Integumentary Vocab and Identification
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Cutaneous Membrane
The skin proper, consisting of the epidermis and dermis layers.
Keratin
Fibrous protein that provides strength, durability, and waterproofing to skin, hair, and nails.
Keratinization
Process by which cells move from deep layers to surface, accumulating keratin and eventually dying to form protective barrier.
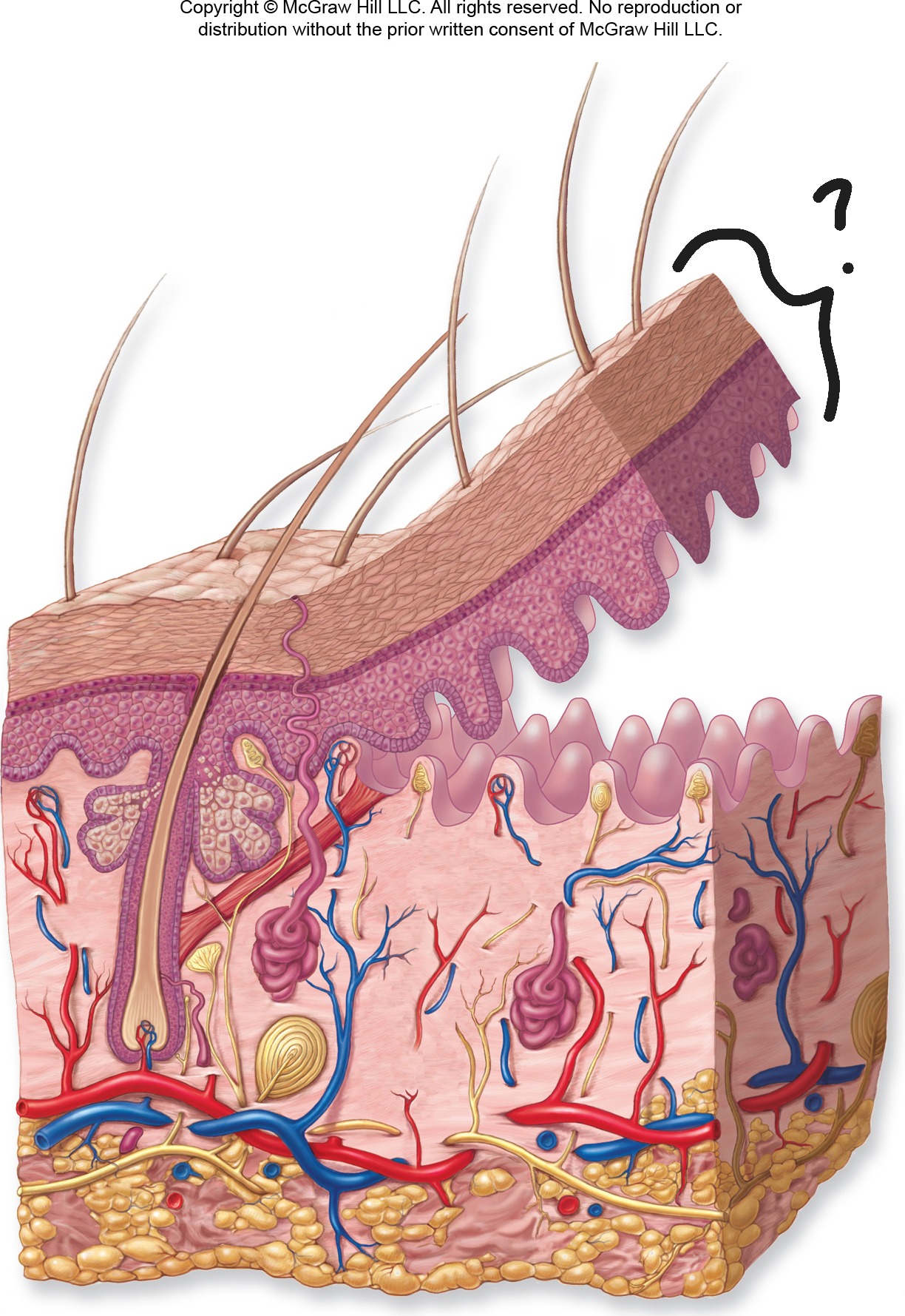
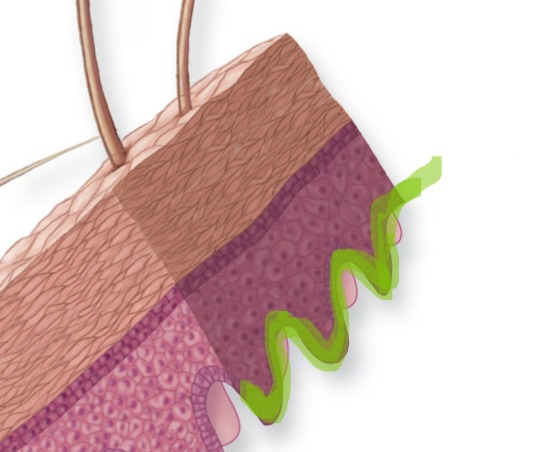
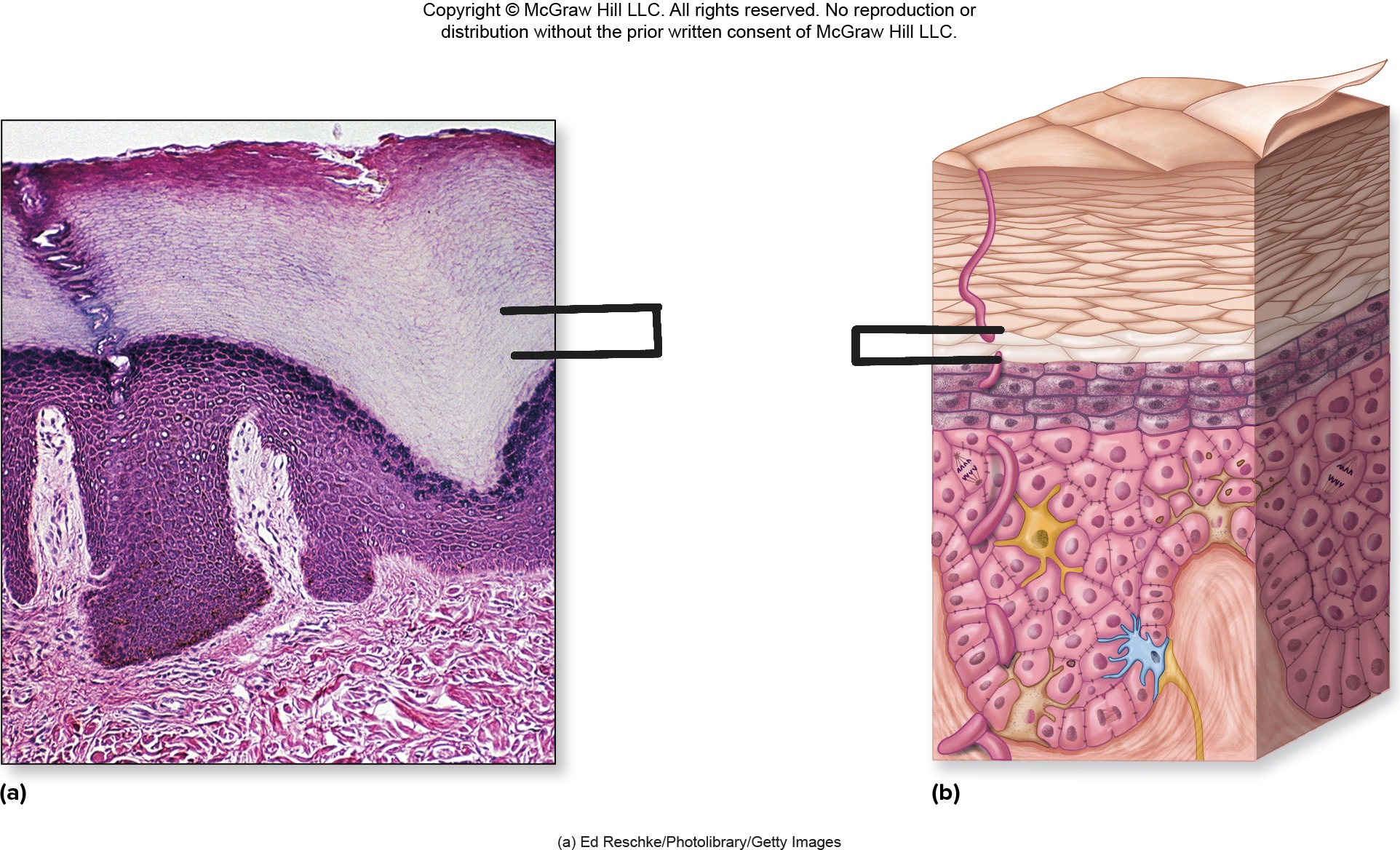
Epidermis
Outermost layer of skin;.
Epidermis - Make up
stratified squamous epithelial tissue that is avascular (no blood vessels). Contains 4-5 layers depending on location
Epidermis - Image
Dermis
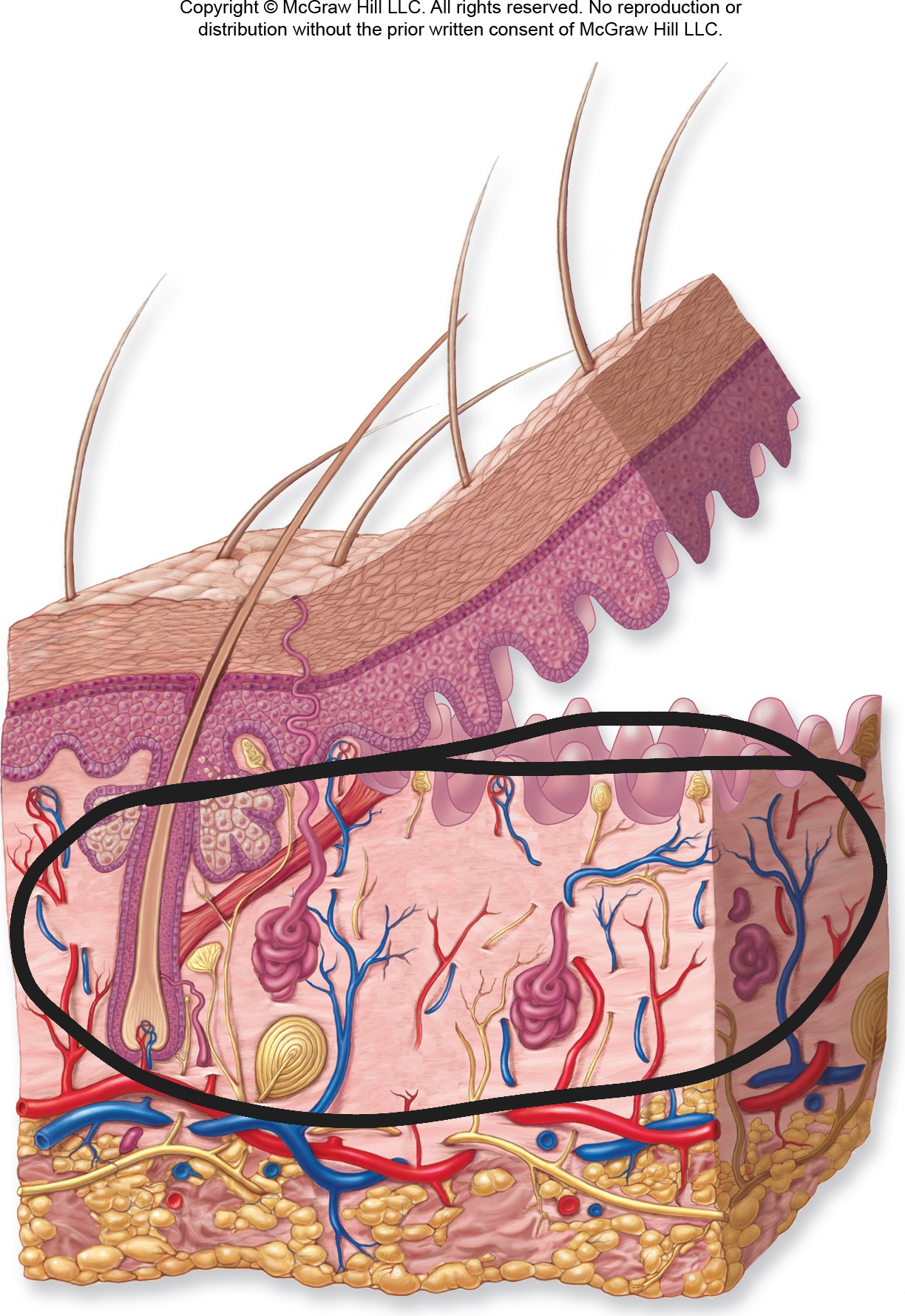
Middle layer of skin
Dermis - Make up
Made up of connective tissue. Contains blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and glands. Has two sublayers
Dermis - Image
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer)
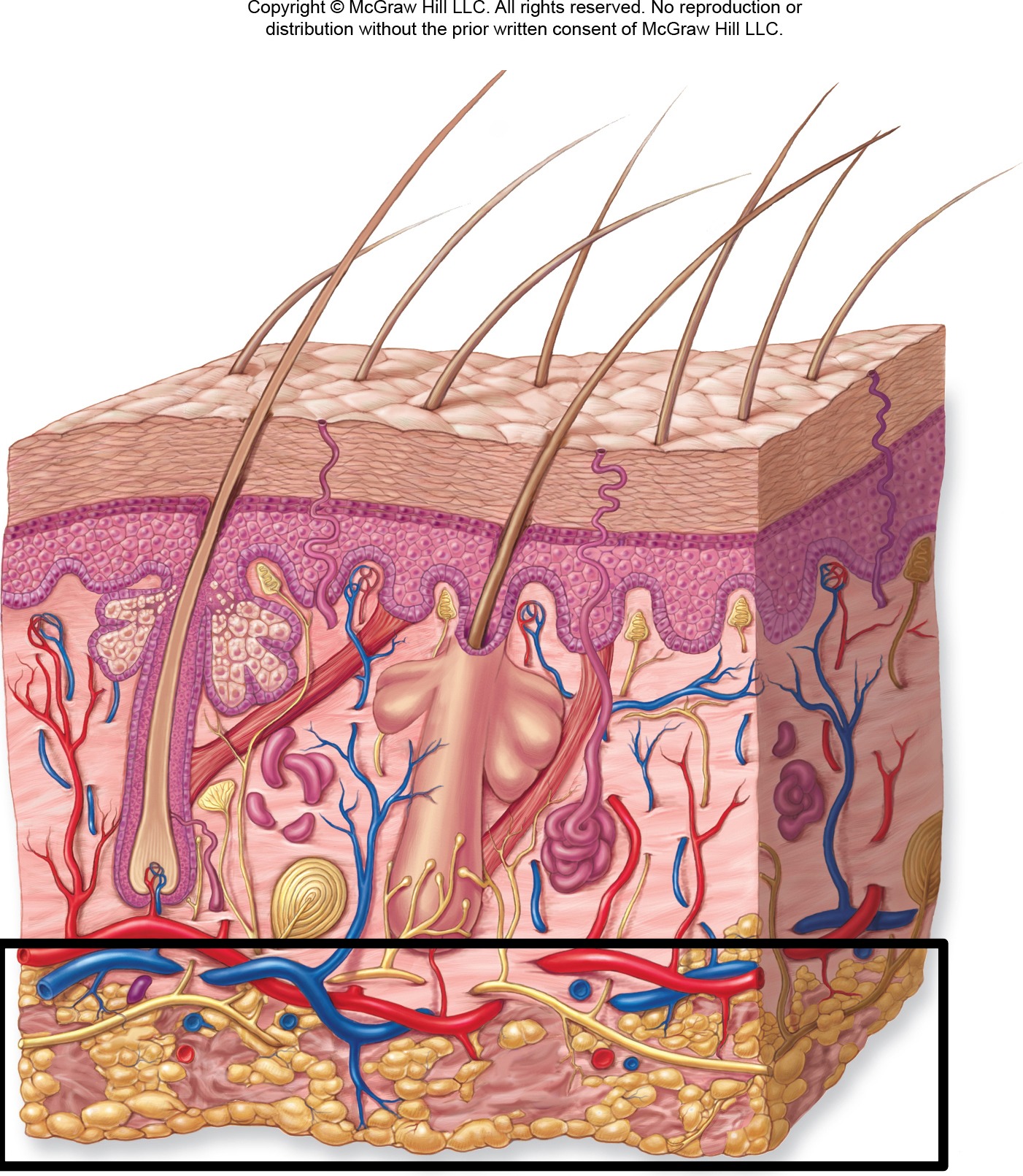
Deepest layer beneath dermis.
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer) - Make up
Composed of adipose and areolar connective tissue. Provides insulation, energy storage, and shock absorption.
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer) - Image
Stratum Basale
Deepest layer of epidermis.
Stratum Basale - Make up
Single layer of stem cells that continuously divide. Contains melanocytes.
Stratum Basale - Image
Stratum Spinosum
Layer above stratum basale.
Stratum Spinosum - Make up
Several layers of keratinocytes connected by desmosomes. Contains Langerhans cells.
Stratum Spinosum - Image
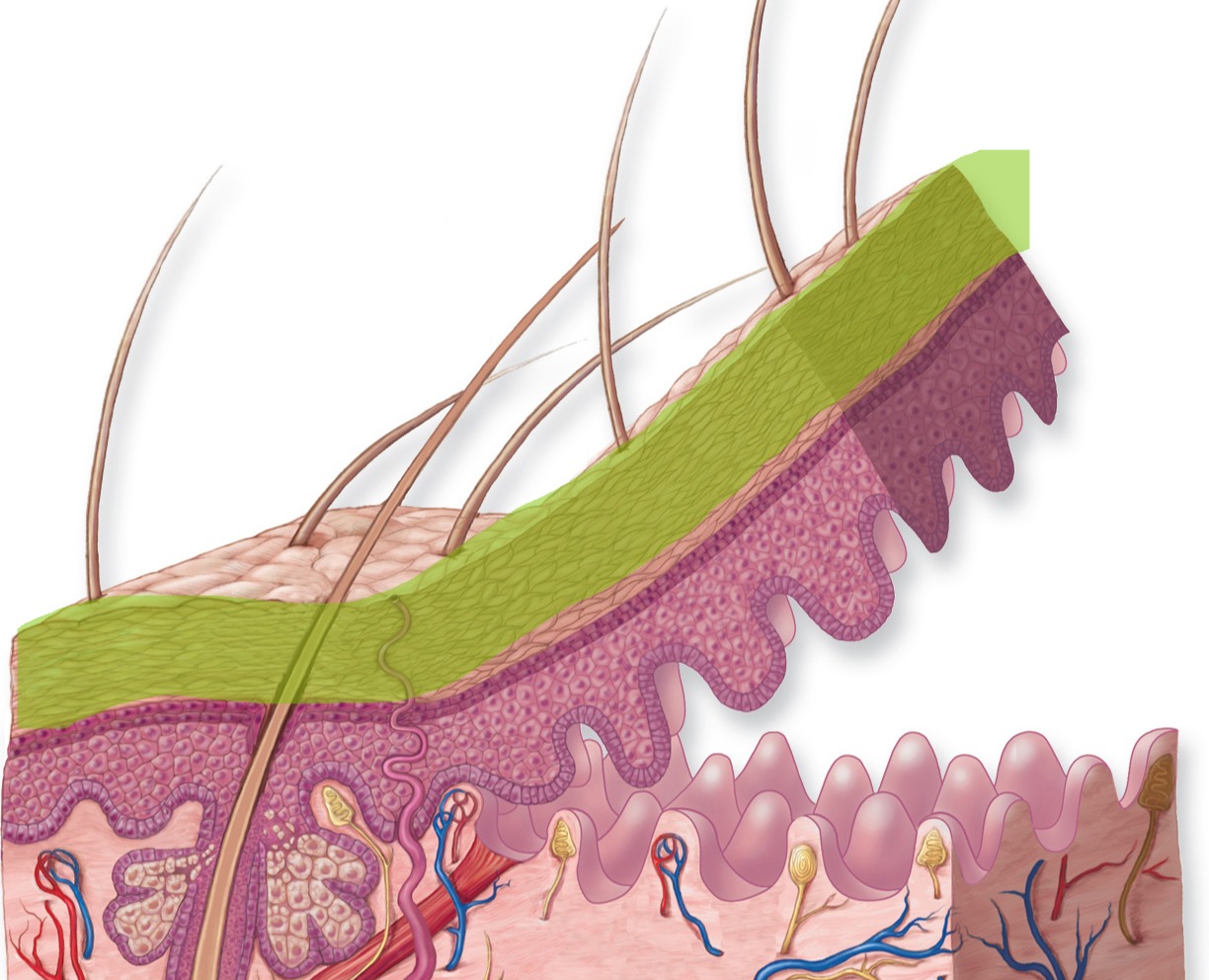
Stratum Granulosum
Middle layer
Stratum Granulosum - Make up
3-5 layers of flattened cells containing keratohyalin granules. Cells begin to die here.
Stratum Granulosum - Image
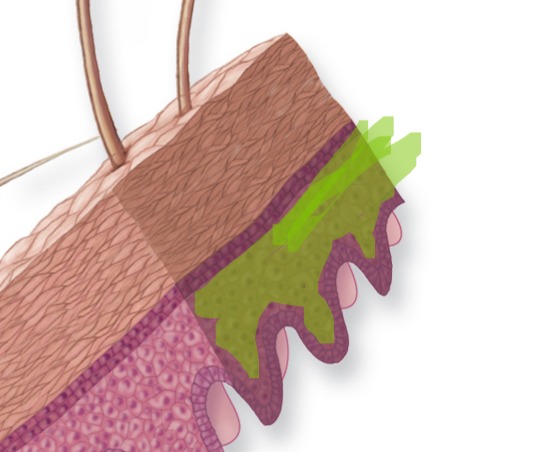
Stratum Lucidum
Clear layer found only in thick skin (palms, soles).
Stratum Lucidum - Make up
Consists of 2-3 layers of dead, transparent cells.
Stratum Lucidum - Image
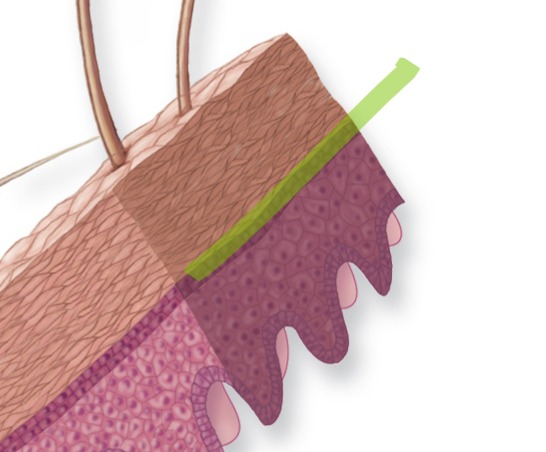
Stratum Corneum
Outermost layer of epidermis
Stratum Corneum - Make up
20-30 layers of dead, flattened, keratin-filled cells that are continuously shed.
Stratum Corneum
Keratinocytes
Produce keratin protein. Migrate from basal layer to surface over ~30 days. Most abundant cell type in epidermis.
Melanocytes
Cells that produce melanin pigment. Located in stratum basale. Protect nucleus from UV radiation.
Langerhans Cells
Immune cells in stratum spinosum. Part of body's defense system against pathogens.
Merkel Cells
Sensory cells in stratum basale that detect light touch when paired with nerve endings (tactile discs).
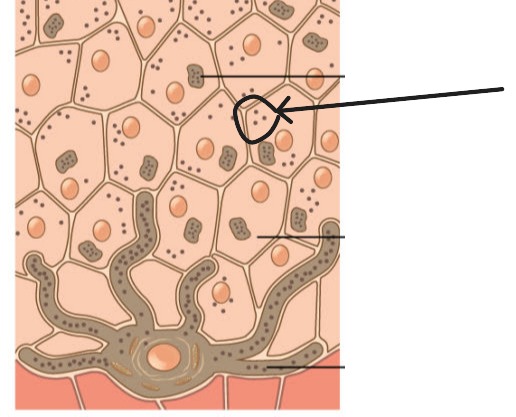
Melanin
Primary pigment determining skin color. Protects against UV radiation. Stored in melanosomes.
Melanin
Eumelanin
Brown/black type of melanin. More common in darker skin tones.
Pheomelanin
Red/yellow type of melanin. More common in lighter skin tones and red hair.
Melanosomes
Vesicles containing melanin that are transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes.
Melanosomes
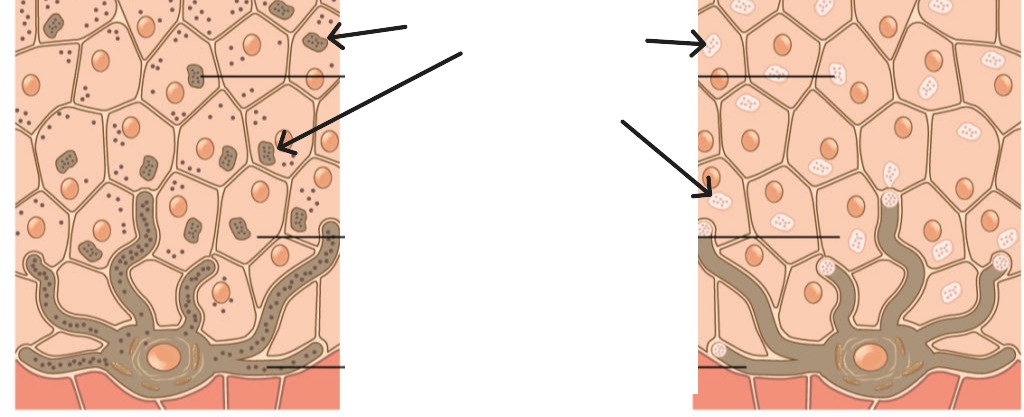
Carotene
Yellow/orange pigment obtained from diet (vegetables). Contributes to skin color, especially in palms and soles.
Cyanosis
Blue-purple discoloration of skin due to low oxygen levels in blood.
Erythema
Redness of skin due to increased blood flow (sunburn, inflammation, emotion).
Jaundice
Yellow discoloration due to excess bilirubin in blood (liver dysfunction).
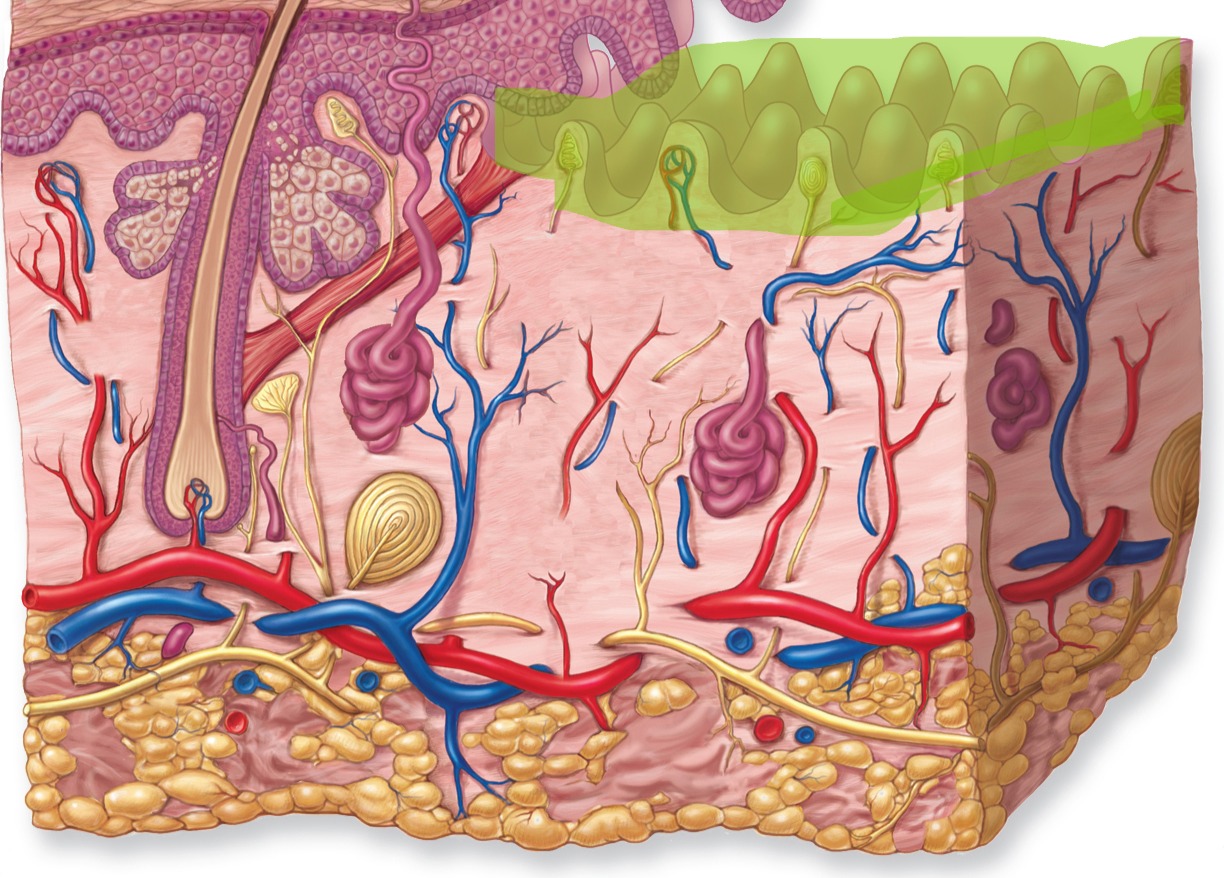
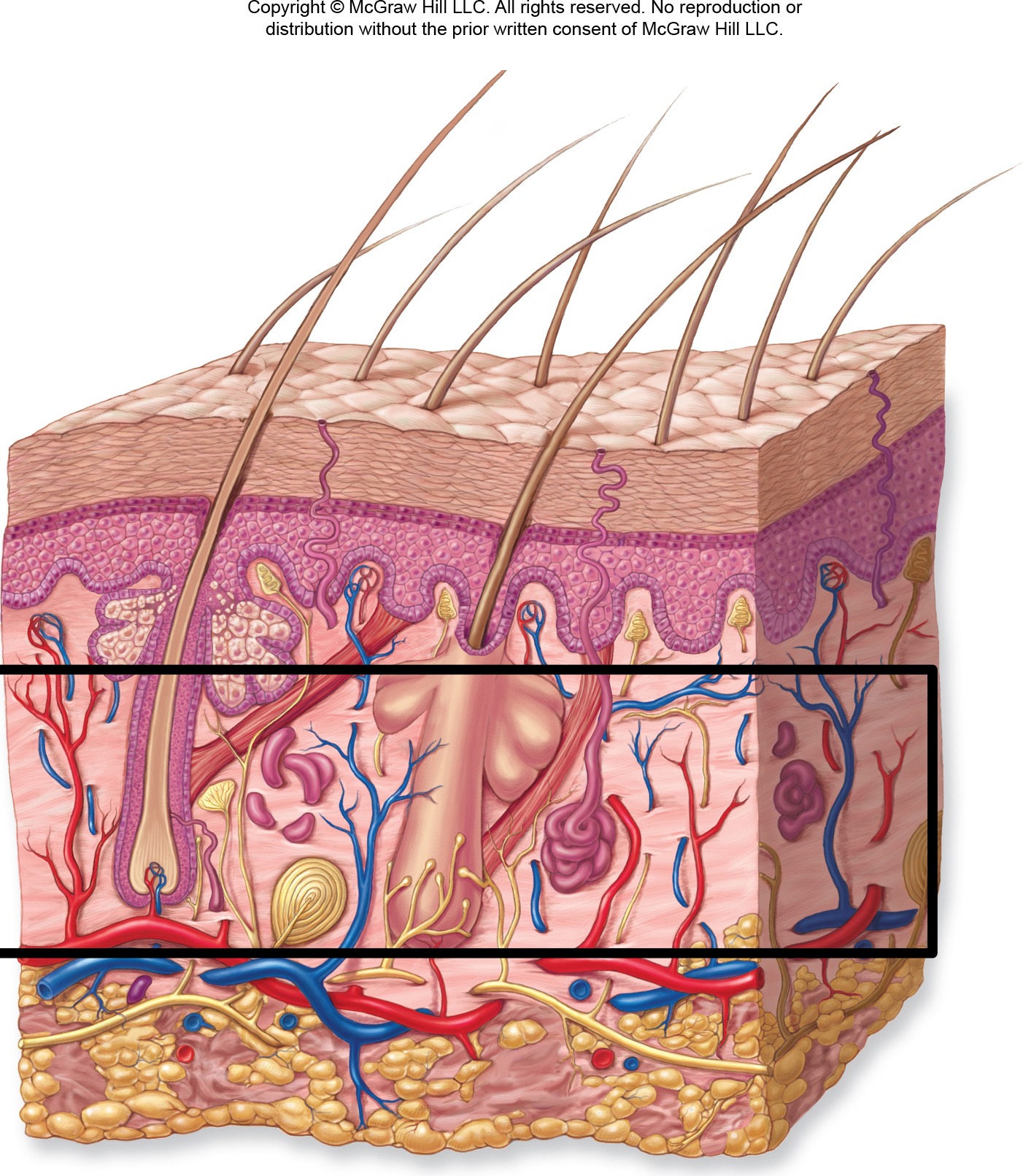
Papillary Layer
Upper layer of dermis
Papillary Layer - Make up
Areolar connective tissue with dermal papillae projecting into epidermis.
Papillary Layer
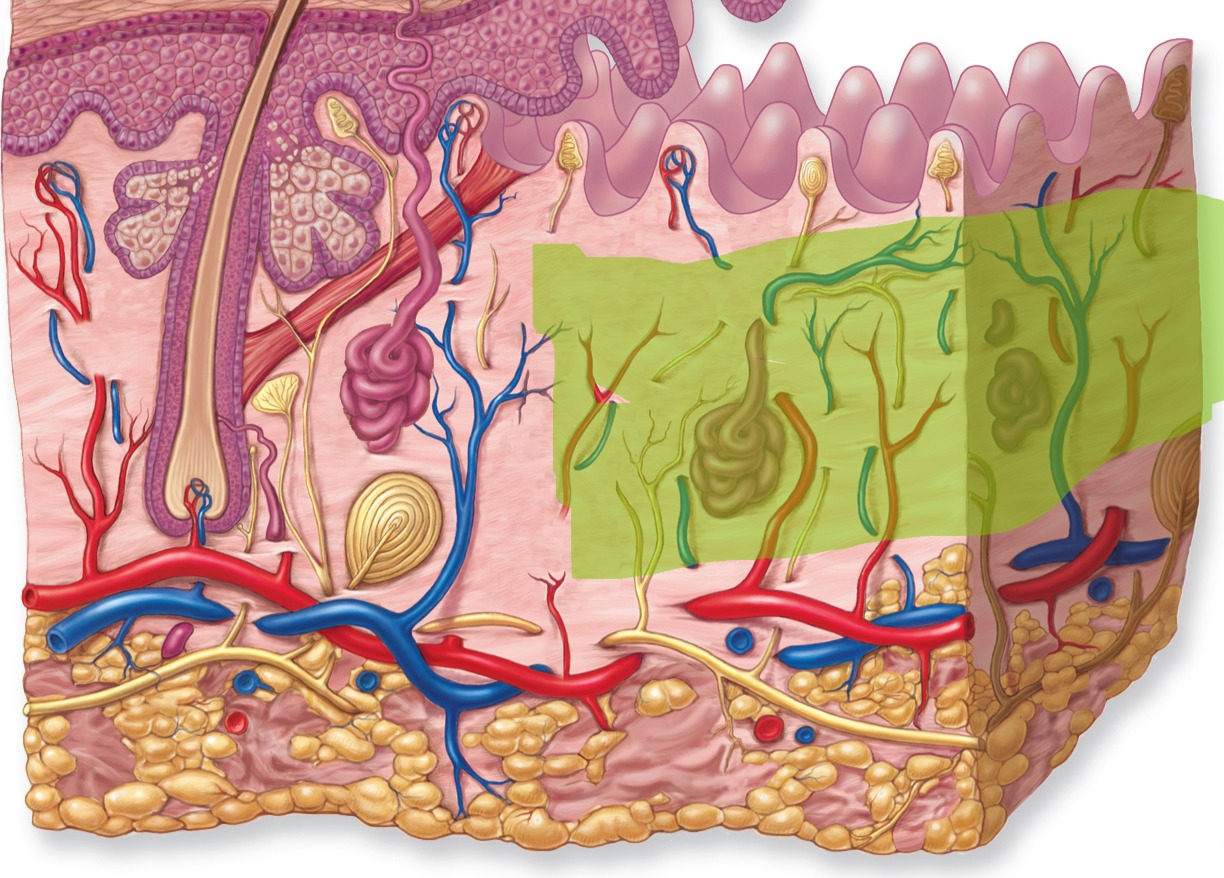
Reticular Layer
Lower layer of dermis.
Reticular Layer - Make up
Dense irregular connective tissue with collagen and elastin fibers.
Reticular Layer
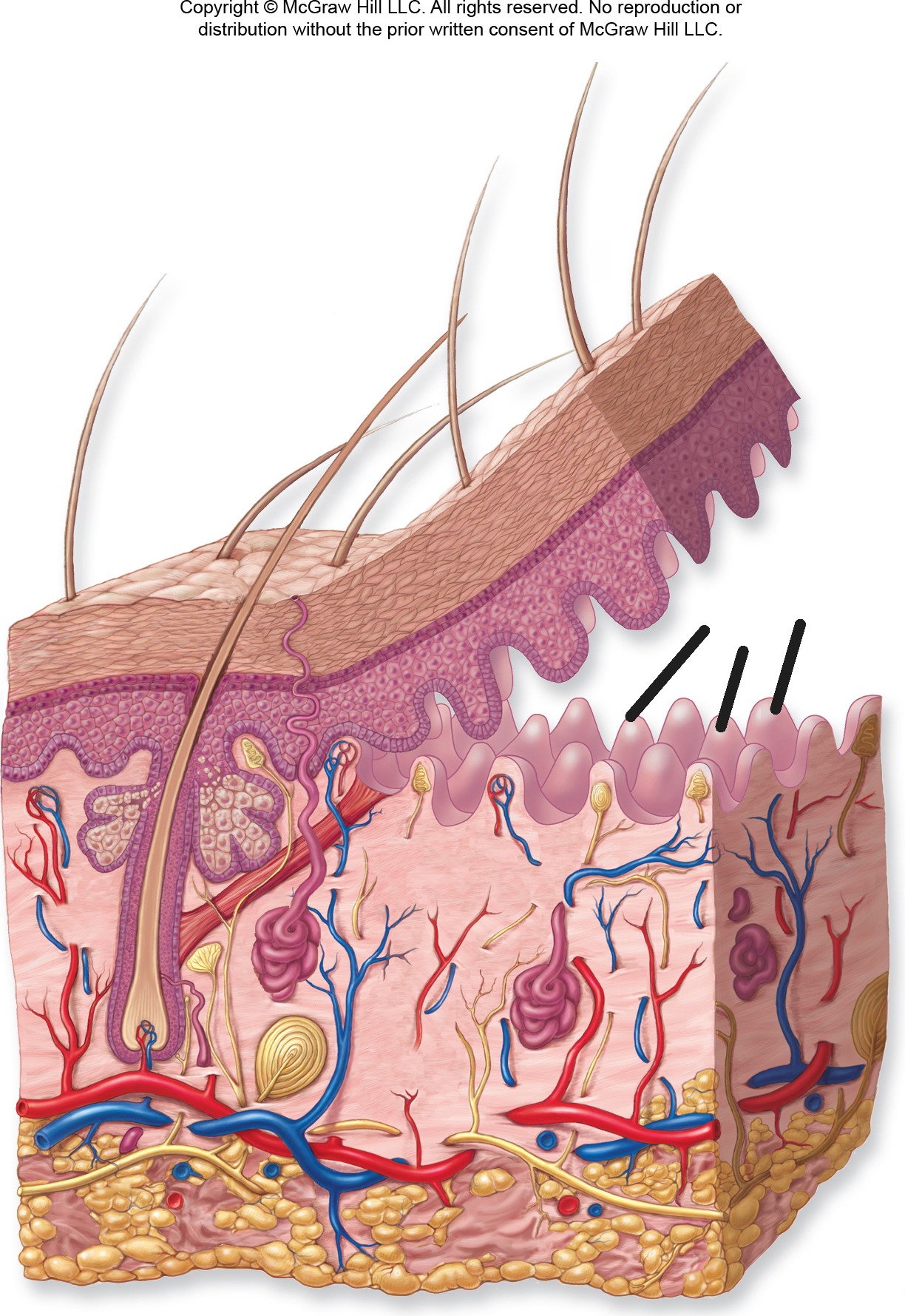
Dermal Papillae
Projections of papillary dermis into epidermis. Create fingerprints and increase surface area for attachment.
Dermal Papillae
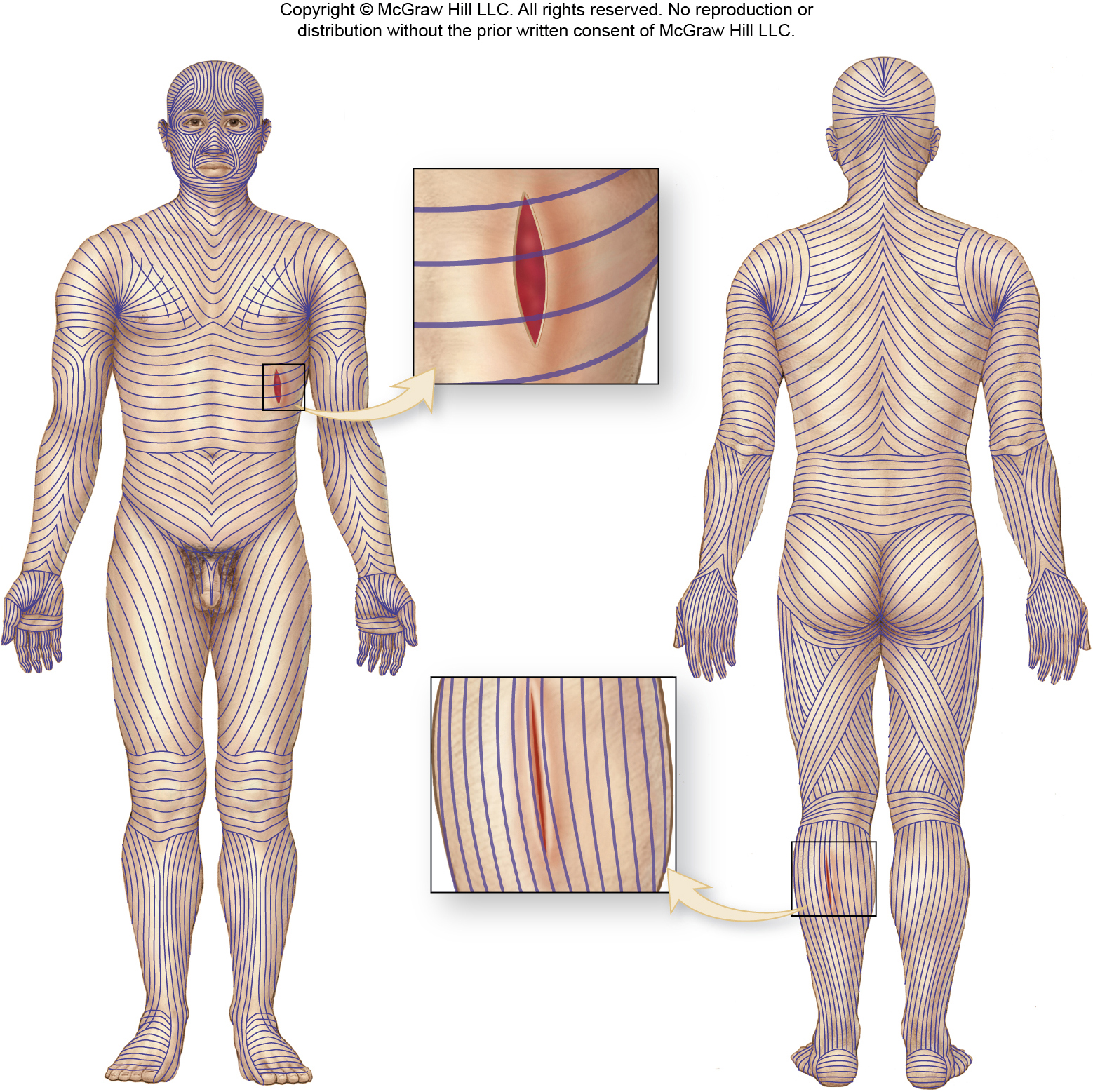
Lines of Cleavage (Langer Lines)
Natural tension lines in skin created by collagen fiber arrangement. Important for surgical incisions.
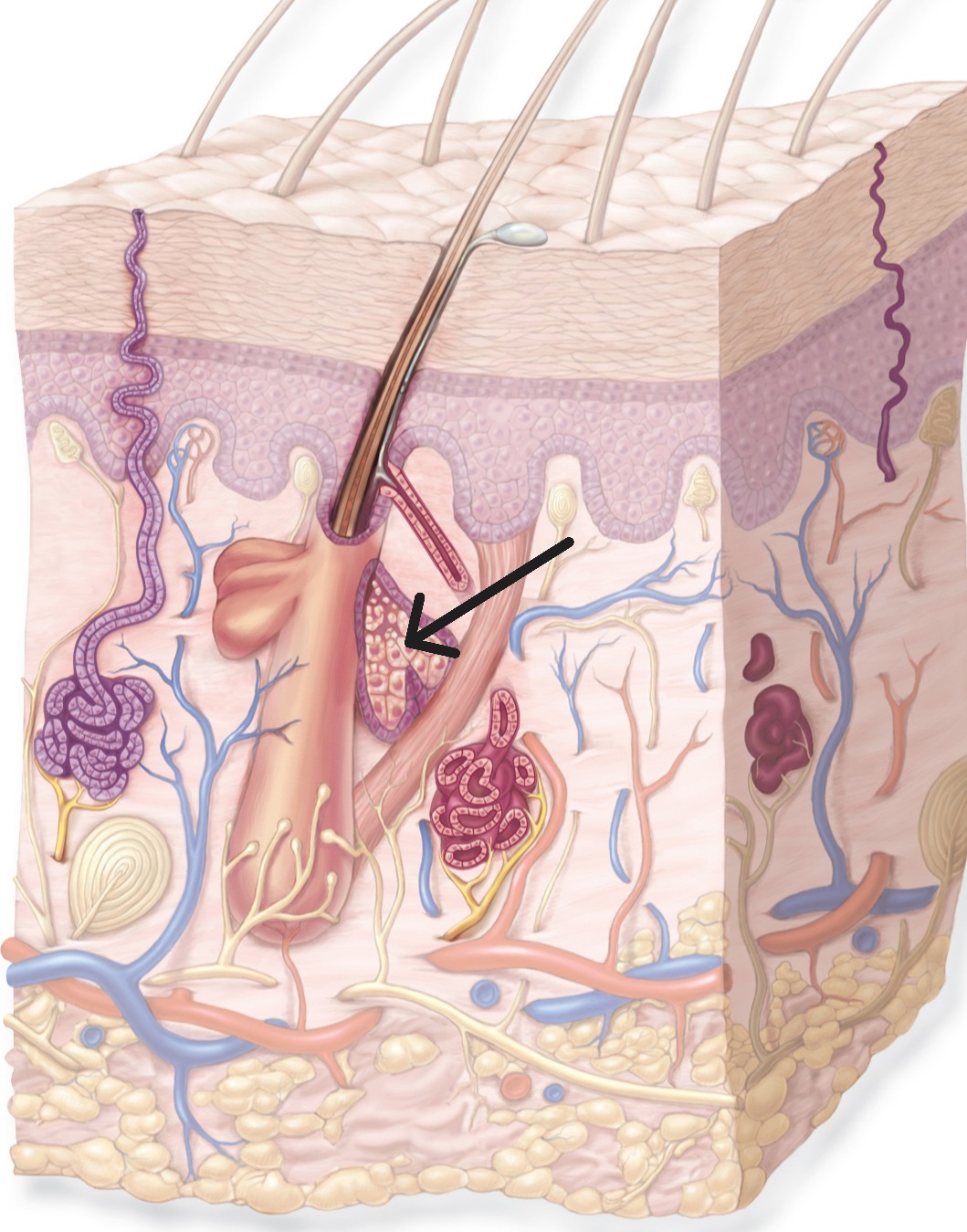
Sebaceous Glands
Oil glands associated with hair follicles. Produce sebum to lubricate skin and hair, inhibit bacterial growth.
Sebaceous Glands
Sebum
Oily secretion from sebaceous glands. Contains lipids that waterproof and protect skin.
Sudoriferous Glands
Sweat glands. Two types
Eccrine (Merocrine) Glands
Most common sweat glands. Produce watery sweat for temperature regulation. Abundant on palms, soles, forehead.
Eccrine (Merocrine) Glands
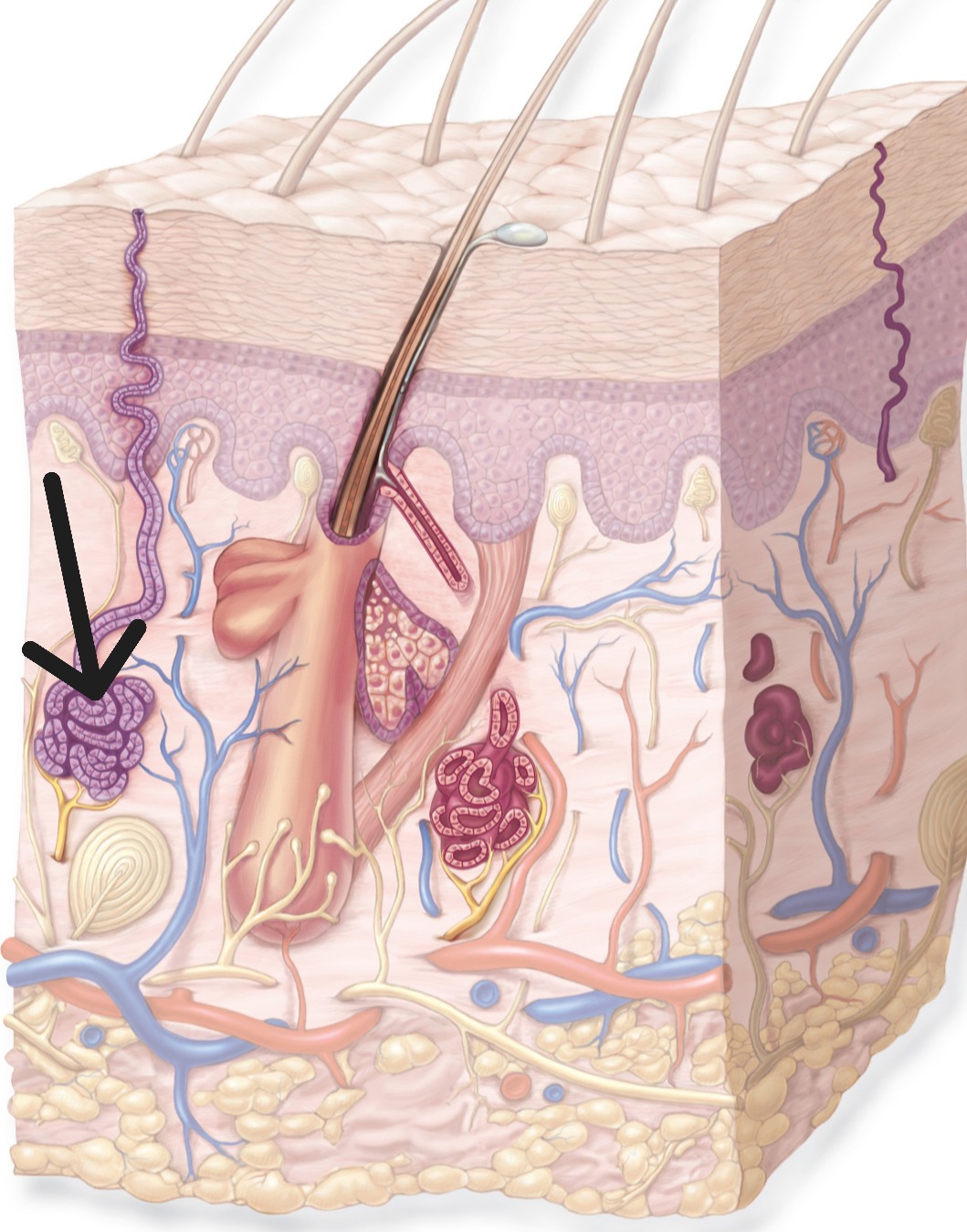
Apocrine Glands
Sweat glands associated with hair follicles. Located in armpits, groin, around nipples. Produce protein-rich secretion.
Apocrine Glands
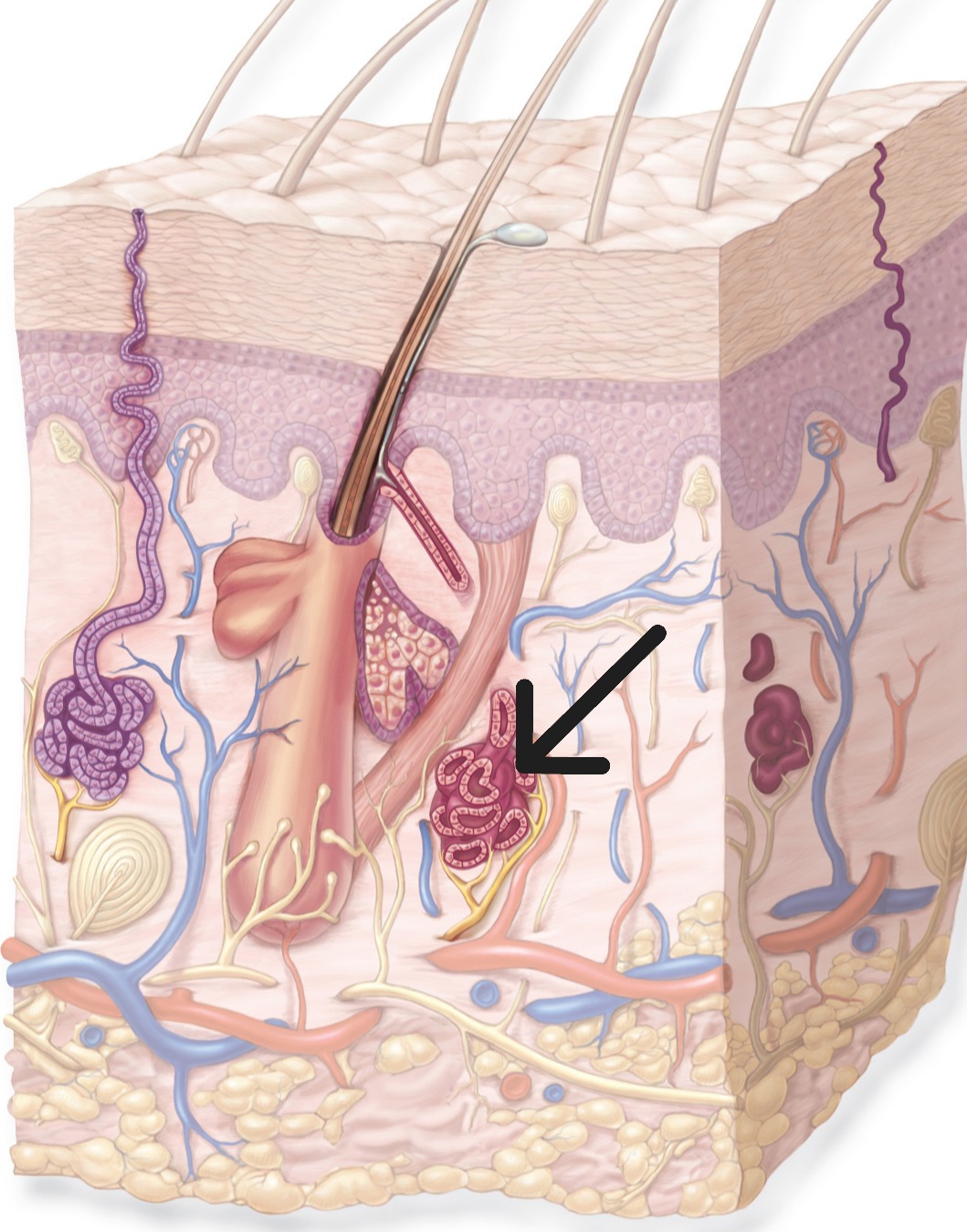
Ceruminous Glands
Modified apocrine glands in ear canal that produce earwax (cerumen).
Mammary Glands
Modified apocrine sweat glands that produce milk in females.
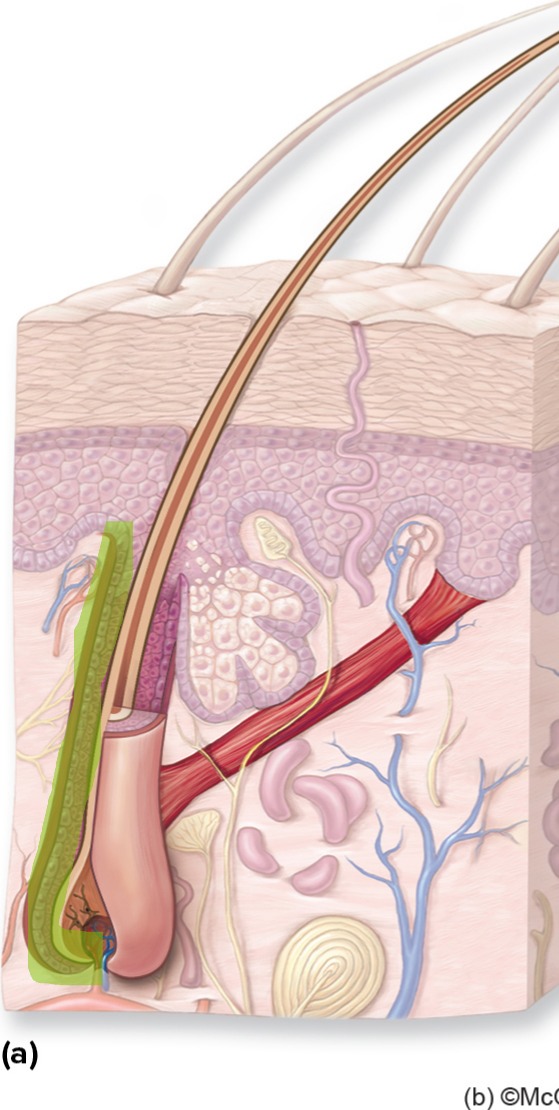
Hair Follicle
Structure in dermis where hair grows. Composed of epithelial and connective tissue layers.
Hair Follicle
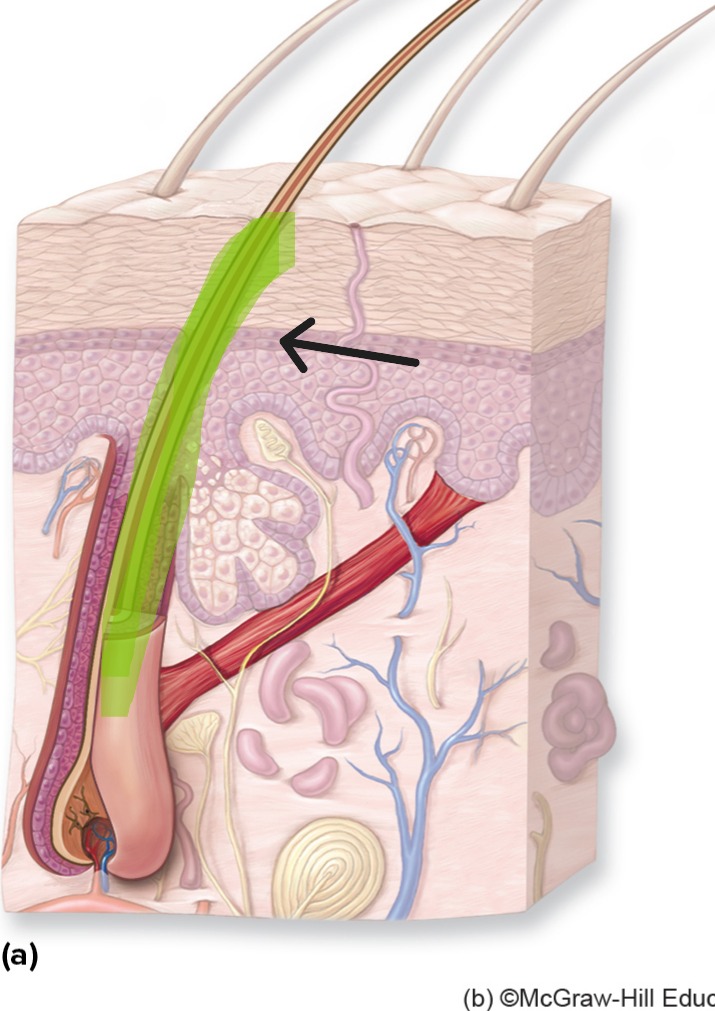
Hair Shaft
Visible portion of hair above skin surface.

Hair Root
Portion of hair within follicle, from bulb to skin surface.
Hair Bulb
Enlarged base of hair follicle containing matrix and dermal papilla.
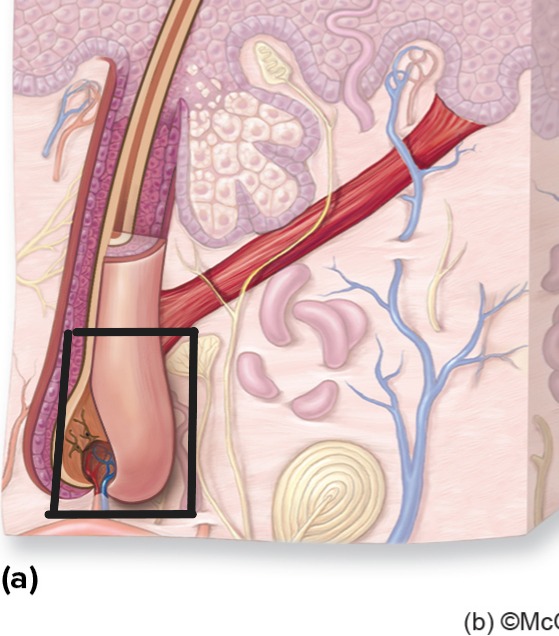
Hair Matrix
Growing region in bulb where cell division produces hair shaft. Contains trichocytes and melanocytes.
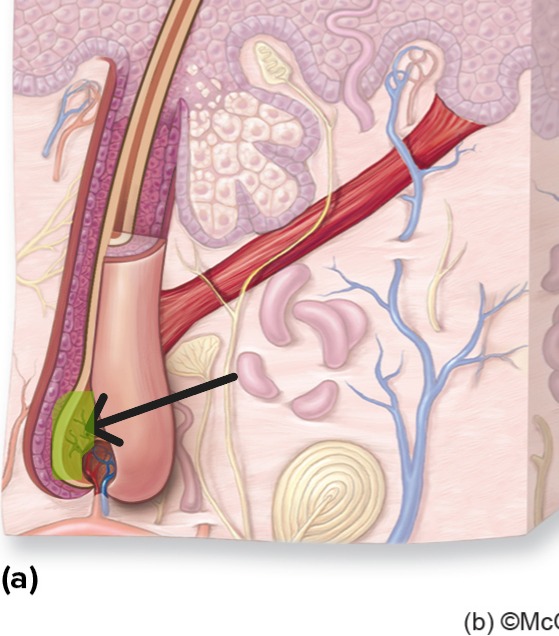
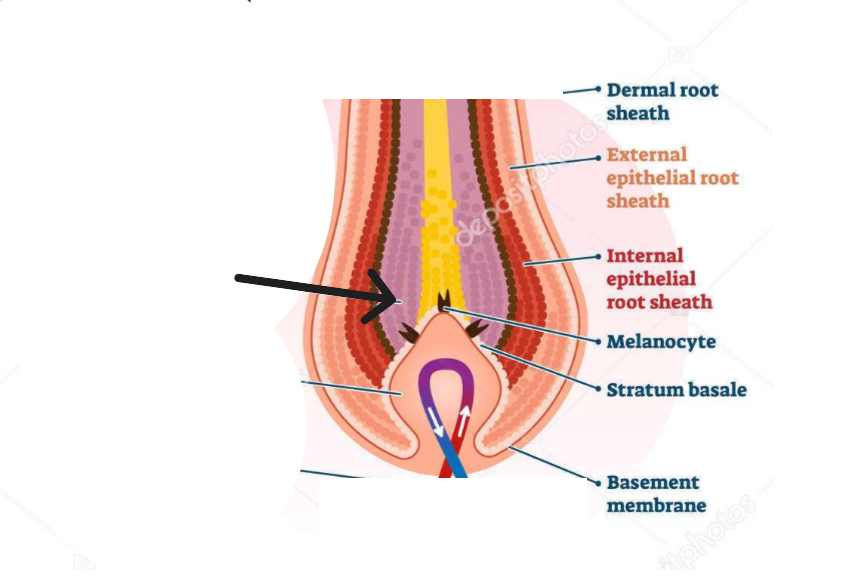
Hair Papilla
Cluster of cells in hair bulb that directs hair growth and supplies nutrients.
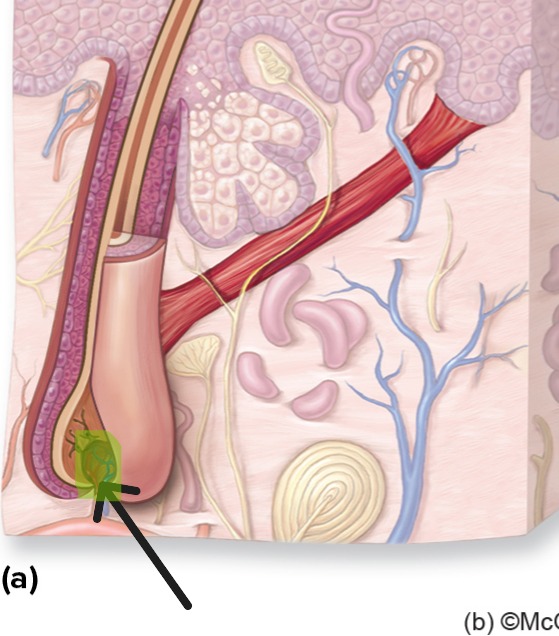
Trichocytes
Specialized cells in hair matrix that produce hair shaft.
Arrector Pili Muscle
Smooth muscle attached to hair follicle. Contraction causes "goosebumps" and hair to stand up.
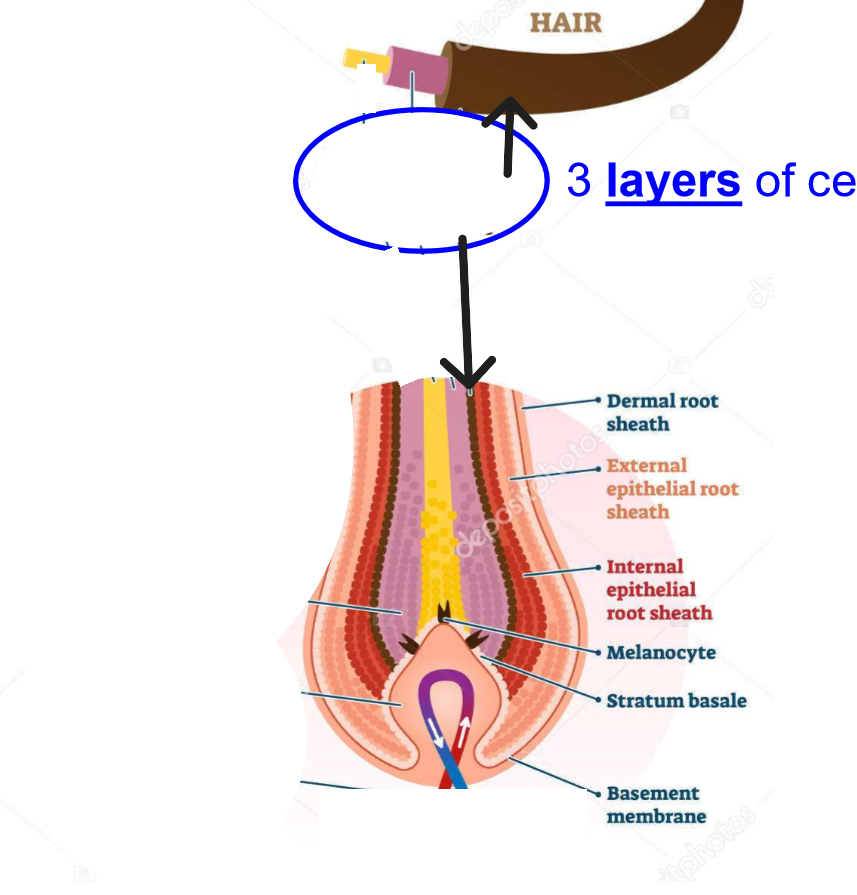
Hair Cuticle
Outermost layer of hair shaft. Overlapping scales that protect inner layers.
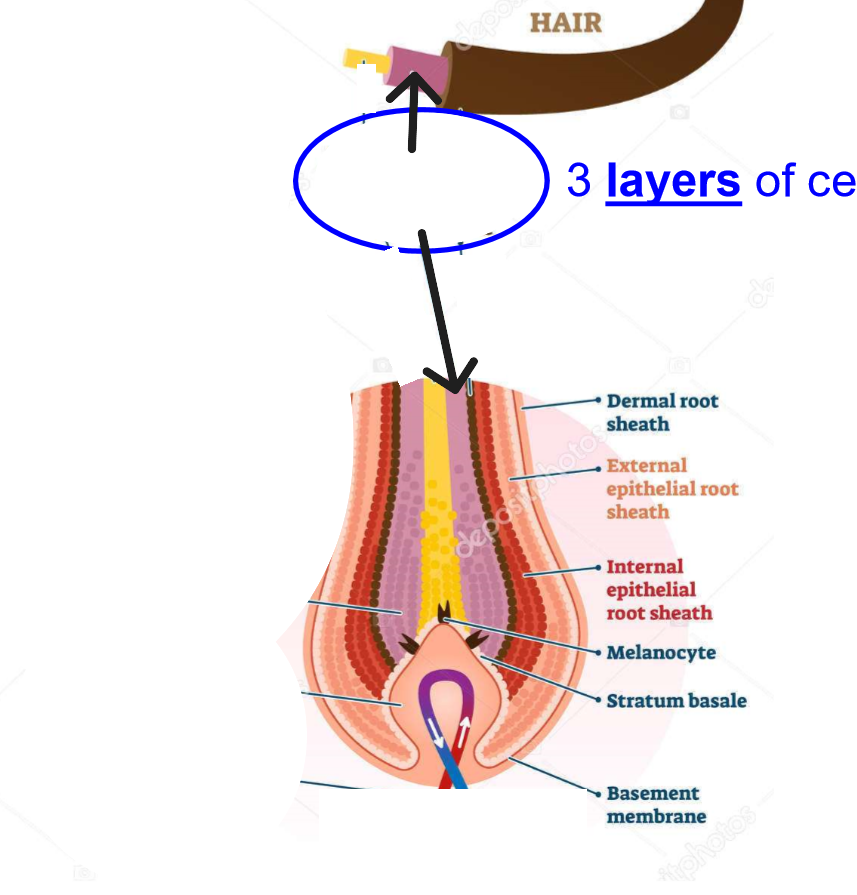
Hair Cortex
Middle layer of hair shaft. Contains most of hair's mass and determines strength and color.
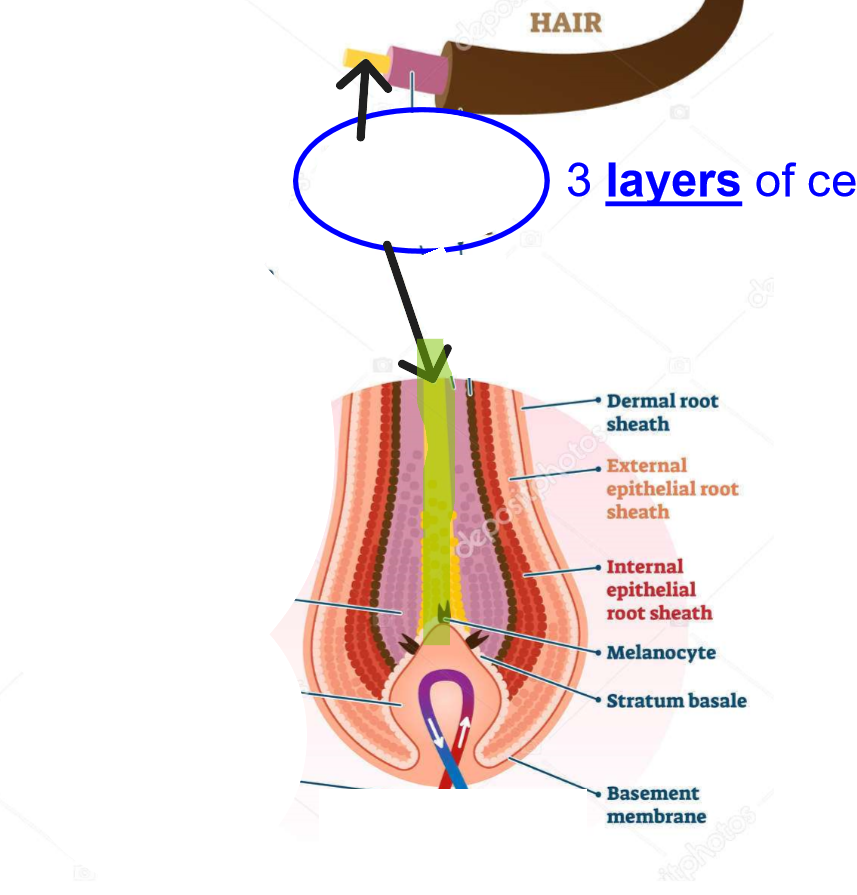
Hair Medulla
Central core of hair shaft. May be absent in fine hair.
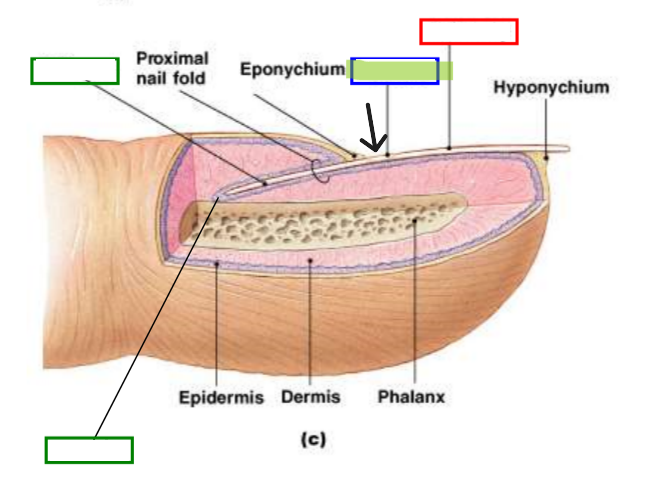
Nail Plate (Nail Body)
Visible portion of nail made of dead, keratinized cells.
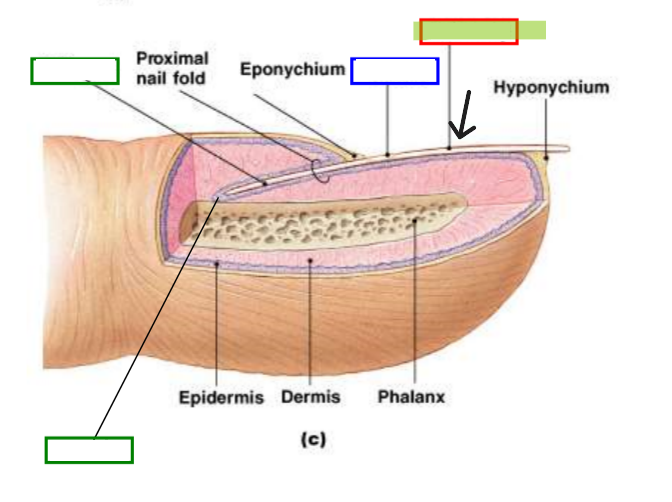
Nail Root
Portion of nail embedded in skin at base.
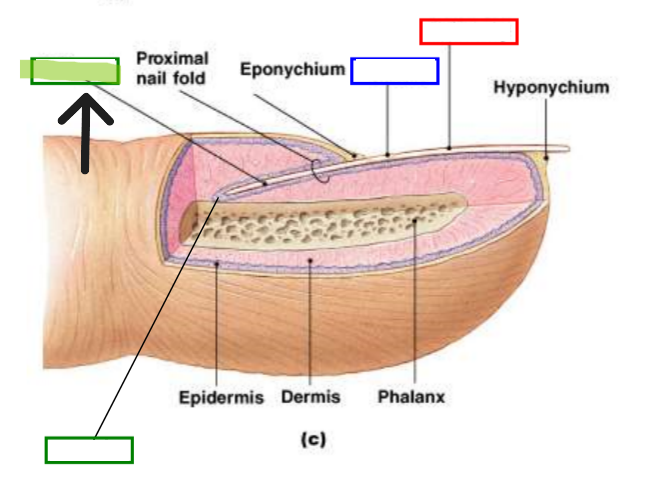
Nail Matrix
Growing region under nail root where new nail cells are produced.
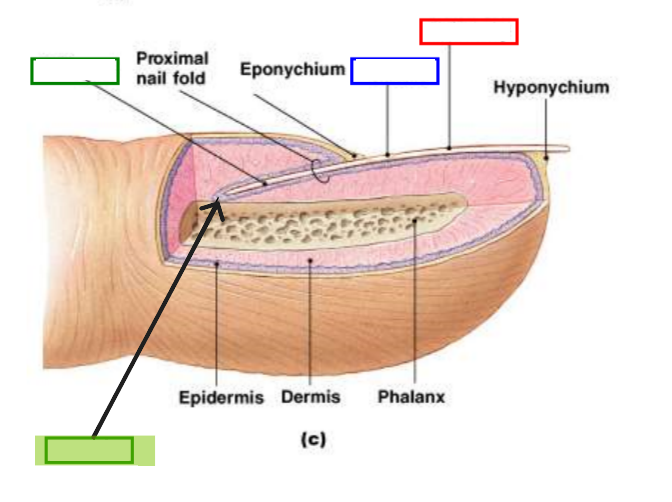
Nail Bed
Tissue beneath nail plate that nourishes growing nail.
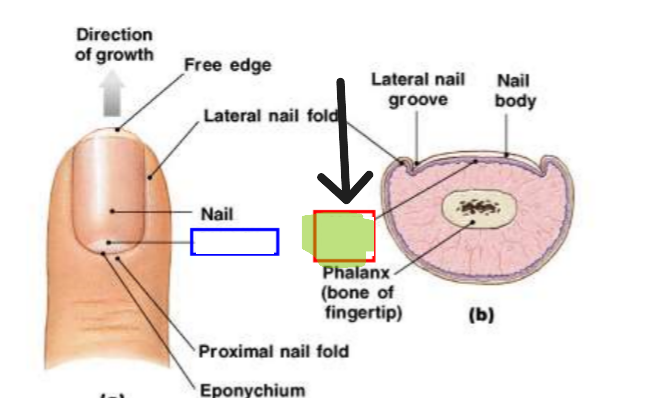
Lunula
Pale crescent visible at base of nail. Represents visible part of matrix.
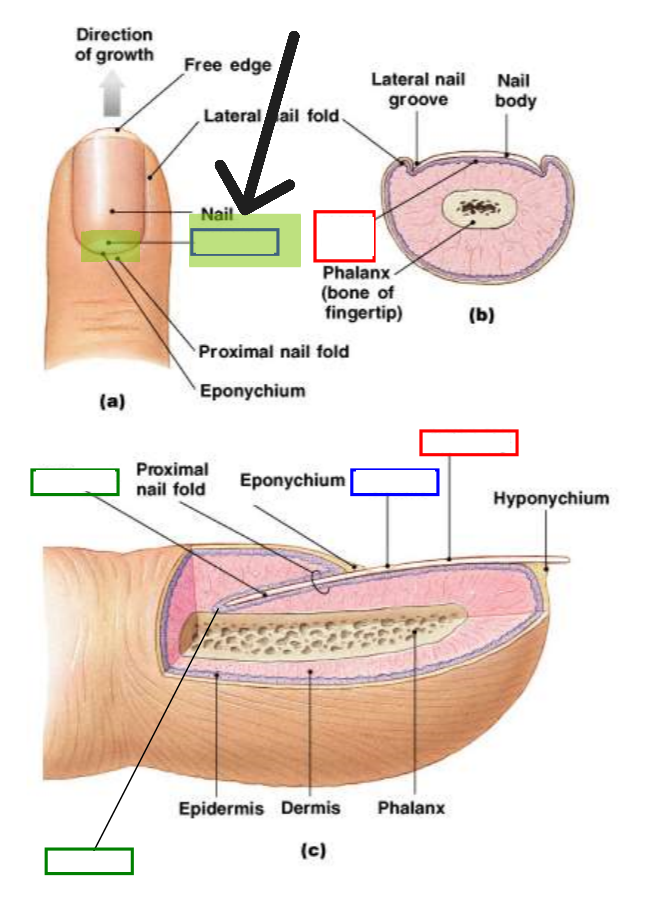
Lunula
Free Nerve Endings
Detect pain, temperature
Tactile (Merkel) Discs
Sense of touch and pressure
Lamellated Corpuscles
Sense Vibrations
Transepidermal Water Loss
Normal process of water evaporation through skin.
Anhidrosis
Inability to sweat normally.
Hyperhidrosis
Excessive sweating.
Alopecia
Hair loss or baldness.
Hirsutism
Excessive hair growth, especially in women.