Choice Behavior and Self-Control Theories
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Choice behavior
Deciding among multiple possible behaviors.
Momentary maximization theory
Choosing options for immediate maximum reward.
Self-control choices
Decisions balancing immediate and long-term rewards.
Concurrent schedules
Multiple reinforcement schedules active simultaneously.
Herrnstein's matching law
Response proportion equals reinforcement proportion.
Deviations from matching
Variations in response patterns from predicted matching.
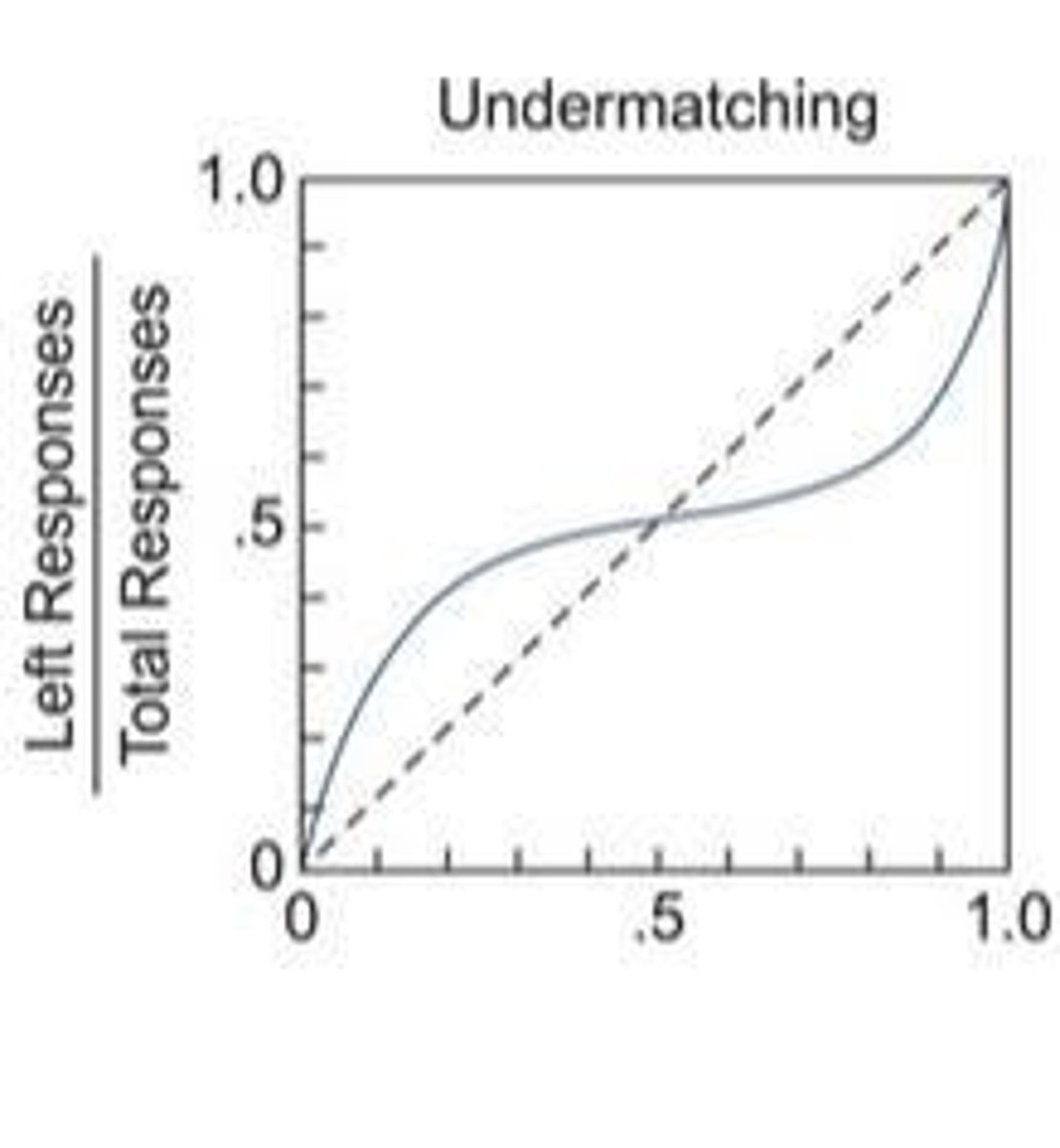
Undermatching
Responses closer to equal than reinforcement proportions.
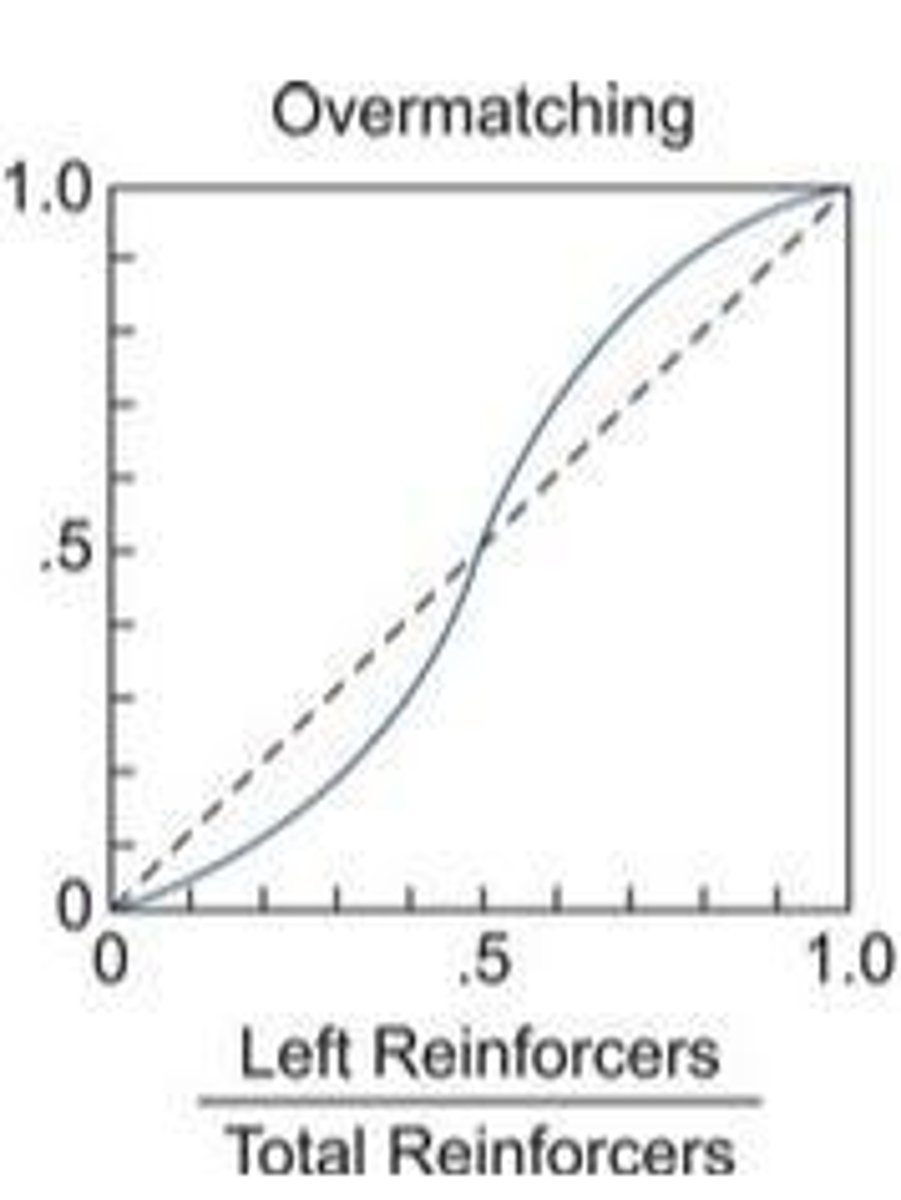
Overmatching
Responses more extreme than reinforcement proportions.
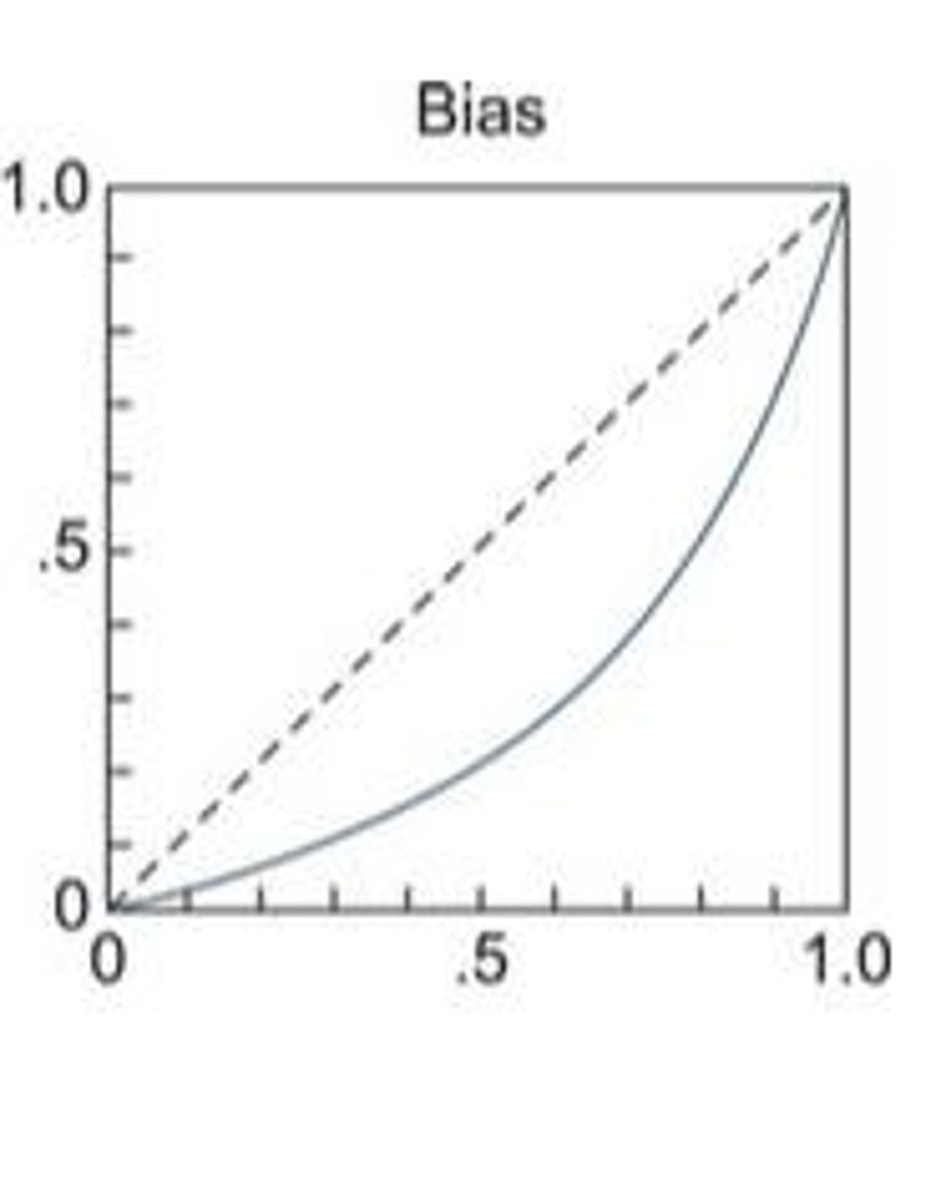
Bias
Preference for one response over predicted matching.
Generalized matching law
Incorporates bias and response difficulty in matching.
Delay discounting
Value of rewards decreases with time delay.
Ainslie-Rachlin theory
Self-control involves choosing smaller immediate rewards.
Self-control in children
Ability to delay gratification for future benefits.
Improving self-control
Strategies to enhance ability to resist temptation.
Risk taking
Choosing options with uncertain outcomes.
Tragedy of the commons
Shared resource depletion due to individual self-interest.
Optimization theory
Maximizing satisfaction through choice of options.
Quality of reinforcement
Influence of reward quality on response behavior.
Amount of reinforcement
Total quantity of rewards received from responses.
Concurrent VI schedules
Variable interval schedules operating at the same time.
Matching law for quality
Response proportions based on quality and quantity of rewards.
Optimization vs Matching
Comparison of maximizing satisfaction versus reinforcement matching.
Optimization Prediction
Behavior often aligns with matching rather than optimization.
Momentary Maximization Theory
Selects highest value response at each moment.
Optimization Theory
Maximizes long-term gains from choices.
Delay Discounting
Value decreases as delay to reinforcer increases.
Delay Discounting Formula
V = M / (1 + kD) for value calculation.
Self-Control Choices
Choice between immediate and delayed reinforcers.
Pre-commitment
Decision made in advance to avoid change.
Ainslie-Rachlin Theory
Reinforcer value decreases with increased delay.
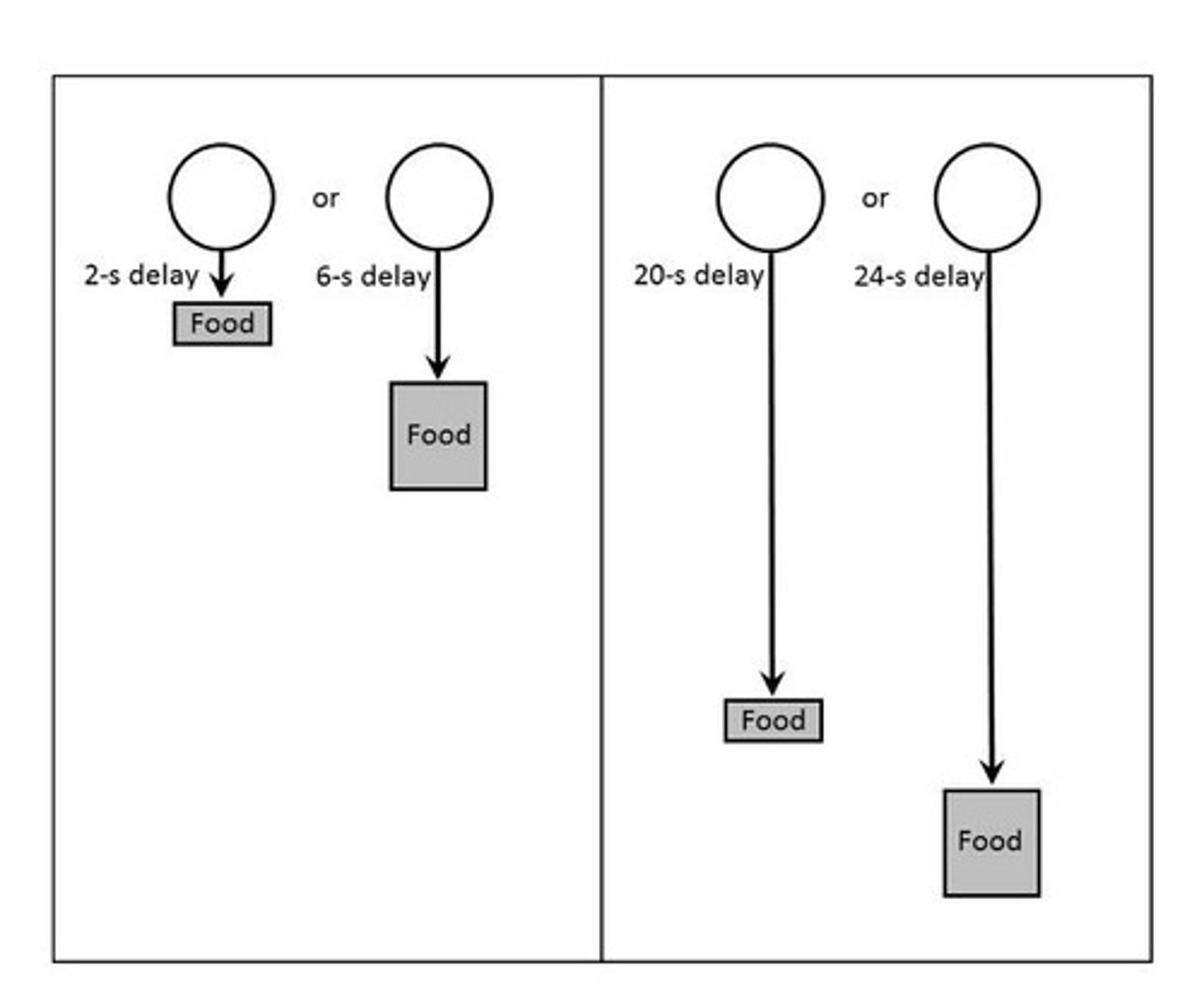
Green et al. Study
Pigeons preferred shorter delays with less grain.
Punisher Prediction
Opposite preference shift observed with punishers.
Mischel's Marshmallow Test
Children struggle to wait for preferred snacks.
Influences on Self-Control
Age, IQ, education, and income affect self-control.
Improving Self-Control
Strategies include pre-commitment and visualization.
Risk Prone
Preference for risky alternatives in scarce resources.
Risk Averse
Preference for safer alternatives when resources are plentiful.
Tragedy of the Commons
Shared resources are overused by individuals.
Consequences of Overuse
Costs of resource depletion affect the entire group.
Visualizing Delayed Reinforcer
Imagining rewards can enhance self-control.
Distracting from Larger Reward
Distraction helps manage desire for immediate rewards.
Discounting Rate Parameter (k)
Influenced by IQ, education, income, and drug use.
Behavioral Variability
Individual behavior changes moment to moment.
Immediate Reward Strategy
Provide instant rewards for choosing delayed options.
Theories of imitation
Frameworks explaining how imitation occurs in learning.
Motor learning
Process of acquiring and refining motor skills.
Knowledge of results (KR)
Feedback about the outcome of a performance.
Knowledge of performance (KP)
Feedback about the quality of a performance.
Adams' two-stage theory
Stages of motor-skill learning: cognitive and motor.
Schmidt's schema theory
Generalized motor program guiding motor actions.
Response chains
Sequential actions leading to a final outcome.
Instinct
Innate behaviors not learned through experience.
Operant response
Behavior influenced by reinforcement or punishment.
Bandura's social learning theory
Learning through observation and imitation of others.
Mirror neurons
Neurons activated by observing actions of others.
Effects of mass media
Influence of media on attitudes and behaviors.
Modeling in behavior therapy
Using imitation to teach or modify behaviors.
True imitation
Imitating behaviors never previously performed.
Generalized imitation
Imitation extending to new situations without reinforcement.
Attentional processes
Focus required to observe and imitate behaviors.
Retentional processes
Memory processes for retaining observed behaviors.
Motor reproductive processes
Physical ability to reproduce observed behaviors.
Incentive and motivational processes
Desire to imitate based on perceived rewards.
Bobo doll experiment
Study demonstrating influence of modeled aggression.
Video self-modeling
Using video of oneself to encourage behavior change.
Trowbridge and Cason experiment
Study on drawing accuracy with feedback.
Knowledge of Results (KR)
Feedback on outcome of a motor task.
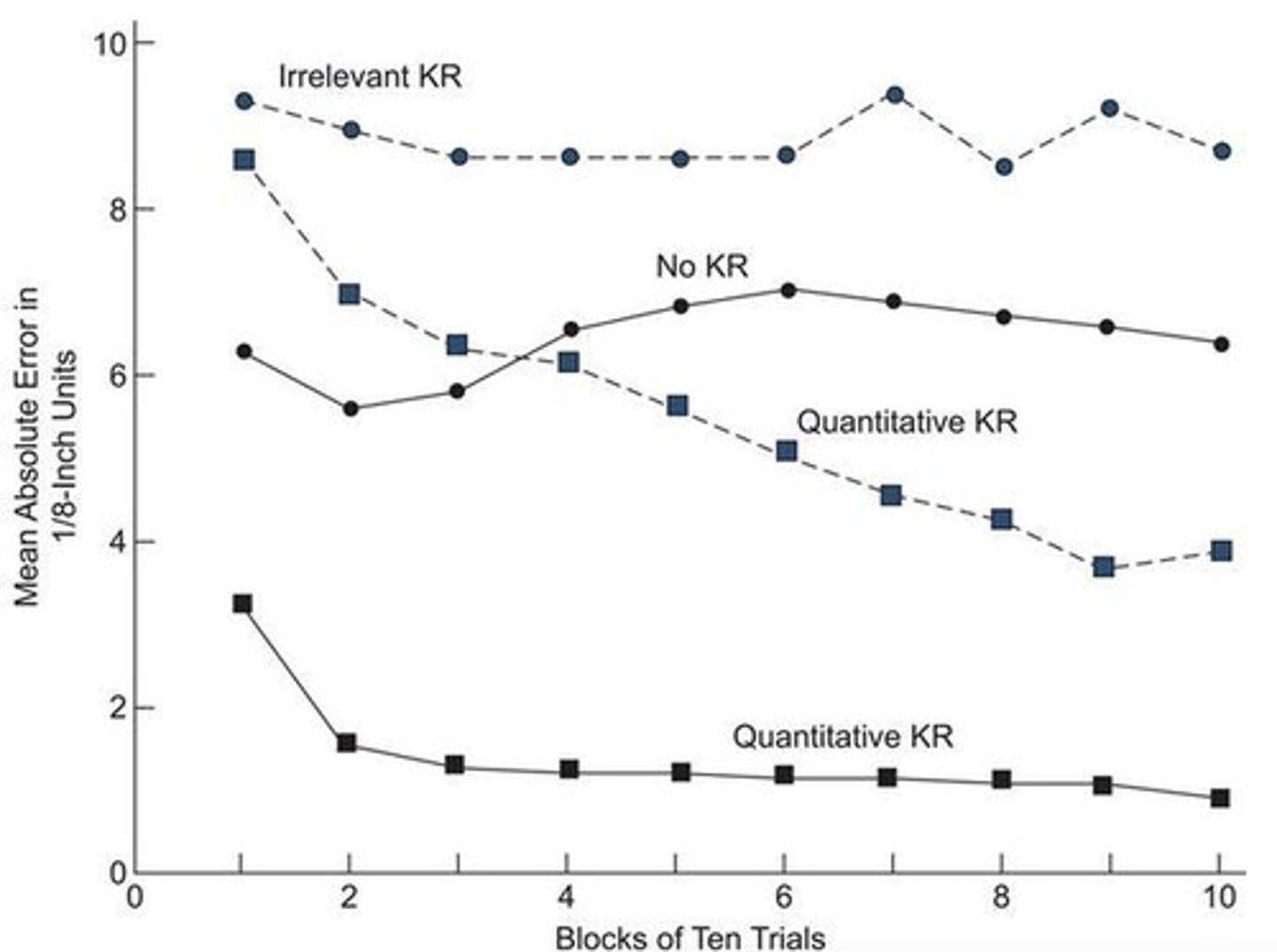
Qualitative KR
Feedback indicating 'right' or 'wrong' performance.
Quantitative KR
Feedback on direction and extent of error.
Irrelevant KR
Feedback that provides no useful information.
Knowledge of Performance (KP)
Feedback on the performance of component behaviors.
Mental Practice
Rehearsing skills mentally without physical movement.
Positive Transfer
Practice on one task enhances learning another task.
Negative Transfer
Practice that hinders performance in a new task.
Verbal-Motor Stage
Initial learning stage relying on verbal feedback.
Perceptual Trace
Internal sensation for distinguishing good from bad movements.
Motor Stage
Later learning stage relying on internal feedback.
Schema Theory
General rules acquired through practice of motor skills.
Motor Schema
Generalized motor rules applied to various situations.
Response Chain
Sequence of movements triggered by kinesthetic sensations.
Motor Program
Neural mechanism controlling movements without sensory feedback.
Variability in Practice
Diverse practice conditions enhance motor schema development.
Sparrow and Summers Study
KR delivered intermittently during verbal-motor stage.
Bilodeau et al. Study
Different KR frequencies affect learning of lever movement.
Movement Sequences
Ordered movements requiring correct timing for execution.
Conditioned Reinforcer
Stimulus reinforcing behavior through repeated practice.
Reaction Time
Time taken to respond to a stimulus.