STRESS - PSYCH
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Maladaptive Coping Definition
are negative ways of dealing with stress. Though these behaviours temporarily distract you from your stress, they eventually lead to physical and emotional harm.
Maladpative Examples
· Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol
· Using drugs
· Angry outbursts
· Denying/ignoring the problem
· Self – harm
· Negative thoughts
· Isolating yourself
· Binge eating or eating in response to stress
Adaptive Coping Definition
empower you to change a stressful situation or adjust your emotional response to stress.
Adaptive Examples
· Deep breathing
· Exercise
· Meditation
· Positive thoughts
· Taking a bath
· Reading a book
· Aromatherapy
What is stress?
The non-specific response of the body to any demand for change. Not what happens to you but how you react to it
Name of Bad stress
Distress
Name of Good stress
Eustress
Distress description
The negative stress response, often involving negative affect and physiological reactivity: a type of stress that results from being overwhelmed by demands, losses, or perceived threats.
Eustress description
The positive stress response, involving optimal levels of stimulation; a type of stress that results from challenging but attainable and enjoyable or worthwhile tasks.
Effects of distress
triggers physiological changes that can pose serious health risks, especially if combined with maladaptive ways of coping
Effects of eustress
It has a beneficial effect by generating a sense of fulfilment or achievement and facilitating growth, development, mastery, and high levels of performance.
Examples of distress
Living with chronic pain
from a progressive illness
like rheumatoid arthritis.
Being unable to make your
mortgage payments and
thinking about losing your
home.
Having someone at school,
work, or home deliberately
mistreat or ignore you
Examples of eustress
Feeling nervous and excited
about meeting a person
you're attracted to for a first
date.
Looking forward to
attending your graduation
ceremony.
Training for your first
marathon.
Planning for and going on a
vacation.
Who defined stress? what year was it?
Hans Selye (1936)
What are stressors?
Conditions of threat, challenge, demands, or structural constraints that, by the very fact of their occurrence or existence, call into question the operating integrity of the organism
Types of stressors
Environmental
Psychological
Cultural
Social
Enviornmental stressor examples
1. Cataclysmic events
2. Stressful life events
3. Daily hassles
4. Ambient stressors
Cataclysmic events
sudden catastrophes that demand major adaptive responses from all individuals directly affected by the event such as floods, earthquakes or volcanic eruptions.
Stressful life events
major incidents in the lives of people that typically require personal or social adaptive responses. E.g. change in family status or economic conditions.
Daily hassles
typical events of ordinary life that cause frustration, tension or irritation. Environmental events (e.g. noisy party) work issues (e.g. arguments), or interpersonal problems (e.g. arguments) are some examples.
Ambient stressors
background conditions, passing unnoticed unless they interfere with some important goal or threaten health.
Psychological stressors
Events or situations that challenge an individual's mental or emotional equilibrium. They are often subjective, varying significantly from person to person depending on their experiences, coping mechanisms, and personal resilience.
Who created the Social Adjustment Theory? What year was it created?
Holmes and Rahe, 1967
what is the social readjustment rating scale?
43 – item list of typically experienced life change events commonly used by researchers interested in the impact of stress on health and well-being
What is social adjustment?
refers to the amount and duration change in one's usual routine resulting from various life events.
What is the purpose of the social readjustment scale?
It was designed to predict the allostatic load (physiological cost) of the transient social adjustment required when certain life events occur.
Sample of the social readjustment scale
convenience sample (n = 394) of males (n = 179) and females (n = 215) who varied in age, class, education, marital status, religion and race.
Results of the social readjustment rating scale
Based on empirical work, Rahe found that a score of about 150 suggested that the respondent would remain healthy over the next 12 months while those falling ill over the same period were typically found to score >300
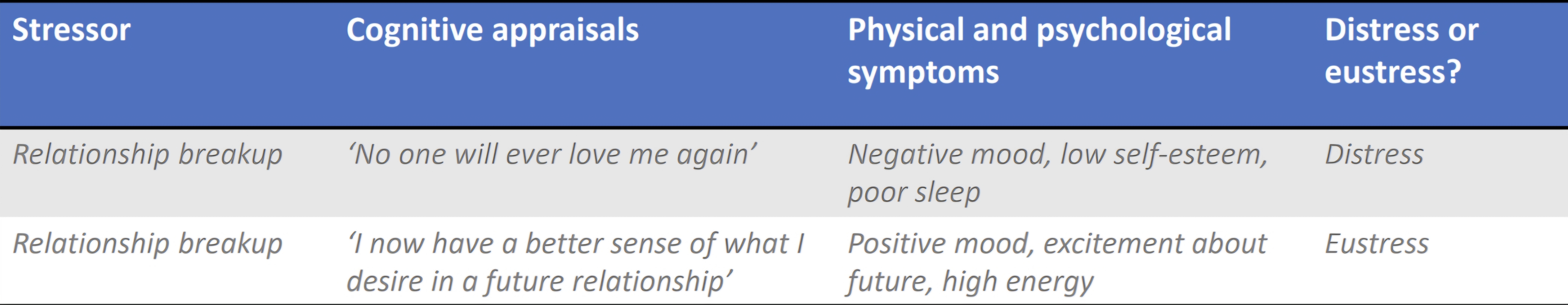
Role of cognitive appraisals in stress response

Who created General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)? What year/s was it?
Hans Selye, 1938;1983
What is General Adaptation Syndrome?
A process in which the body tries to accommodate stress by adapting to it.
What are some examples of the effects of chronic stress?
Enlargement of the adrenal cortex
Constant release of stress hormones
Significant decrease in white blood cell count
Bleeding ulcerations of the stomach and colon
Death of the organism
What was the experiment that Selye undertook for GAS?
Selye's experiments were created to stess rats, which he then observed their physiological responses as a result of repeated exposure to stress
What were the stages of GAS?
1. Stage One: Alarm Reaction
2. Stage Two: Stage of Resistance
3. Stage Three: Stage of Exhaustion
What happens during the alarm reaction?
• Several body systems are activated
• Primarily Nervous + Endocrine system → Cardiovascular, Pulmonary and Musculoskeletal systems.
• All senses are put on alert until danger is over.
What happens during stage of resistance?
• Body tries to revert back to a state of physiological calmness/homeostasis by resisting the alarm.
• Perceived threat = homeostasis isn’t reached.
• Body stays active → less intensity than alarm stage but still enough to cause increased metabolic rate
in organ tissues.
• One or more organs working overtime → final stage
What happens during stage of exhaustation?
• One or more of the organs targeted by specific metabolic processes can no longer meet the demands placed upon it and fails to function properly.
• Can result in death of the organ, or possibly death of the organism.