Chapter 42: The Immune System
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
a general term describing microorganisms and non-living microscopic particles that cause disease/illness to its host
pathogen
bacteria, fungi, and parasites are examples of what types of pathogens?
living organisms
viruses and prions are examples of what types of pathogen?
non-living infectious “particles”
a non-living infectious particle that has an absense of organelles, and can’t generate or store energy is a ___
virus
true or false: viruses only have single stranded DNA that codes for proteins required to assemble virions
false. viruses can have single or double stranded DNA, or RNA that codes for proteins required to assemble virions
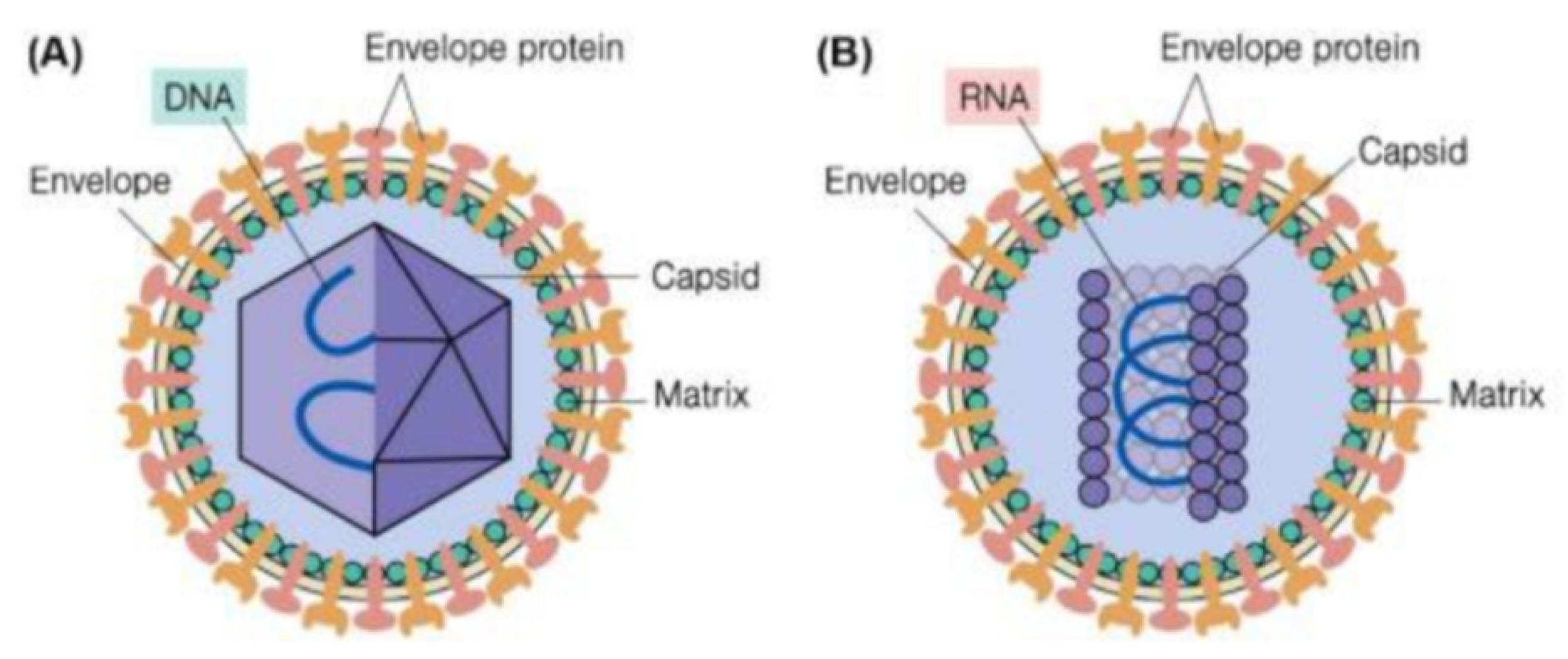
the protein shell that encapsulates the viral genome, acting as protection
capsid
true or false: some animal viruses have a lipid bilayer membrane around the nucleic acid and capsid
true
“virus fuses to host cell” describes which step of the virus life cycle?
step 1
“virus RNA, reverse transcriptase, integrase, and other proteins enter host cell” describes which step of the virus life cycle?
step 2
true or false: viral DNA is formed by reverse transcription in step 4 of the virus life cycle
false. viral DNA is formed by reverse transcription in step 3 of the virus life cycle
true or false: viral DNA is transported across the nucleus and integrates into the host cell in step 4 of the virus life cycle
true
during step 5 of the virus life cycle, new viral RNA is used as genomic RNA and to make ___
viral proteins
during step 6 of the virus life cycle, new viral RNA and proteins move to the cell surface, and a new ___ forms
immature virus
during step 7 of the virus life cycle, the virus matures when ___ releases the proteins for maturation
protease
true or false: viruses can replicate without a host; thus, they’re considered alive
false. viruses cannot replicate without a host; thus, they are not considered alive
non-living infectious particles that cause neurodegeration are ___
prions
what disease was caused by prions in the early 80s in cows, and early 90s in humans?
Mad Cow Disease
Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) was the ___
first human case of prions
true or false: prions look like misfolded brain proteins, and have the capacity of changing normal-shaped proteins into abnormal shapes
true
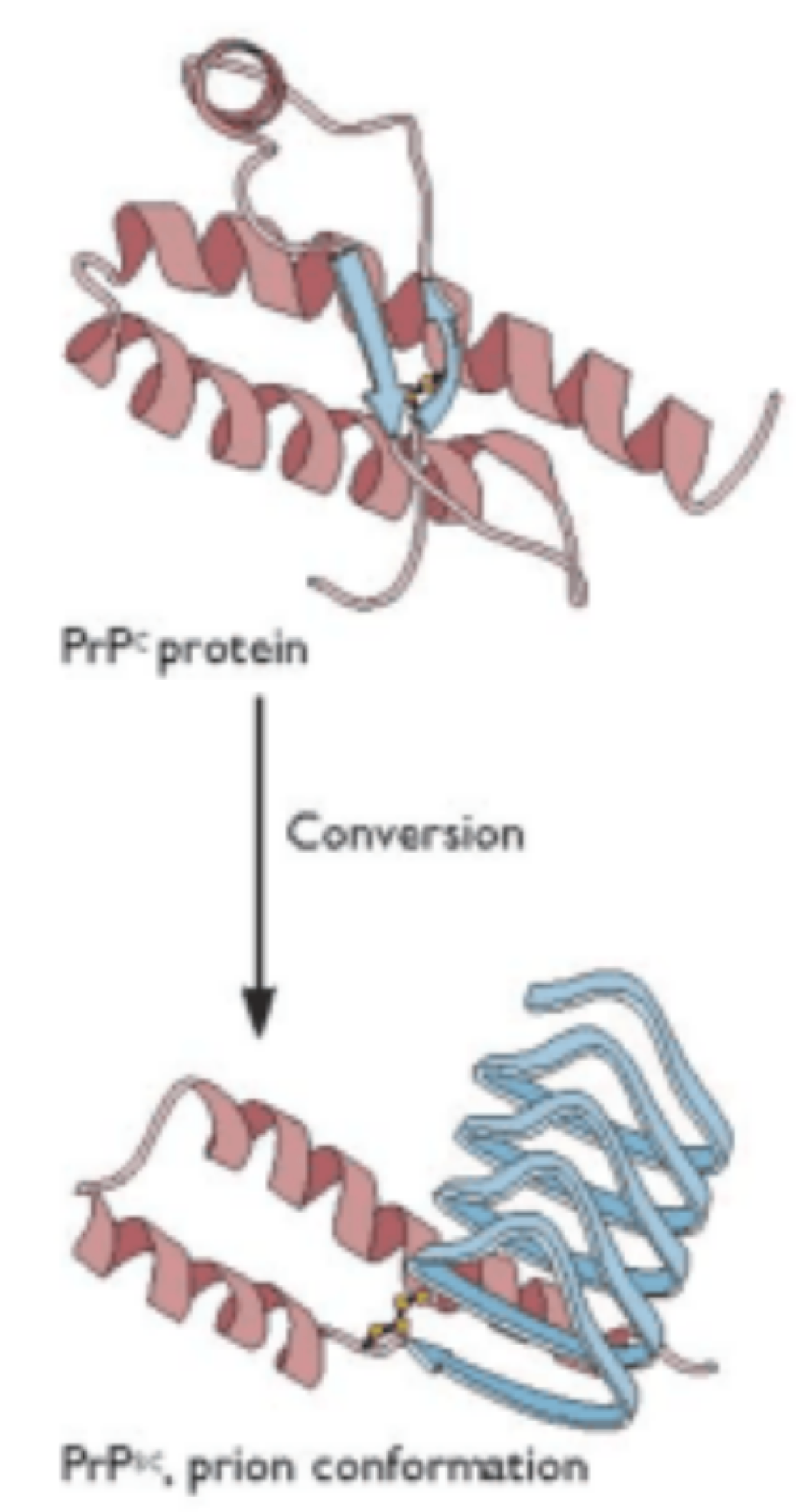
prions become self-propagating, filling neurons with debris, which leads to ___
cell death
defense mechanisms that keep pathogens out are ___
physical/chemical barriers
this type of physical/chemical barrier has multiple layers, constantly renewed cells, an acidic environment, and antimicrobial peptide
skin
these types of physical/chemical barriers have lysozyme, which cleaves chemical bonds in peptidoglycan
saliva, mucus, tears
this type of physical/chemical barrier has gastric acid
stomach
this type of physical/chemical barrier outcompetes bacterial pathogens for resources
commensal (resident) bacteria
nonspecific, fast-acting defense mechanisms make up the ___
innate immune response
these molecules are found in microbes, essential for their survival, and are recognized by Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) in the innate immune response
pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
leukocytes that destroy foreign cells via phagocytosis and are found in almost all tissue are called ___
macrophages
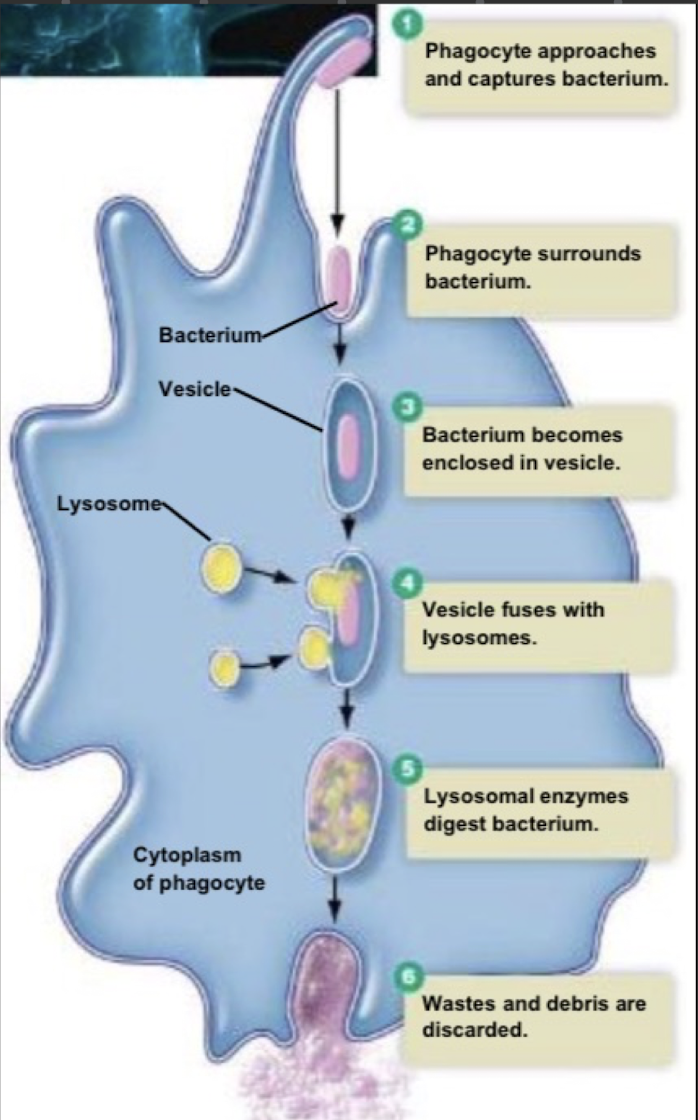
leukocytes that release cytokines once activated by PAMPs, and activate the adaptive immune system are called ___
dendritic cells
these additional components of the innate immune response are plasma proteins that circulate in an inactive state, and become activated once pathogens are present
complement proteins
true or false: complement proteins cause pathogen lysis, which are holes in bacterial cell walls
true
these additional components of the innate immune response are lymphocytes that attack cancer and virus-infected cells
natural killer cells (NK)
this additional component of the innate immune response is defined as an abnormally high level of temperature that makes your body less hospitable to pathogens and increases the body’s ability to fight infection
fever
recognizes and targets specific pathogens and foreign substances are defense mechanisms that make up the ___
adaptive immune response
this foreign macromolecule (protein or polysaccharide) reacts with immune system cells, and is one way the adaptive immune system distinguishes between “self” cells and invaders
antigen
these are proteins secreted by B lymphocytes that bind to specific antigens, and is one way the adaptive immune system distinguishes between “self” cells and invaders
antibodies (immunoglobulins)
these molecules initiate immune responses against pathogens and tumors, and are one way the adaptive immune system distinguishes between “self” cells and invaders
major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
true or false: the adaptive immune system uses “memory” to remember initial exposure and responds more slowly and calmly on frequent exposures
false. the adaptive immune system uses “memory” to remember initial exposure and responds more quickly and aggressively on frequent exposures
this immune response is part of the adaptive immune system, and uses B lymphocytes (B cells) to secrete antibodies
humoral-mediated immune response
these cells recognize antigens, then differentiate into memory B (fast response for future encounters) and plasma cells (antibody secretion)
B cells
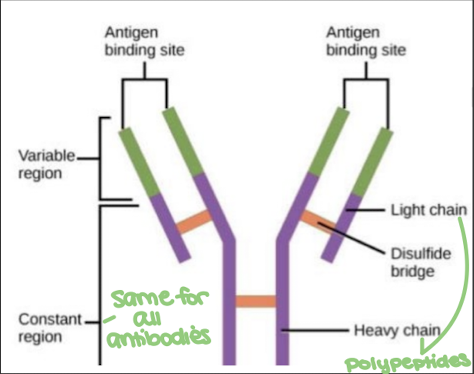
true or false: antibodies recognize antigens based on the constant region (binding site)
false. antibodies recognize antigens based on the variable region (binding site)
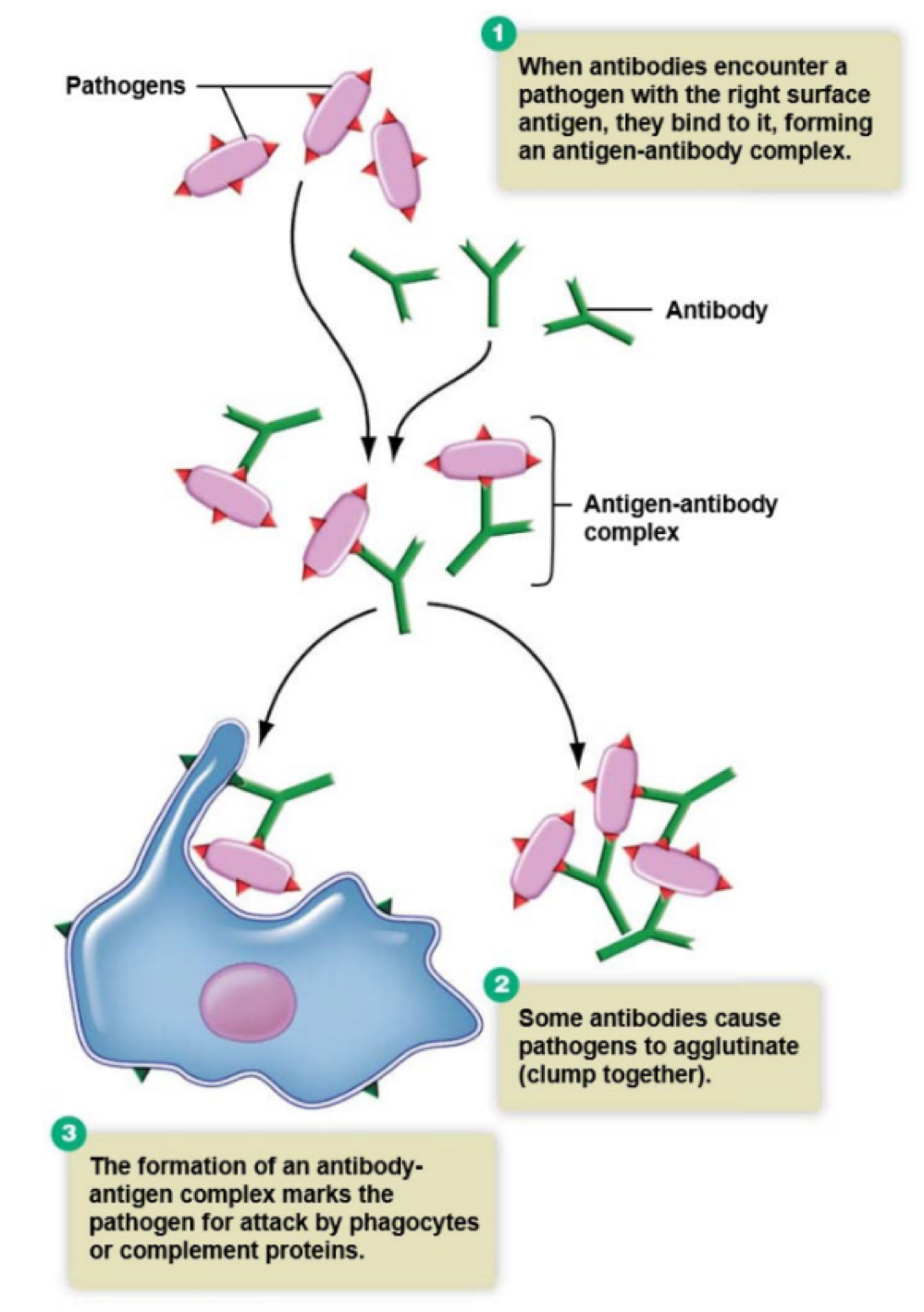
antibodies inactivate pathogens by marking them for destruction by phagocytosis, which is a process caused ___
agglutination
this immune response is part of the adaptive immune system, and use T lymphocytes (T cells) to directly attack enemy cells or coordinate the immune response
cell-mediated immune response
these cells originate from stem cells in bone marrow, mature in the thymus, and can be CD4 or CD8
T cells
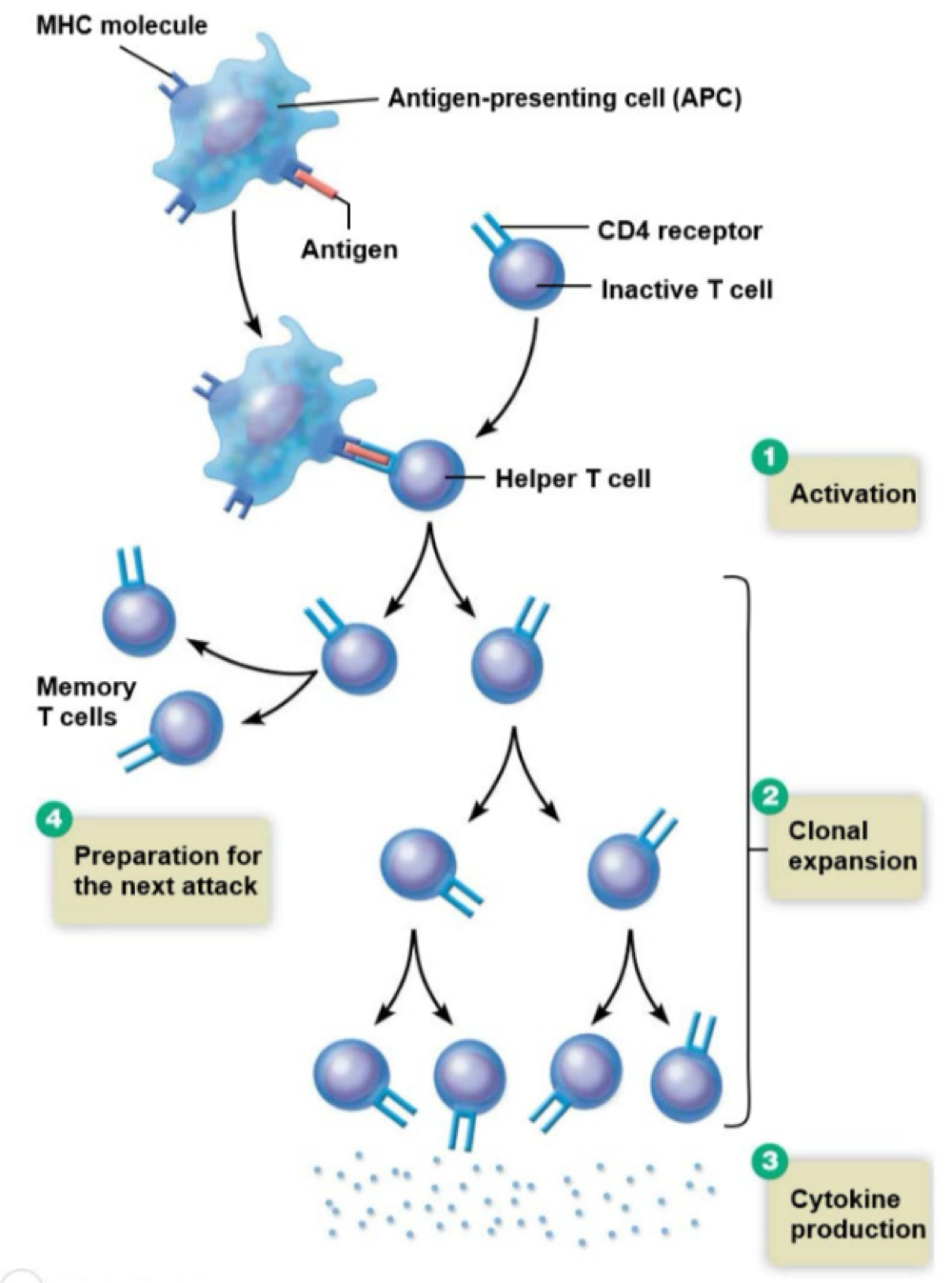
these CD4 cells are apart of the cell-mediated immune response, secrete cytokines, direct the immune response, and target HIV infection
helper T cells
these CD8 cells are apart of the cell-mediated immune response, and directly attack and destroy abornmal (e.g. tumors, infected) cells and pathogens
cytotoxic T cells
true or false: CD4 and CD8 T cells are both memory cells
true
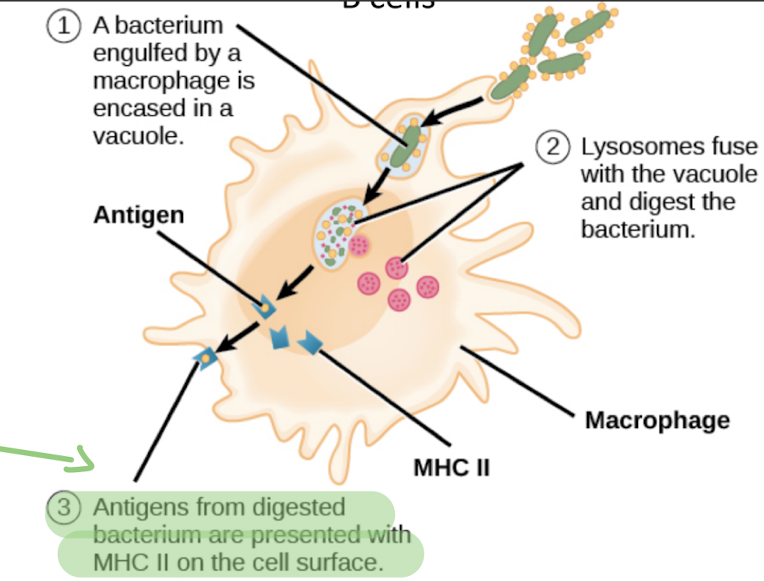
in the cell-mediated immune response, these cells must first show the antigen to T-cells so they can be recognized
antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
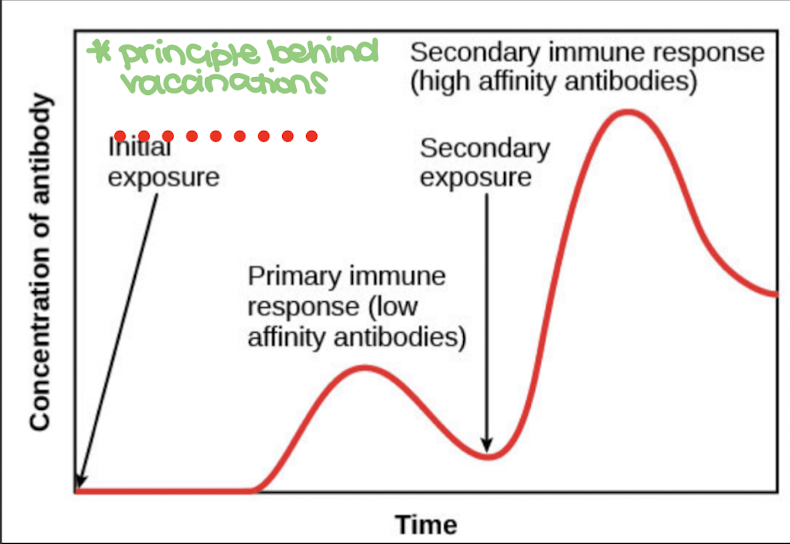
this immune response Is a type of immune memory that occurs on first antigen exposure, during which antibody production takes 3-6 days
primary immune response
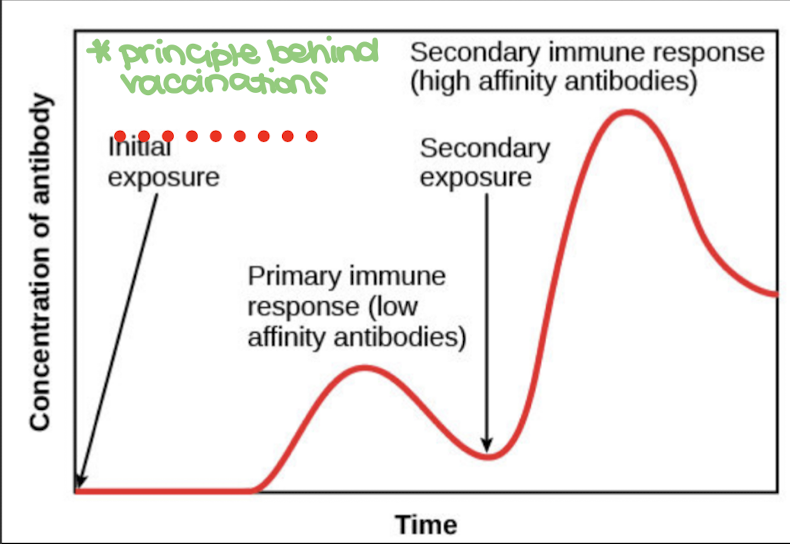
this immune response Is a type of immune memory occurs on second and subsequent antigen exposure
secondary immune response
the failure/insufficiency/delay in the immune system response, which may be acquired or inherited, is called ___
immunodeficiency
this disease is caused by infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
this virus is transmitted via body fluids (blood, semen, breast milk, and vaginal secretions)
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
true or false: HIV targets helper T cells and uses them as virus factories once infected
true