Ch. 1 part 3 - Biological Perspectives & Research Methods
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What are biological perspectives?
View that most development is guided by biological processes such as genetic inheritance, epigenetic changes and physiological processes
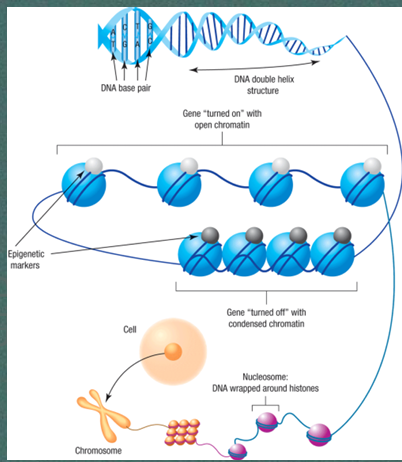
How are all traits encoded in humans?
By DNA

What are genes turned into and what do they account?
Condensed into 23 pairs of chromosomes genes and they account for inherited traits
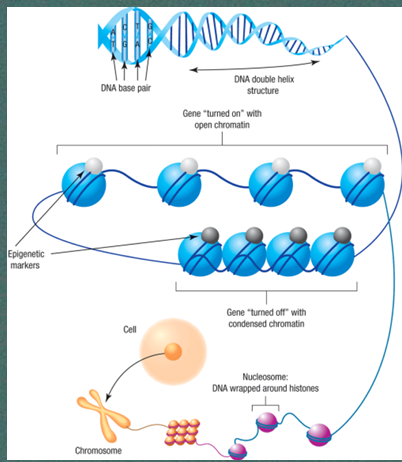
What can lead to protein production?
genes
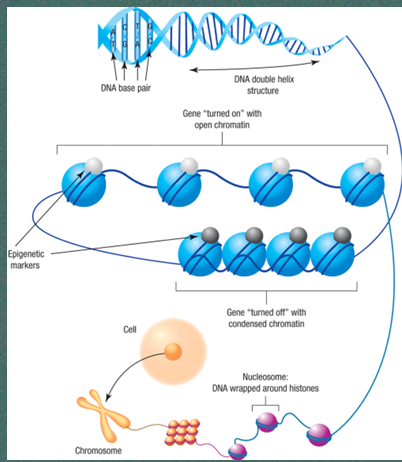
Epigenetic factors
molecular markers that can change gene function; inherited or acquired
What are evolutionary theories?
They seek to identify behaviour resulting from genetic inheritance from our ancestors, drawn from ethology, how biological makeup influences survival behaviours and traits.
Behavioural genetics
Study of how heredity affects behaviour and causes individual difference
Evolutionary psychology
Hardwired cognitive and social thinking patterns which have been shaped by time
What did Konrad Lorenz discover?
Gosling birds genetically programmed to imprint first moving object they see as their mother (for survival)
What are the pros of biological/evolutionary perspective?
Provides accurate description of basic biological and genetic processes
What are the limitations of the biological/evolutionary perspective?
lack of attention to social factors
lack of experimental evidence
What is the scientific method?
Process of creating and answering questions using careful controlled techniques that include systematic orderly observation and collection of data
What are the steps of the scientific method?
Identify questions of interest (describe)
formulate an explanation (explain, make hypotheses to test)
Carry out research; operationalize hypothesis, select research method, collect & analyse date (influence; use research conclusion to inform practices)
What’s a theory?
Broad explanations and predictions about phenomena of intrest
What’s a hypothesis?
Prediction that is testable and falsifiable
Ice cream improves mood among students is an example of a theory or hypothesis?
Theory (not testable)
Ice cream is associated with higher satisfaction score among students is an example of a theory of hypothesis?
hypothesis (testable and falsifiable)
Aliens don’t exist is an example of a theory of hypothesis?
theory (non-testable and non-falsifiable)
What is a correlational research?
seeks to identify if an association exists b/w two factors, but doesn’t provide info about causality
What is experimental research?
research designed to discover causal relationship between two factors, involve introducing a change to see its consequence
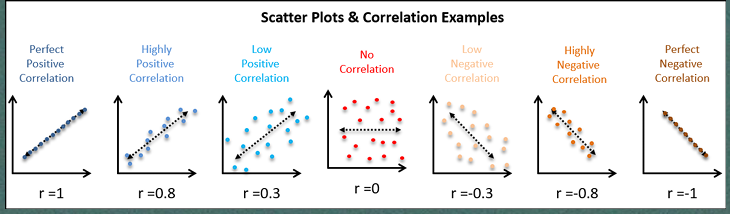
What’s a correlational coefficient?
mathematical correlations, scores ranging from R = -1 to 1, magnitude shows degree of association, positive, no and negative correlation
Why can’t causality be established in correlational studies?
due to a third confounding variable that affects the potential result (hidden variable)
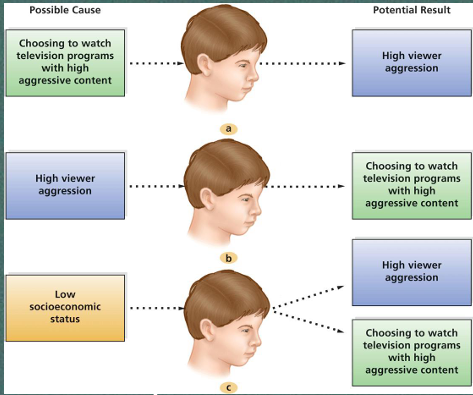
What are types of correlational studies?
Naturalistic observation, qualitative research (document & describe), case studies and surveys
all which focuses on observations without manipulation
What is psychophysiological method?
Focuses on relationship b/w physiological processes and behaviour
What is EEG?
Electroencephalography - measures brain activity
What is CT scan?
Computed tomography scan - takes x-ray to give detailed structure of brain
What is fMRI?
Functional magnetic resonance imaging - measures change in brain oxygen levels
What is an experiment?
different experiences are devised for two groups of people being studied to compare outcomes - includes control and experimental group
Independent variable
variable that is manipulated
Dependent variable
variable being inspected for any change due to experimental manipulation (responding variable)
How are participants divided proportionally in experiments?
participants are randomly assigned into groups
To build confidence of experimental results, what must to occur?
Research experiments must be replicated
Meta-analysis
statistical procedures that allow researchers to combine results from multiple studies
What is a sample?
group of participants chosen for the experiment that represent the population under consideration
What is field study?
Investigation carried out in a naturally occurring setting
What is laboratory study?
Investigation carried out in a controlled and standardized setting
What is theoretical research in development?
testing some developmental explanation and expand scientific knowledge
What is applied research?
provides practical solutions to immediate problems
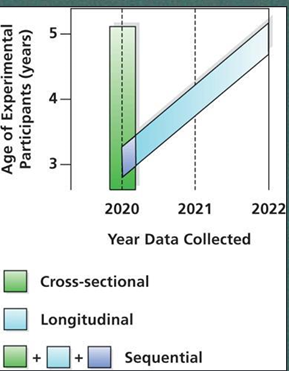
What are cross-sectional studies?
Measure people of different ages (population) at same point in time
whole bunch of groups right now
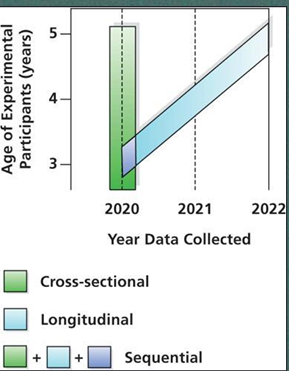
What are longitudinal studies?
Measure individual change, in the same group over multiple points in time (same individuals)
same group over time

What are sequential studies?
Measure different age groups over multiple time points
a bunch of groups over time
What are the pros and cons of cross-sectional studies?
takes lesser time to complete
make conclusions in age-related differences in development, not changes due to aging
Cohort effects might make confound (3rd variable) results
Changes of selective attrition (dropout)
What are the pros and cons of Longitudinal studies?
Provide insight into direction of development w/ age
Huge time investment
Participants can show practice-effects
chances of attrition (drop-out)
What are the pros and cons of sequential studies?
help make distinction between effects of age-related change and age difference on development
huge investment
What are research ethics?
applied to research activities to minimize harm and maximize benefits
researchers must protect participants from any form of harm (physical & psychological)
Must have consent from participants
Use of deception must be justified
Participants must be confidential