FAB Applied
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from Combined Handbook
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Langer’s lines (AKA tension/cleavage lines)
follow orientation of collagen fibres in the dermis → incisions made parallel to these lines heal more rapidly + neater scars
Venepuncture + venous cannulation
venepuncture → use median cubital vein
venous cannulation → use cephalic vein (fairly large + constant position)
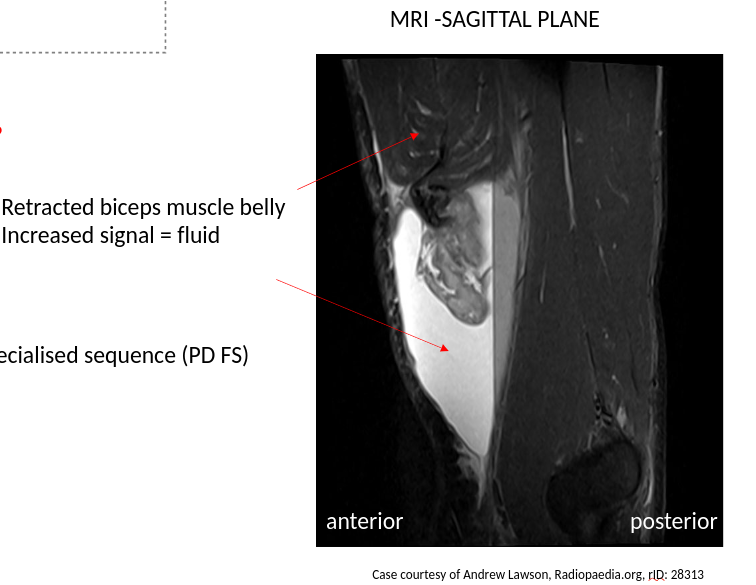
Popeye muscle
ruptured biceps tendon (proximal)
usually the long head → retracted muscle bunches up in arm, leads to bulge → short head intact so functional loss is minimal → seen in 40 - 60 yr old patients with previous shoulder problems (secondary to chronic wear + tear of tendon)
younger patients may rupture biceps tendon after a fall
distal biceps ruptures
often at the insertion into the radial tuberosity → followed by reduced strength in forearm supination + elbow flexion (requires surgery)
Humeral shaft fractures
can lead to complications like radial nerve injury (recall its location in spiral groove) → so may result in wrist drop due to compromised wrist and finger extension
90% of radial nerve palsy (associated with these fractures) recover spontaneously
supracondylar fractures
common childhood fracture
fracture of distal humerus (proximal to epicondyles)
associated with FOOSH
serious complications involve rupture/compression of brachial artery + median nerve injury (these lie anteriorly)
if pulseless hand (due to brachial artery compression) → this is an emergency
elbow dislocation
most common fracture in children → FOOSH
second most common dislocation (after shoulder) in adults
posterior dislocation is most common form of elbow dislocation
ulnar nerve runs posterior to medial epicondyle → so risk of ulnar nerve entrapment (if posterior dislocation)
brachial artery + median nerve may also be injured (but less common)
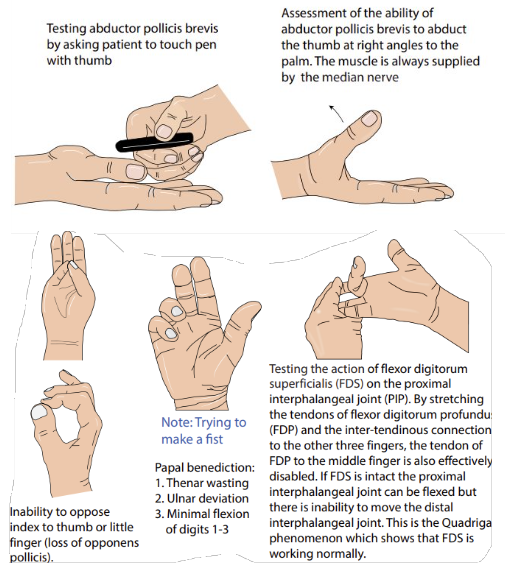
carpal tunnel syndrome
median nerve entrapment (via compression) in carpal tunnel
presents with pain and paresthesia in distribution of median nerve
thenar eminence muscle weakness
management → night splints to prevent wrist flexion, steroid injections + (extreme) surgery to remove flexor retinaculum
rupture of extensor pollicis longus tendon
fractures of distal radius can cause this (due to association with dorsal Lister’s tubercle)
unable to extend interphalangeal joint of the thumb
scaphoid fracture
commonly caused by FOOSH
scaphoid is palpable on floor of anatomical snuffbox → so presents with snuffbox tenderness (treat with applying a plaster cast + X-ray in 4 weeks)
undisplaced fracture may not be visible at first so follow up X-ray will reveal a fracture as it is healing or no fracture (so cast can then be removed)
if fracture left untreated, can lead to avascular necrosis of proximal fragment
tennis elbow
lateral epicondylitis caused by repetitive wrist extension + gripping activities → leading to pain over the lateral elbow (common extensor origin) → leads to degenerative tear
resisted wrist extension aggravates the pain
rest/steroid injections
golfer’s elbow
medial epicondylitis caused by repetitive wrist flexion + gripping activities → resulting in pain over the medial elbow (common flexor origin)
rest/physical therapy
erb’s palsy
injury to brachial plexus upper trunk (C5, C6) → from excessive downward traction on upper limb (e.g during difficult delivery/motorcycle accident)
shoulder abduction + elbow flexion + supination affected → leads to waiter’s tip
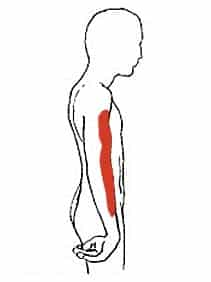
klumpke’s palsy
injury to lower trunk of the brachial plexus (C8, T1) → often due to hyperabduction of shoulder (typically during childbirth)
weakness/wasting in the hand's intrinsic muscles leading to a claw hand deformity
median nerve injury
distal lesions → carpal tunnel syndrome
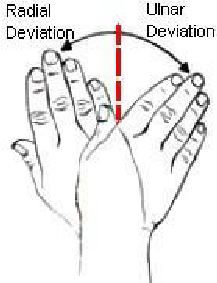
proximal lesions → inability to flex index + middle fingers + distal thumb phalanx → weakness/wasting of thenar eminence → inability to oppose + abduct thumb → impairment of precision grip → ulnar deviation at wrist
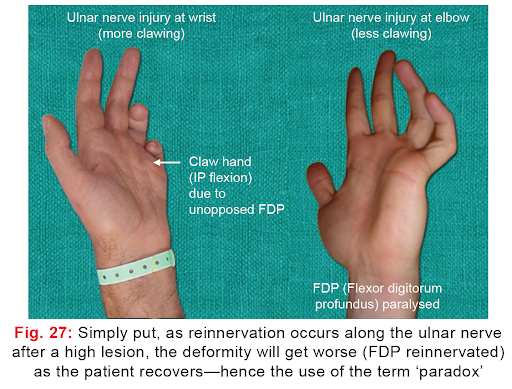
ulnar nerve injury
distal ulnar lesion → claw hand (extension of metacarpophalangeal joints + flexion of interphalangeal joints of ring and little fingers → due to paralysis of interossei and lumbrical muscles
proximal ulnar lesion → weakness in wrist flexion and adduction, impaired grip strength, sensory loss in the little finger + half of the ring finger → greater functional disability as flexor digitorum profundus branches lost but less deformity (ulnar paradox)
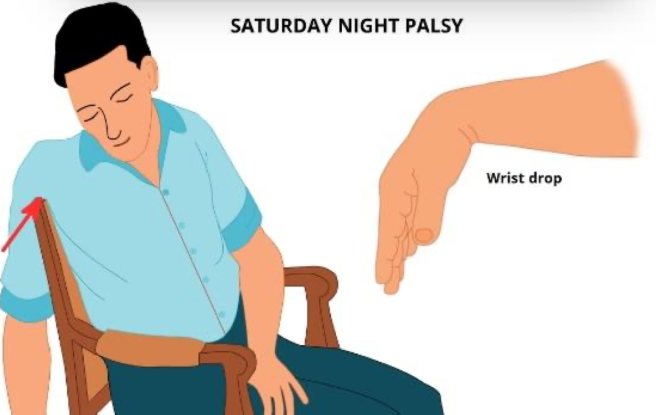
radial nerve injury
wrist drop (inability to extend wrist + fingers + thumb)
weakness of power grip (this depends on synergistic contraction of both flexors and extensors)
wrist drop and loss of active elbow extension suggest more proximal injury (axilla?)
Saturday night palsy shown →
breast cancer
most common cancer for women
axillary palpation crucial to understand lymphatic drainage of breast → for surgery
sentinel node = first lymph node/group of nodes that drain the cancer → biopsy here determines stage of cancer
axillary clearance = surgical removal of axillary nodes (but may result in long thoracic nerve injury → serratus anterior paralysis + winged scapula) → can also lead to lymphoedema (especially when combined with radiotherapy)
remember “APICAL” pneumonic for lymph nodes
clavicular fractures
common in young active males/elderly individuals
direct trauma to shoulder
force transmitted from acromioclavicular → sternoclavicular
acromioclavicular dislocation
direct trauma
little disability (yay!)
palpable + visible swelling over joint
glenohumeral dislocation
most common dislocated large joint
anteroinferior dislocations → most common
head of humerus lies anteriorly under coracoid process → recurrent dislocation is common here
damage to axillary nerve possible → deltoid paralysis → loss of sensation in arm’s “regimental badge” area
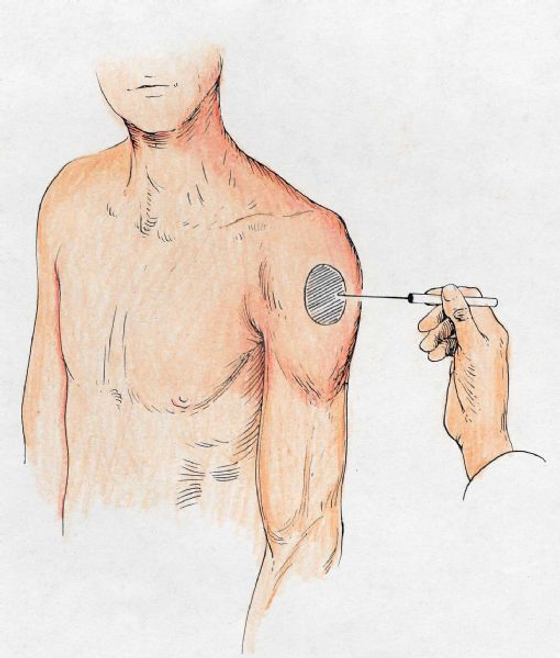
rotator cuff rupture
difficulty initiating abduction
patient may compensate by leaning over to the affected side → allows gravity to assist abduction before deltoid kicks in
scapular fractures + scapulothoracic disorders
rare → result of high energy, blunt force trauma
glenohumeral joint function impaired → posterior shoulder pain → rotator cuff bursitis/tendinitis
degenerative changes in the spine
vertical forces thru the spine → with rotational flexion/extension movements in upright posture → produce arthritic degenerative changes in facet joints + intervertebral diswcs
more likely to occur in lumbar spine
abnormal lateral curve = scoliosis
prolapsed intervertebral disc
if anulus fibrosus degenerates + ruptures → nucleus pulposus protrudes through it and puts pressure on cord/nerve roots
most common in lower lumbar region
developmental spine defects
spina bifida → incomplete fusion of posterior elements of vertebra (common in lumbar region)
meninges/spinal cord/roots may herniate thru the defect → several neurological deficits
pulled elbow
subluxation of the radius head out of the anular ligament
occurs when the hand of a child is suddenly pulled with force
subluxation = partial dislocation, where two bones that form a joint are still partially in contact but are not in their normal alignment
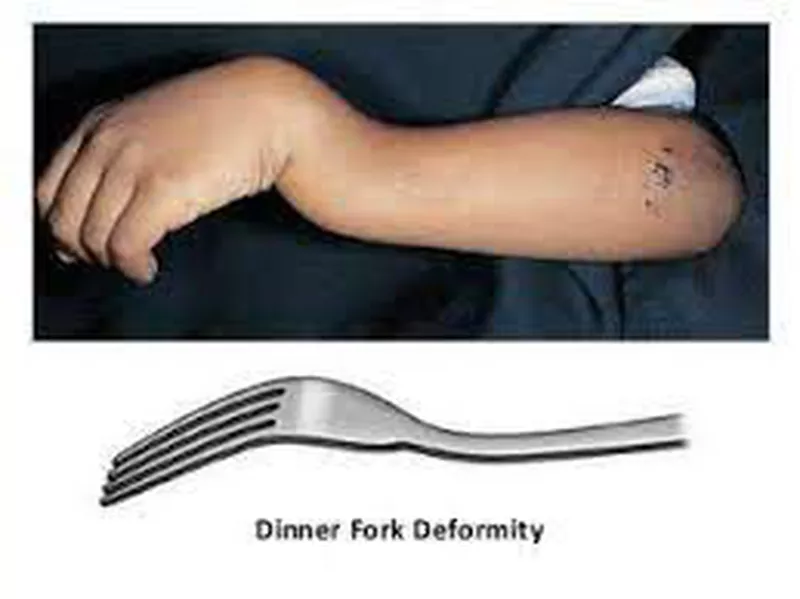
Colles’ fracture
non-articular fracture of distal radius → from FOOSH
common in patients over 50 yrs old
distal fragment is driven posteriorly + superiorly → dinner-fork deformity
reduction is necessary
Dupuytren’s contracture
(contracture = permanent tightening/shortening)
contracture of the palmar fascia → fixed deformities in the hand + finger joints
surgical treatment → removing strands of contracted fascia without damaging the interwoven digital nerves
tenosynovitis
inflammation of flexor tendons + synovial sheaths (from chronic repetitive use/trauma/arthritis)
symptoms → pain, swelling, difficulty moving the inflamed joints
trigger finger → finger remains in flexed position
metacarpal fracture
boxer’s fracture → resultant transverse/short oblique fracture at neck of 5th metacarpal
Guyon’s canal
fibro-osseous tunnel between pisiform + hook of hamate
site of ulnar nerve compression
(but less common than median nerve carpal tunnel compression)
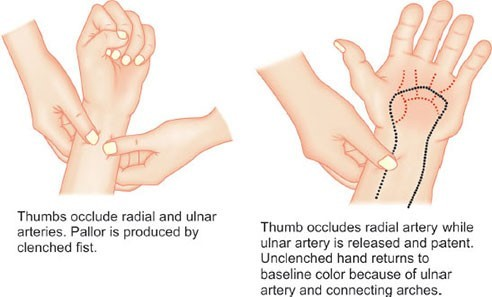
Allen’s test
assess collateral circulation to hand
most people should have dual blood supply via anastomoses between deep and superficial arches
puncture + cannulation of radial artery can lead to injury + ischaemia in subjects without dual blood supply
internal jugular vein surface marking
runs from lobe of ear to → sternoclavicular joint
access from triangular space between sternal + clavicular heads of sternocleidomastoid/ deep to posterolateral border of SCM
important for insertion of central venous lines → closely related to lung apices so care must be taken to avoid puncturing pleura (take a chest radiograph after procedure)
external jugular vein surface marking
runs from lobe of ear to → midpoint of clavicle
important for insertion of central venous lines → closely related to lung apices so care must be taken to avoid puncturing pleura (take a chest radiograph after procedure)
torticollis/wryneck
spinal accessory nerve irritation (as lies next to lymph nodes so these can irritate spinal nerve if inflamed)
SCM + trapezius excessive contraction → head pulled down to affected shoulder, face rotated in opposite direction
in babies → SCM may tear during childbirth → can cause this
lymph node biopsy can also cause this
complete loss of function? → droopy shoulder (trapezius paralysis + unopposed SCM action)
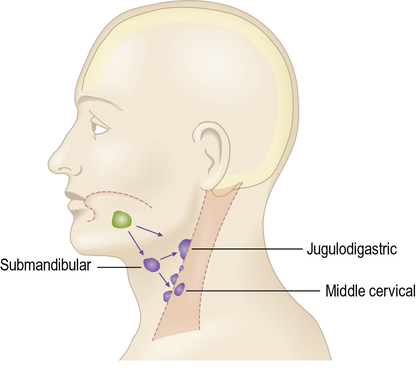
acute tonsillitis
jugulodigsatric lymph nodes (in triangles of neck) → enlarged
wounds in posterior triangle
can damage brachial plexus on its way to upper limb
thoracic outlet/inlet syndrome
compression of neurovascular structures in thoracic inlet/outlet (just above 1st rib but behind clavicle)
affected structures → brachial plexus lower trunk, subclavian vein, subclavian artery
symptoms → ischaemia, swelling, pain, paraesthesia of hand, wasting of muscles supplied by C8 + T1 roots
cervical rib from C7 can be a possible cause
tracheostomy (in children)
tracheostomy = surgical procedure creating an opening (stoma) in the front of the neck to access the windpipe (trachea)
left brachiocephalic vein crosses to the right behind the manubrium
may lie above suprasternal notch in children
at risk during a tracheostomy
referred phrenic nerve pain
inflammation of subphrenic organs (e.g gallbladder) → can involve peritoneum → cause referred pain to C3, C4, C5 dermatomes → shoulder tip
pneumothorax
entry of air into pleural cavity (either from penetrating wound of parietal pleura/rupture of pulmonary lesion into the pleural cavity) → leads to lung collapse
with a chest wound, blood may enter pleural cavity → haemothorax
inhaled foreign bodies (lungs)
right main bronchus is wider + shorter + more vertical
so inhaled foreign bodies more likely to pass down right bronchial tree
supine position → likely to pass to the apical lower lobe segment (1st lobe to arise posteriorly) → risk of pneumonia
standing/sitting position → likely to pass to one of the basal bronchi
carcinoma of bronchus
primary lung cancer (AKA bronchogenic carcinoma) → most arise in mucosa of large bronchi + produce a persistent/productive cough or haemoptysis (coughing up blood)
lung tumours metastasise early to bronchopulmonary lymph nodes → to other thoracic nodes
common metastases → brain, bones, other parts of lung, liver, adrenal glands
other cancers often commonly metastasise to the lungs
pericardiocentesis
fluid aspiration (removal) from the pericardium → needle inserted immediately left of xiphisternum + directed upwards to tip of left scapula → allows aspiration without lung puncture
relief of cardiac tamponade (emergency situation, no time for ultrasound)
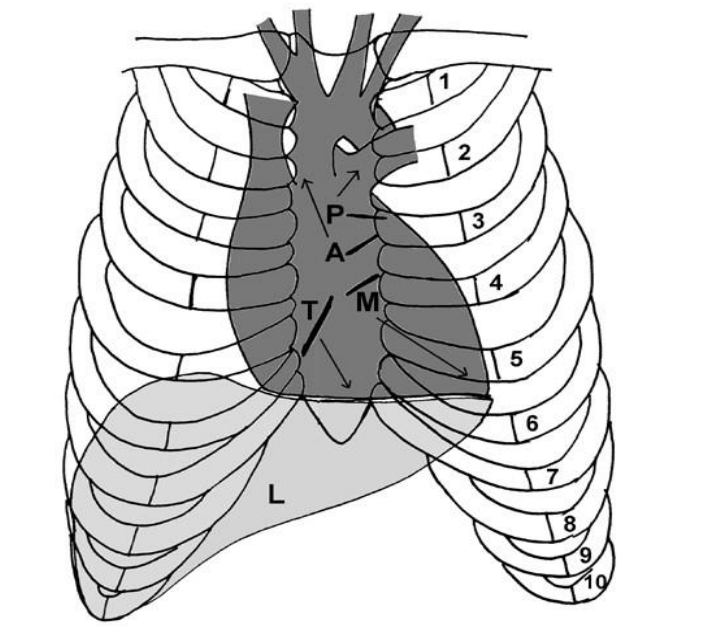
heart surface markings
vertical line of valves (superior to inferior) → “PAMT”
right: 3 - 6 costal cartilages
left: 2nd costal cartilage → 5th intercostal space
auscultation points:
Pulmonary valve → 2nd and 3rd left intercostal spaces
Aortic valve → 2nd right intercostal space radiating up to the neck
Mitral valve → apex, 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line
Tricuspid valve → lower left sternal edge, may also be heard on the right
coronary artery disease
stenosis/occlusion of coronary arteries (from atherosclerosis due to lipid deposition)
anastomoses between coronary arteries not very effective → myocardial infarction is a common consequence
treatment → angioplasty (radiologically controlled balloon dilatation) / coronary bypass grafting (using great saphenous vein/internal thoracic artery/radial artery)
conduction defects (heart)
often cause by ischaemia (coronary artery disease)
damage to heart’s conducting system
disturbances of cardiac muscle contraction
occlusion of nodal branches of right coronary artery → may result in heart block (to different degrees)
pacemaker may need to be implanted → to maintain appropriate ventricular contraction rate
congenital heart defects
septal defects → differential pressures between 2 sides of heart → blood flow from left to right → no cyanosis → surgical repair
persistent ductus arteriosus → blood passes from left to right → initially no cyanosis but right heart is strained → right heart pressure may rise until shunt reversal so cyanosis
tetralogy of Fallot → pulmonary outflow stenosis, interventricular septal defect, right ventricular hypertrophy, over-riding aorta
right heart pressure rises → blood shunted from right to left → cyanosis
oesophageal varices
portal hypertension → dilatation of lower oesophageal submucous veins
can rupture → severe haemorrhage
treatment: endoscopic band ligation (stops acute bleeding + prevents recurrent bleeding)
chylothorax
presence of lymphatic fluid in pleural space
secondary to leakage from thoracic duct
malignancy (e.g lymphoma) or trauma can cause this
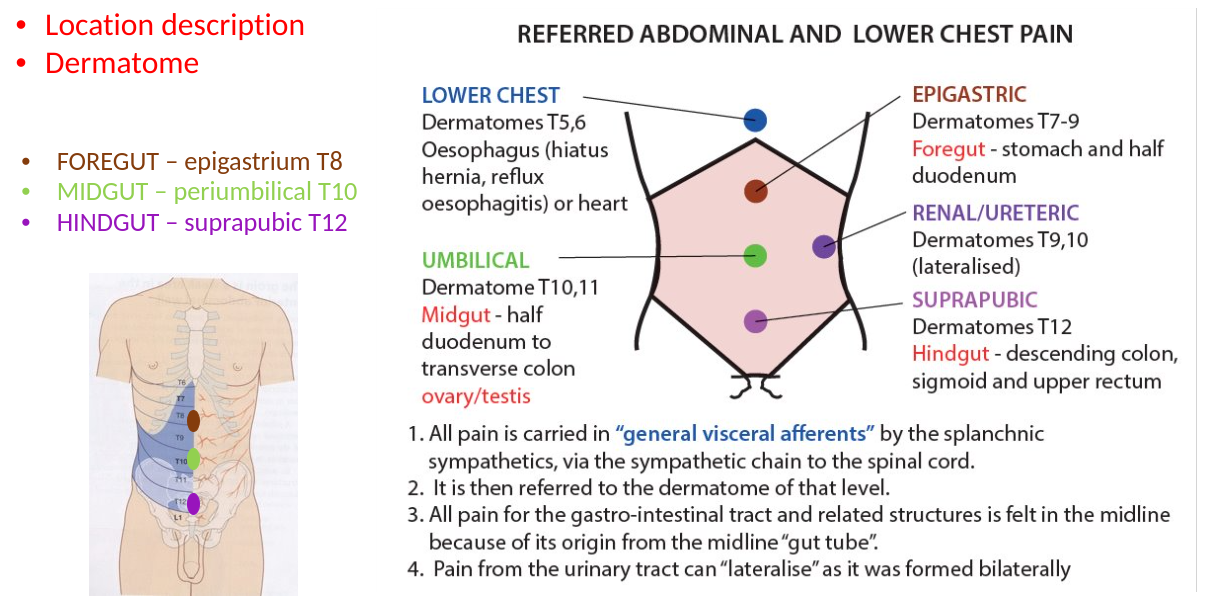
referred pain (from splanchnic nerves)
pain from foregut structures → referred to epigastric region (general viscerals with greater splanchnic nerve)
pain from midgut structures → referred to umbilical region (general viscerals with lesser splanchnic nerve)
pain from hindgut structures → referred to suprapubic region (general viscerals with least splanchnic nerve)
intercostal nerve block
injection of local anaesthetic directed towards the costal groove in upper part of intercostal space → to directly reach intercostal nerve
(different concept to triangle of safety)
diaphragmatic paralysis
injury to phrenic nerve
bilateral damage → can lead to rapid ventilatory failure
trachea-oesophageal fistula
congenital abnormality
connection between trachea and oesophagus
other congenital issues → blind-ending oesophagus/atresia
abdominal incisions
longitudinal incisions → exploratory operations (along midline or paramedian)
muscle-splitting incisions → McBurney incision for appendicectomy
subcostal incisions → access to liver, biliary tract + spleen
suprapubic (Pfannenstiel) incisions → gynaecological/obstetric operations
acute appendicitis referred pain
(midgut)
referred to periumbilical region → as inflammation profresses, parietal peritoneum is involved so pain is localised to right iliac fossa
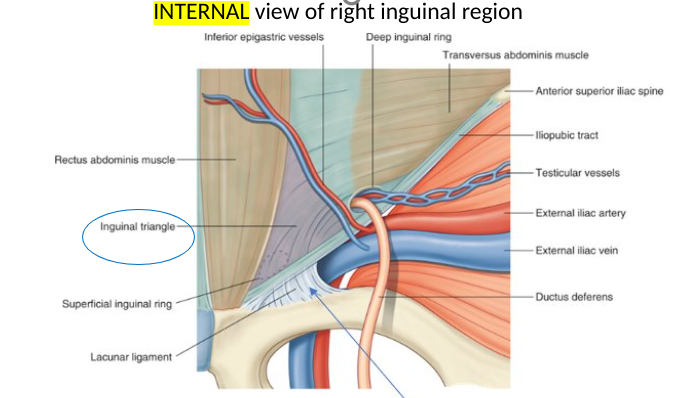
inguinal hernia
inguinal canal → site of weakness
direct hernia → protrudes thru weakend conjoint tendon, medial to inferior epigastric artery
indirect hernia → passes thru deep ring, initially lateral to inferior epigastric artery but then down to canal → can reach scrotum
femoral hernia
thru femoral canal (below + lateral to pubic tubercle)
more frequent in women
prone to strangulation (requires emergency surgery)
exomphalos (congenital abdominal)
defect in abdominal wall
herniation of intra-abdominal contents into base of umbilical cord
omphalocele can form (can range from an umbilical hernia to a large mass containing most of the visceral organs)
ectopia vesicae AKA exstrophy (congenital abdominal)
defect of anterior wall of the bladder + anterior abdominal wall → results in exposed, everted posterior bladder wall
umbilical hernia
common in neonates, particularly premature births
usually herniation of small bowel → neck of hernia is wide so strangulation is rare
close spontaneously within first few years
peritanitis (abdomen)
bacterial contamination during surgery/gut rupture post-infection or inflammation
allows gas + gastric contents + bile + faecal matter to enter peritoneal cavity
pain in overlying dermatome + rigidity in anterior abdominal muscles
ascites (abdomen)
excess fluid in peritoneal cavity
caused by secondary carcinoma, cirrhosis or other things
gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD)
reflux of gastric contents into oesophagus → heartburn + acid regurgitation
incompetent lower oesophageal sphincter can be a cause
associated with hiatus hernia → portion of stomach prolapses thru oesophageal opening in diaphragm
peptic ulceration (abdomen)
posterior gastric ulcers can erode into the splenic artery → causes torrential haemorrhage
gastric contents can enter lesser sac
pyloric stenosis can be congenital or acquired → congenital most common in boys in first few weeks (presents with projectile vomiting) → acquired cases from peptic ulceration
carcinoma of the stomach
poor prognosis
because impossible to ensure complete removal of involve lymphatics due to extensive drainage
appendicitis
inflammation
→ leads to thrombosis of appendicular artery → then necrosis → then perforation
pain referred to T10 dermatome (around umbilicus) → as inflammation progresses, will irritate parietal peritoneum → somatic innervation so pain felt in right iliac fossa
appendix on a mesentery → mobile so may be difficult to diagnose
differential diagnoses include Meckel’s diverticulum (which lies on antimesenteric border of ileum) or ectopic pregnancy (where the fetus embeds NOT in the uterus, often in the ampulla of fallopian tubes → erodes away that area)
Meckel’s diverticulum
embryological remnant of vitellointestinal duct (connects gut tube to yolk sac)
typically 3 - 5cm long → found within 60-100cm of ileocaecal valve
can become inflammed
differential diagnosis for appendicitis
situs inversus (congenital abdominal)
all organs are transposed to opposite side
appendix is therefore in the left iliac fossa → clinical signs/symptoms may be confusing
congenital malrotation of the gut → normal rotation of bowel does not occur fully → appendix may be in an abnormal position
colicky pain
comes and goes in waves
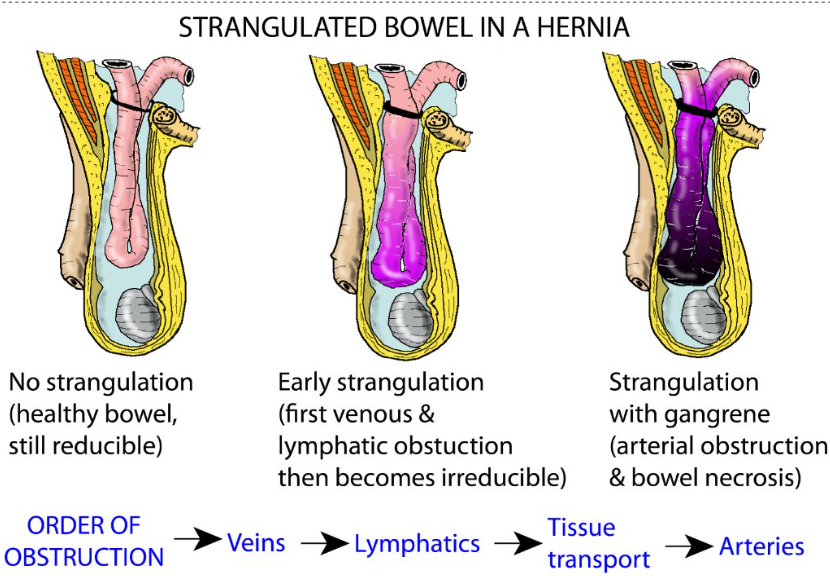
hernia language (reducible - irreducible - strangulated - obstructed)
Reducible – can be pushed back into the abdominal cavity with gentle manual pressure.
Irreducible – cannot be returned to the abdominal cavity AKA incarcerated
Strangulated – a hernia that is so tightly incarcerated outside the abdominal wall that the intestinal or omental blood supply is cut off putting it at risk of ischaemia, followed by necrosis and possible perforation leading to peritonitis.
Obstructed – occurs when a part of the intestine (usually small bowel) becomes twisted within the hernia, causing an intestinal obstruction. The hernia can become increasingly painful. Vomiting may also result.
Note : can be either strangulated, obstructed or both
indirect vs direct inguinal hernias
indirect → passes thru inguinal canal and both rings
direct → does not enter deep ring (but may go thru superficial ring) → thru Hasselbach’s triangle
deep inguinal ring surface marking
midpoint of inguinal ligament
½ between ASIS and pubic tubercle
femoral artery surface marking
midinguinal point
½ between ASIS and pubic symphysis
Hasselbach’s triangle
where direct inguinal hernia protrudes thru
lateral border: inferior epigastric vessels
medial border: rectus abdominis (lateral side)
inferior border: inguinal ligament
why are femoral hernias more prone to strangulation?
narrow femoral canal
rigidity of femoral ring
valvulae conniventes AKA Kerckring folds
circular folds of small intestine
more common in jejunum
tend to be more central than large bowel
hernia management
immediate: decompression + IV fluids + pain relief
if hernia is irreducible → surgery needed
surgical: laparoscopic with a mesh (to strengthen abdominal wall)
abdominal hernia symptoms
abdominal pain
obstruction → constipation → vomiting
bowel hernia complications
spermatic cord layers are continuous with abdominal wall muscles

patent processus vaginalis
failure to obliterate processus vaginalis
→ congenital indirect inguinal hernia
abdominal aorta levels
T12 → coeliac trunk
L1 → superior mesenteric artery
L3 → inferior mesenteric artery
abdominal pain dermatomes (a chunky one, just a heads up)
take a break
lock in mf

imaging for appendicitis
ultrasound → preferable for younger patients (lack of ionising radiation)
CT → highly sensitive + specific (used with an IV contrast)
appendicitis management
RISK? → it could rupture blood vessels → toxic digestive stuff and enzymes spill out into peritoneal cavity
immediate → resuscitation + antibiotics + pain relief
non-surgical → if patient is stable, antibiotics + CT/US-guided drainage of peri-appendiceal abscesses administered
surgical → if patient becomes peritonitic (abdomen becomes swollen and red) → appendectomy (open or laparoscopically)
colorectal carcinoma (differentials)
3rd most common cancer
differential diagnoses → diverticulitis/diverticular mass or stricture → gynaecological mass (uterus or ovary) invading or causing compression of bowel
Diverticular disease vs Diverticulitis
Diverticulosis = multiple pouches (diverticula) in the colon
Diverticular disease = when they are symptomatic – bloating, pain, constipation etc
Diverticulitis = clinically inflamed
low fibre diet in West a possible cause?
typically in sigmoid colon
diverticular disease complications
rectal bleeding
diverticular bleeding is the most common cause of acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding
acute inflammation
obstruction
abscess formation
perforation
fistula formation (rare)
sigmoid volvulus
has a relatively narrow mesentery → so quite mobile → prone to twisting
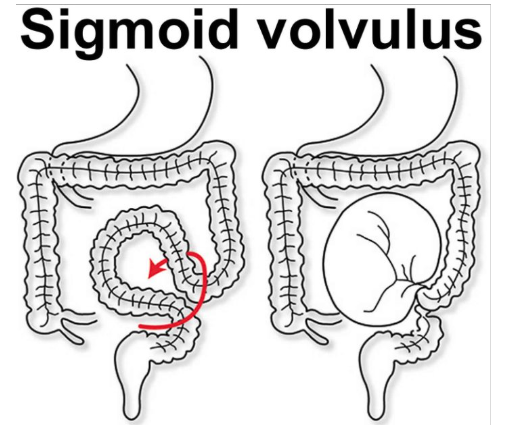
sigmoid volvulus → coffee bean sign
on a radiograph →
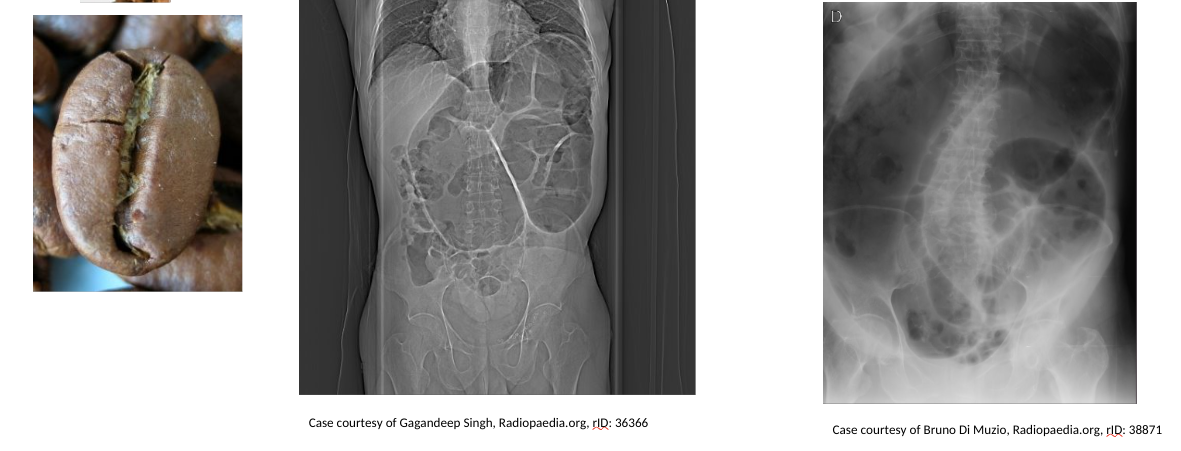
Popeye’s muscle radiograph
watershed area (hint: think vascular)
regions of the body, that receive dual blood supply → from the most distal branches of two large arteries
e.g splenic flexure of the large intestine
upper limb pulses
motor median nerve testing
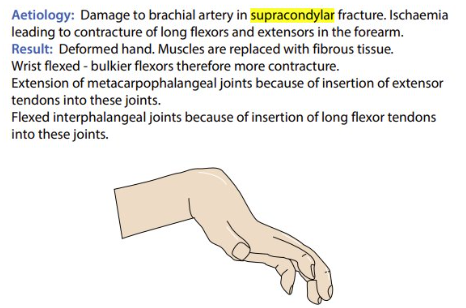
Volkmann’s Ischaemic Contracture
supracondylar fracture
brachial artery damage → ischaemia → contracture (permanent shortening + stiffening) of forearm long flexors and extensors
deformed hand → muscles replaced with fibrous tissue → wrist flexed
extension of metacarpophalangeal joints + flexion of interphalangeal joints
supracondylar fracture management

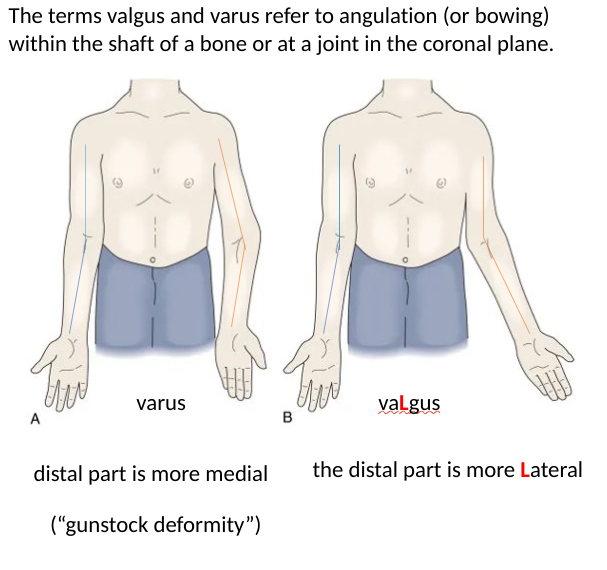
varus vs valgus
the example in diagram is a complication of supracondylar fracture
what is an autonomous sensory zone?
part of dermatome that has no overlap from adjacent nerves