MGMT 382 Final Review
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Infrastructure
Refers to the fundamental facilities needed for the operation of an economy or enterprise.
Infrastructure Examples
buildings, roads, and power supplies for an economy,
•IT infrastructure for an enterprise
Types of IT Infrastructure
Decentralized infrastructure, Centralized infrastructure, Distributed infrastructure
Decentralized Infrastructure
Involves little or no sharing of information systems
Gives users the liberty to develop applications that meet their needs and maintain control over the applications they develop.
Decentralized Infrastructure Advantages
Users have full control over application development and data.
Decentralized Infrastructure Example
Each department in an organization maintains separate systems without shared resources.
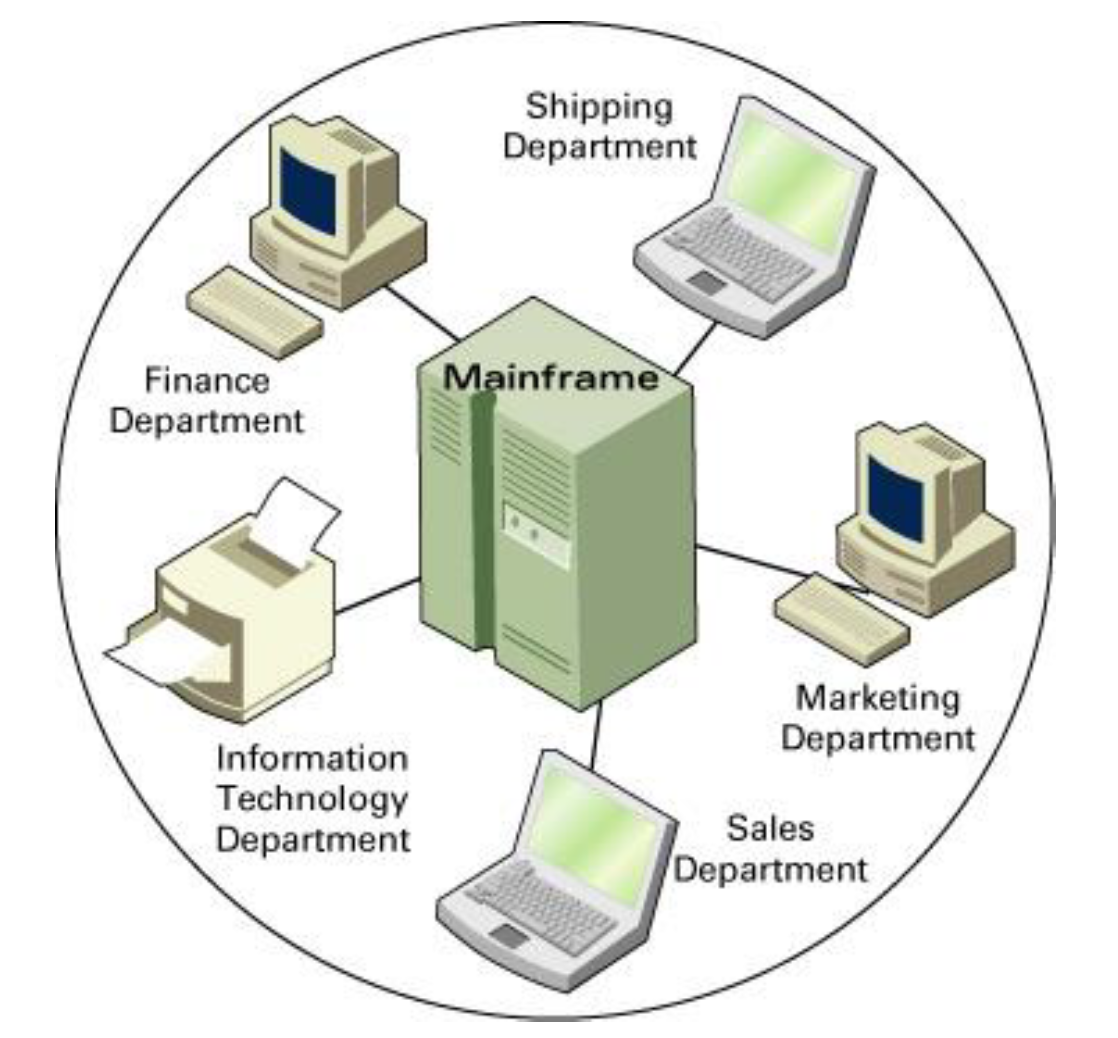
Centralized Infrastructure
• Involves sharing of information systems in one ____ area or one ____ mainframe.
• Mainframes were originally the only computers available for business.
Centralized Infrastructure Advantages
Easier to control and secure; more efficient for large organizations.
Centralized Infrastructure Examples
A mainframe that supports all departments in a company.
Distributed Infrastructure Types
Client/server, Peer 2 Peer
Client/Server Infrastructure
• Has one or more computers that are redacted which provide services to other redacted computers.
• Is a form of distributed infrastructure
Client/Server Infrastructure Example
• The Internet, where web servers deliver content to user browsers.
• Server (e.g., WWW server) is continuously active, ready to accept requests from client programs.
• Client is browser, sending requests to server program.
• When a user clicks on a link, the requested link is translated by browser into HTTP. The server knows exactly what files to request from which other servers, since every link contains a URL with this information.
Peer-to-Peer Infrastructure
• All devices act as both client and server, sharing resources equally.
• A form of distributed infrastructure.
Peer-to-Peer Infrastructure Example
BitTorrent, where users share pieces of files with one another directly.
Distributed Infrastructure
• Involves distributing the information and processing power of IT systems via a network.
• By connecting all the information systems, all locations can share information and applications.
Distributed Infrastructure Advantages
Facilitates sharing and redundancy across multiple locations.
Distributed Infrastructure Example
An international company with servers in each major region for local data access.
Cloud Computing
- No infrastructure at all!
- Web-based apps, storage, and processing not tied to a known, static place.
Ex: Gmail, web games, cloud software
Business Implications of Cloud Computing
• Reduces IT capital investment through decreased need of in-house maintenance and dependency on physical assets.
• Redistributes costs due to multi-tenancy, facilitating centralization of infrastructure. Efficiency increases as more users are added (economies of scale), which lowers subscription fees
Competitive Strategy
Companies can pursue differentiation, cost leadership, or a focused approach targeting niche markets
Differentiation Strategy Key Success Factors
•Understanding customer needs and preferences
•Commitment to customers
•Knowledge of company's capabilities
•Innovation
How can an IT help a company be different?
- How does Amazon differentiate from traditional bookstores? - Long Tail
- Sharing economy (Uber, AirBnB)
- Financial companies utilizing data analytics
How does Amazon differentiate from traditional bookstores?
Utilizes IT to expand product range (long tail strategy).
How does Uber and AirBnB use IT to differentiate?
Sharing Economy: by using peer-to-peer technology.
How do financial companies use IT to differentiate?
Use data analytics for personalized services.
Cost Leader Strategy
Reducing fixed and variable costs with IT.
Reduce Fixed Costs with IT
•Digital storefronts - no physical retail space
•Telecommuting - lower expenses related to office space
•VoIP - using the Internet for phone calls
•Cloud computing - rent servers or software site licenses on an as-needed basis "in the cloud"
•Post pandemic, more employees are expected to work from home
Reduce Variable Costs with IT
•Crowdsourcing: use non-paid non-employees to create value
- Example: platform economy
Stuck-In-The-Middle
Attempting to simultaneously pursue both a low cost strategy and a differentiation strategy
Difficult to achieve low cost with the added costs of differentiation
Danger of Stuck-In-The-Middle - PS
• Challenge for Startups: Limited resources to compete broadly may lead to being "______" if they attempt to do everything.
• Solution: Focus on core strengths or niche areas instead of trying to match large corporations across the board.
Porter's Five Forces Model
Tool to assess an industry's competitive environment by analyzing the competitive forces of suppliers, entrants, buyers, substitutes, and rivalry amongst existing competitors
Rivalry among Existing Competitors Conditions
• High Number of Firms: Increased competition for customers.
• Slow Market Growth: Firms fight harder for limited market share.
• Homogeneous Products: Greater likelihood of price competition.
• High Exit Barriers: Firms stay and compete rather than exit.
Threat of New Entrants Conditions
Factors Reducing Barriers:
• Low customer brand loyalty.
• Minimal legal protections or patents.
• Readily available inputs.
• Absence of network effects.
Threat of New Entrants: Barriers to Entry
Product or service feature that customers have come to expect and all entering companies must offer
How does IT build up higher entry barriers?
• Banking—online banking
• Grocery stores—mobile payment
How does IT lower entry barriers?
Sharing economy competing with incumbents, e.g., Airbnb vs. hotels, Uber vs. taxi companies, P2P lending vs. conventional consumer credit providers
Threat of Substitute
Decrease industry profitability, while increases in complements increase industry profitability.
• Erode profits by stealing business and intensifying industry rivalry.
• Complements boost demand for the product in question, thereby increasing profit opportunities.
How do switching costs effect substitutes?
can reduce the threat
• Costs that make buyers reluctant to switch to other products or service
• IT can help increase the switching cost of consumers. For example, Amazon provides a profile of a consumer's shopping and purchasing habits through sophisticated technologies such as collaborative filtering.
Factors Affecting Supplier Power
Concentration of upstream industry
Ability to substitute inputs
Threat of forward integration by suppliers, e.g., Baxter International, manufacturer of hospital supplies, acquired American Hospital Supply, a distributor
How does IT help lower supplier power?
Case: Think about publishers' bargaining power with Amazon versus their bargaining power with Barnes & Noble
How can IT help increase the switching cost of customers?
• Netflix: set up and maintain your movie list
• United Airlines: frequent flyer program
• Apple iTunes: buy/manage your music
Value Chain Analysis Objective
Enables one to understand where economic value is created within a firm.
Value Chain Analysis Method
• Identify processes that add value (e.g., production efficiency, quality control).
• Identify and eliminate processes that add minimal or no value.
Value Chain
Value is created as products or services move through a sequence of activities, forming a "chain" of value.
Purpose of the Value Chain
Represents the firm as a collection of activities, each contributing to overall value.
Value Chain Support Activities
• management, accting, finance, legal
• human resource management
• research and development
• procurement
Value Chain Primary Activities
- inbound logistics (receive and store raw materials)
- operations (make the product)
- outbound logistics (deliver)
- marketing and sales
- service after sale
Inbound logistics primary activity
• Real time integrated scheduling, shipping, inventory mgmt
• Advanced planning scheduling across the company & suppliers
Operations primary activity
• Integrated information exchange, scheduling, decision making
• Real-time capacity information to sales department
Outbound logistics primary activity
• Real time transacting and processing of orders
• Automated real-time customer specific contracts
• Integrated channel management
Marketing and sales primary activity
• Online sales channels
• Direct marketing
• Push/pull advertising
• Real-time customer feedback
• Real-time access to customer information, dynamic pricing, online quote-submission
Post sales services primary activity
• Online support
• Customer self-services
• Real-time field service access to customer account reviews, part availabilities, etc.
Management, Accounting, Finance, Legal support activities
• Web based, distributed financial and ERP systems
• Online investor relations
HR management support activities
• Self-service personnel and benefits administration
• Web-based training
• Internet based sharing and dissemination of company information
R&D support activities
• Collaborative product design, across locations
• Knowledge directories accessible from all parts of the organization
Procurement support activity
• Internet enabled demand planning
• Direct and indirect procurement via marketplaces, exchanges, auctions, and buyer-seller matching.
ERP
Enterprise Resource Planning: Improve connections among business processes
Success Factors of McDonald's
• Consistency: Delivers consistent food quality worldwide (e.g., burgers and fries).
• Franchise Model: Approximately 85% of locations are franchises, driving growth and standardization.
• Efficient Operations: Designed for speed and convenience, to maximize customer satisfaction.
McDonald's Planned Solutions
Innovative Steps:
• New Payment Options: Rolling out credit and debit card payment systems.
• Self-Ordering Kiosks: Improving convenience and reducing wait times.
• Bathroom Cleanliness Initiative: "Cleanest bathrooms in the business."
• ERP System - "Innovate": A web-based, real-time system to manage global operations.
McDonald's Goals of the "Innovate" System
• Provide even more consistent products
• Provide real-time information (data) across the globe
- Executives given a bird's-eye view of the entire system
- Improve customers' experience
- Speed up the trip and make the trip more convenient
• Handle employees' turnover issues
McDonald's Functions of Innovate
• Data analysis: Executives gain global data access through a dashboard.
• Supply chain management
- Link all of the 30,000 restaurants and 300 approved vendors 24/7 to the back-office system and its corporate office
- Monitor the usage of food and packaging supplies
• Human Resources: Streamlined training and access to benefits data.
• Employee Scheduling: Improved crew management and scheduling.
McDonald's Reasons for the Failure of "Innovate"
• Cost-benefit analysis: benefits hard to justify the costs
- Had McDonald's made the $1 billion investment, it would have needed to achieve at least a 1.5% increase in annual sales, or roughly $231 million a year.
• Lack of expertise: - McDonald's had shown no expertise in large-scale information system implementations.
• Resistance from franchisees - Franchisees were still complaining about another project—the "Made For You" cooking system.
- "Made For You" cost $30,000 - $60,000 per restaurant.
- "Made For You" slowed down services.
• Lack of technology: high-speed bandwidth connection• A main technical hurdle in 2002
What are the value added processes of McDonald's as a fast food company?
Fast Delivery; Product Consistency; Brand Recognition
What are the value reduced processes of McDonald's as a fast food company?
High Turnover in HR; R&D Limitation: Lack of menu innovation; Management Systems: Outdated data and information systems
McDonald's Can "Innovate" eliminate or improve the value reduced processes?
Yes. HR, management (not R&D though).
McDonald's Can "Innovate" enhance the value added processes?
Probably no
Does McDonald's Need a Real-Time System?
Assessment: Real-time systems may not be essential for McDonald's business model.
Brick & Mortar
Traditional "street-side" business that deals with its customers face to face in an office or store that the business owns or rents.
Brick & Mortar Pros
•Touch & feel
•Face-to-face communication / customer service
•Immediacy
Brick & Mortar Cons
•Limited selections
•Limited geographic reach
•Limited price comparison
•Cost(rent, utilities etc.)
E-Commerce
Commerce enhanced by IT, especially the Internet. Includes Click & Order, Click & Mortar, Digital Pure Play
Importance of E-Commerce
•In 2023, online sales constitute a significant portion of consumer spending.
•Over 85% of retail and business-to-business firms now operate an online channel.
Categories of E-Commerce
B2B, C2B, B2C, C2C
Click & Order Pros
•Convenience
•Product variety / availability
•Price comparison
•Lower prices
•Unlimited geographic reach
Click & Order Cons
•Immediacy
•Technology dependent
•Inconsistency between what I bought and what I expected
Why do consumers shop online?
•Convenience
•Lower prices/easy price comparisons
•Larger products selection
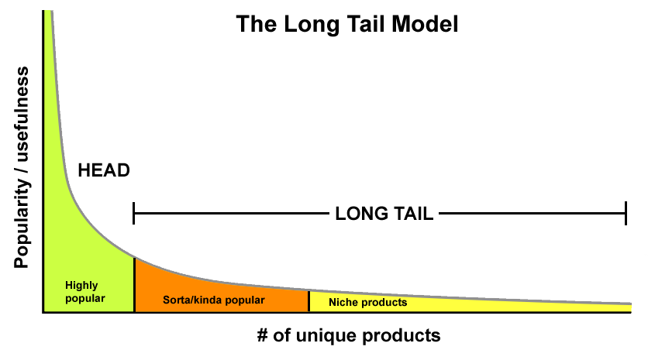
Long Tail
Business strategy that focuses on selling a large number of niche items with low demand
Drivers of long tail (supply-side)
Why do retailers offer increased product variety online?
• Reduced costs:
- Centralized warehouse, inexpensive rents
- Dropped shipping costs
- Electronic delivery of products
• Increased revenue: - Local brick-and-mortar stores serves a market within a limited radius, but online retailers have no geographic constraints.
Drivers of long tail (demand-side)
Why do consumers buy obscure/niche products online?
• Search tools
• Passive tools: recommender systems, online advisors,dynamic/personalized storefronts, etc.
• Online reviews
Pareto Principle
By Vilfredo Pareto in his study of wealth distributions in Italy in 1906. Widely found in product sales and city population distributions. 80% of results come from 20% of inputs. Focus on the critical top 20%, not the trivial many
Lock-Ins
Refers to the situation that a particular technology or product is dominant, and the cost of switching to alternative technologies or products is high.
Types of Lock-Ins
Vendor and Technology
Vendor Lock-In
• Makes a customer dependent on a particular vendor for providing products or services, and unable to switch to another vendor without incurring substantial switching costs.
• Costs also generates barriers for market entry, which may lead to antitrust actions against the monopoly.
Examples of Vendor Lock-In
• Mobile phone service: contracts
• Refund policy with gift cards
Technology Lock-In
• A form of economic path-dependence whereby the market selects a technological standard, and because of network effects the market gets locked-in or stuck with that standard even though market participants may be better off with an alternative.
Switching Costs
Costs that customers incur when changing from one provider or product to another.
Switching Costs Types
Durable purchases and replacement, brand-specific training, information and data, loyalty programs, and contractual commitments
Durable Purchases Switching Cost
Investments in specific products make switching costly due to replacement expenses.
Brand-Specific Training Switching Cost
Switching to a competitor can require costly retraining.
Information and Data Switching Cost
When a vendor controls valuable customer data, it becomes harder for customers to switch.
Loyalty Program Switching Costs
Encourage repeat business by offering rewards that only accrue through continued use of the same provider.
Contractual Commitment Switching Costs
Require customers to stay with a vendor for an agreed period.
Platform
A foundation tech or set of components (could also be a service) used beyond a single firm. Allows multiple parties ('market sides') to transact across the platform. Value grows with users
Network Effect
The effect of a user has on the value to other users.
More users = more value. Examples: social media, phone networks, email, mobile service
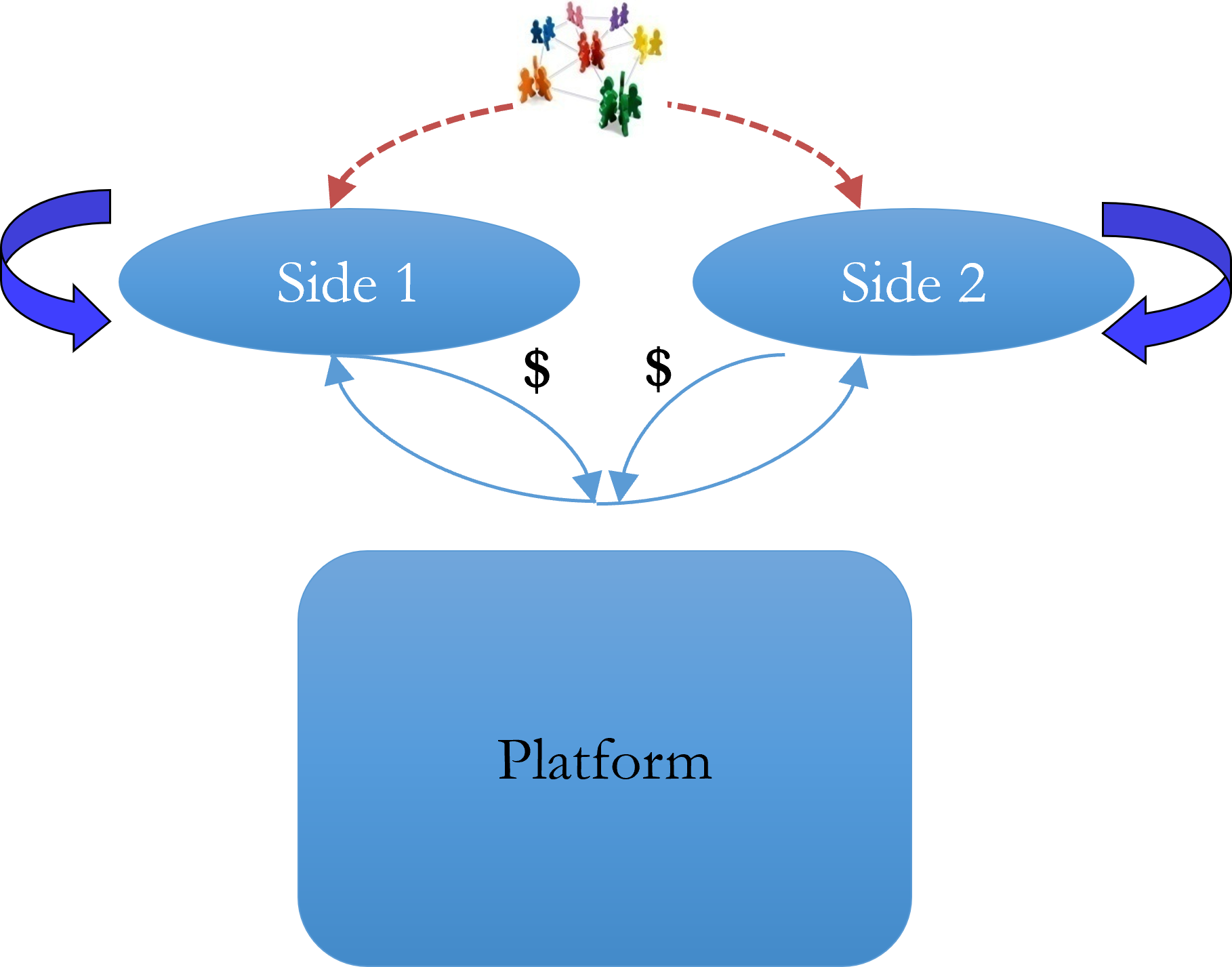
Two-Sided Networks
Has 4 network externalities
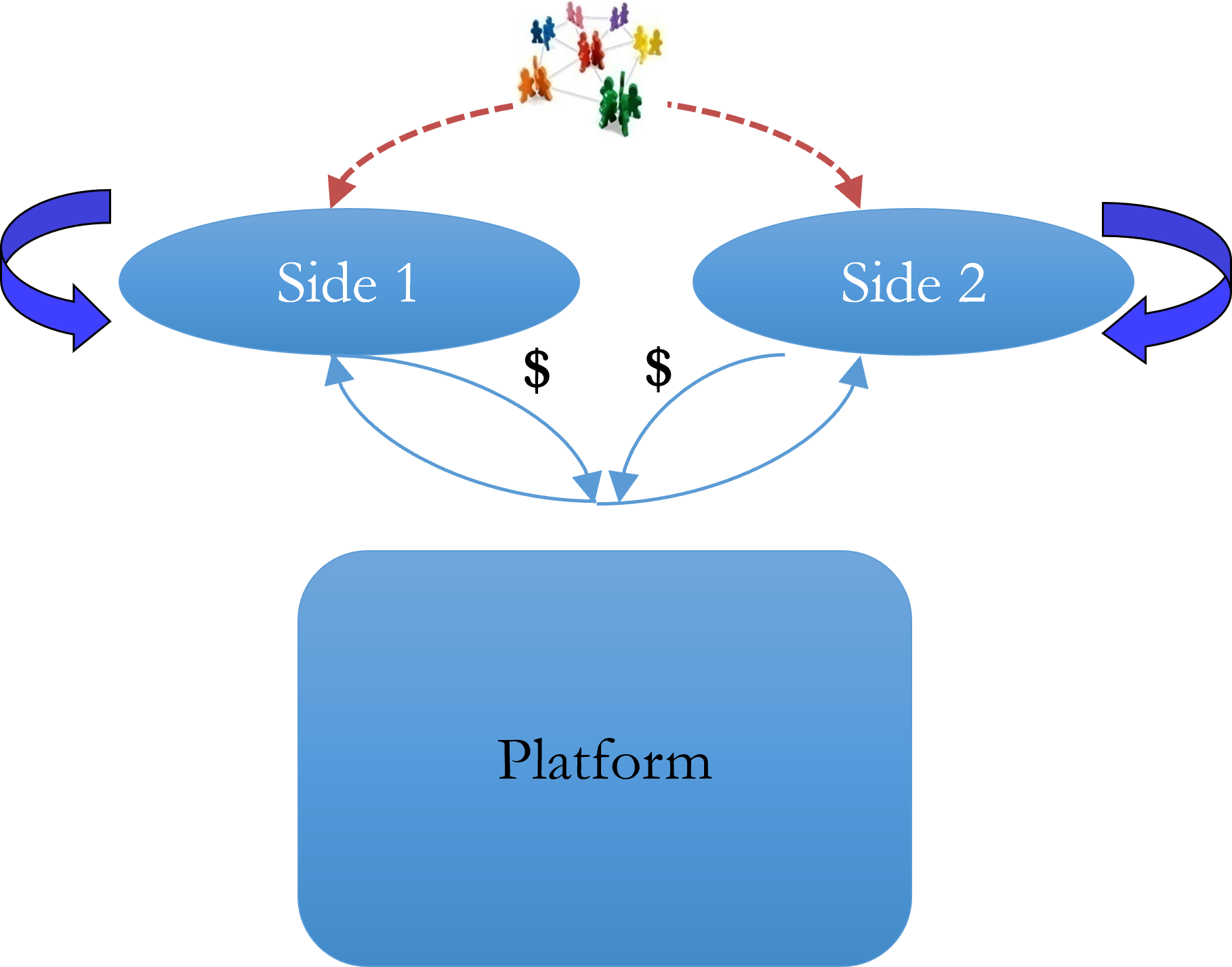
Same-side effect
Value increases with more users on the same side (e.g., more sellers on eBay).
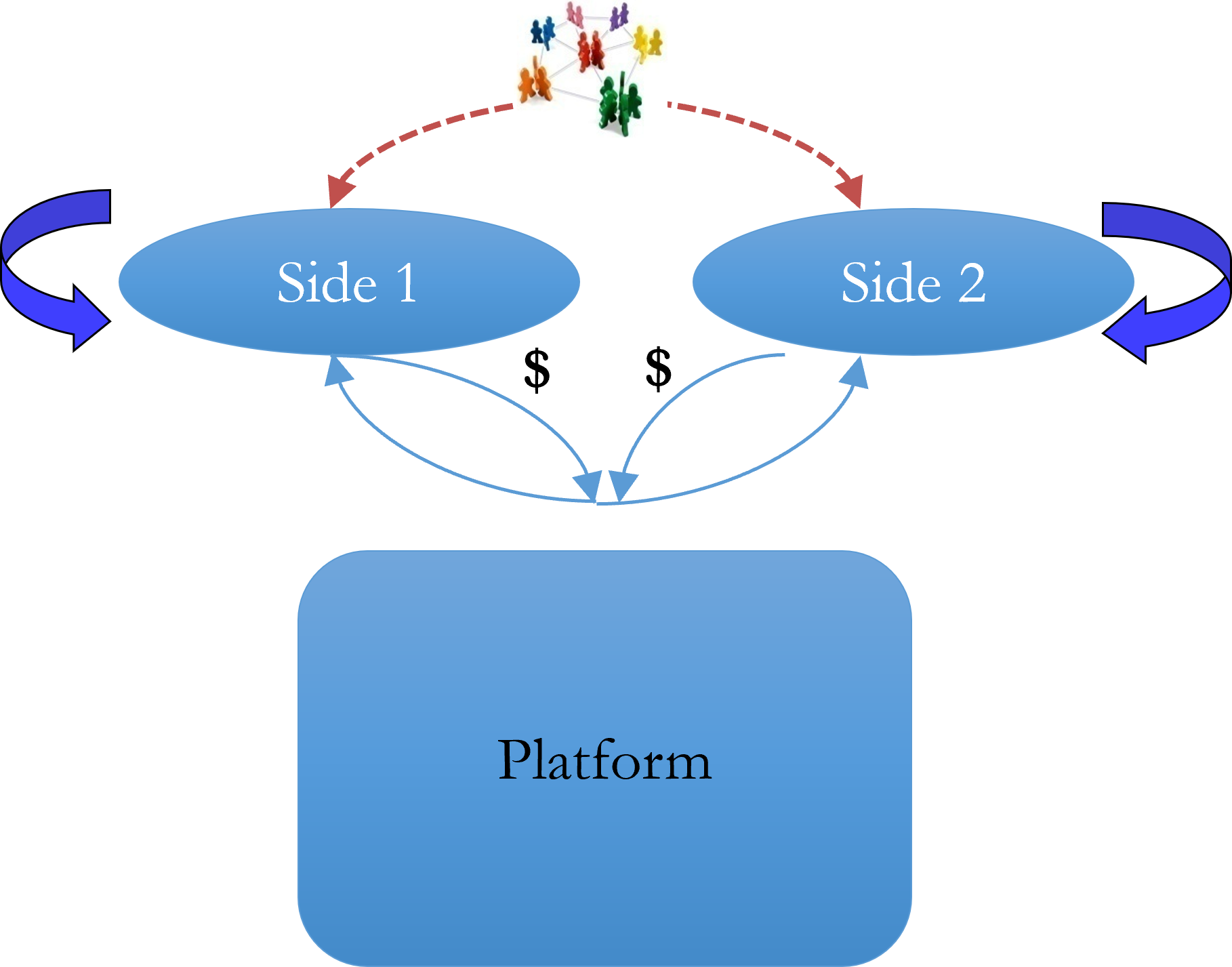
Cross-side effect
Value increases as the number of users on the opposite side grows (e.g., more riders attract more drivers on Uber).
Homing Costs
Costs incurred by users to stay active on multiple platforms (e.g., maintaining listings on Airbnb and VRBO).
Switching Costs for Platforms
Associated with moving from one to another, often influenced by network size and user investment.
Winners-Take-All Networks
Arise when there are strong network effects (Facebook vs gas engine) and large multi-homing costs (Operating systems vs credit cards).