Dysphagia
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Swallowing is
a sequence of neurologically controlled movements involving the muscles of the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, esophagus and stomach
Dysphagia
when the muscles or nerves of this process are damaged, swallowing is no longer normal
Due to neuroplasticity (brains ability to rewire/change over time)…
individuals that experience this damage may still be able to swallow certain food/drinks and/or use certain strategies to aid in swallow safety and regain function
what they regain can vary (factors)
compensatory strategies
Dysphagia =
whereas
Aphagia=
difficulty swallowing
whereas
inability to swallow
Dysphagia is
difficulty swallowing due to damage to or removal of muscles and/or structures involved in swallowing
disordered, disrupted, damaged, destroyed
Dysphagia is NOT primary diagnosis [i.e.dysphagia following stroke] it is a
SYMPTOM of a neurological disease or structural abnormality
Dysphagia is often described most often by its “signs” including
coughing/choking during or after meals
food sticking in throat
regurgitation
odynophagia =pain on swallowing
drooling
unexplained weight loss
nutritional deficiency
last two could be peds/old
SWAL QUAL
a survey of quality of life of patients with dysphagia
Impact of Dysphagia
functional limitations
ex) limited to specific diet of foods they don’t like
Activities and participation
patients on NPO may be reluctant to go out to eat
Environmental factors
use of personal care providers may be needed
As SLPs' we want to prevent the complications of Dysphagia
aspiration
dehydration
malnutrition
weight loss
elderly/weight loss
Aspiration
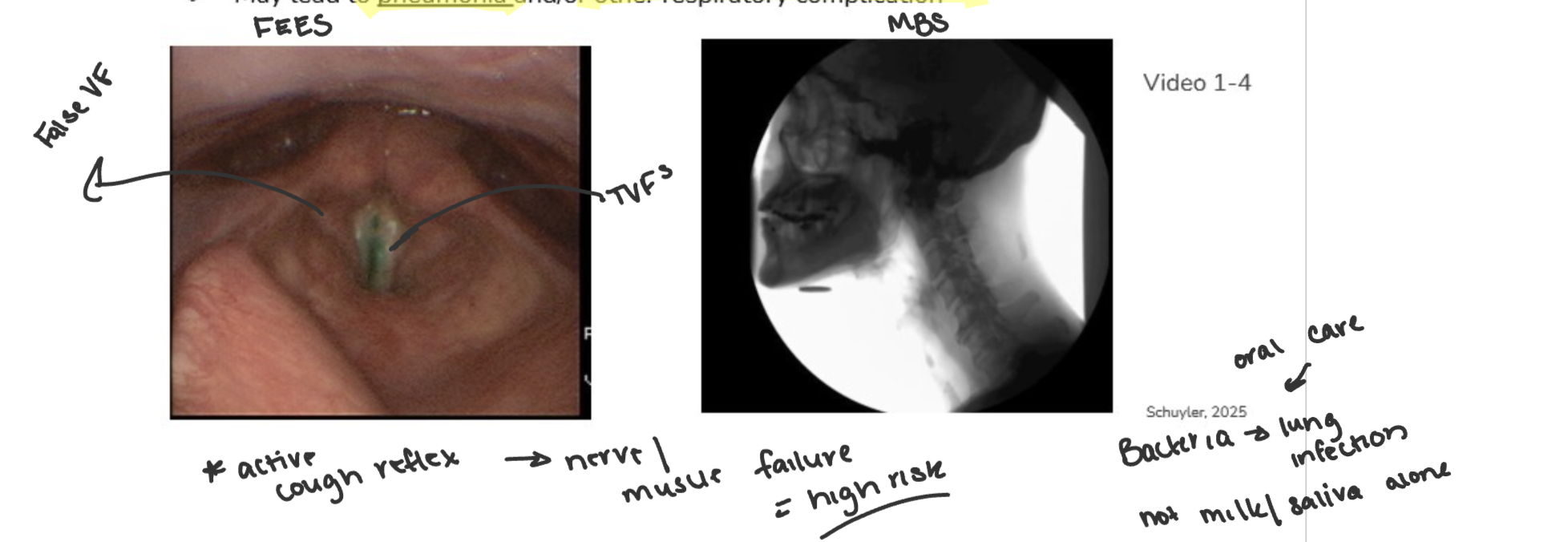
food, liquid, pill or secretions pass into airway below the level of the TRUE VFs
may lead to pneumonia and/or other respiratory complication
dehydration
state when not enough water in the body to maintain healthy fluid levels
may be caused by
drying medications
forgetting to drink
excessive perspiration
malnutrition
when body doesn’t get enough nutrients
may be due to inability to ingest food safely, fear of eating/drinking, reluctance to eat [inability to digest/absorb nutrients=GI]
results in inability to maintain health, muscle weakness and strain on heart
Weight loss
may impact coordination of muscles and muscle mass (those used to swallow), immobility, delayed recovery from injury/illness
unplanned weight loss may be a result of swallowing disorder ESPECIALLY ELDERLY
to combat
temporary NPO
nutritional consultation
Elderly and weight loss
affects recovery from medical problems
may be a subtle sign of depression
may be due to inability to eat preferred foods
fear of pneumonia
dental problems
dementia
Aspiration Pneumonia
pulmonary infection from acute or chronic aspiration of fluid, food or oral secretions from mouth OR stomach (reflux) into the airway/lungs
can be life threatening
not all aspiration leads to pneumonia
45% of adults aspirate in sleep
Treated with antibiotics; however if the CAUSE isn’t ELIMINATED, INFECTION = RECURRENT
weak cough/pulmonary disease higher risk
Community/hospital acquired pneumonia
result of acquired bacterial infection
hospital=nosocomial 48-72 hours following admission
complicated by pre-existing conditions (age, illness, aspiration, GERD)
TX= antibiotics
DX of PNA —> symptoms
symptoms
dyspnea (short of breath), fever, crackles during lung auscultation (Stethoscope)
completed with CXR interpreted by physician
DX of PNA —> presentation
CXR RIGHT LOWER LOBE most frequently involved with aspiration related
bilateral lower lobe = aspiration upright
right upper lobe more common = aspiration prone position
Impact of Dysphagia on quality of life
general health
psychological well-being
financial well being
voice
general health
inability to swallow may lead to a decline in overall health
Psychological Well-being
eating is SOCIAL FUNCTION + nutritional necessity
individual may no longer be able to participate in preferred, social activities
food=enjoyment
dysphagia =diet=regain health
Financial well-being
may be need for special foods, supplements, enteral (FT) or parenteral (vein) dysphagia therapy, devices (prepare food)
cost of healthcare system for TX of PNA, recurrent hospitalizations
voice
evidence suggests patients with swallowing disorders often have voice changes
repeatedly coughing (aspiration)
GERD erodes VF’s stomach acid
laryngopharyngeal reflux, excess mucus and/or laryngitis —> dysphagia indicators/causes
Causes of Dysphagia
Natural aging (not necessarily dysphagia)
neurological/degenerative diseases
esophagitis
CVA - stroke
Head injury/ TBI
dementia (middle to late)
Head and neck cancer and/or TX (radiation/chemo/surgery)
weakens/stiffens/removal of structures
Medications
if dysphagia is from the brain stem =
severe
Causes of Dysphagia Cont’d
tumors
trauma
intubation/extubation (breathing tube pulled in and out VF’s)
systemic (parkinsons, diabetes, high blood pressure)/autoimmune disease
infection
inflammatory disease/chronic reflux
congenital disorders (at birth —> down syndrome)
reflux gastroesophageal, laryngopharyngeal
muscle tension dysphagia
Infants and children
sucking, swallowing, feeding disorders often overlooked until failure to thrive condition
significant impact on the inability to achieve nutrition enough to grow and develop
CAUSES —> gestational (utero) factors, preterm birth, neurological disorders, anatomical disorders
improvement in neonatal care, instrumentation and study of nutritional impact
Early Intervention
reduced PNA rate in acute care (no aspiration=no pneumonia)
may improve recovery from head and neck cancer
reduces length of hospital stays ($/emotional)
positive impact of dysphagia TX for neurological disease accompanied by dysphagia
Prevent extensive comorbidities that result from the interaction of swallowing disorders w/ other diseases
SCREENING procedures target patients early for swallowing intervention
Testing for Dysphagia
no single test that is 100% accurate for DX dysphagia or its cause
prevalence of dysphagia dependent upon Dx
screening procedures (history/caregiver)
Clinical swallow evaluation CSE/Bedside swallow eval cost effective
instrumental evals: more invasive
modified barium swallow MBS OR VFSS videofluoroscopic swallow study
flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing FEES
Acute Care
length of stay
example
short 2-5 days
hospital (ICU or NICU)
Subacute Care
length of stay
example
5-28 days
hospital rehab unit
Rehabilitation facility
length of stay
example
varies (few weeks-months)
MOST INTENSIVE THERAPY
skilled nursing short term rehab section; outpatient clinic
Skilled nursing facility
length of stay
example
patients too medically complex to go home and/or unable to manage independently
may have dysphagia due to disease effect AND aging process
LONG TERM
nursing home
Dysphagia team
SLP
GI
nurse/CNA (skilled nursing/hospital)
dietition/nutritionist
OT
Respiratory therapist
patient/family
radiologist (MBS)
medical doctor/NP
oncologist/neurologist/ENT
ASHA roles + responsibilities
must be possessed, required to complete, and based upon education and experience
identify signs/symptoms of dysphagia
practice interprofessional collaboration
advocate for services for individuals w/ feeding/swallowing disorders
code of ethics
set of ethical guidelines to which we adhere
reflects what we value as professionals and establishes expectations for our scientific and clinical practice based on principles of duty, accountability, fairness and responsibility
intended to ensure the welfare of the consumer and to protect the reputation and integrity of the professions
all members have right to bring allegations of ethical dilemma to ASHA board of ethics —> sanctions when violated
4 principles of ethics
Put the client’s welfare first (including research participants).
Stay competent—keep learning and improving (CEUs).
Be honest with the public and share accurate info.
Respect the profession, work well with others, and follow professional standards.
Ethical considerations and swallowing
ethical dilemmas arise when clinical recommendations conflict w/ patients wishes = advanced directives [patients preference medically] OR the decision maker/health care proxy
Health care proxy
alt. person who makes decisions if patient isn’t capable
1) respect for autonomy
2) beneficence
3) nonmaleficence
4) justice
Each competent individual should have the rights to decide how one is medically managed
Clinicians should take positive action to do good for patients and act to prevent or remove harm
Don’t cause deliberate harm to patient
Patients needs should be addressed in a fair and equitable manner
THEMES OF THESE GUIDELINES
involve the patient and family in decision making
educate family about risks and benefits
accurately identifying progress/prognosis
encourage regular follow up to ensure fair/consistent care for all patients
Impact of Dysphagia
Estimated that in the U.S.,
300,000-600,000 people
with clinically significant
dysphagia are diagnosed
annually
● Nearly 70% of these are older than 60
older than age 60
Epidemiology
prevalence and cause of a disorder
Swallowing difficulties may arise from
mechanical problems of the swallowing mechanism
neurological disorders
GI disorders
loss of organs due to surgery or traumatic injury
dysphagia/aphagia may involve
disruption of the timing of the events needed to swallow
xerostomia
dry mouth
With the onset of Dysphagia, the body is
not able to cope as well with the primary disease
dysphagia exacerbates the primary disease