Properties of Laser Beams, Optics, and Beam Matter Interaction
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
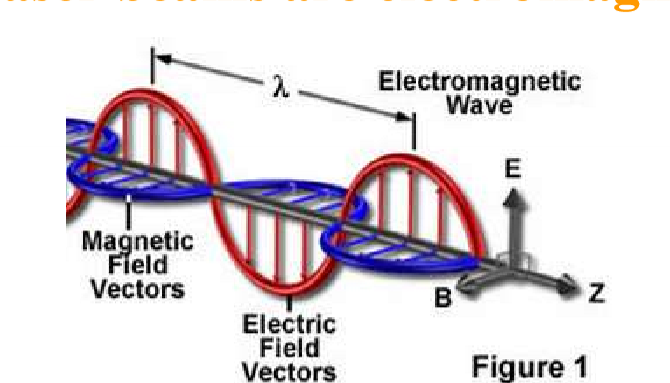
EM Wave Description:
Electric and Magnetic field vectors propogate perpendicular to each other
What is laser wavelength determined by
Lasing medium (e.g. stimulated emission transitions)
Laser Intenstiy Eq and Units
W/cm²

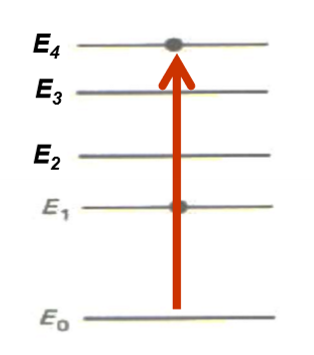
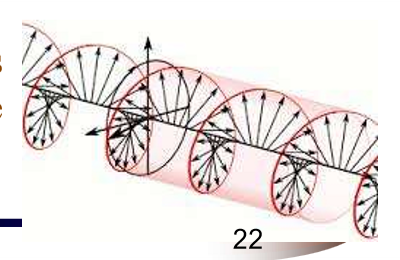
What happens in Transverse Electromagnetic Mode: (TEM)
Photons travelling at right angles to optical axis will not be amplified
Photons travelling along the optical axis will be amplified
Photons travelling zigzag between the mirros will produce complicated patterns, known as transverse electromagnetic mode
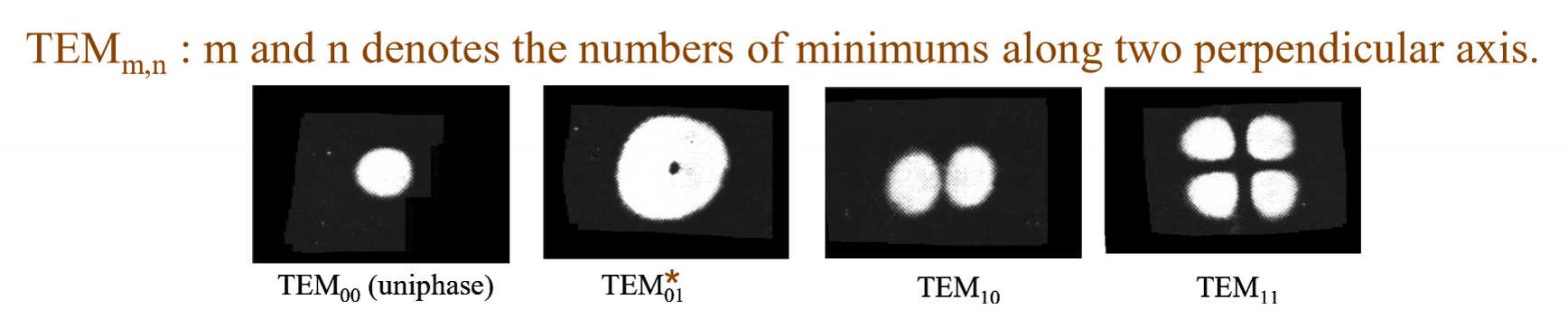
What do m and n denote
What is Laser Intensity Distribution
How Laser Energy is distributed
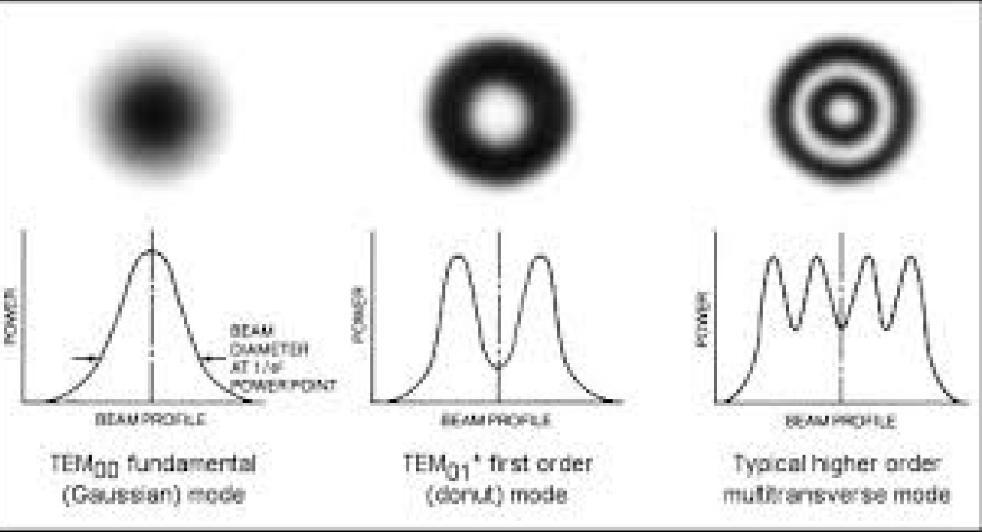
What is a Gaussian Beam
The most desirable beam shape for focusing a laser A

Advantages of Gaussian Beams: (2)
The intensity distribution is maintained during propogation (ie same distribution at front and back of laser (front and far field)
Constant phase across the whole wave-front
What is TEM01
What is it good for
Doughnut Mode: Made from an oscillation between two orthogonal TEM01 modes
Good for surface treatment and high quality cutting
Modes higher than first order are called
High-order modes
Intensity distribution of high order modes………
Vary with distance and time for real lasers
Transverse mode affects: (3)
Beam divergence
Focus spot size
Beam distribution at focus
Higher order TEM often leads to
Non uniform intensity distribution, thus less stable processing
What is M² and what is it used for
Beam Quality Factor
Used to describe high-order modes of power
what is b? and eq?
A constant called the Rayleigh Length
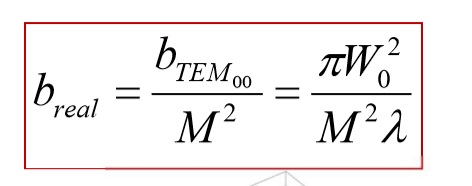
What is W0?
The beam waist
Smallest radius of converging laser beam
M² = 1 means
Gaussian Mode
M² > 1 means
Other modes
What happens at higher modes to b?
Rayleigh Length is reduced
The smaller the M² means
The better the beam quality
So in short, M² measures
Beam quality in space - it tells you how tighlty the beam can be focused, and how fast the beam diverges after focusing
What is the definition of Beam Diameter for Gaussian Mode:
Diameter at which Intensity drops to I0 / e²
r = w (where r = distance form beam axis, w = beam radius)

Definition of beam diameter for High-Order Modes:
Diameter within which 1- 1/e² of total power exists (86% of total power)
Beam radius eq (for Gaussian Mode)
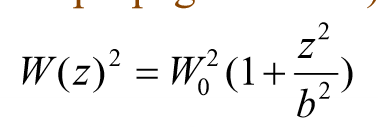
What is W(Z)
Beam radius at distance z from the beam waist
What is z
Distance from beam waist

How does wavelength affect beam divergence
Longer beams lead to higher beam divergence
Greater lambda = Greater W0 = Greater W(z)
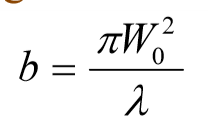
What does Rayleigh Length define:

How is the optical cavity of a laser defined?
With curved mirros so the diameter reaches a minimum in the cavity (Beam Waist)
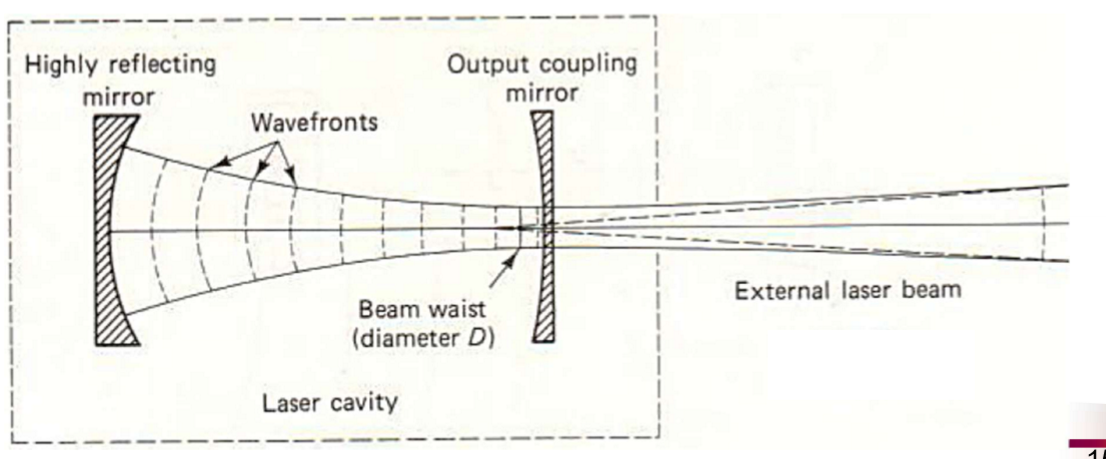
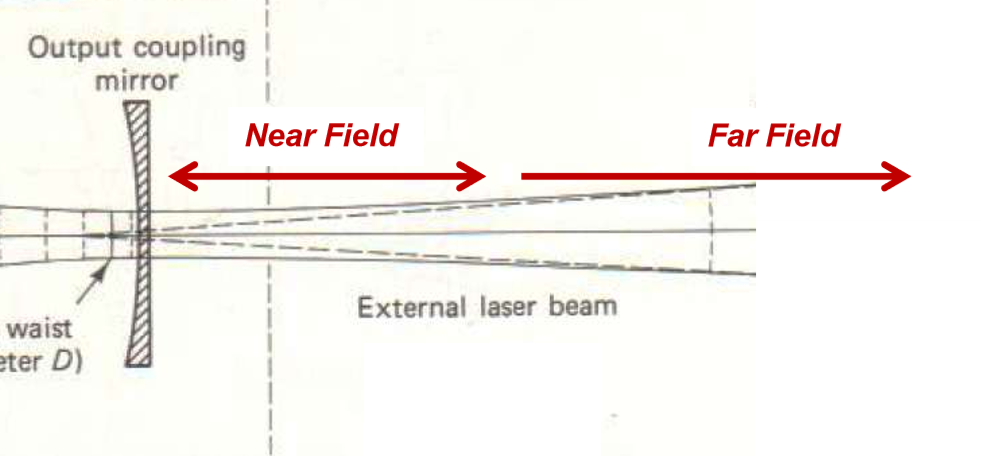
Near and Far FIelds Definintions
Near Field: z << b, W(z) ≈ W0
Far Field: z >> b, W(z) ≈ W0 * z/b
What is Divergence Angle
The radius increase per unit beam lengthEq
W far field eq (expanded with b)
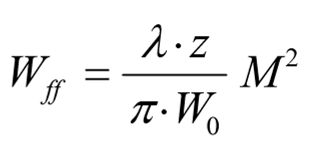
Divergence angle at ff

Thus Divergence Angle is:
Proportional to wavelength and M²
Inversley proportional to Beam Waist
Average Power for Pulsed Lasers
Average Power = Pulse Energy x Frequency
Peak Power for Pulsed Lasers
Peak Power = Energy per Pulse / pulse duration
Power Density Eq

What is Polarisation
The orientation of the Electric Field Vector
What is Linear Polarisation
Direction of E oscillation is in one direction only, and is not changing with time

What does P-Polarised mean
If the beam polarisation is parallel to the plane of incidence
Note it is NOT parallel to the surface, (in fact perp to surface), bc it is parallel to plane of incidence
Still a form of linear polarisation
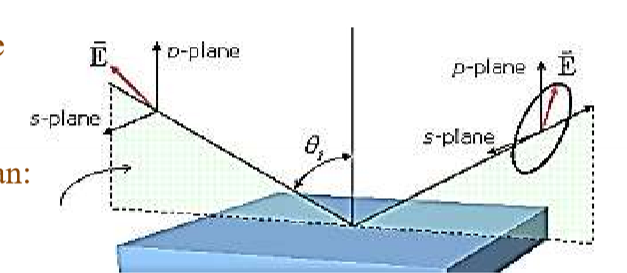
What does S-Polarised mean
If the beam polarisation is perpendicular to the plane of incidence (ie parallel to surface)
Still a form of linear polarisation
Circular Polarisation:
Direction of E oscillation rotates circularly with constant angular velocity
Amplitude remains constant
What are non-standard focusing optics:
Designed for specific processes and applications

What are lenses used for
Power densities of < 10kW/cm²
What is a Singlet
A lens that consists of a single piece
What is a Plano Convex Lens
A spherical single lens that has single positive focal length, and converging incident light, creating real images

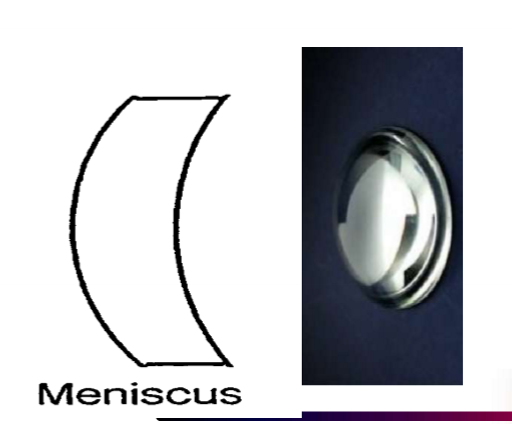
What is a Meniscus Lens:
A lens which has one convex surface and one concave surface, which cancels some of the spherical distortions
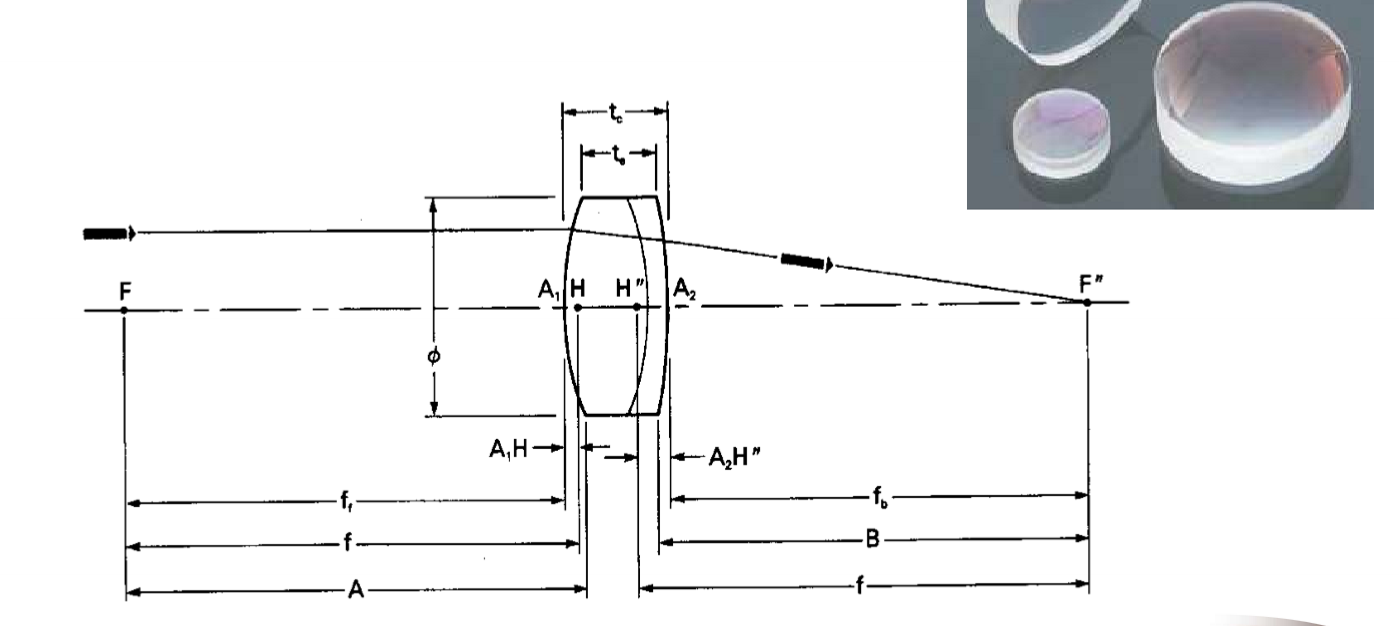
What is a Doublet (Achromat):
Two Lenses cemented together to cancel spherical abberation
One lens is Positive (Converging) and one is Negative (Diverging)
They have different refactive indexes
What are the materical requirements for lenses
High transparency
Thermally Stable
Laser wavelengths (names) and example lens materials
CO2 uses Far infrared, often uses Zinc Selenide
YAG laser and Diode laser use Visible to near infrared, use Glass or Borosilicate Crown Glass
Excimer uses Ultraviolet, uses saphhire
What are Focusing Mirros used for
Highest power densities (>10kW/cm²)
2 types of mirror
Parabolic mirror
Spherical Mirror
Parabolic mirror adv + disadv
Good optical properties
Expensive
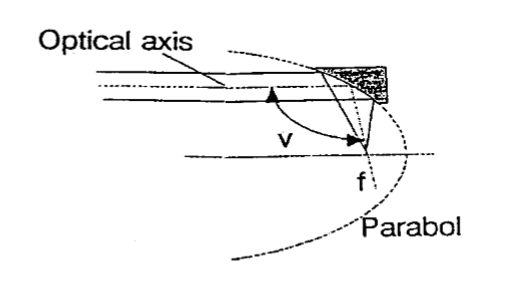
Spherical mirror adv + disadv
Produces more distortions (innacurate)
Cheaper than Parabolic Mirrors
Requirements for materials to make mirrors
High Reflectivity
High thermal conductivity
Low thermal expansion coefficient
Diff types of material combos:
Copper with Silver or Gold Coating, Highest reflection to IR beams (99.4%), High thermal conductivity, Used for most CO2 Laser Beams
Silicon + Silver, 98.9% reflective, high thermal stability + low weight
Mo + Ag Coating, 98.9% reflective, Durable and rugged
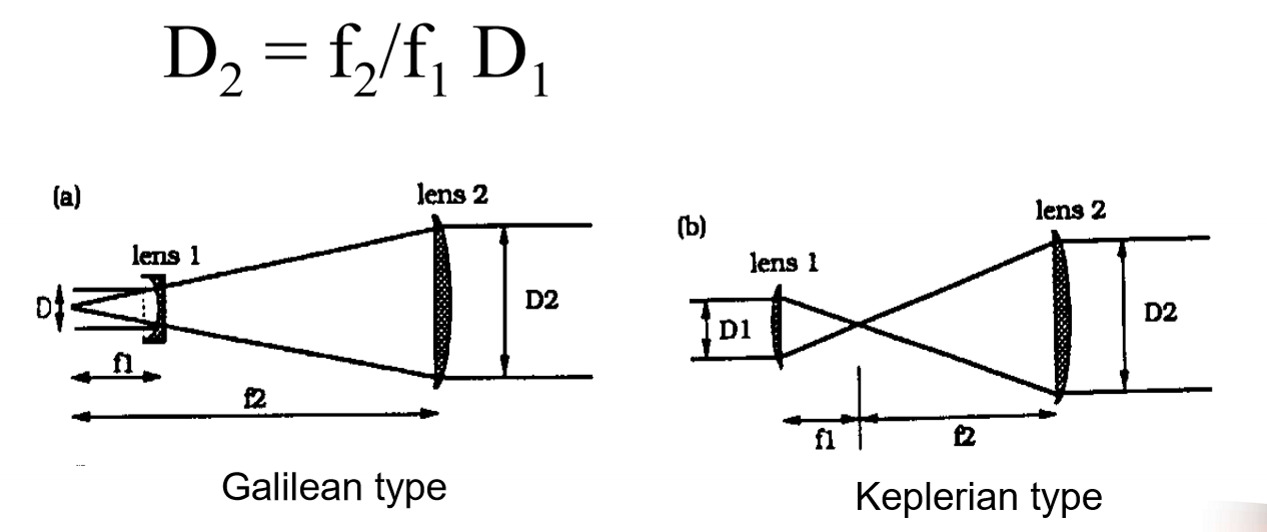
What is a Collimator + 3 points:
A Beam expander which increases beam diameter (made of 2 lenses)
Reduces power density
Reduces beam divergence
Improves focusability (reduced focus spot size) (after beam expands it makes it easier to focus)
Equation + what it looks like
2 Types of Beam Scanners:
x-y scanner (scanning galvanometer)
Polygon Scanner
How do x-y scanners/ galvanometer scanners work
Uses a pair of mirros on galvo motors
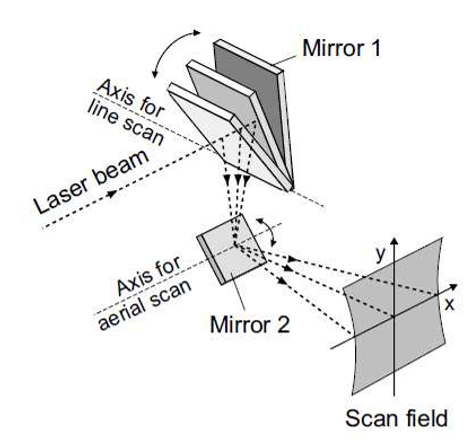
How do Polygon Scanners work
Applications?
For a x-y scanning pattern, one axis is scanned using a standard galvo-mounted mirror, and the other axis is scanned using a polygon mirror
For high-speed applications

What is a Circular Polariser and two types:
Something used to convert a linearly polarised beam into a circularly polarised beam (useful to remove orientation sensitivity)
Reflective
Transmissive
Reflective type:
Applications
Setup
Used for high power
¼ dielectic coating on a flat mirror, so that p-polarised component (reflected from mirror) is λ/4 out of phase with the s-polarised component (reflected from dielectric)
Transmissive Type:
Applications
Setup
Low power applications
Laserbeam is transmitted through a birefringent material, inducing a λ/4 phase shift between horizontal and vertical polarisation components
Optical Fibre Basic Principle (and diff between modes?):
Cladding has a lower refractive index than the core, causing TIR to occur
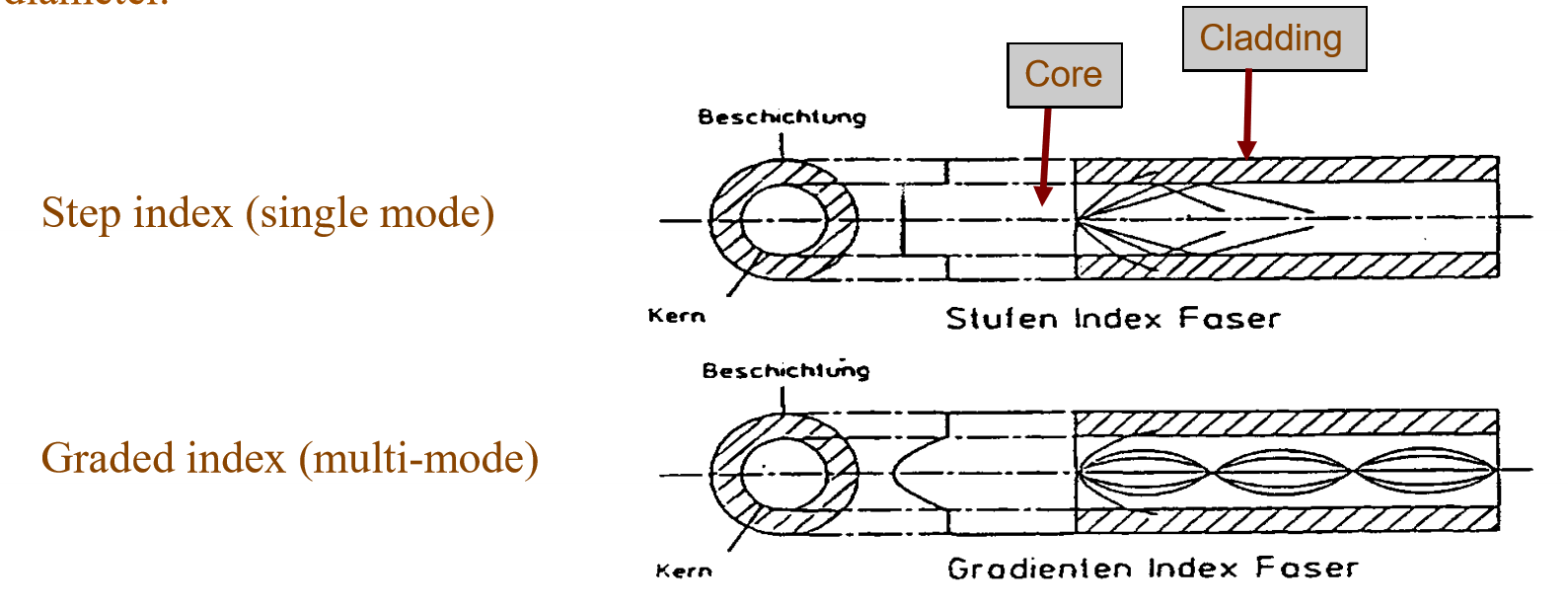
Focal spot size is generally limited by
Fibre core diameter
Minimum laser focused spot diameter eq:
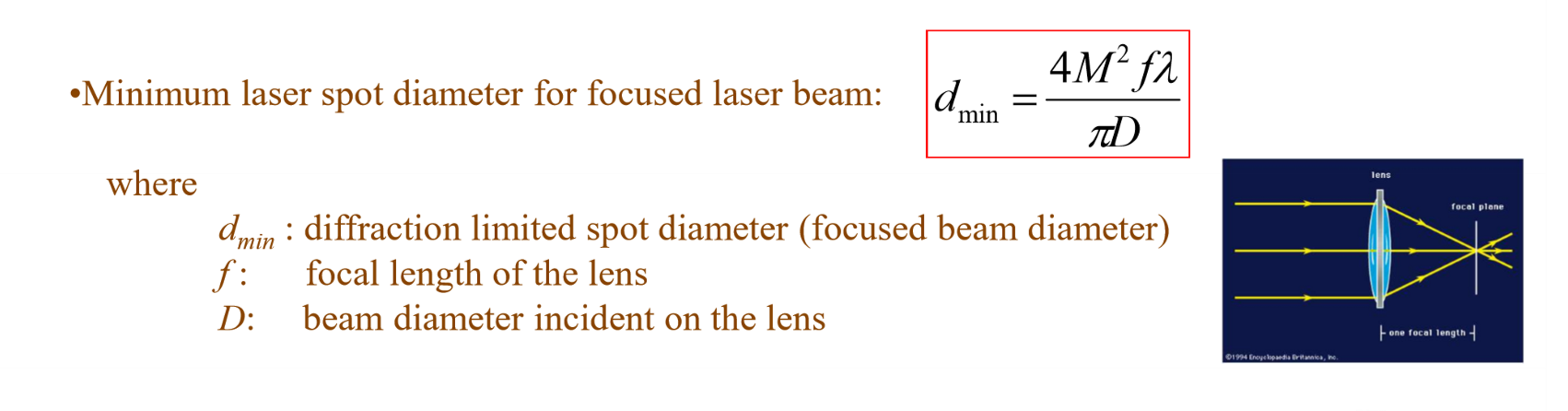
F number (focal number) equation:

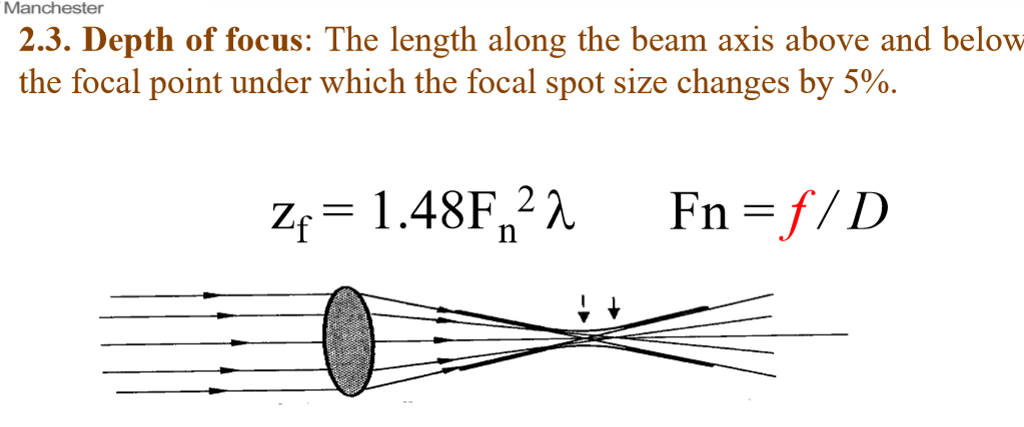
What is Depth of Focus and Eq:
The length along the beam axis, above and below the focal point, under which the focal spot size changes by <5%
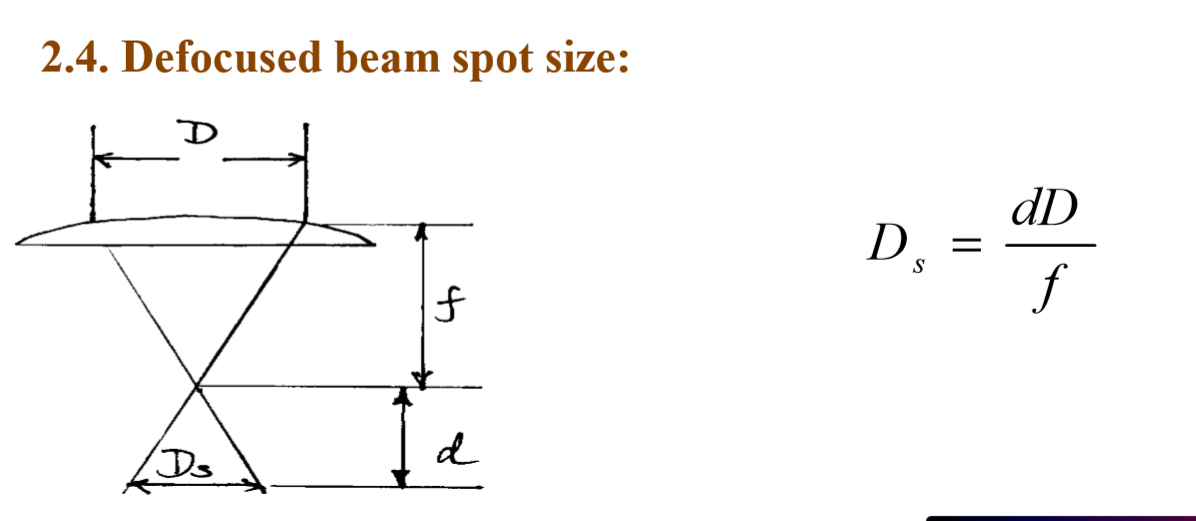
Defocused Beam Spot Size eq
Difference in refactive index for transparent and absorbing materials
Transparent: Refractive index is a real number
nt = n
Absorbing: Refractive index is a complex number
na = n + ik
n is the real refractive index
k is the extinction coefficient
What is the absorption coefficient and equation
The rate at which light will attenuate (decay) after it propogates below the surface of a absorbing material
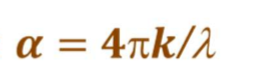
Transmitted Intensity Equation
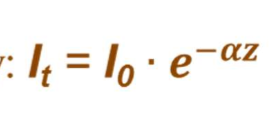
What is Transmitted Intensity proportional to?
Electric field

Reflectivity definition and equation:
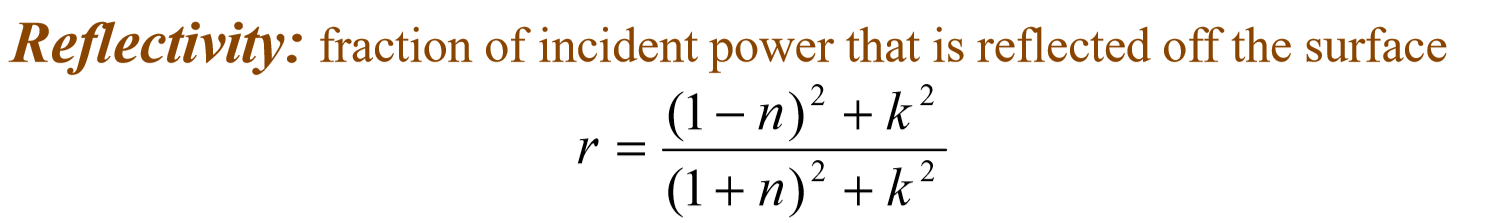
Absorptivity definition and equation:

Metal absorption?
Metals strongly absorb light, α is range of 10^5
What is skin depth/absorption length
The depth at which most of the optical power is absorbed
z = 1/α
(Because I = I0 * e^( -α*z), when z = 1/α, I = I0 / e)
3 types of laser absorption mechanisms:
Fresnel Absorption
Inter-band Absorption
Photo-Chemical Absorption
What happens in Fresnel Absorption
Incident photons cause electrons to vibrate, which indusces heat in the body.
It is a pureley thermal interaction, photon energy converts into thermal energy
What is Inter-band Absorption
When the absorption of a single photon causes an electron to transition band
Why is inter-band absorption impossible on metals for the lasers we studies
Metals require photon energy >10eV
Photon energy of CO2, YAG and Excimer are all too small (max being excimer at 4.9eV)
Therefore, not possible, not eneough energy in photon

What happens in Photo-Chemical Absorption:
Molecule bonds are directly broken by the laser beam, without causing a temperature rise, known as cold machining
Only happens for short wavelength ie high photon energy lasers such as Excimer lasers, when fired at polymer materials that have low bond energies