Session 11: Thyroid Gland and its Disorders
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Anatomy of thyroid gland
Where is it found
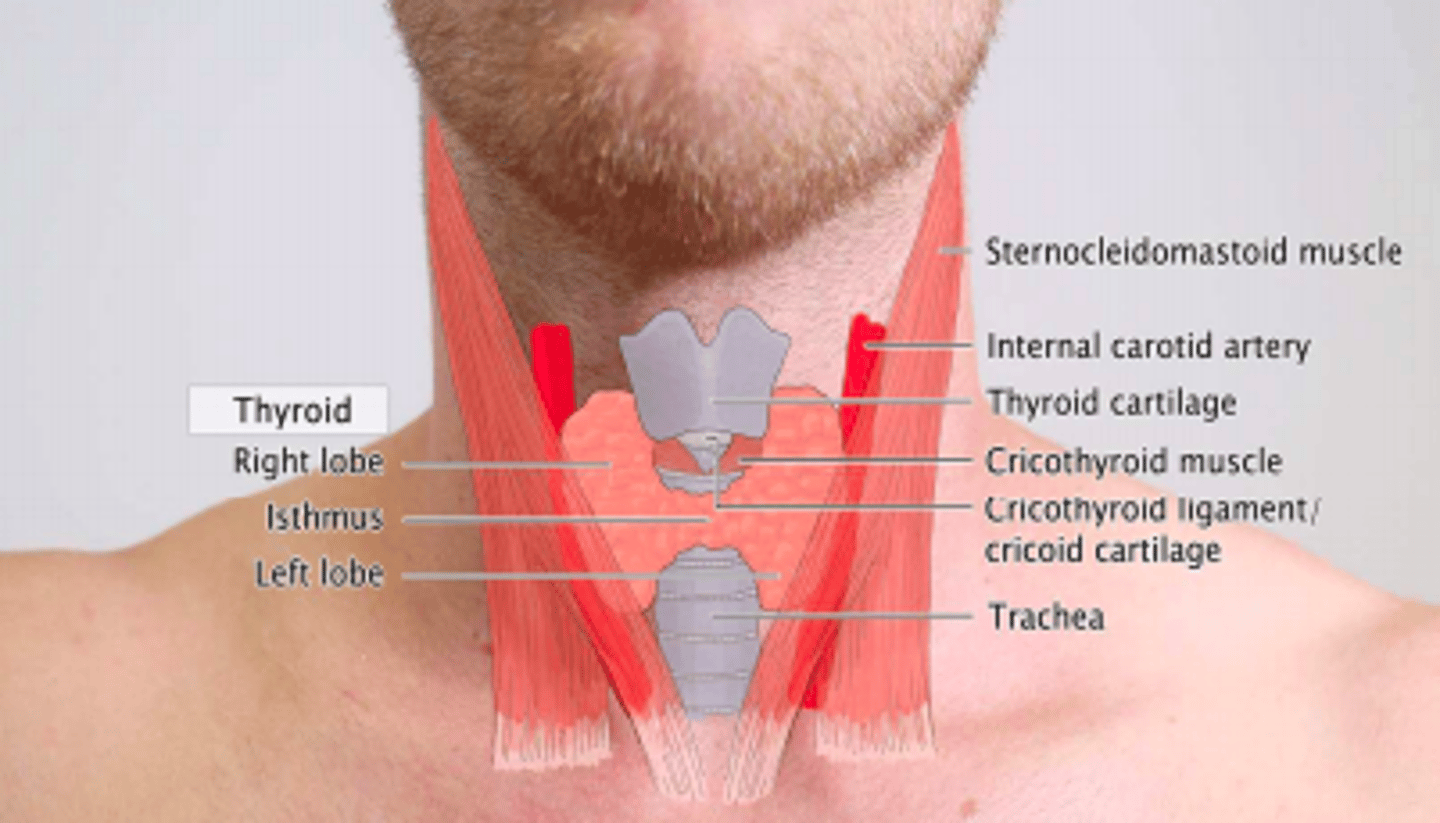
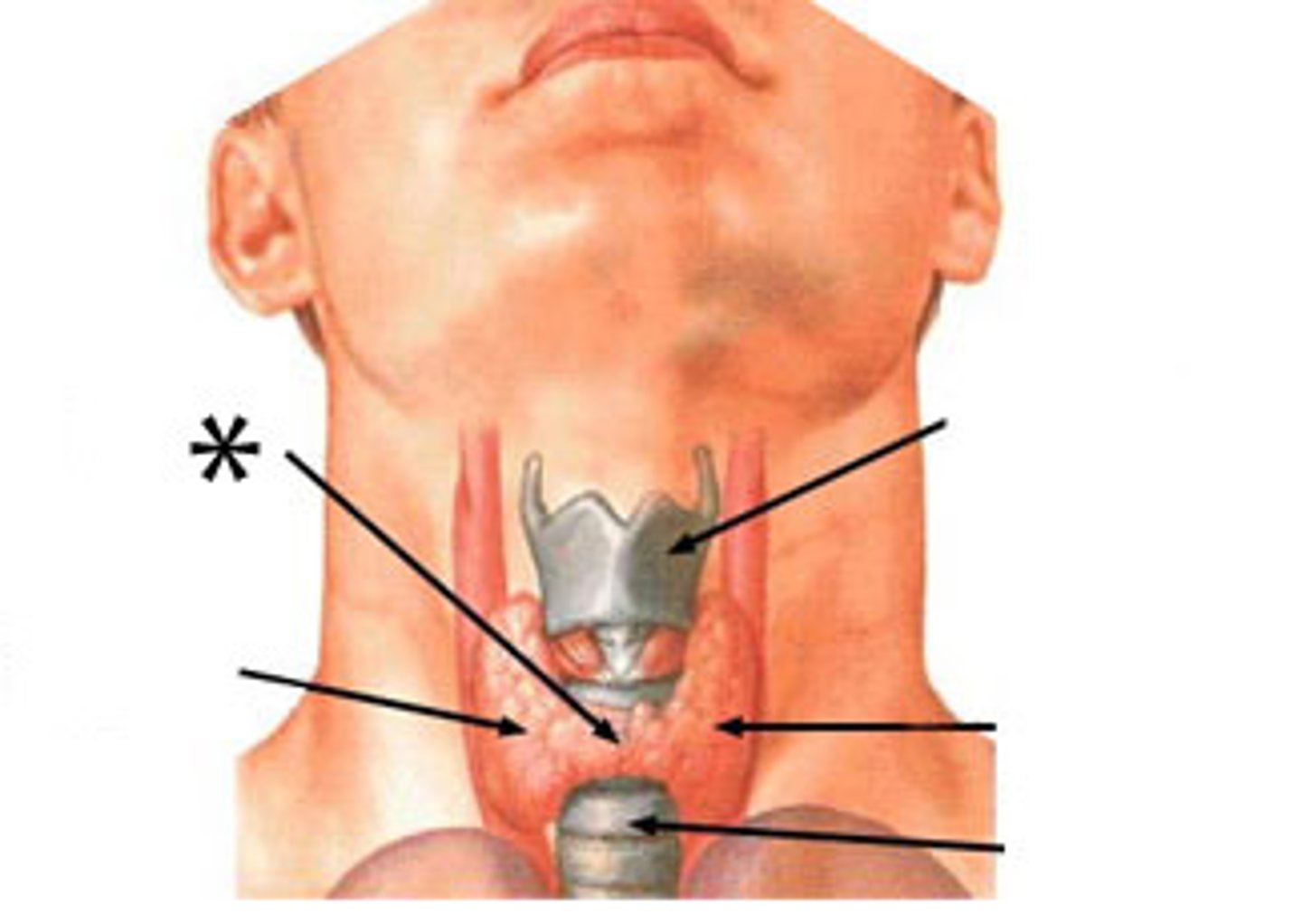
Thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland
Location
- Inferior to larynx
- Anterior to trachea
- Behind hyoid bone
What type of gland is the thyroid gland?
Ductless alveolar endocrine gland
Function of thyroid gland
Produce thyroid hormones T3, T4 and calcitonin
T3 hormone
Triiodothyronine
T4 hormone
Thyroxine
Calcitonin
Decreases blood calcium levels
The thyroid gland is found in the anterior neck, just below the ___ prominence (Adam's apple)
Laryngeal prominence
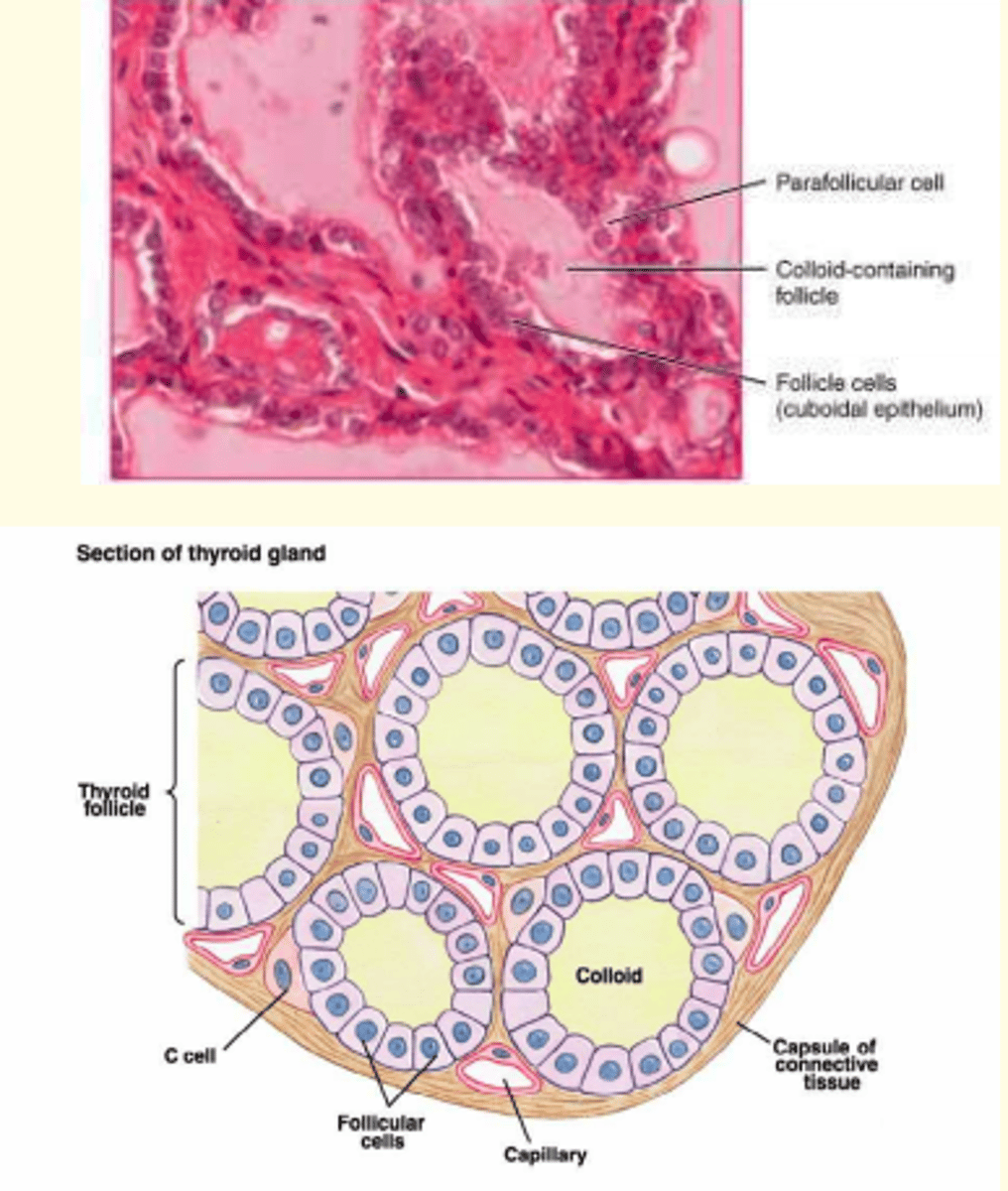
Thyroid epithelia
Simple cuboidal /
Simple columnar
Thyroid epithelia form follicles (big beige purple circles) filled with ___
Colloid
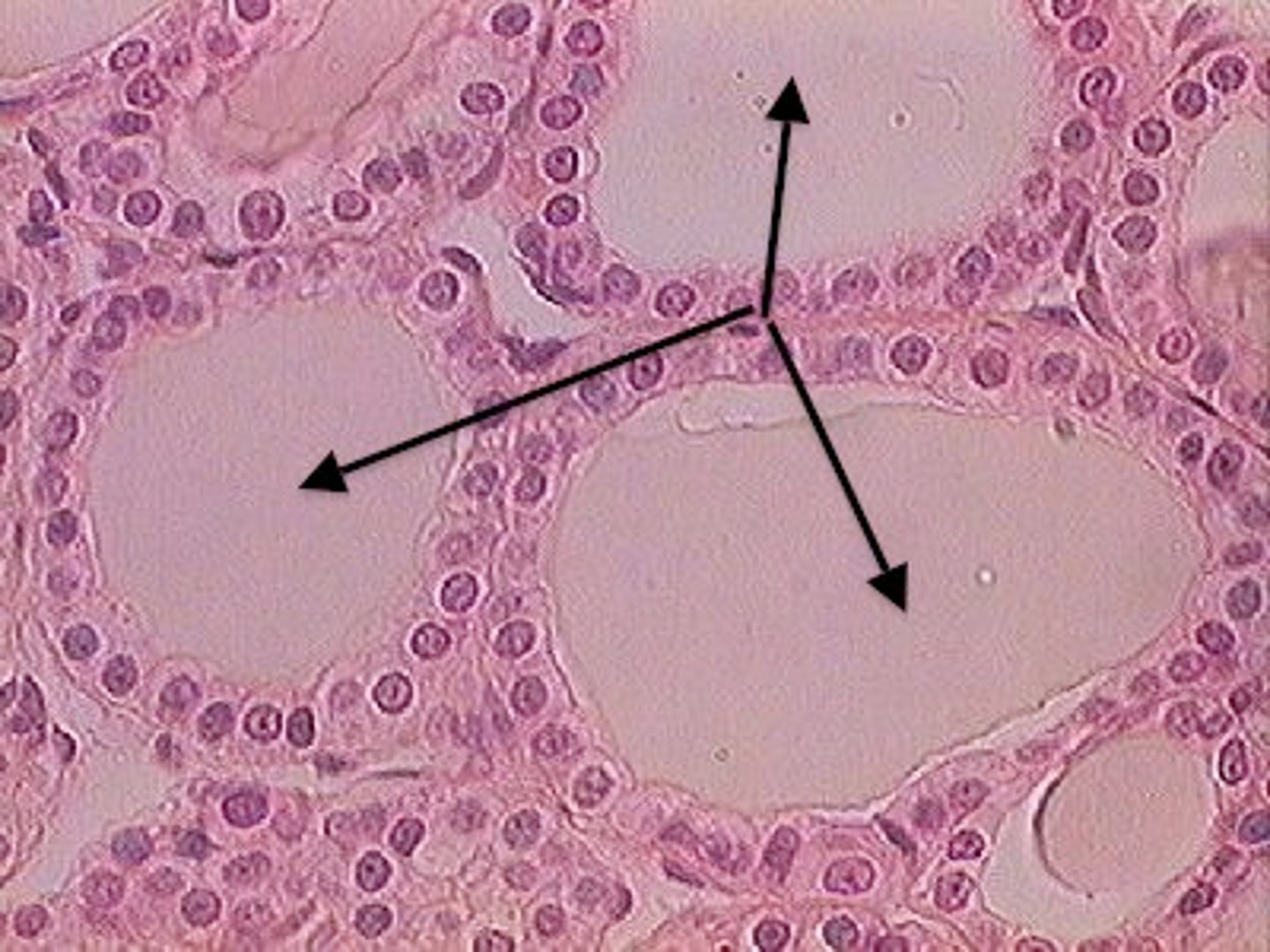
In the spaces between thyroid follicles, ___ cells can be found.
These ___ cells secrete calcitonin, which is involved in the regulation of calcium metabolism.
In the spaces between thyroid follicles, parafollicular cells can be found.
These parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin, which is involved in the regulation of calcium metabolism.
Two conditions in which development of thyroid gland has gone wrong
1) Ectopic thyroid
2) Thyroglossal cyst
Ectopic thyroid mostly superior to standard position
Thyroid gland is located in other parts of the body than where it should be. Mostly superior to its standard position.
This condition can lead to hyperthyroidism
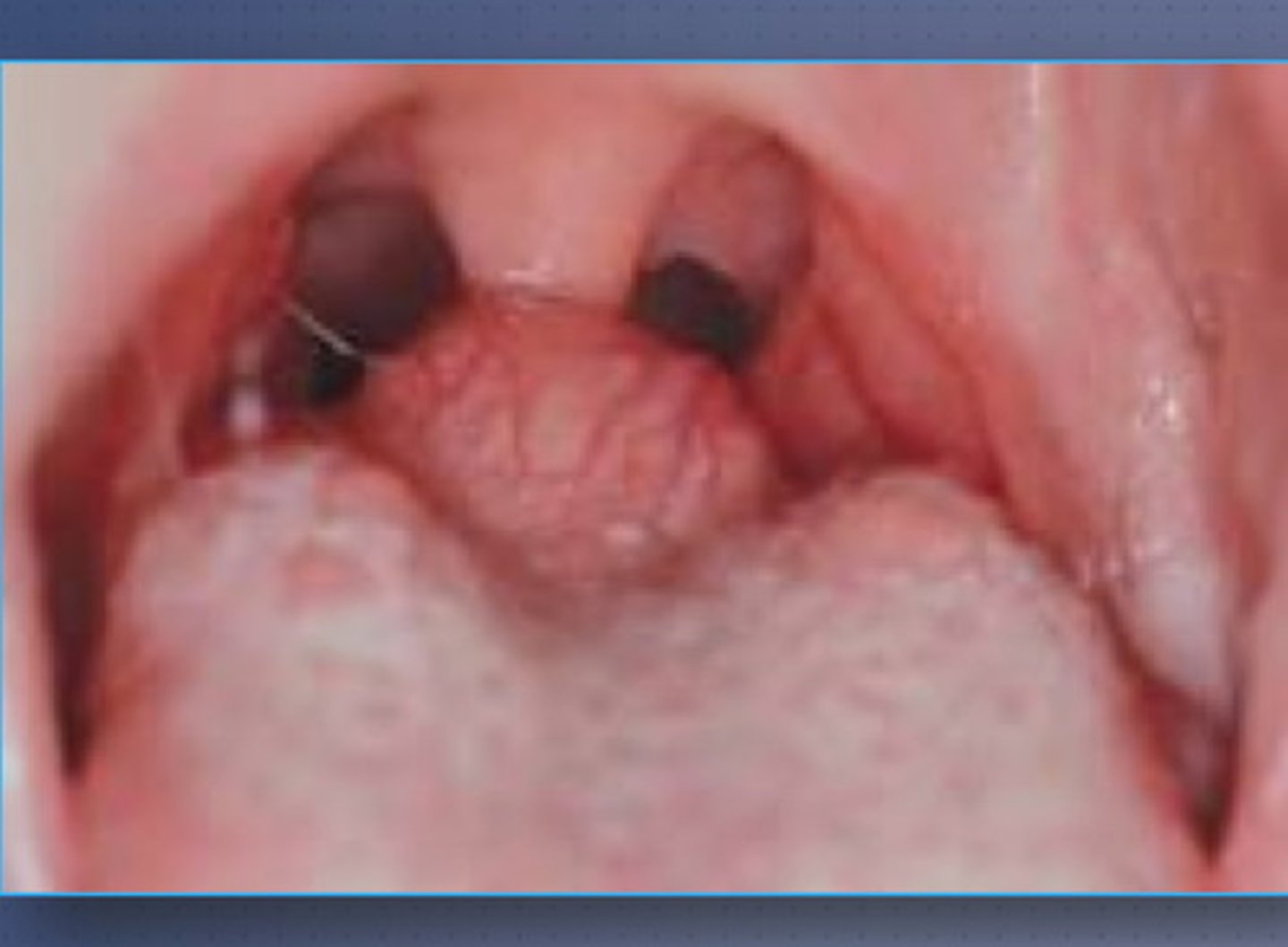
Thyroglossal cyst
A mass or lump in the front part of neck that is filled with fluid.
How is thyroid hormone release regulated?
Negative feedback loops
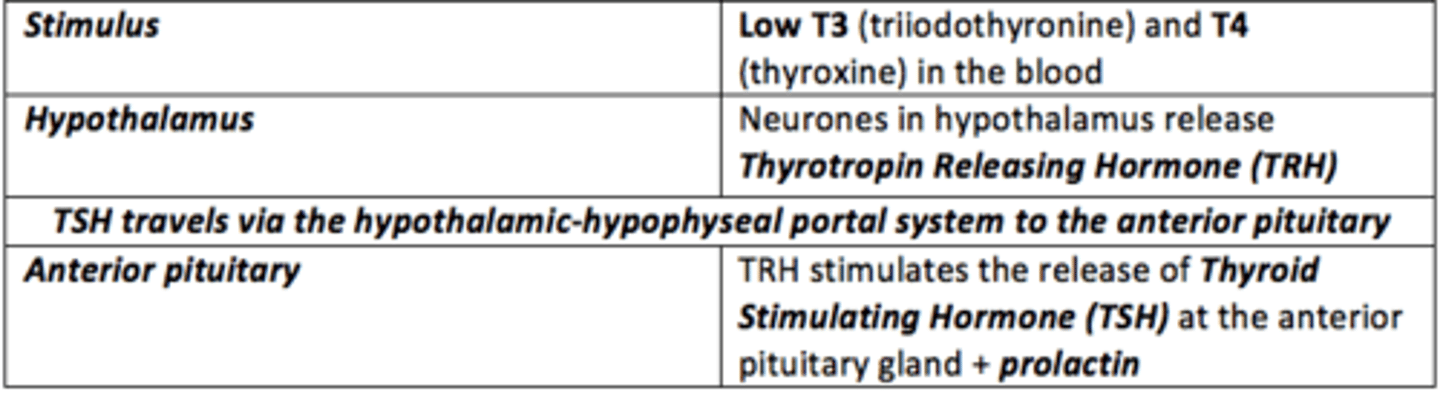
Release of TSH from hypothalamus is stimulated by...
remember: hypo = SLOW/LOW
Low T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) in blood
Release of TSH from hypothalamus is inhibited by...
remember: NEGATIVE feedback loop → change causes opposite change to restore balance
High T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) in blood
The role of TSH (secreted from anterior pituitary)
Increase the growth and enlargement of the thyroid gland
What is one dietary requirement needed for thyroid hormone synthesis?
Iodine is required - this is a basic subunit of T3 and T4
Synthesis of thyroid hormones (mechanism)
(1) inorganic iodide is transported into the gland
(2) intrathyroidal iodide is oxidized to iodine under the influence of H2O2 and peroxidase
(3) iodine is bound in thyroglobulin to tyrosine, forming monoiodotyrosine (MIT) and diiodotyrosine (DIT),
(4) the iodotyrosines are enzymatically coupled to form thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3),
(5) the iodothyronines, T4 and T3, are stored in thyroglobulin until released into the circulation
6) the unused iodotyrosines are deiodinated and the iodide recycled

Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Questions...
What is the name of the transporter that actively transports (via secondary active transport) iodine into the follicular cells of the thyroid?
Sodium-Iodide Symporter
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Questions...
Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a large protein which is rich in what amino acid?
Tyrosine
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Questions...
Sodium gradient is maintained in the follicular cell by what pump?
Sodium-Potassium ATPase pump
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Questions...
Exocytosis of Thyroglobulin into the thyroid follicle lumen - where it is stored as ___
Colloid
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Questions...
Iodide is made reactive by what enzyme?
Thyroid peroxidase
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Questions...
Iodide binds to the benzene ring on Tyrosine residues of Thyroglobulin. First formed is mono-iodotyrosine (MIT). Second formed is...
Di-iodotyrosine (DIT)
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Questions...
Coupling of MIT and DIT give Triiodothyronine (T3).
Coupling of DIT and DIT give ___
Thyroxine (T4)
T3 and T4 are fat-soluble and mostly carried by plasma proteins in the blood.
What are the two plasma proteins that are the main carriers of T3 and T4?
- Thyronine Binding Globulin
- Albumin
Nearly 100% of T3 and T4 is carried by plasma proteins in the blood.
However, it is that <1% of unbound (free) T3 and T4 that are ___ in the blood!
Nearly 100% of T3 and T4 is carried by plasma proteins in the blood.
However, it is that <1% of unbound (free) T3 and T4 that are active in the blood!
Is T3 or T4 more active?
T3 is 5x more active than T4
T3 > T4
T3 and T4 act via nuclear receptors on the cells of target tissues and promote a variety of metabolic pathways.
How does T3 and T4 impact metabolism?
- Increased BMR
- Increased gluconeogenesis
- Increased glycogenolysis
- Increased lipolysis
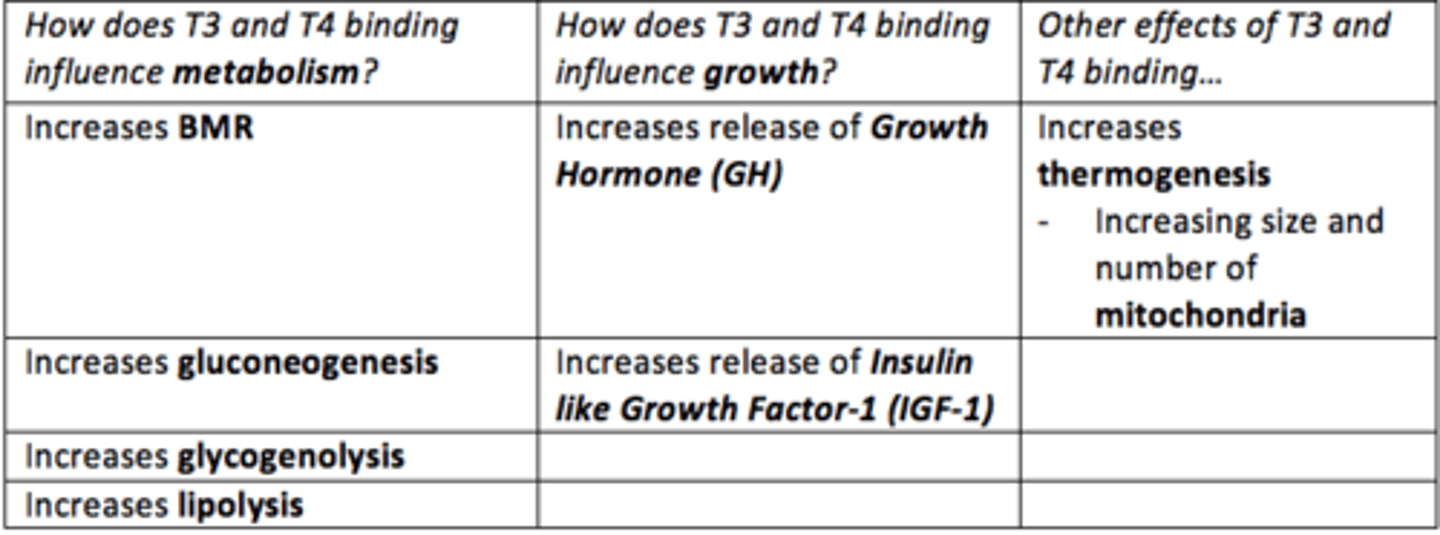
How does T3 and T4 impact growth?
Increases the release and effect of Growth Hormone (GH) and Insulin like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1)
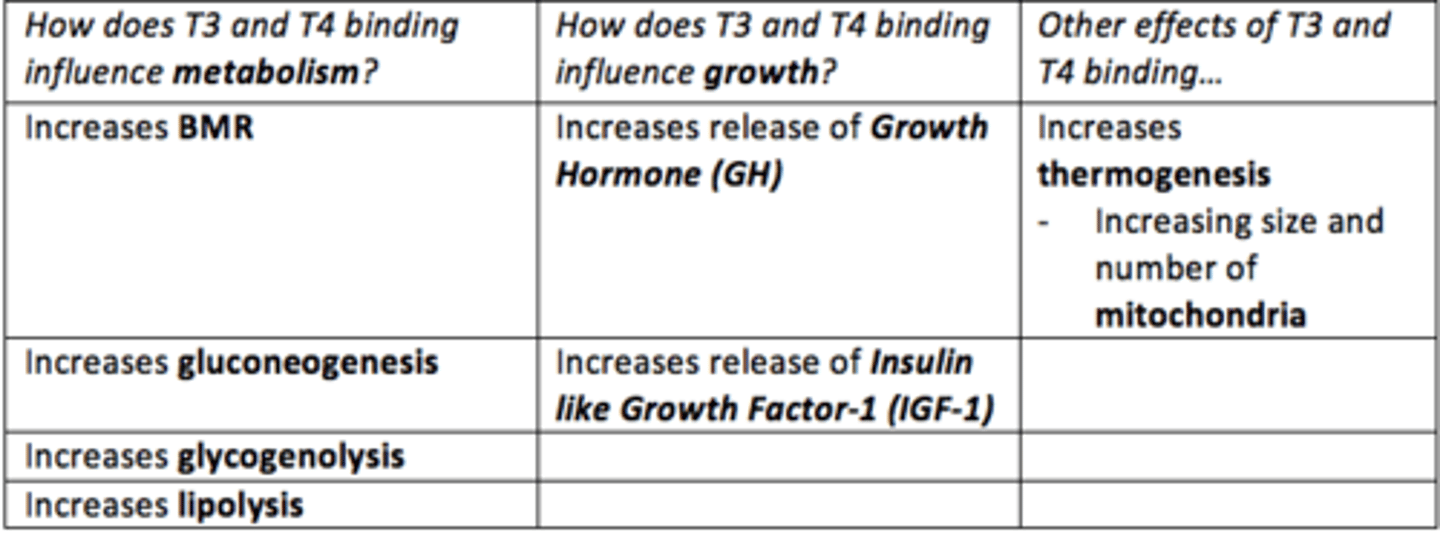
How does T3 and T4 increase thermogenesis?
think: mitochondria
Increasing size and number of mitochondria within cells
T3 and T4 up-regulate the number of Beta-adrenergic receptors in tissues such as cardiac muscle and therefore increases sensitivity to ___ resulting in an increase in HR and cardiac contractility.
Catecholamines
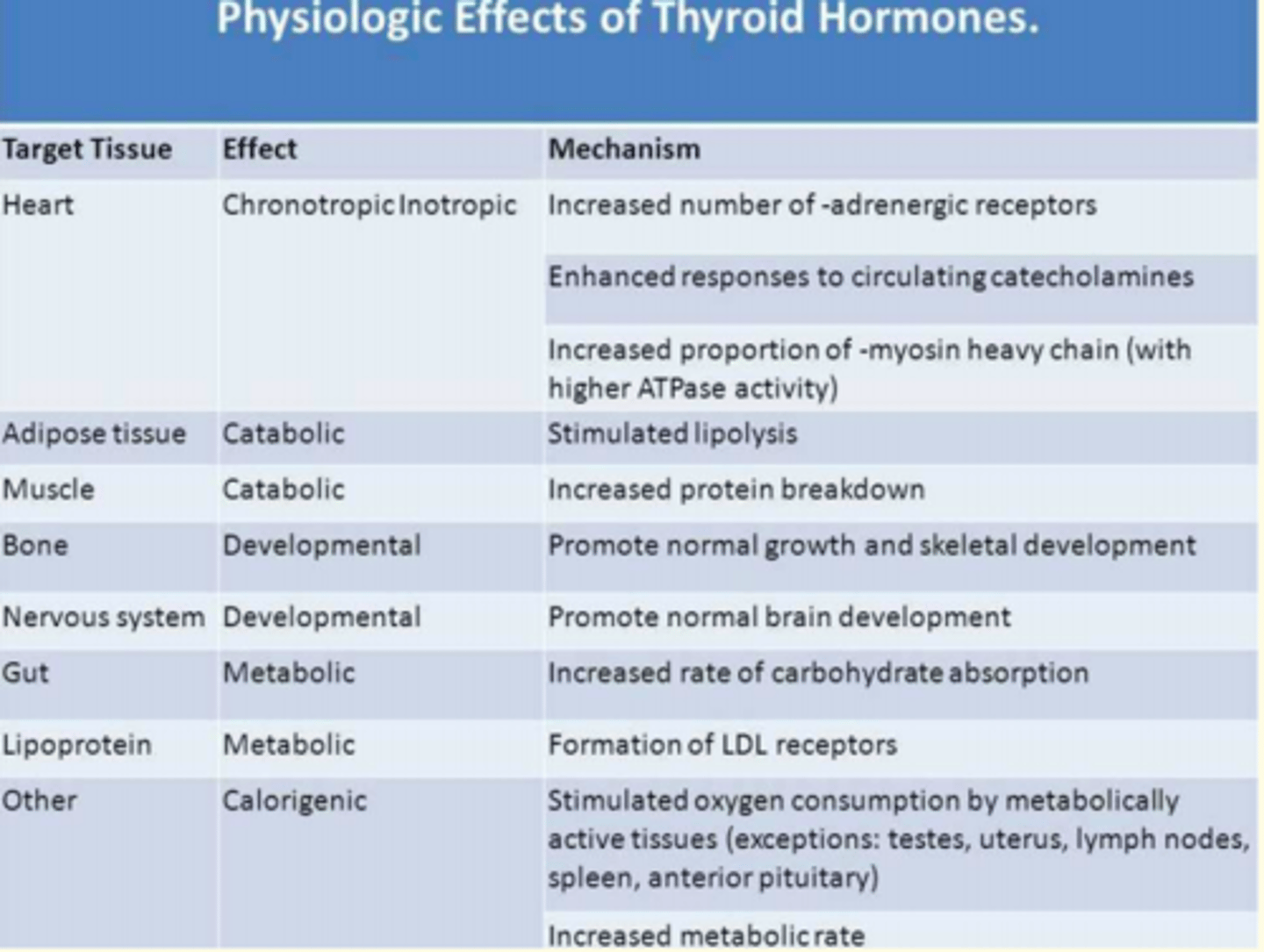
Summary of the physiological effects of thyroid hormones T3 and T4 binding
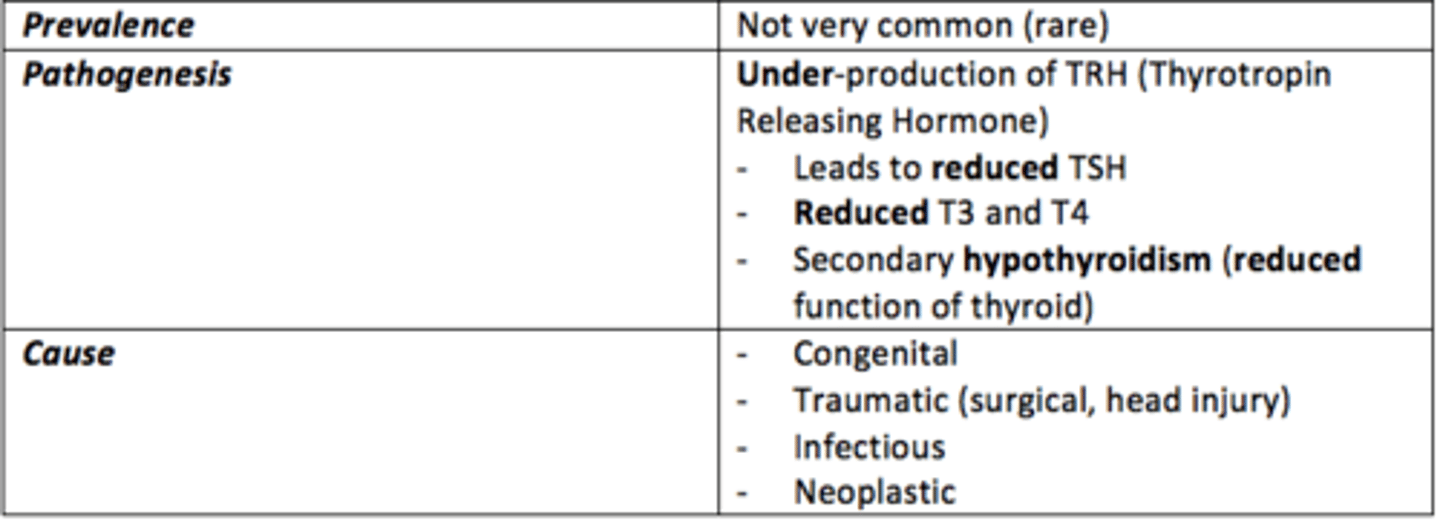
Secondary hypohyroidism
Caused by pituitary or hypothalamic dysfunction (↓ TSH or TRH)
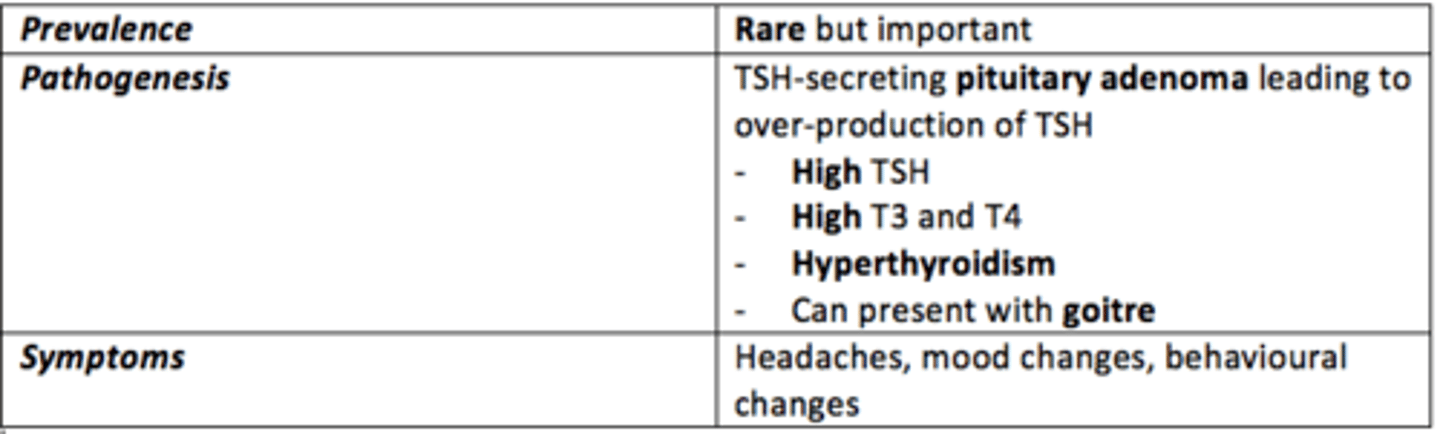
Secondary hyperthyroidism
Defect is present in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland.
Overproduction of TSH due to TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma
Hypopituitarism
Condition of diminished hormone secretion from the anterior pituitary gland
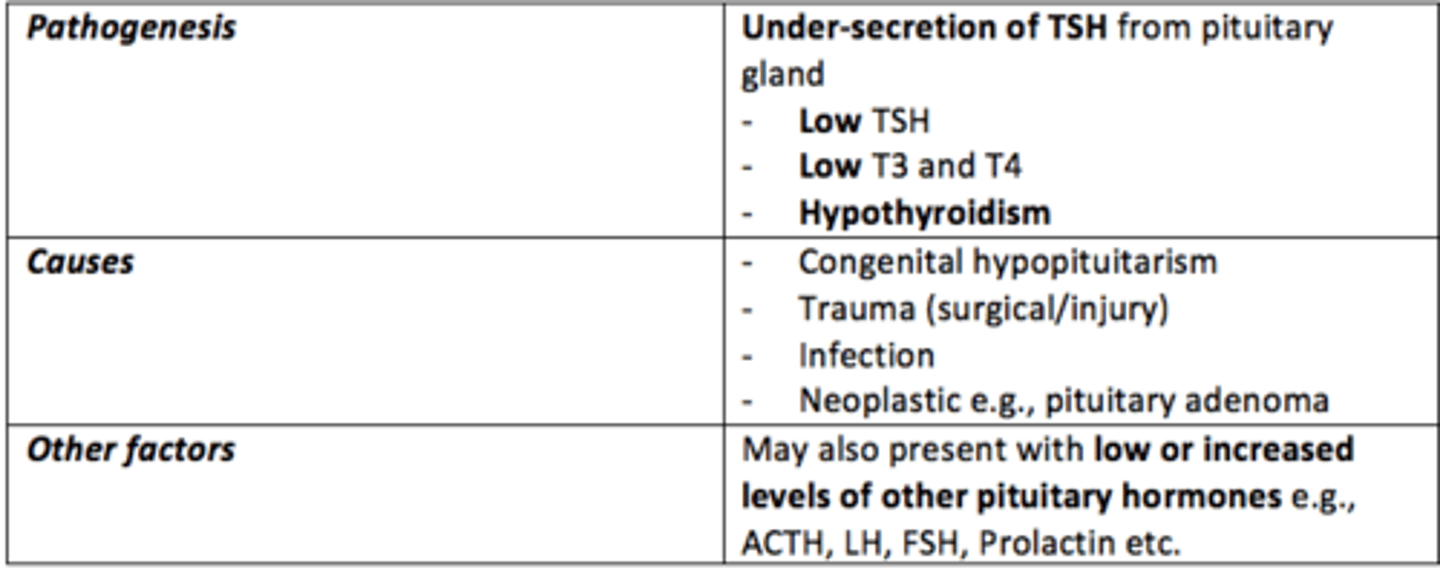
Primary hypothyroidism
Abnormality is present within the thyroid gland itself
Some causes of hypothyroidism
- Congenital
- Autoimmune
- Trauma (post-surgery)
- Iatrogenic = radioactive iodine, Lithium drugs
- Dietary = iodine deficiency
Some causes of congenital primary hypothyroidism
- Agenesis of thyroid gland
- Ectopic thyroid
- Dyshormonogenesis
Some signs/symptoms of congenital hypothyrodism
SIGNS:
decreased activity, fatigue
increased sleep
constipation
feeding difficulty
SYMPTOMS:
macroglossia: large thickened tongue
hypotonia
myxedexia
large fontanelles
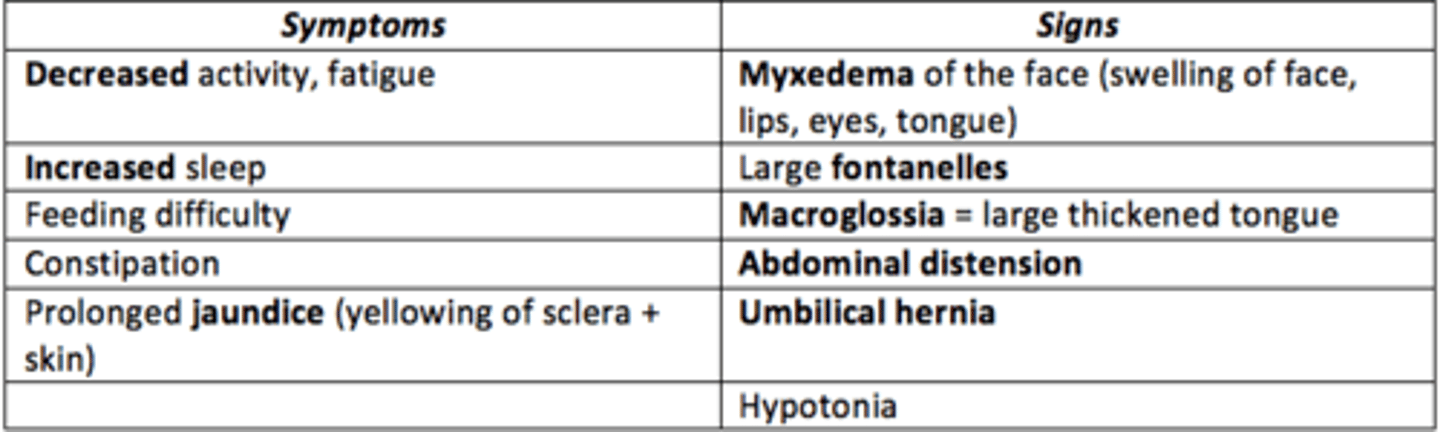
If congenital hypothyrodism is left untreated, irreversible ___ damage can occur
Neurodevelopmental damage
How is congenital hypothyroidism diagnosed?
Heel-prick test (newborn blood spot screening test) 5-days post-birth

What medication is given to children diagnosed with congenital hypothyroidism?
Thyroxine started and continued for life.
Prognosis is excellent if diagnosed and treated early!
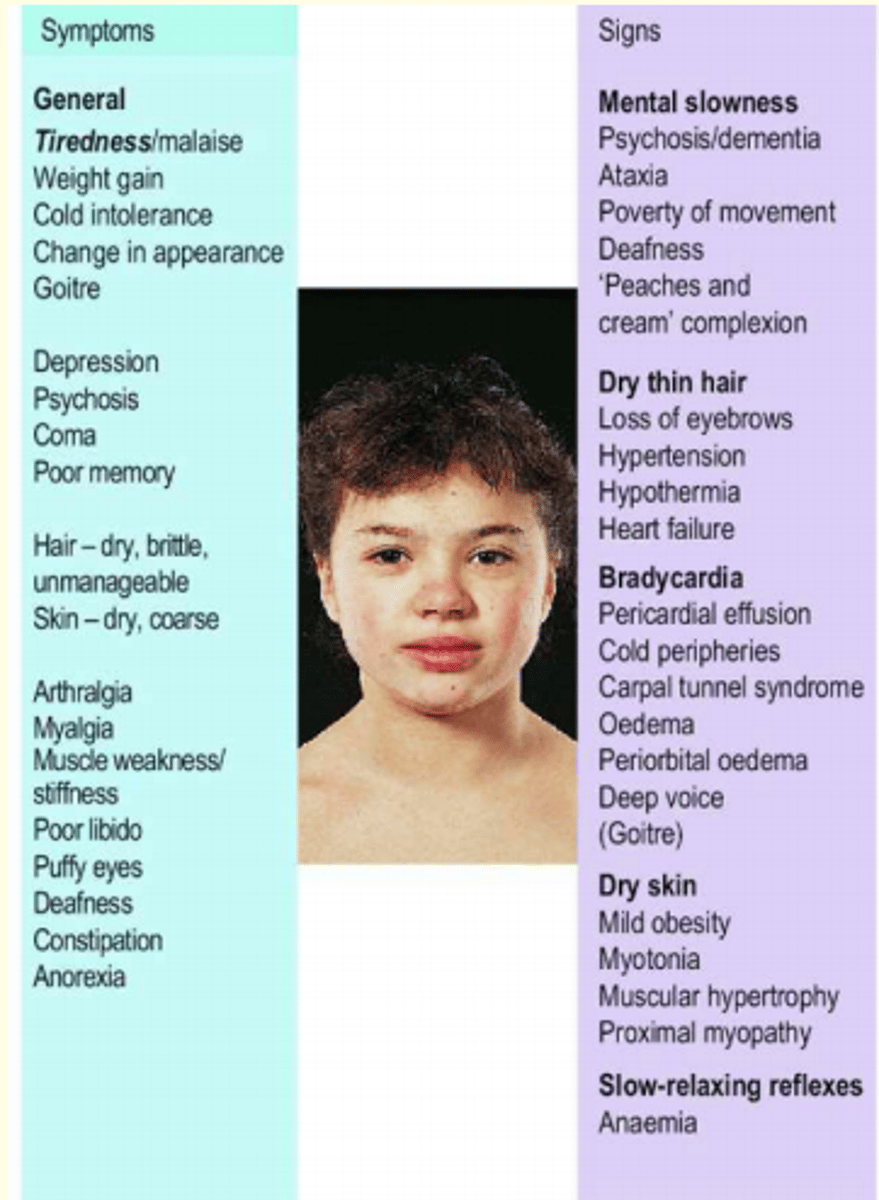
General signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism
Signs:
slow movement/carpel tunnel
dry, thin hair
oedema
dry skin
hypertension
Symtoms:
general tiredness/malaise
depression
puffy eyes
poor libido
Hashimoto's thyroiditis - causes hypothyroidism
An autoimmune disorder that attacks the thyroid gland causing hypothyroidism

Compensated euthyroidism

Sick Euthyroid Syndrome
Inpatients with any acute severe illness may have abnormalities/decreased thyroid hormones and TSH in the absence of any underlying thyroid abnormality.
Avoid measuring TFTs in ill patients, unless strong suspicion of gross thyroid disease

Some causes of primary hyperthyroidism
- Grave’s disease (TSH receptor stimulating antibody)
- Toxic thyroid adenoma
- Toxic multi-nodular goitre (older women)
- Excess thyroxine ingestion
- Teratoma
- Metastatic thyroid carcinoma
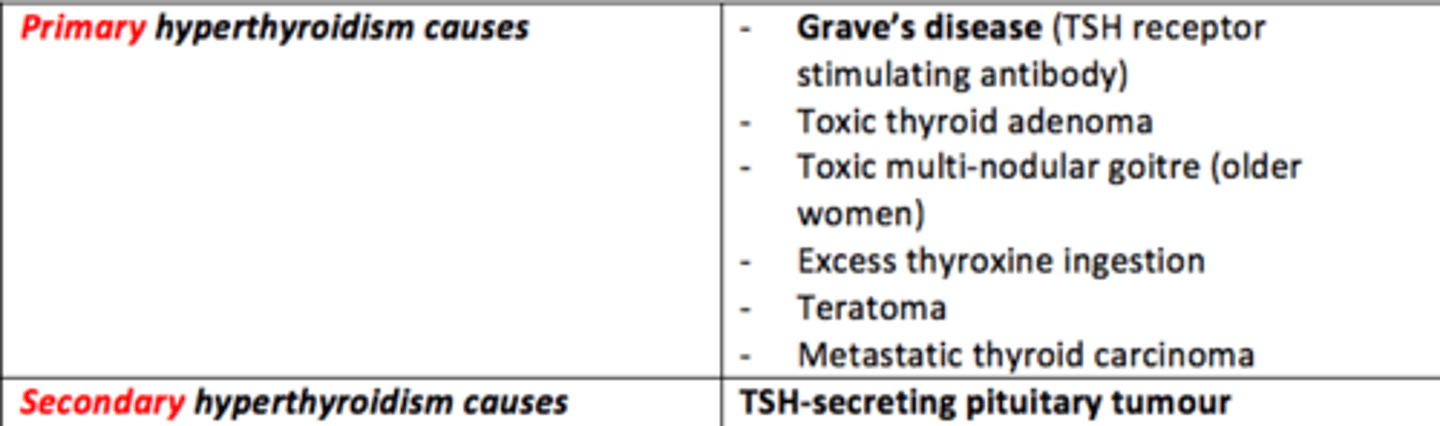
Cause of secondary hyperthyroidism
TSH-secreting pituitary tumour
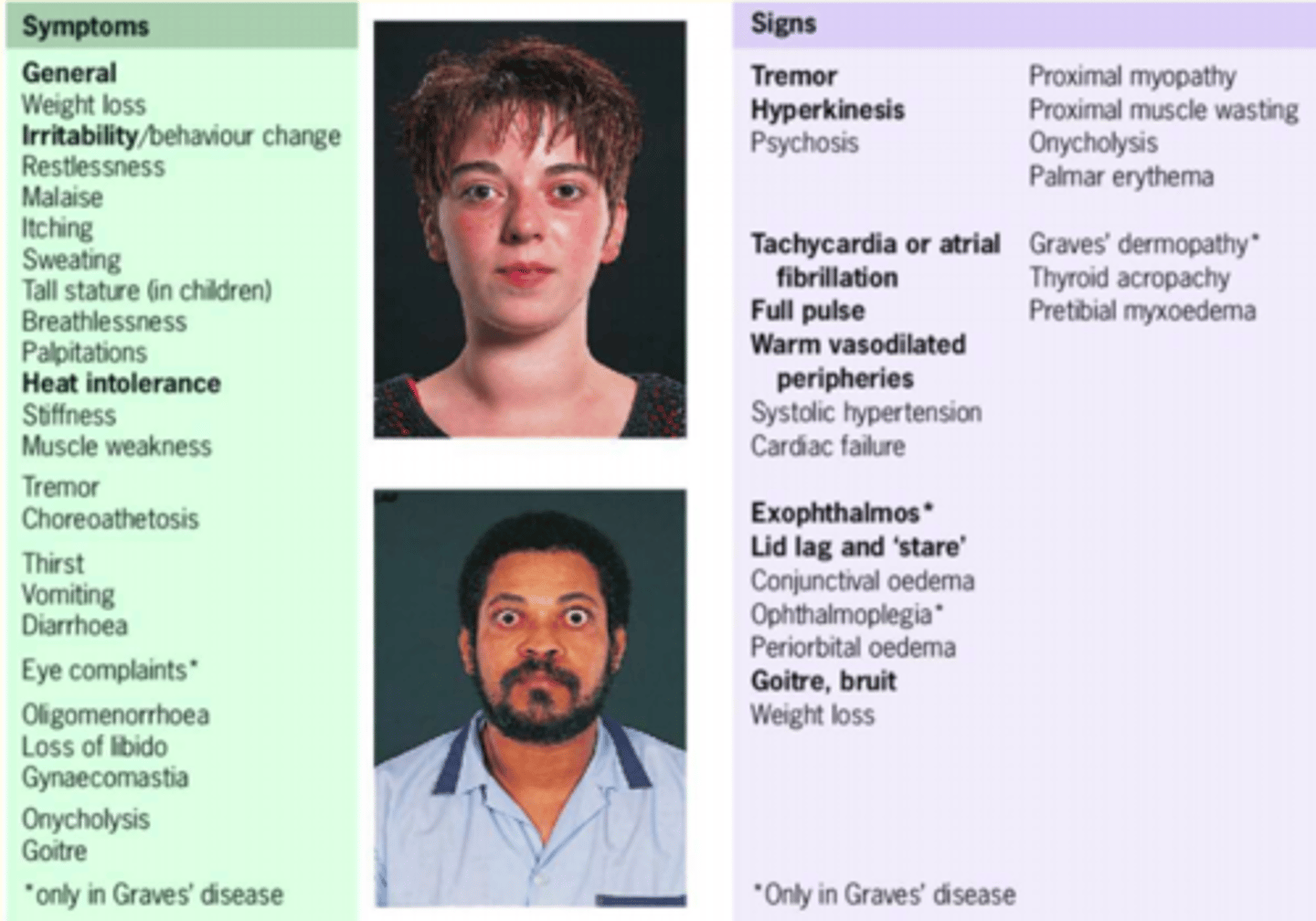
General symptoms and signs of hyperthyroidism
SIGNS:
tremor
warm vasodialated peripheries
hyperkinesis (more movement)
goitre
weight loss
SYMPTOMS:
sweating
palpatations
weight loss
heat intolerance
Grave's Disease: hyperthyroid thyroid function tests
- High Total T4
- High Total T3
- High Free T3 and T4
- Low TSH
- Thyroid receptor stimulating antibody = positive

Treatment for Grave's disease (drug which blocks thyroid hormone biosynthesis)
Carbimazole
What drug can be given for rapid relief of symptoms of tachycardia in Grave's disease?
Beta blockers
4 classes of goitre
1) Diffuse
2) Nodular
3) Tumours
4) Miscellaneous
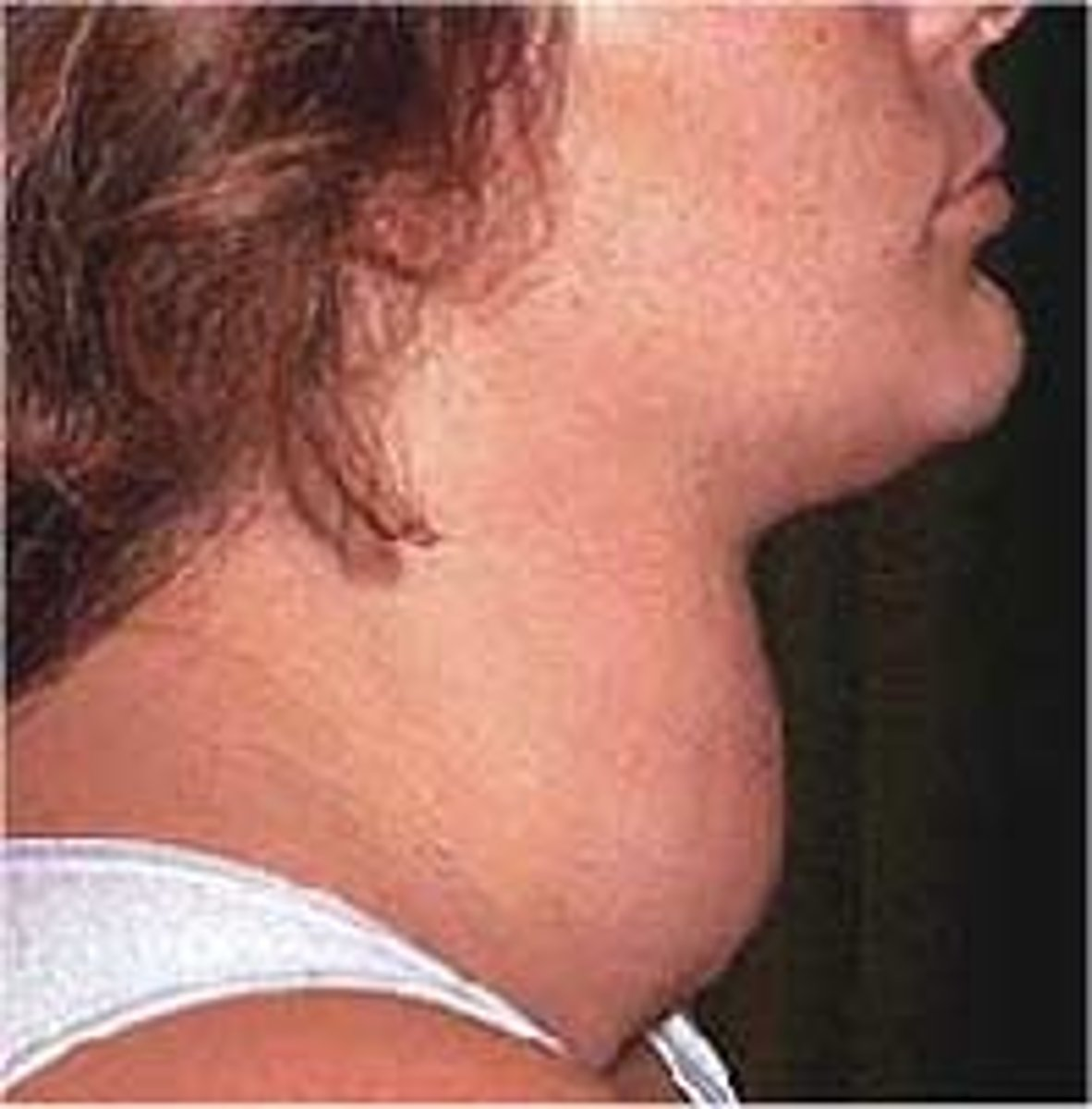
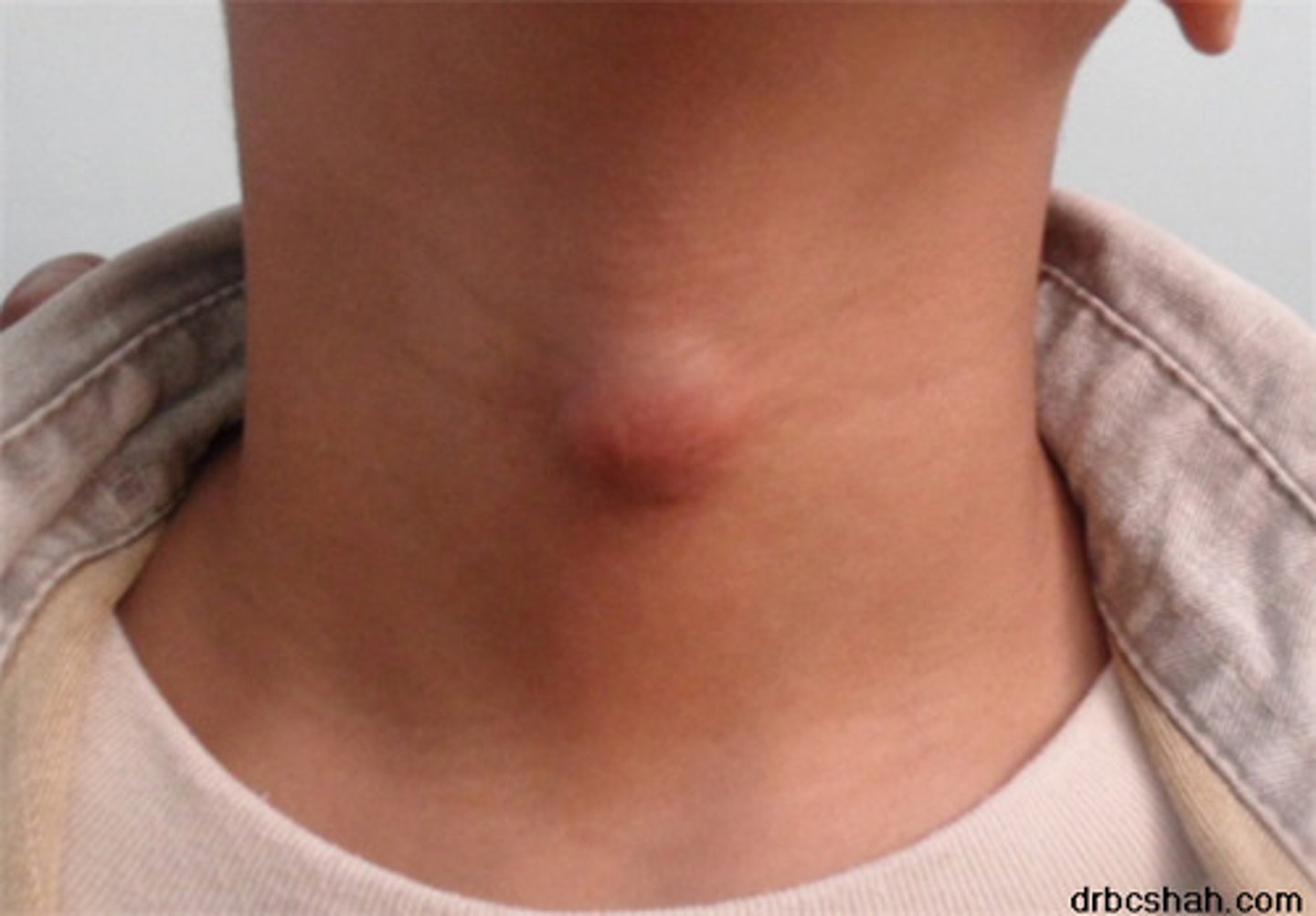
What does this image show?
Goitre
Case study
A woman aged 28 has lost 4 kg over past 4/12 months. No loss of appetite. She is irritable. Her pulse is 125 bpm.
• TSH 0.10 mU/L (0.3-5)
• Free T4 40 pmol/L (9-26).
• TSH receptor antibody positive
• She is started on propranolol tds
Which is the single most appropriate next step?
Carbimazole
3 multiple choice options
T3 thyrotoxicosis
Thyrotoxicosis is a clinical state of inappropriately high levels of circulating thyroid hormones (T3 and/or T4) in the body from any cause.
Which class of hormones do thyroid hormones belong to?
a) Glycoprotein hormones
b) Peptide hormones
c) Amino acid derivatives
d) Steroid hormones
c) Amino acid derivatives
Thyroid hormones are synthesised and stored extracellularly in the form of colloid in follicles of thyroid gland.
True or false?
True
Name the thyroid pro-hormone stored in the colloid.
Thyroglobulin
When the concentration of thyroid hormone in blood gets too low, less TSH is secreted and thyroid hormone production falls.
True or false?
False
Name the cells in the anterior pituitary that release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Thyrotrophs
The thyroid gland secretes three hormones. The two major ones are triiodothyronine (T3) and (thyroxine) (T4).
Which is the third one?
Calcitonin
Name the trace element that is needed for synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Iodine
What is the major thyroid hormone in the blood?
T4 Thyroxine
TSH has trophic effects on thyroid gland that result in increased vascularity, increase in size and number of the follicle cells.
Name the thyroid condition caused by excess TSH.
Goitre
What is the most common form of hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto's thyroiditis (disease)
A cause of primary hyperthyroidism
Graves disease