CAPE Bio (P2) - Membrane Structure and Function
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Explain why the phospholipid bilayer is only permeable to non-polar molecules
Polar or large molecules would either be repelled by its non-polar interior or would be too large to diffuse between the phosphate groups unlike non-polar molecules which can be absorbed by the lipid layer and easily diffuse past the phosphate groups with minimal resistance
Briefly describe the role of cholesterol in the phospholipid bilayer
In animal cells, cholesterol stabilizes the phospholipid bilayer by binding to both polar and non-polar regions of the phospholipids and also preventing them from solidifying or becoming too fluid at extreme temperatures
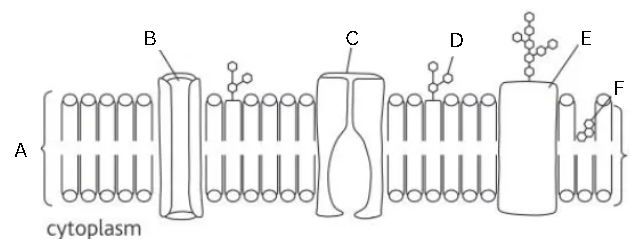
Identify and label this diagram
Fluid mosaic membrane
A - phospholipid bilayer
B - channel protein
C - carrier protein
D - glycolipid
E - glycoprotein
F - cholesterol
Briefly explain the importance of facilitated diffusion
Solutes with net charges are affected by both the concentration gradient and total electrical gradient across a membrane and require relatively large amounts of energy to be transported
Briefly explain the importance of the electrochemical gradient
It powers the diffusion of a charged substance and is necessary for communication between nerve and animal cells in animals
Briefly describe how water potential is affected by concentration
As concentration increases, water potential decreases
Describe the transformation of the animal cell in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions
In hypotonic solutions, animal cells undergo lysis. In hypertonic solutions, animal cells undergo crenation
Describe the transformation of the plant cell in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions
In hypotonic solutions, turgor pressure develops in plant cells and the vacuole expands. In hypertonic solutions, turgor pressure decreases as water leaves the cell and the cell wall experiences less resistance from the vacuole and eventually the plant will plasmolyze and lose its shape
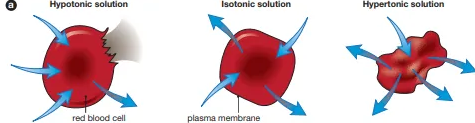
Identify this image
Transformation of an animal cell in hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic solutions
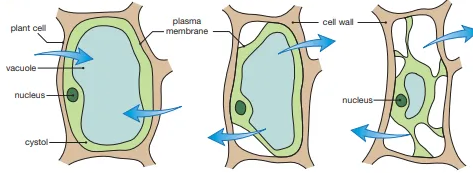
Identify this diagram
Transformation of a plant cell in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions
Briefly explain the mechanisms behind membrane-bound pumps, using the proton pump as an example
They generally break down ATP and use the energy generated to transport cations across a membrane against their concentration gradient. The proton pump catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and uses the energy to transport protons across a membrane against their concentration gradient
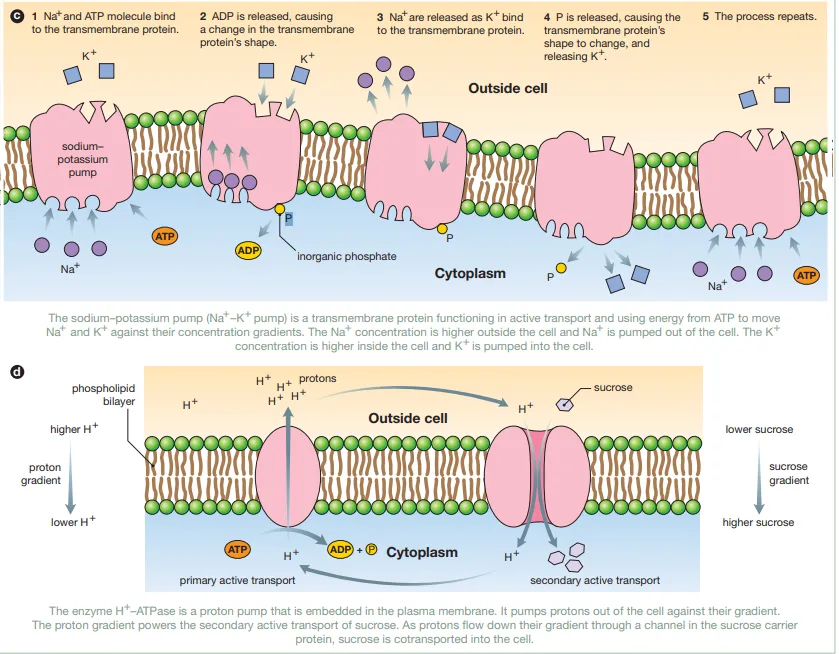
Label this diagram
c - primary active transport
d - secondary active transport
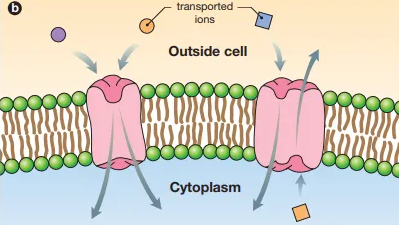
Identify this diagram
coupled transport
Briefly explain how the Golgi complex aids bulk transport
The vesicles it creates fuses with the plasma membrane
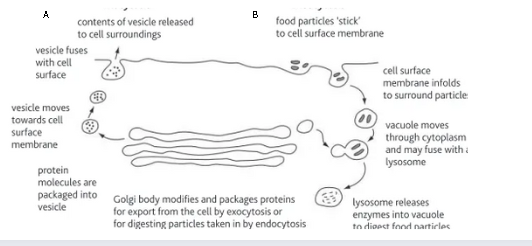
Label this diagram
A - exocytosis
B - endocytosis
Briefly state where endocytosis is useful
Phagocytosis is used by white blood cells as a feeding mechanism. Pinocytosis occurs constantly in the endothelium. Receptor-mediated endocytosis is the mechanism by which cholesterol is taken up by most mammalian cells