Population Ecology
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is lambda and how do you solve for it? What equations is it used in?
finite rate of population growth
N1/N0
discrete, exponential = Nt = lambda^t * N0
What is R and how do you solve for it? What equations is it used in?
geometric population growth rate
R = change in N / N0
R = lambda - 1
discrete logistic growth
Nt+1 = Nt + RN(1-Nt/K)
How do you solve for per capita birth/birth rate (b) and per capita death/death rate (d) ?
Births / N0
Deaths / N0
Lambda for a red panda population is 2. If the population last year was 200, what will the population be next year? Use the discrete model.
lambda = N1/N0
2 = N1/200
N1 = 400
What is the formula for continuous logistic growth?
Nt+1 = Nt + RNt (1-Nt/K)
What does the logitstic growth model assume?
No immigration or emigration
no variation among individuals
no sex or age structure
constant birth and death rate; no density dependence
has a carrying capacity
How does the growth rate change in density dependent populations?
growth rate decreases as density increases
What contributes to a species’ maximum growth rate?
clutch or litter size
age at first breeding
frequency of breeding
parental care
A population of red panda currently has 200 individuals. Over one year, 30 births and 10 deahts are observed. Using the discrete model,
What is little r and how do you solve for it? What equations is it used in?
r = birth rate - death rate (instantaneous rate of growth)
used for exponential/continuous population growth
Nt=N0ert (continuous exponential growth)
What is the formula for continuous exponential growth?
Nt=N0ert
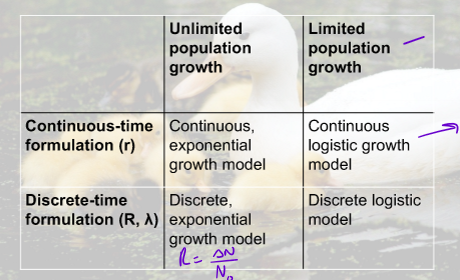
What are the continous exponential growht modles, discrete exponential growth models, and discrete logistic growth model formulas?
continuous exponential: Nt=N0ert
discrete exponential: N1 = N0*lambda^t
discrete logistic: Nt+1 = Nt + RN(1-Nt/K)
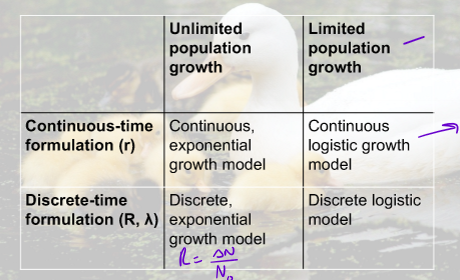
What is the continous exponential growth formula?
Nt+1= Nt * lambda
How do you calculate lambda from R?
lambda = R + 1