Enzymes, Energy, and Metabolism: Key Concepts for Biology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Energy
the capacity to do work
Kinetic energy
energy of motion
Potential energy
stored energy
Chemical bonds
a form of potential energy
Heat energy
a form of energy
Thermodynamics
study of energy and energy transfer
First Law of Thermodynamics
Total energy in the universe is constant; energy can be transferred to different forms.
Photosynthesis
light energy transferred to chemical energy
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The entropy of the universe is always increasing.
Entropy
measure of the disorder in the universe
Free energy (G)
the energy available to do work
Enthalpy (H)
energy in the bonds of a molecule
Entropy (S)
disorder in the universe
Temperature (T)
temperature
G=H-TS
formula for free energy
Chemical Reaction
A + B → C; A, B: reactants, substrates; C: product
∆G
change in free energy; ∆G=∆H-T∆S
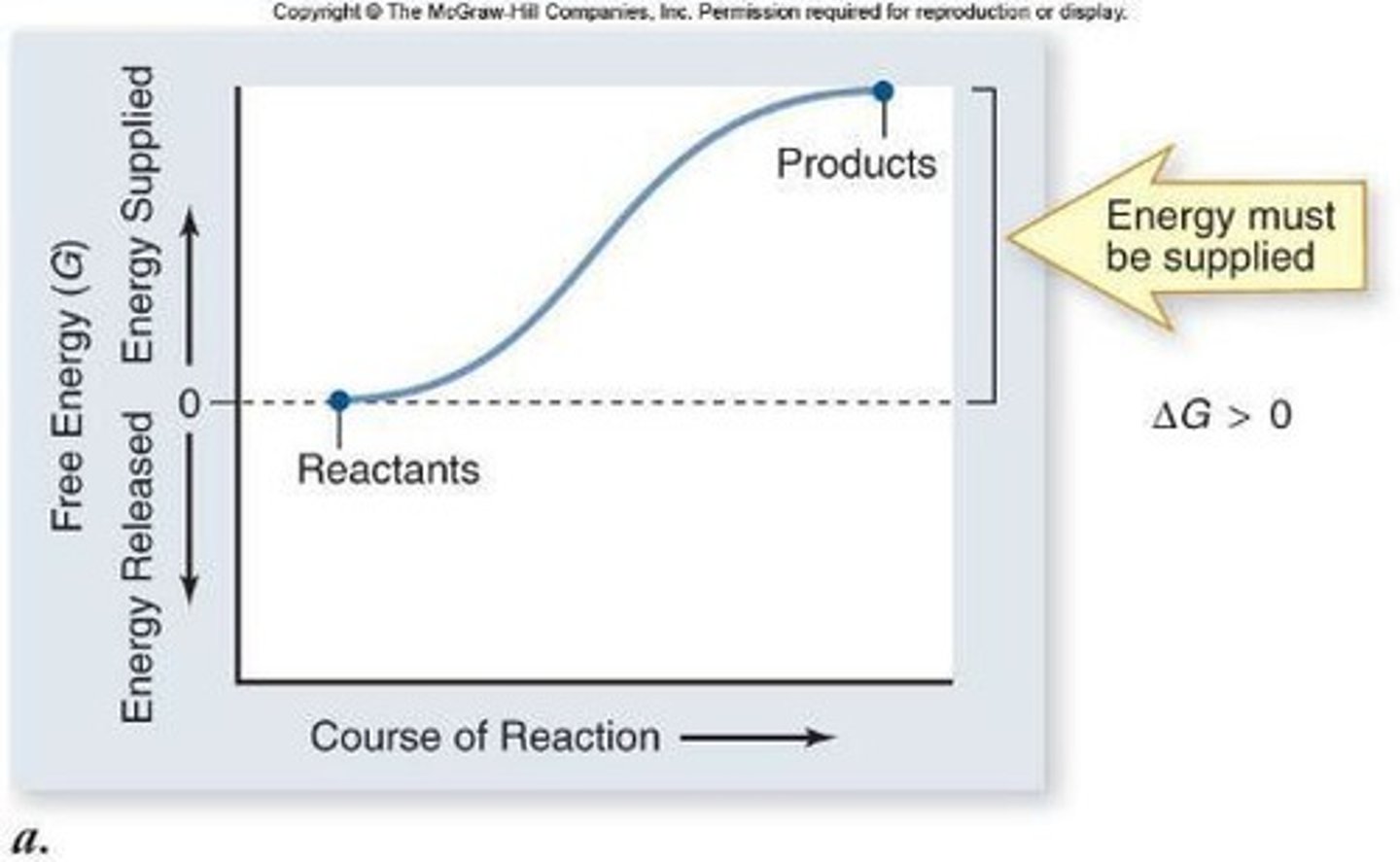
Endergonic reactions
require energy added to the reaction; ∆G is positive
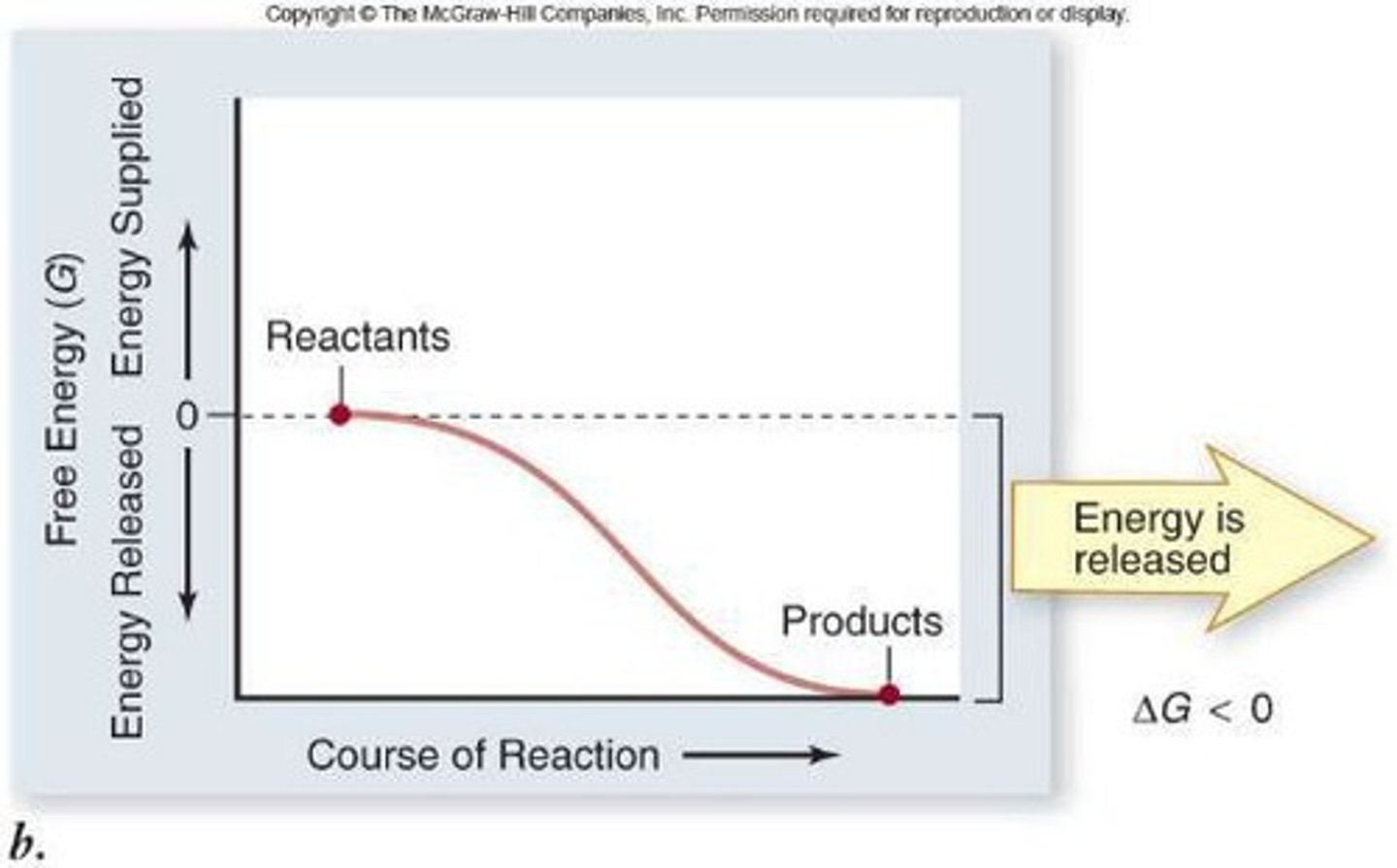
Exergonic reactions
release free energy; ∆G is negative
Activation energy
energy needed to get started for all reactions
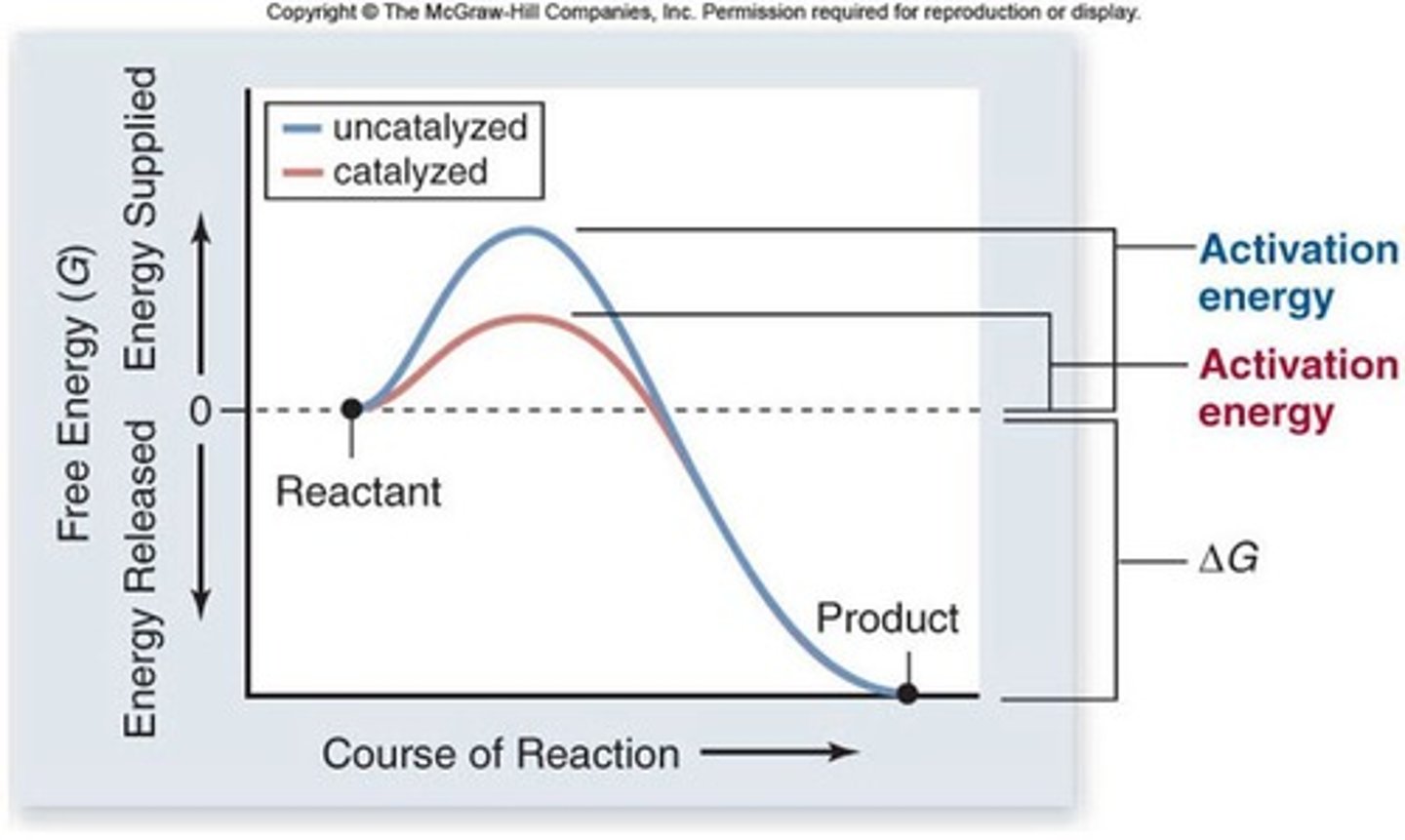
Catalysts
substances that can lower activation energy and speed up reactions
Enzymes
molecules that catalyze reactions in living cells; most are proteins
Active site
a region of amino acids on the enzyme that binds to the substrate
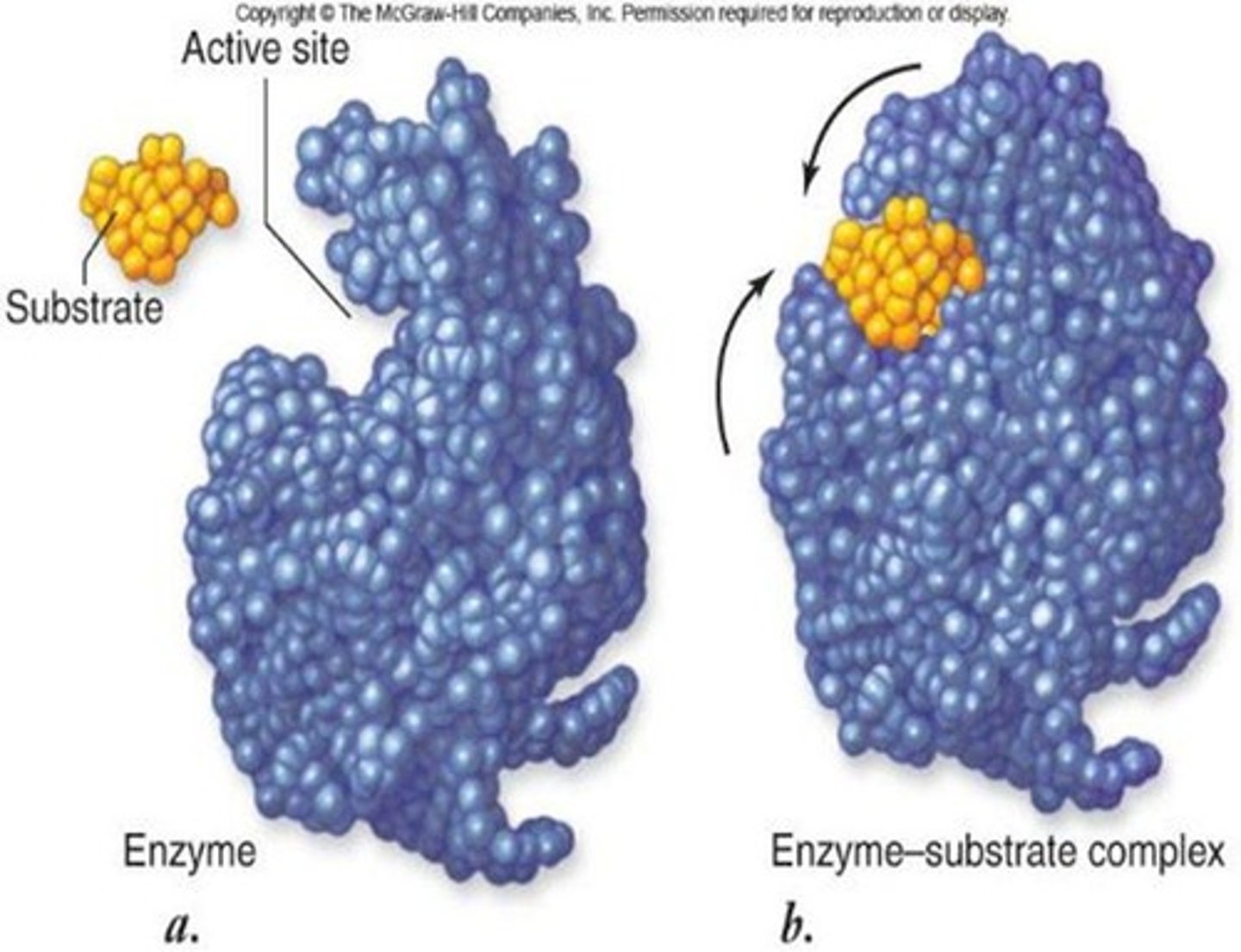
Induced fit
binding where both enzyme and substrate change shape slightly to bind
Cofactors
typically metal ions present in the active site to help enzyme catalyze reactions
Coenzymes
typically small organic molecules often part of oxidation-reduction reactions
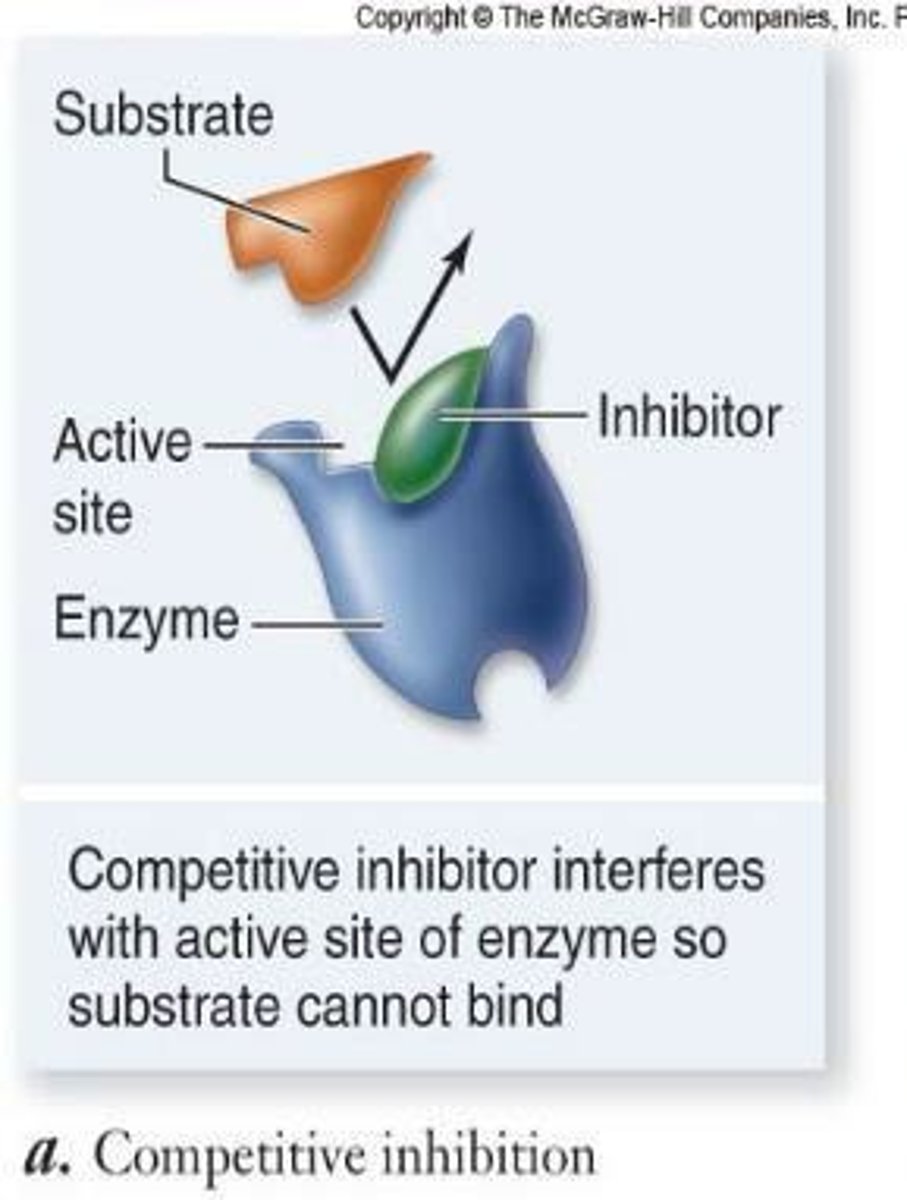
Competitive Inhibition
molecules that temporarily inhibit enzyme function by competing with substrate for active site
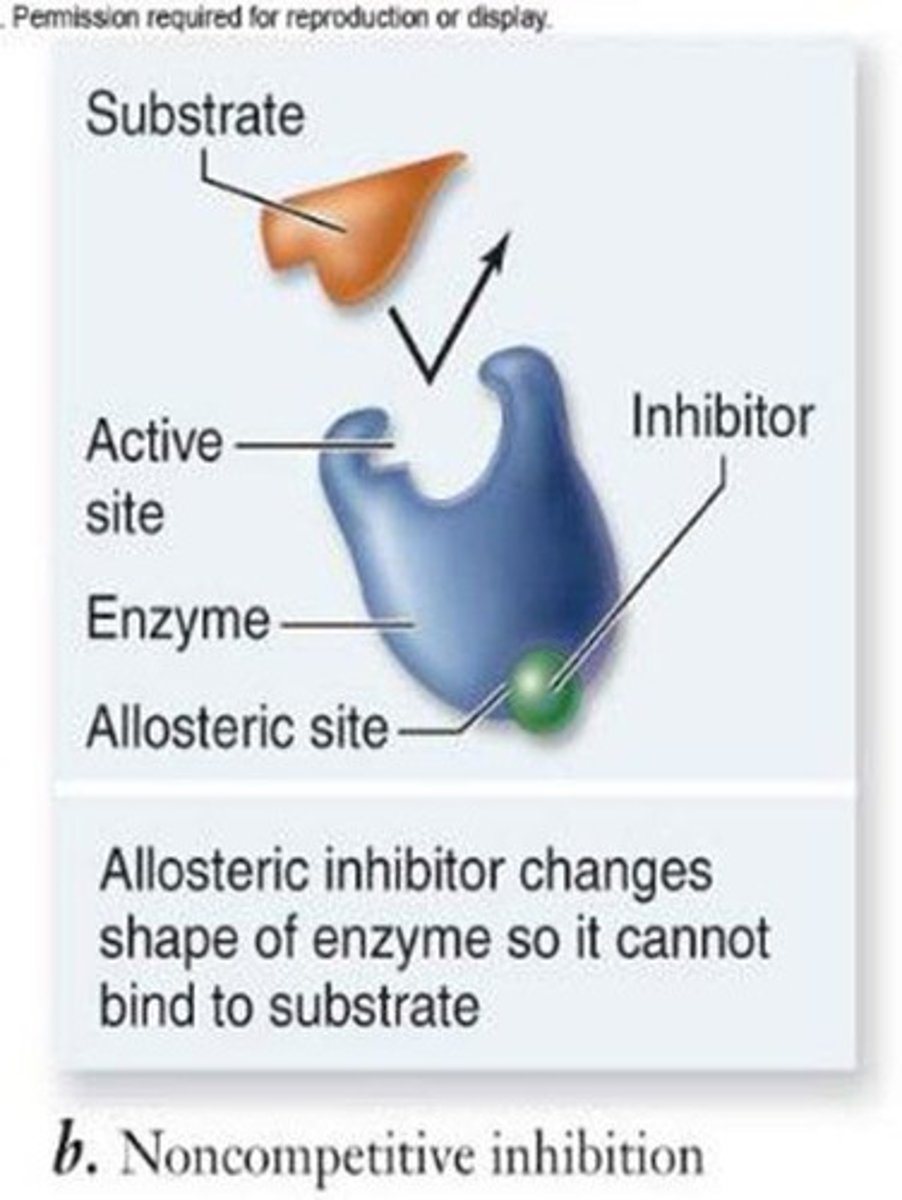
Noncompetitive Inhibition
molecules that temporarily inhibit enzyme function by binding to an allosteric site
Biochemical pathway
a series of linked reactions where the product of one reaction becomes the substrate for the next

Feedback inhibition
end product inhibits the first enzyme in the pathway to ensure it is not running unless needed