Quiz 1 (Lectures 1-4)
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Name the two planar geometric projections and their subcategories:
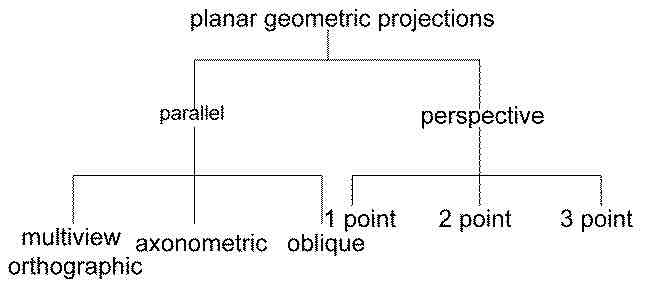
Parallel vs perspective projections:
Parallel:
used in technical drawings
Elements with equal length are equally dimensioned
Dimensions can be measured in drawings
Perspective:
Closer to the eyes’ perception
Elements with equal lengths can have different dimensions
Used in “Photorealistic: rendering (design, architecture)
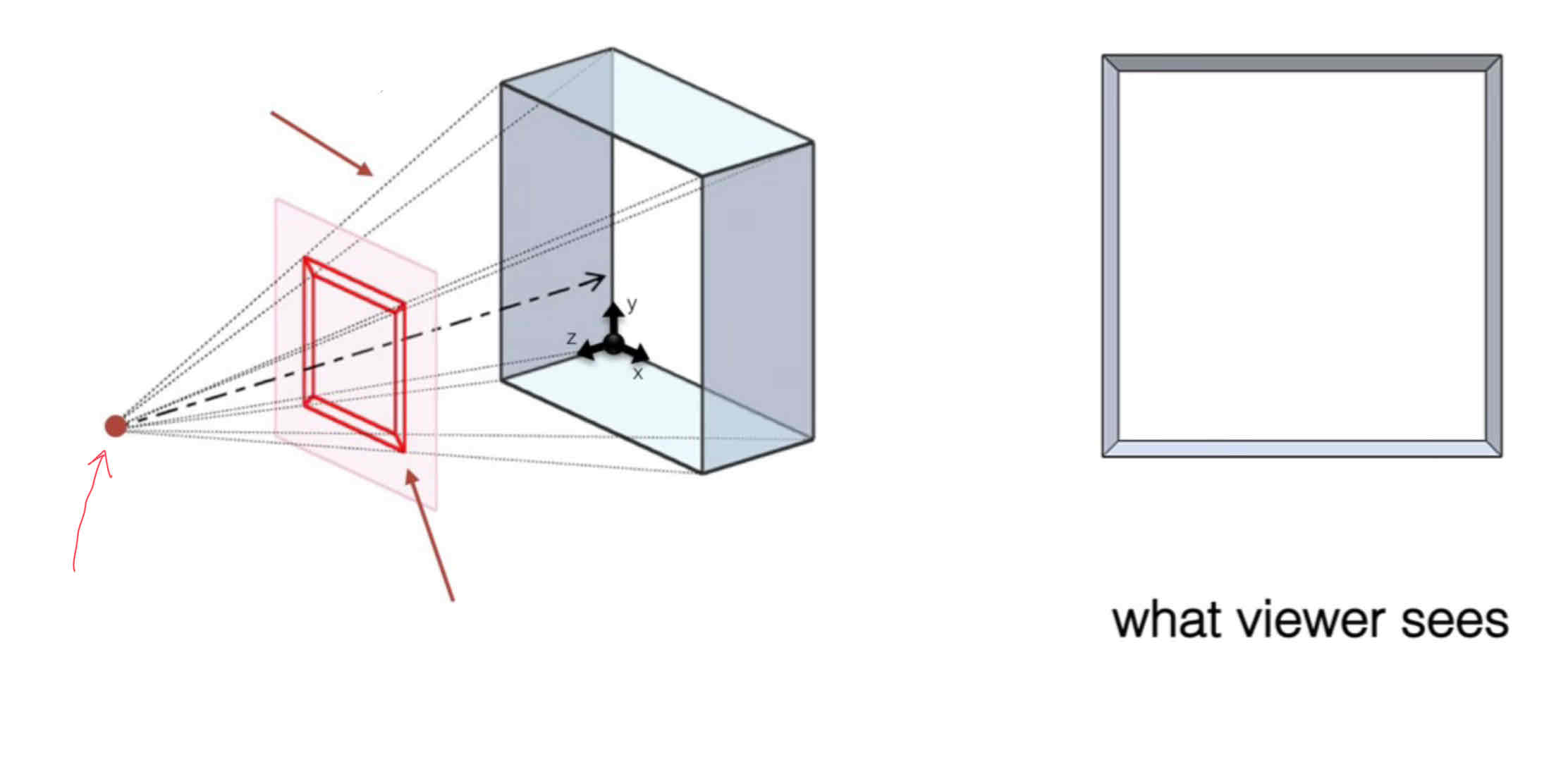
Name this projection method:
Perspective Projection
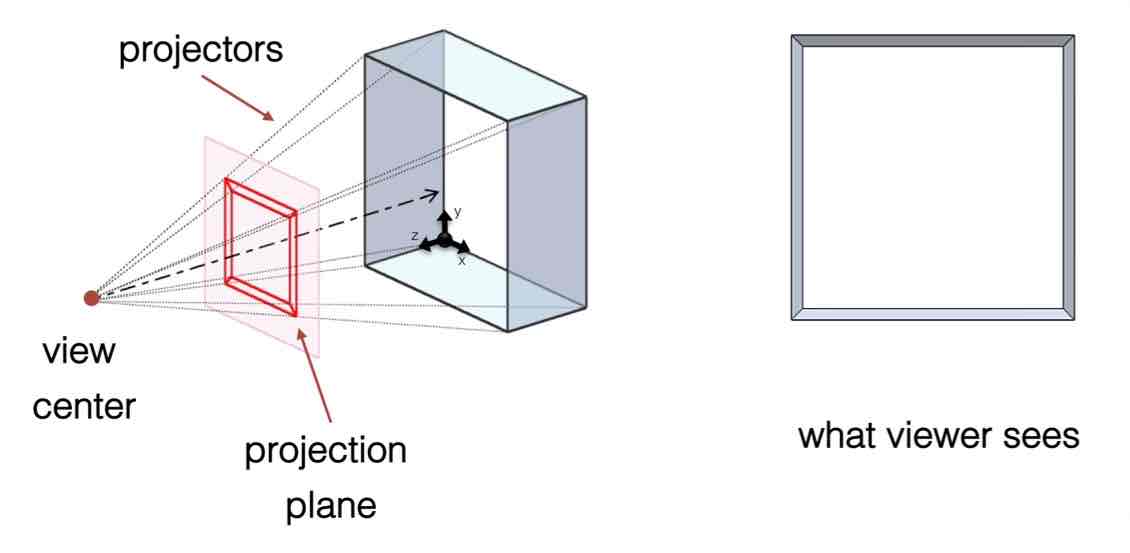
Name this projection method:
Perspective Projection - Orthogonal
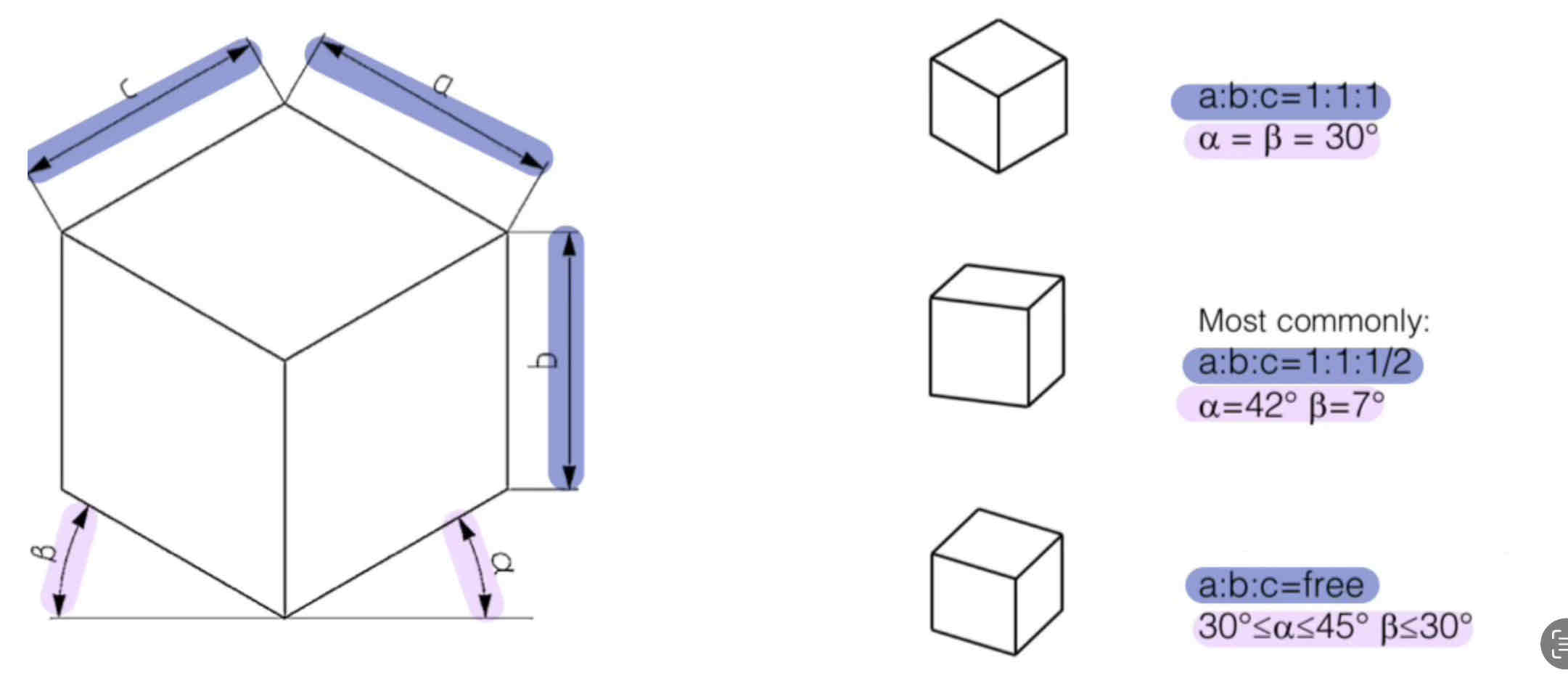
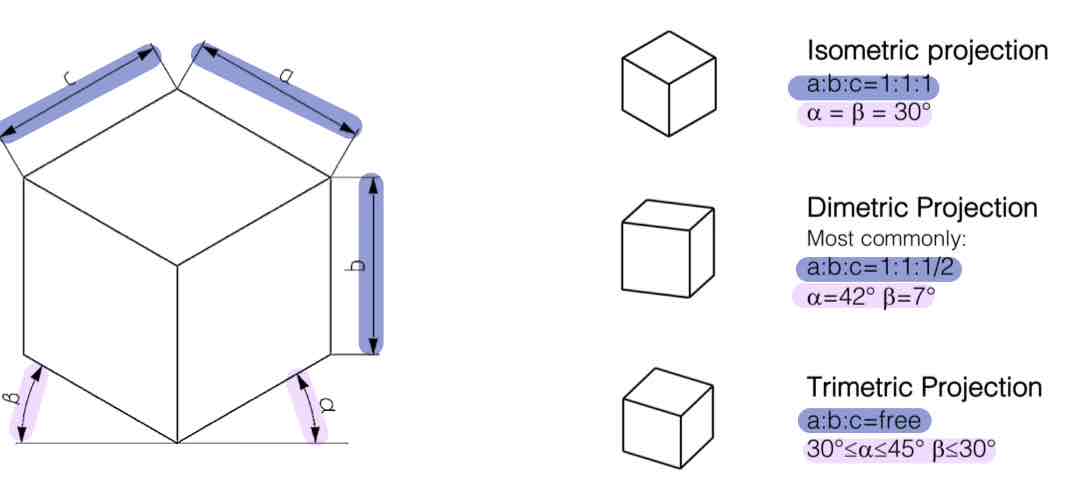
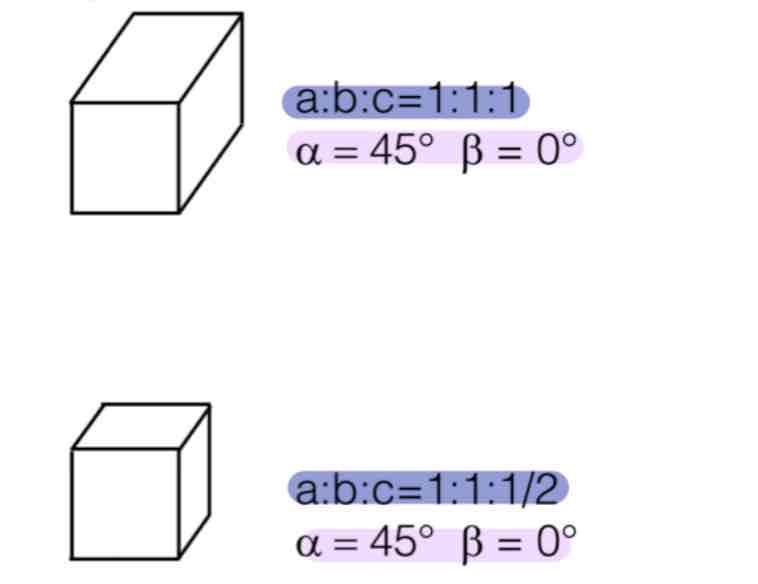
Name this projection method:
Perspective Projection - Axonometric
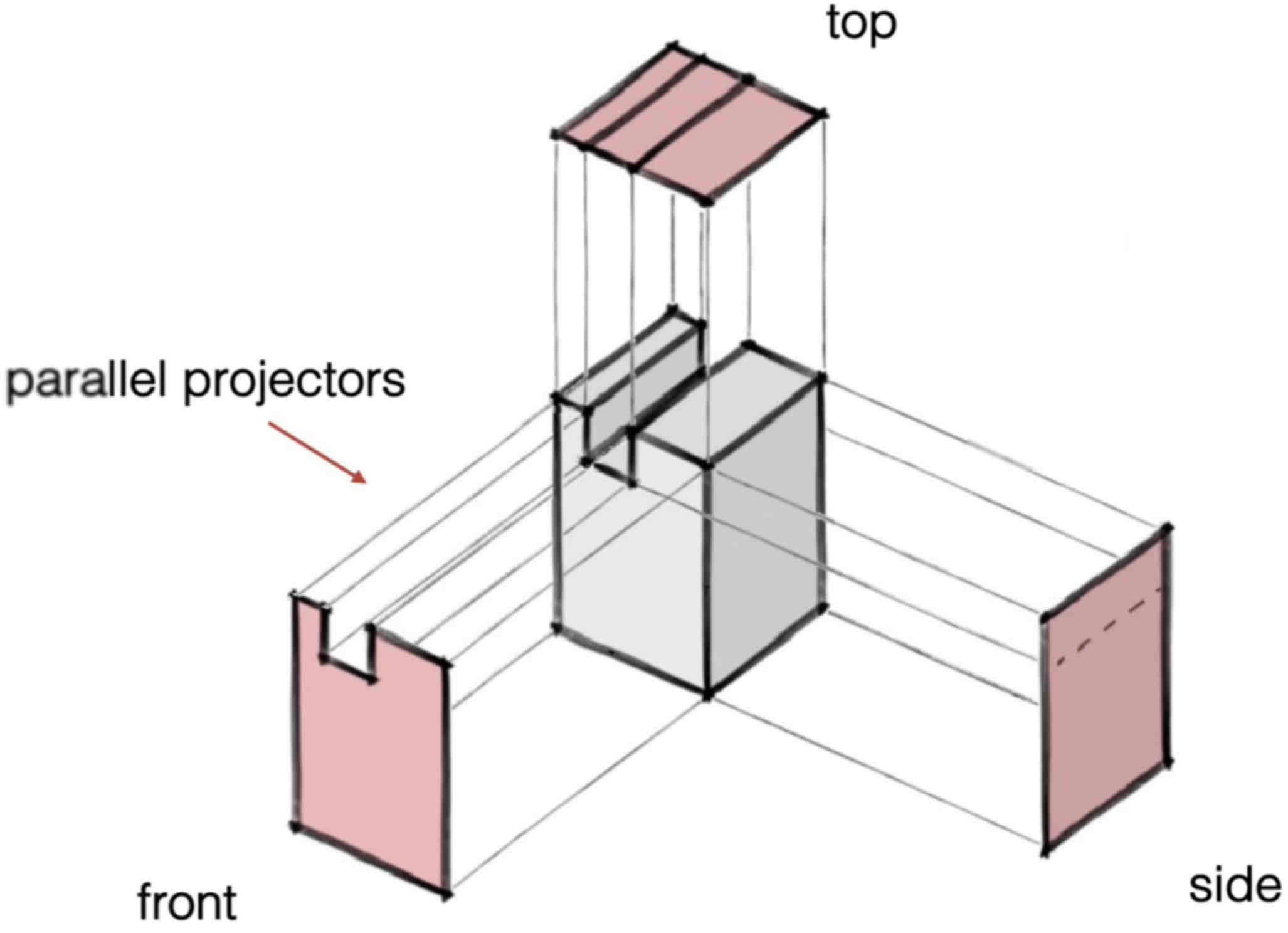
Name this projection method:
Perspective Projection - Oblique
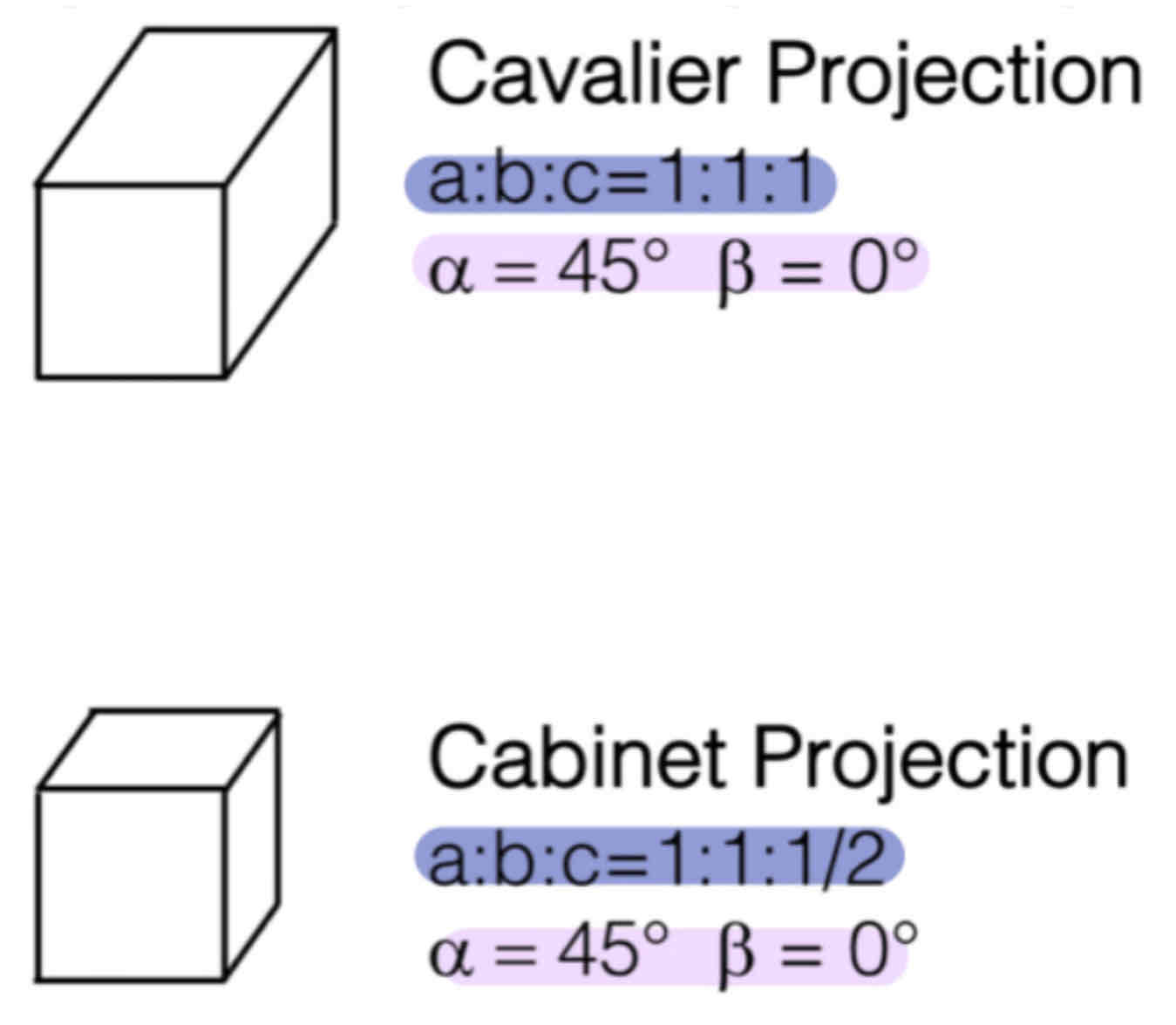
Name this projection method:
Parallel Projection
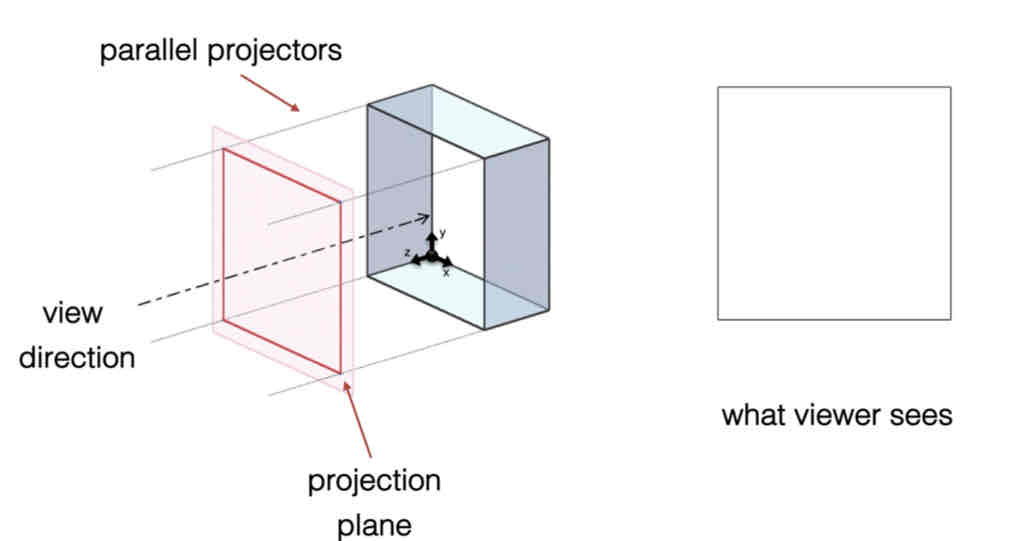
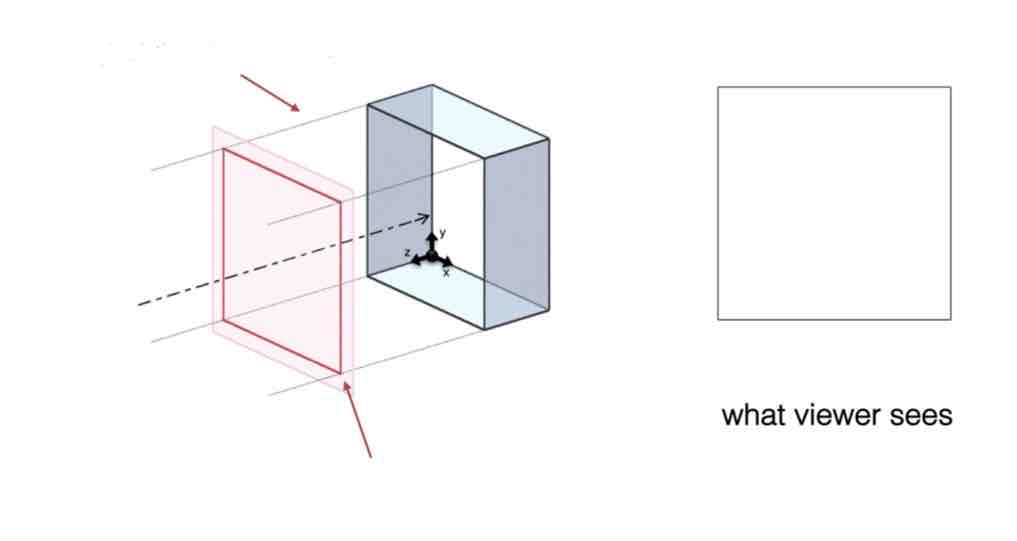
Name this projection method:
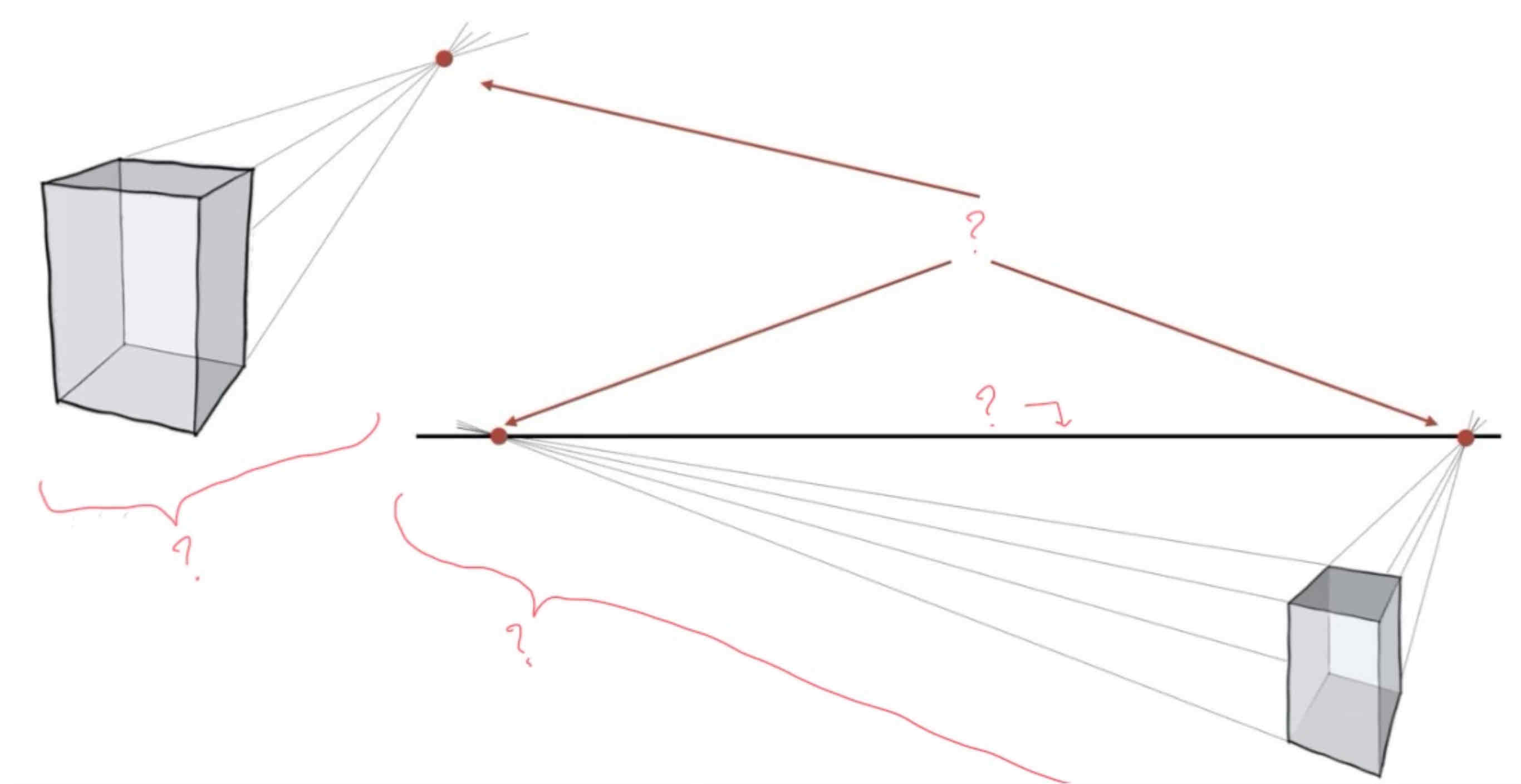
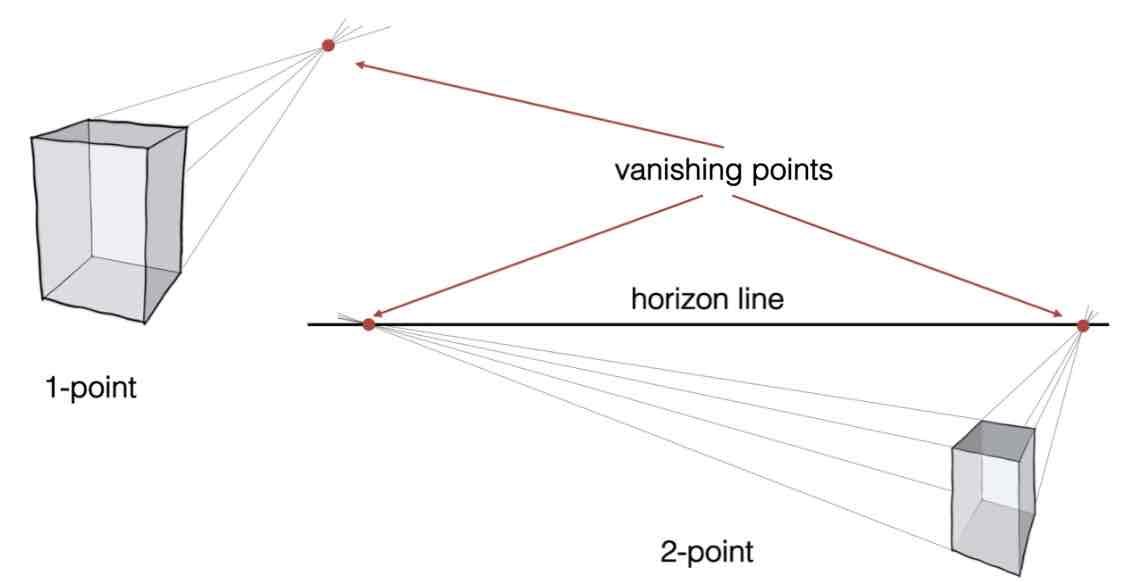
+ what happens if you were to move the vanishing points further / closer?
One- and two point perspective:
if you move vanishing points further: object becomes more orthogonal (rectangular, perpendicular, forming right angles…)
|| closer: object becomes more skewed, looks as if observed from a close distance.
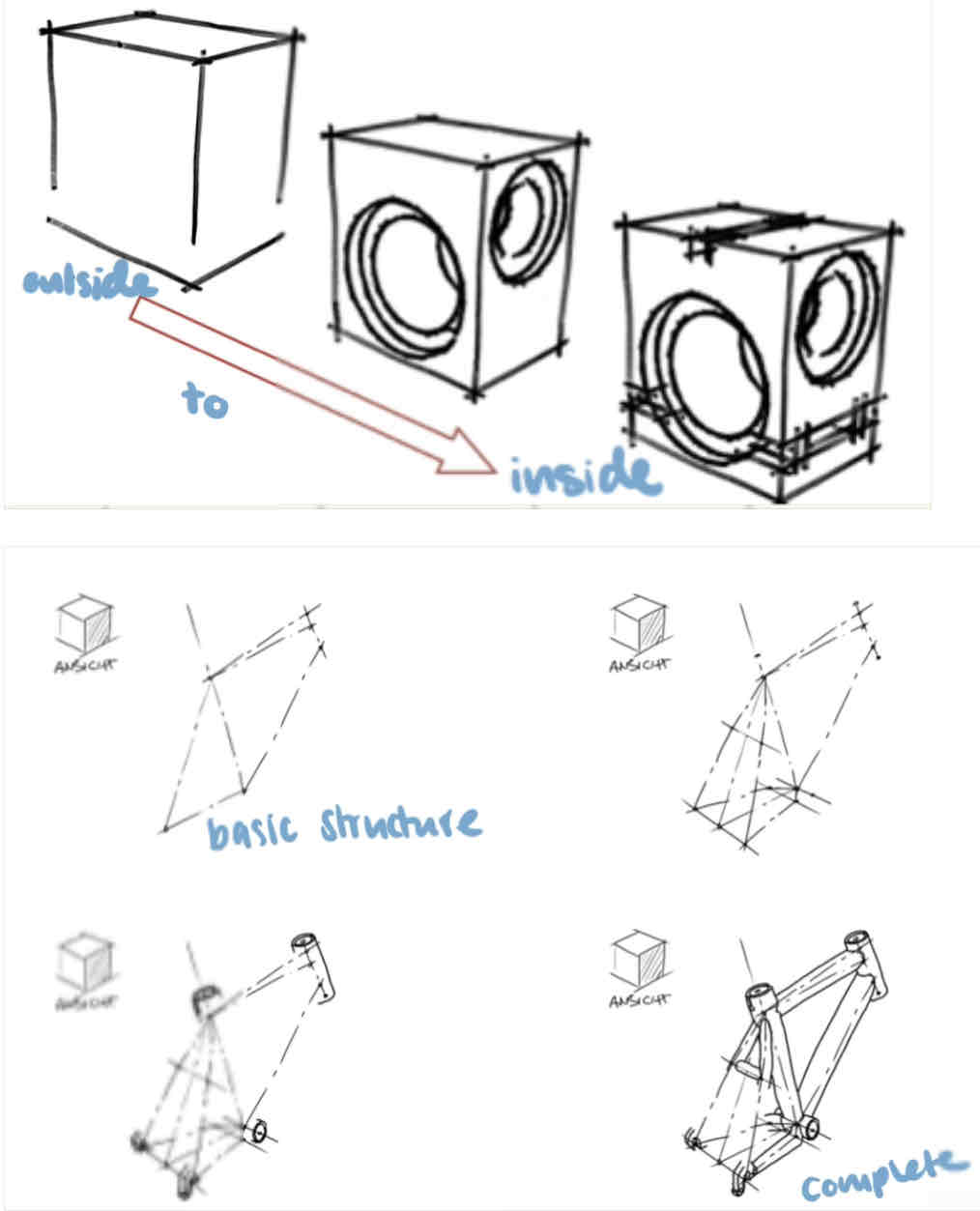
Name the two main sketching techniques:
outline and refine (outside to inside)
Reduce to basic structure and complete (inside to outside)
What are the most important sketching tips? (What to use / make / add / focus on)
Use outlines
Use meshing as an aid
Preserve proportions
Make cuts to show what is necessary
Focus on important aspects
Add comments and annotations
Checklist for sketching - important questions to ask yourself:
is the object / function sketched clearly?
Is the sketch aligned with the goals set?
Is it technically sound and clean?
Are the proportions and scale correct?
Is the perspective clear?
Are annotations needed to understand the sketch?
Sketching: Wrap-Up

Product Development Process:
Name the 6 Phases, as well as the purpose and tasks of phase 1:
Phase 1: Concept Development:
Purpose
Define product requirements
Generalize promising concepts and select one for further development and testing
Tasks include:
Identify lead users and competitive products
Collect user needs
Define product requirements
Develop alternative design concepts and select one
Build and test concept prototypes

Requirement Definition: What are they exactly and why do we need them?
What are they exactly?
Needs product should fulfill
Explicit description of product’s desired form / functionality
Solution is independent
Define the WHAT not the how. Should be as specific as possible.
Why do we need them?
Effective communication, definition of goals / priorities / interface of product
To capture user expectation in binding contract
To ensure fitness of product for its intended use
What are the challenges in understanding user needs?

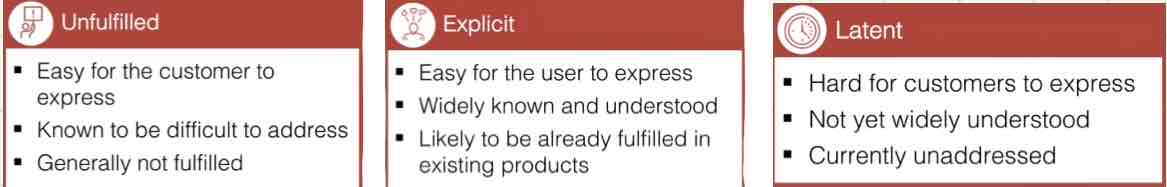
What are the three types of user needs?
Key Requirements when producing:
Prototyping is very important, to also always go back and redefine initial requirements
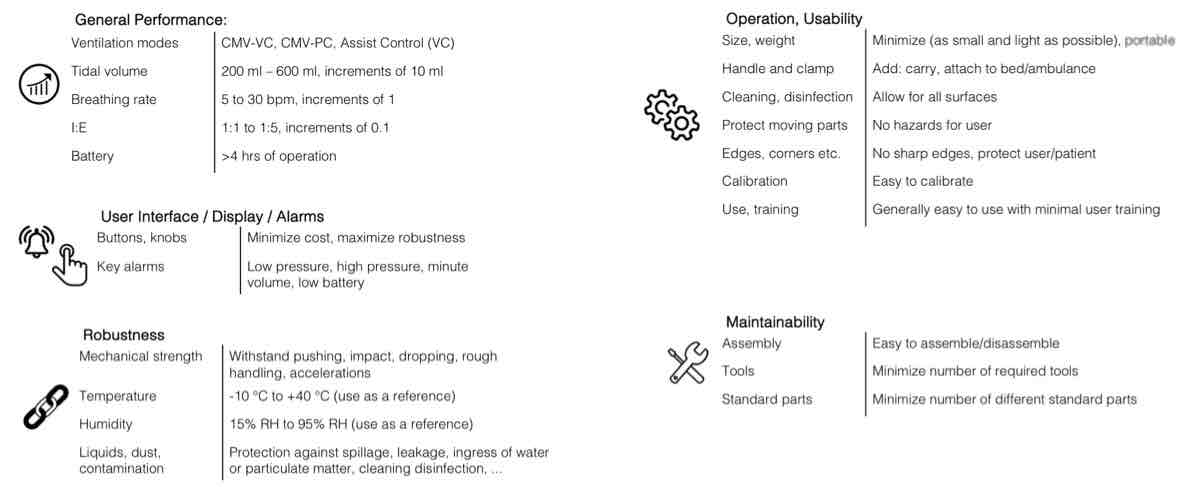
Concept generation and selection - design process and stages:
Design processes do not strictly move in one direction
Jumps between stages could be useful and necessary
Infinite loops should be avoided and a design decision should be considered to revise.
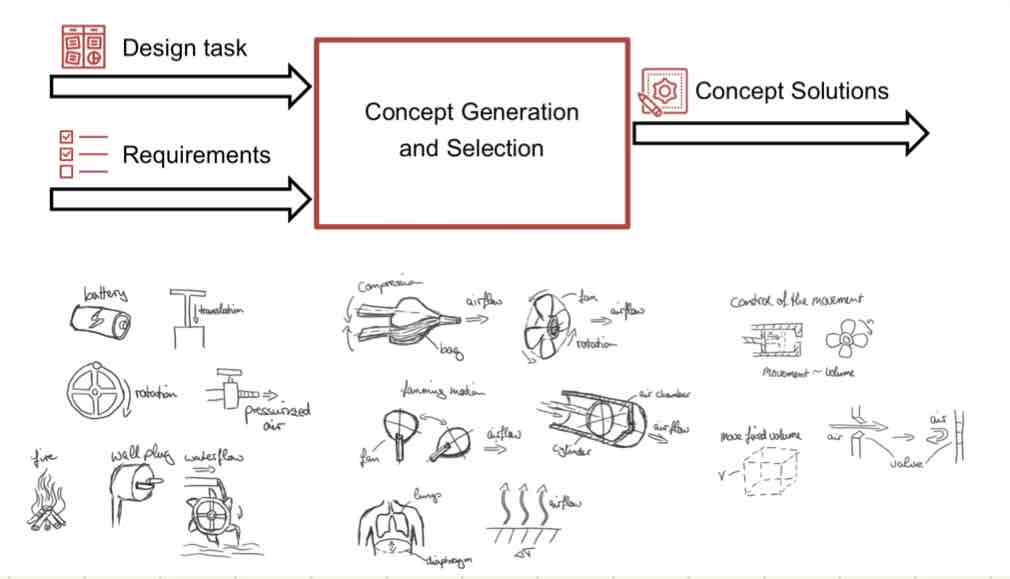
External Search - important steps for deigning and producing machinery / devices
search already existing patents
Determine the state-of-art (= state of newest technology)
Search published literature
Benchmark related products
Interview lead users > Evaluate reactions
Consult experts
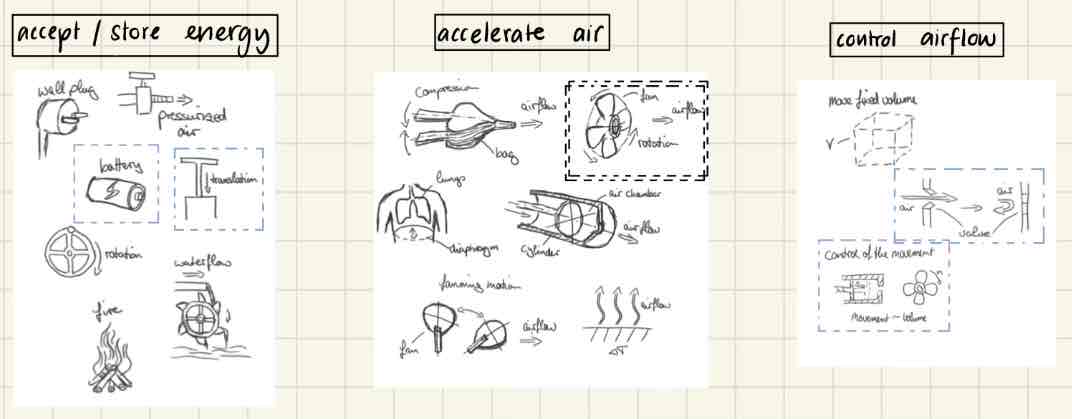
Internal Search (Creativity Methods / Creating a concept combination table)
Creativity Methods
Brainwriting, as many ideas as possible, plenty of sketches, no judgment (Generate ideas in groups)
Create a concept classification tree
Create a concept combination table
Combine different partial solutions to find best combination
Think about physical and geometric interfaces among partial solutions
Refine partial solutions to derive solution / final concept
e.g. in classification tree: Blue: Concept combination A / Purple: Concept combination B
e.g. Ventilator (Picture)
Concept Selection - Explicit vs Implicit:
Explicit: Decision process, discussion
Implicit: Formulation of requirements, task description, favoring of established solutions, dominance of group members.

Concept Generation and Selection - Wrap-Up
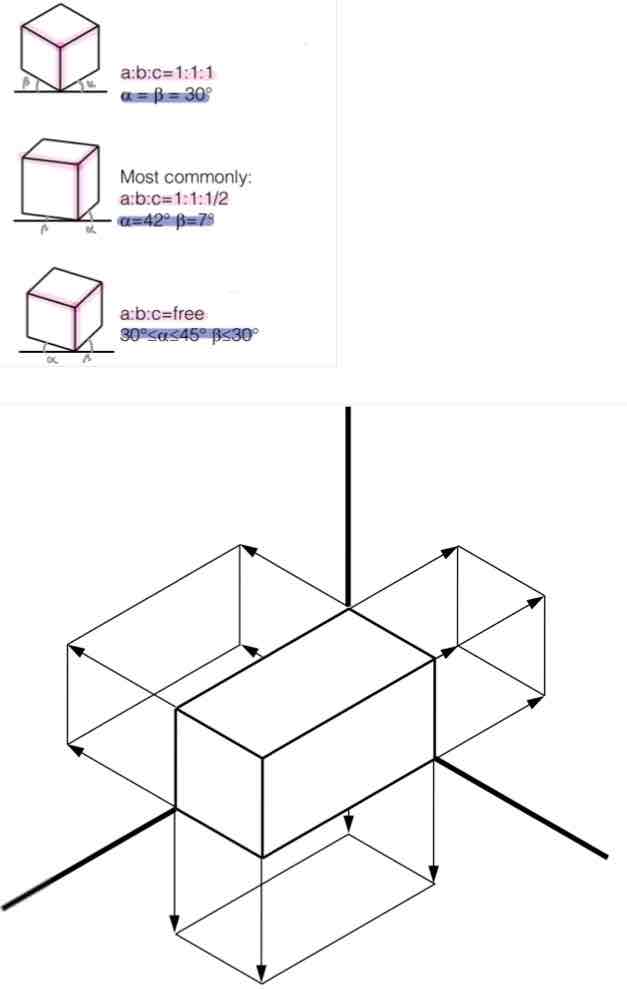
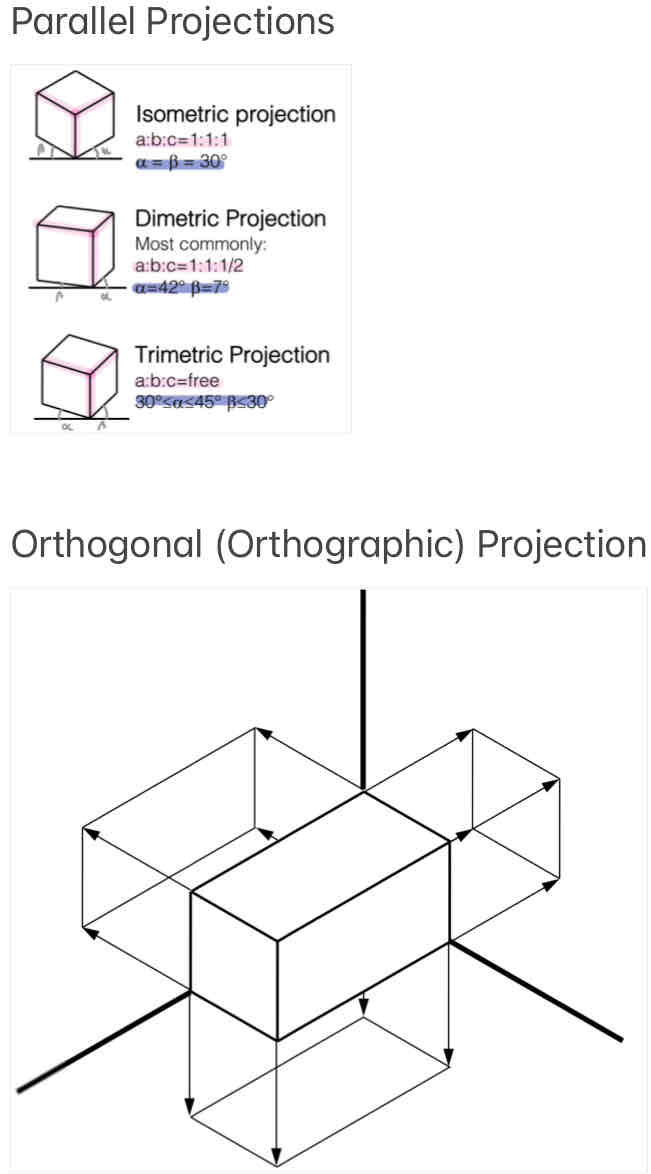
Views - Name these projections
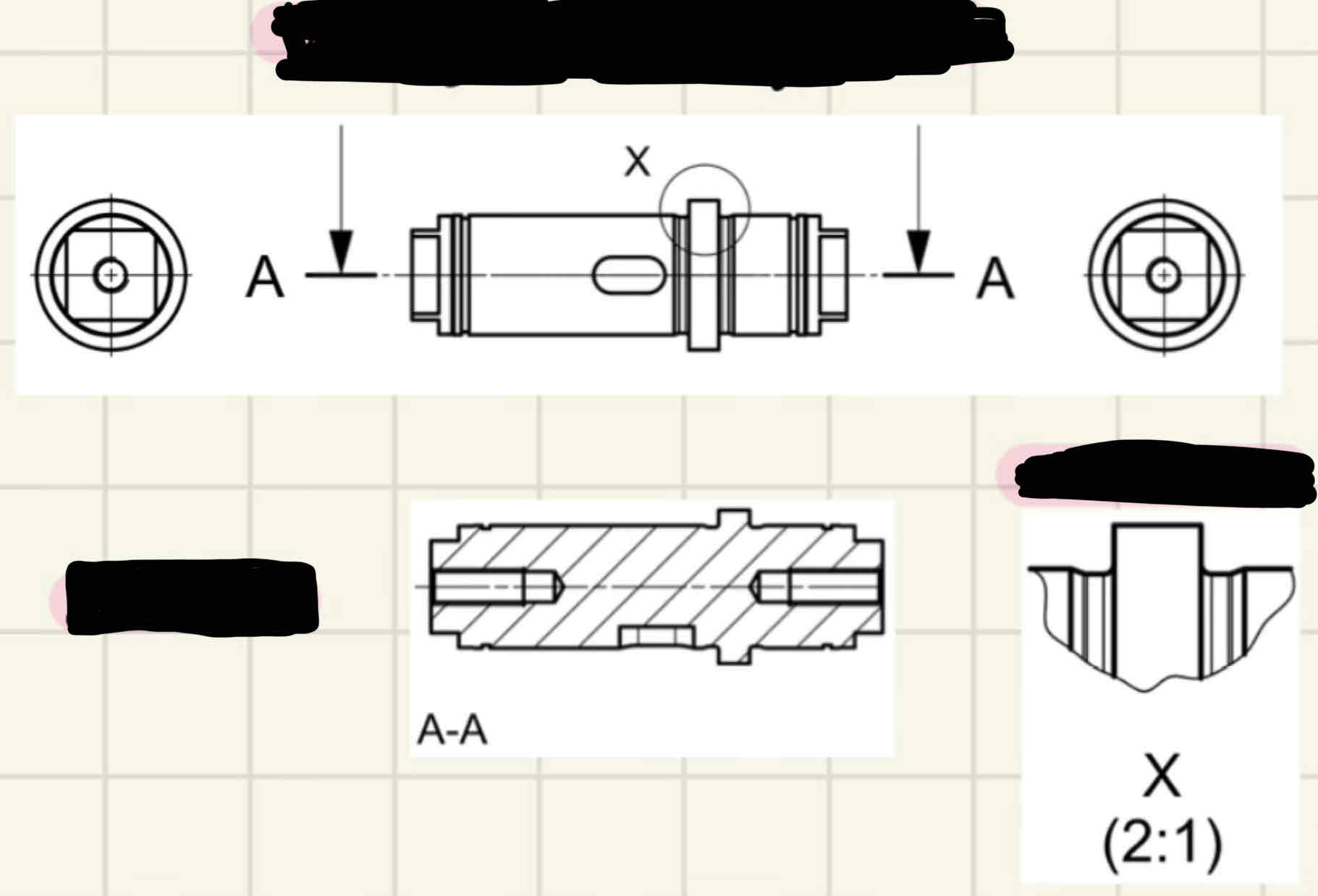
Name the main types of views
Over-/under-dimensioning
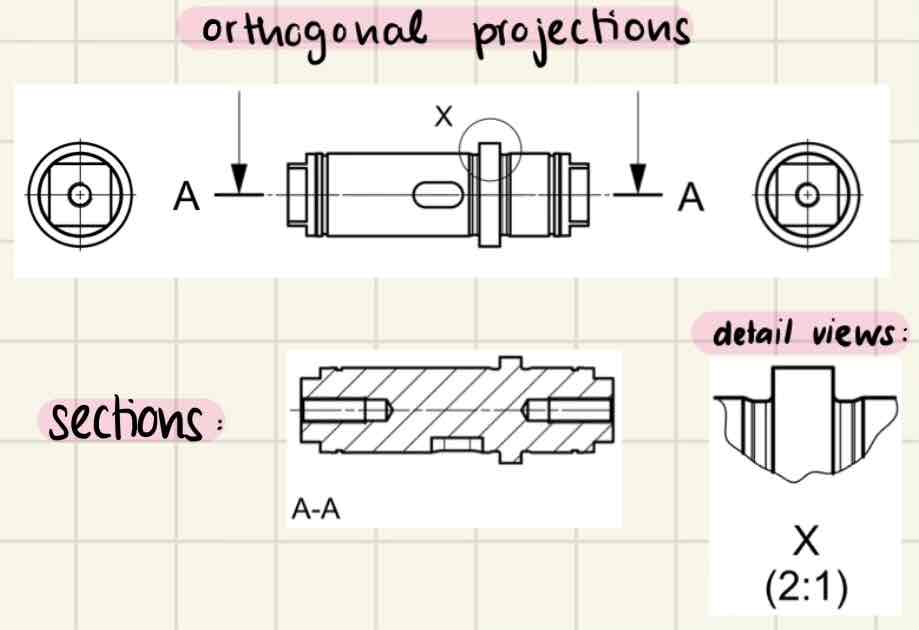

Name the line types:

Name the 5 steps in the technical drawing process:
Chose the principle view
Chose other required views and cuts
Draw views and cuts
Add dimensions
Verify
Arranging Views - first vs third angle projection method:
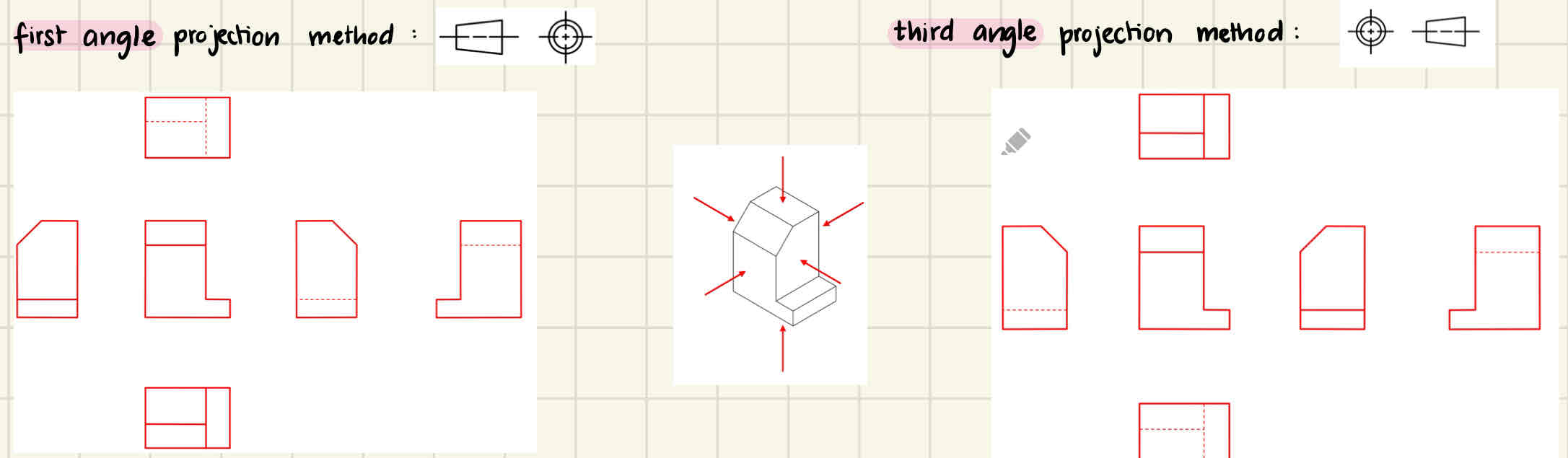
Important to look out for when choosing projected views
Most informative view is used as the principle view
All details have to be shown in a technical drawing
The object has to be presented without ambiguity
Number of views should be limited to the minimum necessary
By reasonable choice of views
By using partial and special views
Unnecessary repetition of details should be avoided
Cuts and sections including stepped view:
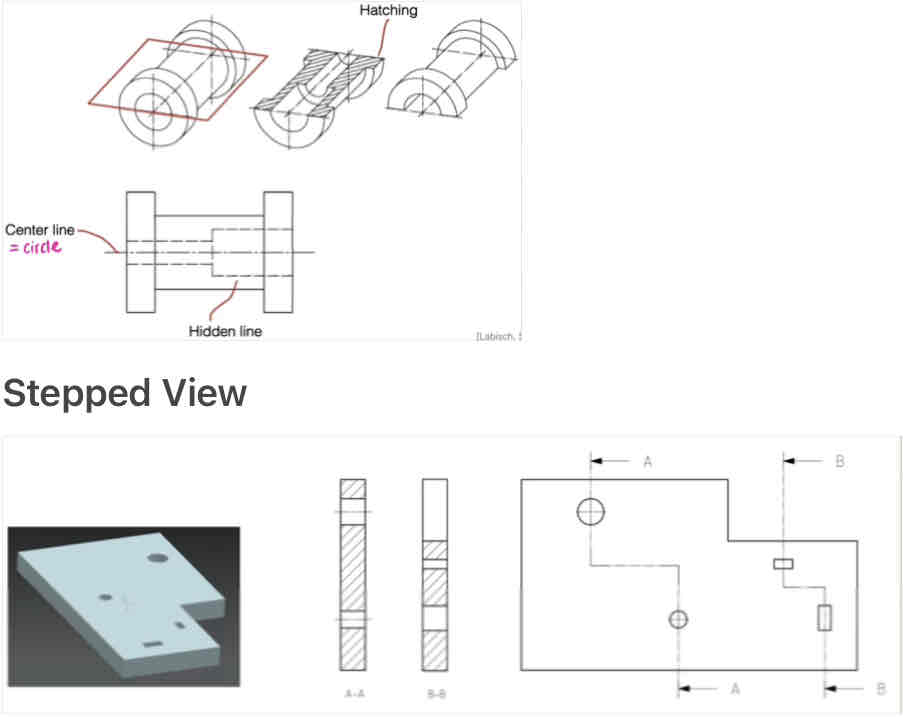
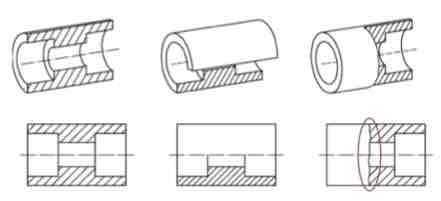
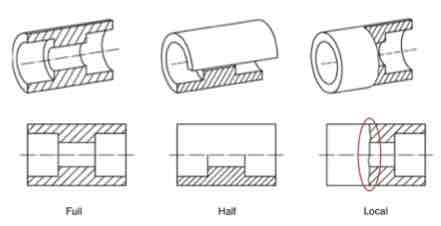
Name the three types of sections:
What are the three possible cut choices?
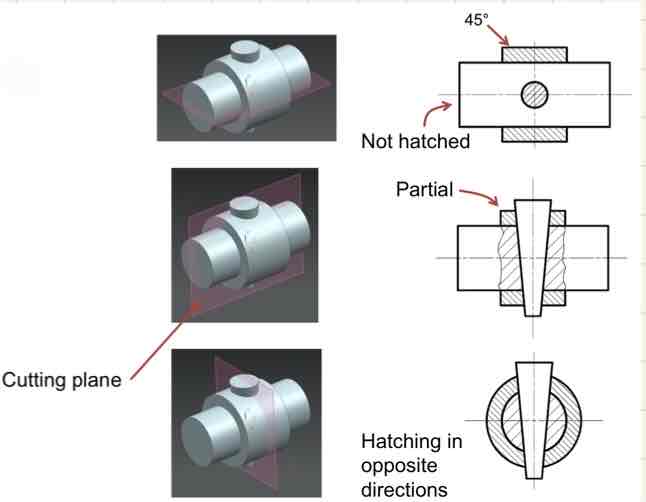
What is hatching? What does it look like?
Hatching: Using parallel lines to show the shape / direction / orientation of an object.
It can also help to differentiate different parts or materials of an object, as well as emphasize edges or contours.
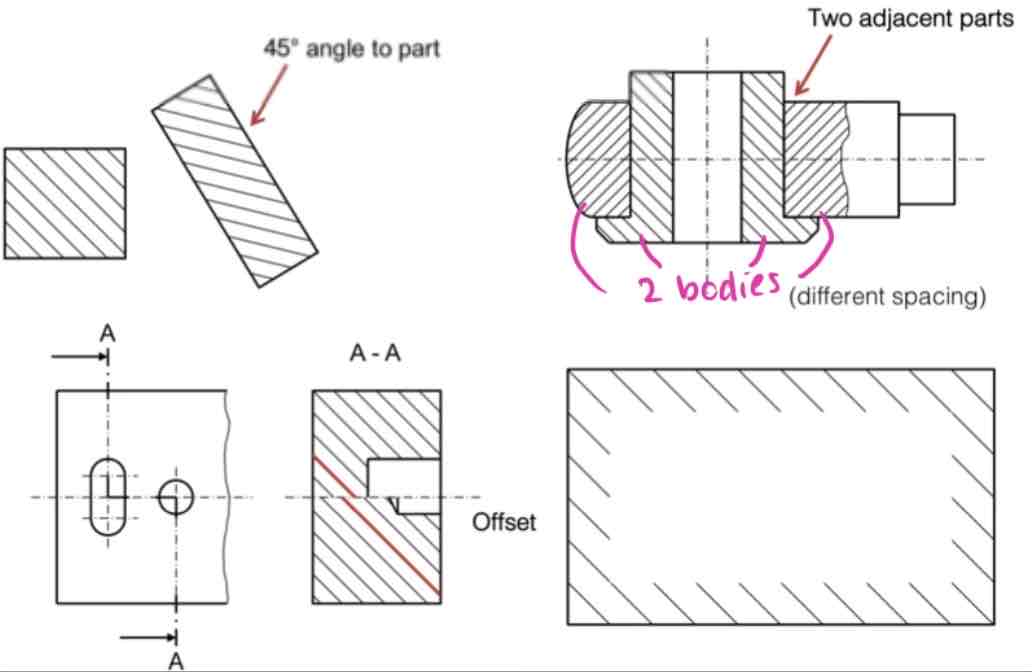
Tips for cuts and sections:
Cuts and sections allow insights into parts and assemblies to illustrate hidden geometries
Cuts and sections have to be drawn and annoyed unambiguously
Cute are almost always needed when there are holes in parts
To avoid complex cuts, local sections can be used
Checklist to verify technical drawings: three questions:
Is principal view most informative view?
Are there sufficient views to fully define the geometry?
Are the smaller details clearly visible?
Projections and cuts - Wrap-Up:

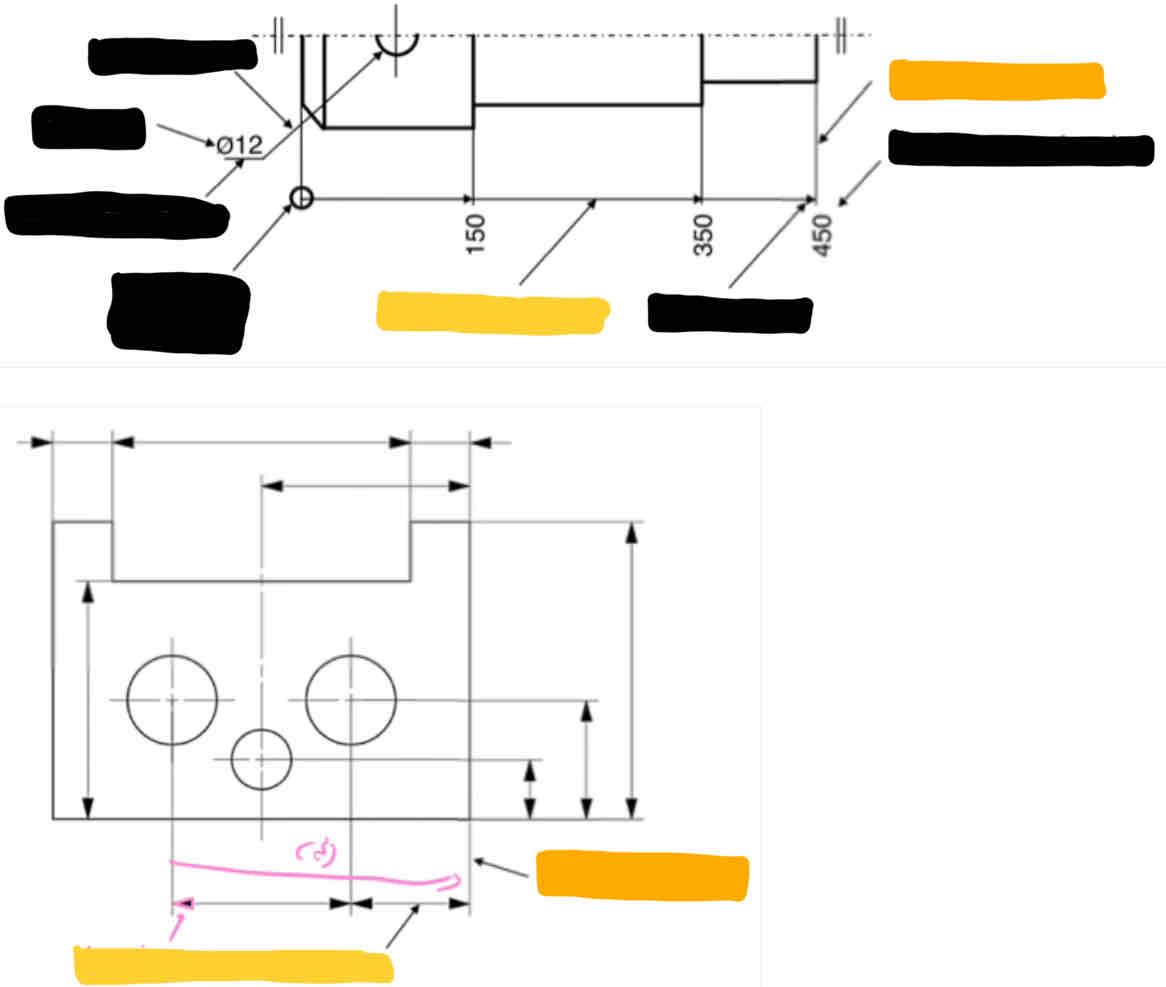
What are elements of dimensioning? And what do we dimension for?
We dimension for:
Function
Manufacturing
Inspection
6 steps of the dimensioning process:
Define outside dimensions
Define functional dimensions
Add required manufacturing dimensions
Add any dimensions for inspection
Add auxiliary dimensions
Verify the dimensioning
What are functional dimensions?
Functional dimensions define the shape, size and location of features that are relevant for the function of a part when assembled (into a final product). Whether a dimension is functional or not depends on the engineering context of the part. If a part is used in a different way, different dimensions may become functional
What are non-functional dimensions?
Non-functional dimensions define the form, size and position of other features, which are not important for the function of a part (when assembled into a final product). They are to be selected and indicated as most suitable for manufacturing and inspection.
What are auxiliary dimensions?
Auxiliary dimensions are just for information and serve to avoid calculations. They supplement functional and non-functional dimensions. They are added in parenthesis. They cannot have tolerances associated to them.
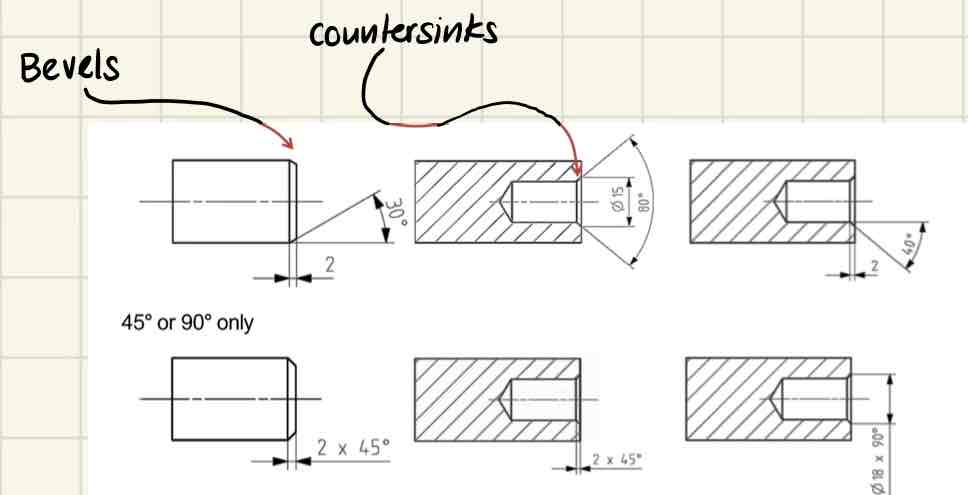
Dimensioning of special elements (Name two)
You have to put angle and linear dimensions for bevels / countersinks.
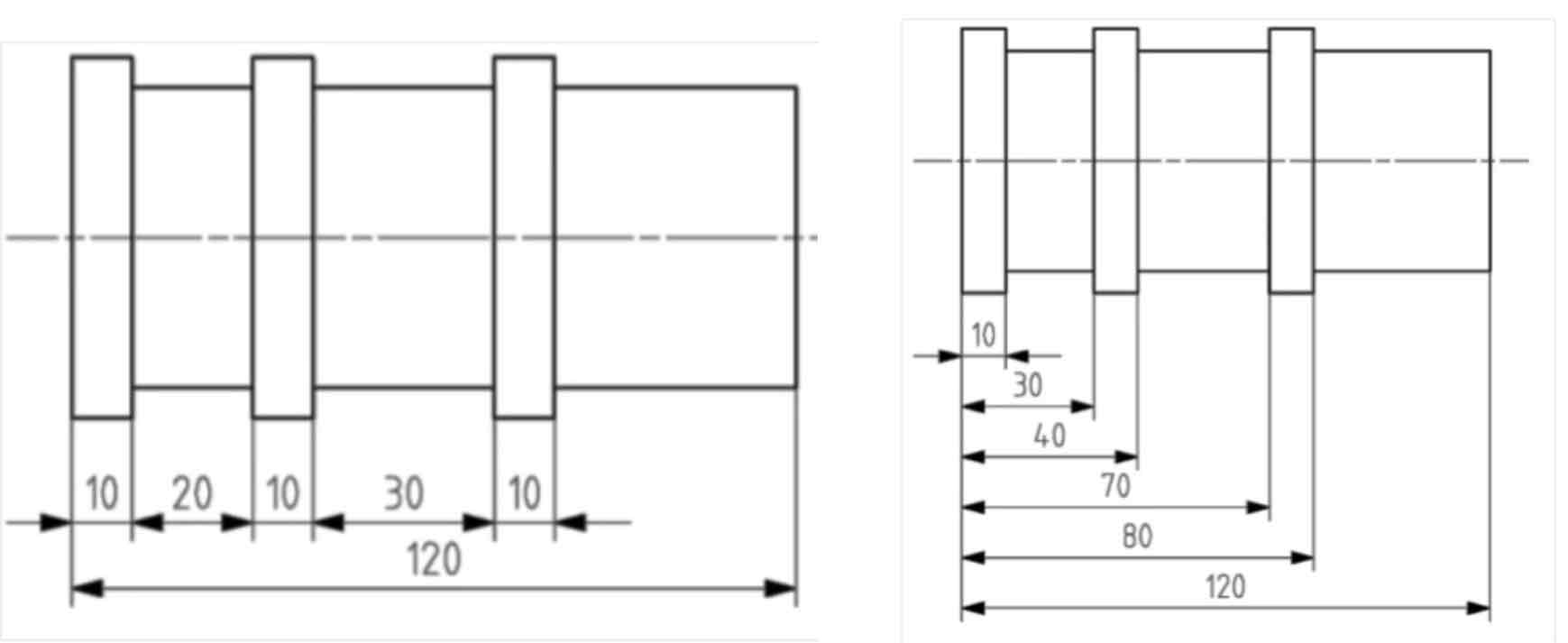
Name the two arrangements of dimensions:
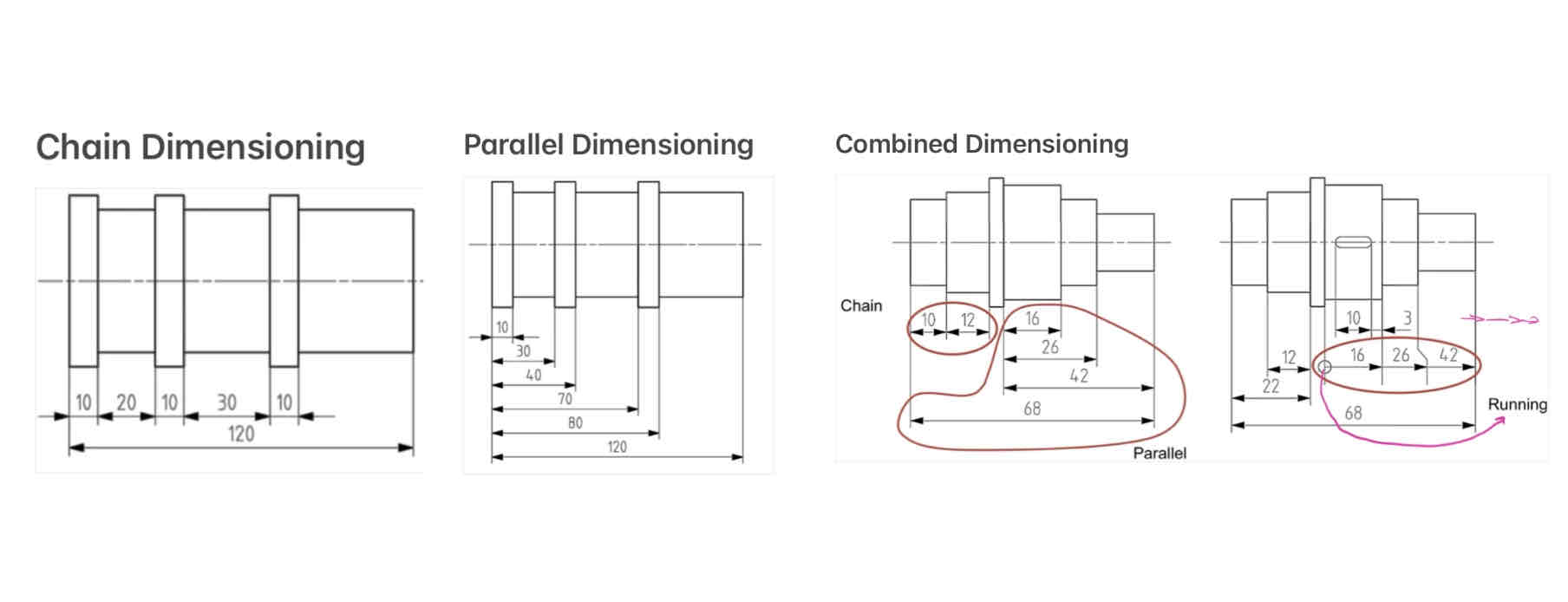
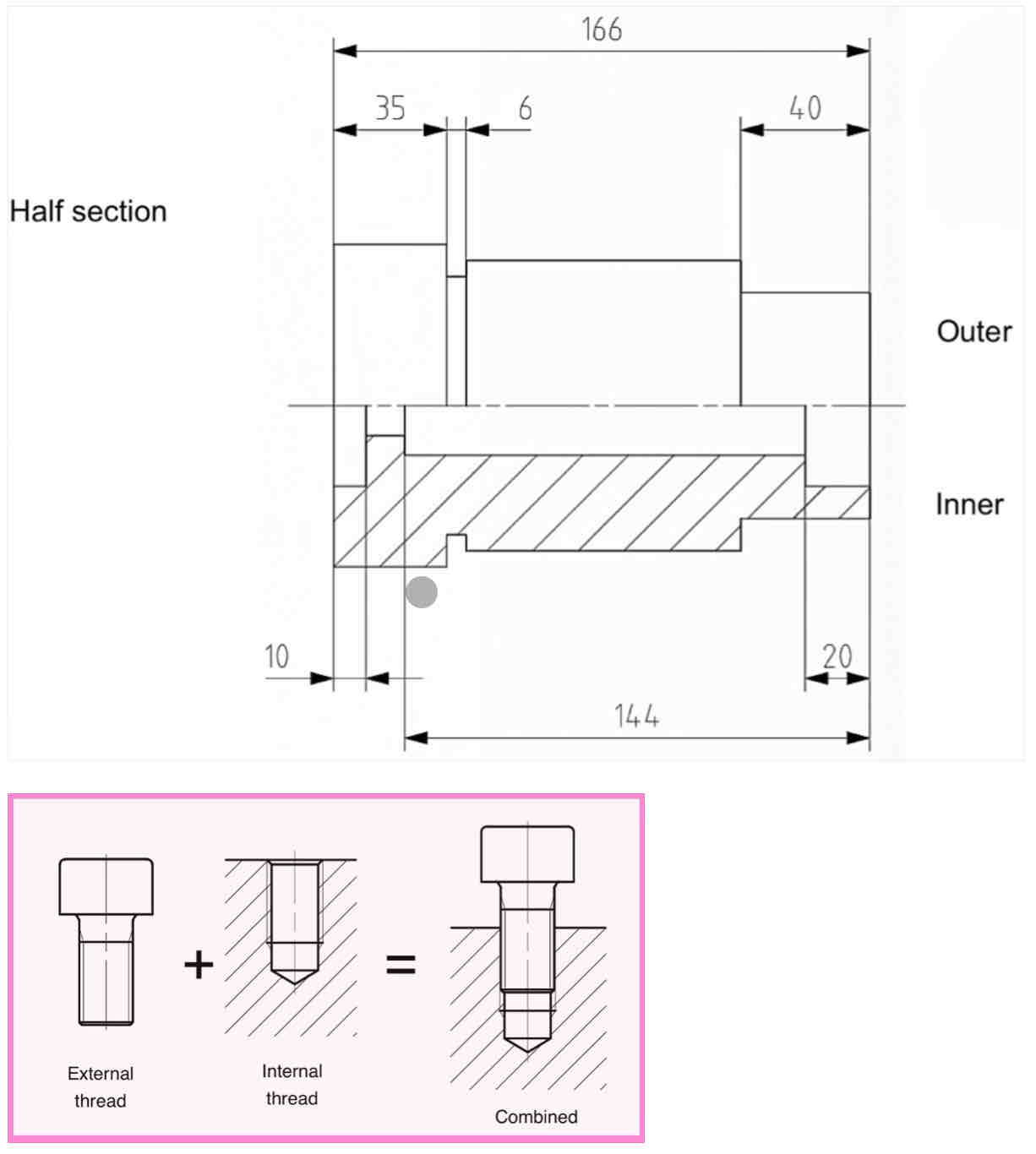
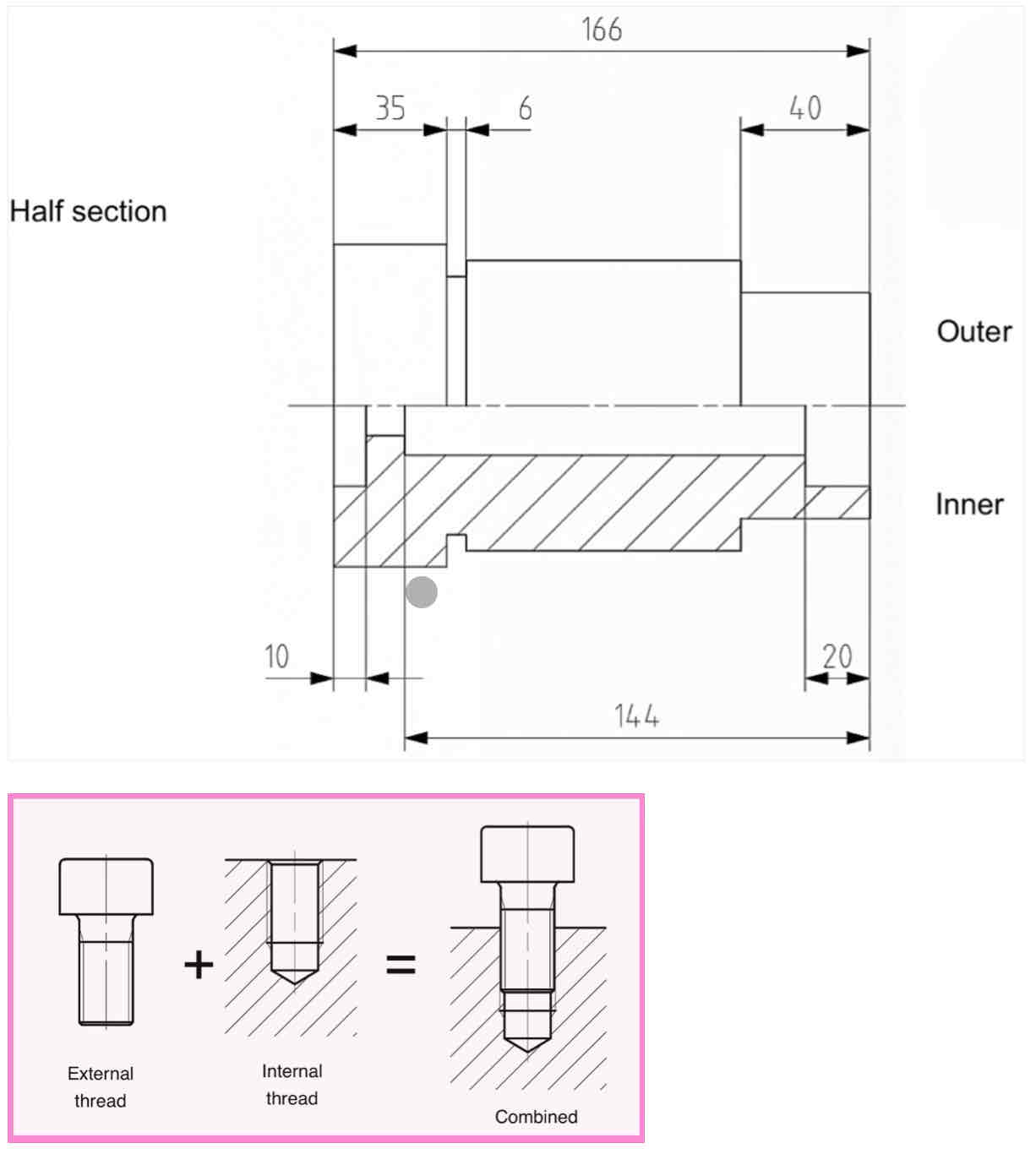
Arrangement of dimensions - what is pictured here:
Arrangement of dimensions - what is pictured here:
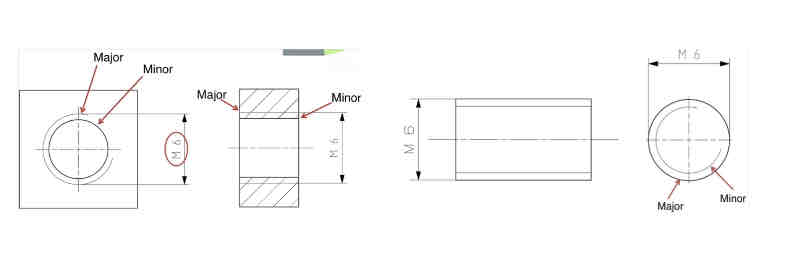
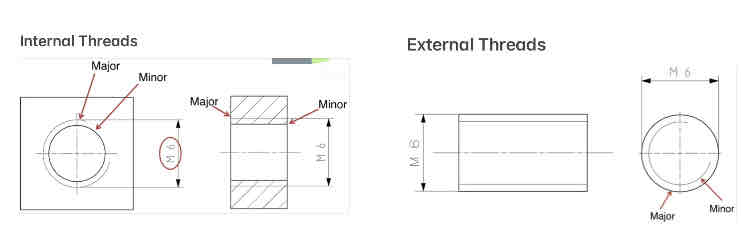
Internal / External Dimensions:

Dimensioning - Wrap-Up: