GERD, PUD, GI Bleeding
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
GERD is due to lower esophageal sphincter (LES) contraction or relaxation?
relax
USUAL symptoms of GERD → 3
heartburn, regurgitation, belching
ALARM symptoms of GERD → 4
dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
odynophagia (pain swallowing)
bleeding
weight loss
Presence of Alarm symptoms OR risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus
______ = 1st line
______ can be collected during procedure
EGD
biopsy
DIAGNOSIS: If typical symptoms of GERD, trial PPI therapy
Responsive to therapy →
Unresponsive to therapy →
GERD
EGD after 2-4 weeks off PPI → if normal, esophageal reflux (pH) monitoring
GERD: NON-PHARM COUNSELING
__________ of bed
__________
Avoid _____________
Include ___________ meals in diet
Eat _________
Avoid _____________
Stop ________
Avoid ________
Avoid __________
Always take drugs ______________
elevate head
-weight
irritating foods
protein-rich
small meals
sleeping immediately after meals
smoking
alcohol
tight fitting clothes
sitting upright/standing w plenty of liquid
GERD Pharm agents (7)
antacids
H2RAs
PPIs
sucralfate
prokinetic
baclofen
vonoprazan
ANTACIDS
Provide rapid symptom relief (<5 min)
Used as __________________________ for immediate symptom relief
short duration of action → requires ______
DDIs → 4
_________ combination serves as protective barrier for esophagus against gastric contents and -freq of reflux of episodes, may be superior to antacid alone
adjunct therapy to PPI/H2RA
freq admin
TCN, ferrous sulf, sulfonylureas, quinolone ABs
alginic acid
H2RAS
Low-dose, OTC H2RAs or standard doses given BID may be beneficial for _____ GERD
Patients not responding may be hypersecretors and require ________
BUT more cost-effective and effective to switch to ______
indications → 2
ADMINISTRATION → 3
DDIs → Many interxns with _______ / CYP450
Precautions →
mild
higher doses
PPI
alone for mild, at bedtime adjunct to PPI for nocturnal symptoms
at onset, 30-60 min before, or BID w/o regard to meals
cimetidine
renal/advanced age dose adj
PPIs
rapid symptom relief and ___________ in mod-sev GERD
Recommended ________ for troublesome symptoms
PPIs can interfere with the _____ of certain drugs
Formulations?
ADEs → 4
AVOID ABRUPT DC → If receiving continuous therapy _____, taper over _____ (-50% every week)
Add H2RA/antacid during taper if needed
higher healing rates
empirically
abs
DR cap/tab
C diff, fractures, vit B12 def, blocks clopidogrel (CYP2C19 inhib)
>6 month → 3-8 weeks
SUCRALFATE (CARAFATE)
MOA:
ADEs → 2
DDIs →
ONLY RECOMMENDED FOR ..
mucosal protective agent
constipation, bloating
take other meds 2h before or 6h after
GERD in pregnancy
2 agents →
ONLY recommended for …
GERD + gastroparesis
metoclopramide/Reglan, prucalopride/Motegrity
BACLOFEN
MOA:
ADEs → 3
*Consider trial of baclofen if symptoms despite optimal PPI therapy
GABA agonist
dizzy, somnolence, constipation
VONOPRAZAN (VOQUEZNA)
MOA: __________ → -gastric acid secretion
Approved for _________ (superior to lansoprazole)
Cost?
blocks K+ binding to PP
erosive esophagitis
EXPENSIVE
Erosive Esophagitis / Barrett’s Esophagus
1st line + duration
2nd line + duration
PPI indefinitely OR ___________ for LA grade C or D Erosive esophagitis
PPI → 8-12 weeks EE, 6-12 months maintenance
vonoprazan → 8 weeks EE, 6 months maintenance
anti-reflux surgery
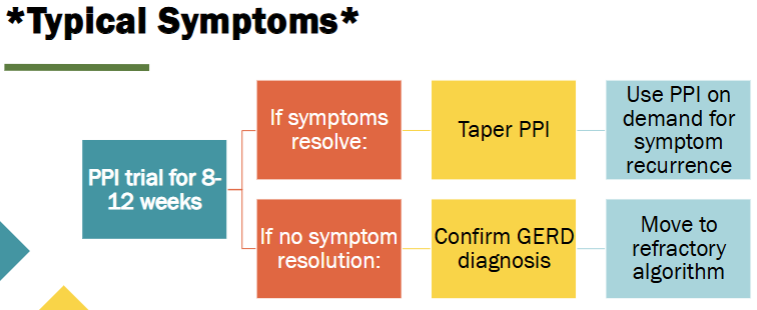
REFRACTORY GERD
Persistent symptoms AFTER ______ of double-dose PPI
Best approach is to …
Treatment → 6
8-12 weeks
Optimize PPI therapy
daily PPI → reassess 8-12 wks → confirm timing 30-60 min b4 meals → BID PPI → +H2RA bedtime → switch PPI
GERD PHARM MONITORING
Antacids / H2RAs
PPIs
General → 2
renal, sx after 2 weeks
hepatic, sx after 8 weeks
DDIs, develop of alarm/extraesophageal sx
Which of the following represents an alarm GERD symptom?
a. Regurgitation
b. Chronic cough
c. Dysphagia
d. Heartburn
C
Which of the following drugs is considered a risk factor for the development of bone fractures?
a. Metoclopramide
b. Famotidine
c. Rabeprazole
d. Alginic acid
C
When attempting to deprescribe PPI therapy, which of the following is an appropriate recommendation? Select ALL that apply.
a. Adding an H2RA when the PPI is discontinued
b. Changing to an immediate-release PPI formulation
c. Overlapping an H2RA with PPI therapy before discontinuation
d. Tapering down to the lowest dose that controls symptoms
A, C, D
The preferred initial treatment option for a 45-year-old male presenting with a 1-week history of GERD symptoms is:
a. Promotility agent
b. Proton-pump inhibitor
c. Anti-reflux surgery
d. Endoscopic therapy
B
Which of the following is a potential adverse effect of long-term PPI therapy?
a. Hypercalcemia
b. Clostridium difficile infection
c. Vitamin A deficiency
d. Hypokalemia
B
A 47-year-old man did not achieve resolution of symptoms on omeprazole 40mg BID. GERD diagnosis was confirmed. What is appropriate?
a. Confirm timing at start of meal
b. Switch to baclofen
c. Add cimetidine
d. Taper PPI
C (next step is +H2RA at bedtime)
Which of the following is/are appropriate initial treatment options for a patient with erosive esophagitis noted on endoscopy? Select ALL that apply.
a. famotidine for 12 weeks
b. pantoprazole for 10 weeks
c. vonoprazan for 8 weeks
d. baclofen for 6 months
B, C
Common causes of chronic ulcers → 3
H pylori
NSAIDs
critical illness (stress)
Differential Diagnosis
GERD →
PUD →
burning, exacerbated by some foods
pain/discomfort abdomen, relieved by eating/drinking
ULCER COMPARISON
H pylori vs NSAID-induced
H pylori → duodenum > stomach, superficial
NSAID → stomach > duodenum, deep
PUD: NON PHARM
________ reduction
-
Avoidance of foods causing dyspepsia →
stress/anxiety
smoking cessation
caffeine, spicy, alcohol, etc
H PYLORI
_______ bacterium with flagella that has urease, catalase, and oxidase activity
Urease →
Catalase → survive reactive oxidation by phagocytes → causes ______
Some patients have dyspepsia or GERD symptoms → expect only ______ improv w H pyloria tx
gram -
converts urea → ammonia → neutralizes gastric acid
inflam
modest
H PYLORI DIAGNOSIS
If alarm symptoms or risk factors for peptic ulcer/gastric cancer →
Gold standard, tests for active infxn →
Tests for AB resistance, use if fail 1st line tx →
Active infxn →
Only used in research →
DOESN’T differentiate btwn active vs cured infxn →
Active infxn, 95% sens + specific →
Active infxn, similar accuracy ^
endoscopy
histology stain
culture
biopsy urease
PCR
AB
urea breath test → withhold PPI/H2RA 1-2 wks prior, ABs/bismuth 4 wks
fecal antigen → ^
What is the recommended agent for H pylori treatment in a patient w Penicillin allergy?
BQT (optimized bismuth quadruple)
PUD 1ST LINE THERAPY OPTIONS (3)
Regimen + duration + drugs
BQT → 14d → PPI + bismuth + metronidazole + TCN
Rifabutin triple → 14d → omeprazole + amoxicillin + rifabutin
PCAB dual → 14d → vonoprazan → amoxicillin
PUD: Test of Cure
_____________________ recommended
Should be performed at least ______ after regimen completion
biopsy, UBT, or fecal antigen
4 weeks
55-year-old patient with iron-deficiency anemia, GERD, and gastric cancer (in remission) taking ferrous sulfate, famotidine, pantoprazole, and aspirin. How should he be tested for H. pylori? Select ALL that apply.
A. Polymerase chain reaction
B. Urea breath test
C. Fecal antigen
D. Histology stain
D
Which is a correct instruction for a patient undergoing urea breath test (UBT)?
Select ALL that apply.
A. Stop sucralfate 3 weeks prior
B. Stop cimetidine 2 weeks prior
C. Stop dexlansoprazole 4 weeks prior
D. Stop bismuth subsalicylate 1 week prior
B
38-year-old patient with UBT + for H. pylori. Her current medical problems include acne, PUD, and HTN. Current medications include omeprazole, doxycycline, and amlodipine. NKDA. What is the best treatment option?
A. Rifabutin triple
B. Optimized BQT
C. PCAB dual
D. Levofloxacin triple
B (BQT is the strongest rec 1st line)
She comes back 4 weeks later for test of cure. Her UBT once again comes back positive. What is appropriate therapy now?
A. Rifabutin triple
B. Optimized BQT
C. PCAB dual
D. Levofloxacin triple
A

Which NSAIDs are COX2 selective? (4)
celecoxib
nabumetone
etodolac
meloxicam
RISK FACTORS FOR NSAID-ASSOCIATED PUD
Concomitant use of … (6)
NSAID + low dose ASA
oral bisphos
corticosteroids
anticoagulants
antiplatelets
SSRIs (fluox, parox, sert, etc)
PUD: NSAIDS-ASSOC TREATMENT
-
Admin …
IF must give NSAID →
If symptoms unresolved after …
stop NSAID
H2RA, PPI, or sucralfate x 8 weeks
COX2 selective + PPI/misoprostol
8 weeks → test H pylori → tx if +
MISOPROSTOL
MOA:
Must be dosed ________
Effect is dose-related
ADEs → 2
Important note
PGE1 analog
TID-QID
N/D, abdominal cramping
TERATOGENIC
37-year-old taking meloxicam 15 mg daily for chronic knee pain is diagnosed with PUD. Which is appropriate treatment?
A. Bismuth subsalicylate x 8 weeks
B. Pantoprazole x 4 weeks
C. Famotidine x 8 weeks
D. Misoprostol x 4 weeks
C
What pain regimen should be initiated after PUD treatment?
A. Acetaminophen + ibuprofen
B. Diclofenac + sucralfate
C. Continue meloxicam at lower dose
D. Celecoxib + omeprazole
D
IDIOPATHIC ULCERS TREATMENT →
May need long-term maintenance therapy d/t high recurrence rates
PPI/H2RA x 8 weeks