Volcanoes
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
__ are windows to see inside the earth
volcanoes
Volcanoes help us understand Earth’s ___ processes
interior
Many people live near volcanoes and die because of volcanic ____
eruptions
6 types of lava?
basaltic lava, pahoehoe, pillow lava, columnar joints, andesitic lava, rhyolitic lava
Characteristics of basaltic lava?
mafic
ex: volcanoes of hawaii
aa
AA (type of basaltic lava)
chunky lava, full of vesicles
What are vesicles?
small cavities or holes in volcanic rocks formed by gas bubbles trapped in lava as it cools
Pahoehoe
ropy lava, less viscous than aa
Pillow Lava
piles of ellipsoidal basalt
form underwater
hot lava interacts with cold ocean
“plastic skin” develops (like inflating balloon)
pillow lava
Columnar Joints
basalt fracturing during cooling
roughly hexagonal columns
form when ___, ___, or ___ flows cool
columnar joints; dikes, sills, lava
Andesitic Lava
intermediate
flows slower than basaltic lavas
plus volcanoes (pyroclastic eruption)
example: lascar volcano, chile
andesitic lava
Felsic
Rhyolitic Lava
most viscous lava
plug volcanoes
PRODUCE MOST EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS
ex: mt st helens
andesitic lava
T/F: olcanoes with Si-rich magma not more likely to explosively erupt than volcanoes with non Si-rich magma
false
T/F: magma with lots of gas also makes more explosive eruptions than magma lacking lots of gas
true
Pyroclasts
broken pieces of rock ejected into air
Ash
fine-grained pyroclastic material- easily goes into atmosphere
Pyroclastic Flow
hot ash gas that flows downhill at high speeds
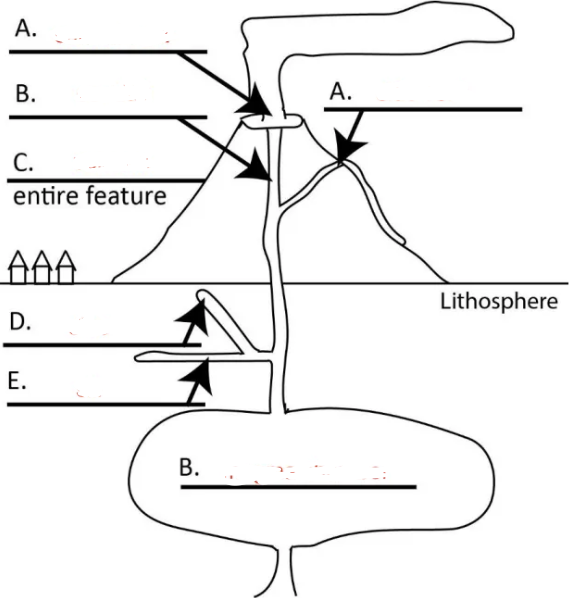
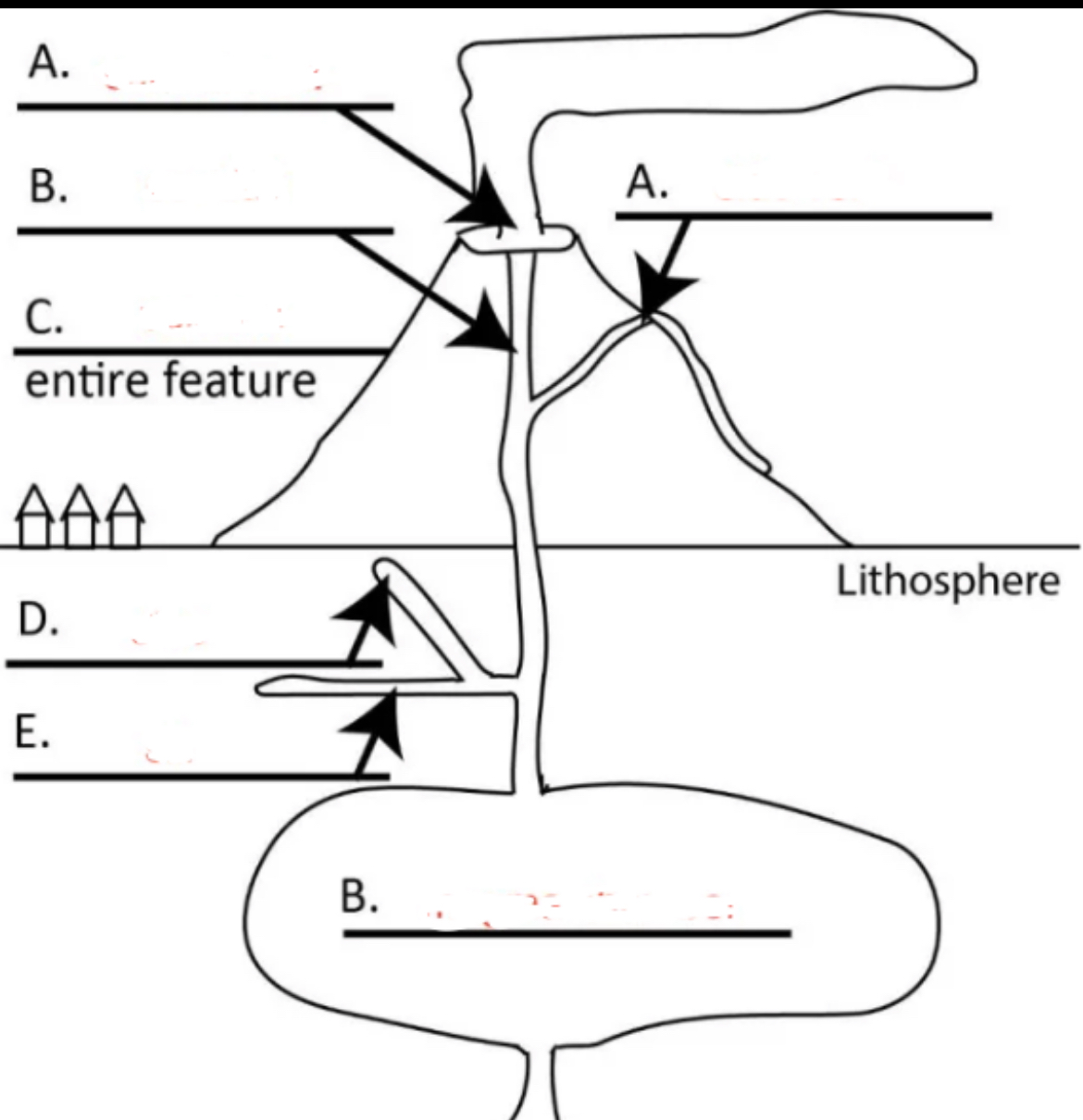
Left A?
central vent
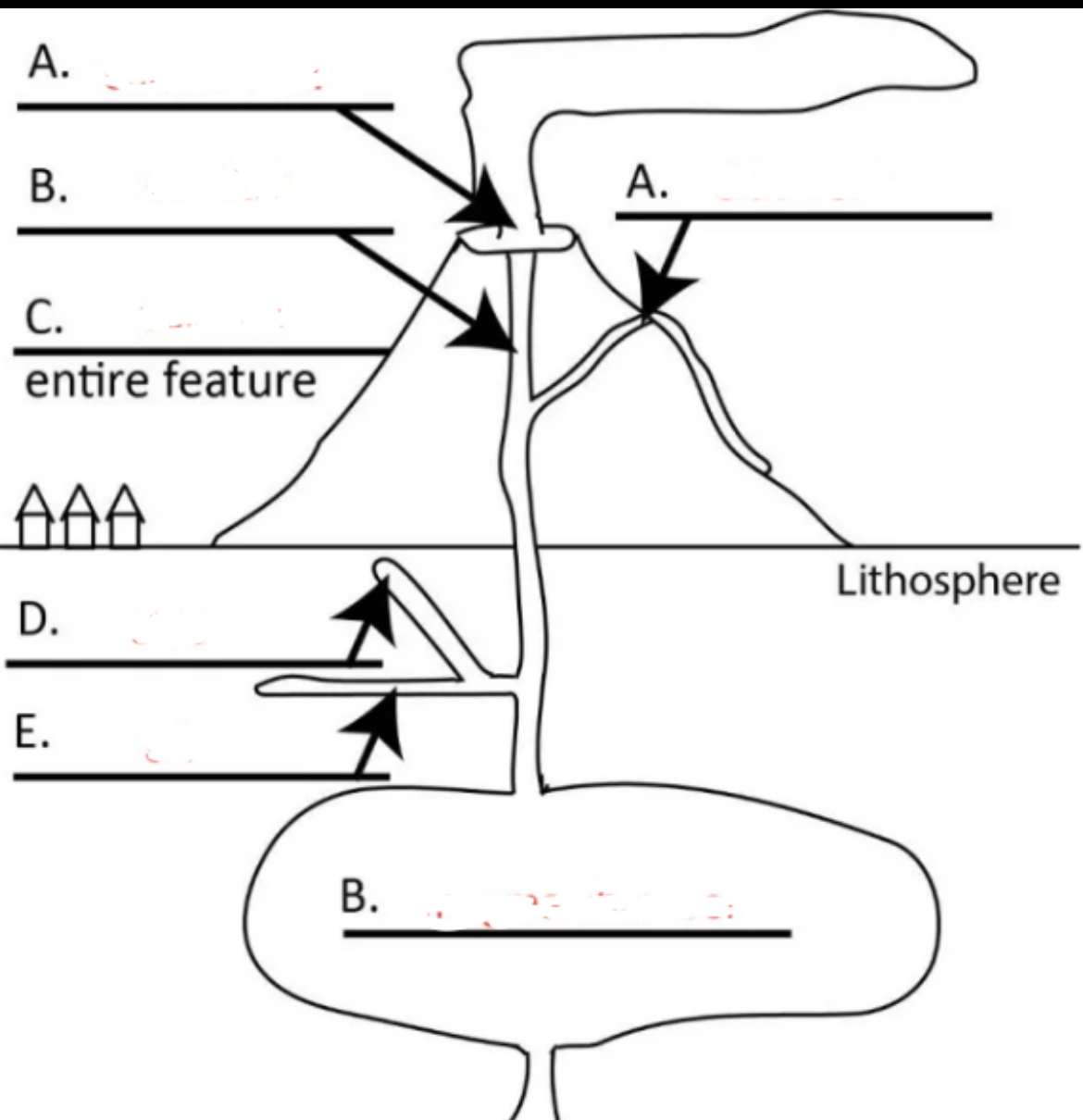
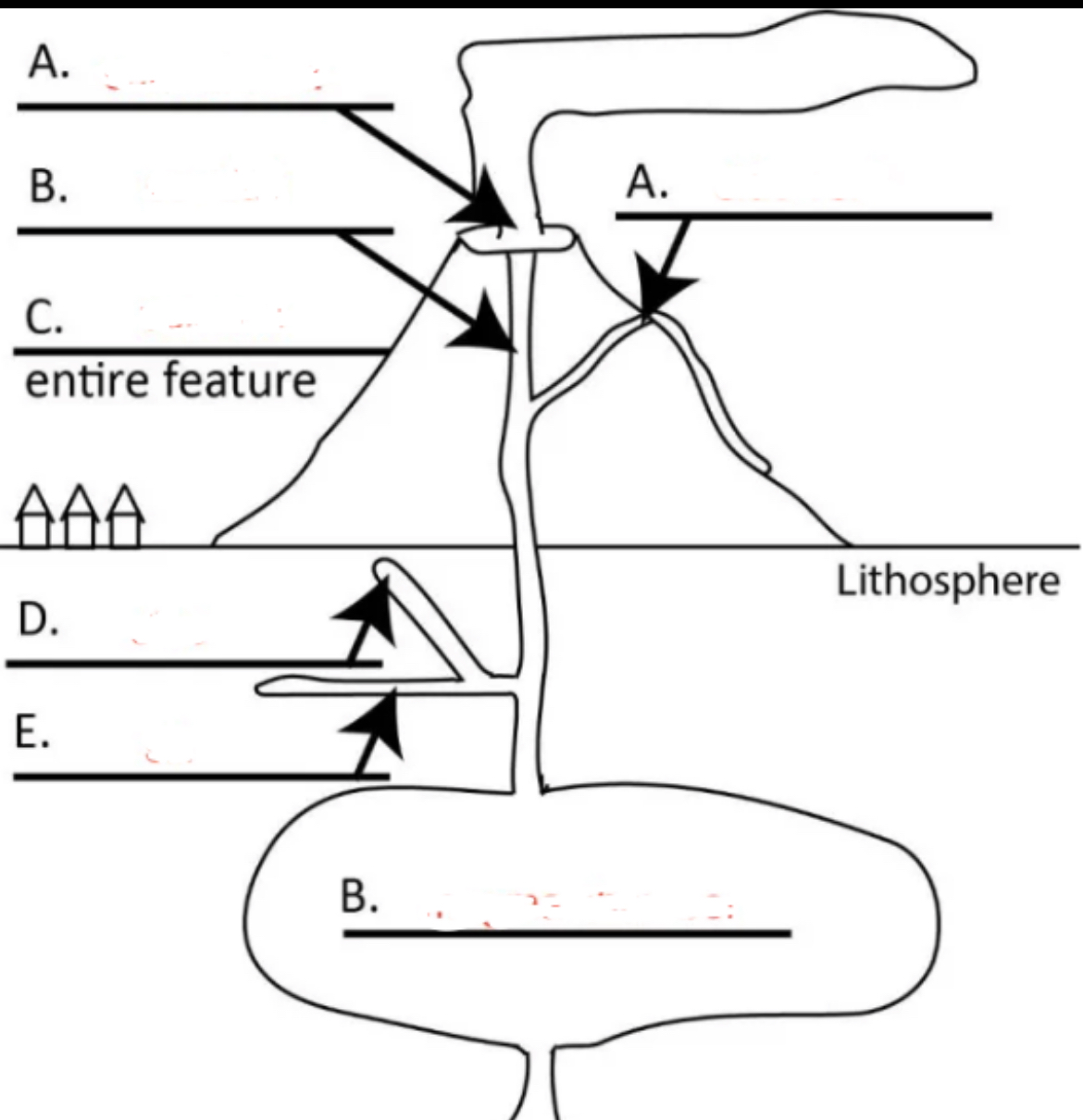
Right A?
side vent
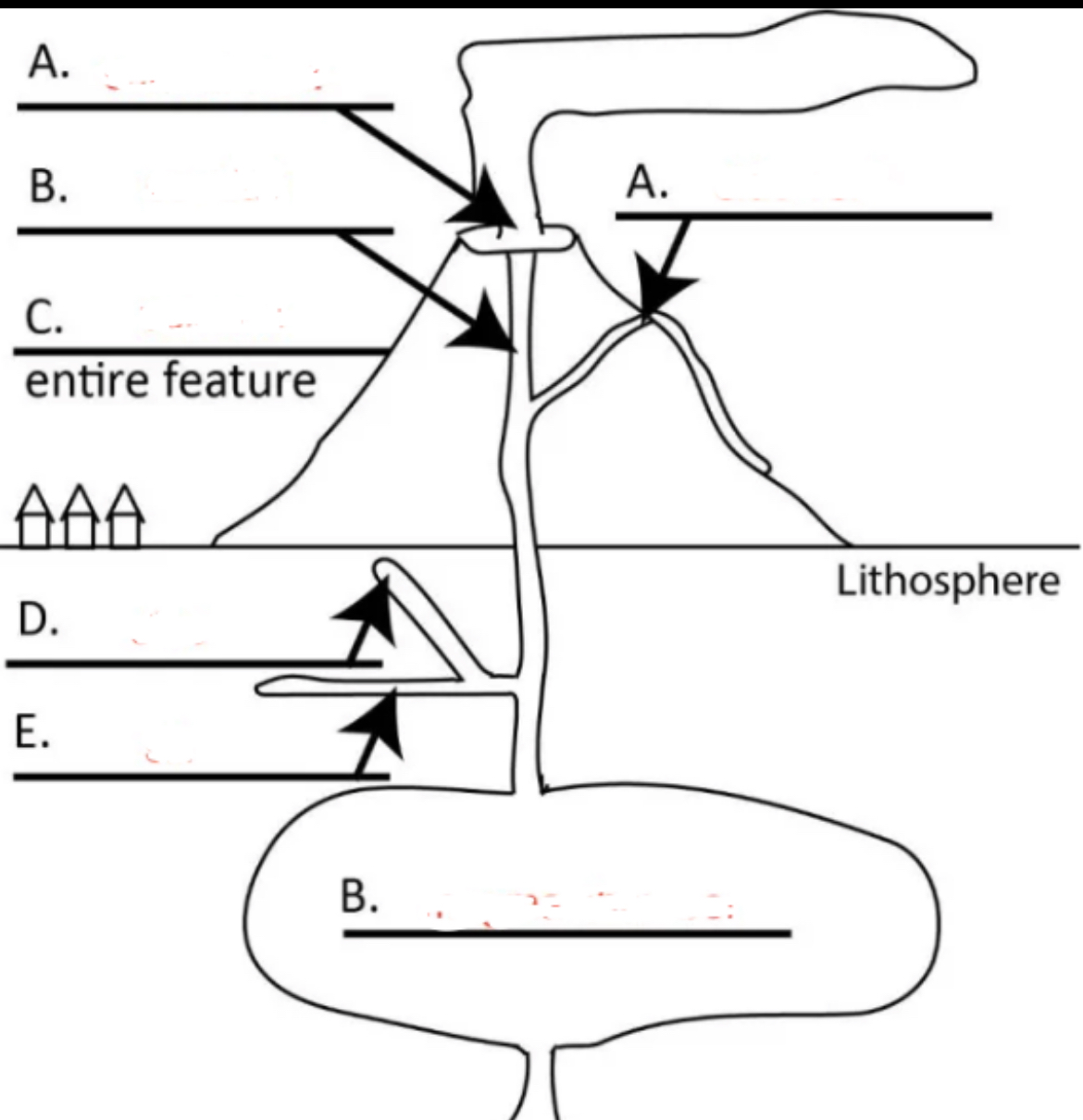
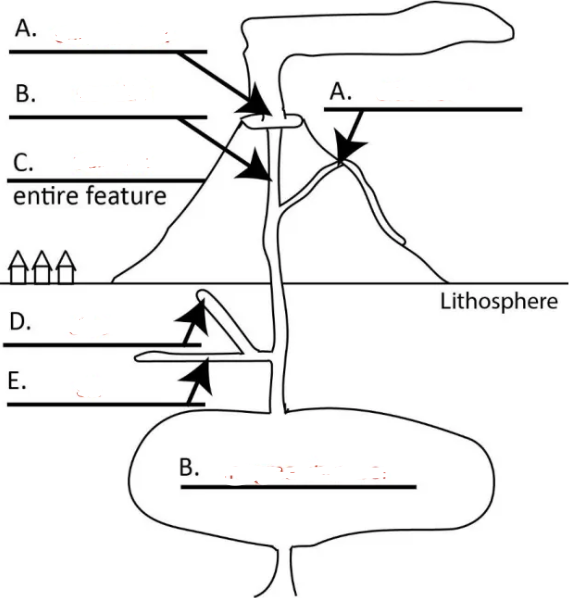
Top B?
conduit
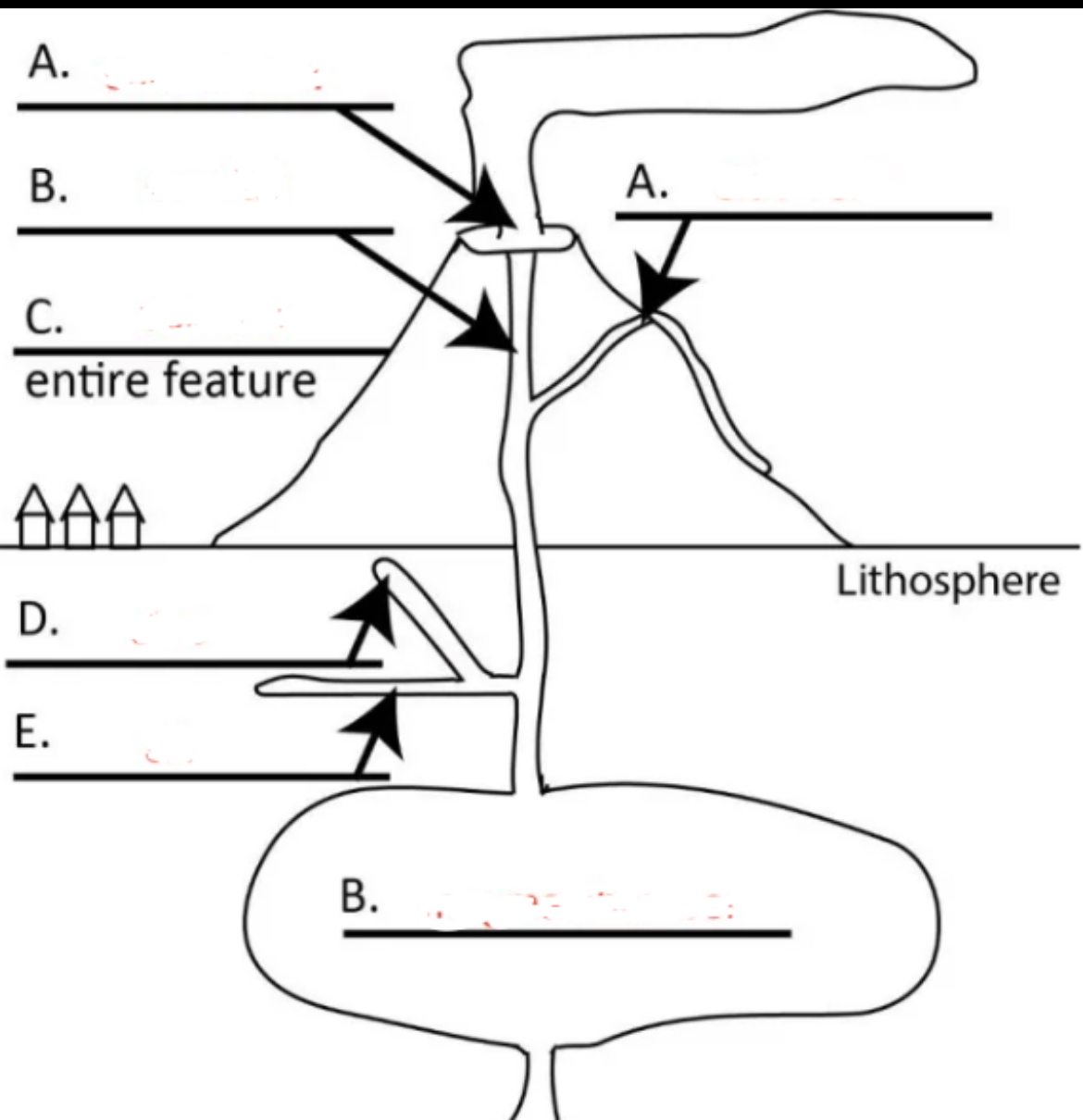
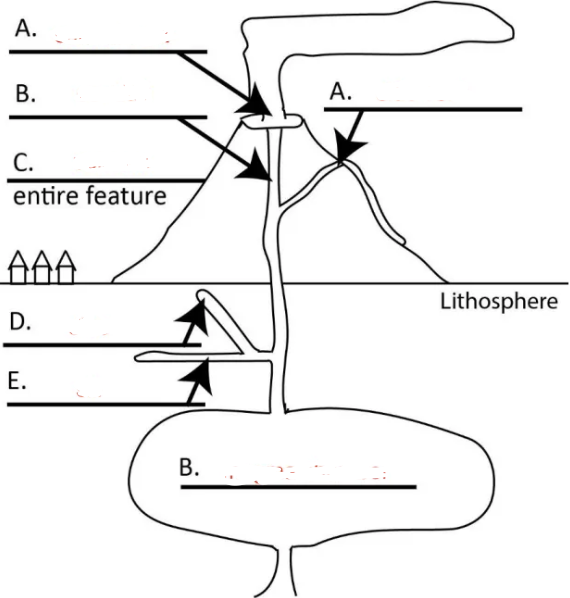
C?
volcano
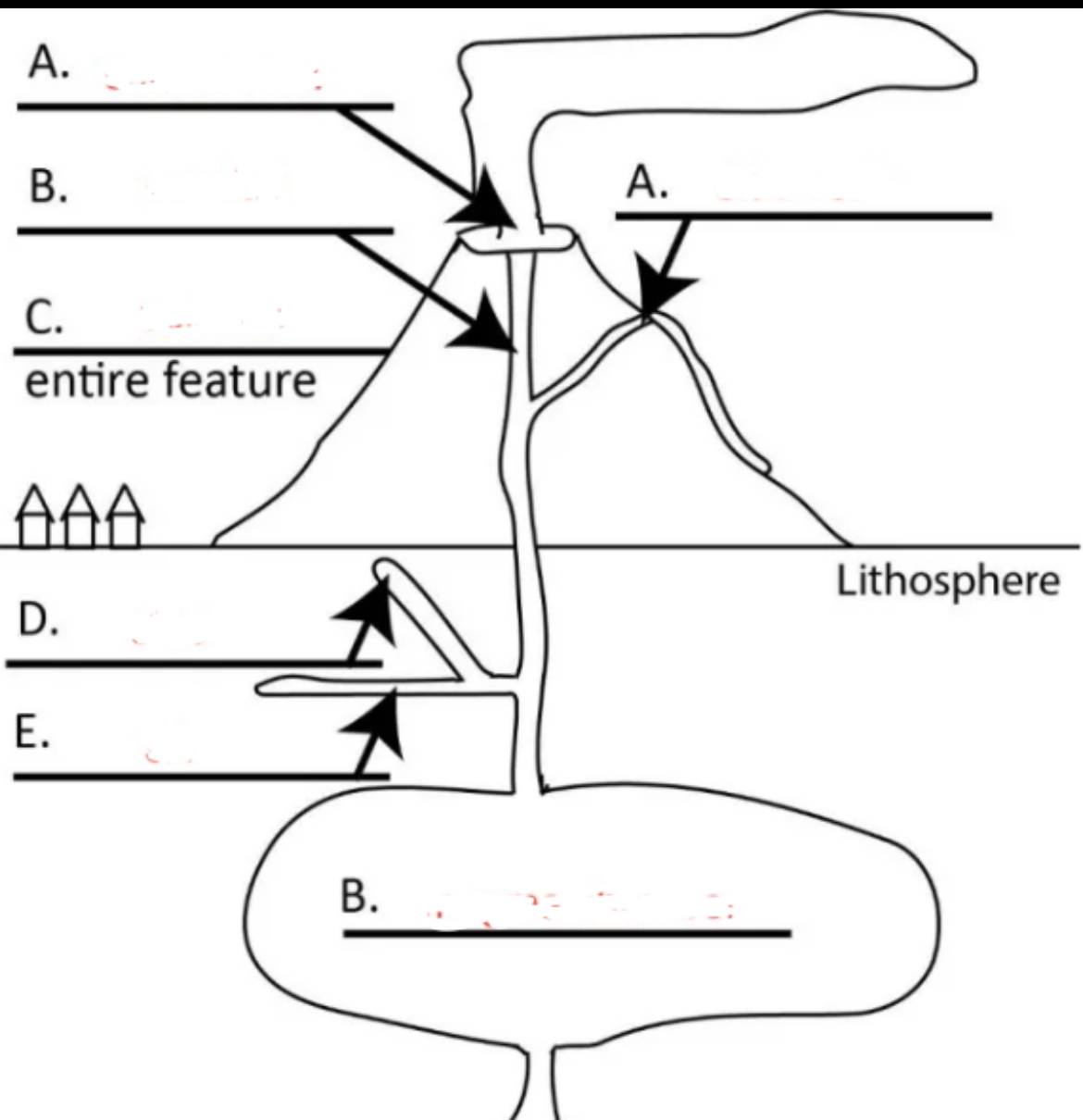
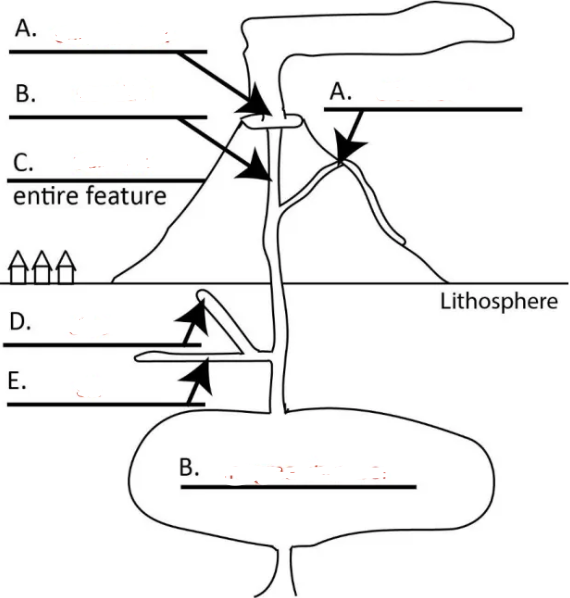
D?
dike
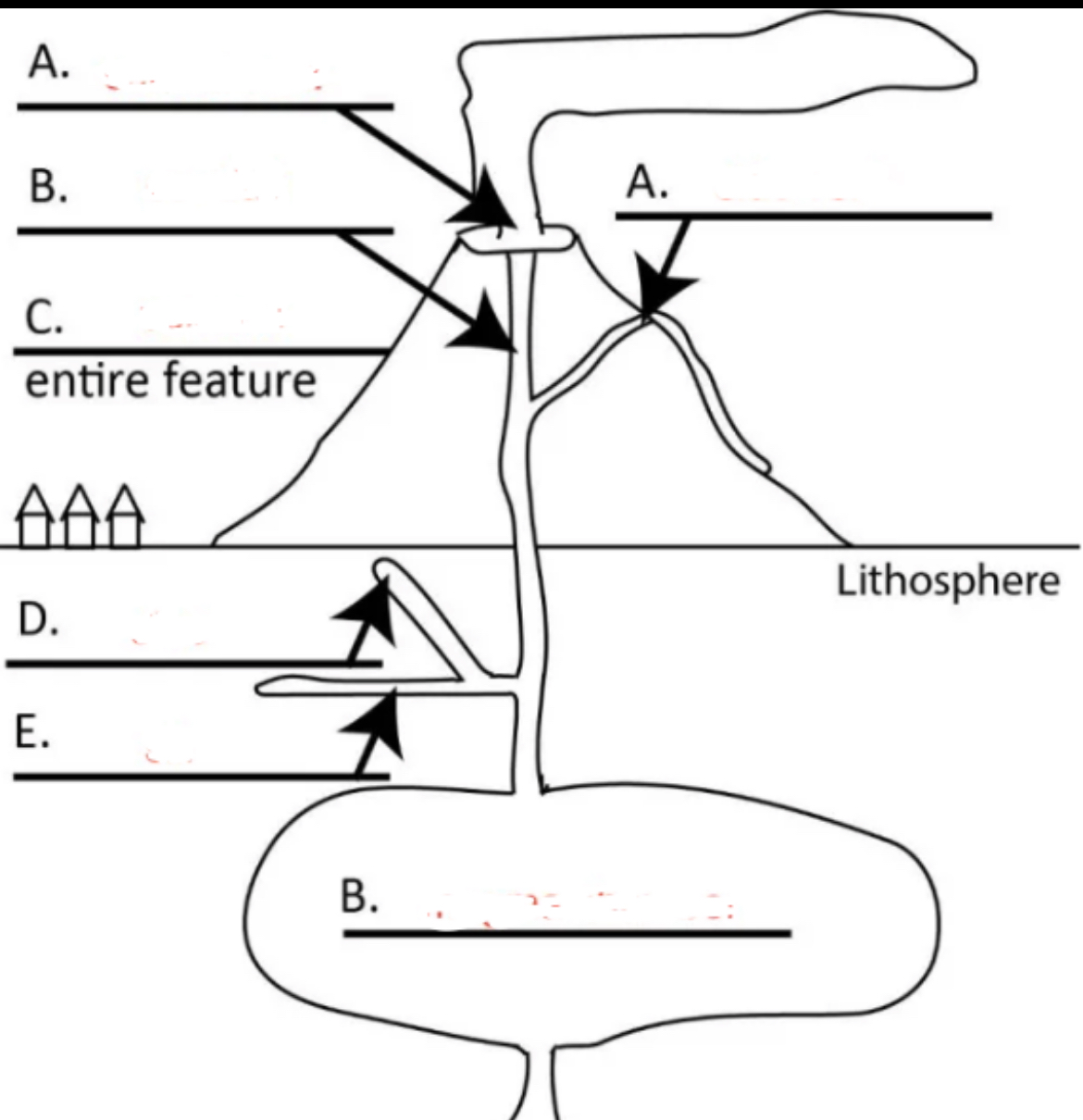
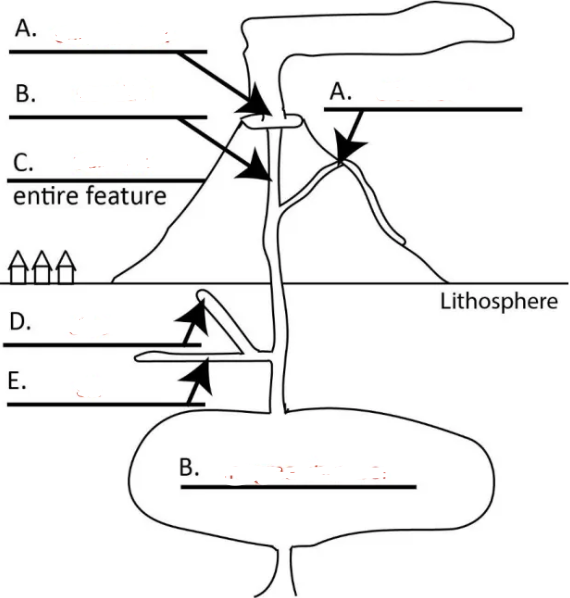
E?
sill
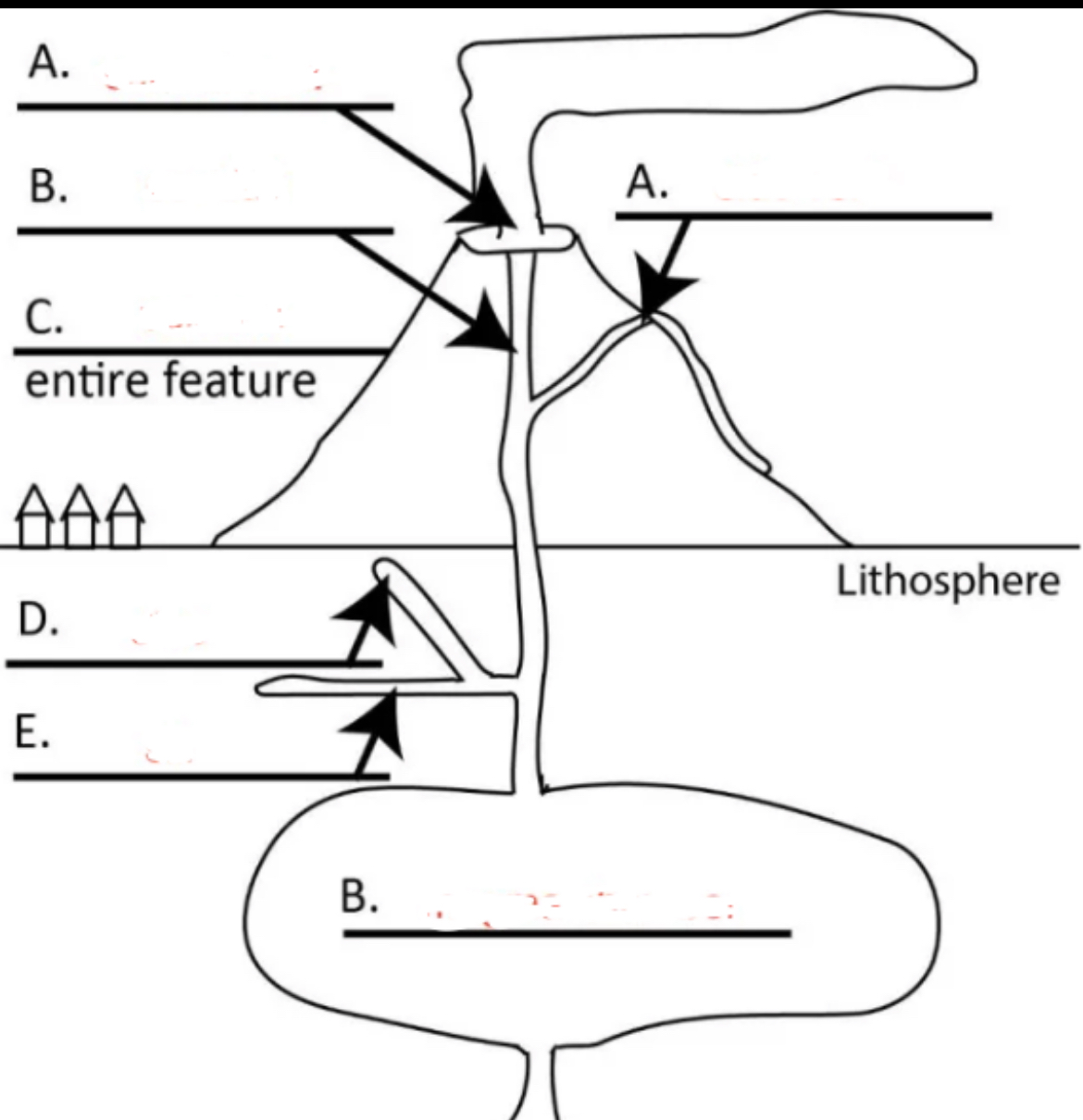
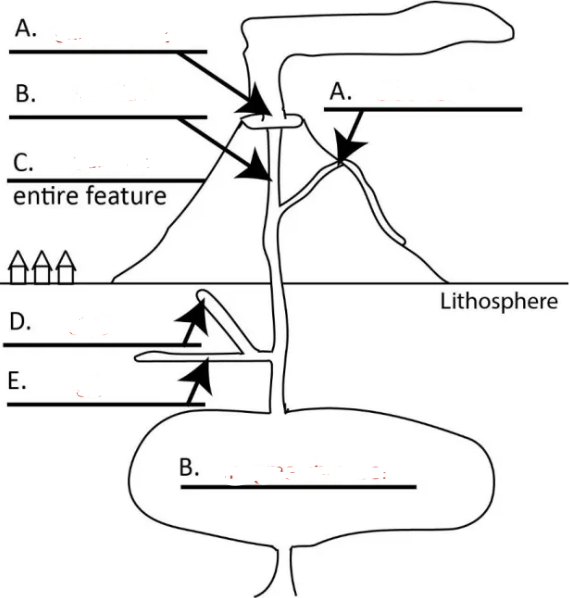
Bottom B?
magma chamber
Volcano
hill or mountain made of lava and other erupted material
Central Vent
primary eruption site at the center of a symmetrical volcano
Conduit
igneous intrusion that feeds central vent
Side Vent
volcanic eruption site from side of a volcano
Dike
wall-like intrusion that cuts across layers of wall rock
Sill
sheet-like (table-top like intrusion) that is formed by magma injection between parallel layers of bedded wall rock (does not cut across layers but layers can be later tilted)
Magma Chamber
large pool of magma in the lithosphere
Magma __ through crust and __ or pushes aside wall rock
rises; melts
Magma forms in ___ & rises through cracks in the crust to form a magma ___
mantle; chamber
Magma erupts from ___ & ___ vents, forming ___ which accumulates on Earth’s surface, forming a volcano
central; side; lava
Shield Volcano
broad, gently sloping volcano formed by low-viscosity lava that can flow over long distances (non-explosive eruptions)
generally >10km tall
circumference: hundreds of kms
ex: mauna loa, hawaii
What Volcano Structure?
shield volcano
Stratovolcano (composite volcano)
a steep sided, symmetrical volcano built from alternating layers of lava flows, ash, and rock fragments
common at CONVERGENT plate zones
ex: mount fuji, japan
What Volcano Structure?
stratovolcano
Cinder Cone (scoria cone)
small, steep-sided volcano built from pyroclastic fragments (like ash, cinders, and volcanic rocks)
usually forms short, explosive eruptions
ex: parícutin, mexico
What Volcano Structure?
cinder cone
Caldera
a large, basin shaped depression formed when a volcano collapses after a massive eruption empties the magma chamber
lots of magma discharged, volcano collapses, leaving an empty magma chamber (or depression)
top of volcano collapses into empty magma chamber, leaving a large hole
ex: crater lake, usa
caldera
Fissure Eruption
tens of kilometers long
LARGEST volcanic eruptions
common at DIVERGENT boundaries (like MOR’s or continental rift zones)
Flood Basalt
forms from fissure eruptions under continents or on ocean floors
timing of 3 largest flood basalt events in Phanerozoic Eon corresponds to the timing of 3 largest known mass extinctions (massive releases of toxic gases & climate poisoning)
ex: columbia river flood basalt
Volcanism occurs where?
at subduction zones, rifts, mid ocean ridges (spreading centers) & hot spots (intraplate volcanism)
What type of plate boundary is a subduction zone?
convergent boundary
What type of plate boundary is a rift?
divergent boundary
What type of plate boundary is a MOR?
divergent boundary
magma comes from partial melting of subducted oceanic crust
example: aleutian islands, alaska
What type of convergence? (O-O or O-C)
o-o (subduction zone)
What geologic features are found at an ocean-ocean convergent plate boundary?
deep ocean trenches, volcanic island arcs, earthquakes, subduction zones
magma is a mixture of: fluids from subducted oceanic crust & re-melted felsic continental crust, & melted materials from the mantle above the subducting plate
lava types include: andesite & rhyolite
example: west coast of south america (andes)
What type of convergence? (O-O or O-C)
o-c (subduction zone)
What geologic features are found at an ocean-continent convergent plate boundary?
trenches, continental volcanic arcs, mountain building, earthquakes
magma comes from decompression melting of the mantle
lava types include: basalt
example: MOR
What kind of divergence? (O-O or C-C)
o-o (mid ocean ridges)
What geologic features are found at an ocean-ocean divergent plate boundary?
mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys, new oceanic crust, shallow earthquakes, hydrothermal vents
magma comes from decompression melting of that mantle & may interact with continental crust
lava types include: basalt, andesite, and rhyolite
example: east african rift
What kind of divergence? (O-O or C-C)
c-c (rifts)
What geologic features are found at a continent-continent divergent plate boundary?
rift valleys, volcanoes, earthquakes, eventual formation of new ocean basins
What is a mantle plume?
a column of hot, solid rock that rises from deep within the Earth's mantle
Hot Spot
magma comes from a mantle plume
mantle plume is stationary, tectonic plates move over stationary plume = creates a chain of volcanoes
lava types include: basalt (if ocean) & rhyolite or andesite (if land)
examples: hawaiian islands (ocean) & yellowstone (land)
__ flows
ash ___
___ gases
lava, falls, volcanic
Lahar
torrential flow of wet volcanic debris
caldera collapse
eruption clouds
lahar
Flank Collapse
catastrophic structural failure of volcano that creates massive landslide
Tsunami
large ocean wave caused by underwater volcanic eruptions, landslides, or earthquakes displacing water
Leading cause of death from volcanoes?
pyroclastic eruptions
Active Volcano ex: mount etna, italy
volcano that is currently erupting, has recently erupted, or is likely to erupt again in the near future
Dormant Volcano ex: mount fuji, japan
volcano that is not currently active, but could erupt again in the future
Extinct Volcano ex: edinburgh’s arthurs seat, scotland
volcano that is not expected to erupt again
historical records, geological records, & oral stories
determine age of erupted rocks (geochronology)
search for active geothermal evidence
shape of volcano (erosion “flattens” volcanoes over time)
how to tell active from dormant & extinct volcanoes:
Predicting Eruptions – long term
monitoring patterns to predict eruptions years or decades in advance
Prediction Eruptions - short term
monitoring tools to predict eruptions days to weeks, to sometimes hours in advance
increased seismic activity
changes in heat flow (from hot magma)
changes in volcano shape
increased gas & steam emissions