Astronomy exam review SNC1W1
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
star
Massive collections of hot gases that radiate large amounts of energy.
planet
A large celestial object that travels around a star.
satellite
A celestial object that travels around a planet or dwarf planet in a closed path.
galaxy
Huge collections of stars, gas, dust, and planets.
astronomy
The scientific study of celestial objects beyond Earth.
dwarf planet
Celestial objects that orbit around a star and have enough mass to be pulled into a stable sphere shape by gravity but do not dominate their orbit.
asteroid
Small celestial objects made of rock and metal.
meteoroid
Chunks of rock and metal that are smaller than asteroids.
comet
Large chunks of ice, dust, and rock that orbit the Sun.
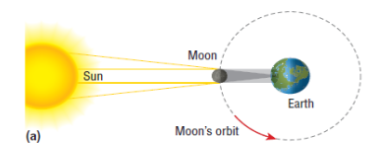
solar eclipse
When the Moon is aligned between Earth and the Sun, it blocks the Sun from being observed from Earth.
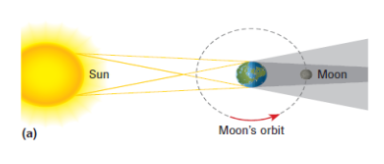
lunar eclipse
When Earth is positioned between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon.
constellation
Regions of the sky where stars can appear as a pattern.
Small to Medium Star (< 5 solar masses) life cycle
Red giant, white dwarf, black dwarf
Large Stars (10 to 30 solar masses) life cycle
Red super giant, supernova, neutron star
Extremely Large Star (> 30 solar masses) life cycle
Red supergiant, supergiant, black hole
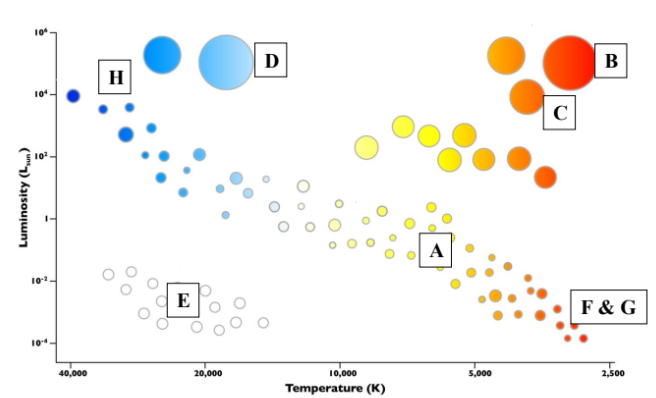
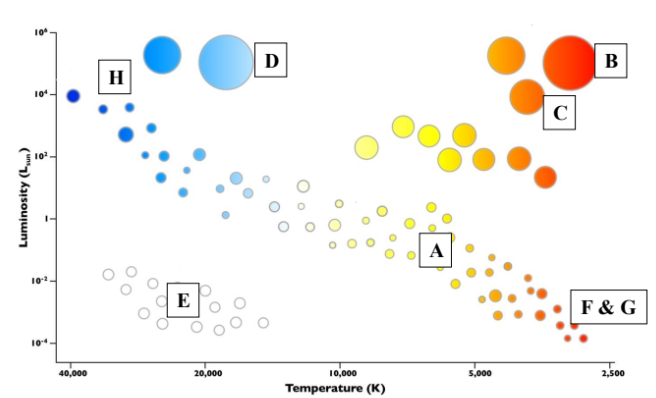
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
A) The Sun D) Blue Supergiants G) Oldest Stars
B) Red Supergiants E) White Dwarfs H) Youngest Stars
C) Red Giants F) Red Dwarfs
ways in which early people used astronomy in their daily lives
Planting and harvesting crops
Navigation
Religious/Cultural significance
Planting and harvesting crops
Stars exhibit patterns marked by the changing of the seasons.
Navigation
People living in areas surrounded by water had no land to use as a reference point, and often used stars for navigation.
Inner planets
Rocky surfaces
small in size
few to no moons.
Outer planets
Large in size
many moons
composed mostly of gases (and some liquids); no solid surface.
Retrograde motion
Certain planets farther from the Sun than Earth exhibit a reversal of direction in their apparent path across the sky due to Earth passing them in its orbit, creating an optical illusion.
Dark Side of the Moon
The side of the Moon that we don't see from Earth, which is not actually dark but remains hidden due to the Moon's synchronous rotation and revolution.
Importance of the Sun for life on Earth
Light, necessary for plants to perform photosynthesis.
Without plants, animals could not exist.
Heat, the Earth would be far too cold for any life to exist, even bacteria.
Reaction to a total eclipse of the Sun
People centuries ago would have reacted in fear or panic due to a lack of scientific knowledge, possibly believing the world was ending or that God was angry.