Chapter 4: Body Tissues and Membranes ~ 4.1 Epithelial Tissue
1/7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
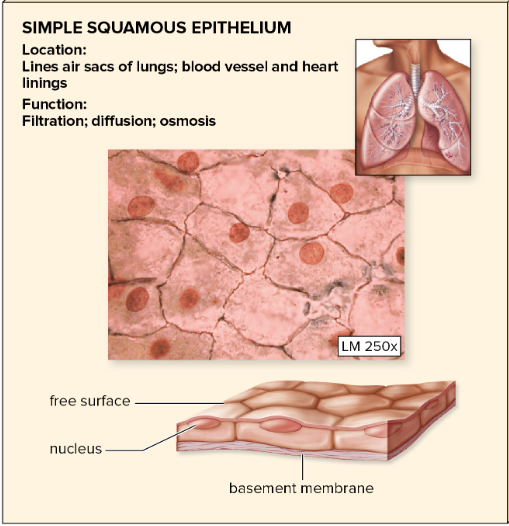
one layer of flattened cells and
located in blood capillaries; air sacs (alveoli) of lungs
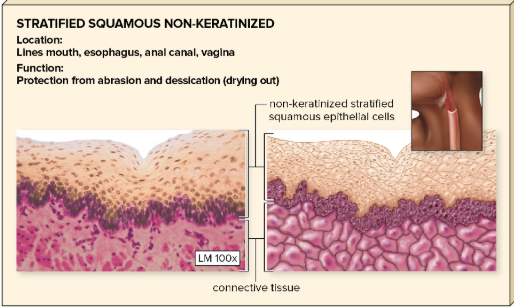
many layers; cells flattened at free surface
in skin, entrances to structures opening to the outside
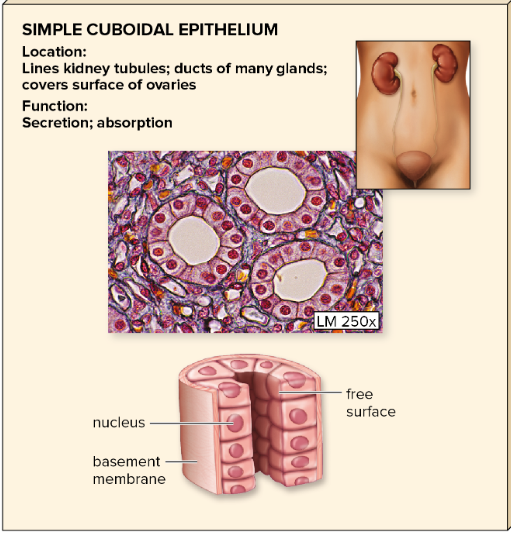
one layer of cube-shaped cells
in secreting glands, ovaries, linings of kidney tubules
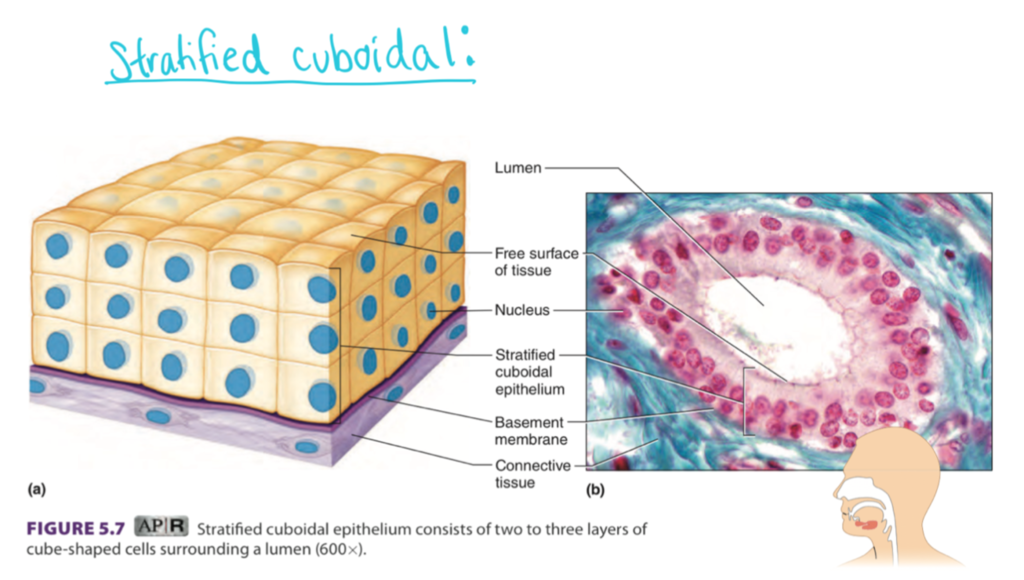
two or more layers of cube-shaped cells
lining of salivary gland and mammary gland ducts
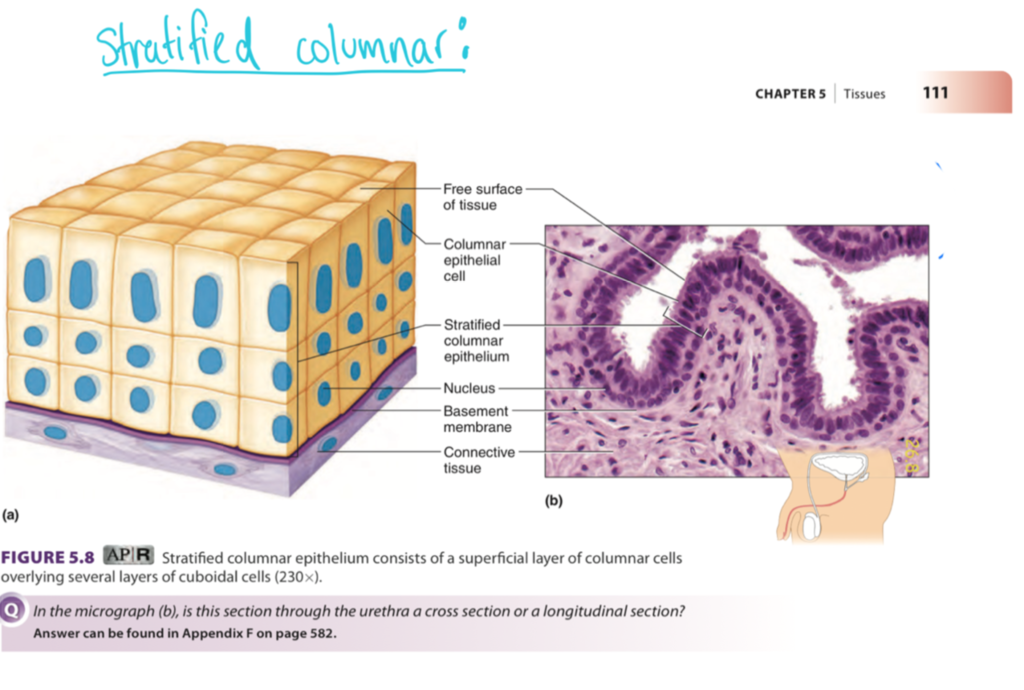
two or more layers of elongated cells
in pharynx (back of throat); male urethra
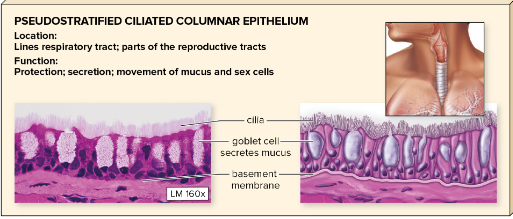
one layer of elongated, tapered cells; apper stratified
in air passages of the respiratory system
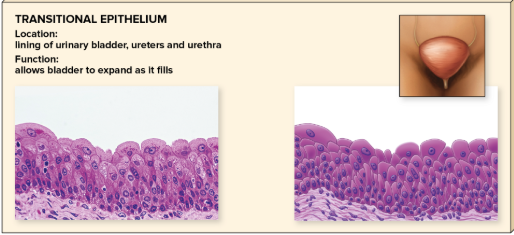
many layers; when tissue stretches, surface layers flatten and appear squamous
in urinary bladder; ureters and urethra
characteristics of of epithelial tissue
rapid rate of mitosis
very tightly packed
protects body from drying our, injury and bacterial invasion
internally, protects, cilia in respiratory tracts sweep up impurities digestive tract they secrete mucus protecting lining microvilli help absorption in kidneys