1. Dental Anatomy and Nomenclature
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
brachydont
What term is describes animals as having short crowns, well-developed roots, and only narrow canals in the roots? This term also means that these animals have short teeth. Cats, dogs, primates, and humans have this type of teeth.
hypsodont
What term describes animals as having high crowns that erupt throughout life providing extra material for grinding food particulates down. These animals have very long teeth that continuously grow for life. Cows, horses, and other herbivores have this type of teeth.
root
Anything below the gingiva is part of the _____.
crown
Anything above the gingiva is part of the _____.
cusp
What part of the tooth is a pronounced point on the occlusal or most coronal portion of a tooth?
enamel
Which structure is the hardest substance in the body? It covers the tooth crown and is made from hydroxyapatite crystals.
apex
What structure describes where the root of the tooth comes out?
dentin
Which structure is made from specialized connective tissue and supports and protects the tooth and pulp?
neck
The cementoenamel junction is also known as what?
96%
Enamel is what % mineral by weight? (hydroxyapatite crystals)
ameloblasts
Enamel is formed by what cells?
when the tooth erupts
Amelogenesis (formation of enamel) stops when? The enamel that the animal has is all they enamel they will get.
cats and dogs mainly use their teeth for the shearing forces rather than chewing
Why do cats and dogs have a thinner enamel layer than humans?
enamel
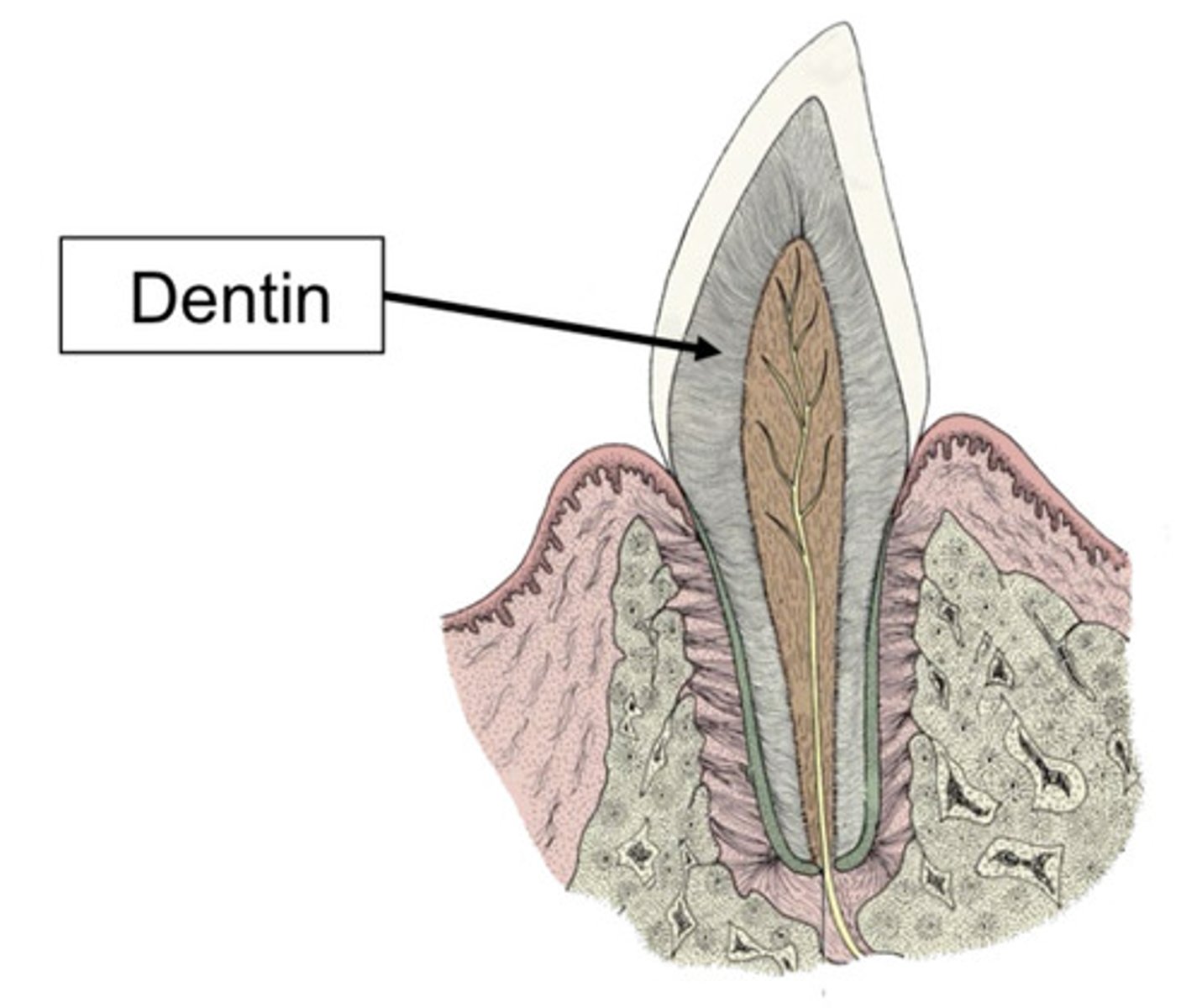
Which part of the tooth is an effective barrier to heat/cold/sweet sensitivities and bacterial entrance into the tooth?
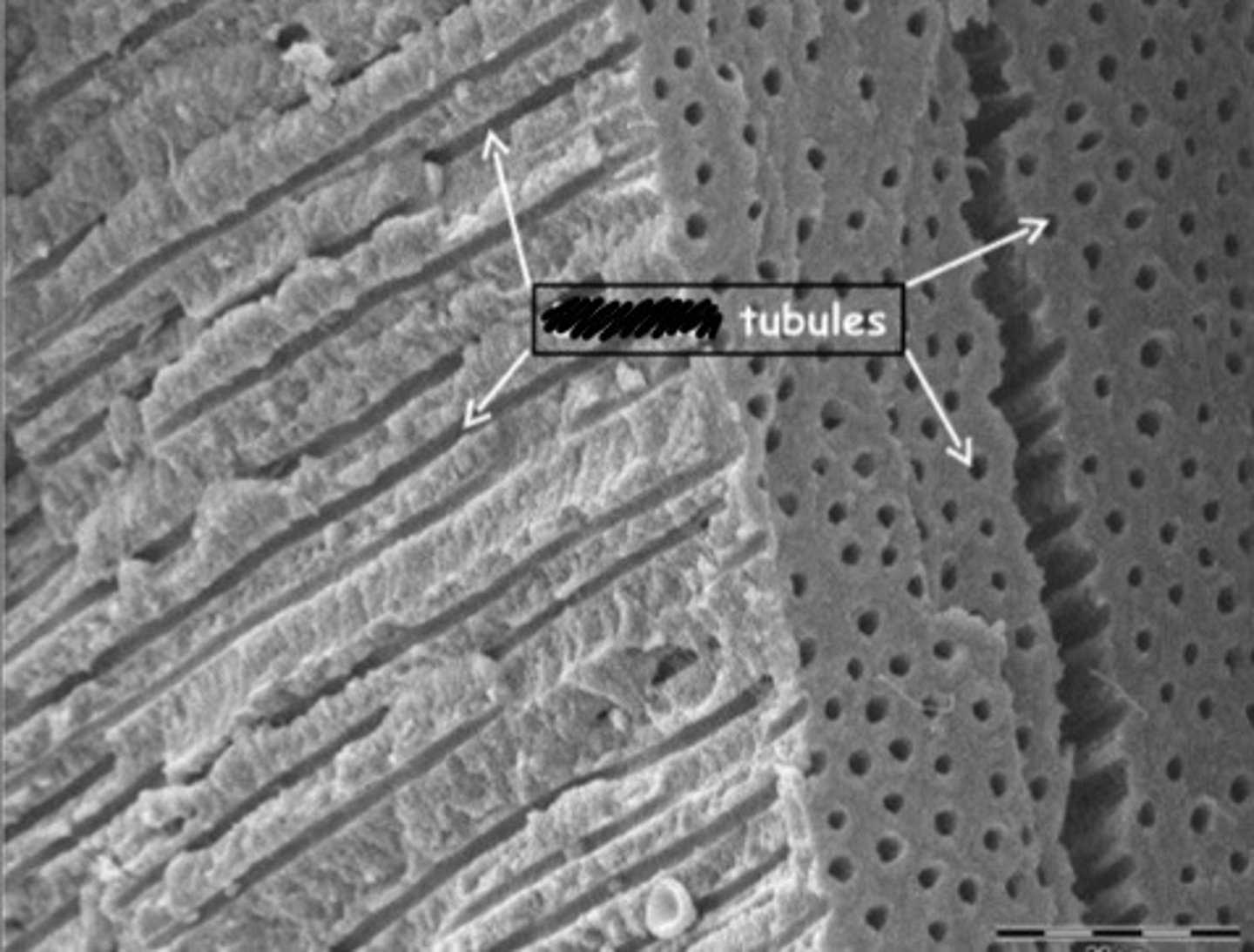
dentin
What structure makes up the bulk of the tooth? It is made up of a bunch of tiny tubules. If these tubules are exposed, the tooth is sensitive and can become contaminated. It is made up mostly of mineral and is produced throughout the life of the tooth.
odontoblasts
Dentin is produced by what cells throughout the life of the tooth?
thicker
Dentin gets [thicker/thinner] with age.
![<p>Dentin gets [thicker/thinner] with age.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/709ad3b1-3ce4-438d-bdc7-e41ca8091131.jpg)
secondary
Odontoblasts lining the pulp chamber and root canal produce [primary/secondary/tertiary] dentin, causing the pulp to become narrower as the animal ages.
tertiary
[primary/secondary/tertiary] dentin is the reparative dentin. When enamel and dentin are gradually lost as the result of an insult (ex: mechanical wear), existing odontoblast-like cells produce this to protect the pulp.
![<p>[primary/secondary/tertiary] dentin is the reparative dentin. When enamel and dentin are gradually lost as the result of an insult (ex: mechanical wear), existing odontoblast-like cells produce this to protect the pulp.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5d36e1b3-0727-488e-8027-6737ae1ae8ab.jpg)
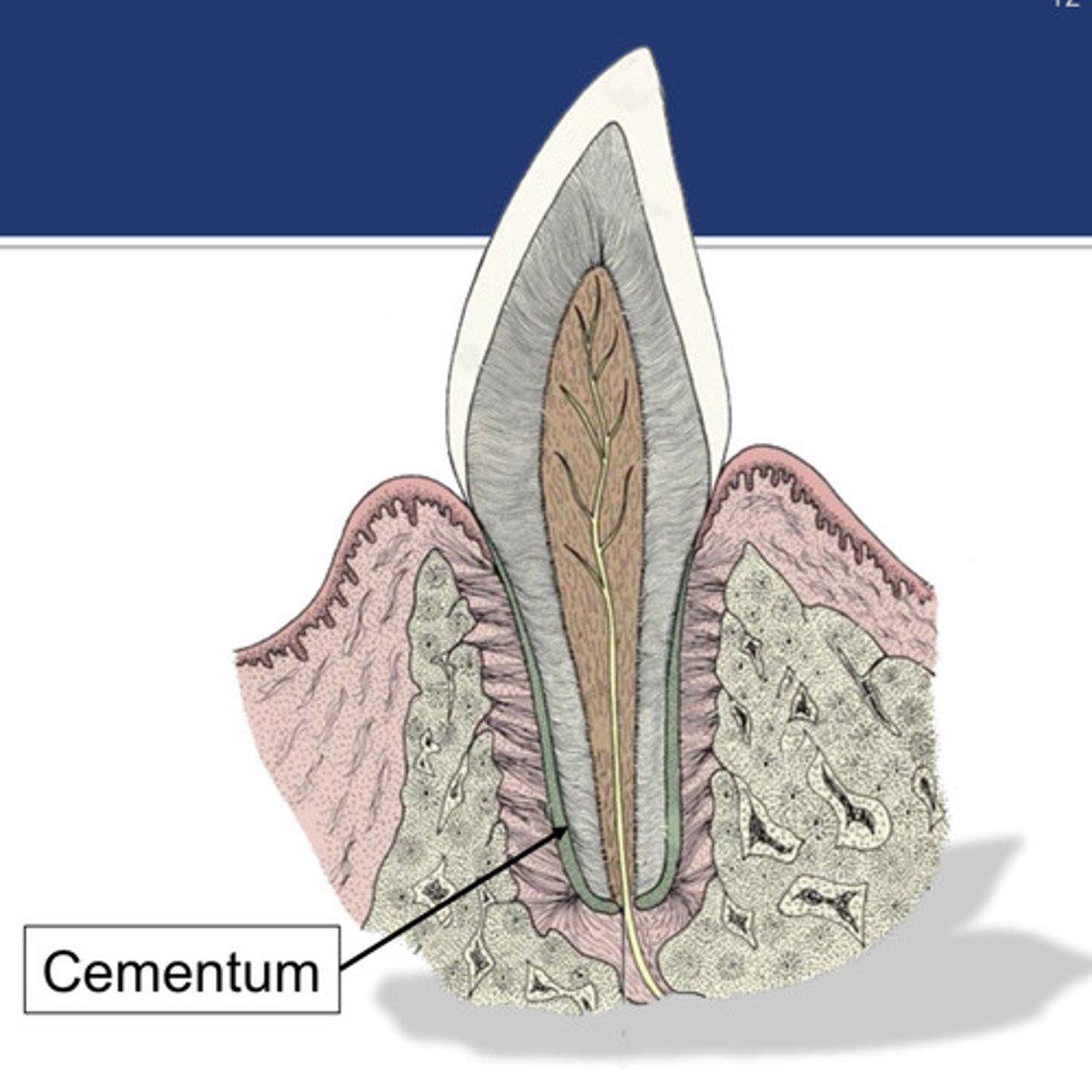
cementum
Which structure covers the outer surface of the root (below gingiva)? The periodontal ligament and gingiva attach to this. The width increases with age. Loss of this structure prevents reattachment of the periodontal ligament.
cementoblasts
Which cells produce cementum (produced at the apex of the root)?
hypercementosis
Chronic irritation can cause _____ and "lock" the tooth into the alveolar socket.
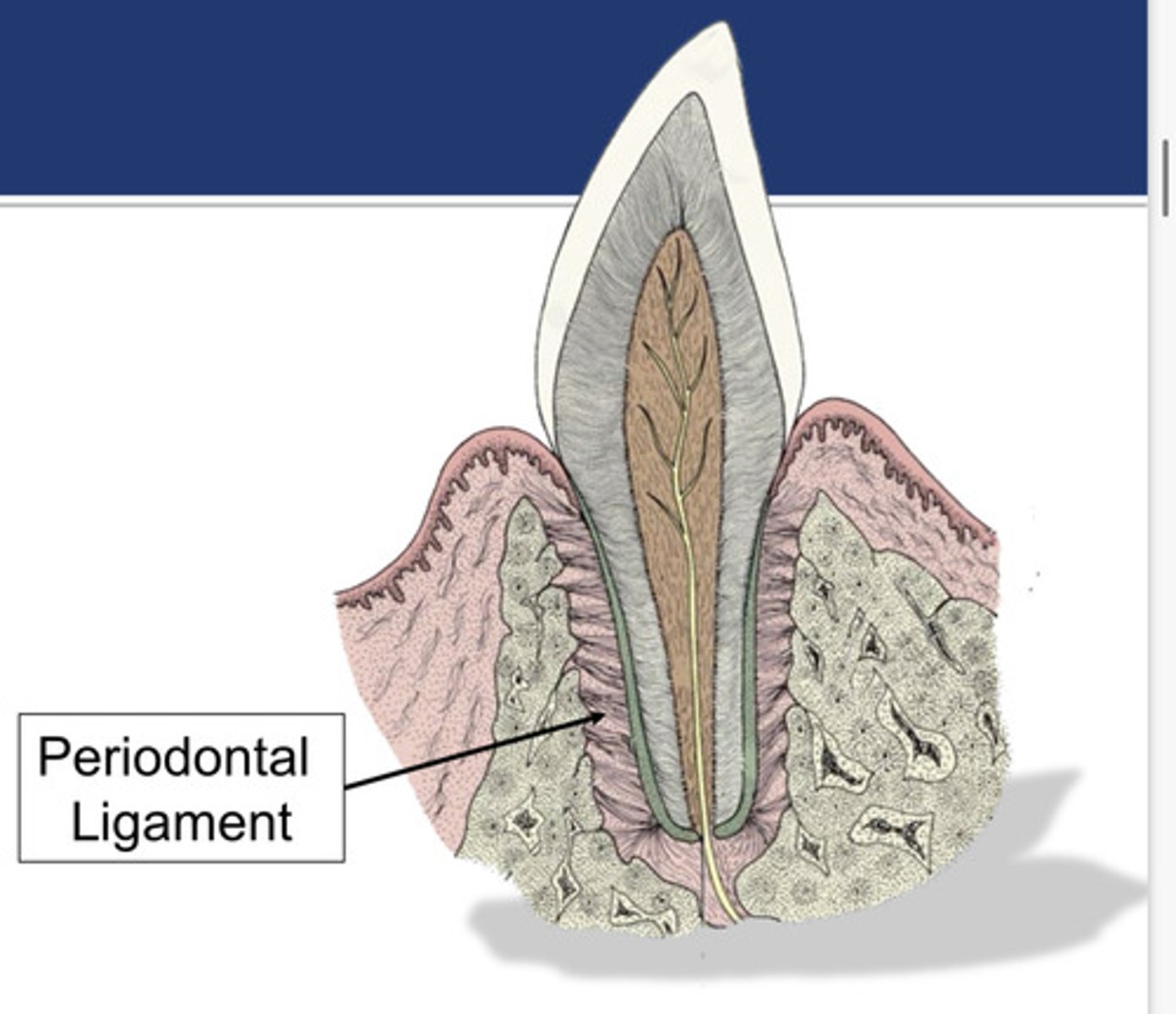
periodontal ligament
Which structure is the connective tissue which fills the space between tooth and alveolar bone? It is composed of horizontal fibers (collagen bundles in various shapes and orientations).
Functions:
- shock absorber
- transmit occlusal forces
- attaches tooth to bone
- supplies nutrients
- provides tactile and proprioceptive info (sensory)
Sharpey's fibers
The periodontal ligament is composed of horizontal fibers. What are they called?
pulp
Which structure is the soft tissue connective tissue containing nerves, blood, and odontoblasts which produce dentin? More of this is present in young teeth.
pulp canal
We need to know the difference between the pulp canal and the root canal. Which is above the gumline?
root canal
We need to know the difference between the pulp canal and the root canal. Which is below the gumline?
1. alveolar bone
2. cementum
3. gingiva
4. periodontal ligament
The periodontium consists of what 4 structures? These structures are affected by, and ultimately lost from periodontal disease/gingivitis.
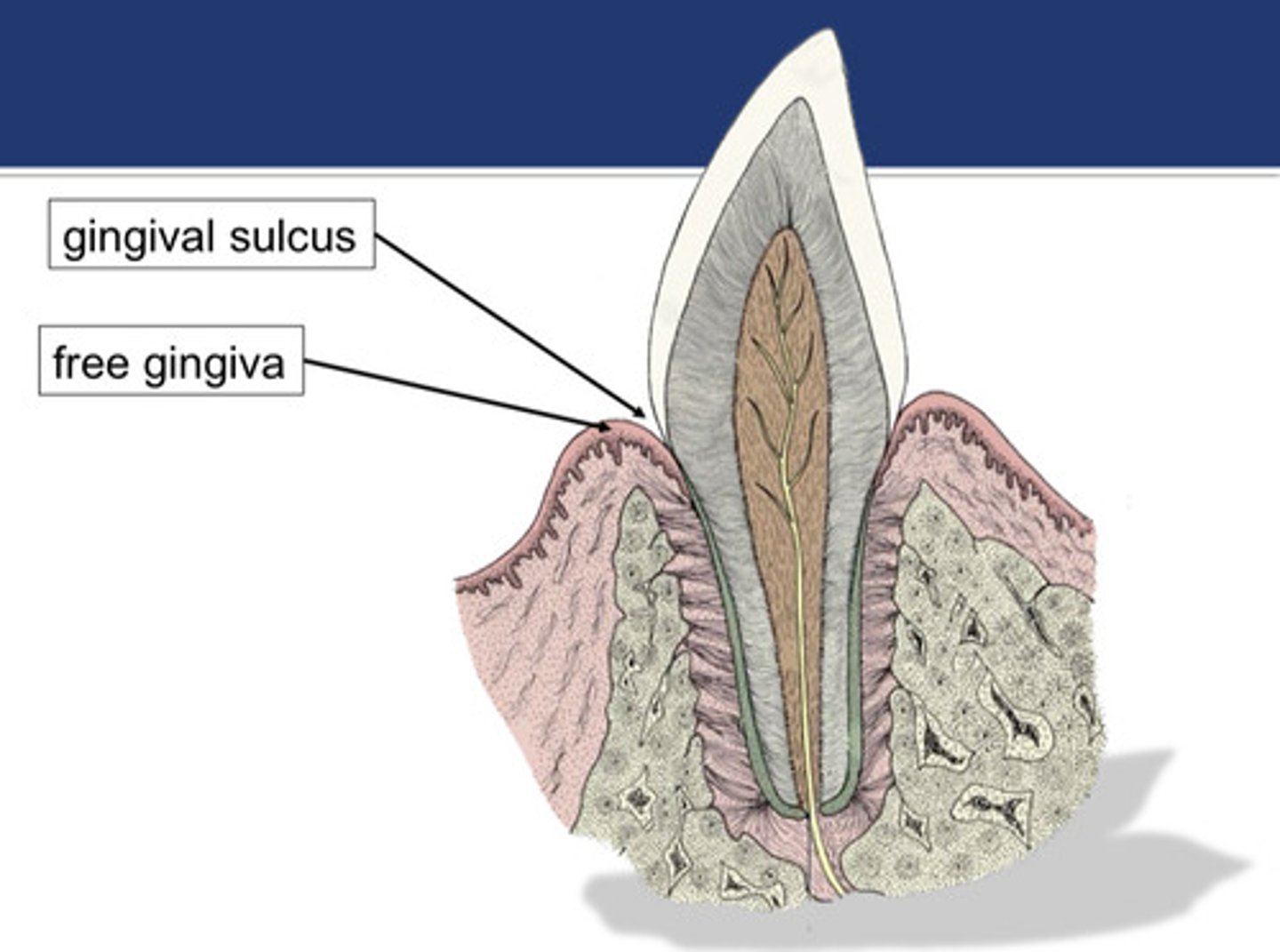
gingival sulcus
What structure is the normal, physiological space between the free gingiva and the tooth surface? This is the area where we floss and probe.
dogs
Which animal normally has a deeper gingival sulcus depth: cats or dogs?
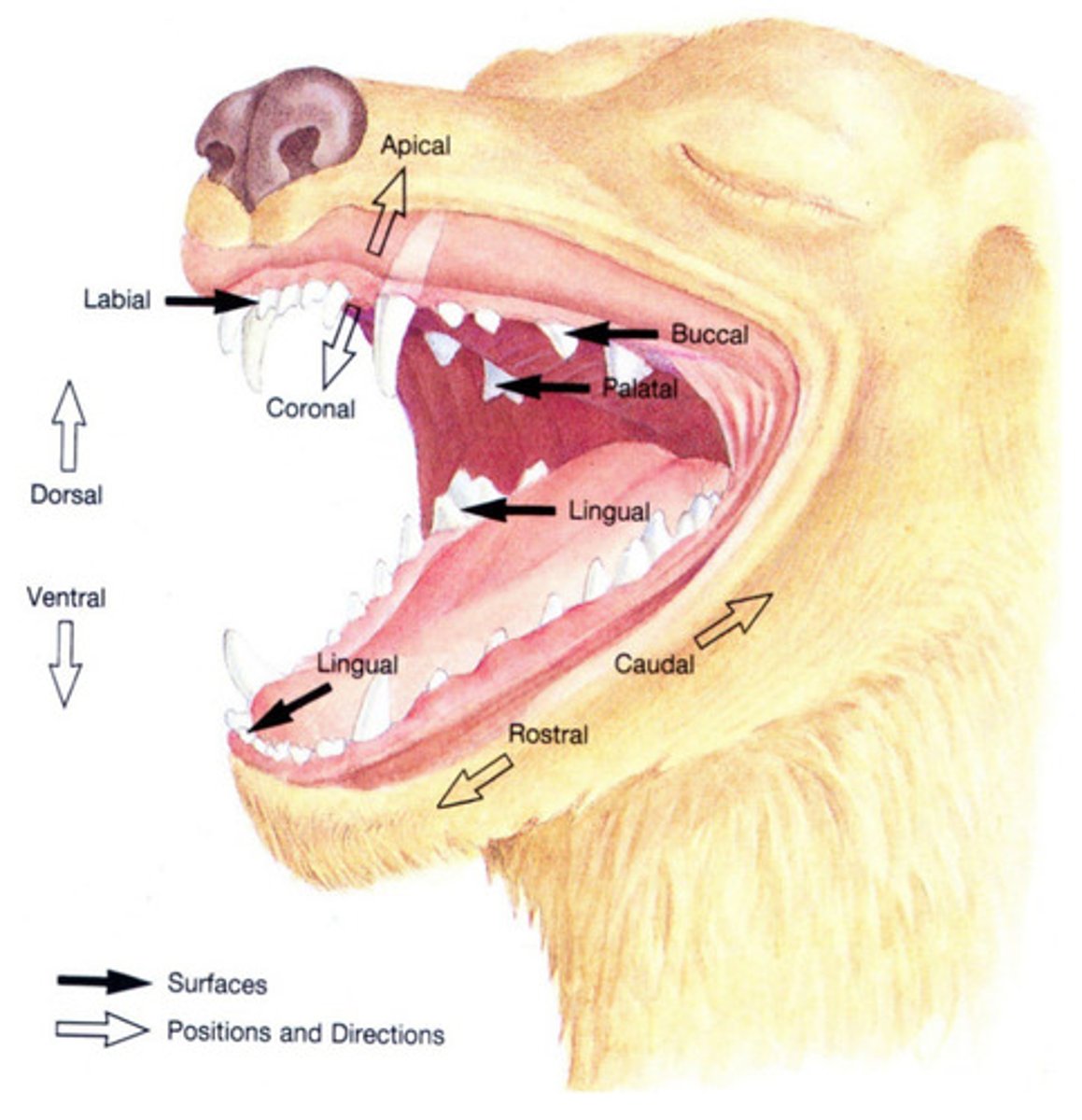
apical
Which term describes an area toward the apex of the root?
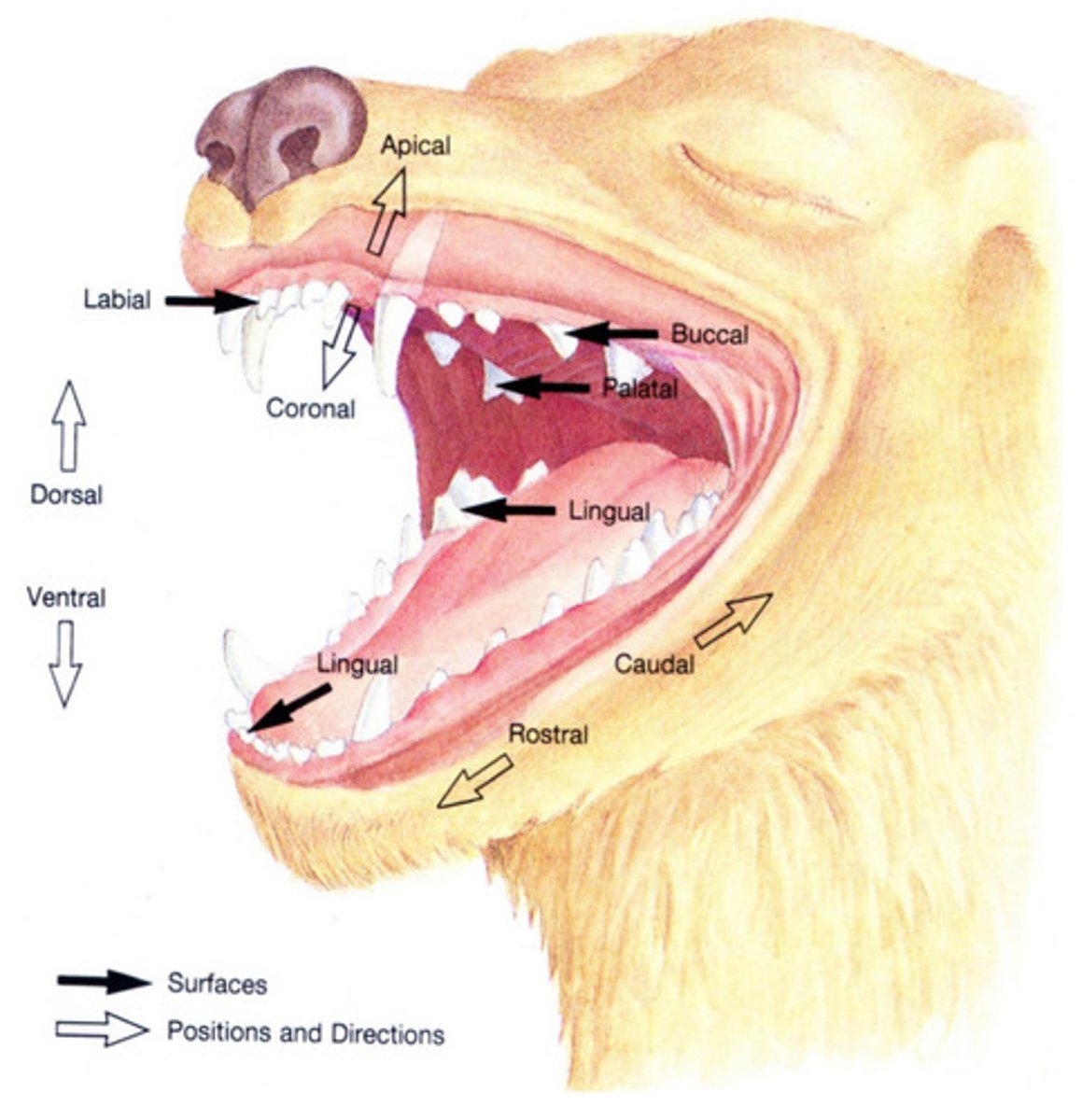
coronal
Which term describes an area toward the tip of the crown?
subgingival
Which term describes an area or structure apical to the gingival margin? Up underneath the gingival margin.
supragingival
Which term describes an area or structure coronal to the gingival margin?
proximal
Which term describes mesial or distal surfaces of a tooth in close contact with an adjacent tooth?
interproximal
Which term describes the space between the adjacent tooth? This is where food will get stuck between teeth.
occlusal
What term describes the surface of a tooth that faces the tooth of the opposing arcade?
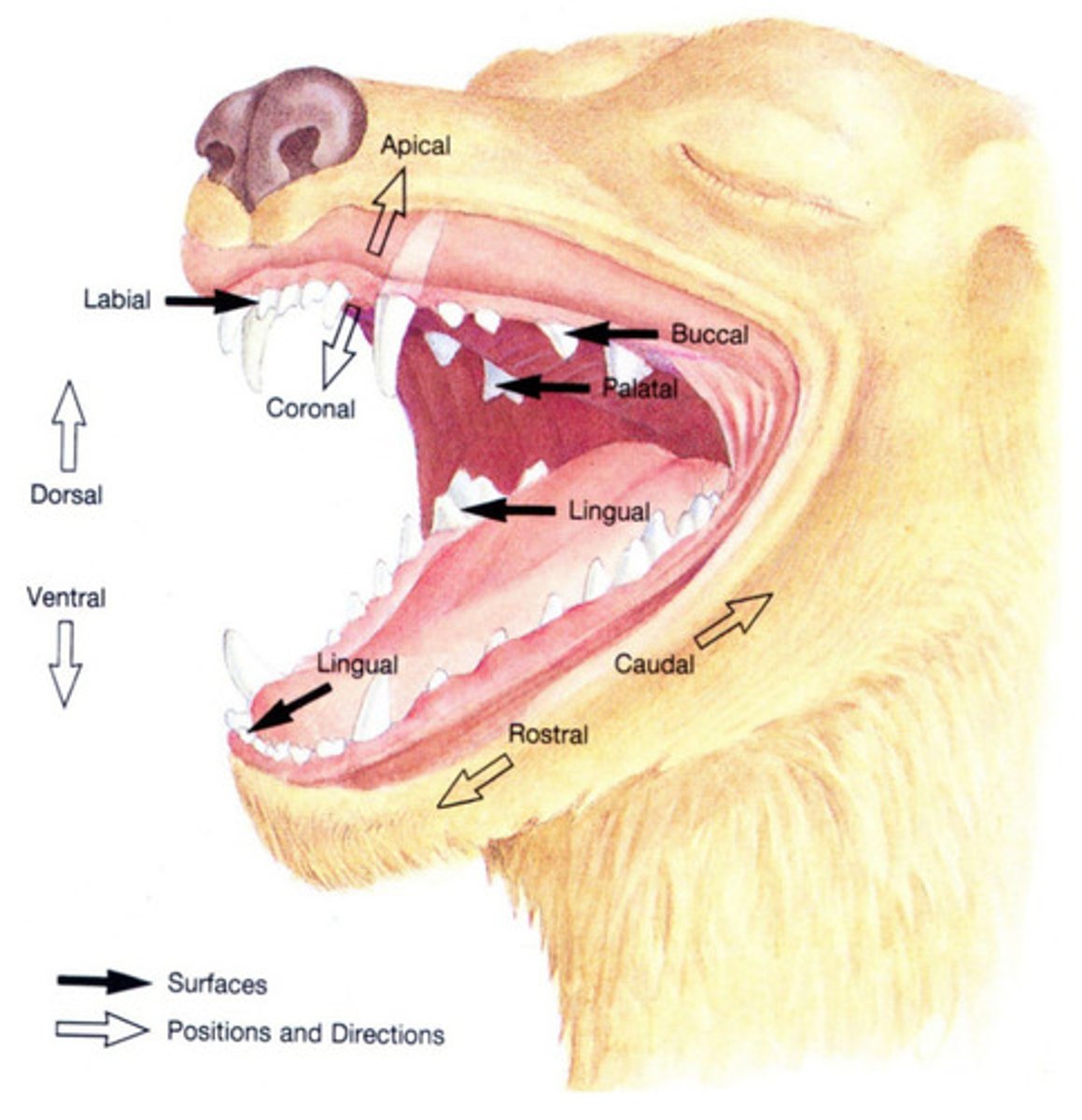
vestibular
Which term refers to the surface of the tooth facing the vestibule or lips? Buccal and labial are acceptable alternatives.
lingual
Which term describes the surface of a mandibular tooth facing the tongue?
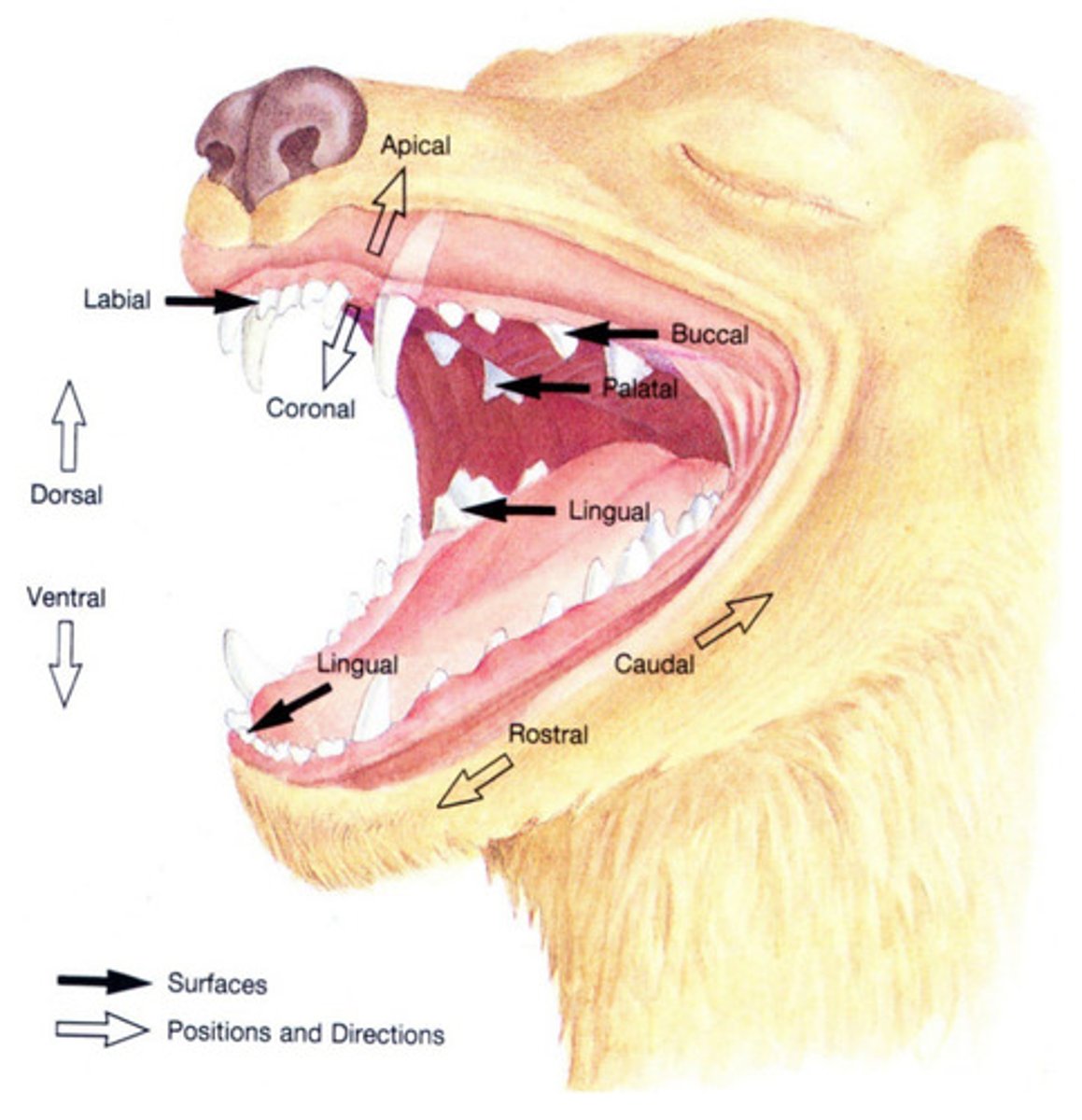
palatal
Which term describes the surface of a maxillary tooth facing the palate?
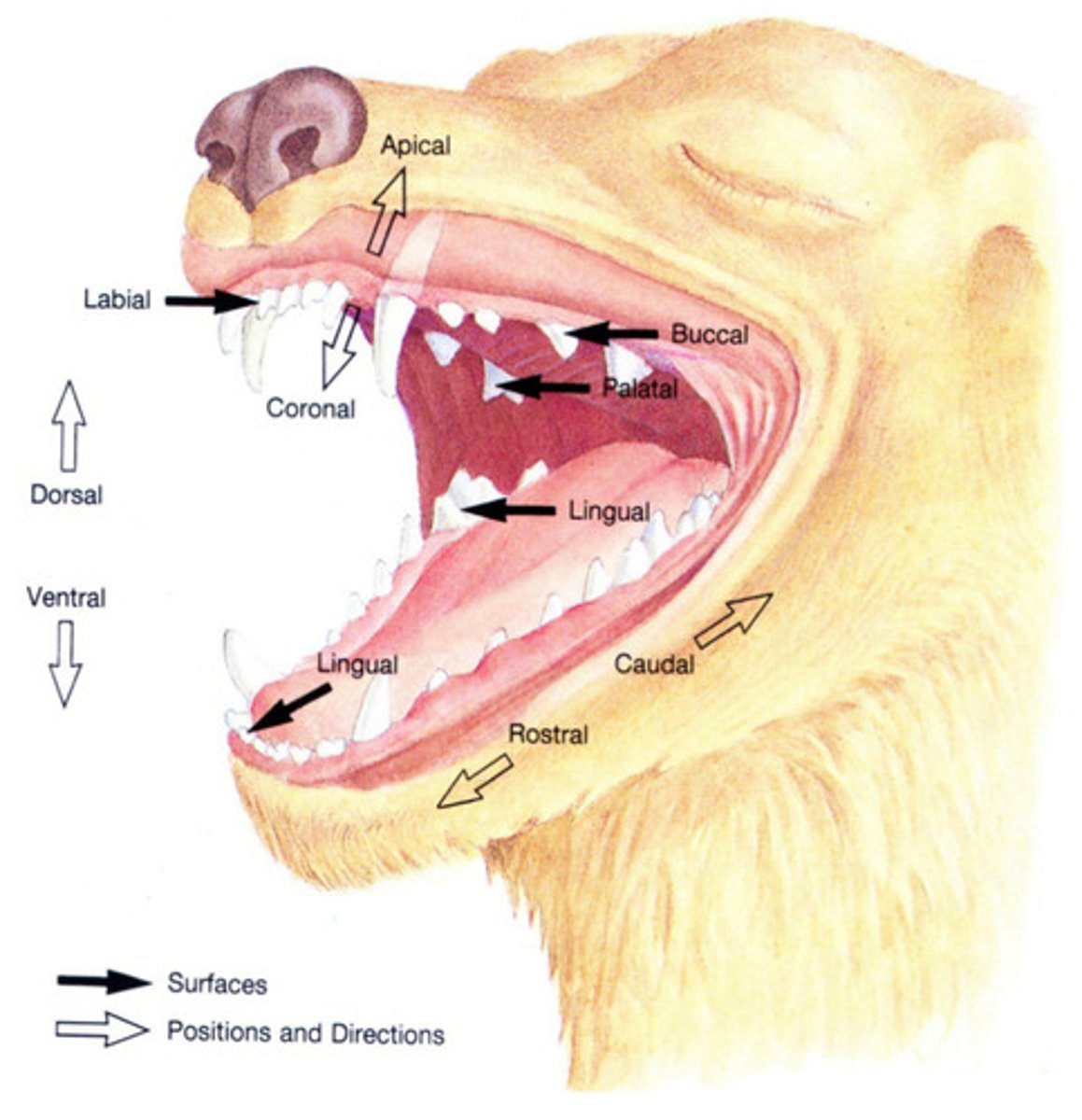
mesial
Which term describes the interproximal surface of a tooth that faces rostrally or towards the midline of the dental arch?
distal
Which term describes the interproximal surface of a tooth that faces caudally or away from the midline of the dental arch?
rostral
Which term refers to a structure closer to, or a direction toward the tip of the nares?
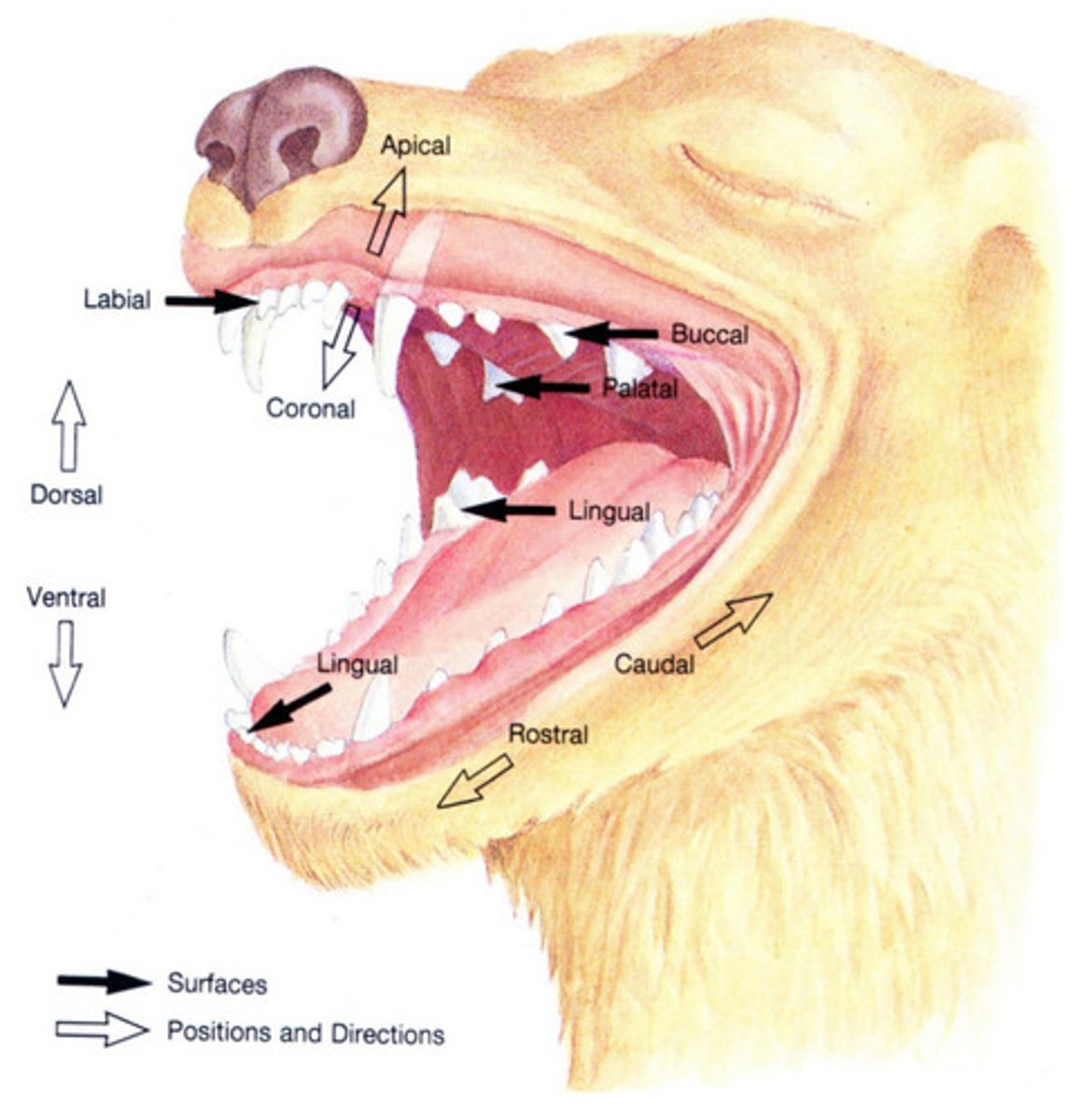
caudal
Which term refers to a structure closer to, or a direction toward the tail?
molars
Even when all of the deciduous teeth have erupted, kittens and puppies still do not have which teeth?
PM1/05
Which premolar is missing on both the maxilla and mandible of puppies?
True
T/F: In canines and felines, all incisors only have 1 root.
mandibular symphysis
Which structure is a fibrocartilaginous structure that may appear on radiographs as if it is not fused?
True
T/F: There are no 3 rooted teeth on the mandible of the dog.
4-6 weeks
When do the canine deciduous incisors erupt?
3-5 weeks
When do the canine deciduous canines erupt?
5-6 weeks
When do the canine deciduous premolars erupt?
3-5 months
When do the canine permanent incisors erupt?
5-7 months
When do the canine permanent canines erupt?
4-6 months
When do the canine permanent premolars erupt?
5-7 months
When do the canine permanent molars erupt?
105, 110, 205, 210, 305, 306, 310, 311, 405, 406, 410, 411
Which teeth are "missing" in cats as compared to dogs?
3-4 weeks
When do the feline deciduous incisors erupt?
3-4 weeks
When do the feline deciduous canines erupt?
5-6 weeks
When do the feline deciduous premolars erupt?
3-4 months
When do the feline permanent incisors erupt?
4-5 months
When do the feline permanent canines erupt?
4-6 months
When do the feline permanent premolars erupt?
5-7 months
When do the feline permanent molars erupt?
04
Canine teeth are always what number?
09
1st molars are always what number?
canines and carnassials
Which teeth are known as the strategic teeth?
maxillary PM4 & mandibular M1 (108 & 208, 309 & 409)
Which teeth are known as the carnassial teeth?
cementum
Which structure attaches to the bone by way of the periodontal ligament?
primary
Which type of dentin is being described?
- present before the tooth erupts
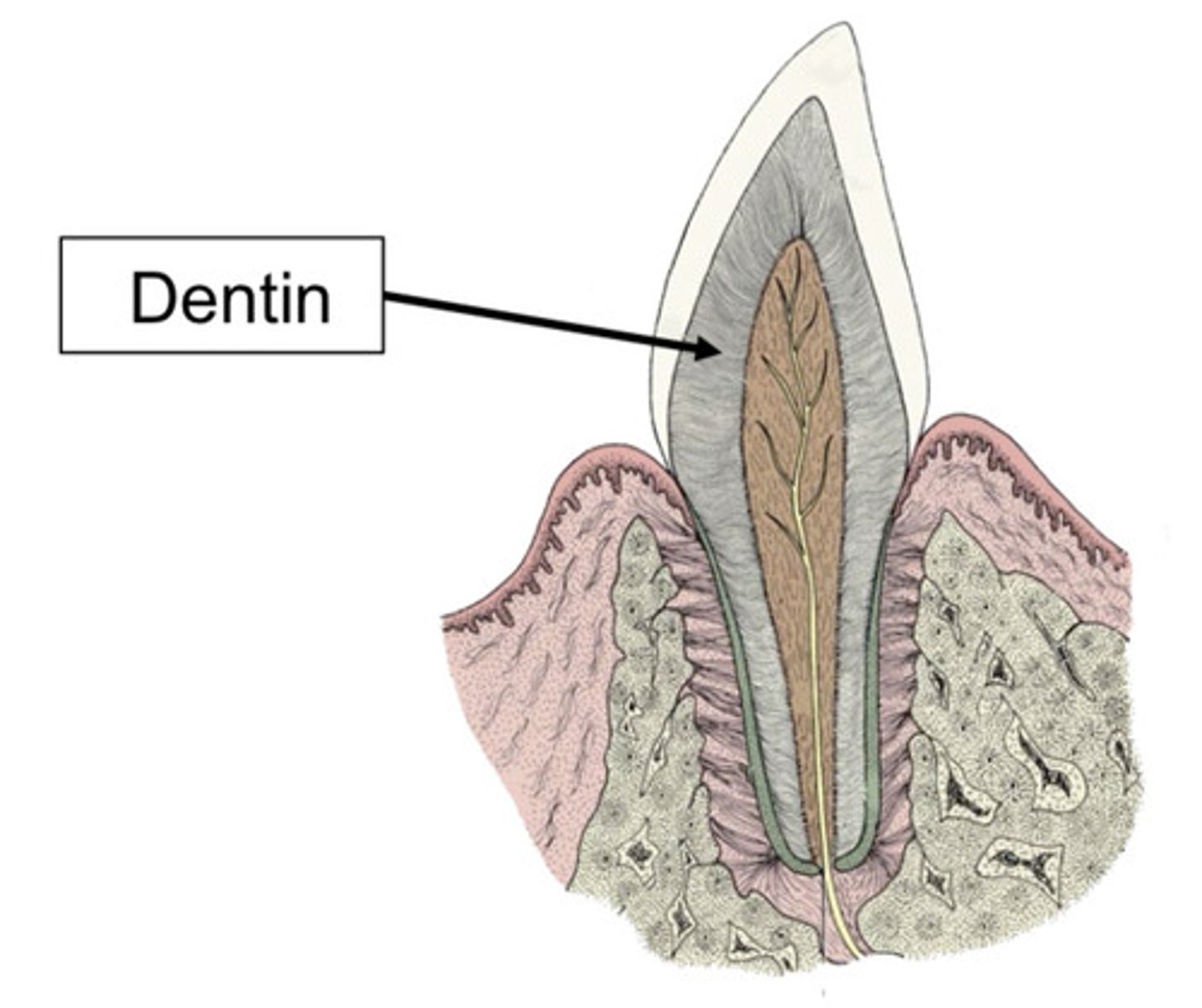
secondary
Which type of dentin is being described?
- present as/after the tooth erupts
tertiary
Which type of dentin is being described?
- reparative
- present after the tooth is broken/worn/damaged
- makes the tooth solid
- generally don't want to remove the tooth if this is present
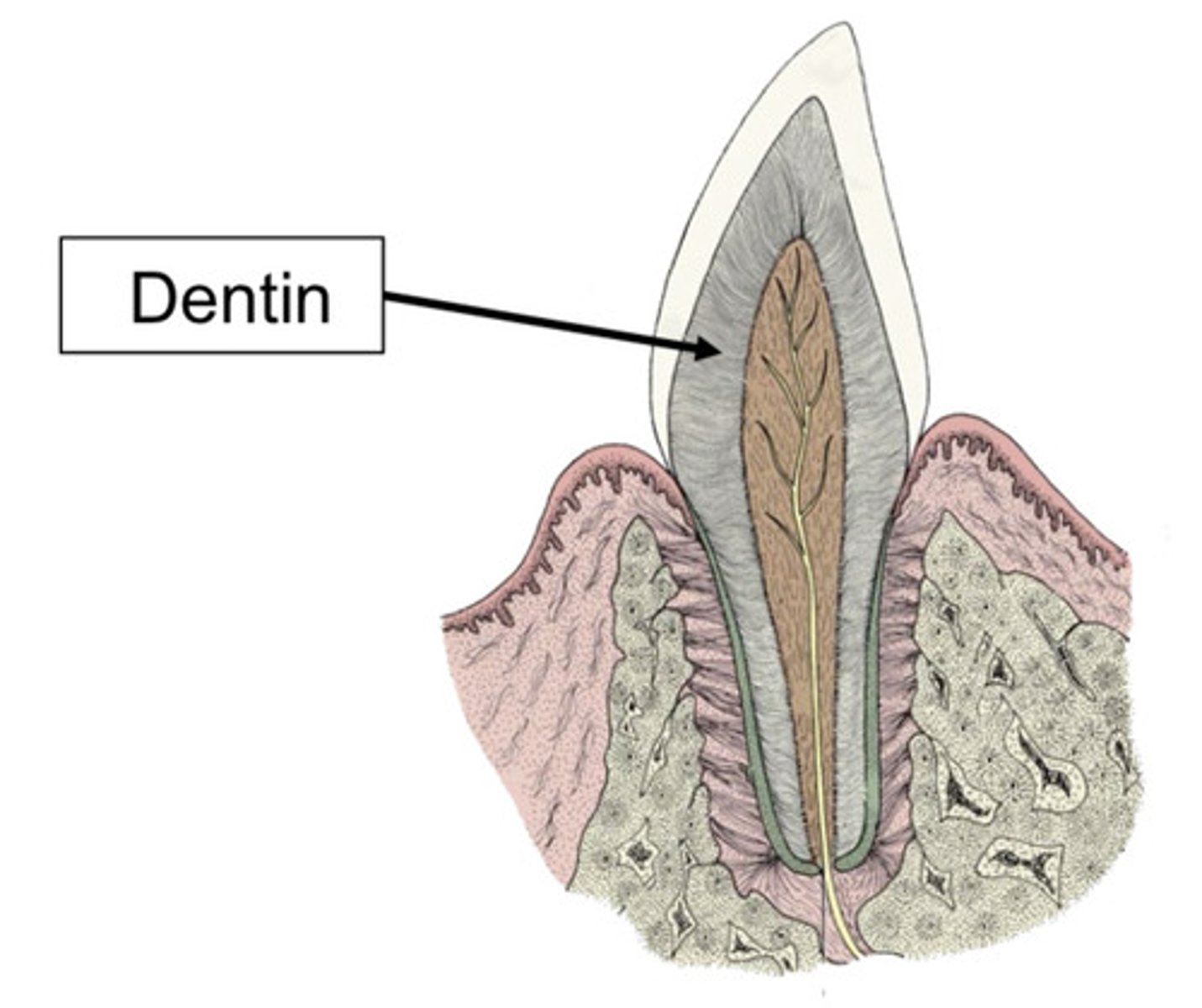
dentin
The tooth may become sensitive when what structure is exposed? The sensation comes through the nerves through the pulp cavity.
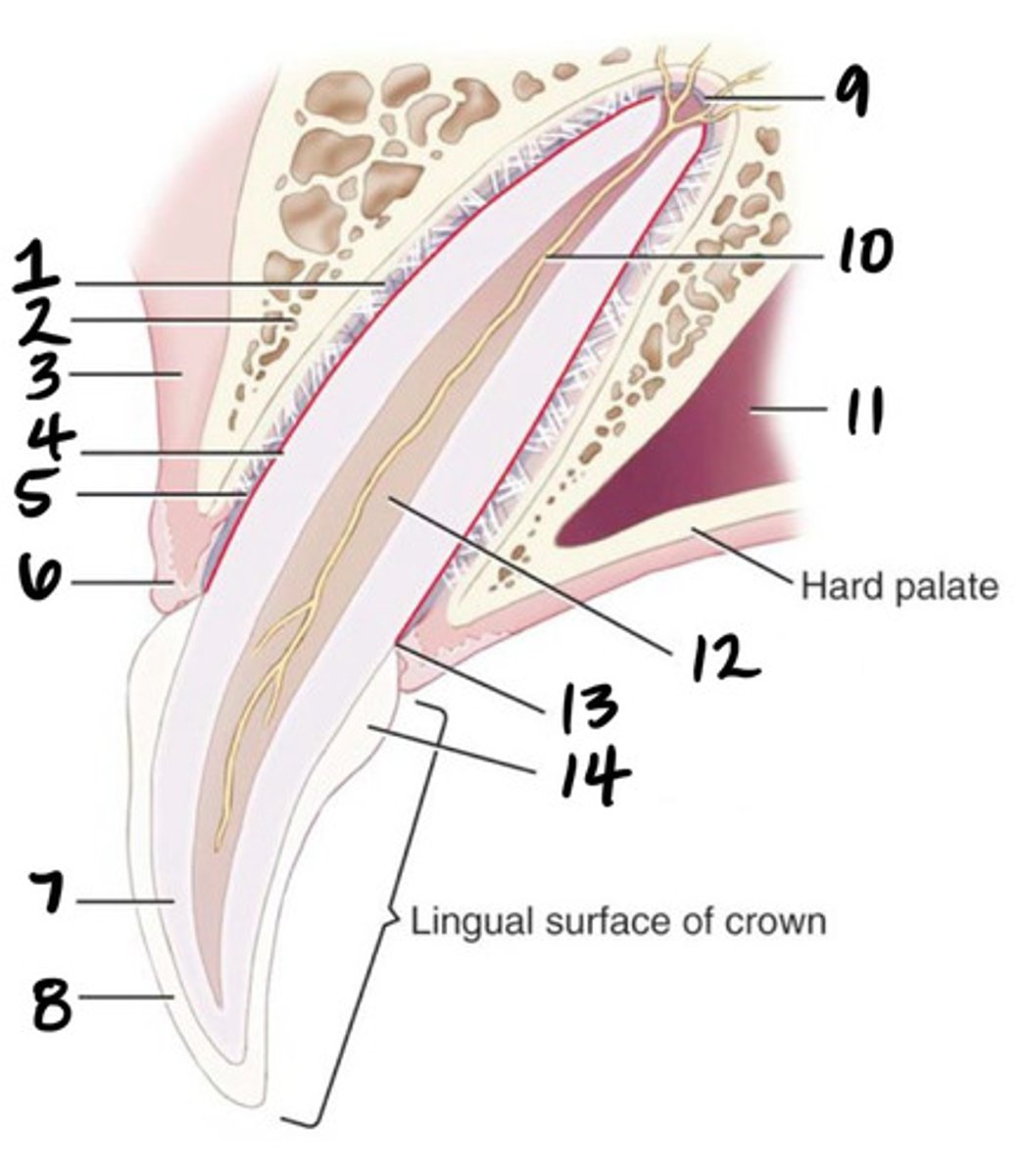
Crown
What structure is represented by #1?
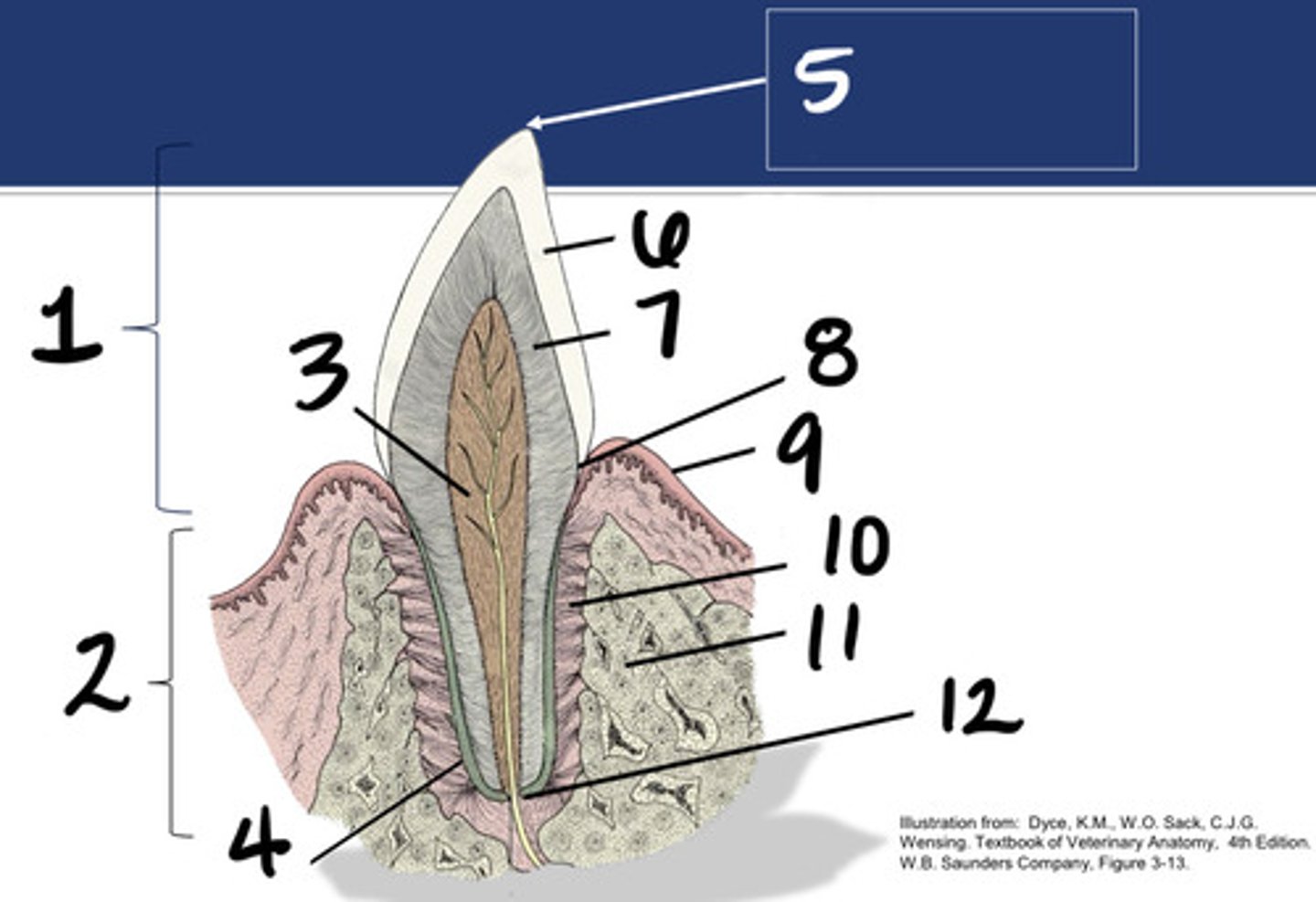
Root
What structure is represented by #2?
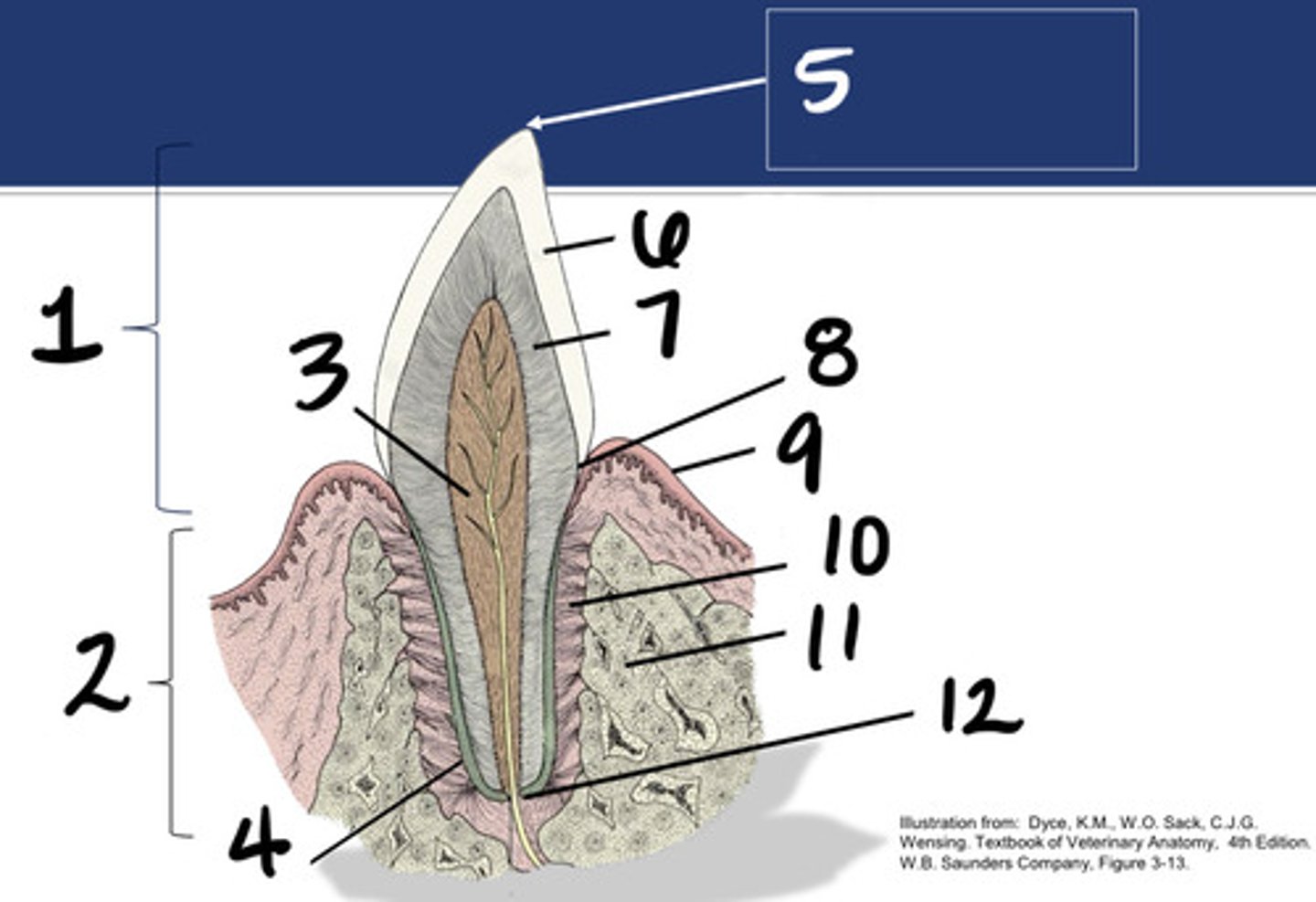
Pulp
What structure is represented by #3?
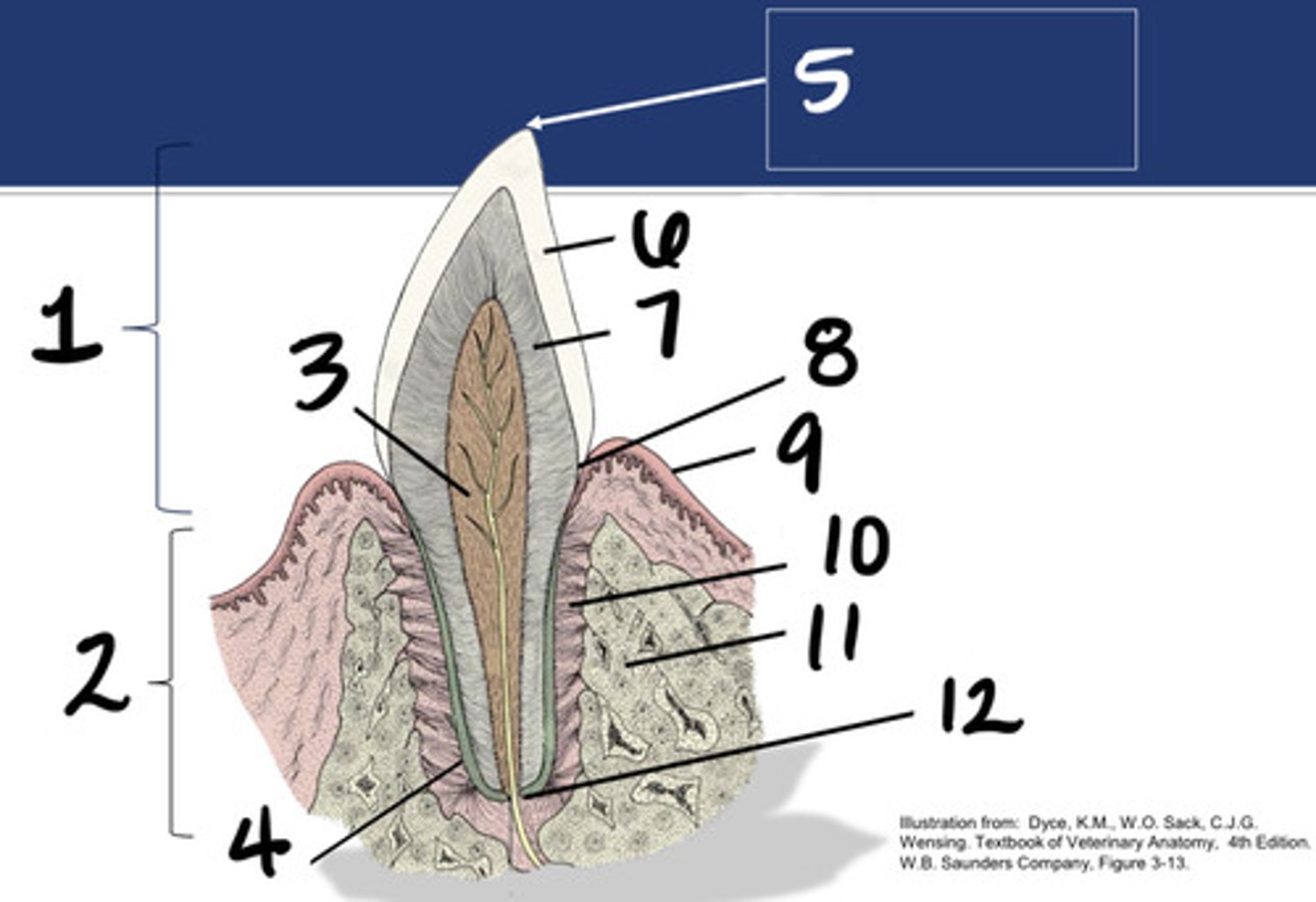
Cementum
What structure is represented by #4?
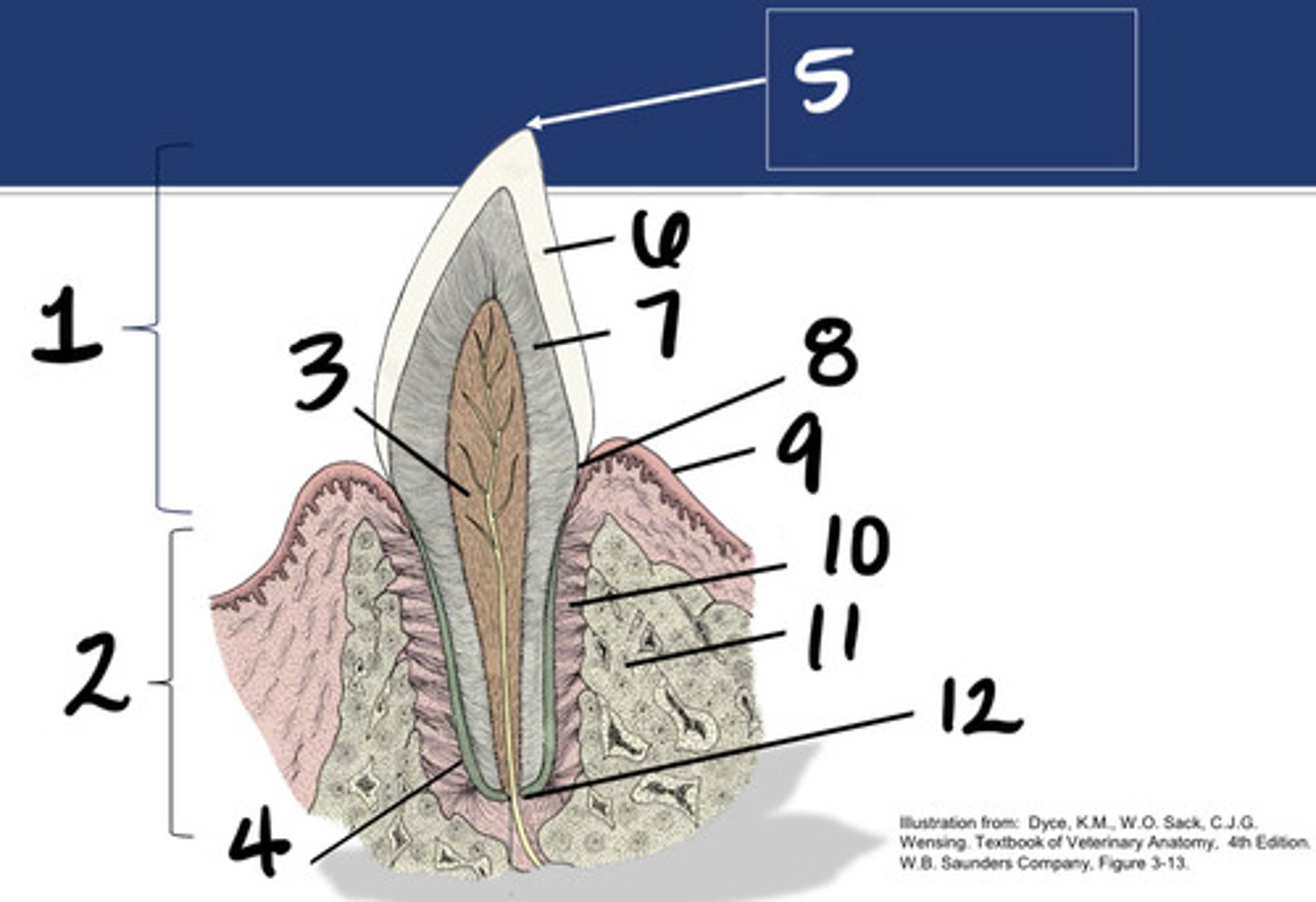
Cusp
What structure is represented by #5?
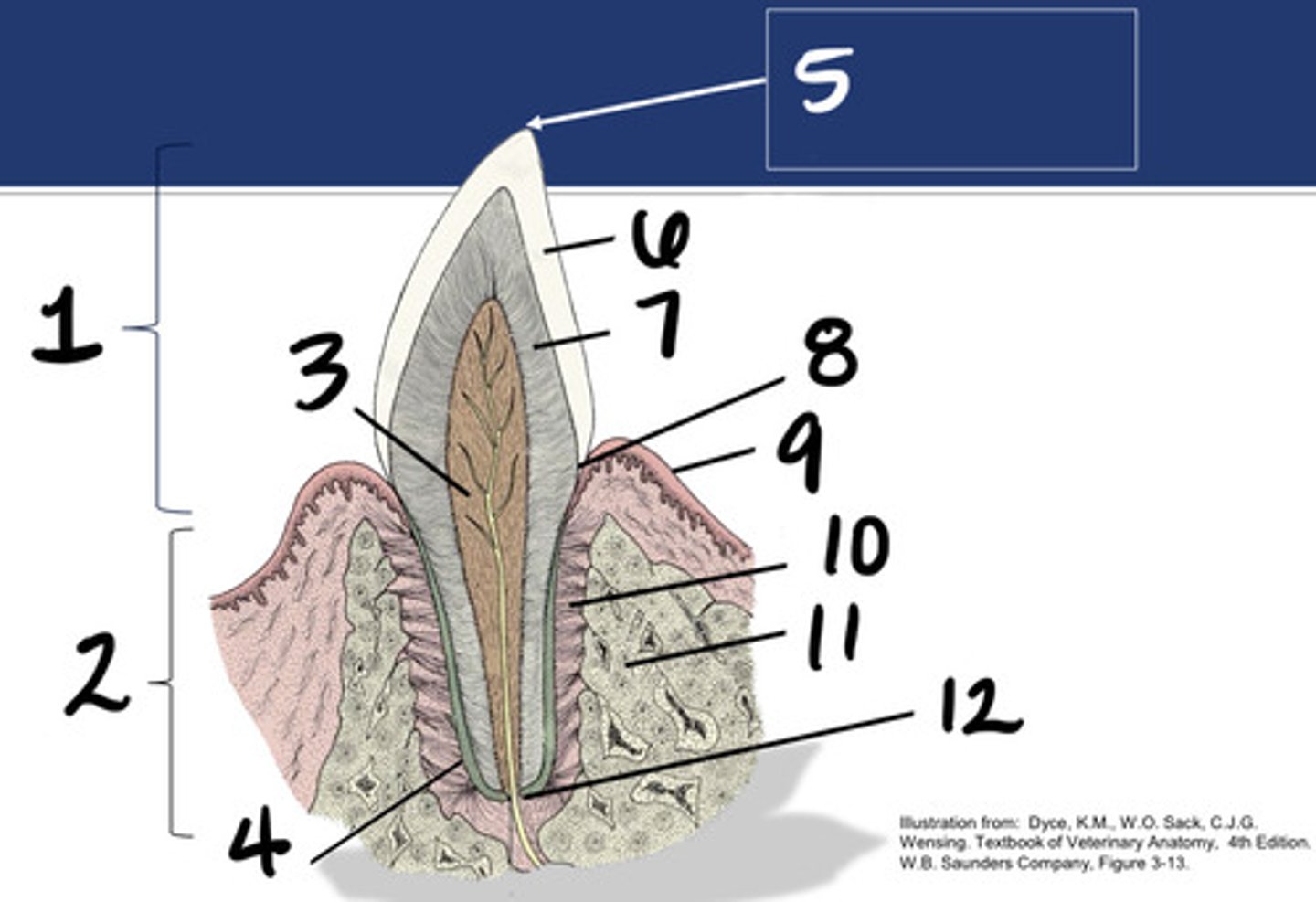
enamel
What structure is represented by #6?
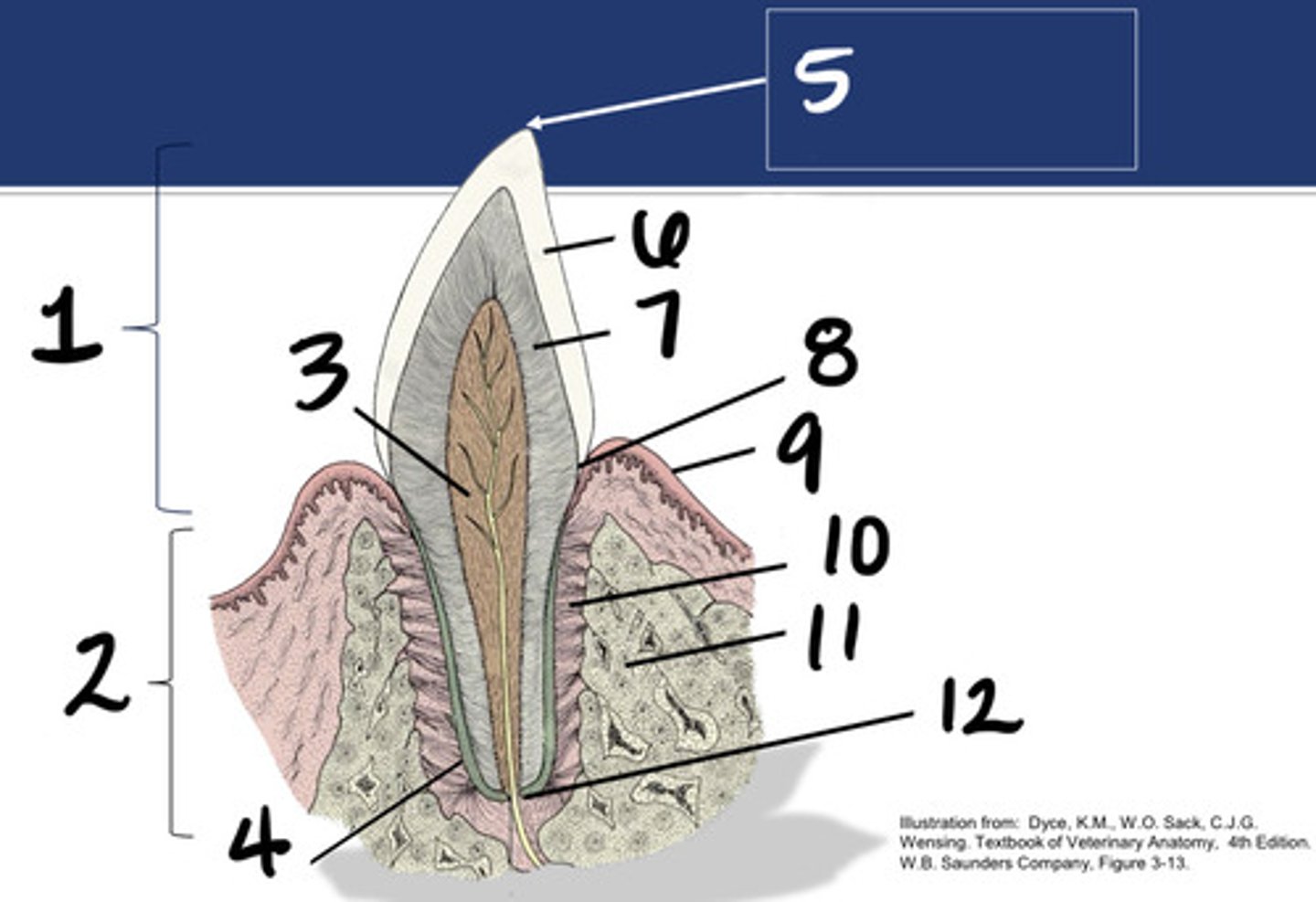
Dentin
What structure is represented by #7?
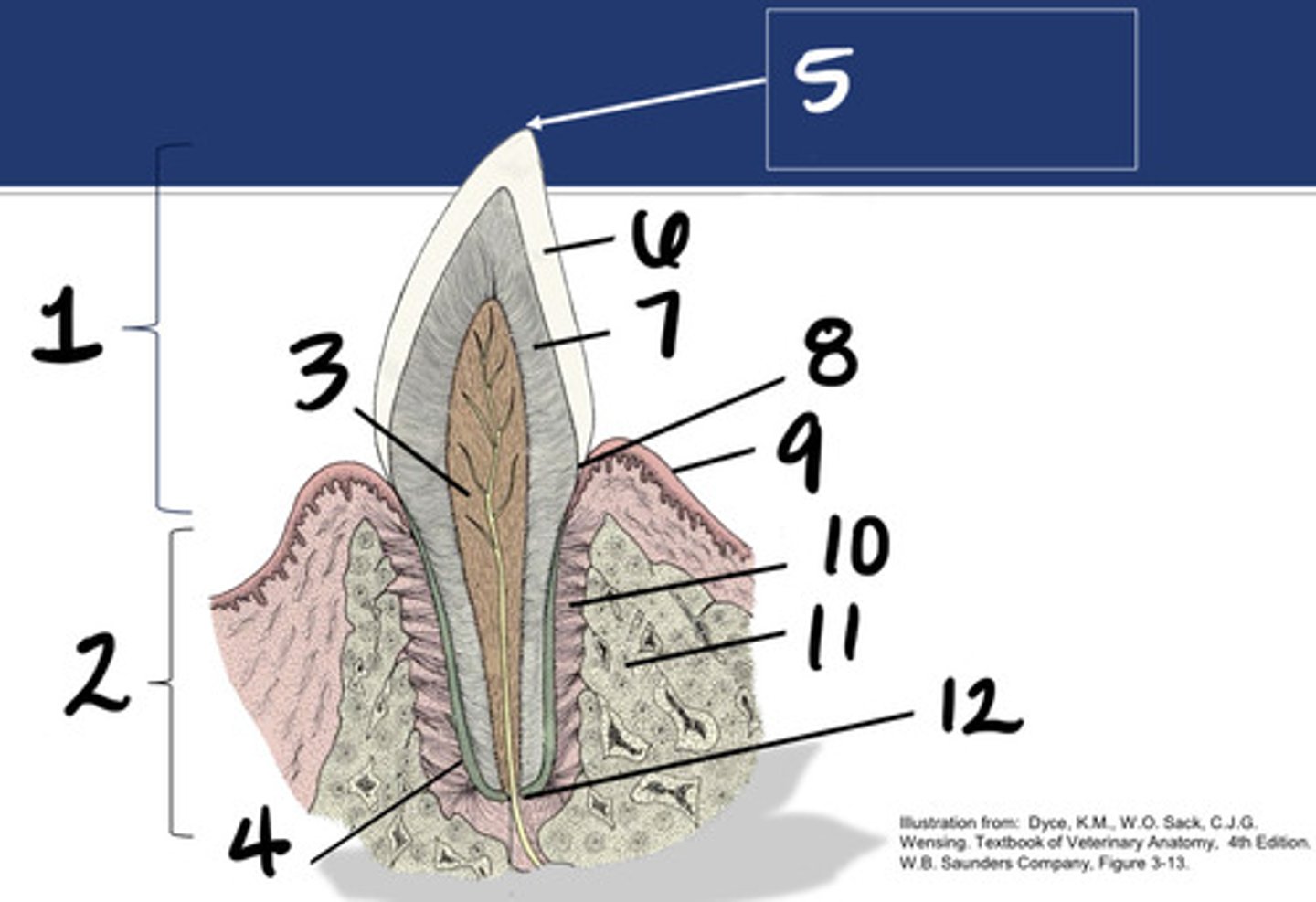
cementoenamel junction (neck)
What structure is represented by #8?
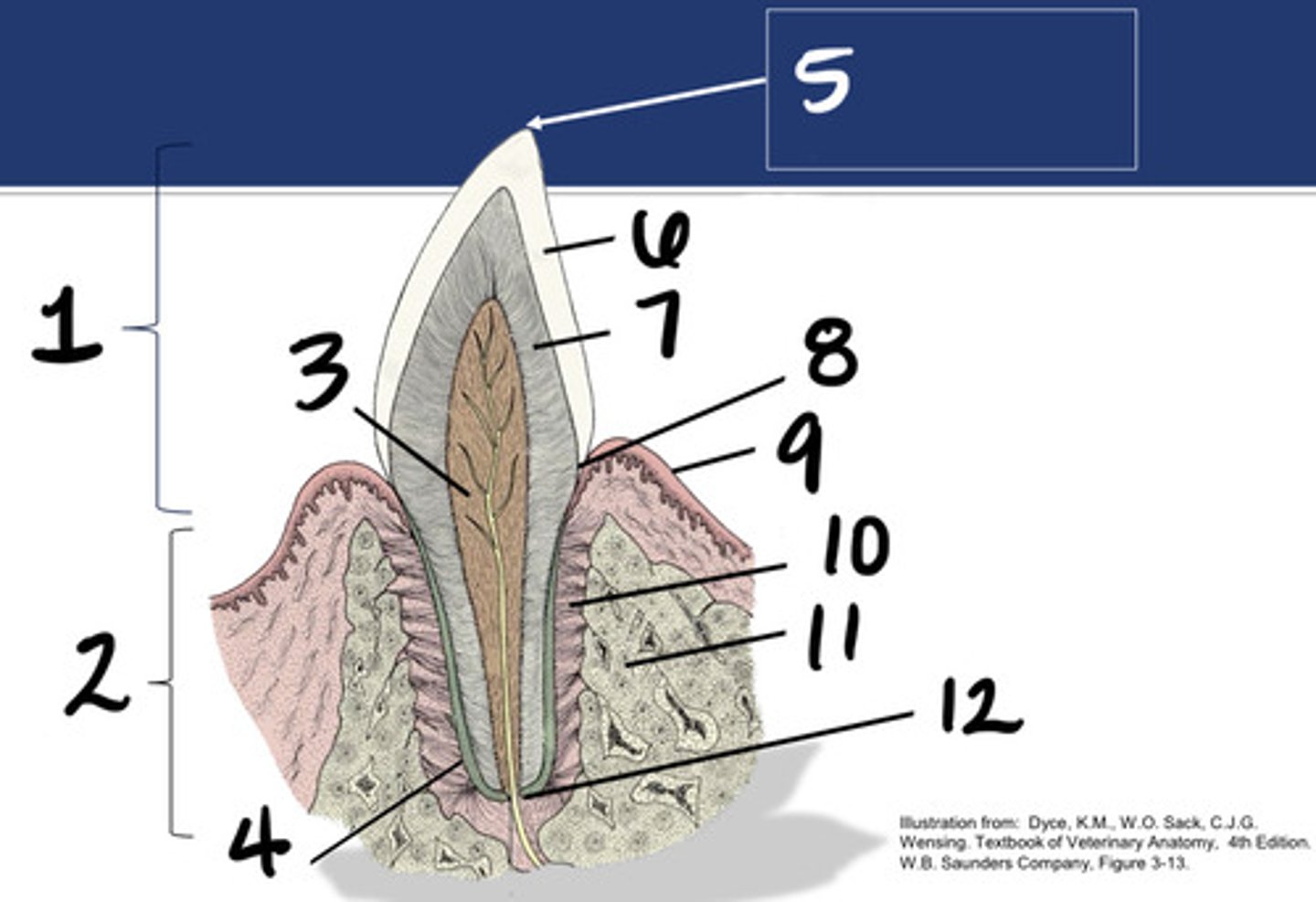
Gingiva
What structure is represented by #9?
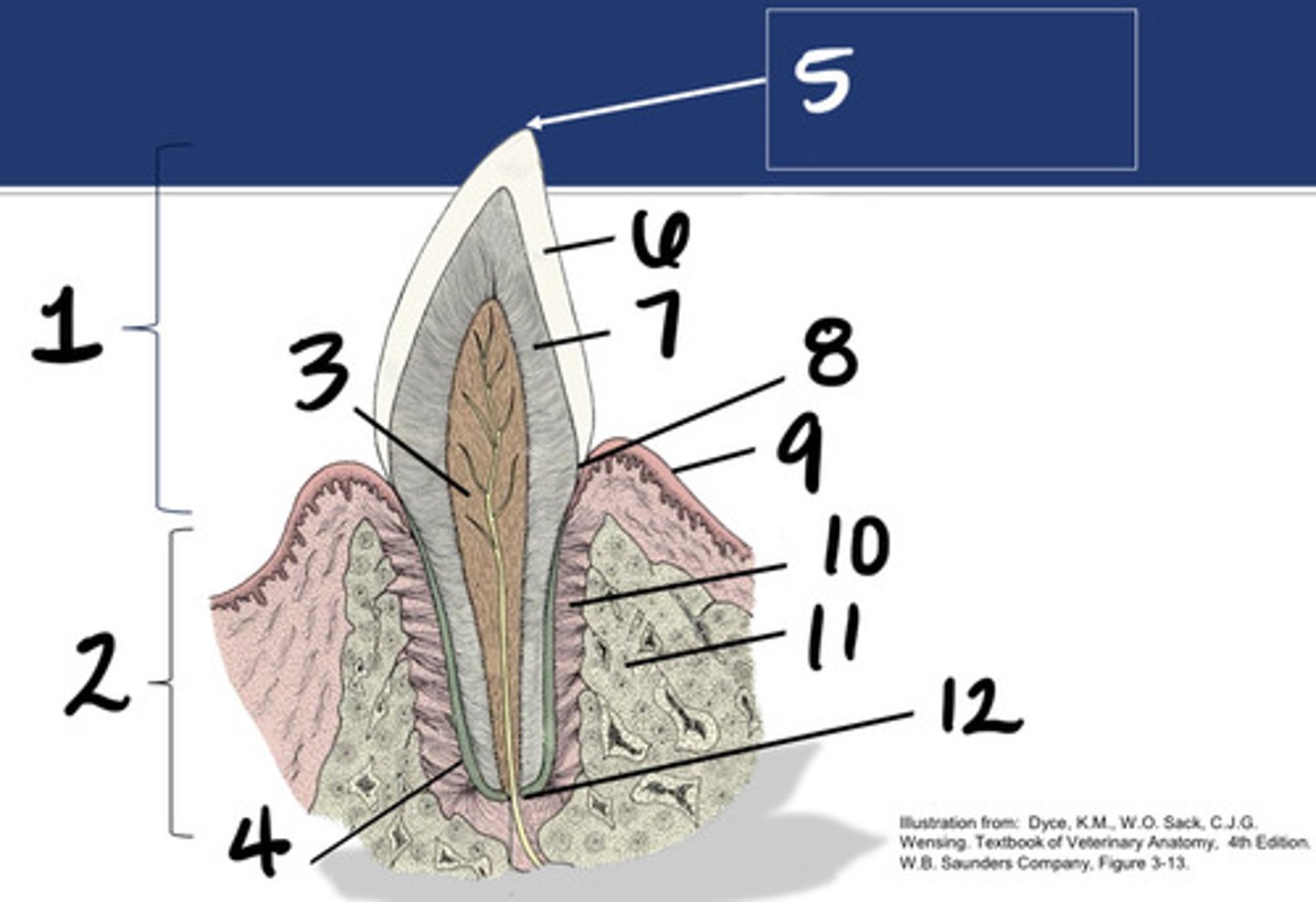
periodontal ligament
What structure is represented by #10?
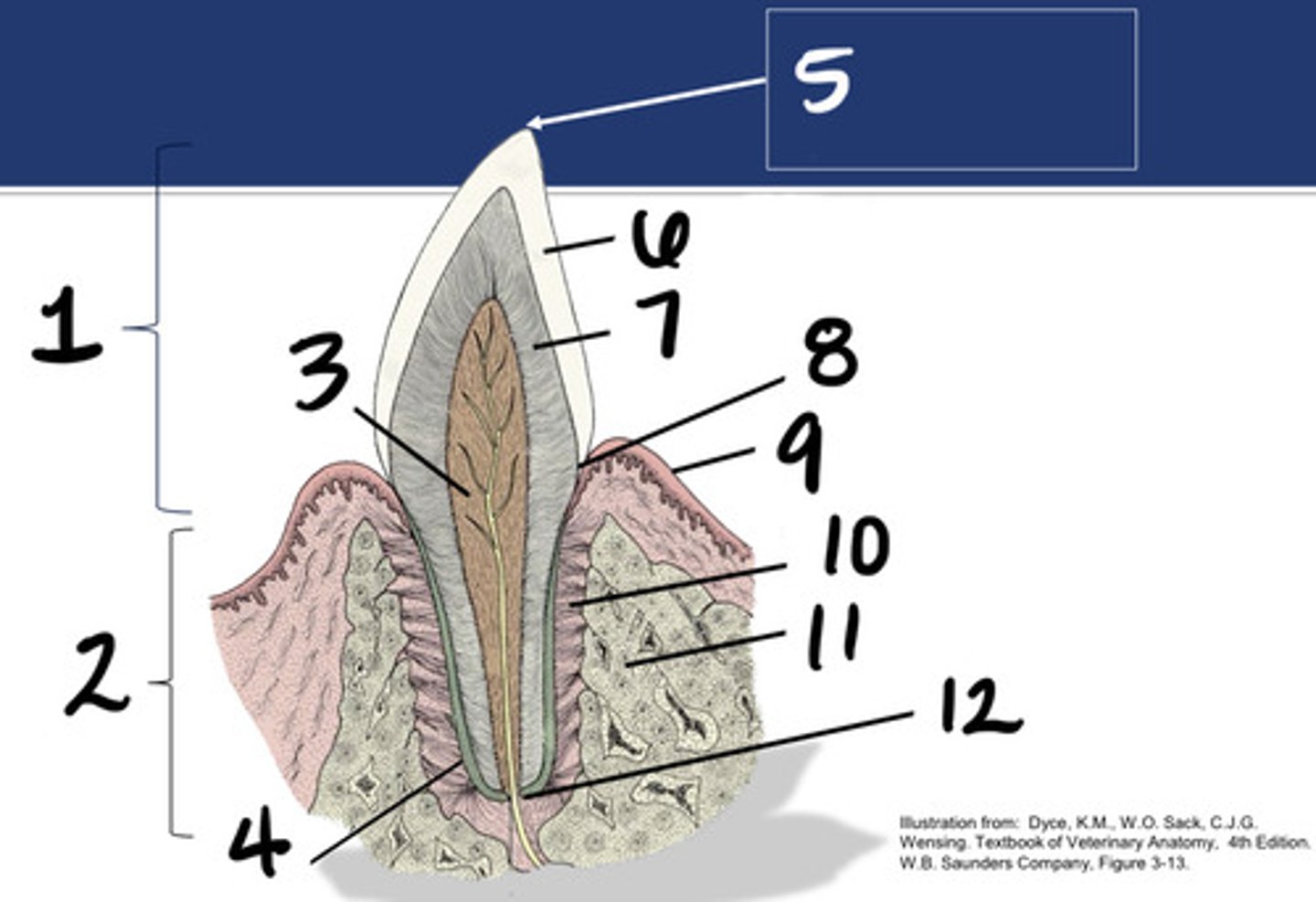
Alveolar bone
What structure is represented by #11?
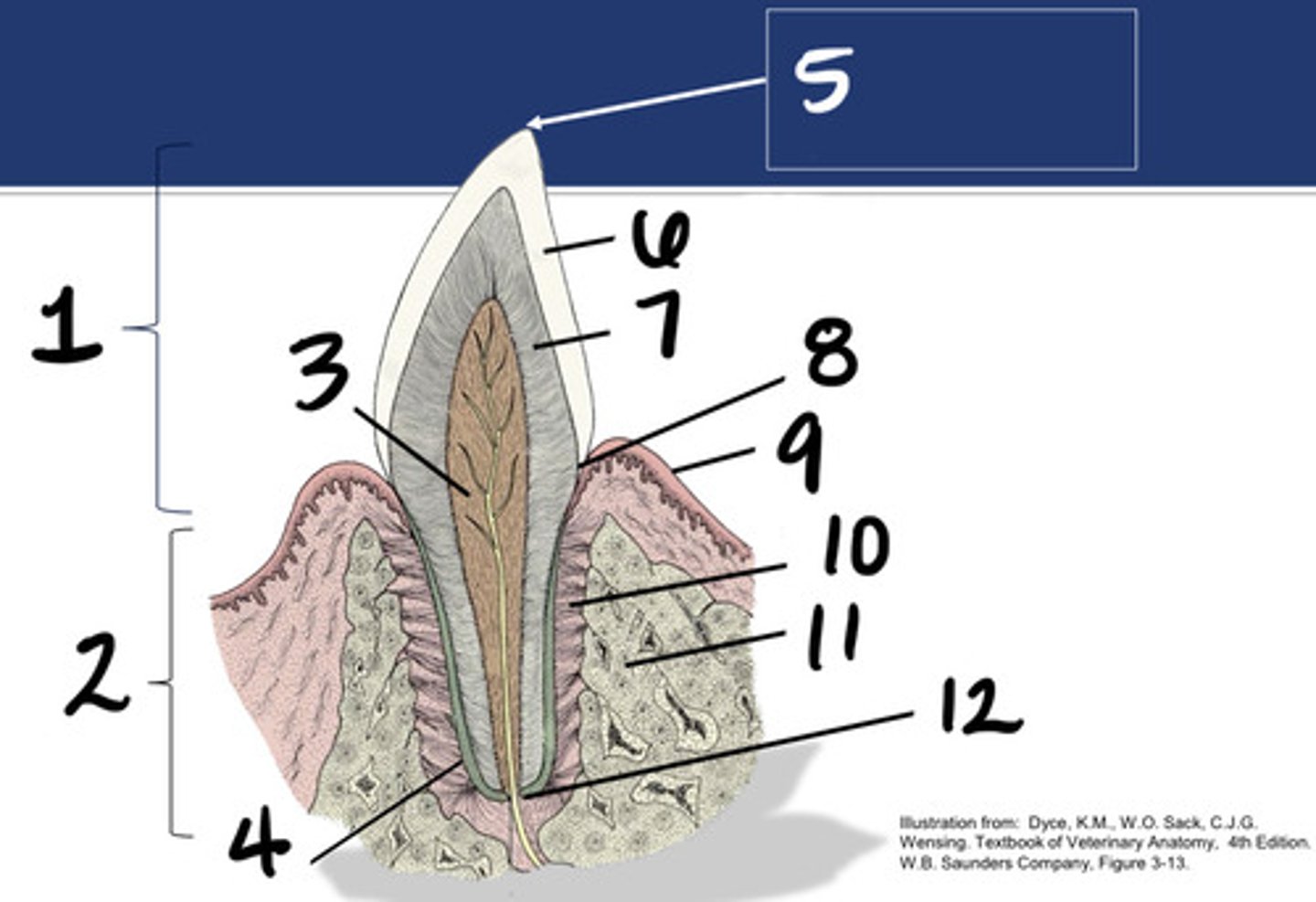
Apex
What structure is represented by #12?
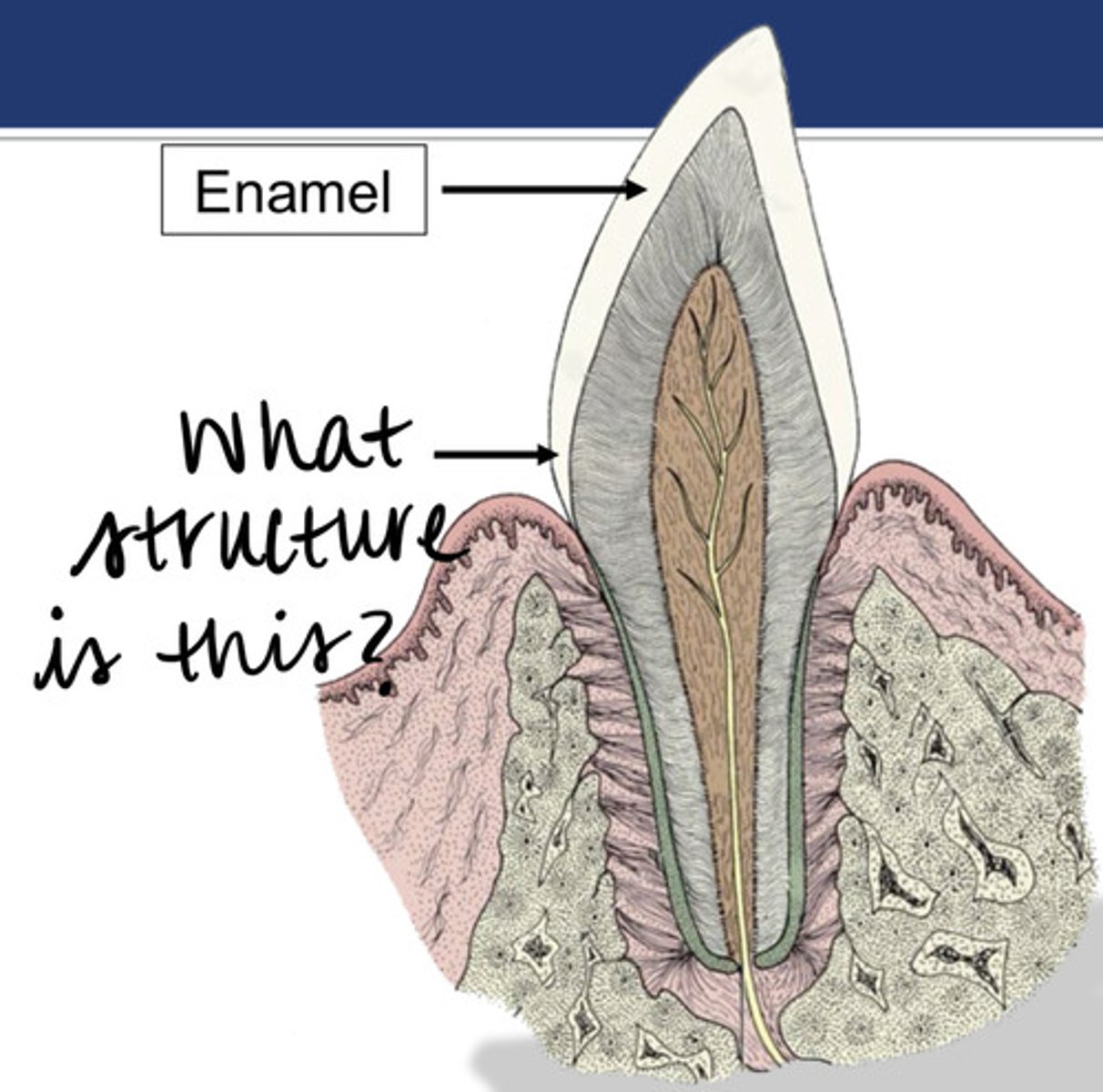
Enamel or dental bulge
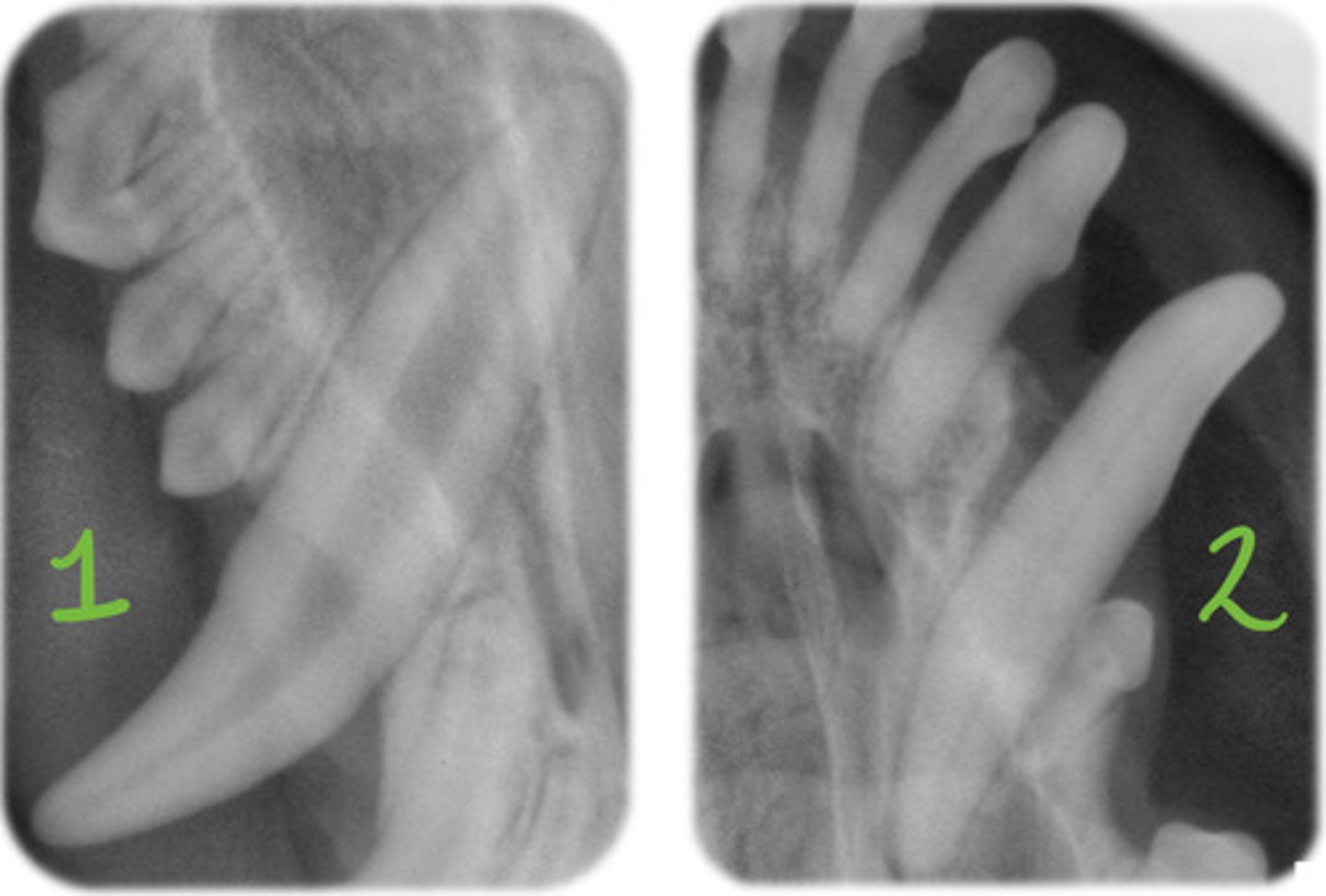
1
Which set of teeth belongs to a younger dog?
pulp chamber
What structure is represented by #1?
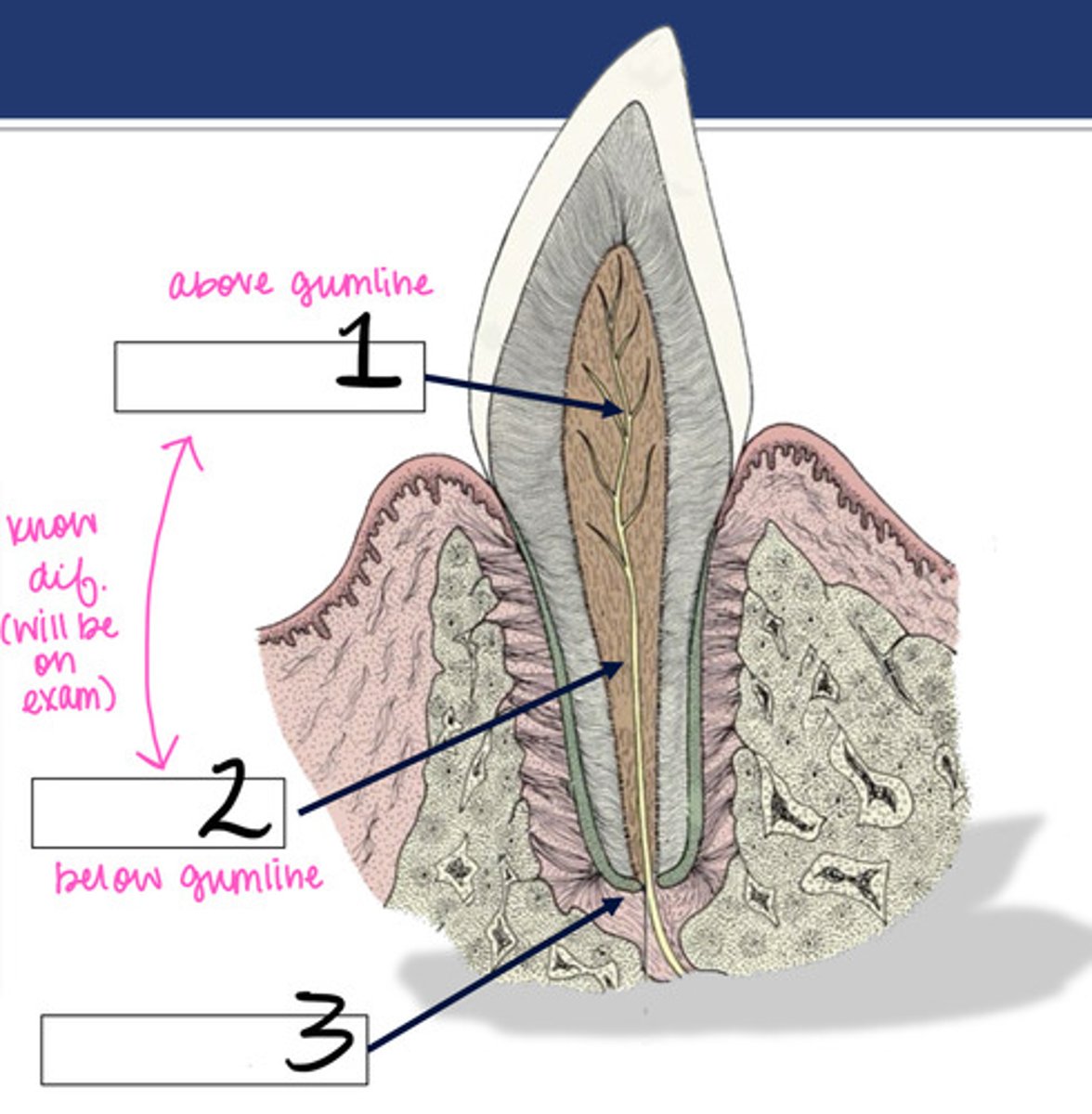
Root canal
What structure is represented by #2?
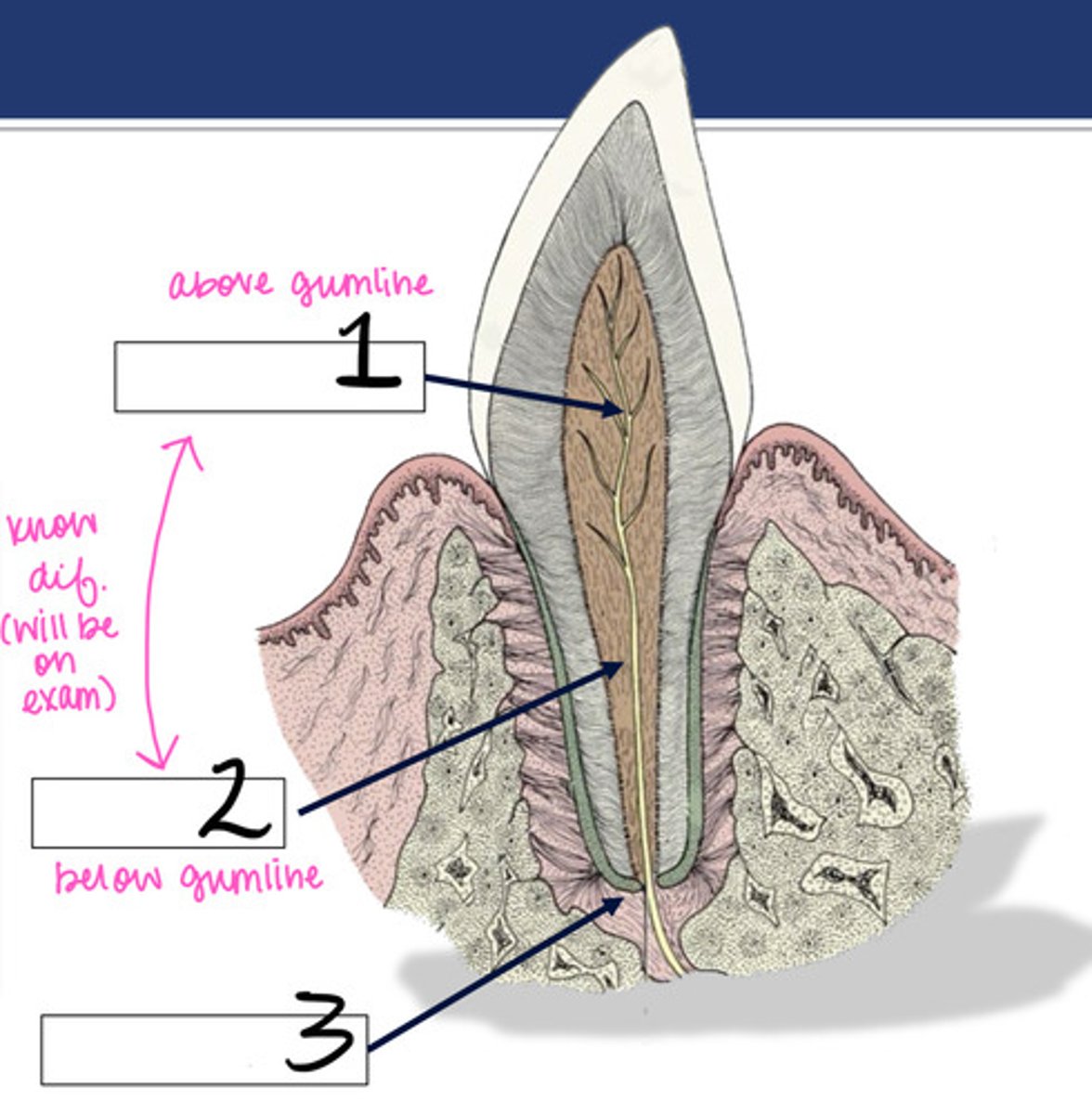
Apical junction
What structure is represented by #3?
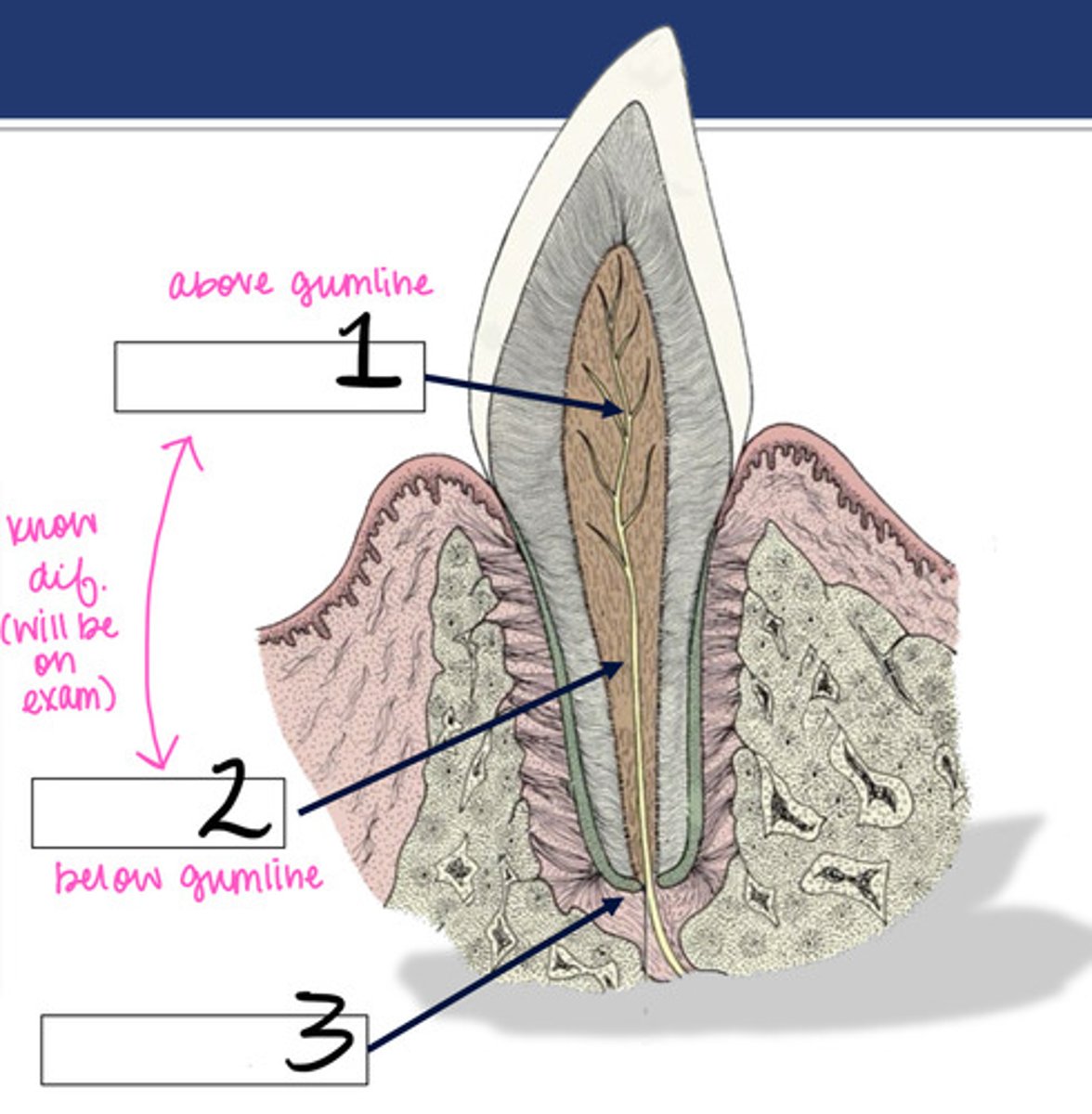
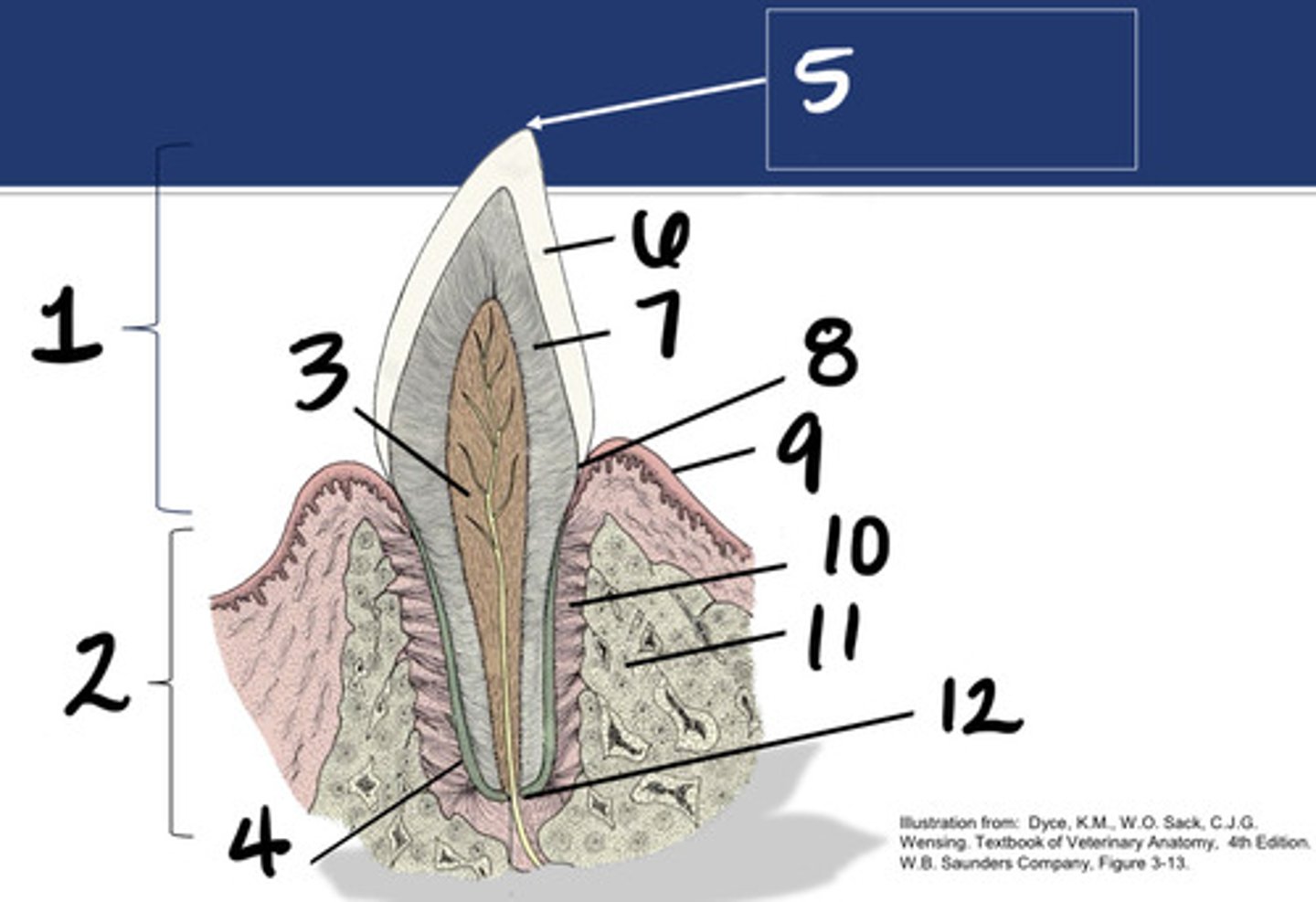
periodontal ligament
What structure is represented by #1?
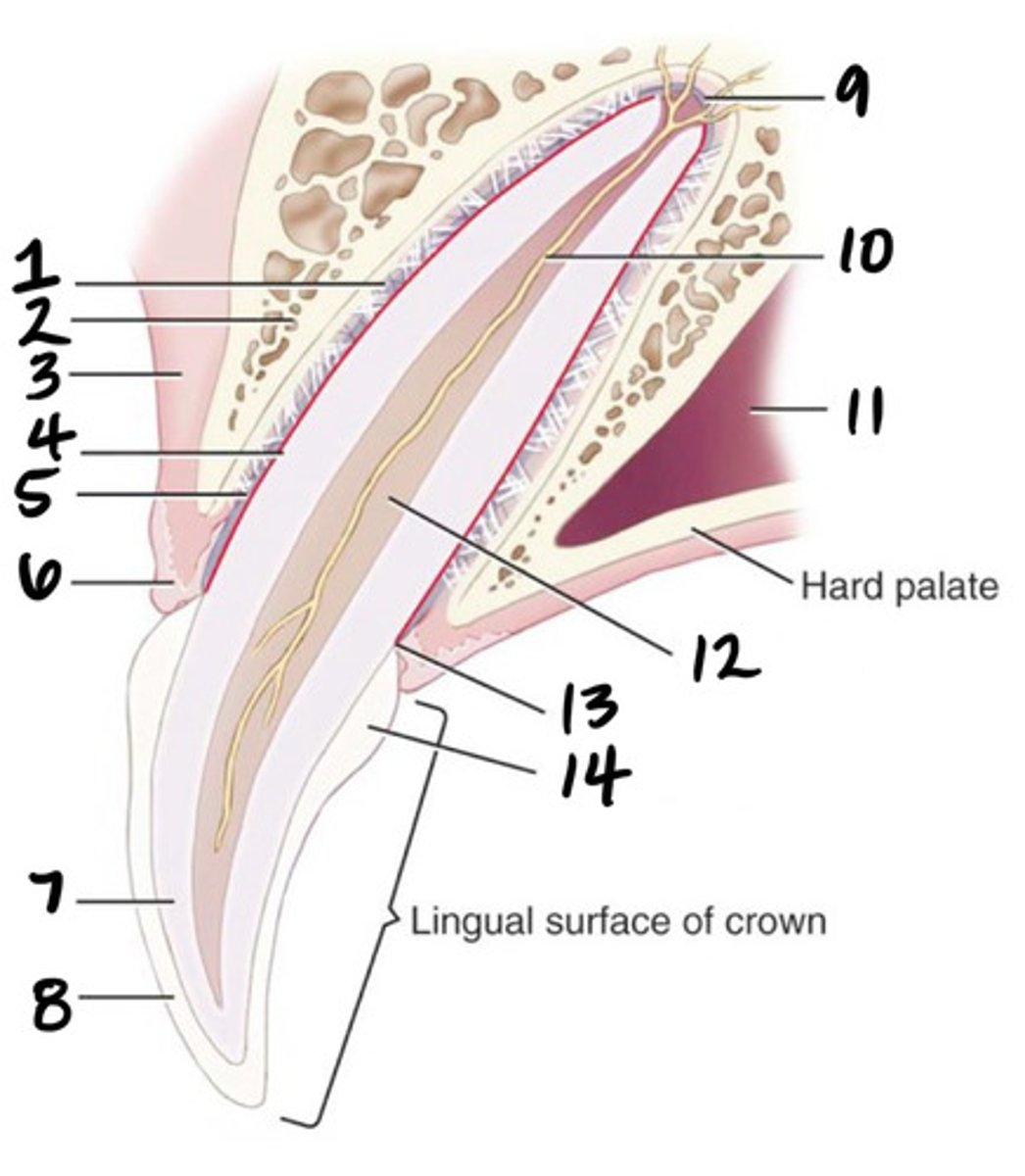
Alveolar bone
What structure is represented by #2?
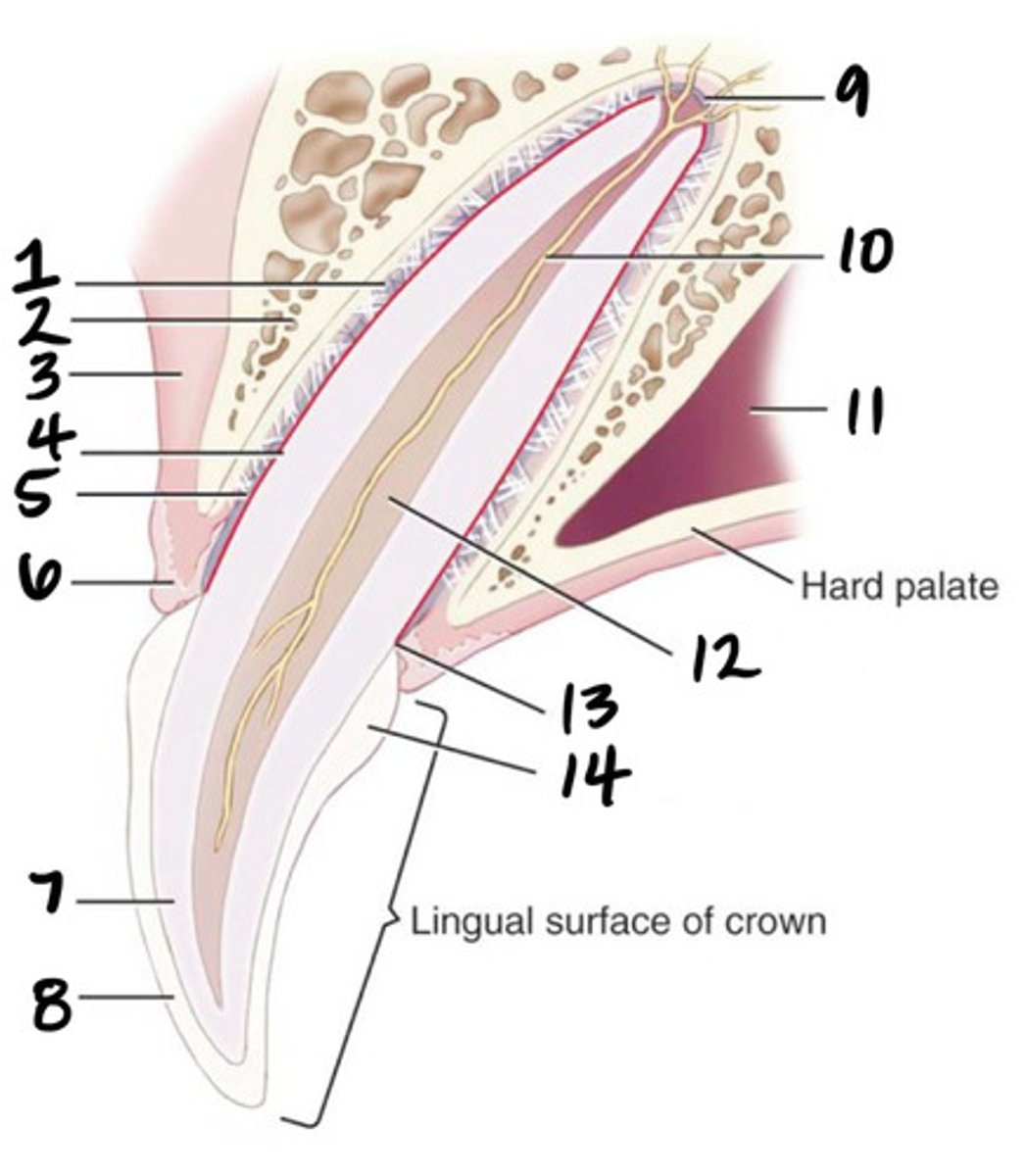
Cementum
What structure is represented by #4?
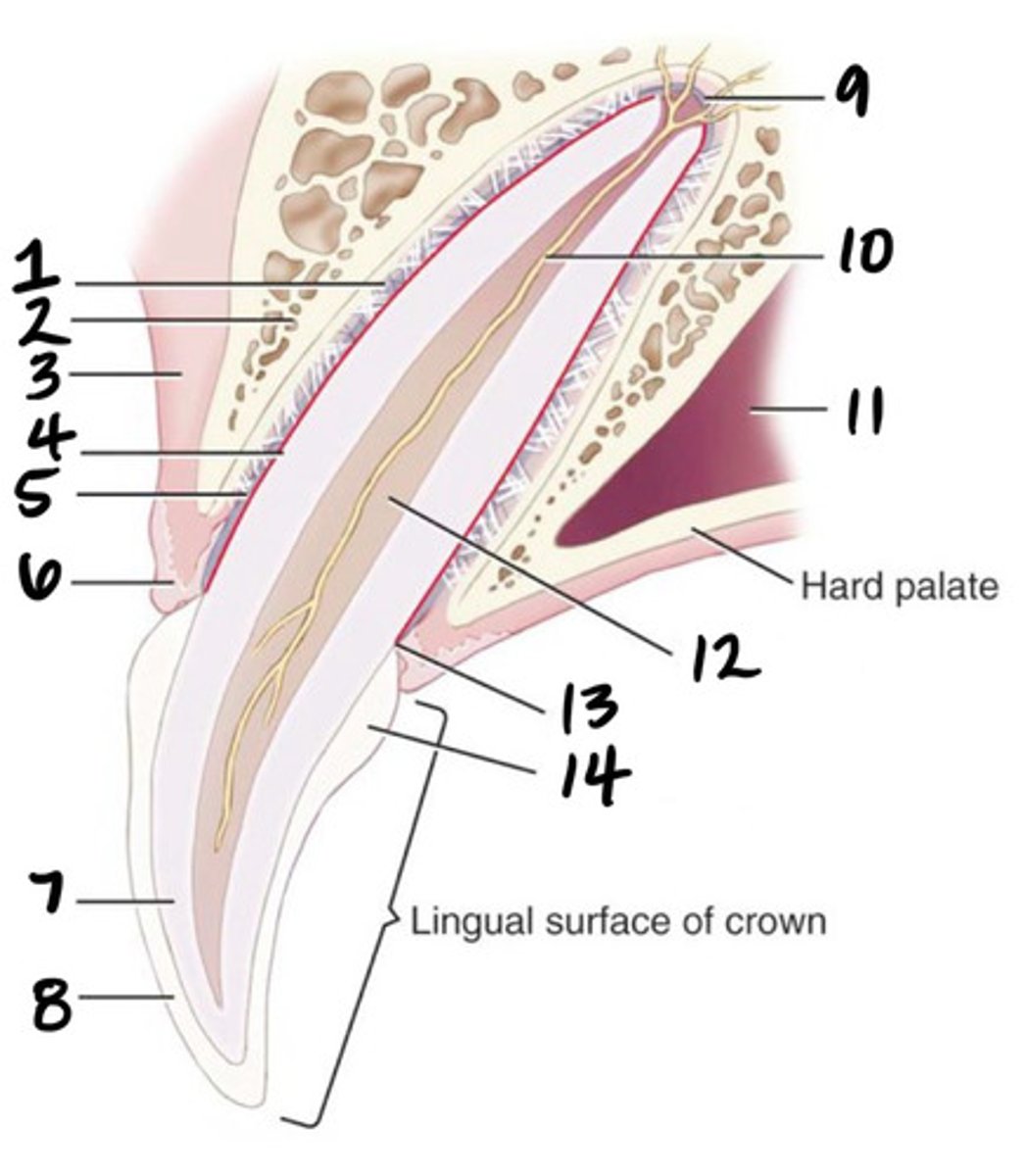
Gingiva
What structure is represented by #6?
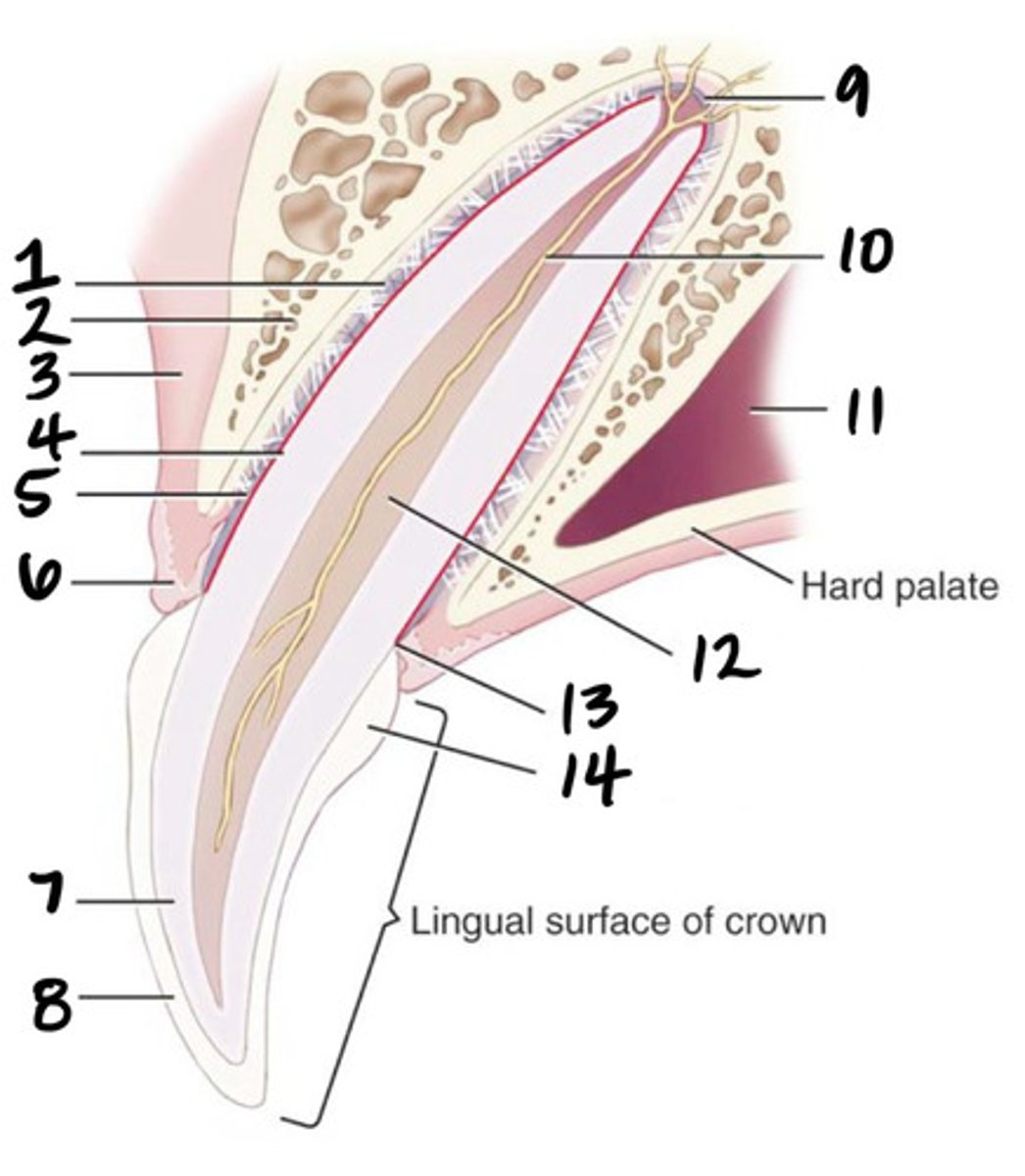
Dentin
What structure is represented by #7?
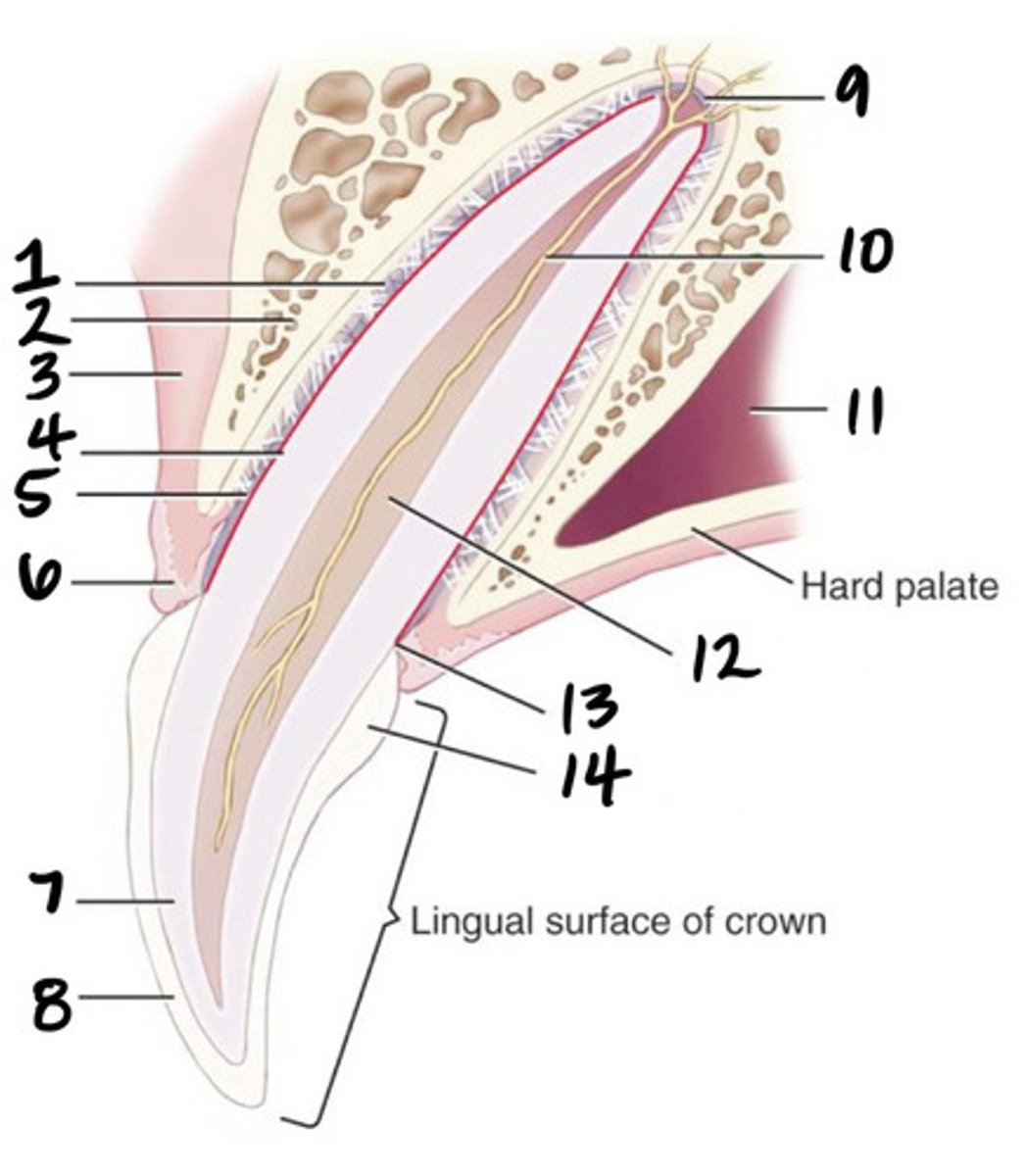
Enamel
What structure is represented by #8?
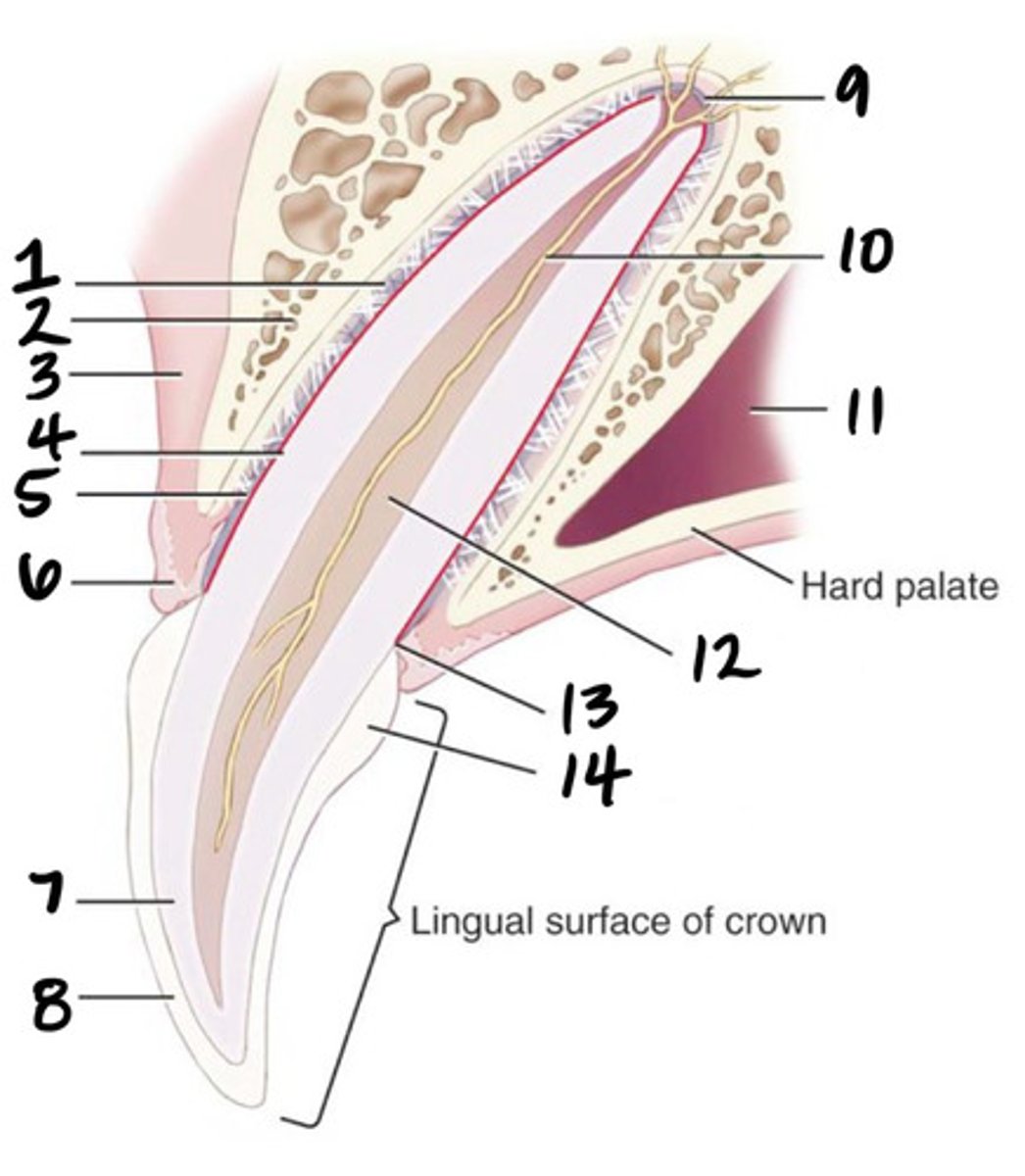
Apical delta
What structure is represented by #9?
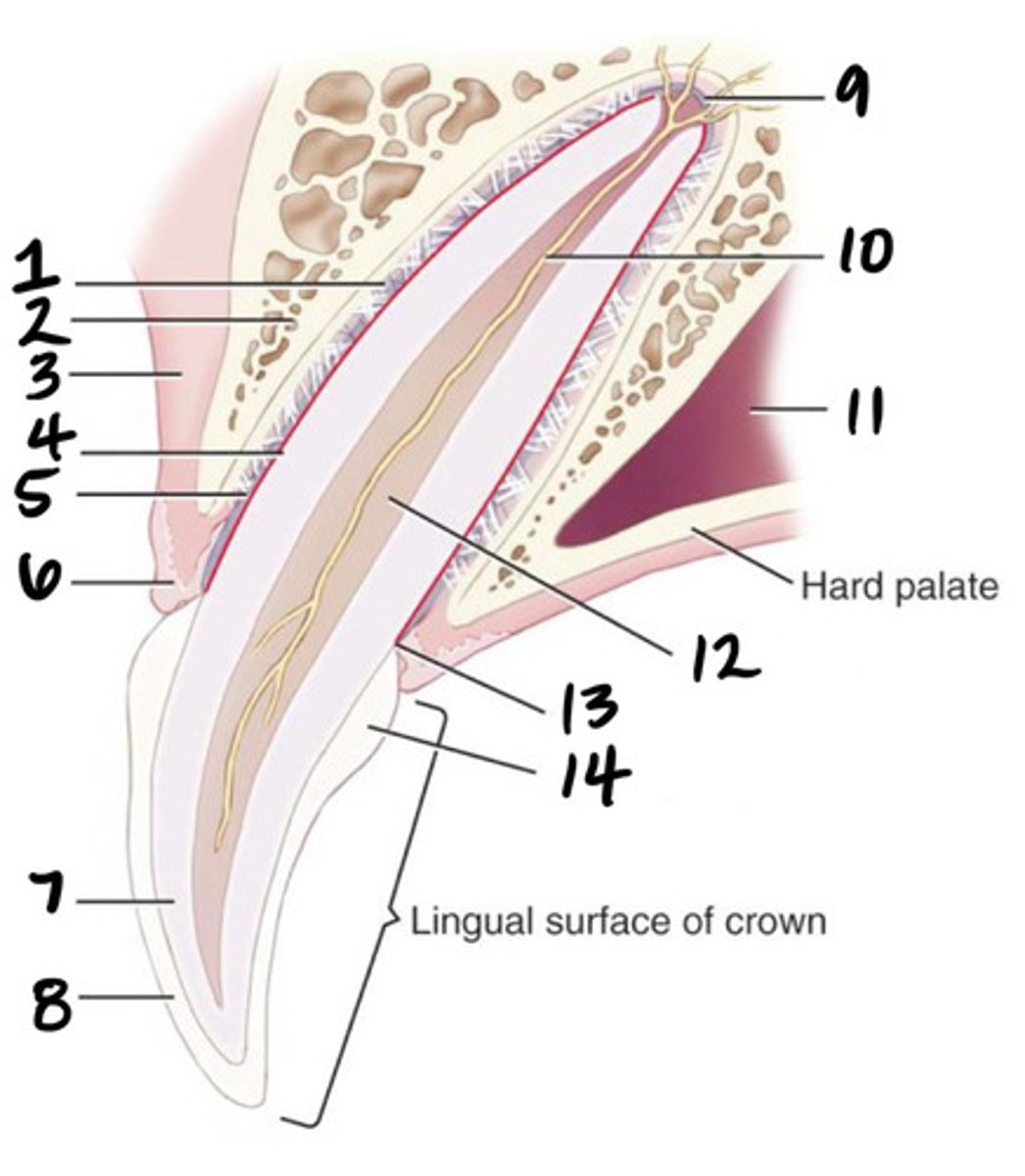
Root canal
What structure is represented by #10?
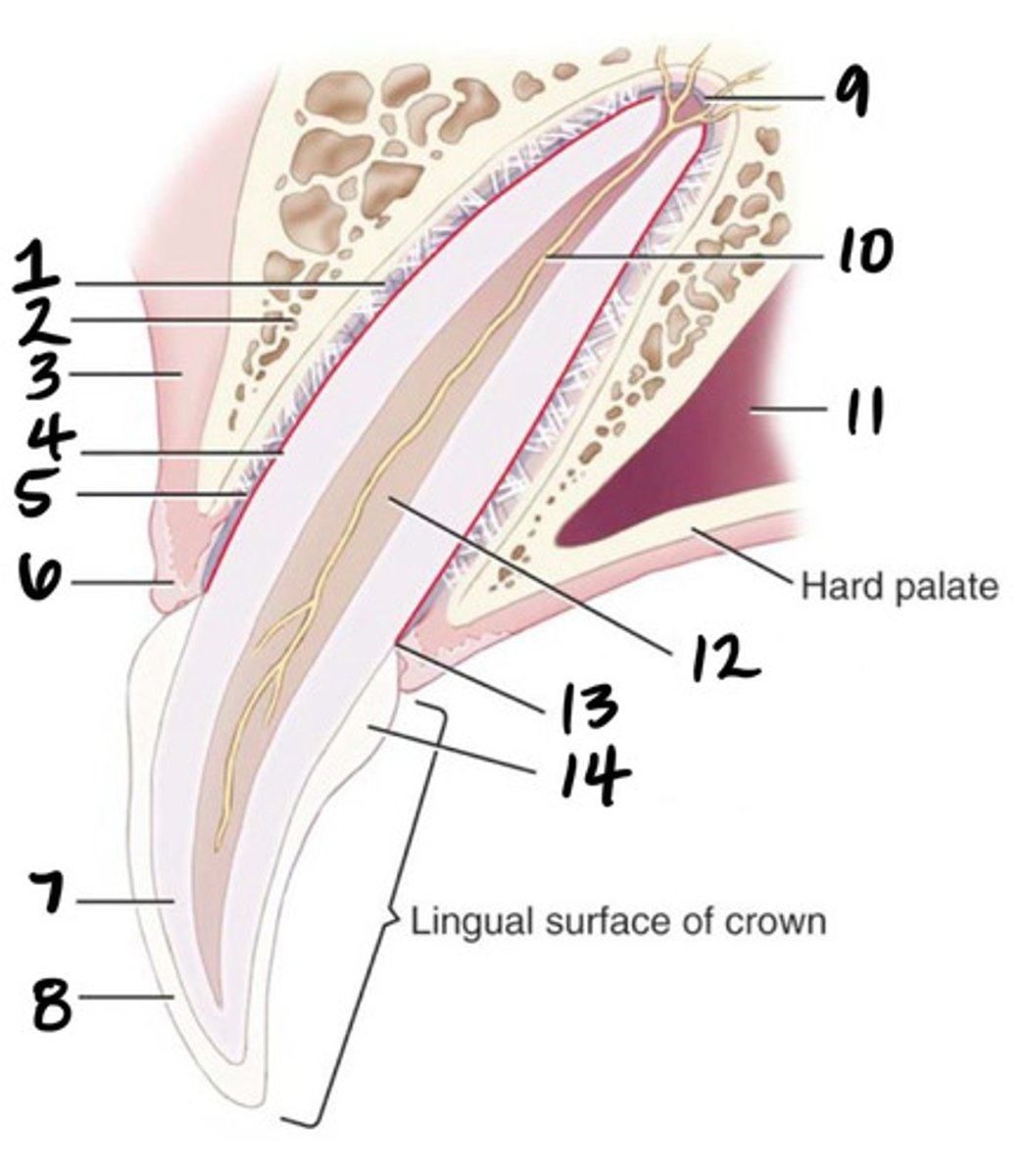
Pulp cavity
What structure is represented by #12?
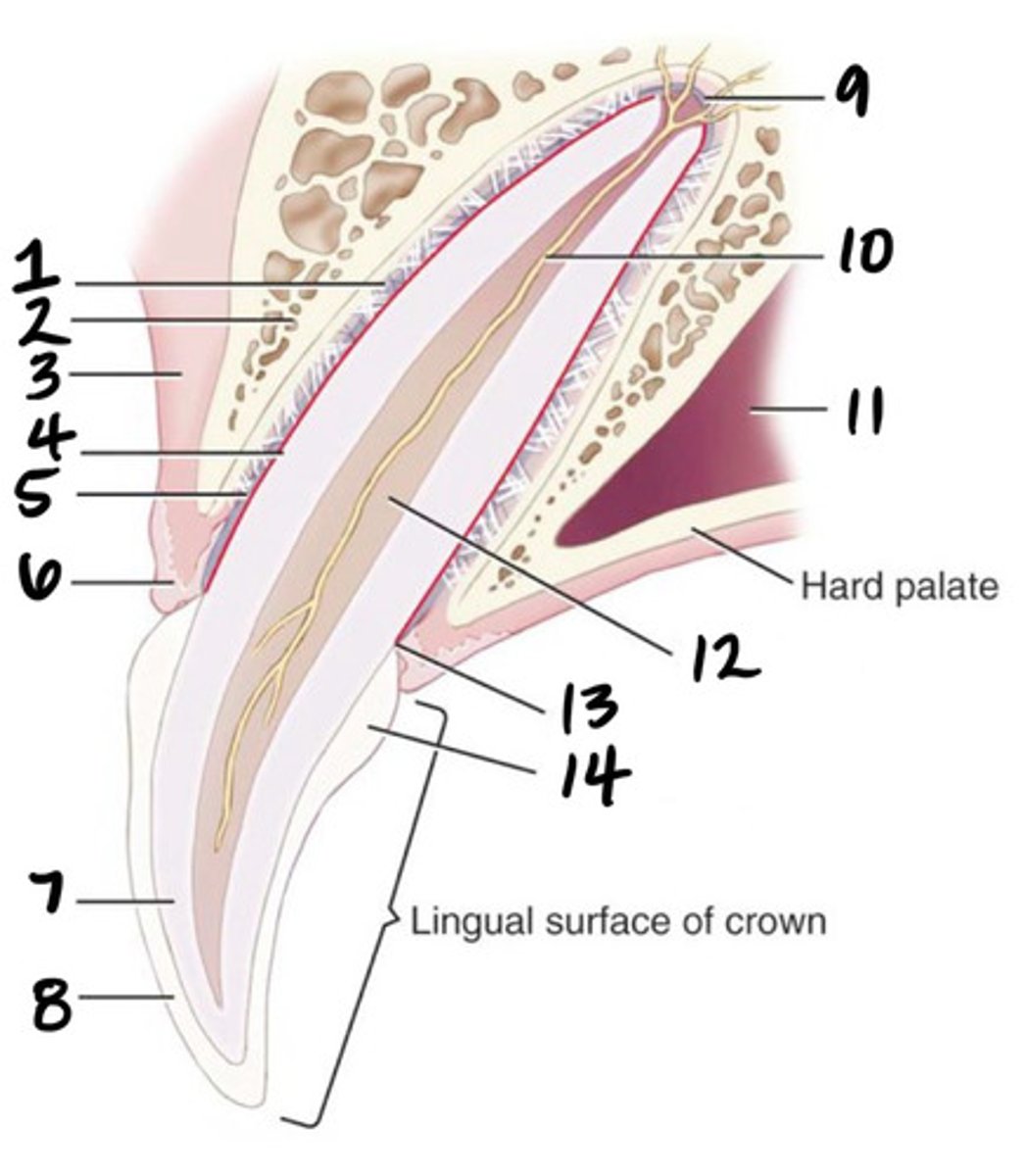
cementoenamel junction (neck)
What structure is represented by #13?