severe decrease)
KDIGO stages of Chronic Kidney Disease, Stage 5
<15 ml/min/1.73m² (kidney failure / end-stage renal disease)
Patients usually require dialysis
Dialysis indication:
- Not based on GFR alone
- Consider: Presence of symptoms (e.g., uremia
→ nausea, confusion) And Metabolic
complications
Cystatin C
Size: 13 kDa, 122 amino acids
Function: Cystatin proteinase inhibitor
Produced by all nucleated cells
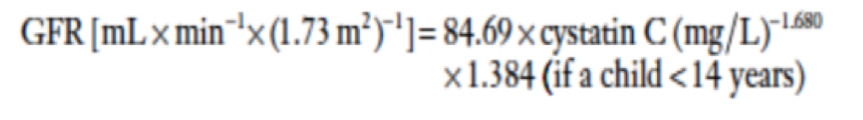
Cystatin C Formula
Proximal tubular Injury
Cystatin C in urine is a marker for ?
Cystatin C production
Relatively constant from 4 months to 70 years
Note affected by: muscle mass, sex, race
Considered better than creatinine as a GFR marker
High IL-10
inhibits cystatin C production
Glucocorticoids
Reduce cystatin C production
Can lead to improper renal function assessment in renal transplant patients
Measurements are difficult and expensive
Limited availability compared to creatinine
assays
Why is Cystatin C not widely used?
Normally completely reabsorbed by proximal tubules
No urinary excretion
Why the Renal Clearance of Cystatin C cannot be directly measured ?
Indirect estimate of GFR
Change in serum Cystatin C concentration are used for what clinical use?
11.6 kilodaltons,99 amino acids
Size of Beta2-Microglobulin
MHC class I molecule
Components Of Beta2-Microglobulin
Present in all nucleated cells
Location Of Beta2-Microglobulin
Plays a role in CD8 (killer T-cell) development
Function Of Beta2-Microglobulin
Elevated levels in multiple myeloma
Elevated levels in lymphoma
Clinical Associations (non-renal) of Beta2-Microglobulin
True
True or false:
B2M is freely filtered at the glomerulus
Fully reabsorbed and degraded
What happens to B2M in the proximal tubule normally?
In renal failure (like cystatin C)
When does plasma B2M concentration rise?
When proximal tubular reabsorption is impaired (e.g., acute kidney injury)
When is B2M excreted in urine?
Sensitive enzyme immunoassays
How is B2M measured?
Sensitive indicator of decreased GFR (more sensitive than creatinine clearance)
What does a rise in plasma B2M indicate?
Not reliable in patients with Immunologic disorders and Malignancy
Limitations of Beta2-Microglobulin
Radionucleotides
Method for determining glomerular filtration (plasma disappearance of the radioactive material)
Exogenous procedure (requires injection)
Radionucleotide Procedures Type?
Radioactive material (e.g., Technetium)
What substance is injected in Radionucleotides ?
Disappearance of the radioactive substance from circulation
What is observed after injection in Radionucleotide Procedures?
125l-iothalamate
Chromium-51 ethylene-diamine-tetra-acetic acid (51 CRP-EDTA)
Technetium-99-labeled di ethylene-training-pentaacetate (99-Tc-DTPA)
Iohexol-non-radioactive agent used for children
markers used in Radionucleotide procedures
visualization of filtration (one or both kidneys)
Assess the viability of transplanted kidney
Clinical Applications for Radionucleotides
Urea
Main waste product of nitrogen-containing compounds in the body.