FINAL EXAM- PROF K
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hoping for the best
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What are the PK differences between single IV bolus and IV infusion? (include Cmax and Tmax)
IV bolus- brief Cmax, Tmax=Cmax
IV infusion- continuous Cmax, Tmax≠Cmax
What is the main advantage of an IV infusion?
the ability to maintain steady-state concentration
What is the abbreviation for each of the following:
steady-state plasma concentration
infusion rate
drug in the body
volume of distribution
elimination rate constant
Cp(ss)
Ko
DB
Vd
Ke
Infusion Rate ____ Elimination Rate
a. >
b. <
c. =
c. = (NOTE: it’s elimination RATE not the elimination rate constant)
Explain the concept of drug accumulation:
a gradual buildup of drug concentrations with continuous or successive doses.
the whole time leading up to steady state concentration is know as the drug accumulation phase
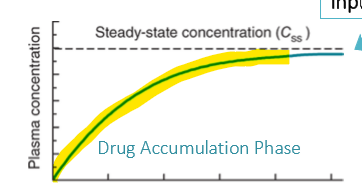
What is the relationship between steady state drug concentration (Cp(ss)) and the infusion rate (Ko)?
directly proportional
What is the relationship between steady state drug concentration (Cp(ss)) and Clearance (CL)?
inversely proportional
Be able to know how to apply all the equations given in the powerpoint. WILL NOT HAVE TO MEMORIZE
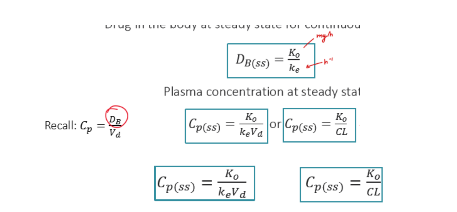
Calculate the steady-state Cp, if a drug (CL= 3L/h, Vd=40 L) is administered as an IV infusion at a rate of 15 mg/h.
(Equation sheet is attached)
Cpss= 5 mg/L
Phenytoin is administered as an IV infusion at a constant rate of 45 mg/h. Calculate the steady-state Cp. Assume Vd=30 L, Ke=0.1155 h-1.
(round to the nearest hundredth in mg/L)
12.99 mg/L
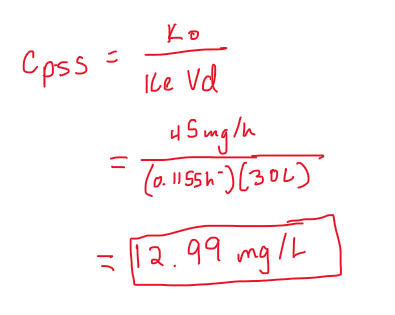
Phenytoin is administered as an IV infusion at a constant rate of 45 mg/h. Determine the elimination rate at steady state. Assume Vd=30 L, Ke=0.1155 h-1.
6 hr
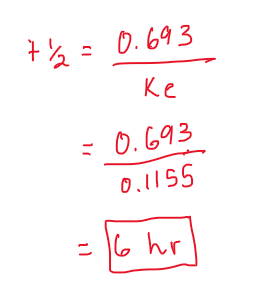
Phenytoin is administered as an IV infusion at a constant rate of 45 mg/h. Calculate the clearance. Assume Vd=30 L, Ke=0.1155 h-1.
(round to the nearest hundredth in L/h)
CL= 3.46 L/h
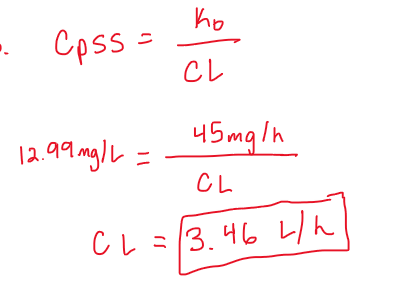
The time required to reach steady state depends on the drug’s ________________.
half-life
Which of the following drugs will take the longest to reach steady state?
a. a drug with a half-life of 10 hours
b. a drug with a half-life of 1 hour
c. a drug with a half-life of 30 minutes
d. a drug with a half-life of 5 hours
a. (longer half-life= longer to reach steady state)
How many half-lives does it typically take to reach steady state?
5 half-lives
Which of the following will NOT affect the time it takes to reach steady state?
a. dose
b. Vd
c. clearance
a
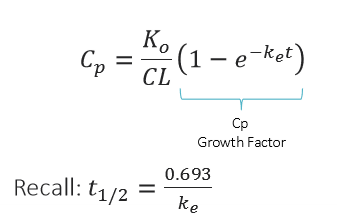
How long will it take to reach steady state if the patient has a Ke= 0.1 h-1 ?
PRACTICE:
An increase in drug dose will not change the time it takes to reach steady-state, but will result in a higher plasma concentration at steady-state.
a. TRUE
b. FALSE
a. (time to steady state is not effected by dose, but CL and Vd)
PRACTICE:
When drug clearance increases (Vd remains unchanged), steady-state plasma concentrations will ________________.
a. increase
b. decrease
b. (bc CL and Cpss are inversely proportional)
PRACTICE:
When drug infusion rate increases (Vd remains unchanged), steady-state plasma concentrations will ________________.
a. increase
b. decrease
a. (infusion rate and Cpss are directly proportional)
My steady-state plasma concentration was measured and found to be 1.4 mg/L, and I had been on an infusion rate of 7.7 mg/h for the past 72 hours. The doctor then says they want to achieve a Cpss of 2 mg/L. What would be my infusion rate to reach that steady-state goal?
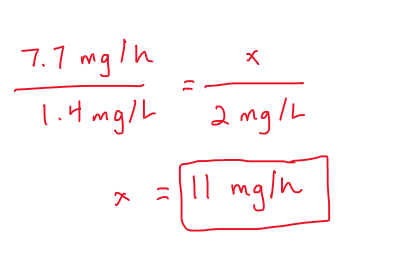
The higher the clearance the __________ steady-state concentration.
lower (think: if you get rid of a drug faster, you will have a lower steady state)
The time to reach steady state is _________________ of the infusion rate.
a. dependent
b. independent
b
If 2 people had similar clearance, but one had a Vd of 15L and the other had a Vd of 49L, which of the following WOULD NOT be effected?
a. time to reach SS
b. t1/2
c. Ke
d. steady state plasma concentration
d
What are the drawbacks of IV infusions? How can this be fixed?
takes 5 half-lives to steady state so it is NOT GOOD in a medical emergency. can be fixed with a LOADING DOSE
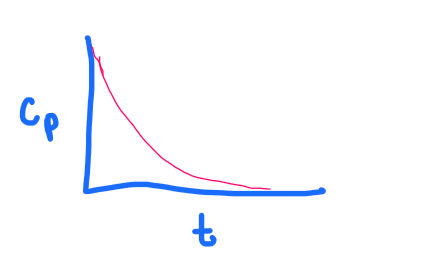
PRACTICE:
What graph does the following depict?
a. 1 compartment, IV bolus
b. 1 compartment, IV continuous infusion
c. 1 compartment, IV continuous infusion WITH a loading dose
d. 2 compartment, IV bolus
a
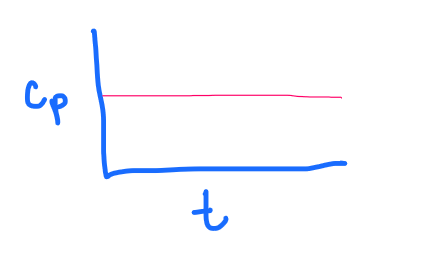
PRACTICE:
What graph does the following depict?
a. 1 compartment, IV bolus
b. 1 compartment, IV continuous infusion
c. 1 compartment, IV continuous infusion WITH a loading dose
d. 2 compartment, IV bolus
c
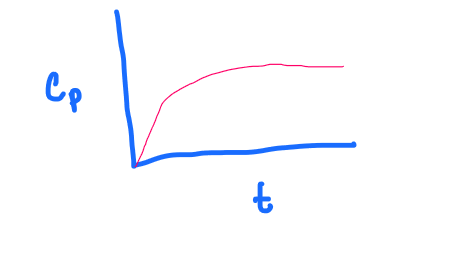
PRACTICE:
What graph does the following depict?
a. 1 compartment, IV bolus
b. 1 compartment, IV continuous infusion
c. 1 compartment, IV continuous infusion WITH a loading dose
d. 2 compartment, IV bolus
b
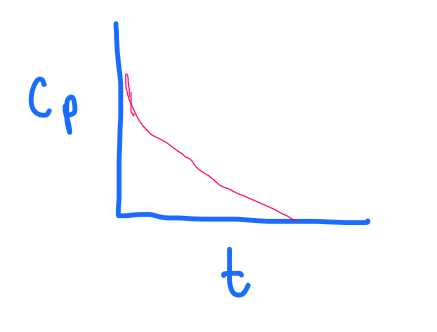
PRACTICE:
What graph does the following depict?
a. 1 compartment, IV bolus
b. 1 compartment, IV continuous infusion
c. 1 compartment, IV continuous infusion WITH a loading dose
d. 2 compartment, IV bolus
d
What is the principle of superposition?
each subsequent dose additively influences the total plasma concentration
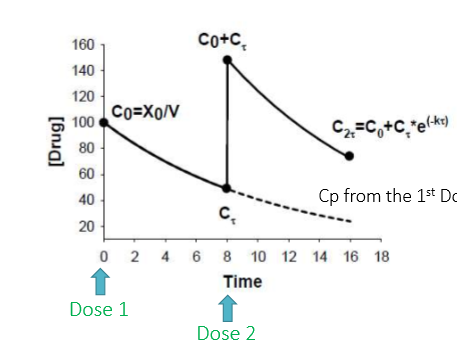
A patient is given vancomycin IV to achieve steady-state peaks and troughs of 10 and 2 mg/L. The patient is estimated to have the following PK parameters: Vd=14.7L and t1/2 = 3h.
If multiple doses are to be given, determine a suitable dose and dosing interval for this patient.
dose= 117.6 mg
tau= 6.97 hr
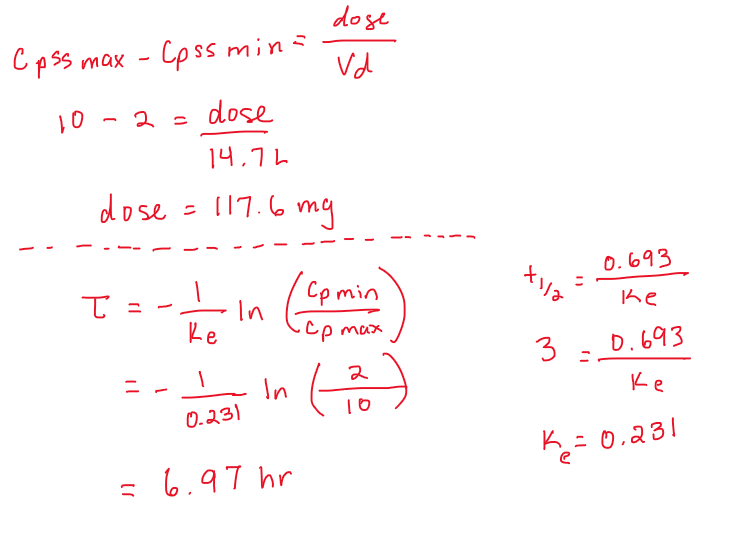
The ________________________ is the time required for the max conc to decline to the minimum conc.
dosing interval

True or False: tau stands for time.
FALSEEEEE (stands for dosing interval)
A patient is receiving 900mg of sulfamethoxazole IV every 14 hours. At steady-state the max and min plasma conc were 75.6 and 32 mg/L. What is the Vd of the patient?
