topic 6 - organisms respond to changes in their environments
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is a stimulus?
A change in an organism’s internal or external environment
Why is it important that organisms can respond to stimuli?
Organisms increase their chance of survival by responding to stimuli
What are kineses?
Non-directional responses to stimuli.
Speed of movement or rate of directional change can change with the intensity of the stimuli.
What is an example of kineses?
Woodlice moving faster in drier environments to increase their chance of moving in an area with higher humidity to prevent drying out.
What are taxis?
Directional responses to a directional stimulus - involves moving towards (positive) or away from (negative) the stimulus.
What is an example of taxis?
Woodlice moving away from light to avoid predators.
How do plants respond to directional stimuli?
Specific growth factors which are hormone-like growth substance that can speed up or slow down plant growth.
Growth factors move from growing regions e.g. shoot / root tips where they’re produced to other tissues where they regulate growth in response to directional stimuli
What are auxins?
A class of growth factors found in root & shoot tips that diffuse backwards to stimulate growth in the cells just behind where they’re produced.
What is an example of an auxin?
IAA (indoleacitic acid)
Where is IAA synthesised?
In the growing regions of the plant - tips of the roots and shoots
How does IAA move around the plant?
By diffusion and active transport from cell to cell, and in the phloem for long distances
How does indoleactic acid (IAA) affect cells in roots and shoots?
In shoots, high concentrations of IAA stimulates cell elongation
In roots, high concentrations of IAA inhibits cell elongation
What happens in cell elongation?
The cell walls become loose and stretchy so the cells become longer.
What is a tropism?
Growth of a plant in response to a directional stimulus - there are two types.
Positive tropism = towards a stimulus
Negative tropism = away from stimulus
What is phototropism?
The growth of a plant in response to light.
Shoots are positively phototropic so the grow towards light.
Roots are negatively phototropic so grow away from light.
What is gravitropism?
The growth of a plant in response to gravity.
Shoots are negatively gravitropic so grow away from gravity
Roots are positively gravitropic so grow towards gravity
What happens in gravitropism in the shoots vs the roots?
In both the IAA is produced by cells in the tip of the shoot vs root and diffuses down. The IAA then moves to the lower side of the shoot vs root increasing the conc of IAA there.
Shoots:
IAA stimulates cell elongation
Cells on the lower side elongate.
The shoot tip curves up /away from gravity.
Negative tropism
Roots:
IAA inhibits cells elongation.
Cells on the lower side stay short.
The root tip curves down/towards gravity.
Positive tropism
What happens in phototropism in the shoots vs the roots?
In both the IAA is produced by cells in the tip of the shoot vs root and diffuses down. The IAA then moves to the shaded side of the shoot vs root increasing the conc of IAA there.
Shoots:
IAA stimulates cell elongation
Cells on the shaded side elongate.
The shoot tip curves towards the light.
Positive tropism
Roots:
IAA inhibits cells elongation.
Cells on the shaded side stay short.
The root tip curves away from the light.
Negative tropism
How is the nervous system organised/characterised?
Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System vs Autonomic Nervous System
What is the Central Nervous System vs the Peripheral Nervous System?
The Central Nervous System(CNS) is made up of the brain and spinal chord.
The Peripheral Nervous System is made up of sensory and motor neurones.
What is the Somatic Nervous System vs the Autonomic Nervous System?
Somatic Nervous System = body nerves - voluntary/consious control & movement
Autonomic Nervous System - involuntary control & movement
What is the Autonomic Nervous System split up into?
Sympathetic system - prepare body for activity by e.g. increasing heart rate
Parasympathetic system - calms body down, returning it to a normal state
What are the different types of neurones and why are there different types of neurones?
Motor
Sensory
Relay/intermediate neurones
There are different types of neurones as each type has a different structure and carries impulses from different starting to ending cells.
What is the structure of a motor neurone?
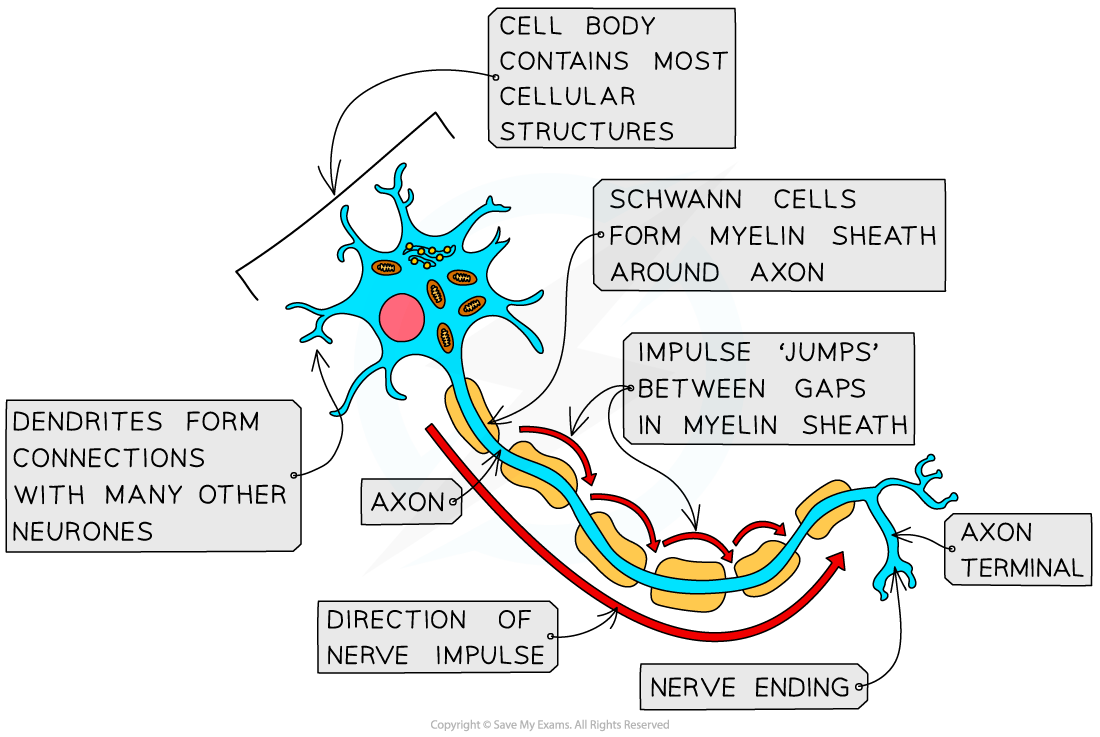
Cell body, dendrons → dendrites, axon, Shwann cells & myelin sheath, synapse
An impluse travels down the neurone from the cell body in the CNS to the synapse to an effector.
What is the structure of a sensory neurone?
Synapse to receptor, dendrites → dendrons, Shwann cells & myelin sheath, nodes of Ranvier, axon , cell body, axon, CNS
There is one long dendrite that carries an impluse from the receptor to the cell body and then a short axon which carries the impluse from the cell to the CNS.
An impulse travels down a sensory neurone from a receptor to the CNS.
What is the structure of a relay neurone?
Cell body in center, axon, dendron → dendrites, synapses
Impulses are carried from a sensory neurone by the dendrons etc to the cell body and then from the cell body to a motor neurone by short axons.
Relay neurones connect sensory and motor neurones within the CNS.
What is the cell body of a neurone?
The actual cell which contains the nucleus and large quantities of mitochondria and RER.
What are the dendrons and dendrites of a neurone?
Dendrons - small extentsions of the cell body which carry nerve impluses towards the cell body.
Dendrites - extentsions from the dendrons
What are the Shwann cells and myelin sheath?
Shwann cells - cells with many membranes that surround the axon providing insulation. The many membranes which wrap around the axon form the myelin sheath.
What are the nodes of Ranvier?
The gap between the Shwann cells.
What is a nerve impluse?
An electrical impluse caused by the movement of ions that travels down an axon or a self propagating wave of electrical disturbance along the surface of the axon membrane.
What is a nerve impluse not?
A nerve impluse is not an electrical current but the reversal between 2 states - resting potential and action potential.
What are resting potential and action potential?
They are the only two states a neurone can occupy - there is no inbetween so a neurone is either “on” or “off”.
Resting potential
(relative) Negative charge inside the axon
~ -65mV
Action Potential
(relative) Positive charge inside the axon
~ +40mV
How does an axon become charged in both resting & action potential?
An axon doesn’t have an electrical impluse/electrons running through it.
Instead it has higher or lower amounts/concs of ions - Na+ & K+ ions. These are transported in or out across the axon membrane which can result in a difference in number of ions between extracellular fluif outside the axon & the cytoplasm inside the axon. This causes a relative difference in charge/voltage between the two.
However as the ions are transported by the membrane this difference in charge isn’t across the whole axon but just the areas near the membrane.
What are the ions involved in resting & action potential?
Na+ & K+ ions. The different amounts of these ions is what causes the relative charges.
How do the Na+ & K+ ions moved by the axon membrane?
Ion Channels - there are channels specific to Na+ ions and ones specific to K+ ions. The channels can also be gated or ungated/leakage channels which are always open but only at the right conc gradient & time.
Na+/K+ pump - active transporter protein which actively transports 2K+ ions into the axon for 3Na+ ions out of the axon
Overall what happens in resting potential?
Action of the Na+/K+ pump
Pumps 3Na+ ions out of the axon into the extracellular fluid
Pumps 2K+ ions into the axon cytoplasm
Requires ATP hydrolysis (duh)
Potassium ion channels open
Most potassium ion channels are open so some K+ ions diffuse down the conc gradient caused by the pumping of K+ ions
However sodium ion channels are closed so no Na+ ions move down their conc gradient
This overall results in more positive ions outside the axon than inside the axon. The membrane is polarised and an electrochemical charge around -70mV is produced.
What is negative feedback?
Feedback which counteracts an external change :
In homeostatsis this is what happens to maintain a “norm”/baseline
Happens control of blood glucose, blood CO2 and blood water potential
What is positive feedback?
Ever increasing change in a certain direction :
Doesn’t really happen but the only similar relationship would be with action potential in the neurones but this is still only up to the threshold
Causal relationship - change causes response which increases change
What are the two hormones involved in homeostatsis of blood glucose?
Insulin - released when blood glucose levels are high
Glucagon - released when blood glucose levels are low
What are the processes involved in homeostatsis of blood glucose?
Glycogenesis - increasing the size of glycogen by adding glucose molcules to the glycogen ends
Glycogenolysis - breaking down of glycogen to release glucose
Gluconeogenesis - making new glucose molecules - largely from glycerol but can be from amino acids
What types of hormones are insulin and glucagon?
They are protein hormones - this means they cannot diffuse into their target cells. Instead they have to bind onto a receptor on the target cell.
What types of cells make up the pancreas?

The main cells & the ones involved in control of blood glucose levels are the Islets of Langerhan - both the alpha and beta ones.
Where is insulin made and stored?
It’s made and stored in the pancreas specfically in the beta Islets of Langerhan cells.
Where is glucagon made and stored?
It’s made and stored in the pancreas specfically in the alpha Islets of Langerhan cells.
How do the alpha and beta pancreas cells release their stored hormones?
The hormones - insulin & glucagon - are stored inside vesicles in the cell cytoplasm. When high or low blood glucose levels are detected by the pancreas cells the hormone vesicles move to and fuse with the cell membrane releasing the hormone stored.
What are the target cells of insulin?
Liver and muscle cells. This means they have insulin receptors embedded in the cell membrane and will carry out glyconeogenesis in response to insulin etc.
What does a target cell of insulin have stored inside it?
The target cells have vesicles storing glucose carrier proteins - GLUT4 is one specific to insulin response
Glycogen molecules
What happens when insulin binds its receptor on a target cell?
The insulin receptor protein in the membrane changes shape
Inside the cell a secondary messanger is activated
This results in the vesicles storing GLUT4 moving towards the cell membrane and fusing with it
The glucose transporter proteins are embedded so there are overall more of them
For facilitated diffusion of glucose into the target cells a conc gradient must be maintained
The secondary messanger “achieves” this as it also activates glycogen synthase via dephosphorylation carried out by an ‘intermediate’ enzyme
Glycogenesisis occurs
The secondary messanger also increases the rate of respiratory enzymes
The overall effect is more facilitated diffusion of glucose into the cell out of the blood, and the use of this glucose to maintain the conc gradient for this
What happens in glycogenesis?
Individual glucoses are added onto the ends of glycogen increasing its size. This is facilitated by the many ends of glycogen as this allows many glucoses to be added at the same time etc.
What happens when insulin detaches from its target cell?
The vesicles storing GLUT4 reform and this deactivates the secondary messanger. This means glycogenesis stops and the activity of respiratory enzymes is not increased/decreased.
What are the effects of insulin?
Increased rate of diffusion of glucose into the target cells
(facilitated by) Increased rate of respiration
Increased glycogenesis
Increased number of glucose transporters in cell membrane of the target cell
What are glucagon’s target cells?
Liver cells. This means the liver cells have glucagon receptors embedded in their cell surface membrane.
What happens when glucagon binds to its receptor on a target cell?
The shape of the glucagon receptor protein changes
This causes the rate of respiration in the target cell to be reduced
The change in shape also activates enzymes involved in glycogenlysis so more occurs
Gluconeogenesis also occurs (more) as a result of the glucagon binding etc
Overall the conc of glucose increases in the target cell and so diffuses via glucose transporter proteins out into the blood, increasing the blood glucose levels as required
What happens in glycogenlysis?
Glycogen is broken down releasing glucose molecules into the cytoplasm.
What happens in gluconeogensis?
New glucose molecules are synthesised normally from glycerol molecules with 2 3C glycerols being converted into 1 6C glucose. The fatty acids from the same lipid can be used in respiration.
Why does the rate of respiration in the target cells need to be reduced when glucagon binds?
The other effects of glucagon cause increases in the quantity of glucose produced by the cell so increasing the avaliability that can be used in respiration. For as much glucose as possible to diffuse out of the cell into the blood as desired less needs to be used up in respiration.
What is adrenaline?
A protein hormone released as a short term stress response - flight or fight - in order to prepare the body to respond.
How does adrenaline affect the body to prepare it?
Increases heart rate and raises blood glucose so faster respiration can occur so more ATP can be released.
What are the target cells for adrenaline?
Includes many cells like the liver cells/ all cells which have receptors for adrenaline embedded in their membrane.
What happens when adrenaline binds to a receptor on a target cell?
The adrenaline receptor - on the inside of the cell - is associated with a secondary messanger
This messanger is adenylate cyclase enzyme and becomes activated when adrenaline binds
The enzyme converts ATP into cAMP
Adenylate cyclase enzyme removes 2 phosphate & attached the remaining phosphate onto different carbon
The cAMP activates protein kinase A which in turn activates the glycogen phosphate enzyme
This allows glucose to be removed & then dephosphorylated before entering the blood
What is the role of the kidney?
To filter the blood to remove toxins like urea, caffiene & food additives.
To regulate the blood’s water potential - osmoregulation & this ties to ion regulation.
What is the structure of the kidney?

What is the structure of the nephron?

