Lab 3 & 4: Skulls (Shark, Necturus, Cat)
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
What are the three parts of the skull?
chondrocranium
splanchnocranium
dermatocranium
What part of the skull does the shark not have?
no dermatocranium
What is the function of the chondrocranium?
shelf on which the brain and associated sense organs rest
What is the function of the splanchnocranium? (shark)
support jaws and gills
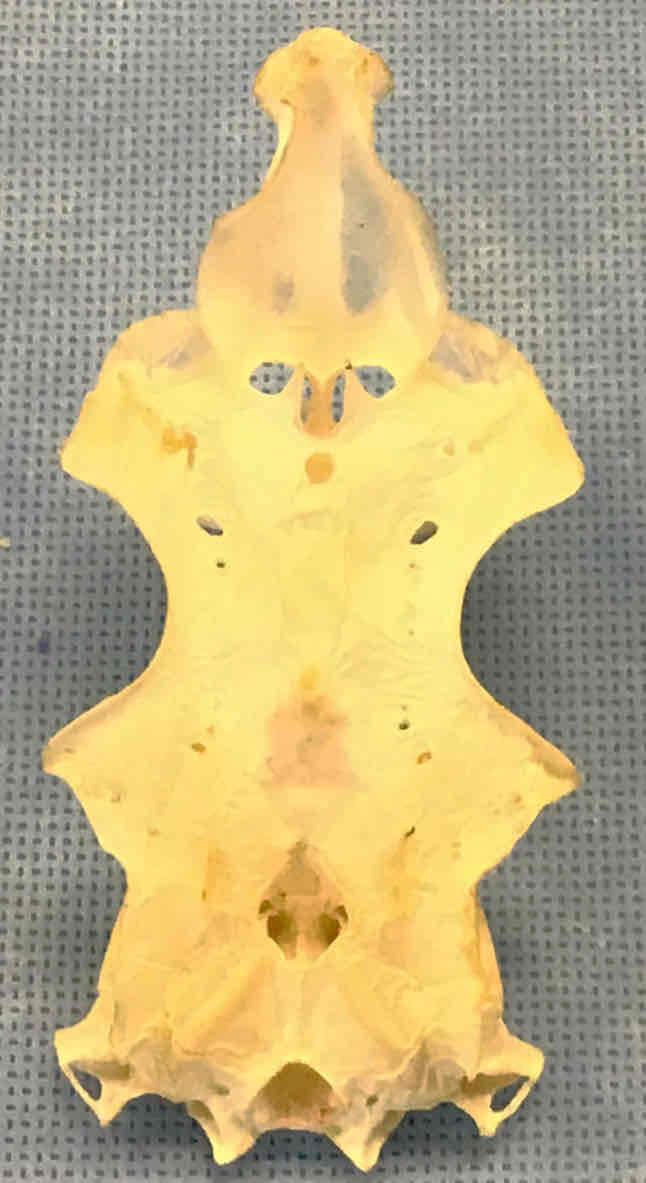

What view of the skull is this?
dorsal view of the chondrocranium (shark)
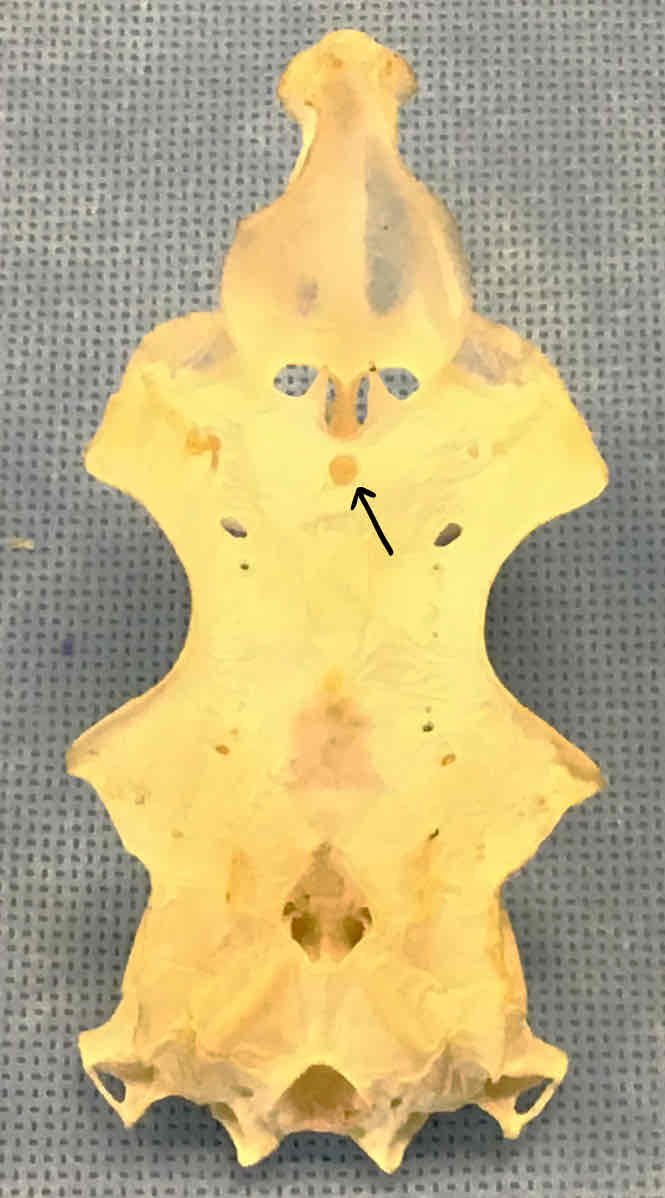
epiphyseal foramen (chondrocranium - shark): opening that the pineal organ projects through
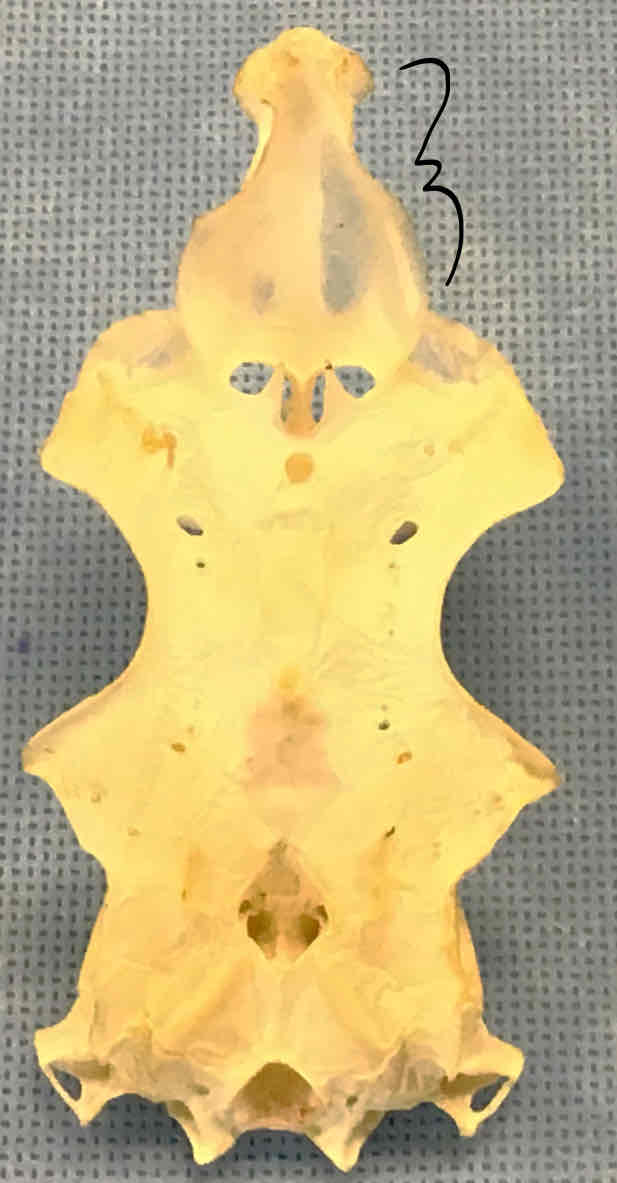

rostrum (chondrocranium - shark): makes up the snout
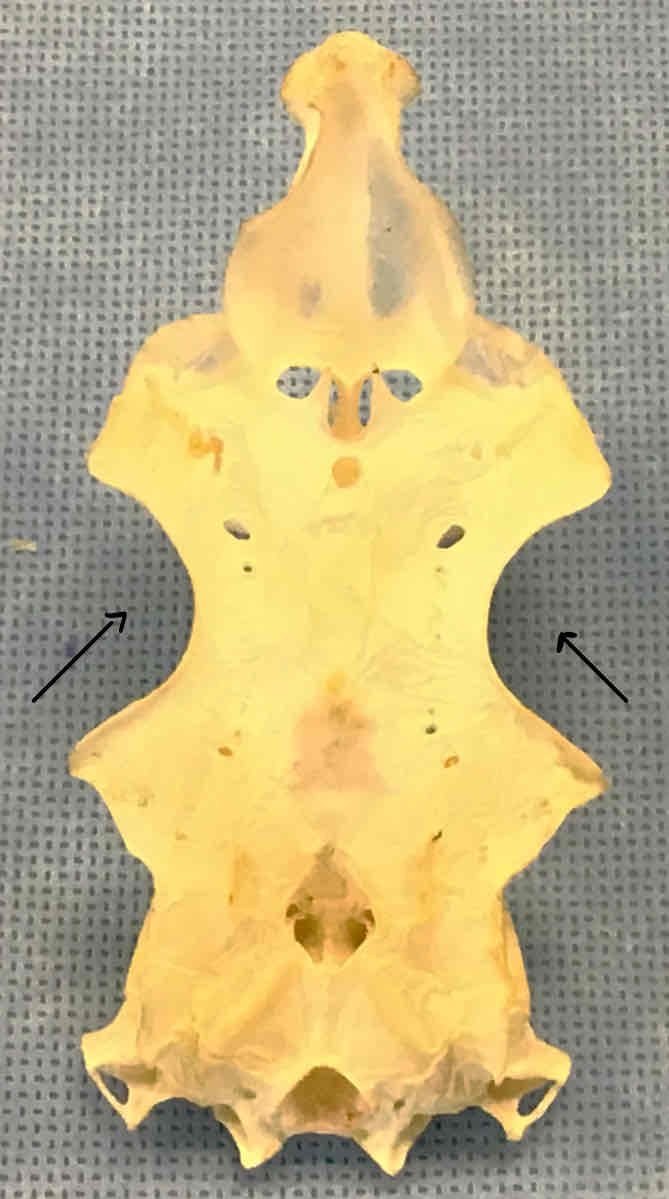
optic capsules/eye orbits (chondrocranium - shark): holds the eyeballs
otic capsules (chondrocranium - shark): contain the semicircular ducts of the ears
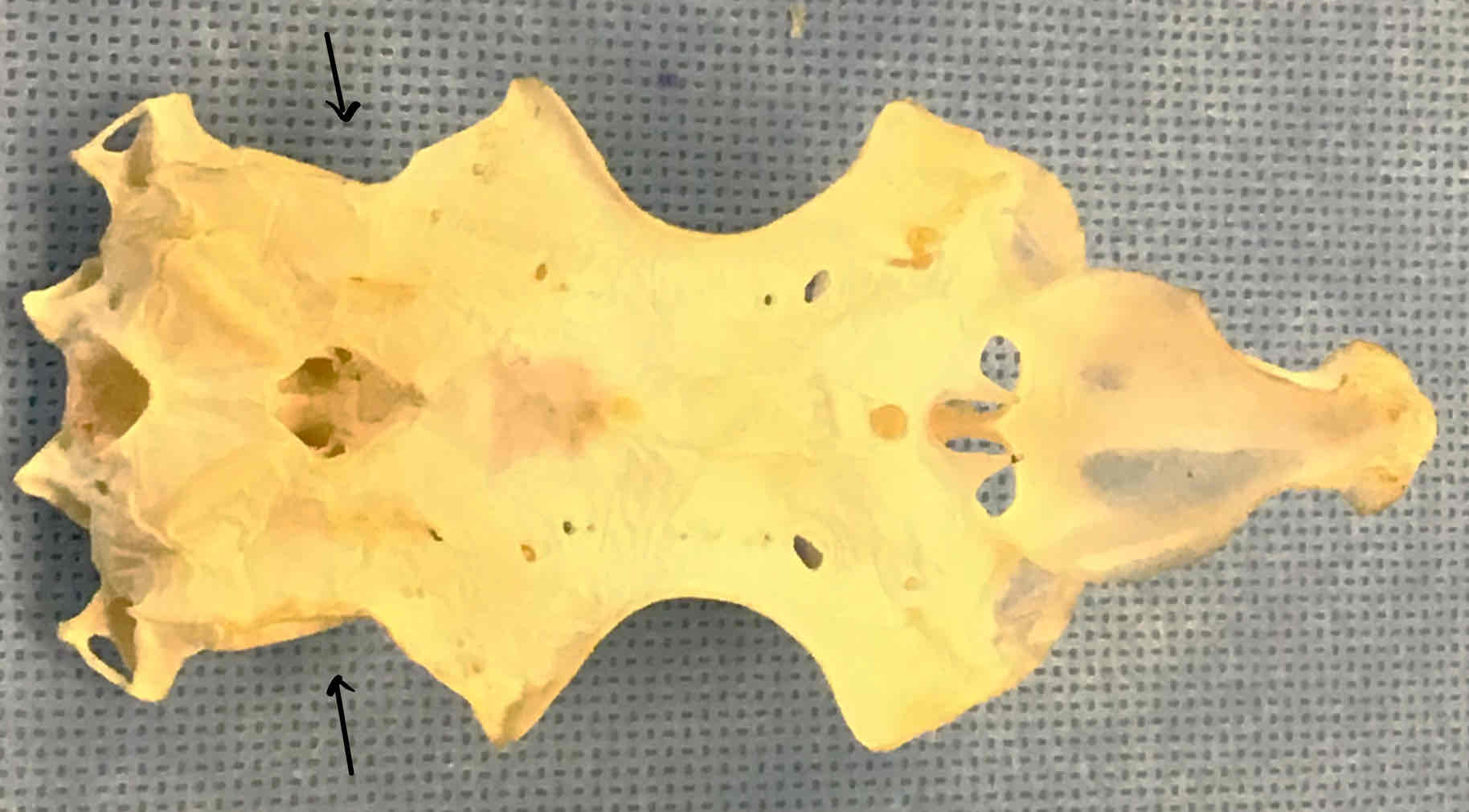
foramen magnum (shark): opening that the spinal cord passes through
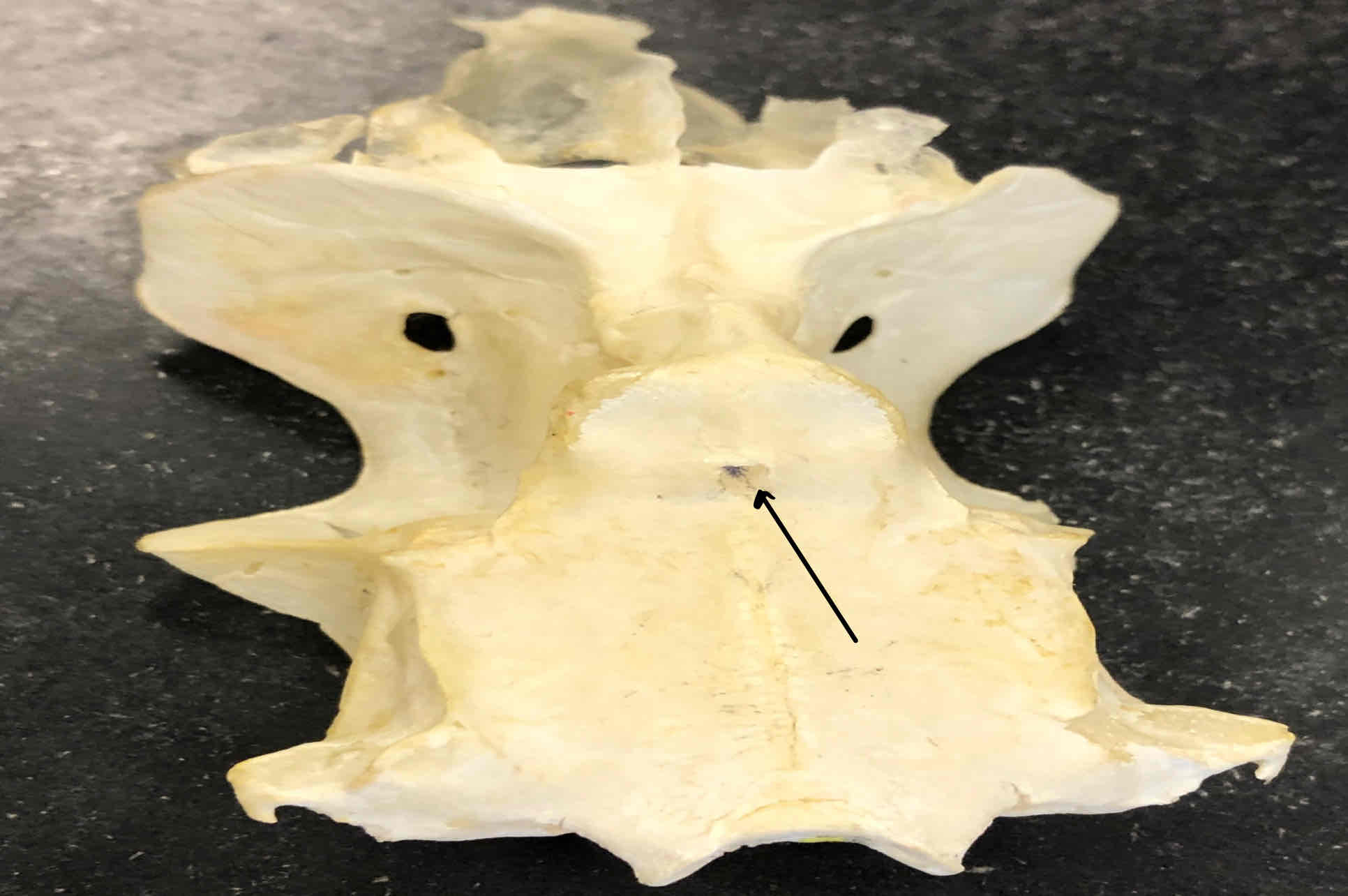
carotid foramen (shark): the opening that internal carotid arteries pass through
basal plate (chondrocranium - shark): where the brain sits
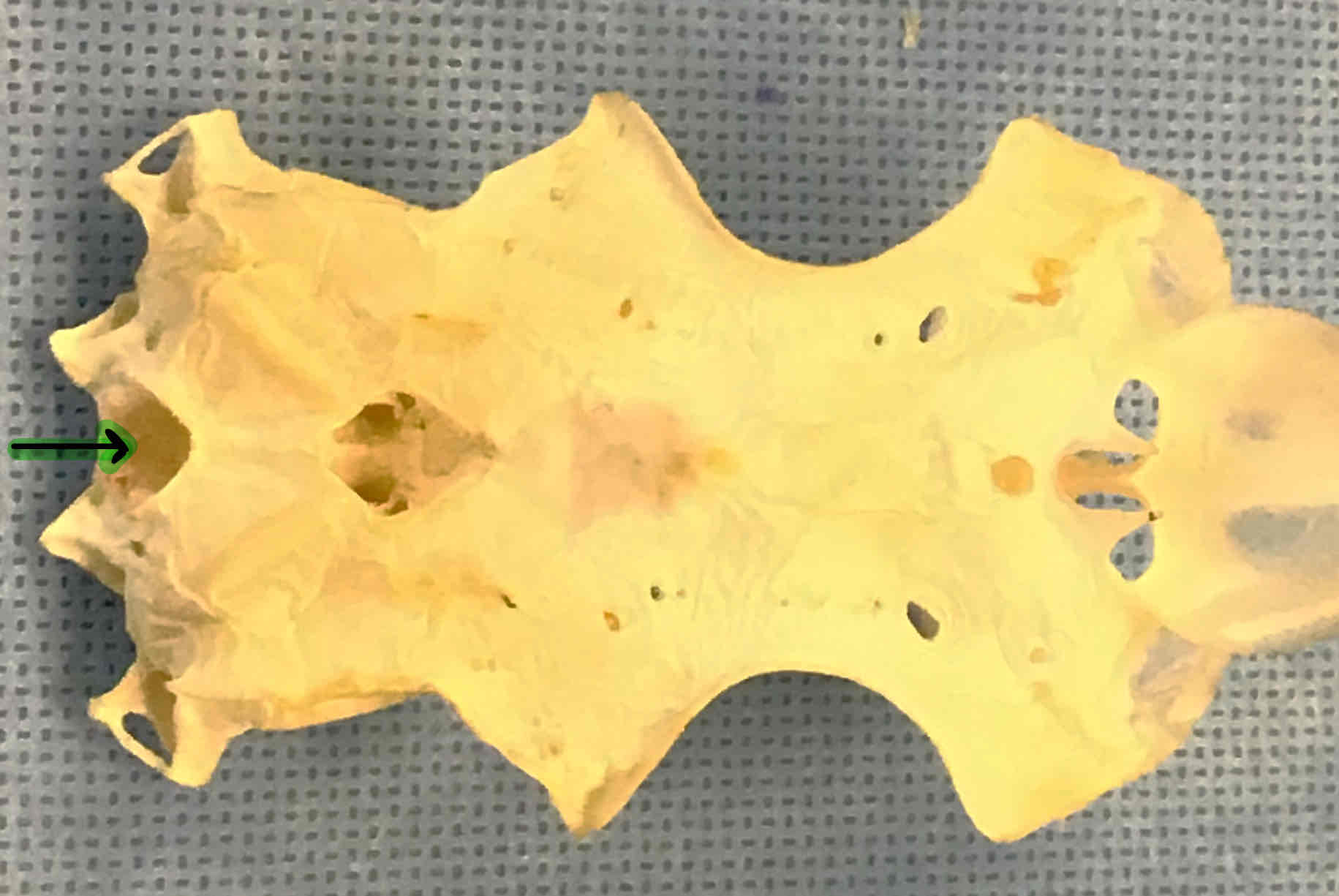
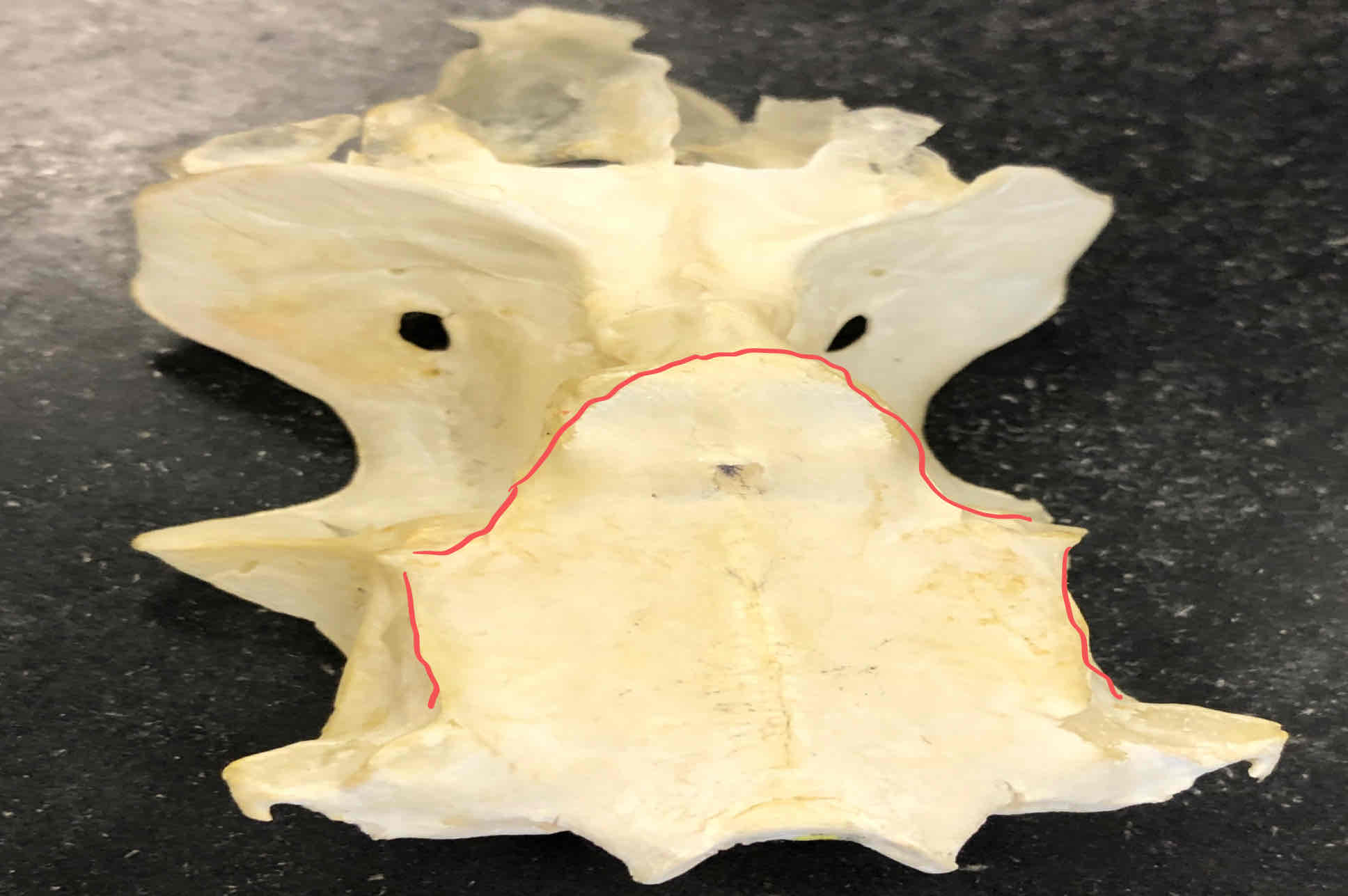
both structures are part of the shark chondrocranium
nasal capsule: contains the olfactory aparatus
eye orbits: houses the eyeballs
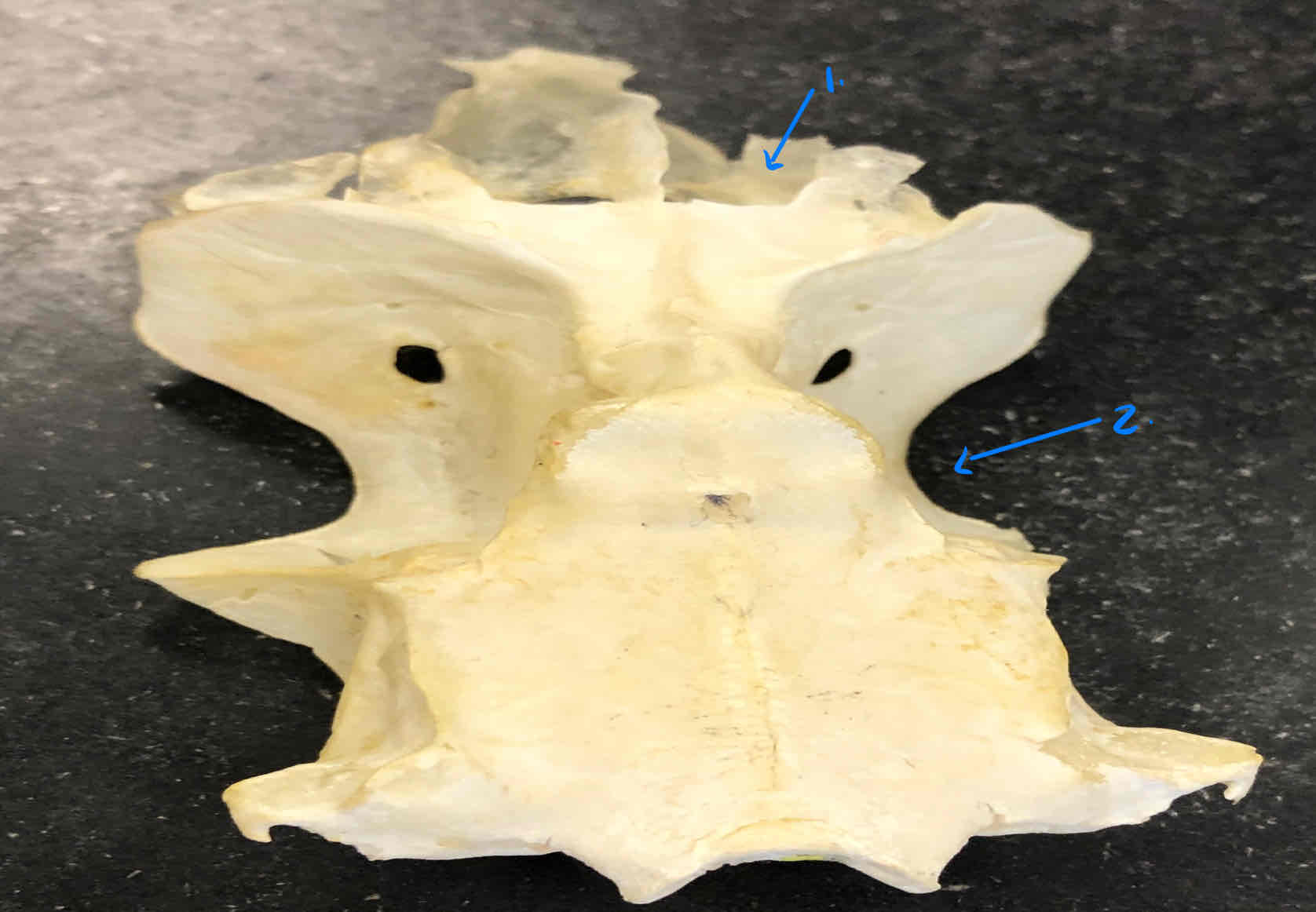
all structures are part of the shark chondrocranium
otic capsule
optic capsule
epiphyseal foramen
nasal capsule
rostrum
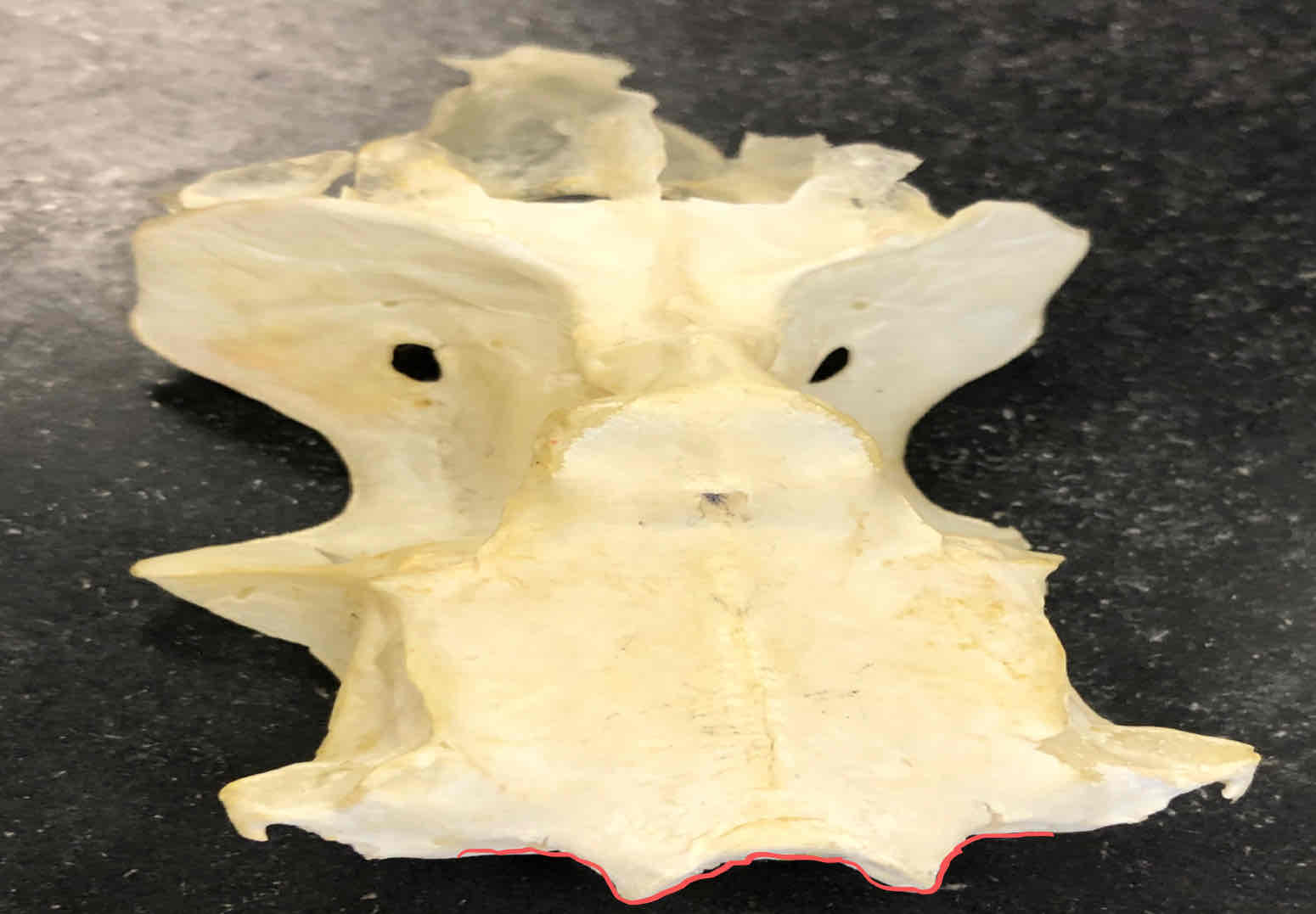
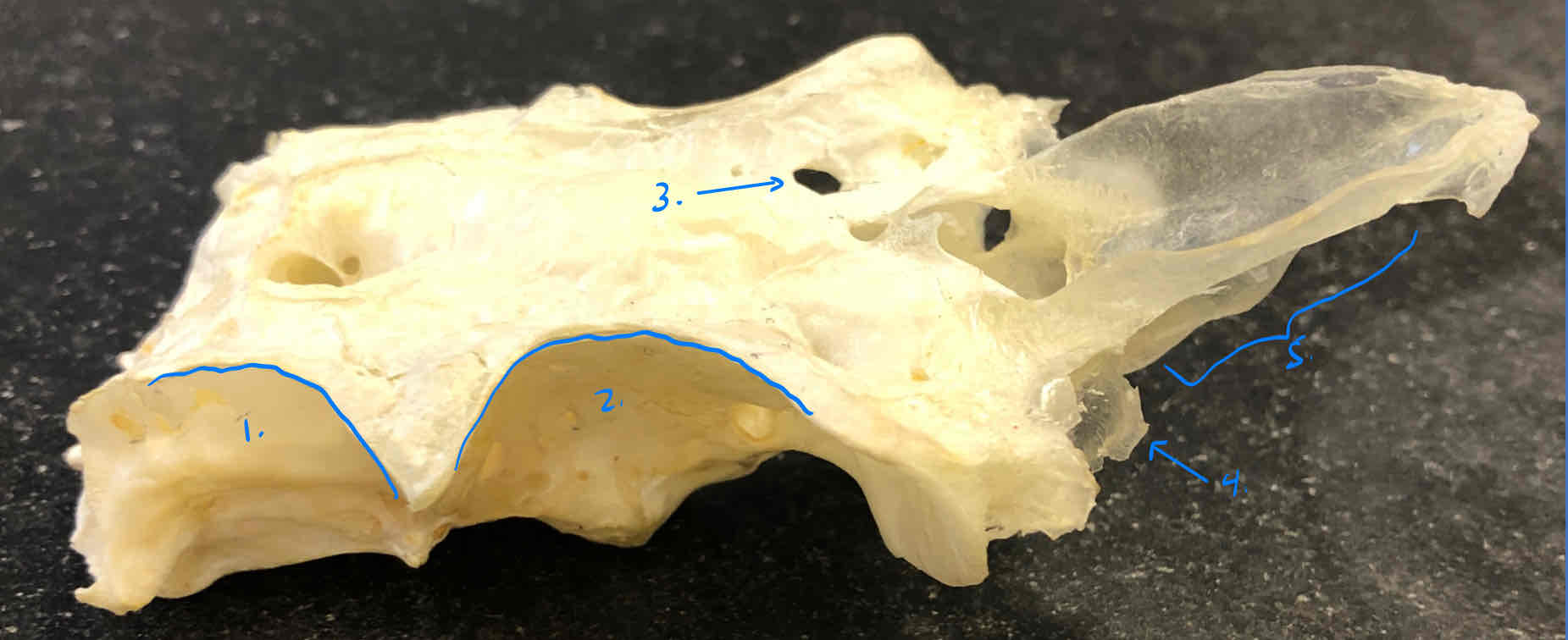
exoccipital bone with occipital condyles (chondrocranium - shark): articulates with the first trunk vertebra
This first gill arch gives rise to what structure in the shark?
the mandibular arch
What structures make up the mandibular arch in sharks?
the palatoquadrate (upper jaw) and Meckel’s cartilage (lower jaw), both parts of the splanchnocranium
What does the second gill arch in the shark give rise to?
the hyoid arch
What main cartilage makes up the hyoid arch in sharks?
hyomandibular cartilage, part of the splachnocranium
What is the function of branchial arches 3-7 in the shark?
surrounds the pharynx and serves as skeletal support for the gills
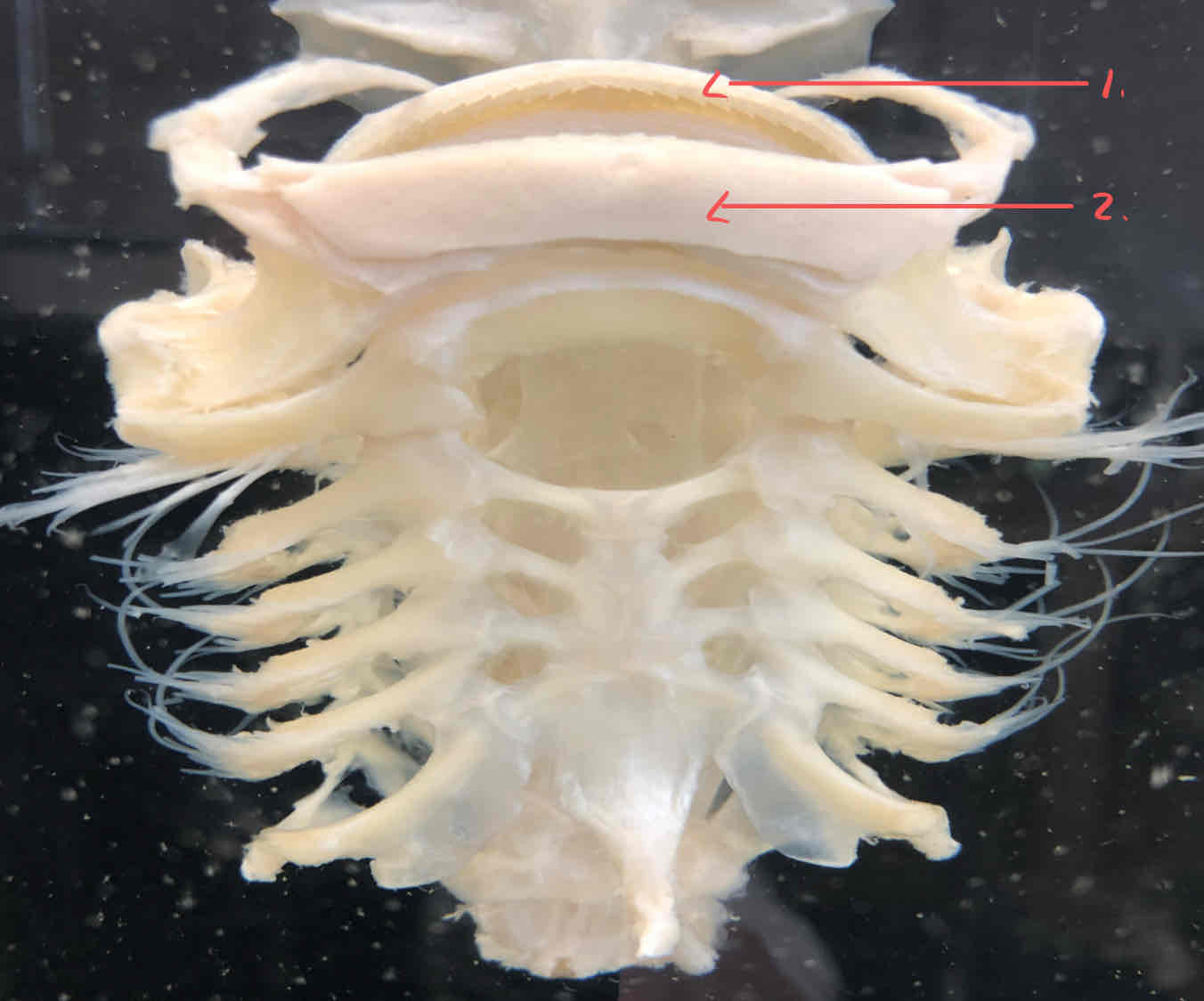
both structures are part of the splanchnocranium of the shark
palatoquadrate: makes up the upper jaw
Meckel’s cartilage: makes up the lower jaw
collectively these cartilages make up the mandibular arch
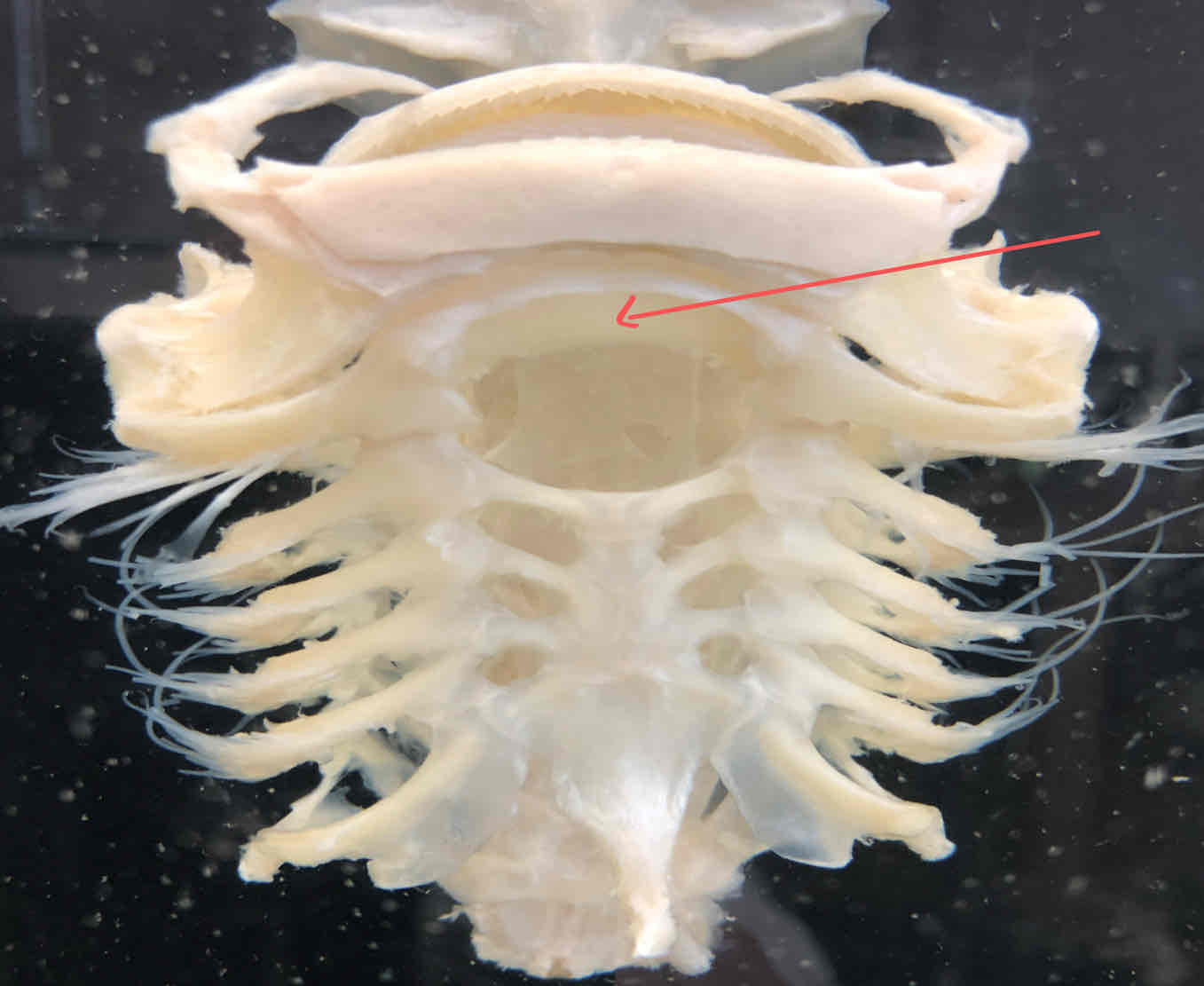
hyoid arch (splanchnocranium - shark): second modified visceral arch that supports the gills
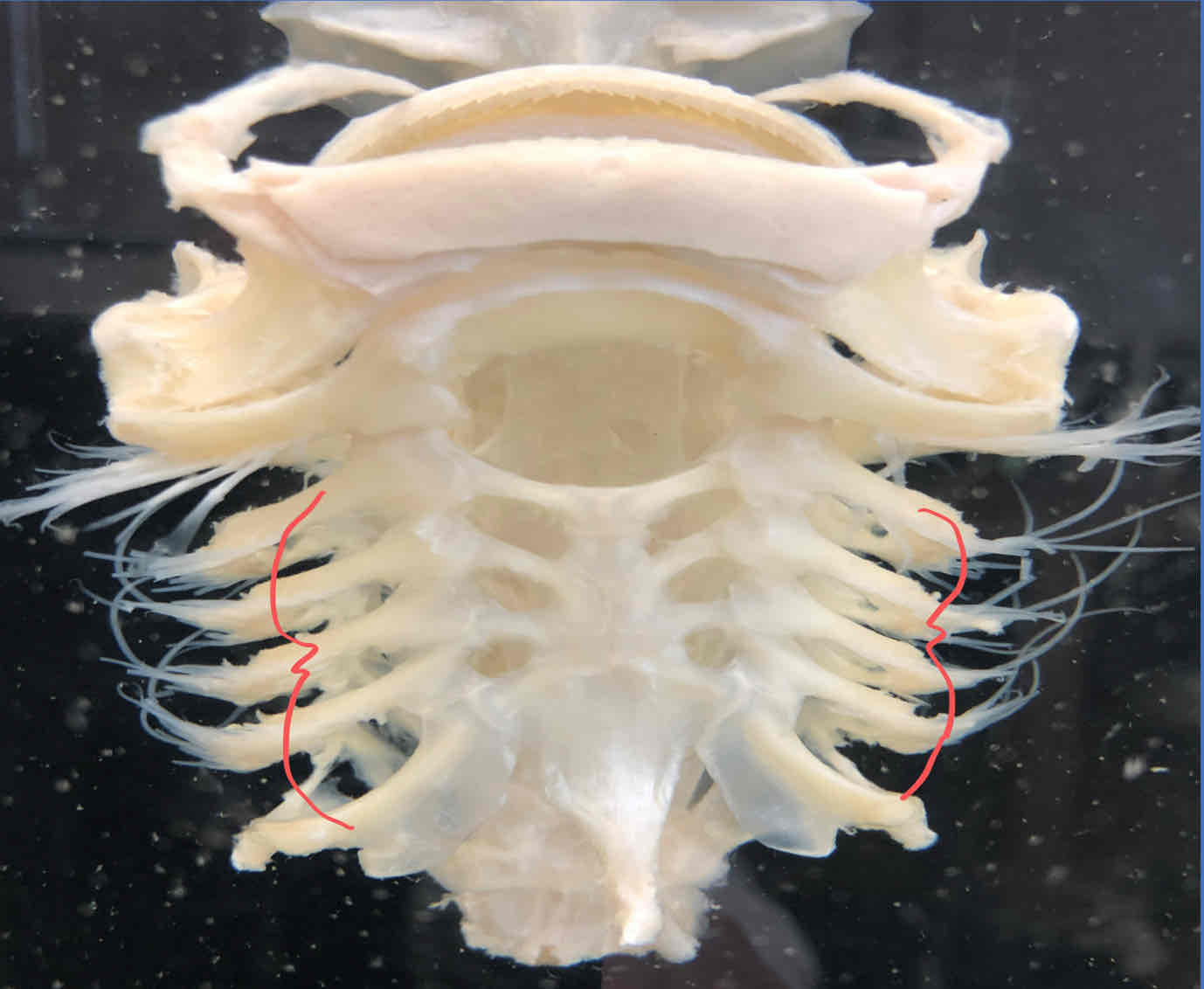
branchial arches (splanchnocranium - shark): surrounds the pharynx and is skeletal support for the gills
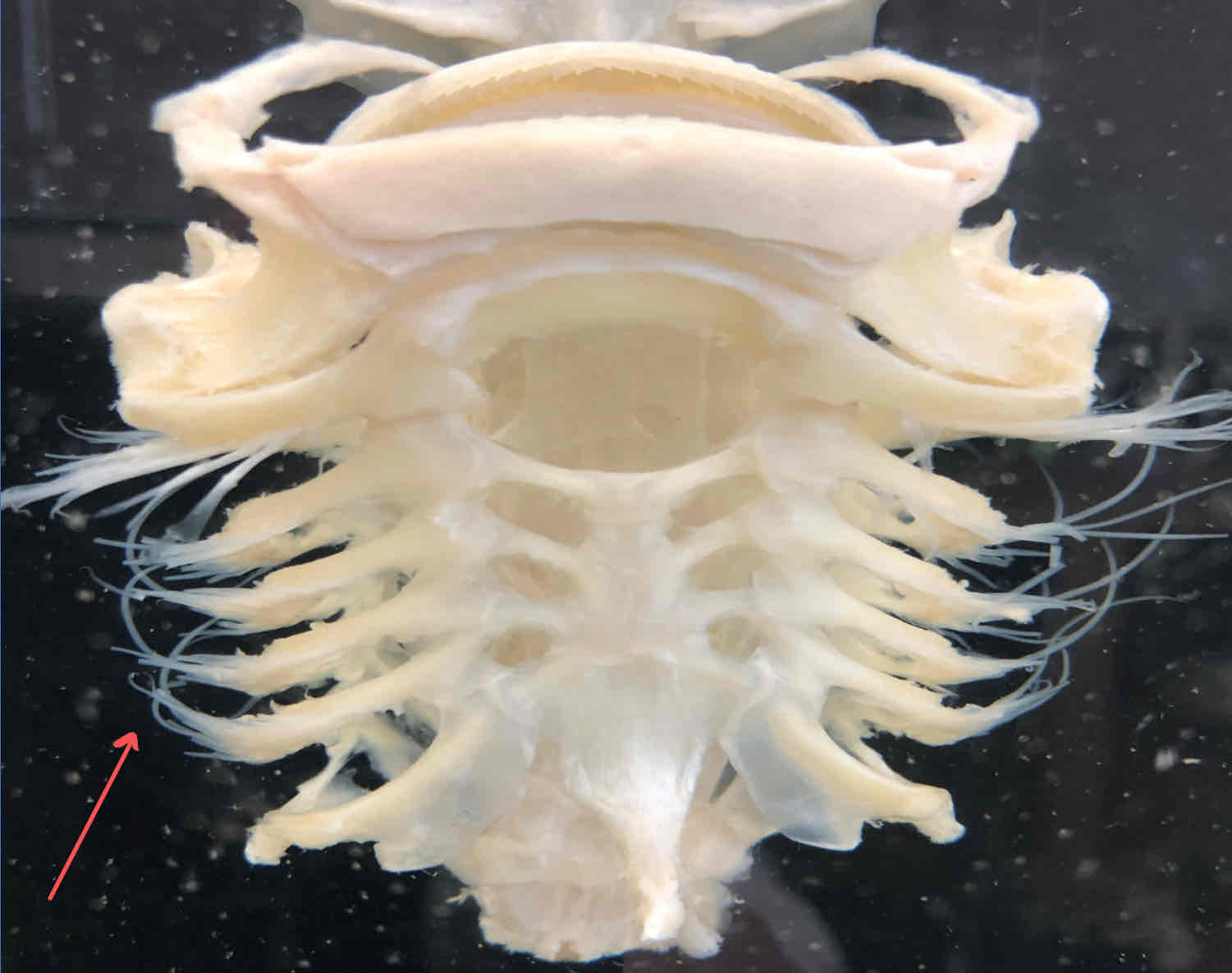
gill rays (splanchnocranium - shark): strengthen the branchial septa, connective tissue that separates adjacent gill pouches
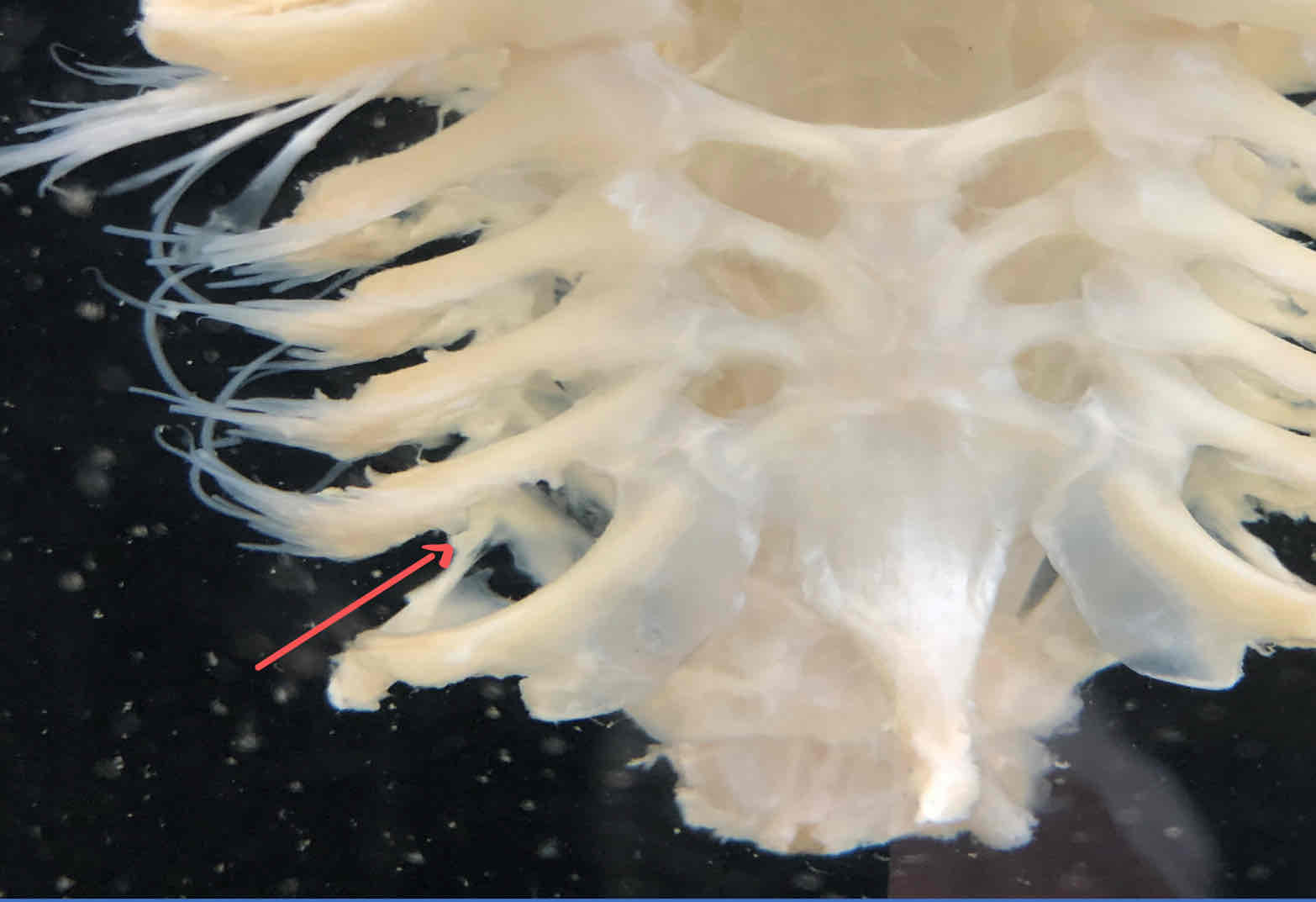
gill rakers (splanchnocranium - shark): act as strainers that prevent food from entering respiratory chambers
What important cartilage in the shark connects the jaw to the chondrocranium at the back of the otic capsules?
hyomandibular cartilgae
What structures of the Necturus are part of the chondrocranium and can only be observed in the acrylic block?
ethmoid plate, occipital condyles, otic capsules
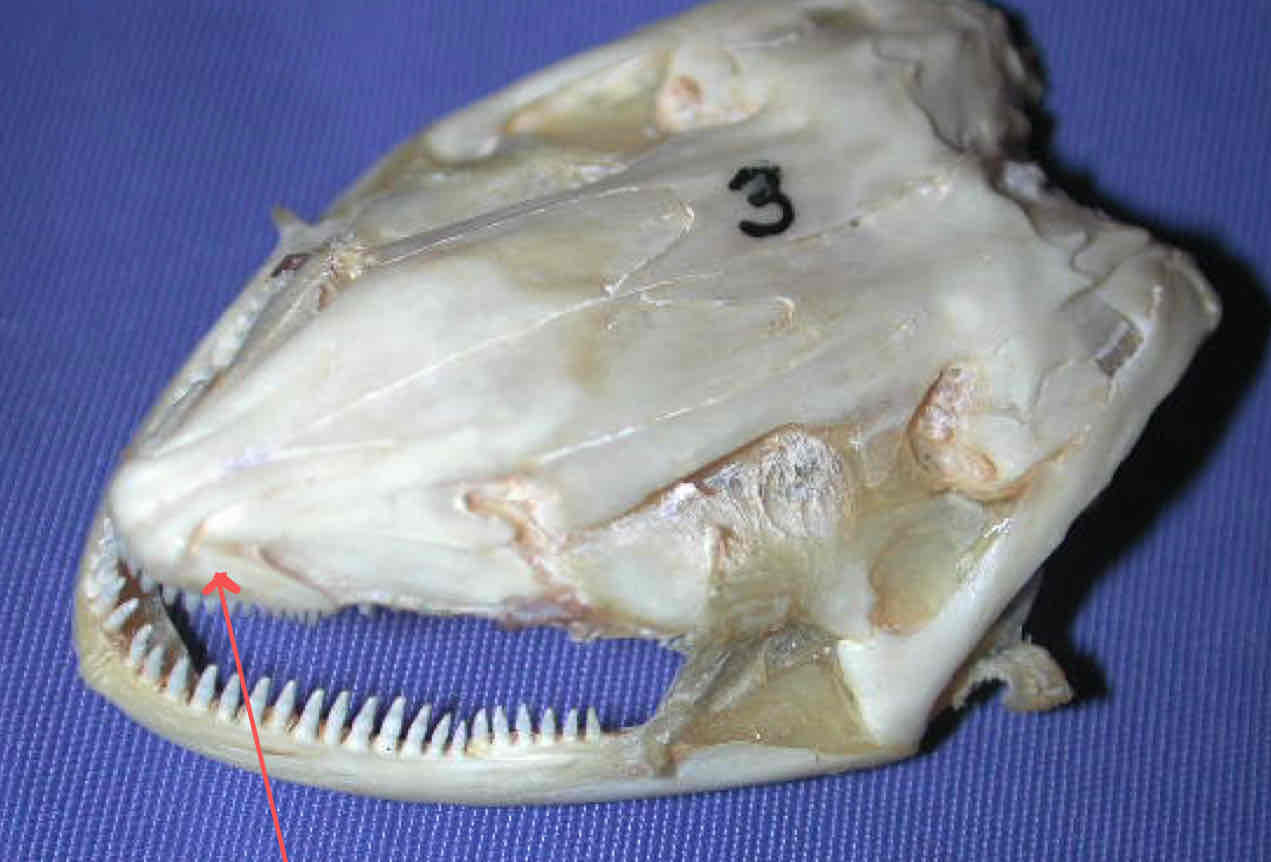
premaxilla (dermatocranium - Necturus): bears teeth and forms the snout tip
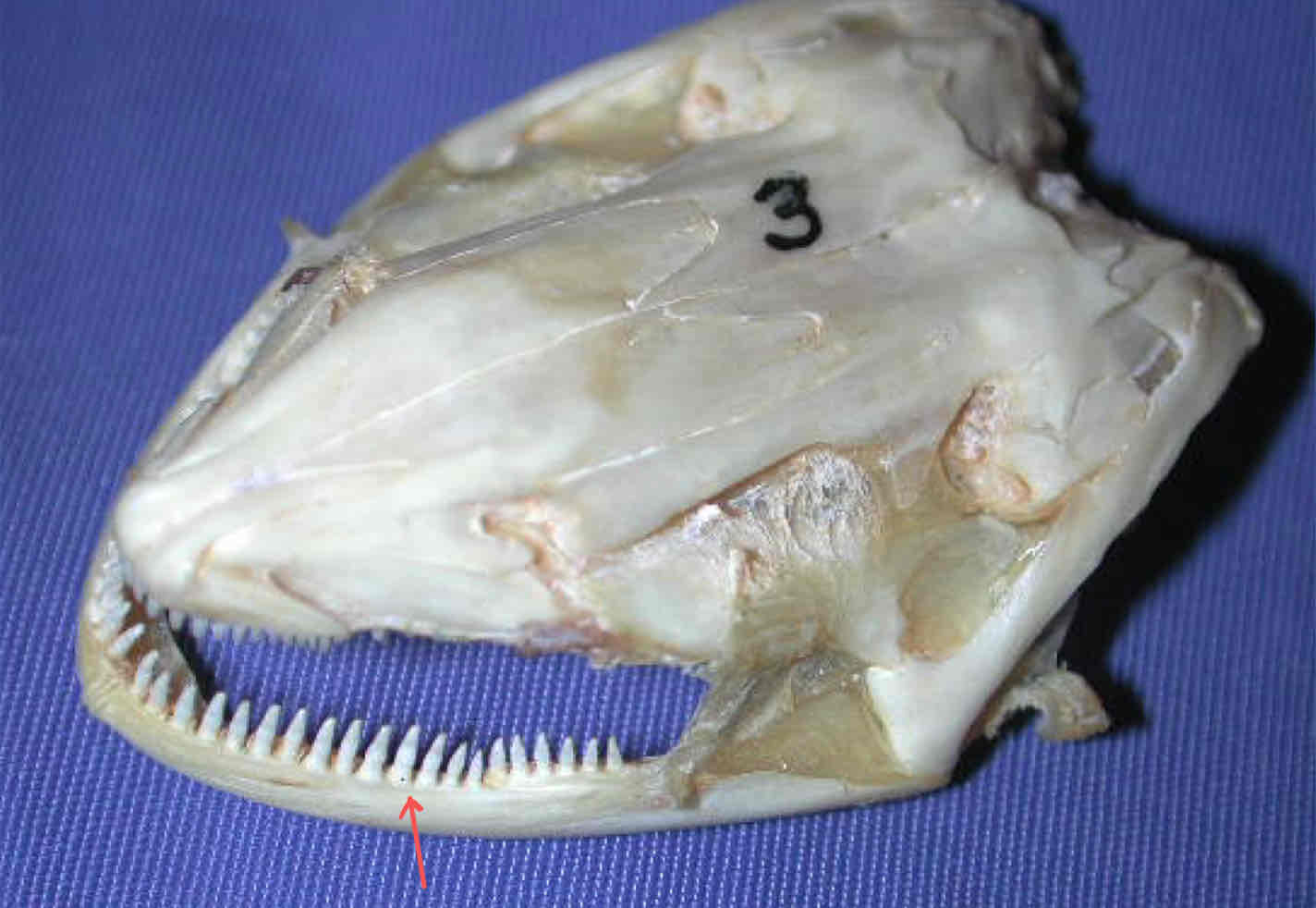
dentary (dermatocranium - Necturus): part of the madible that bears teeth and covers Meckel’s cartilgae
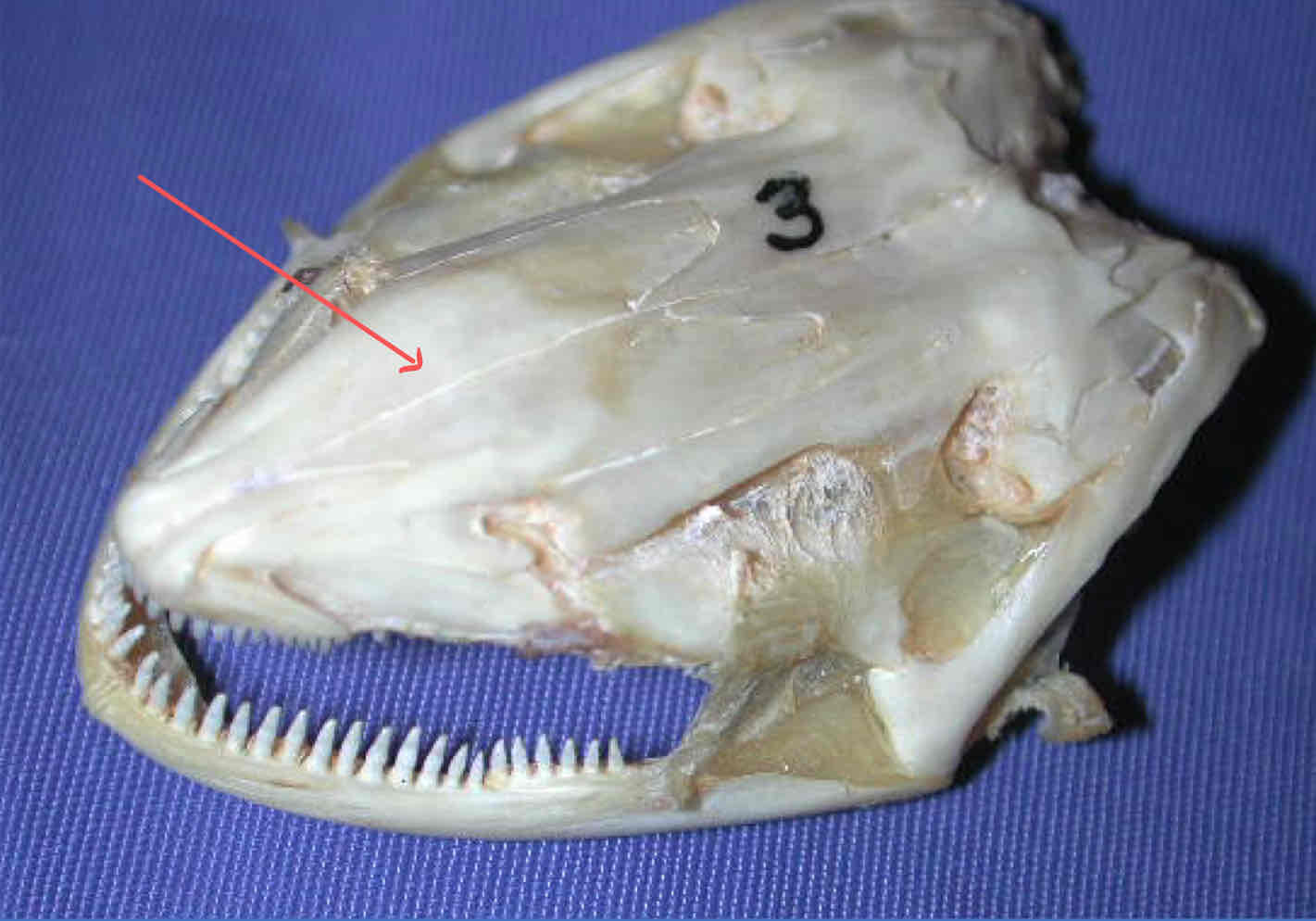
frontal bone (dermatocranium - Necturus): protect the brain
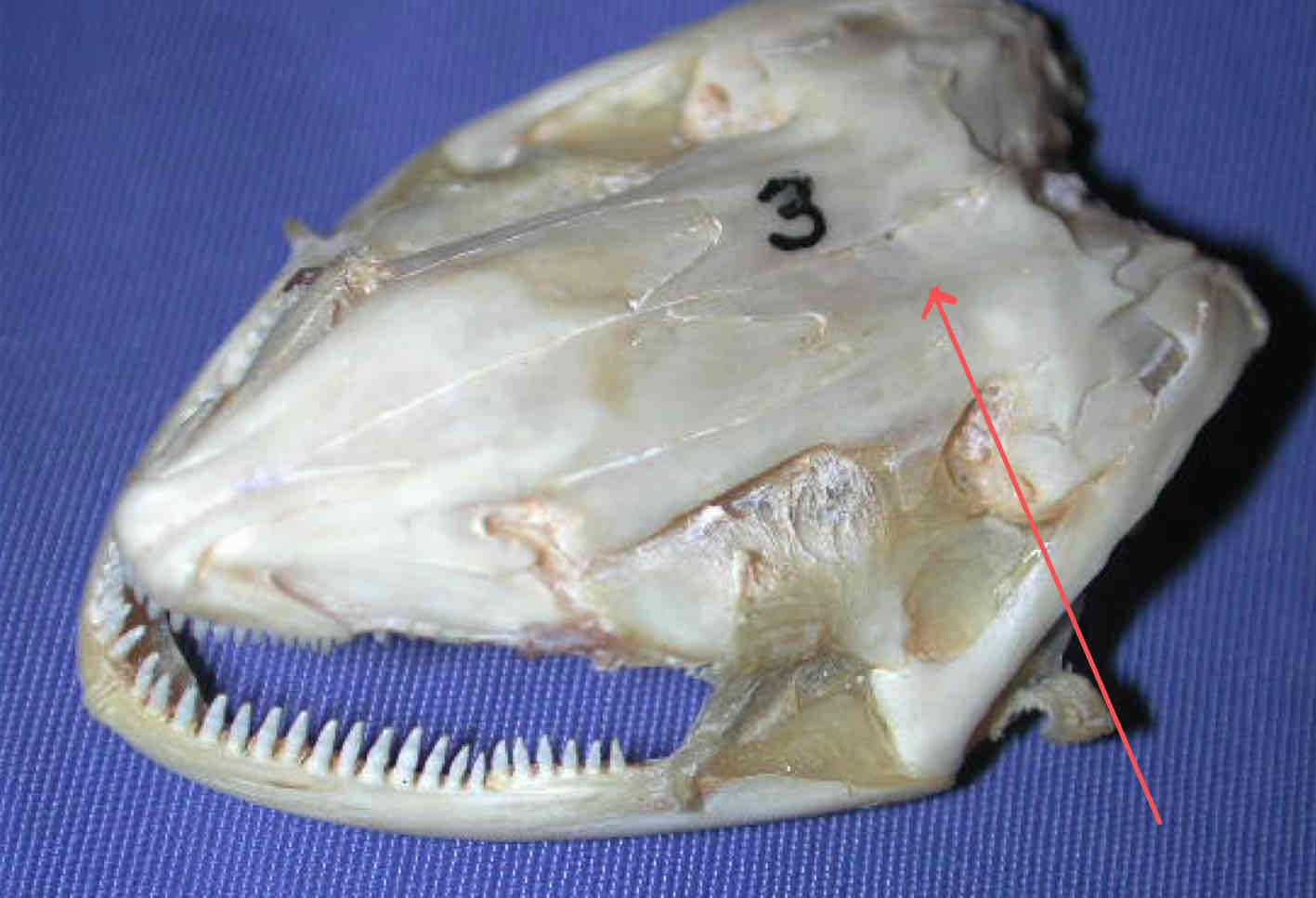
parietal bone (dermatocranium - Necturus): protects the dorsal surface of the brain
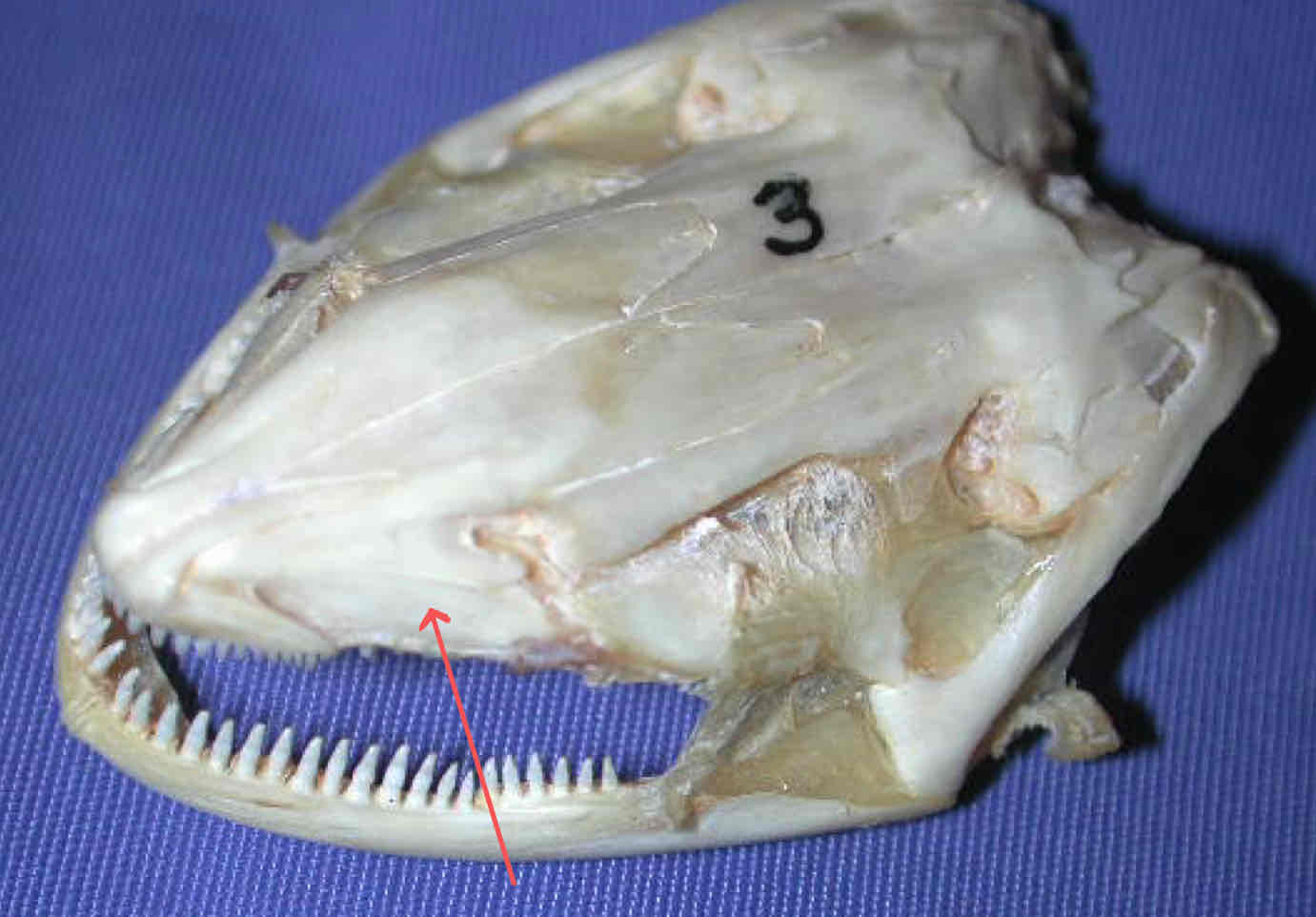
vomer (dermatocranium - Necturus): bears a second row of teeth, sits caudal to the premaxilla
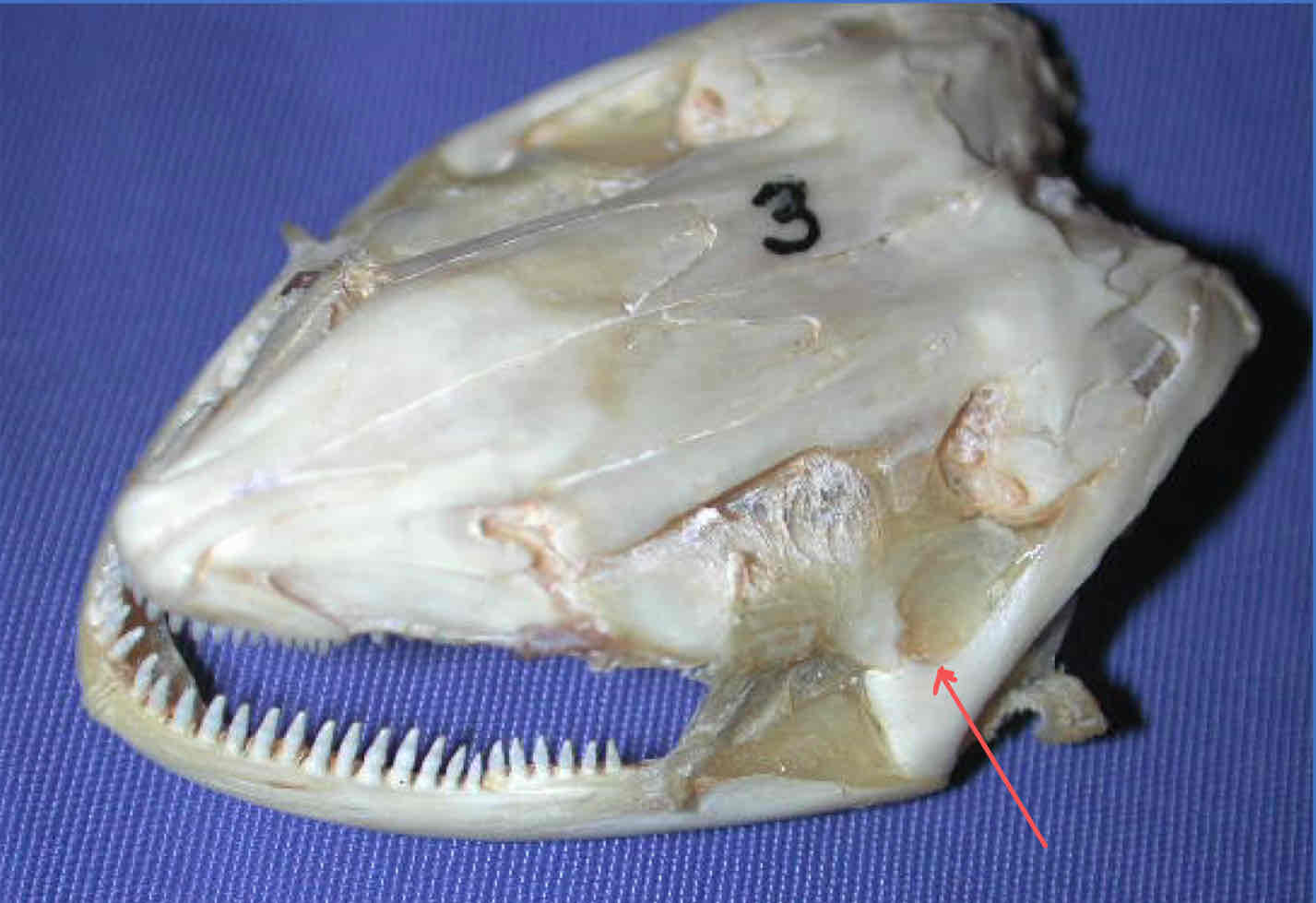
quadrate (splanchnocranium - Necturus): articulates with the jaw
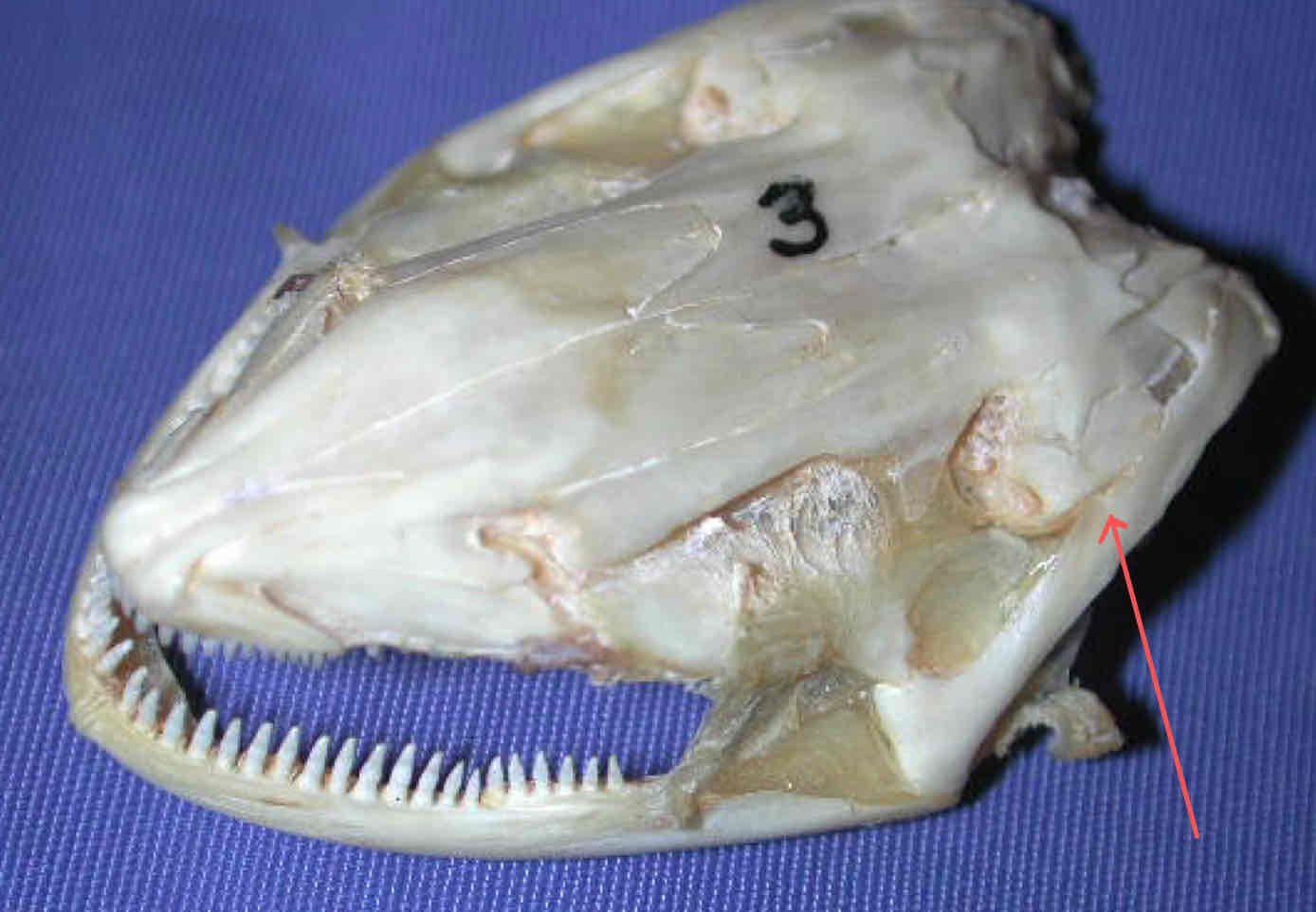
squamosal (dermatocranium - Necturus): articulates with the quadrate
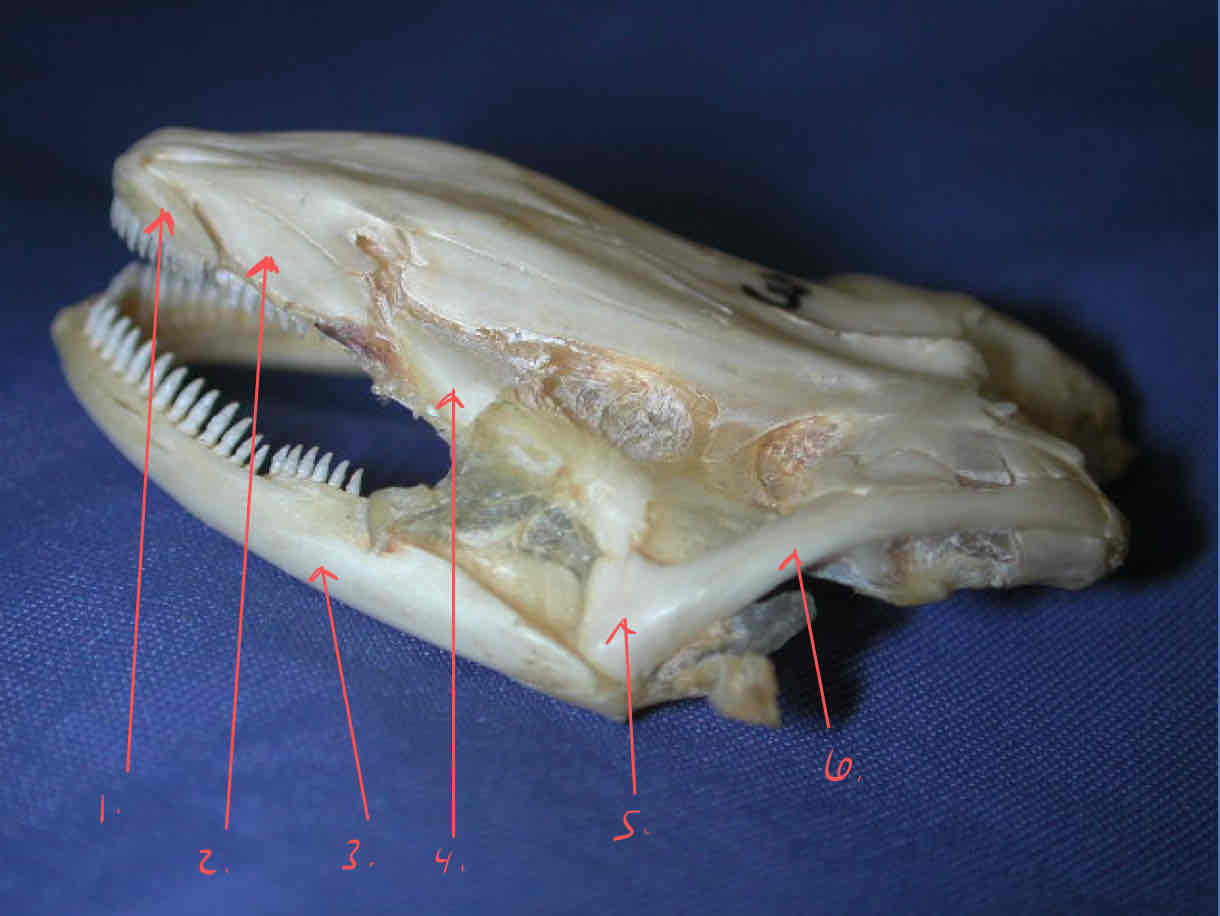
premaxilla
vomer
dentary
pterygoid (dermatocranium): bears teeth, caudal to the vomers
quadrate (splanchnocranium)
squamosal
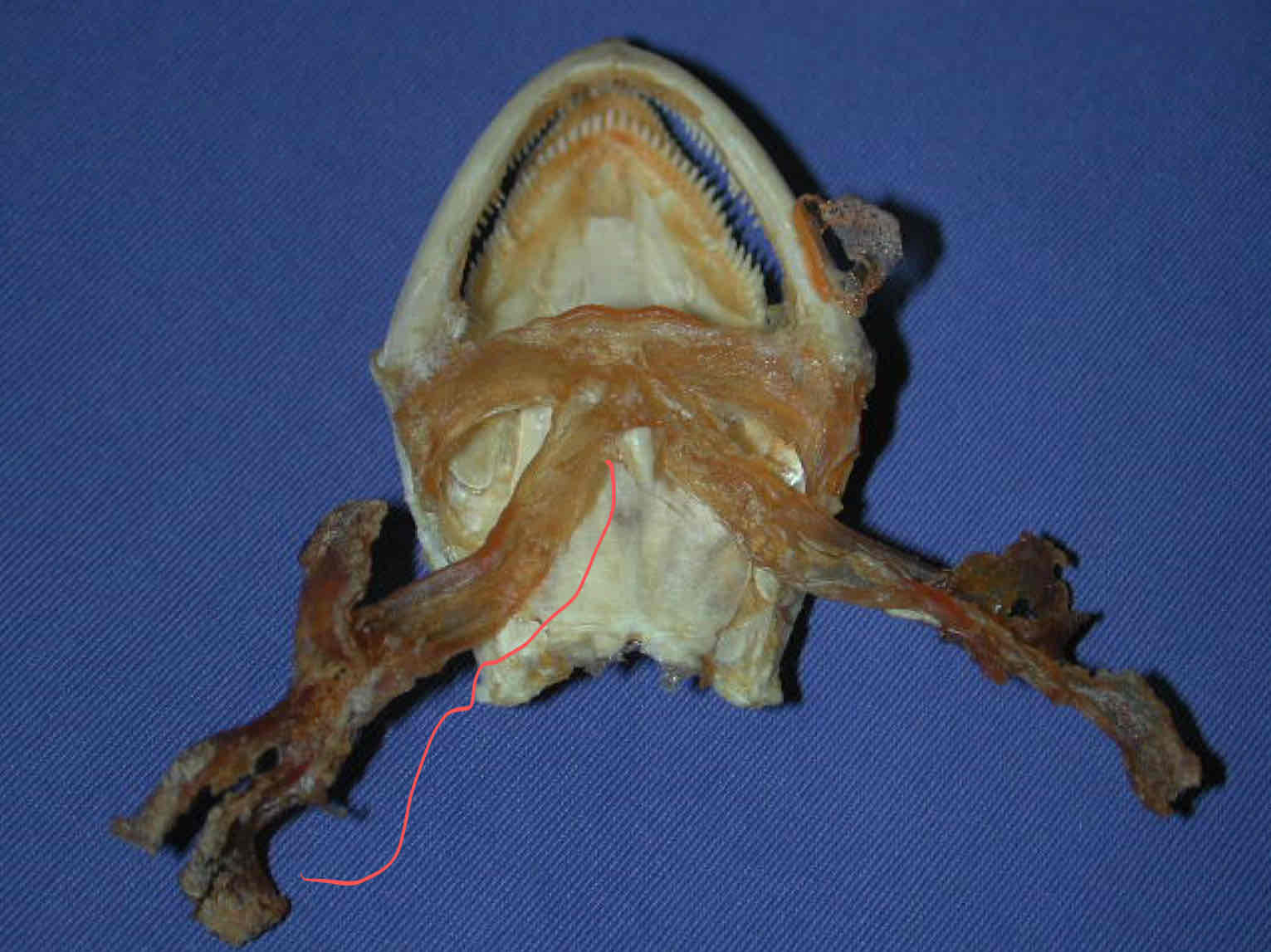
hyoid apparatus (splanchnocranium - Necturus): supports the gills
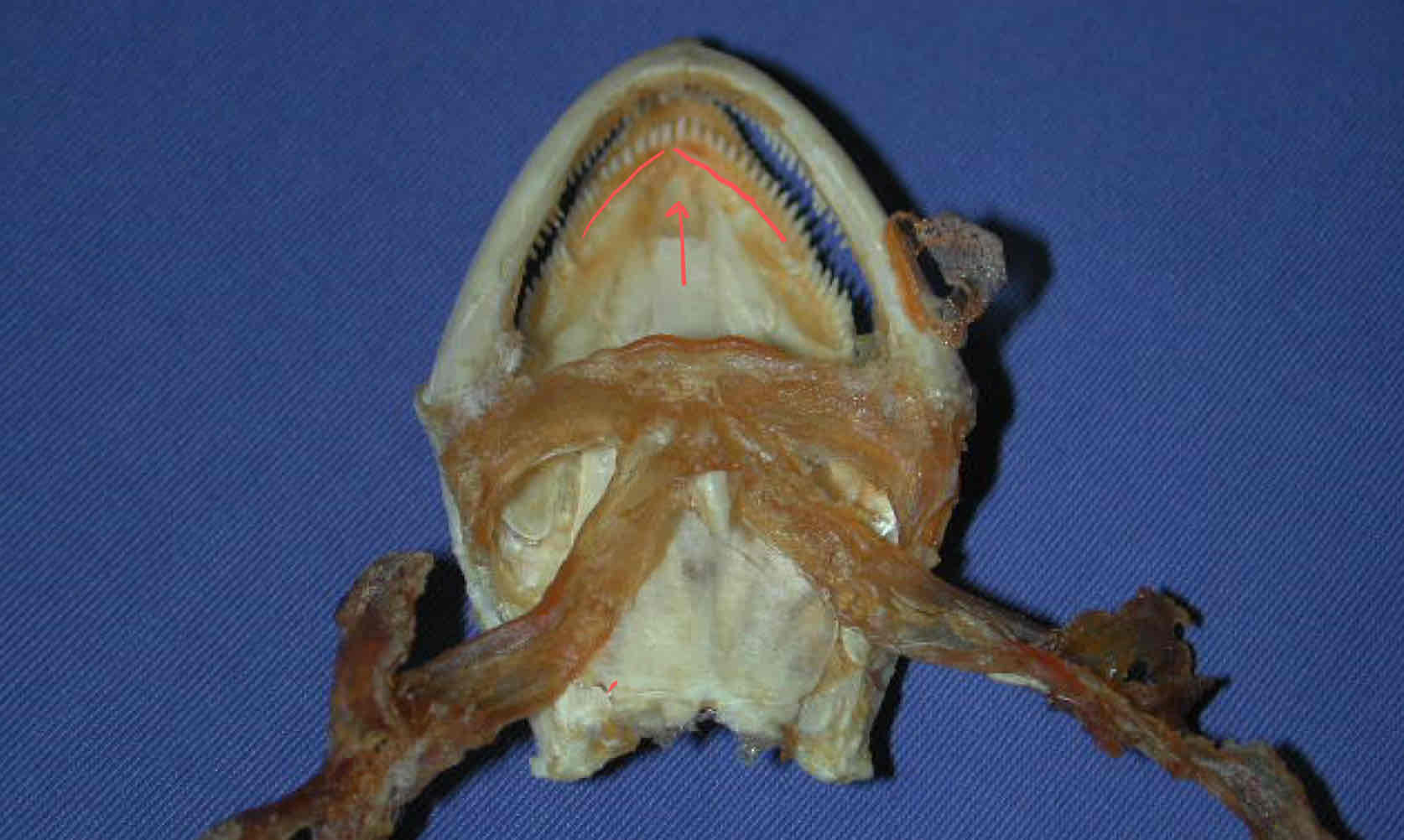
vomers
Where is Meckel’s cartilage located in the Necturus?
It is covered by the dentary but can be observed caudally. It is part of the splanchnocranium and articulates with the quadrate cartilage and bone
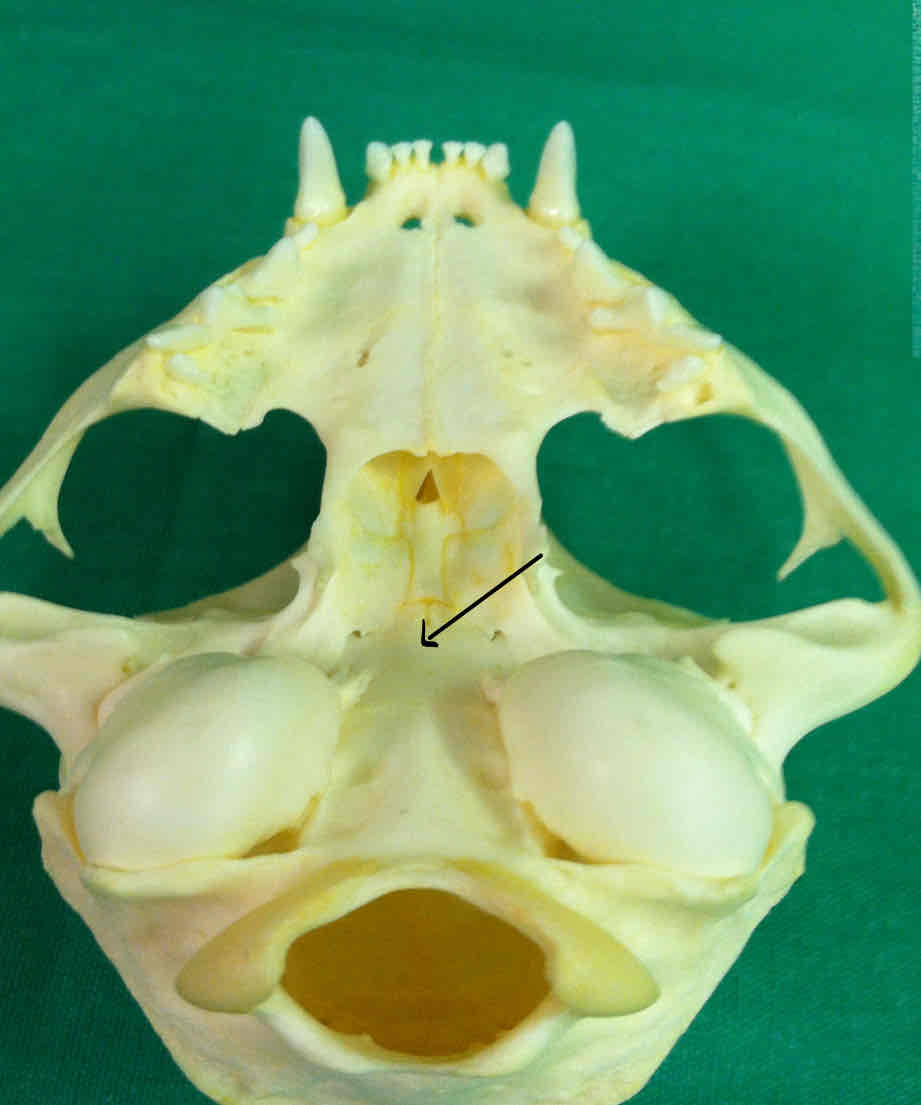
What is the hard palate of the Necturus called?
the parasphenoid - it extends from the occipital condyles to the vomers
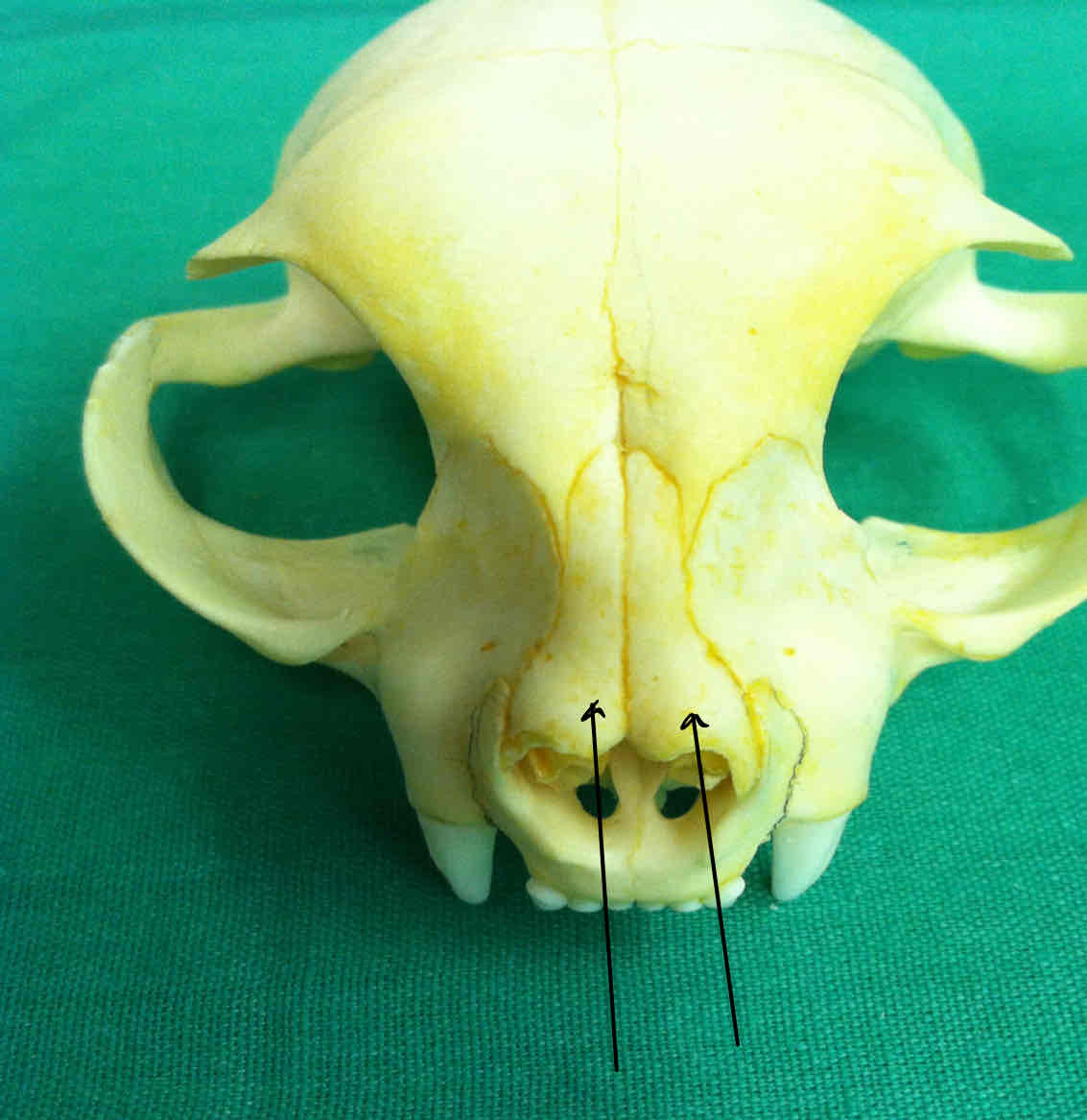
nasal bones (dermatocranium): covers the nasal cavity
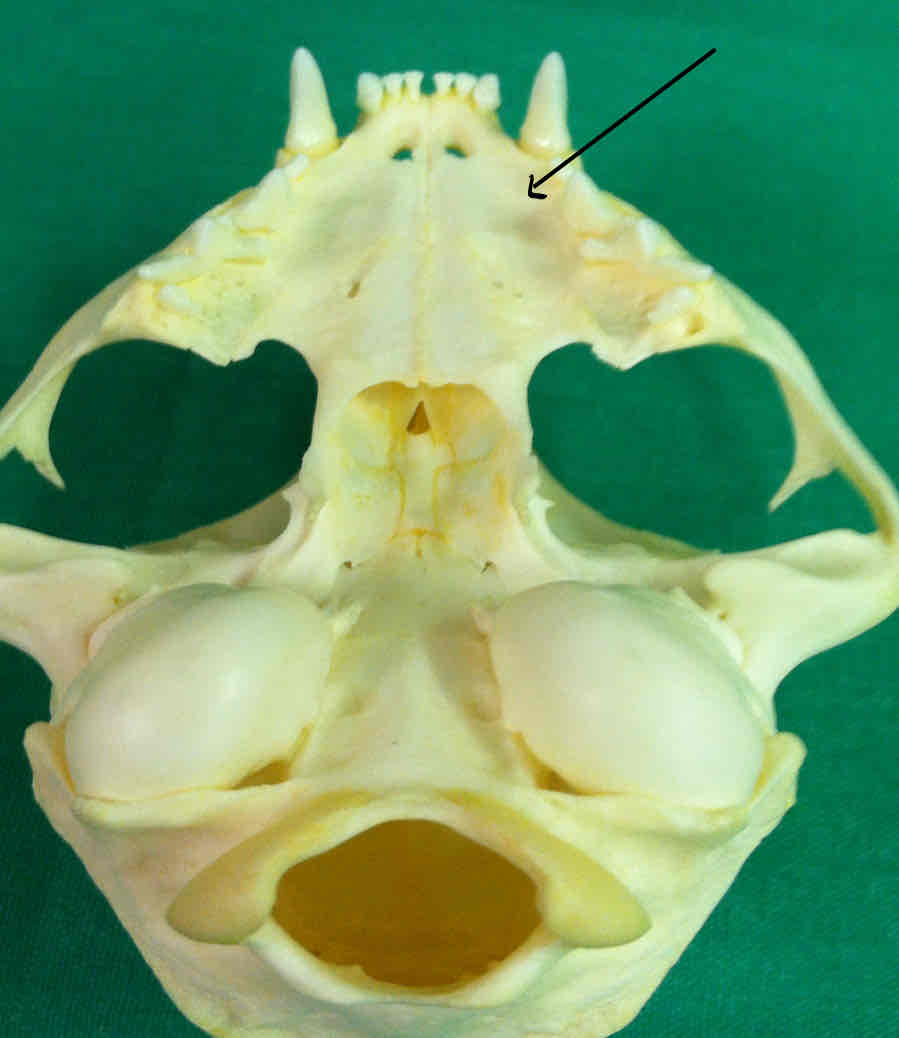
premaxilla (dermatocranium): holds the incisors; the palatine process of the premaxilla contributes to the hard palate
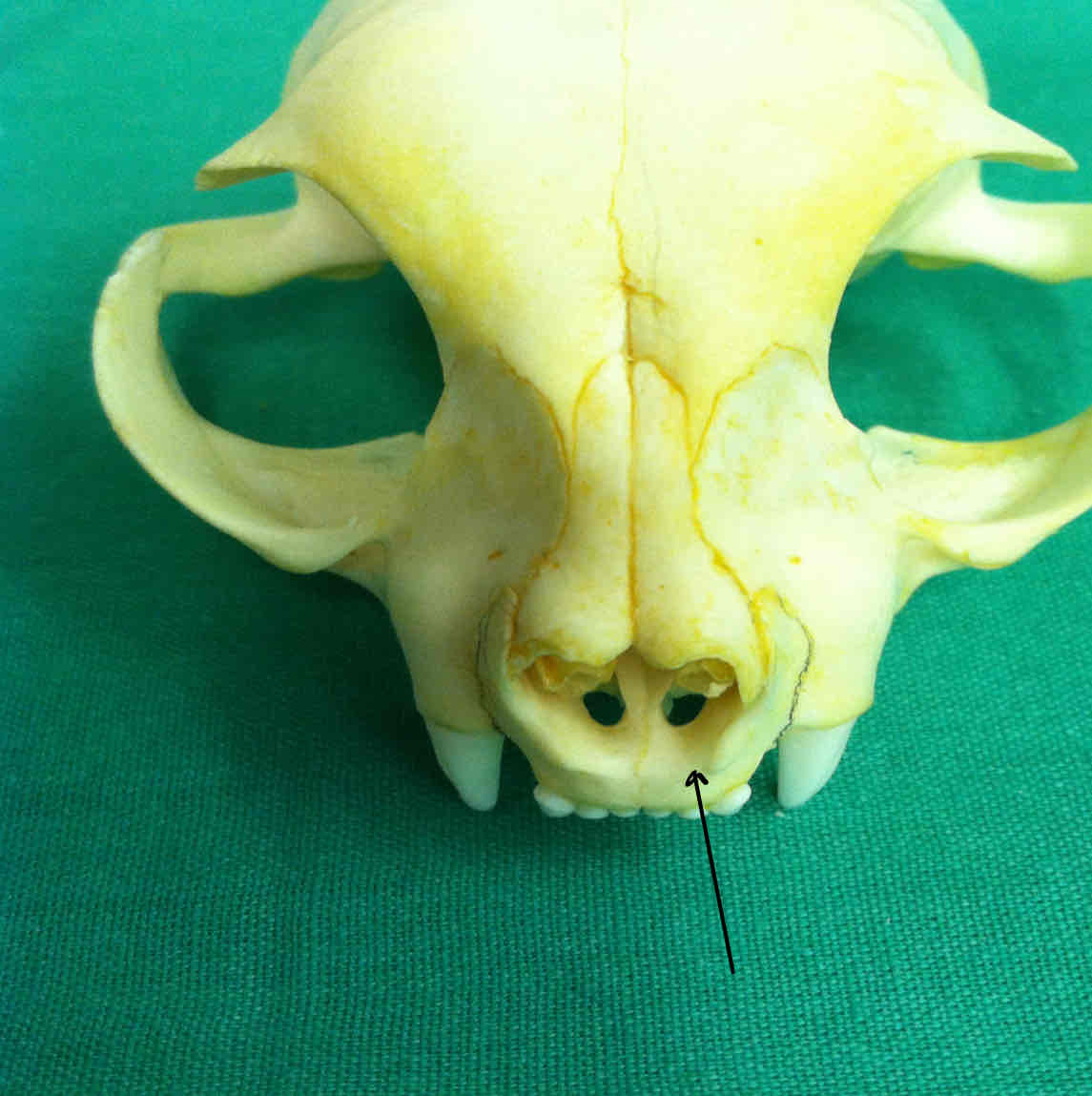
maxilla (dermatocranium): holds the canines and premolars, palatine process of the maxillae contribute to the hard palet
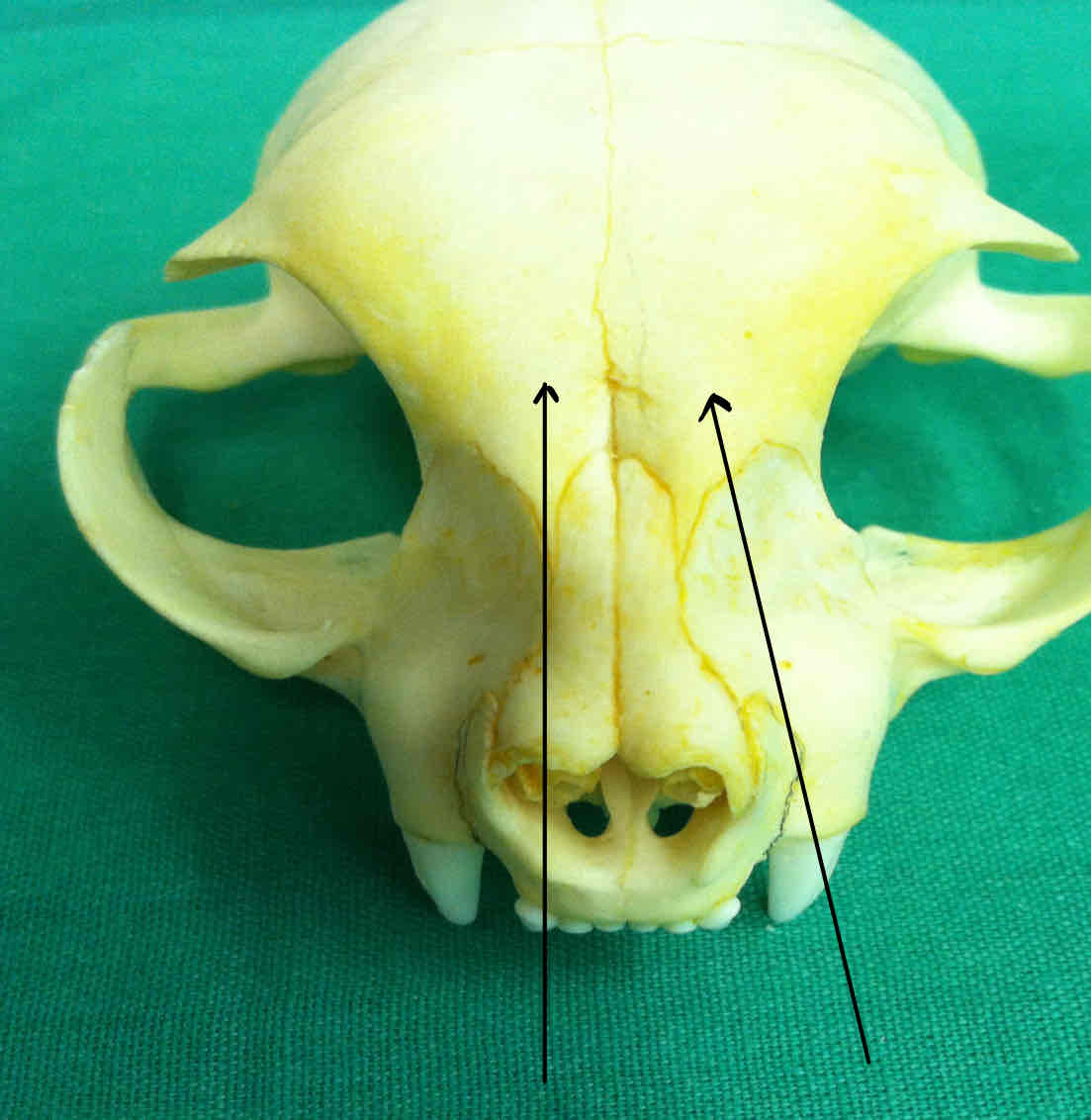
frontal bones (dermatocranium): protect the brain
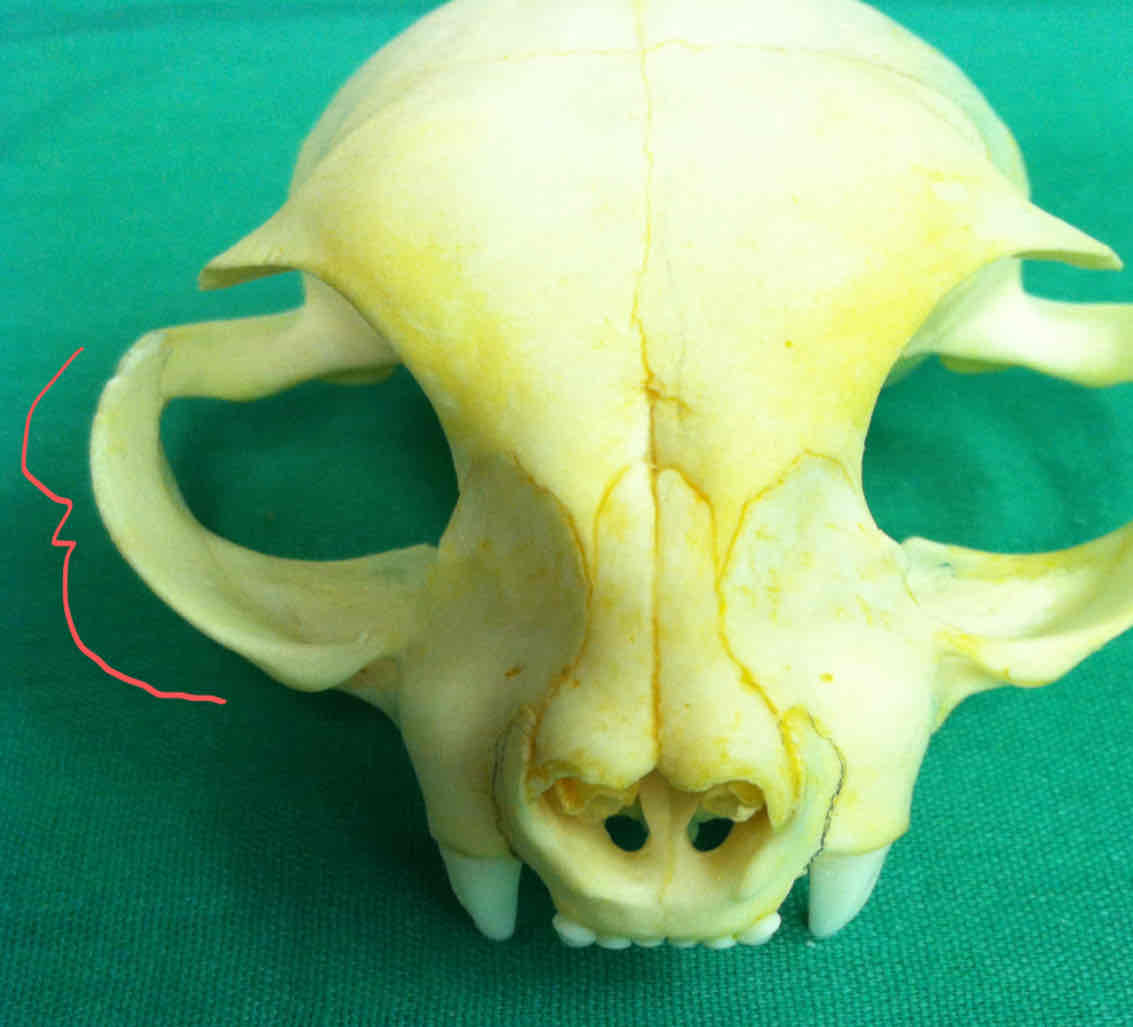
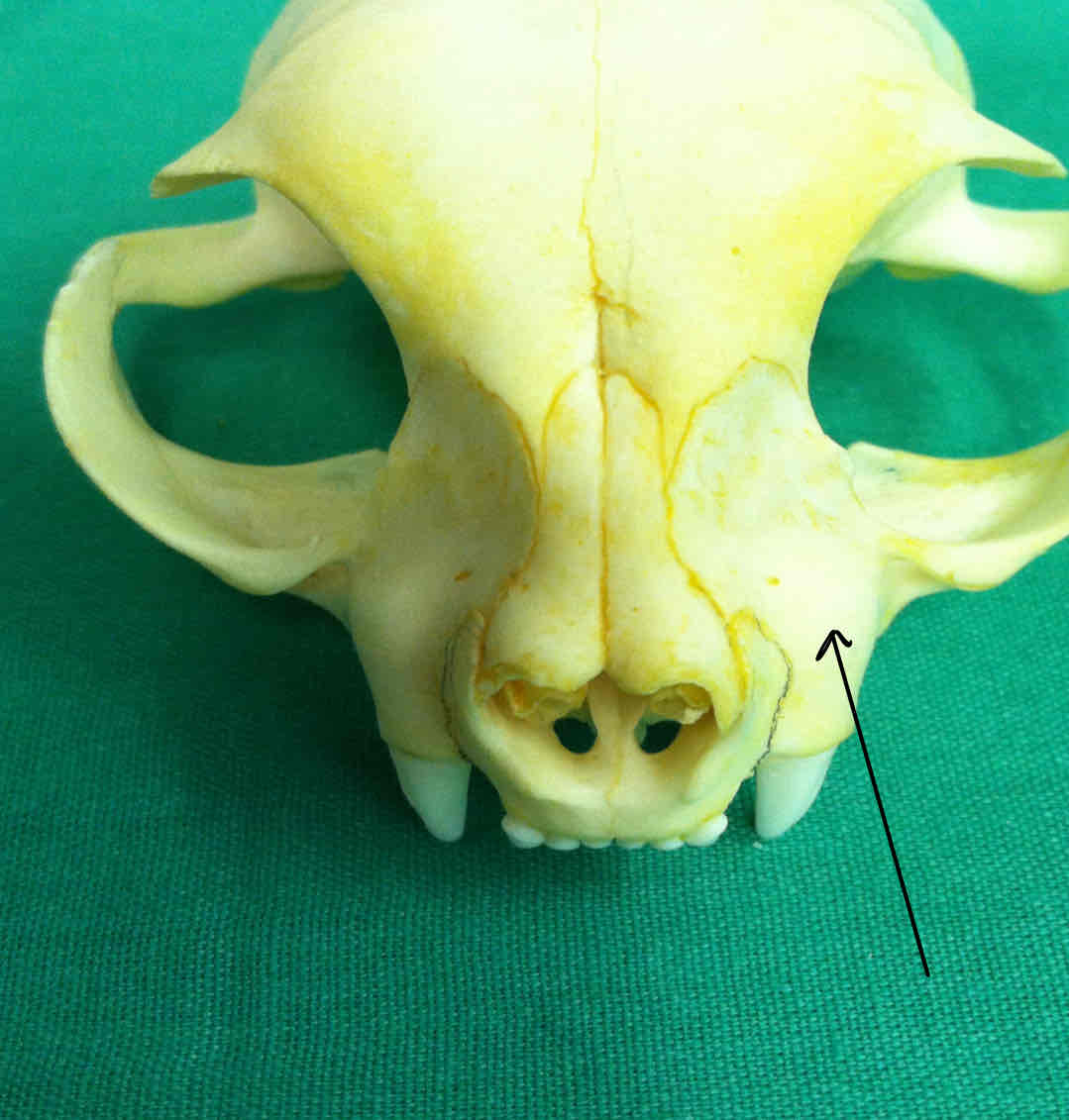
zygomatic arch (dermatocranium): makes up the cheekbone and forms the lateral boundary of the eye orbit
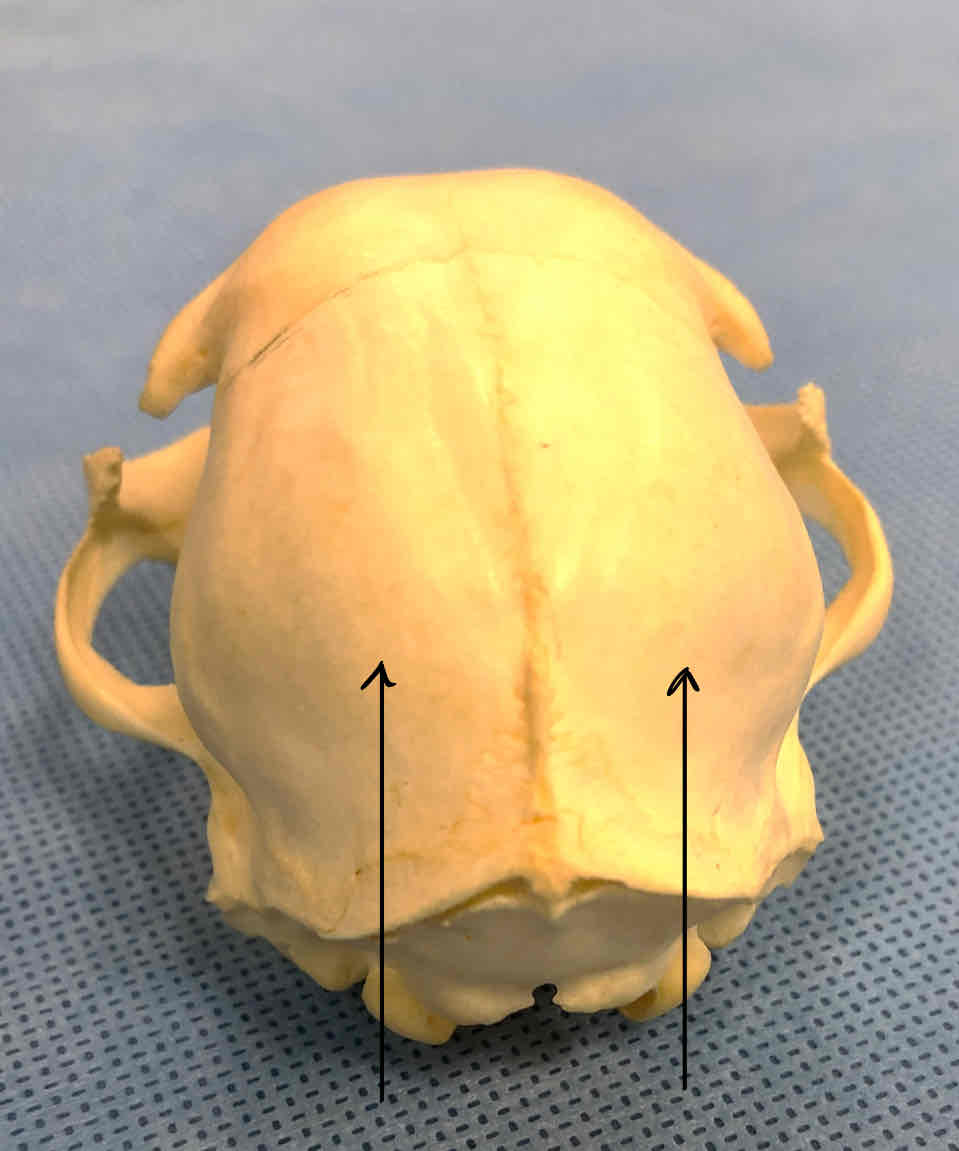
parietal bones (dermatocranium): protects the dorsal surface of the brain
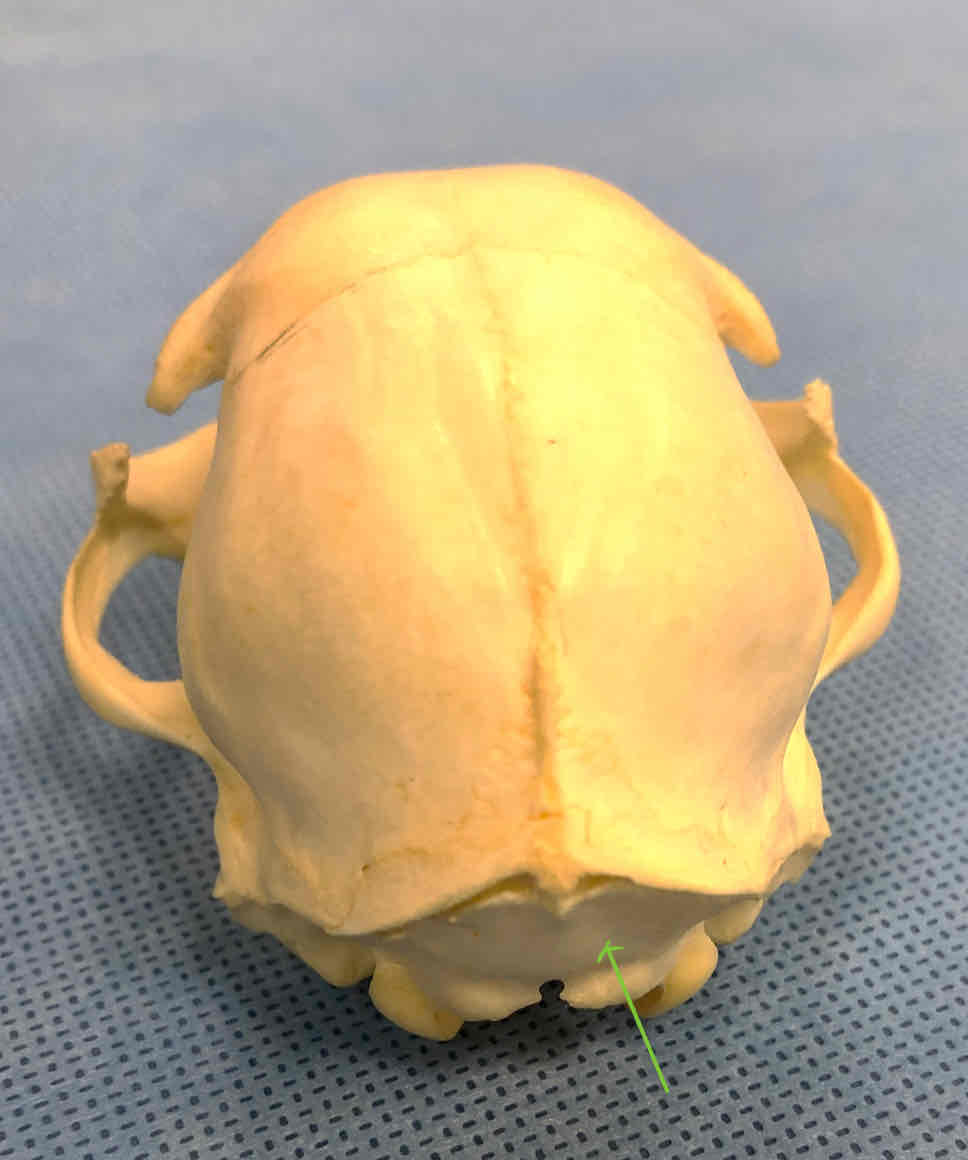
occipital bone (chondrocranium): forms the caudal part of the skull; has occipital condyles that articulate with the atlas
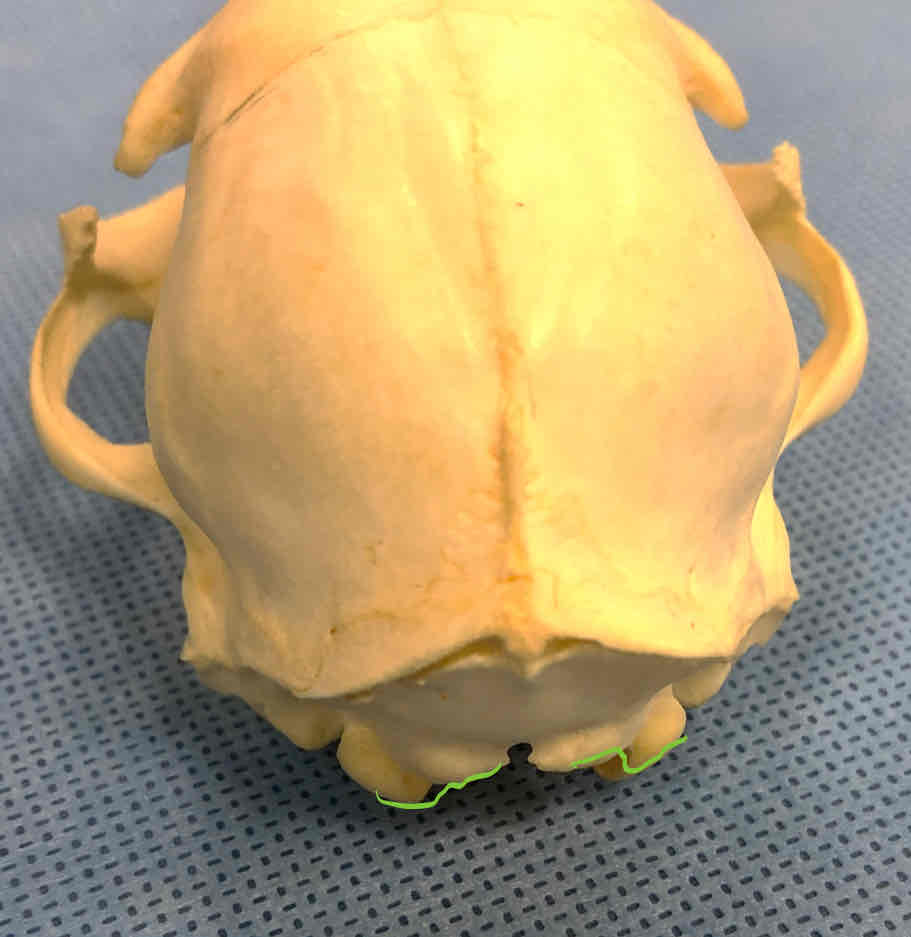
occipital condyles (chondrocranium): articulate with the atlas
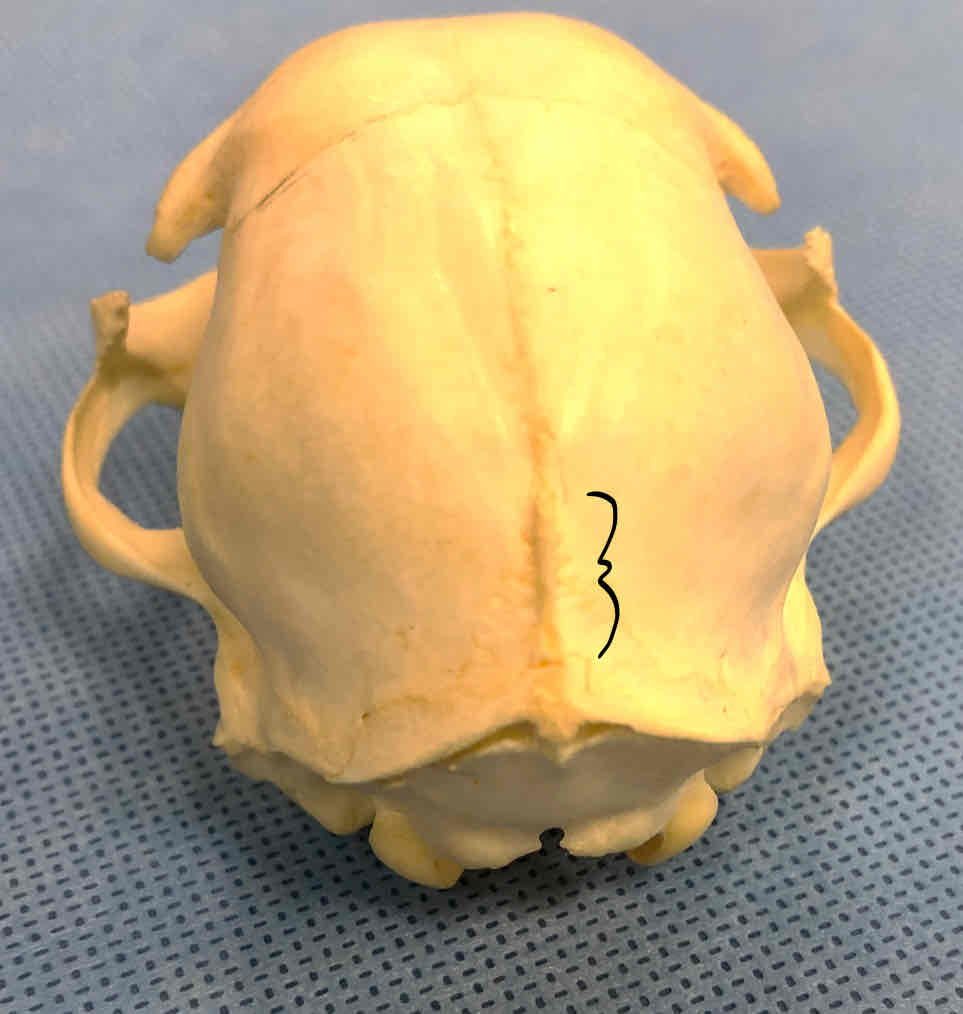
sagittal crest (dermatocranium): a medial projection from the interparietal and a site for muscle attachment
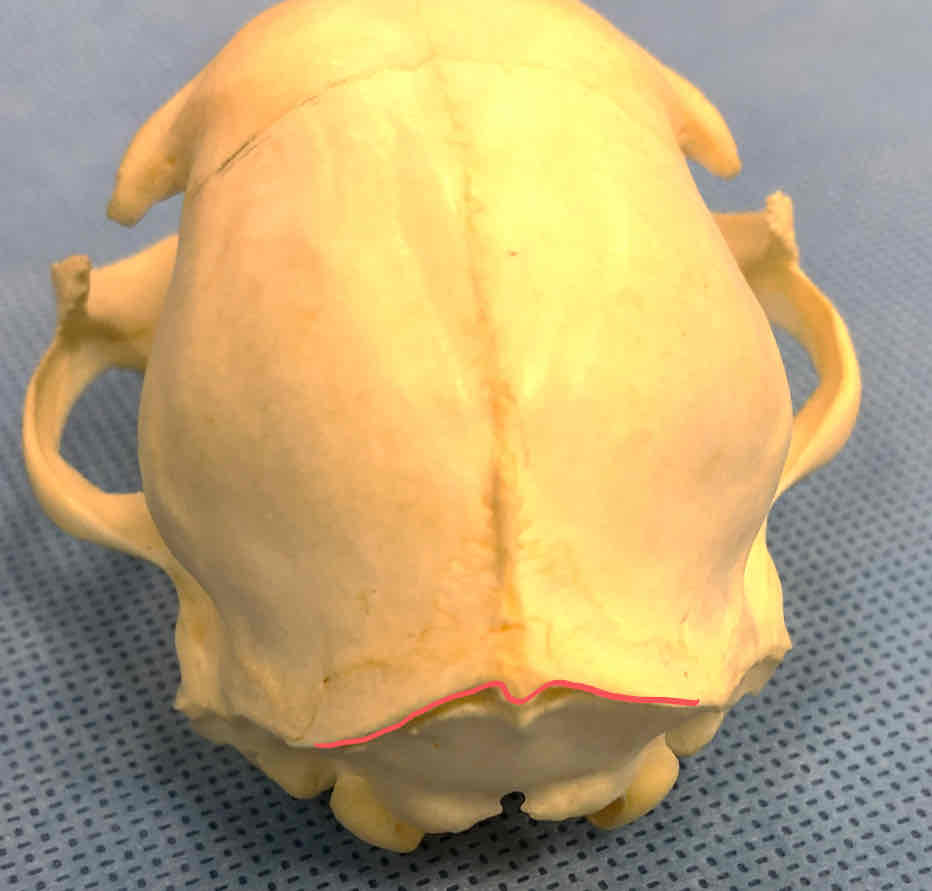
nuchal crest (or lambdoidal ridge) (dermatocranium): attachment site for muscles and tendons involved in movement of the head
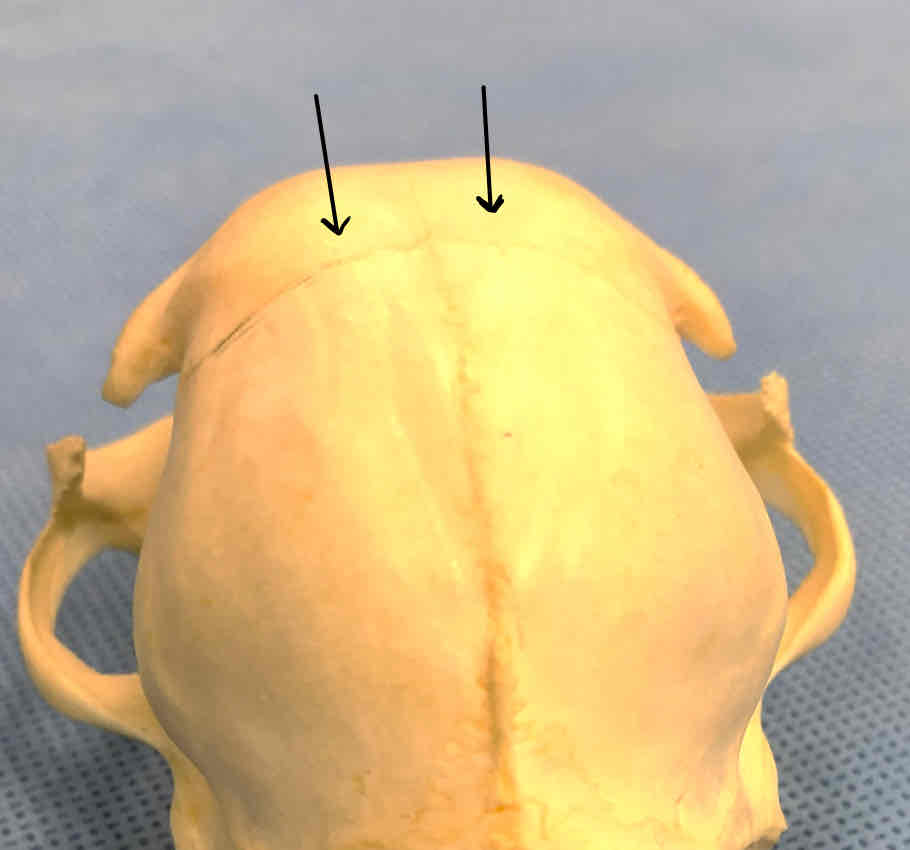
frontal bones (dermatocranium): protects the brain
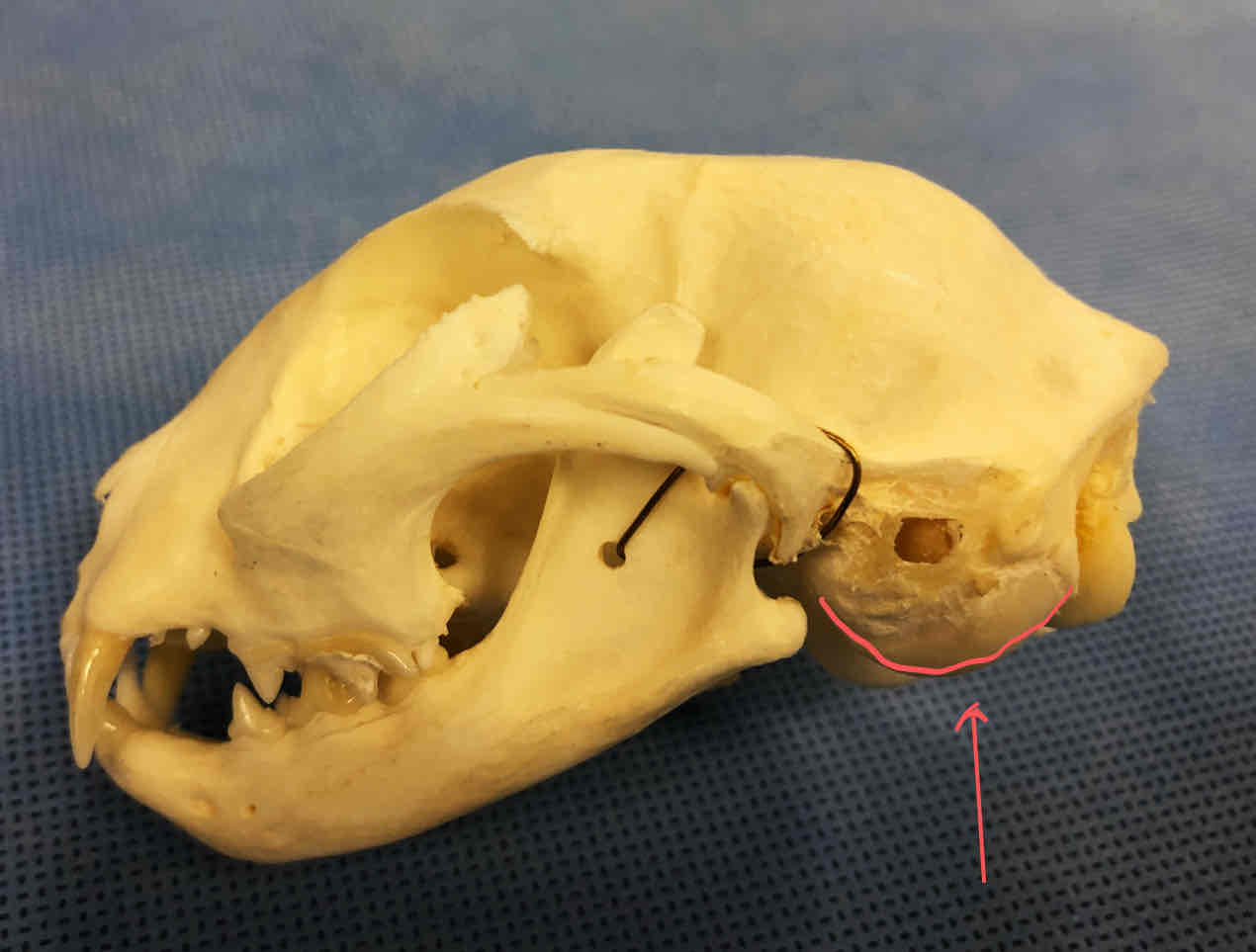
tympanic bulla (dermatocranium): part of the temporal bone, contains the bones of the middle and inner ear
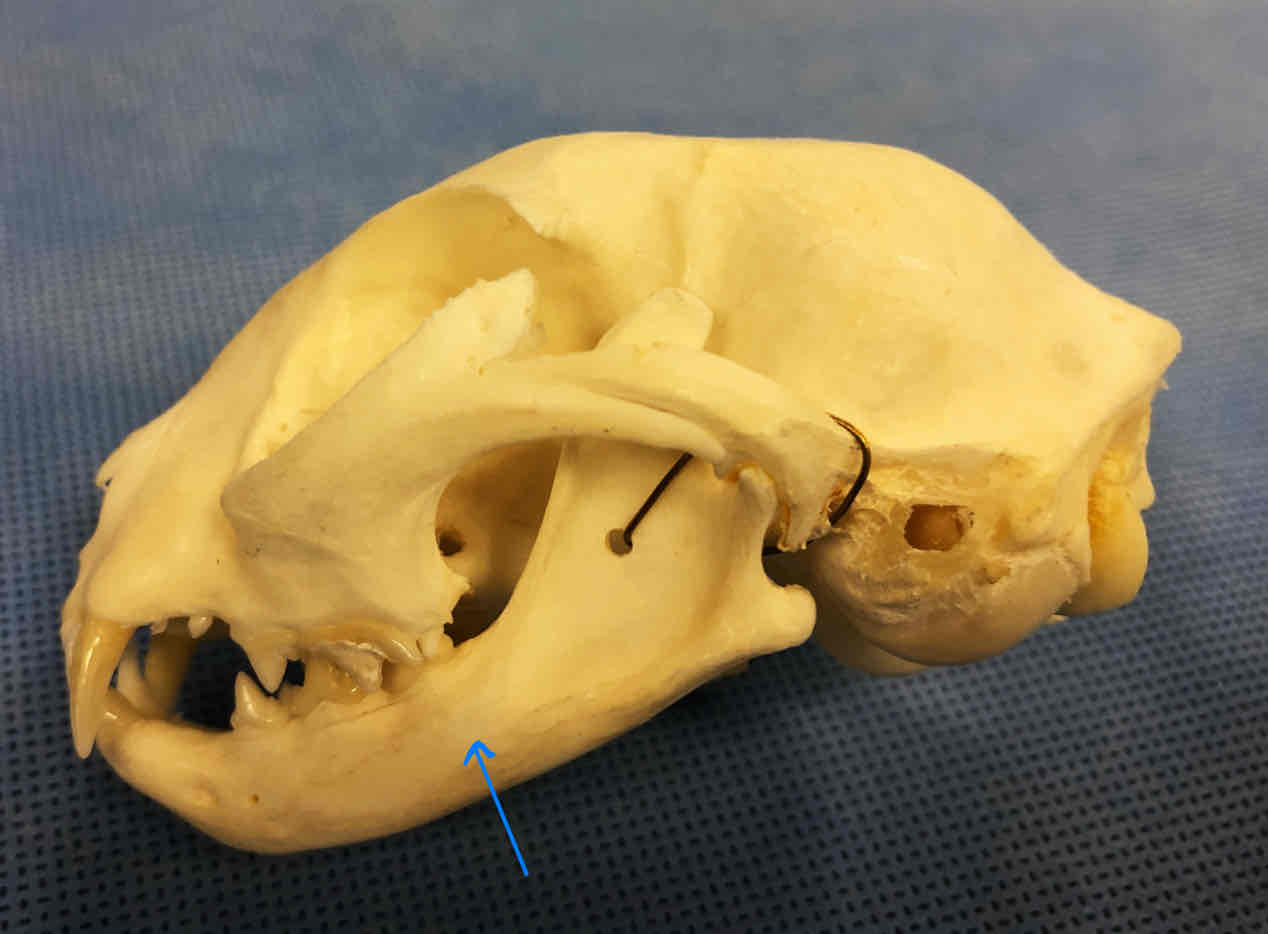

mandible (dermatocranium): makes up the lower jaw, each half is considered a dentary
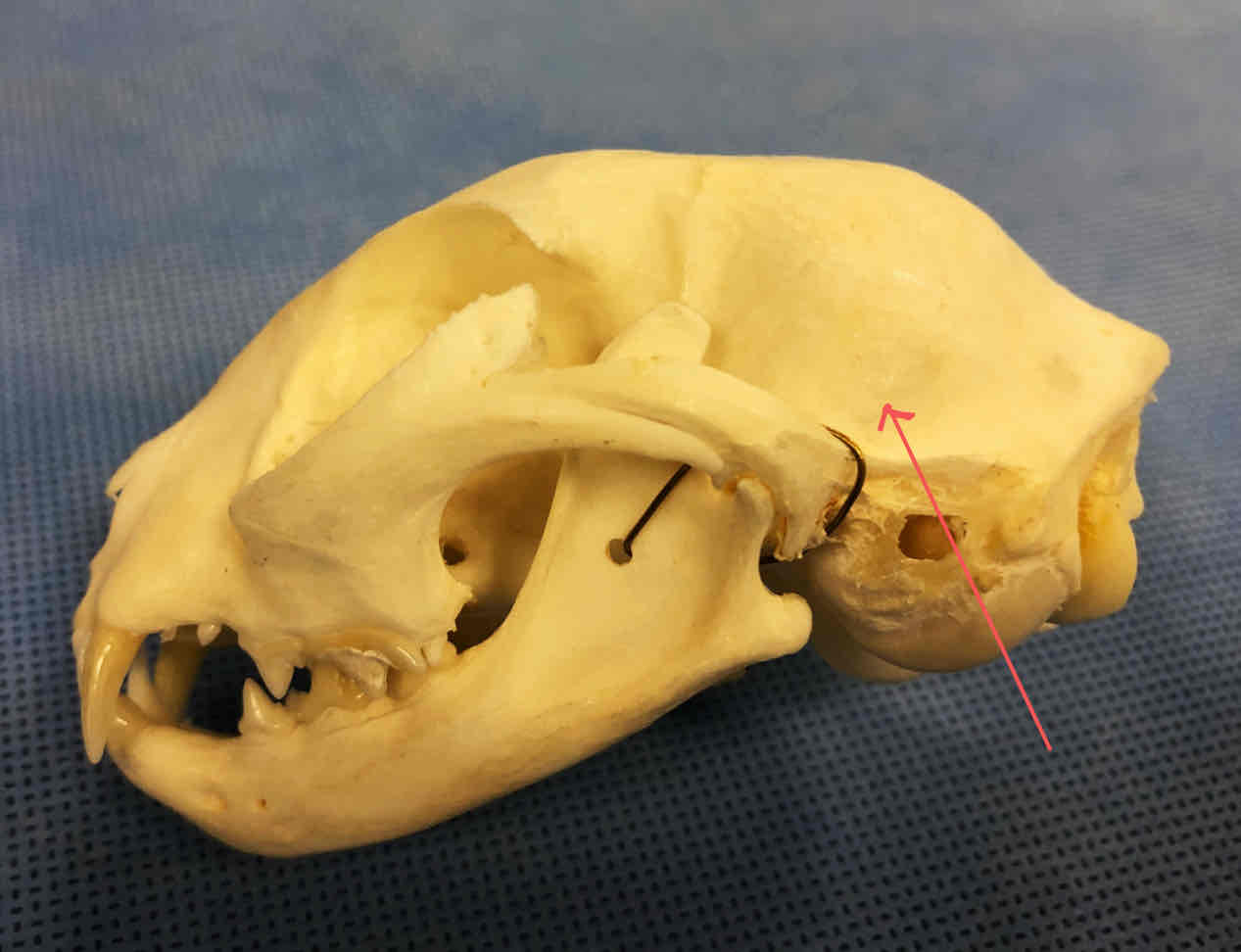
squamous portion of the temporal bone (dermatocranium): makes up the caudal part of the skull
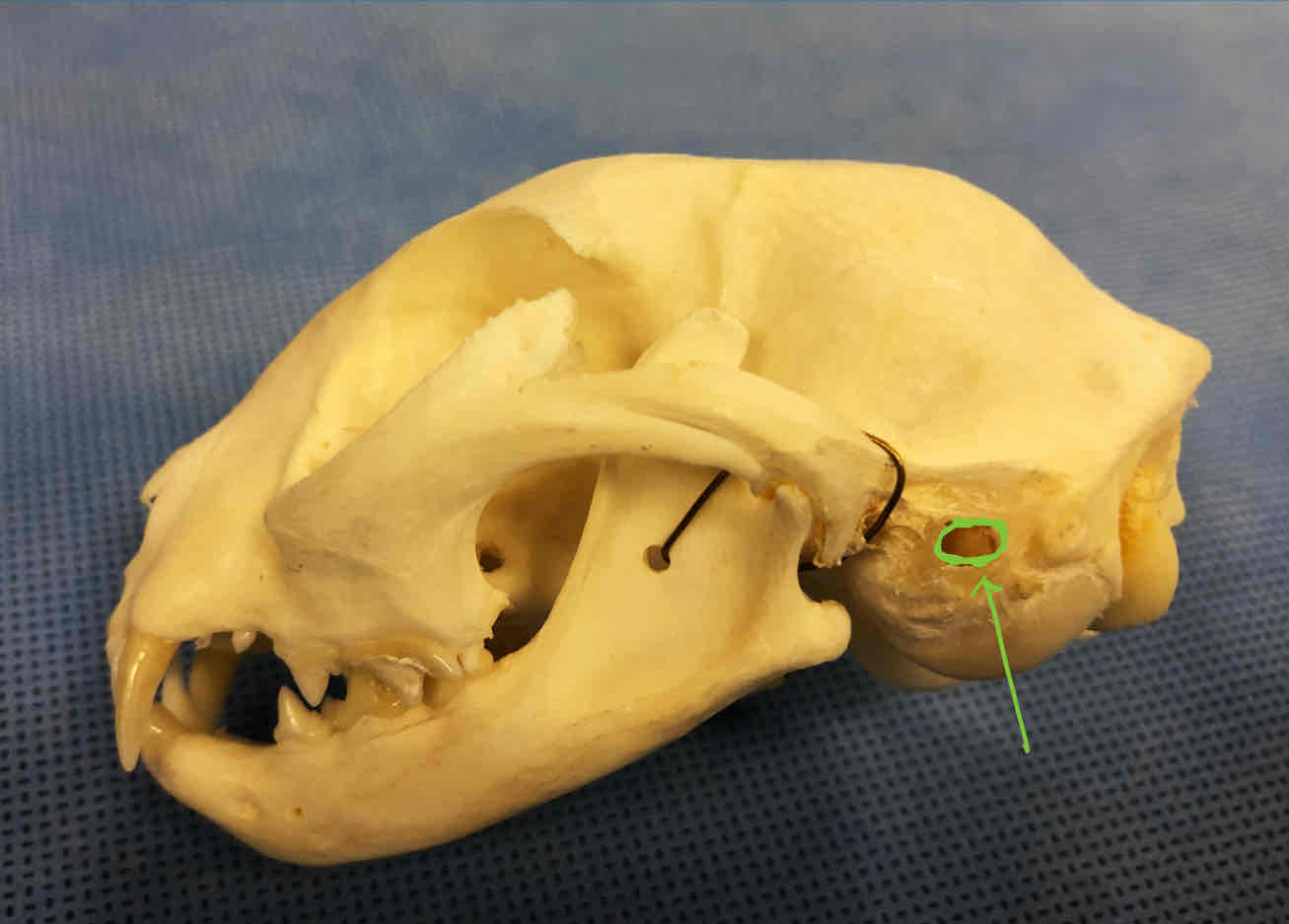
external auditory meatus: opening that leads to the tympanic/middle-ear cavity, ear canal is through hear; located on the tympanic bulla
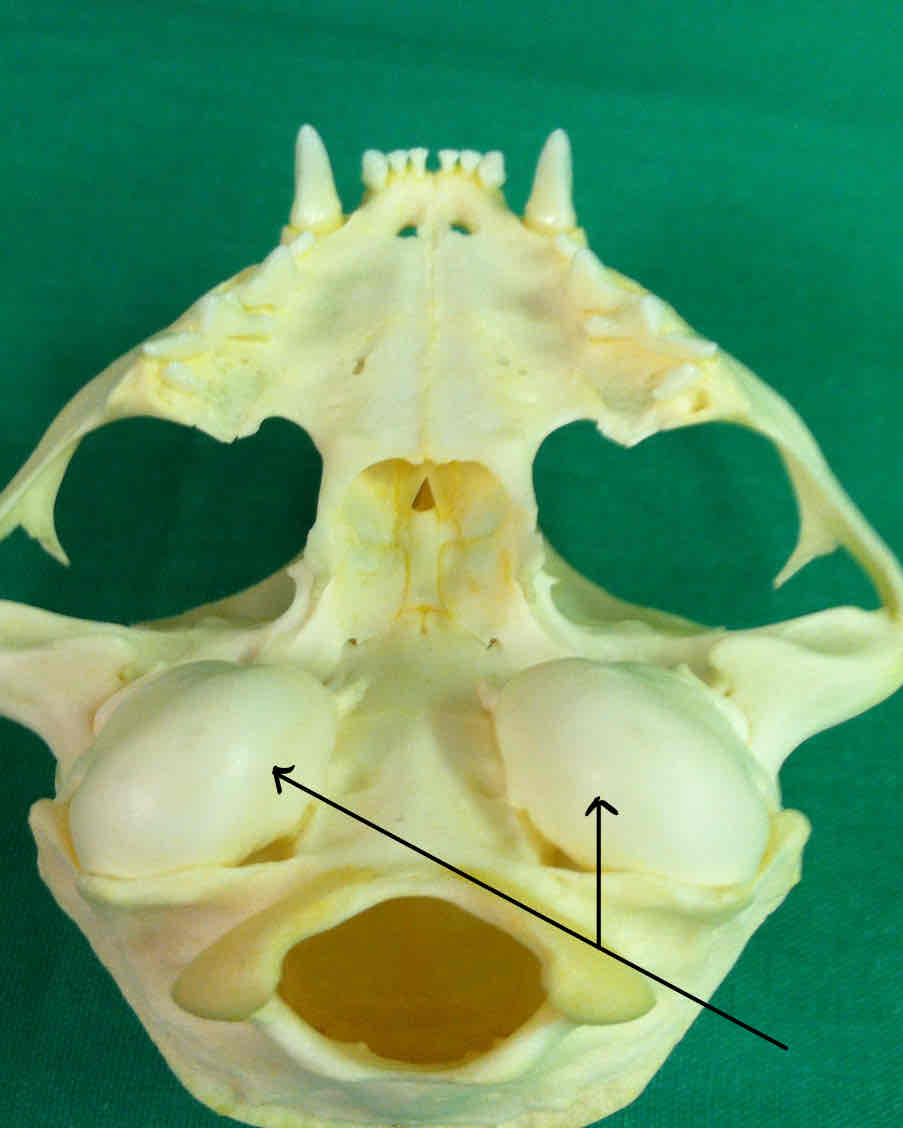
tympanic bulla (dermatocranium): part of the temporal bone, contains bones of the middle and inner aer
occipital bone (chondrocranium): forms the caudal part of the skull and has occipital condyles that articulate with the atlas
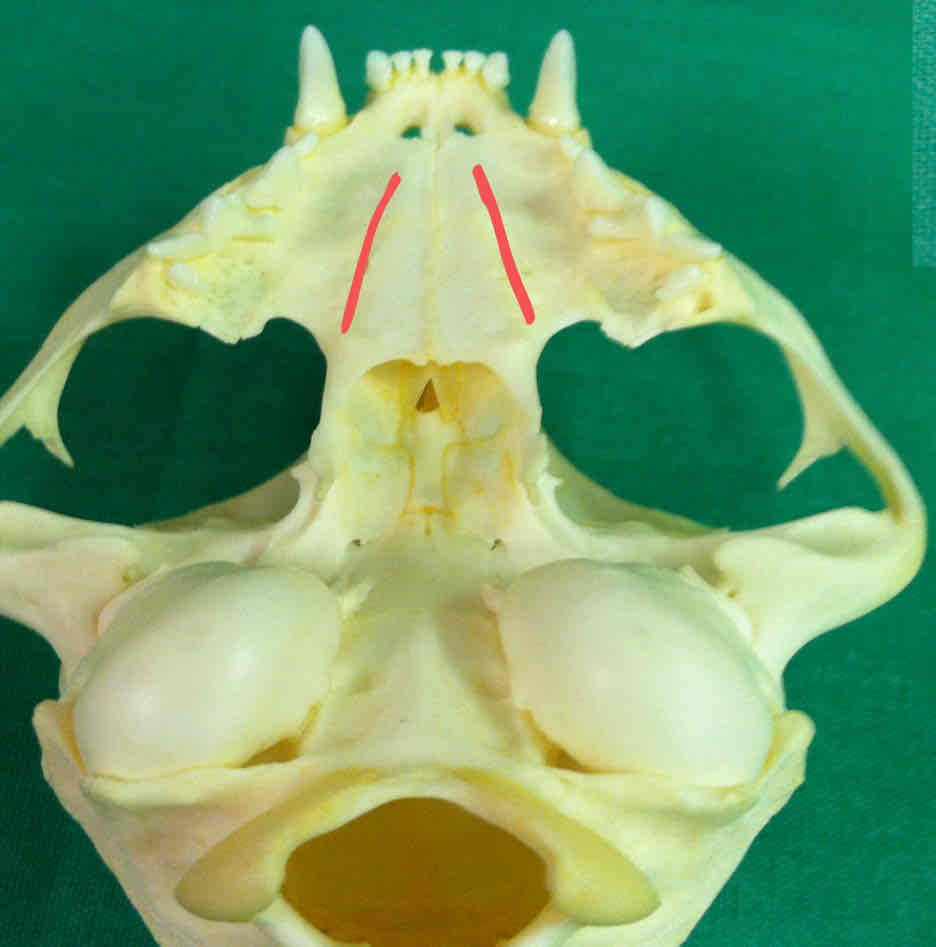
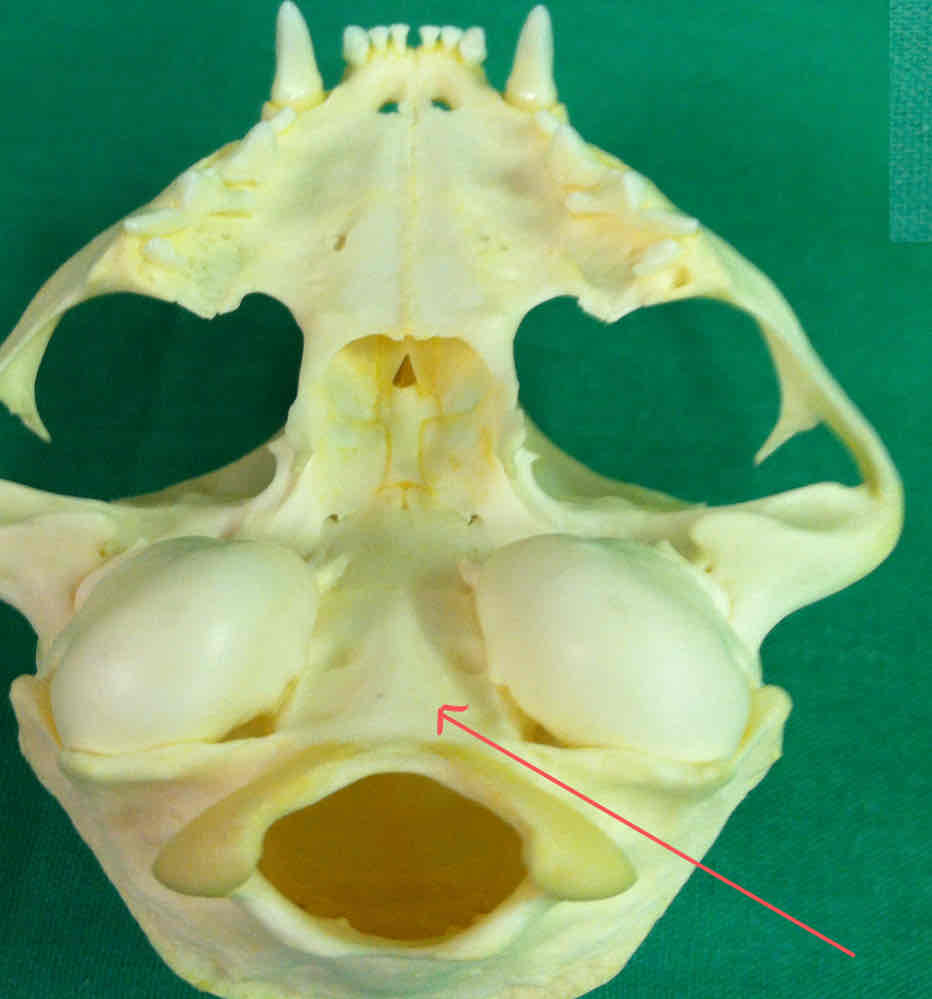
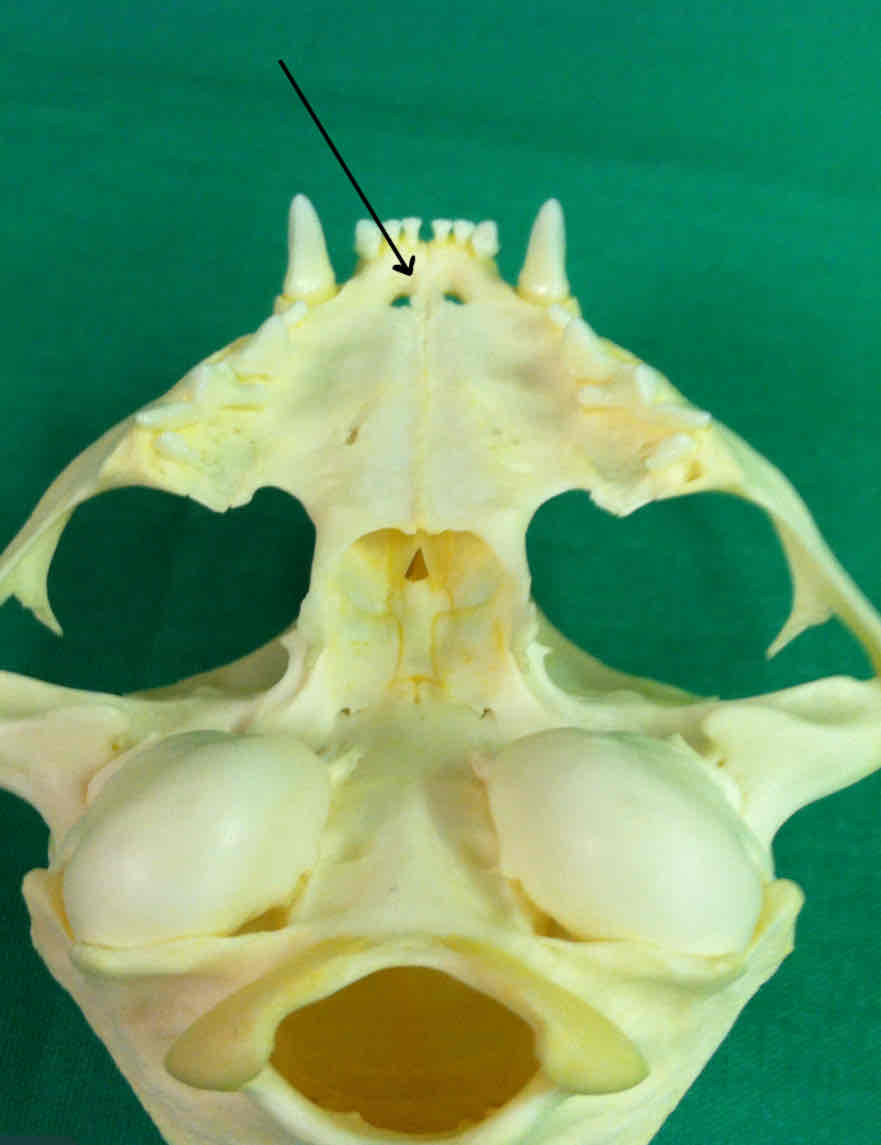
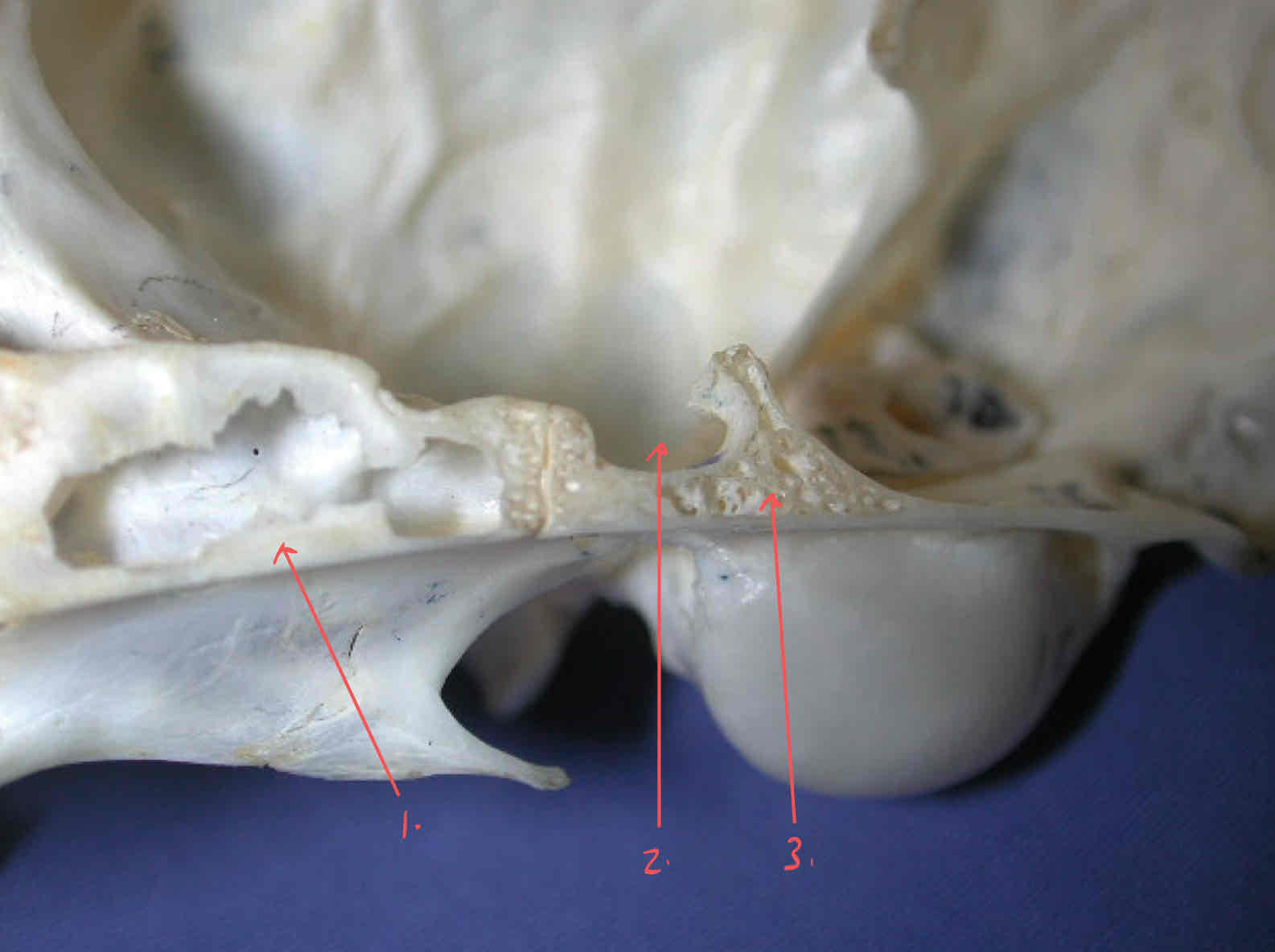
palatine bones (dermatocranium): paired bones that make up part of the hard palate
premaxilla (dermatocranium): Holds the incisors, palatine process of the premaxilla makes up part of the hard palate
maxilla (dermatocranium): Holds the canines and the premolars, palatine process of the maxillae contribute to the hard palate
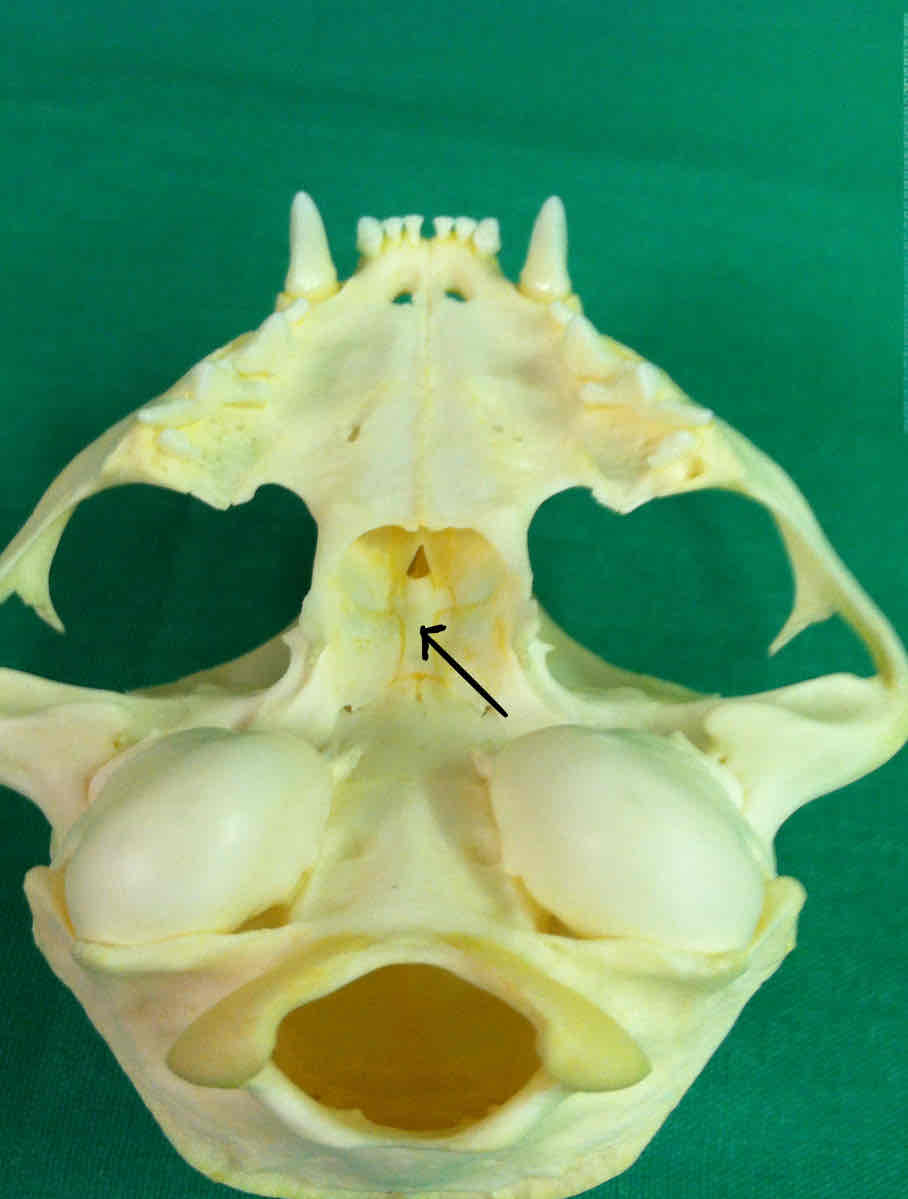
presphenoid (chondrocranium): makes up part of the brain shelf
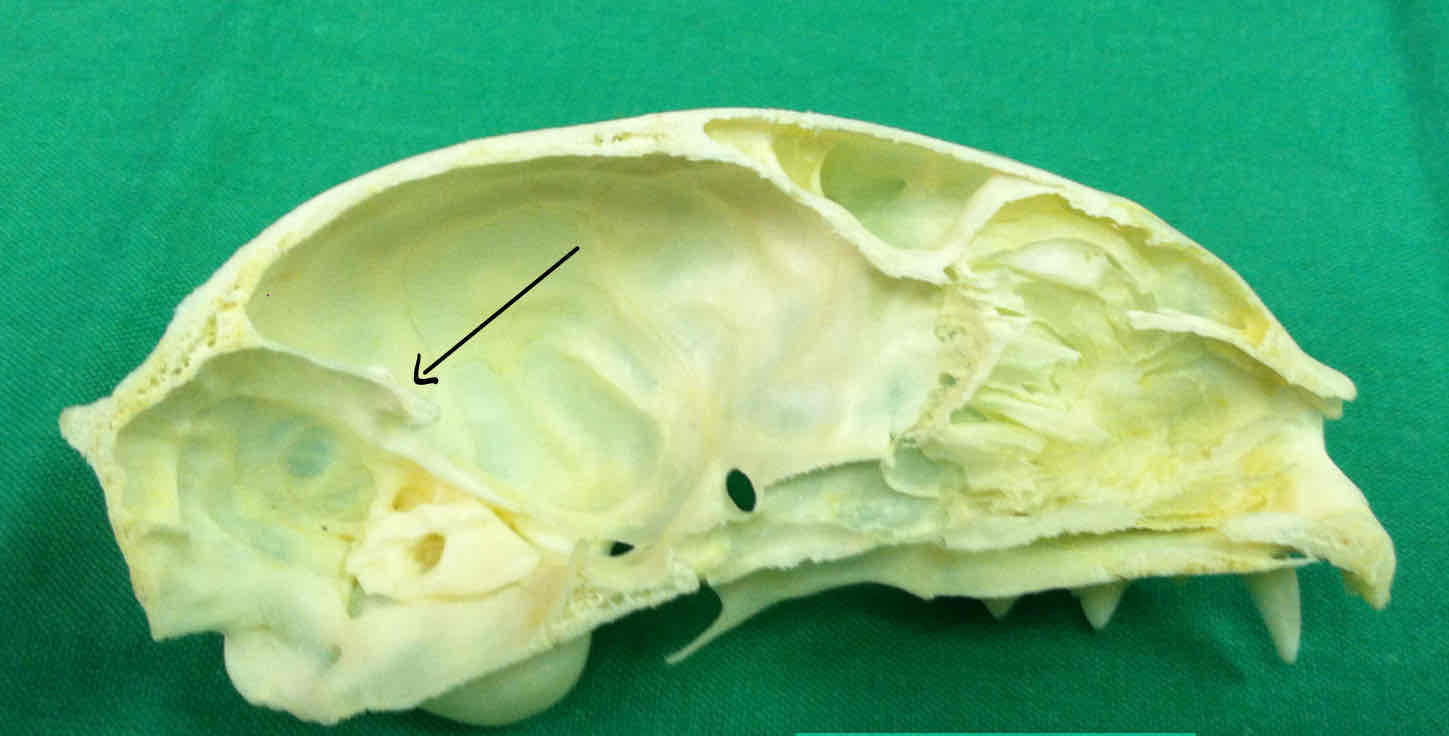
basisphenoid (chondrocranium): forms a portion of the floor of the cranium
cerebellar fossa: surrounds the pons, the cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata
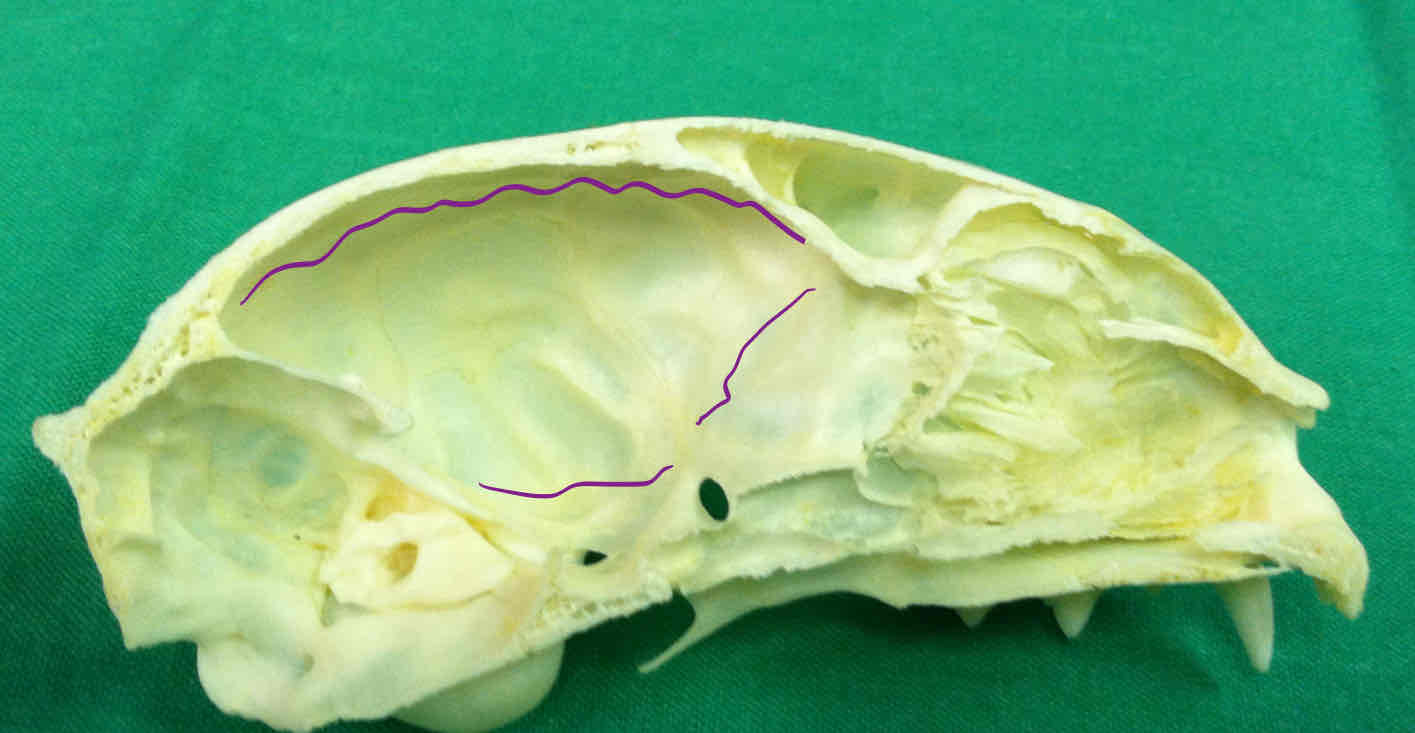
cerebral fossa: houses the cerebrum, the diencephalon, and the mesencephalon
tentorium (dermatocranium): marks the caudal end of the cerebral fossa and separates it from the cerebella fossa
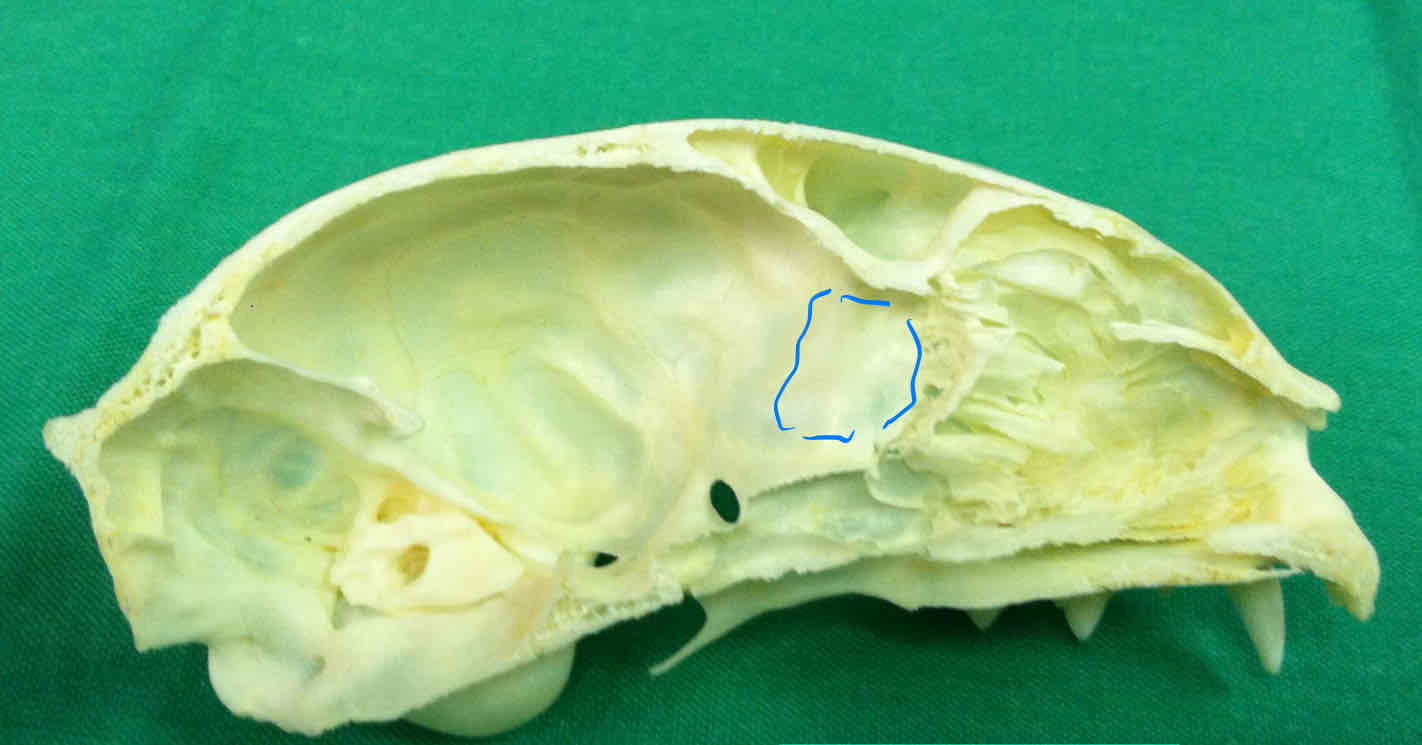
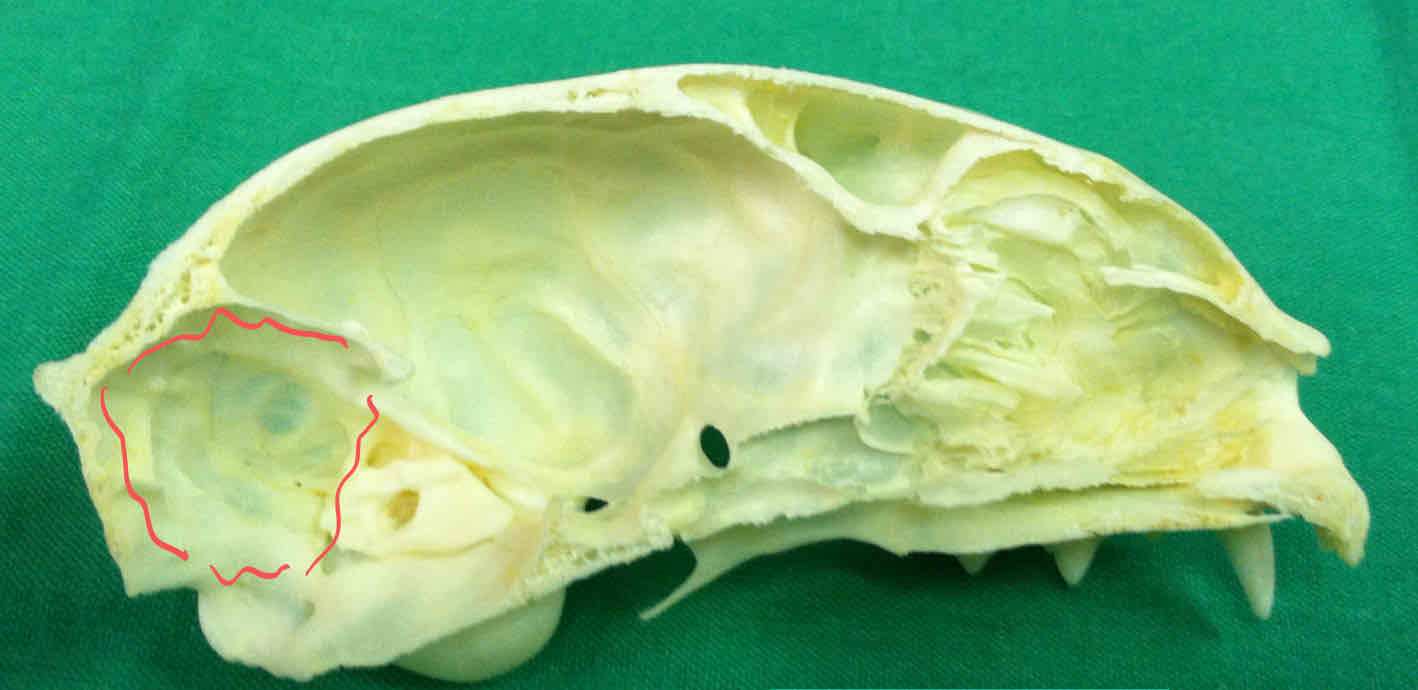
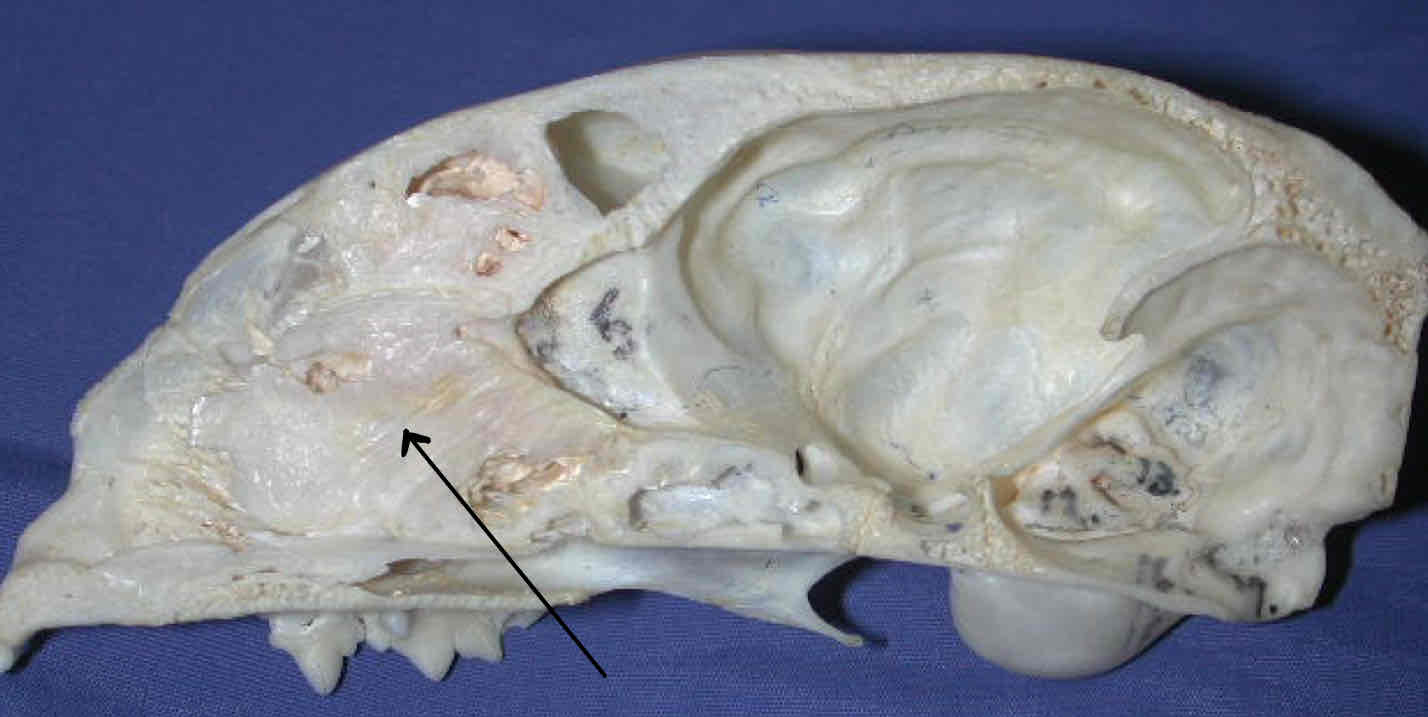
olfactory fossa: houses the olfactory bulbs, where olfactory fibers synapse
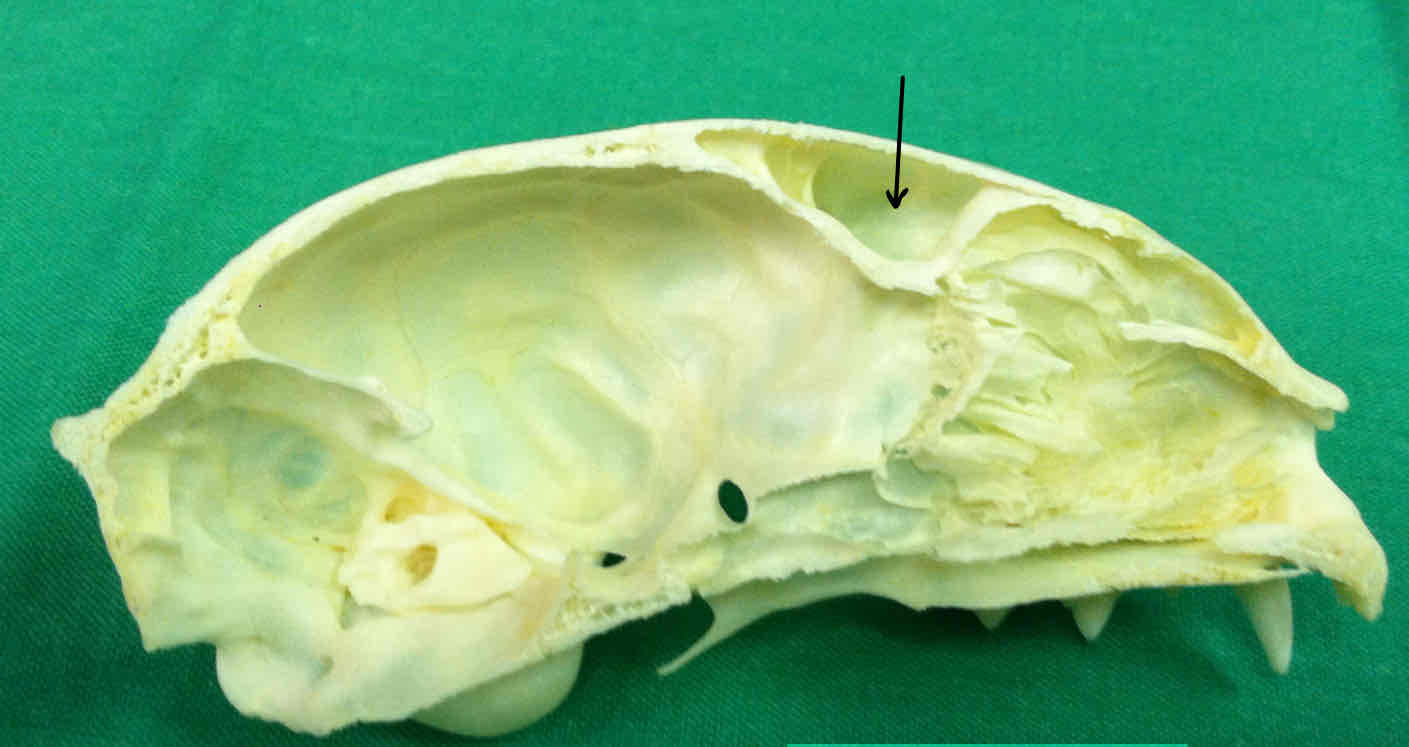
frontal sinus: air-filled space that reduces weight in the skull
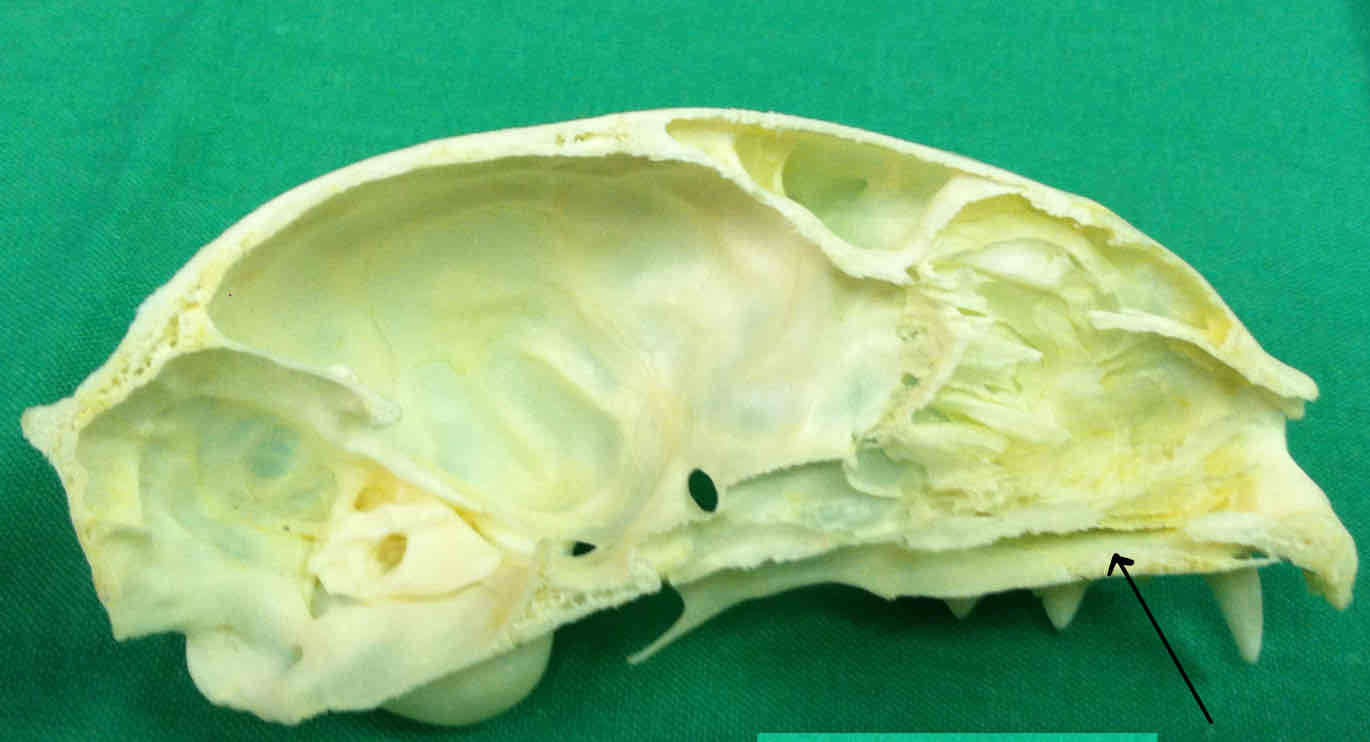
palatine bone (dermatocranium): paired bones that make up part of the hard palate
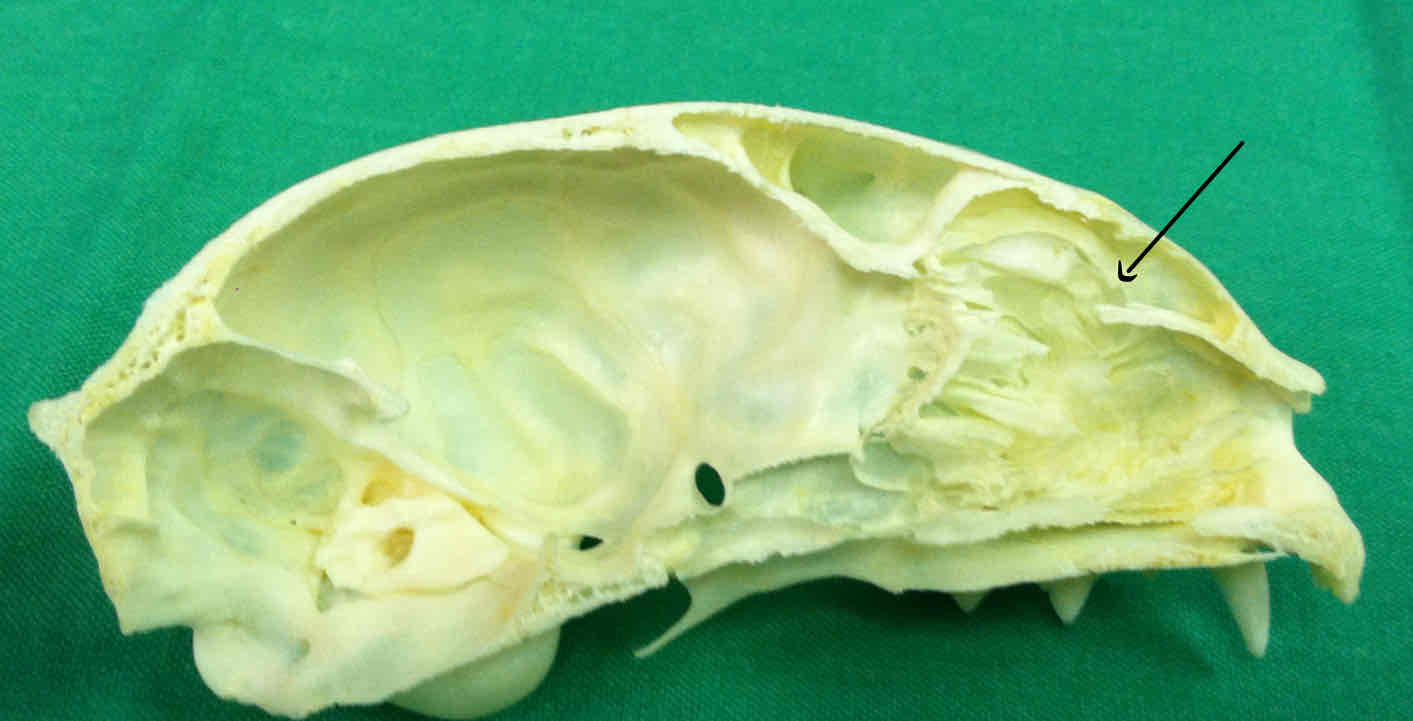
nasal sinus and nasal cavity: houses the nasal turbinates, which filter and warm air
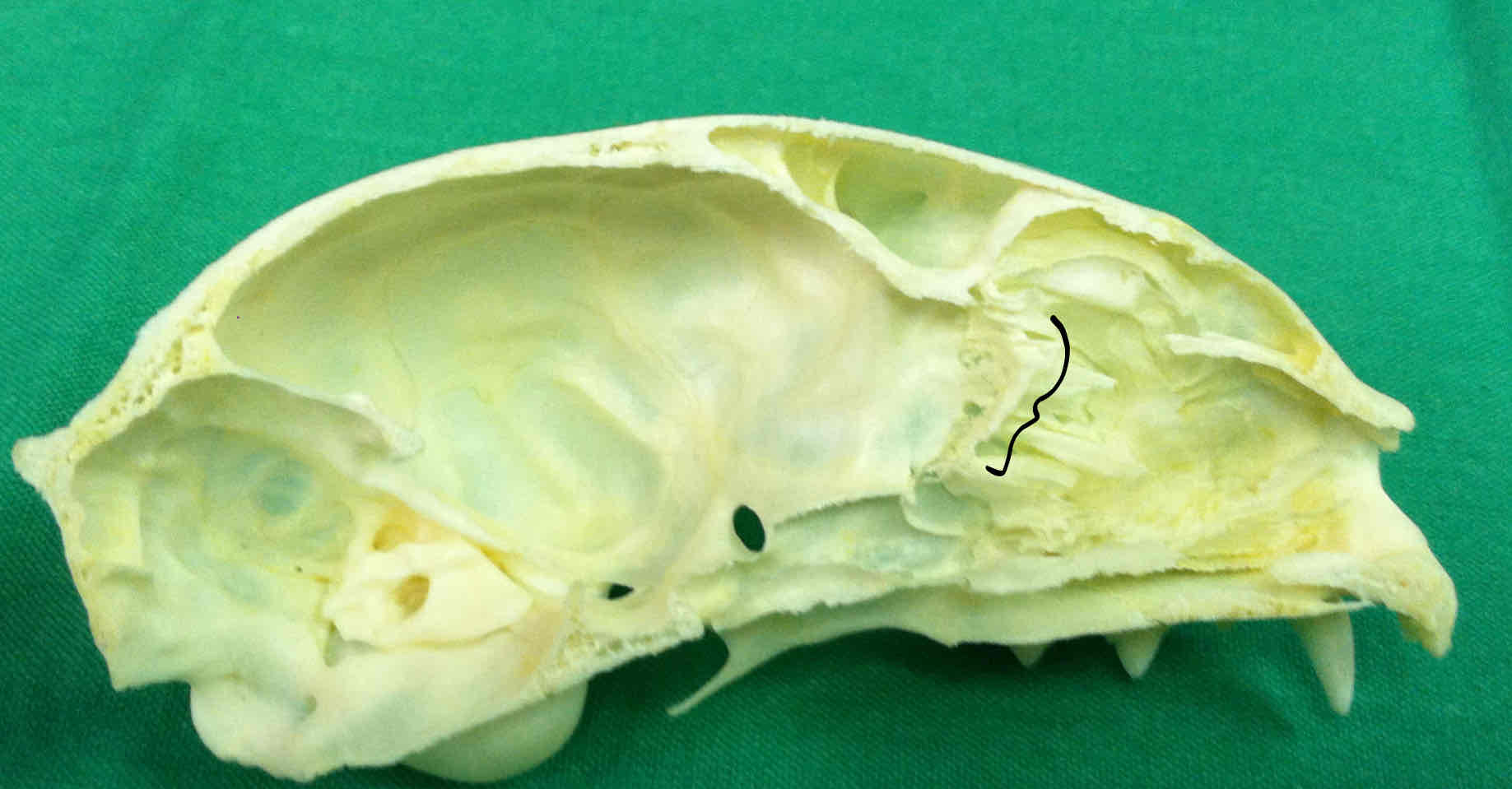
ethmoid bone (chondrocranium): an unpaired nasal bone that is associated with the nasal cavity, made up of turbinates and contains the cribriform plate
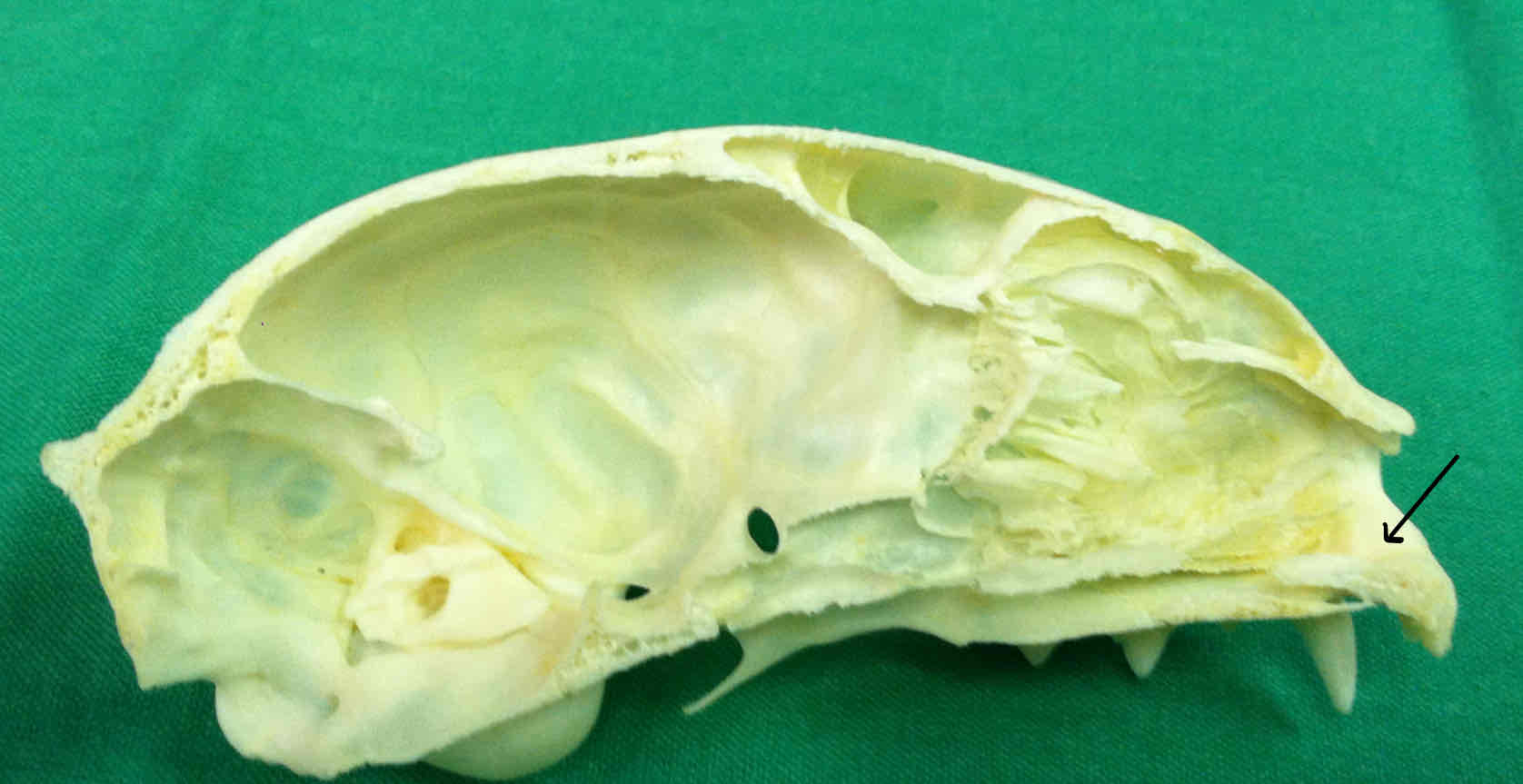
premaxilla
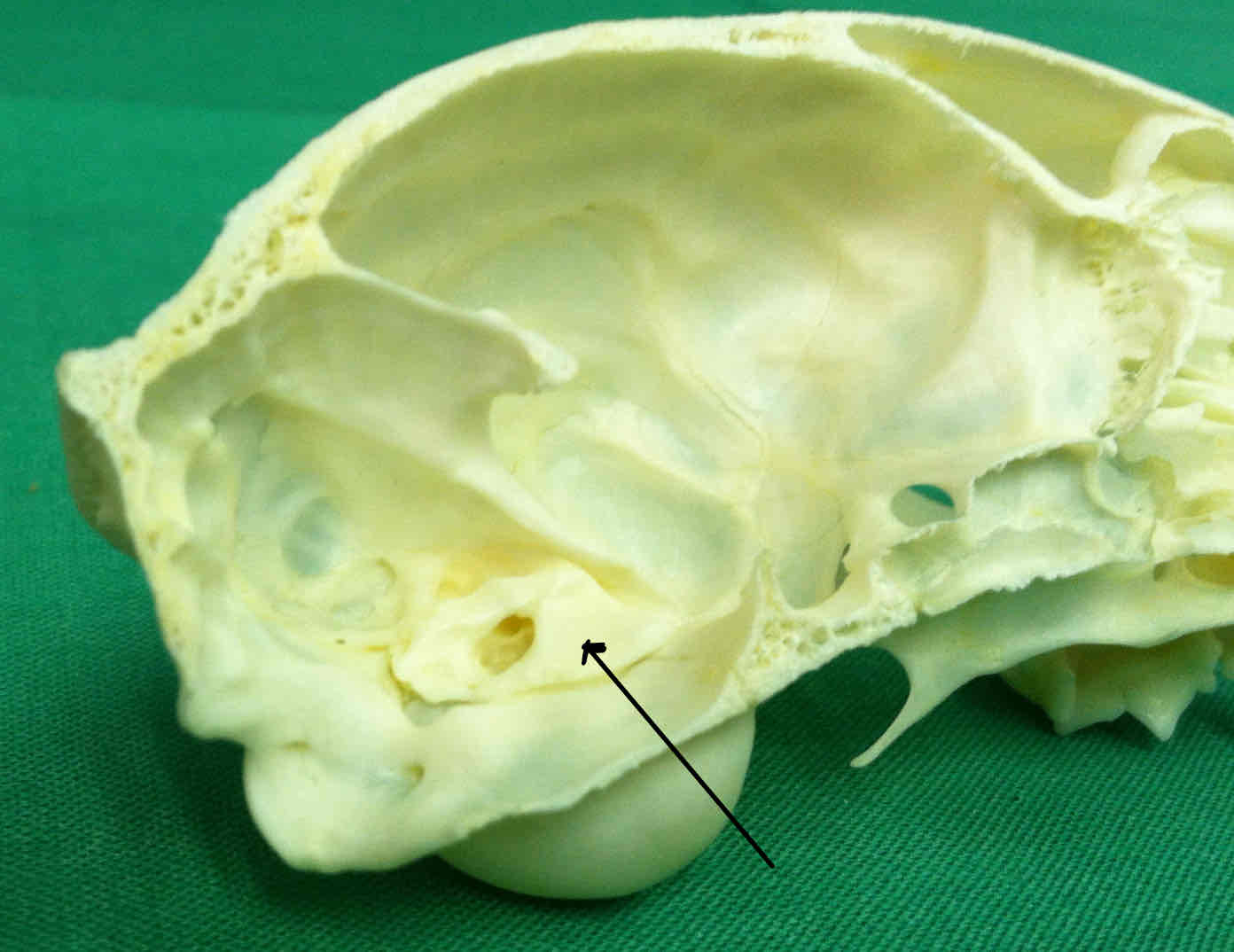
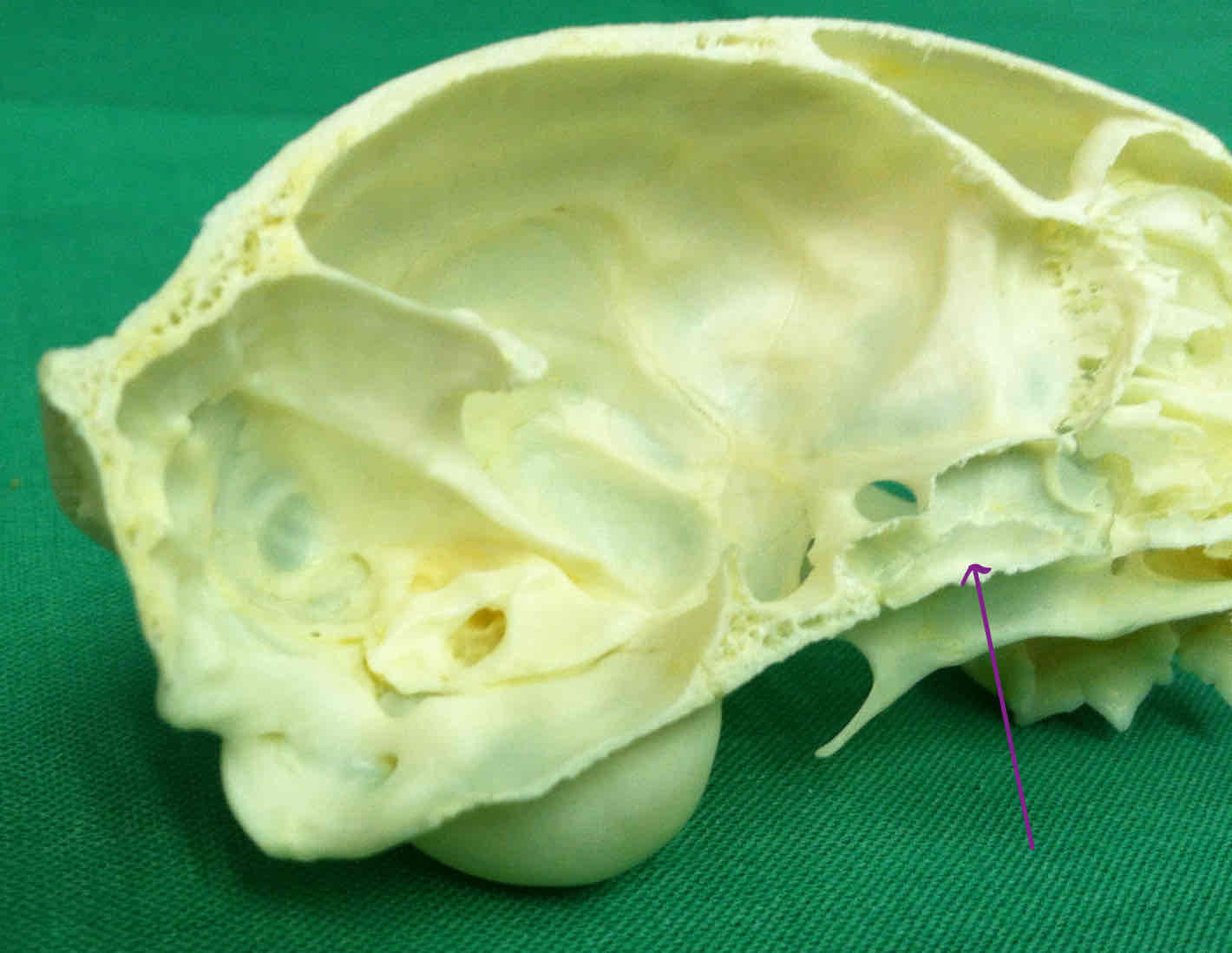
petrous portion of the temporal bone (chondrocranium): contributes to the floor of the cranial cavity
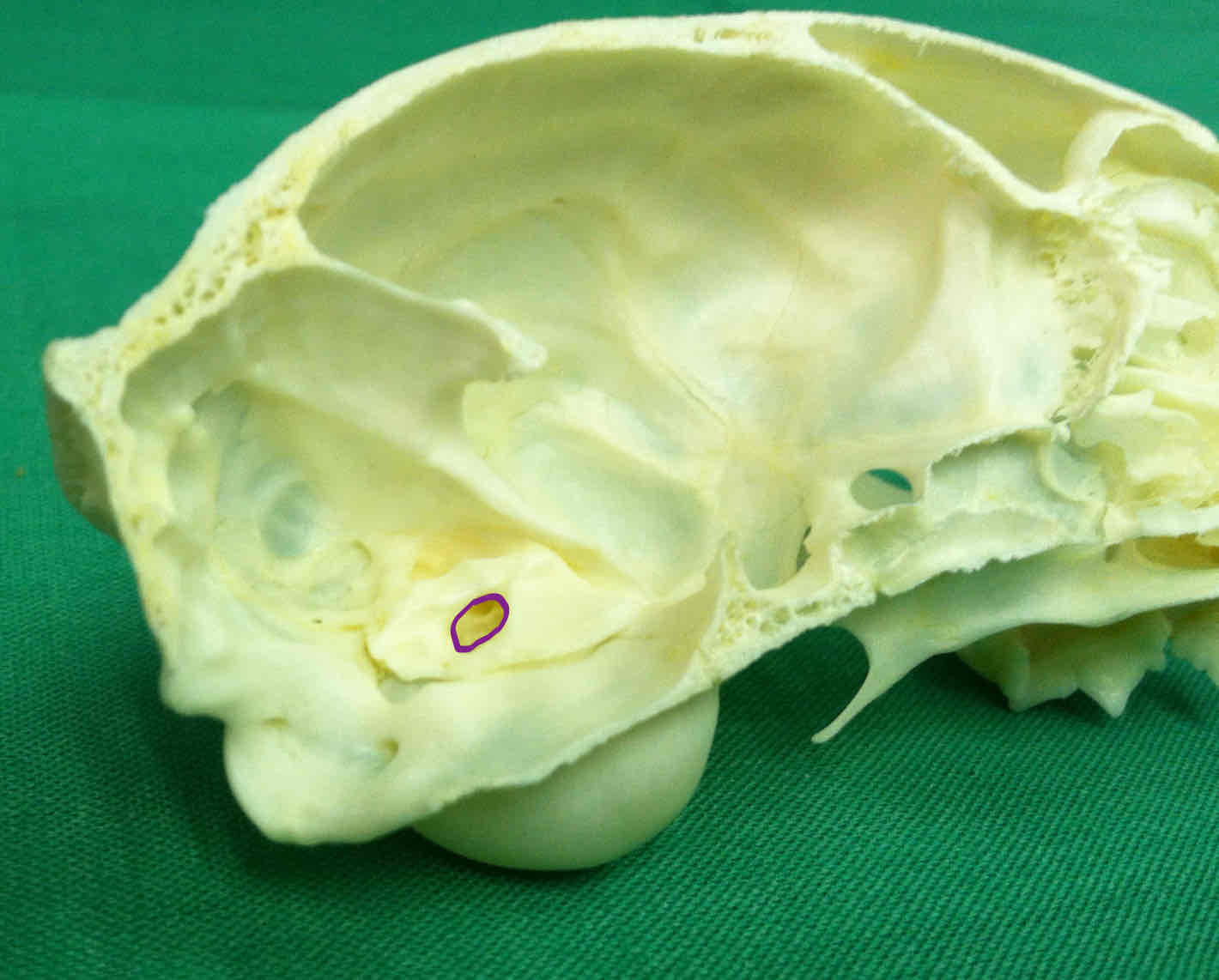
internal auditory meatus: on the petrous portion of the temporal bone; the opening that allows cranial nerves to pass to the brain
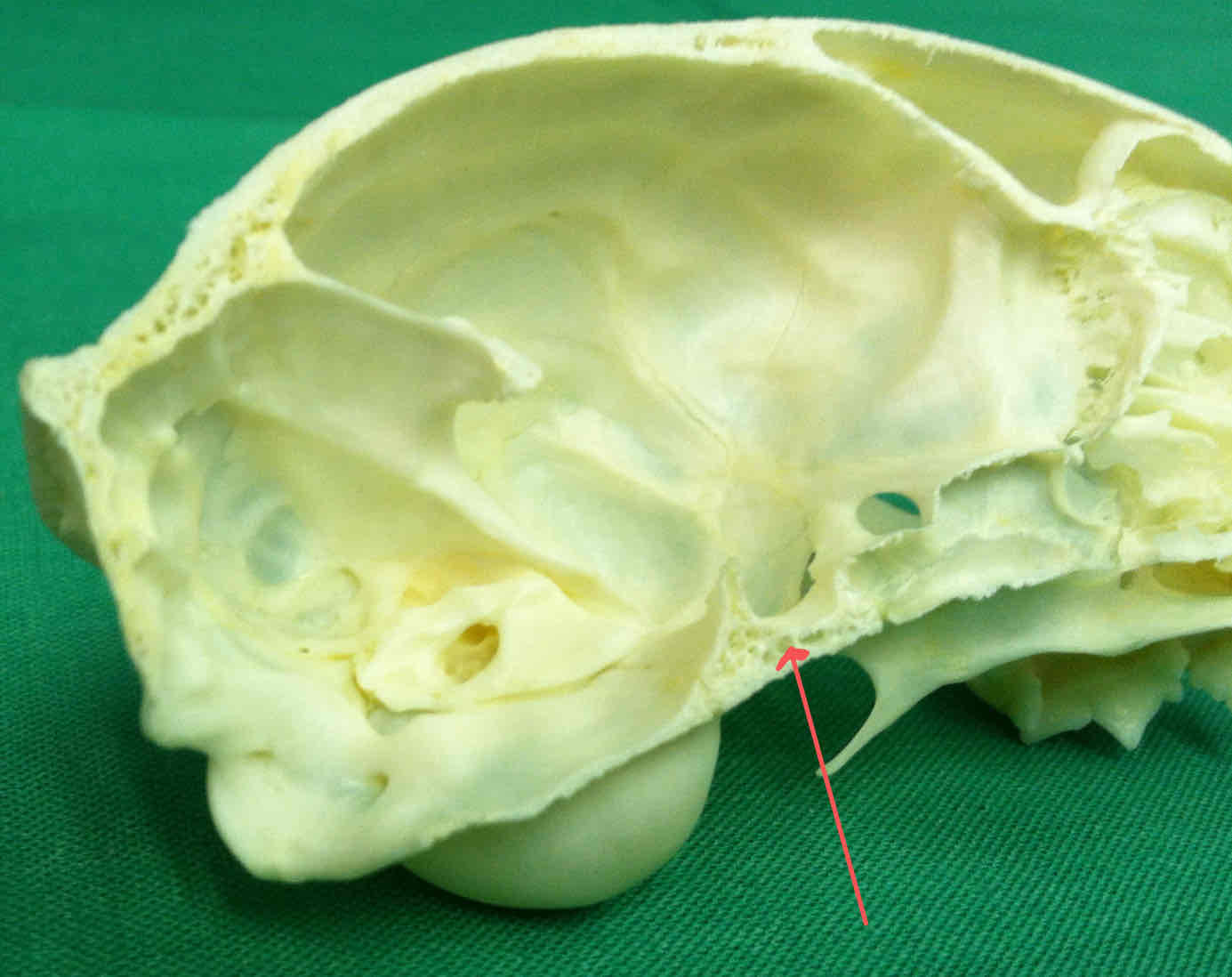
basisphenoid (chondrocranium): forms a portion of the floor of the cranium
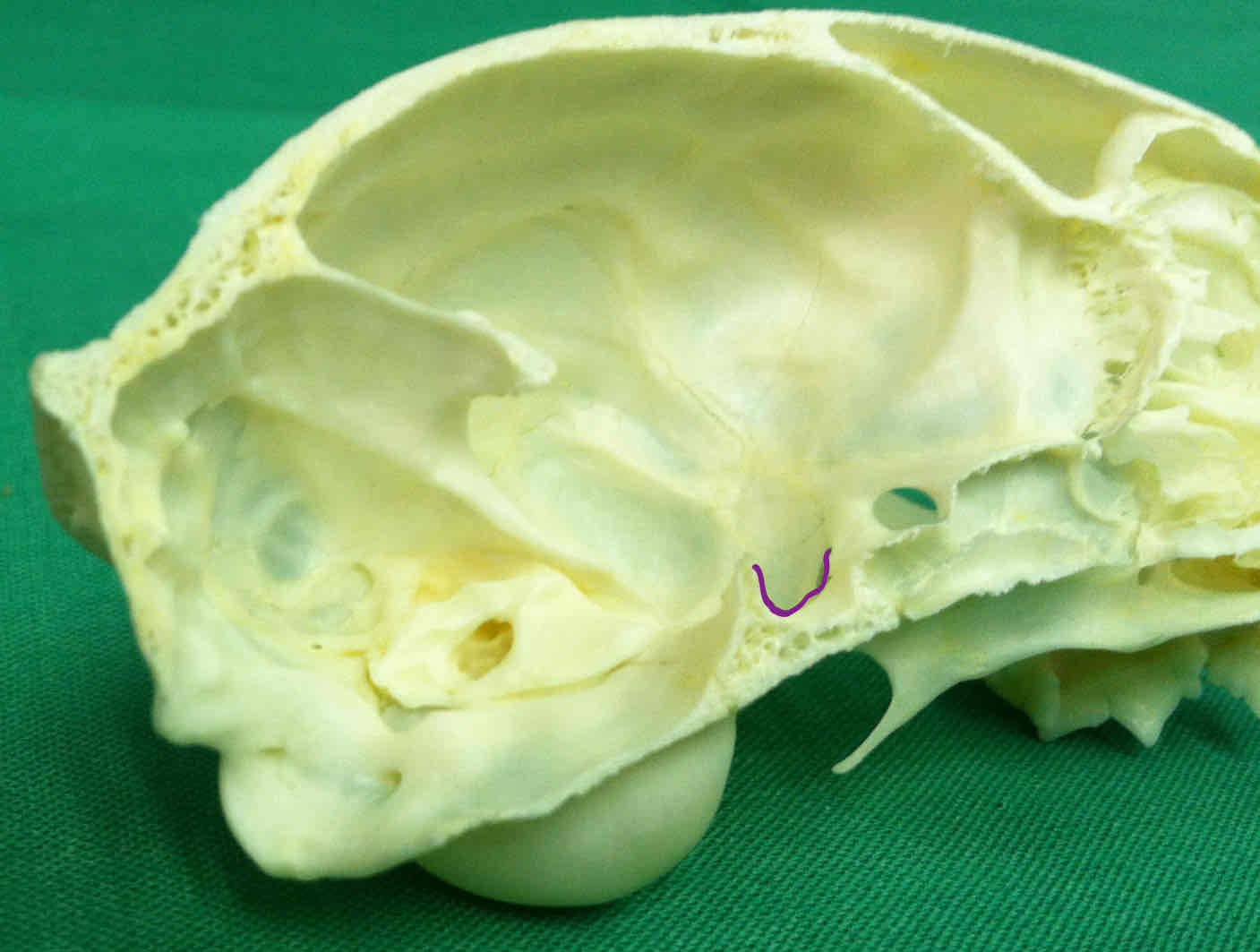
sella turcica: part of the basisphenoid, the pituitary gland rests on the shelf of this bone
presphenoid (chondrocranium)
ethmoid bone (chondrocranium) obscured by the perpendicular plate
presphenoid
sella turcica
basisphenoid
all parts of the chondrocranium
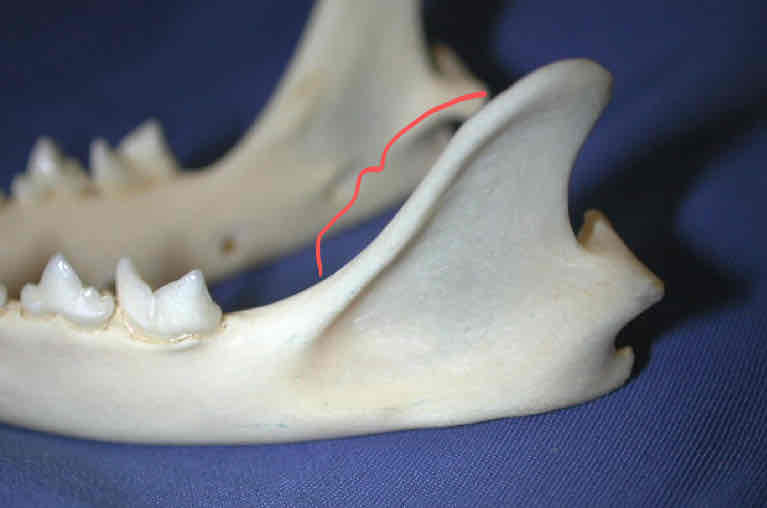
masseteric fossa (dermatocranium): the triangle shaped depression where part of the masseter muscle attaches
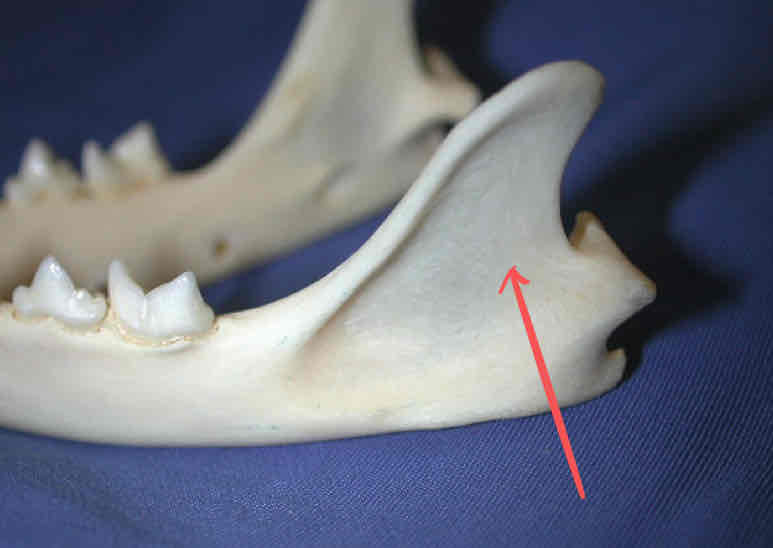
coronoid process (dermatocranium): Location for attachment of muscles of mastication to the jaw. Part of the ramus of the mandible.
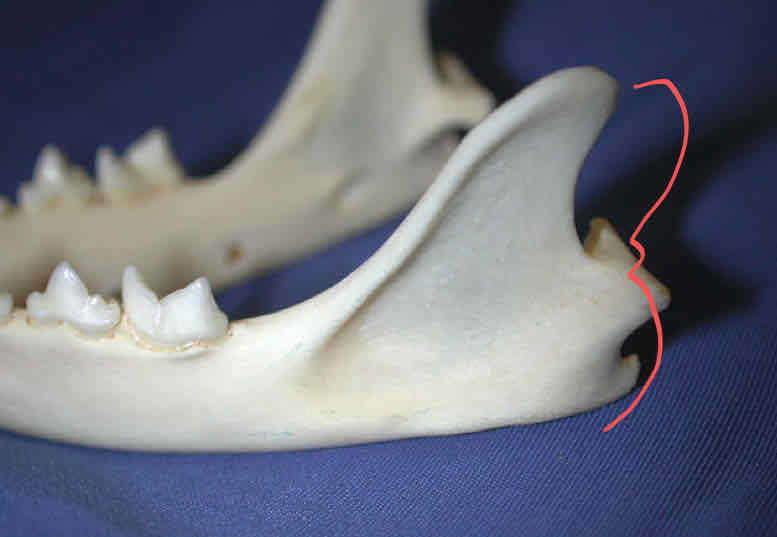
ramus
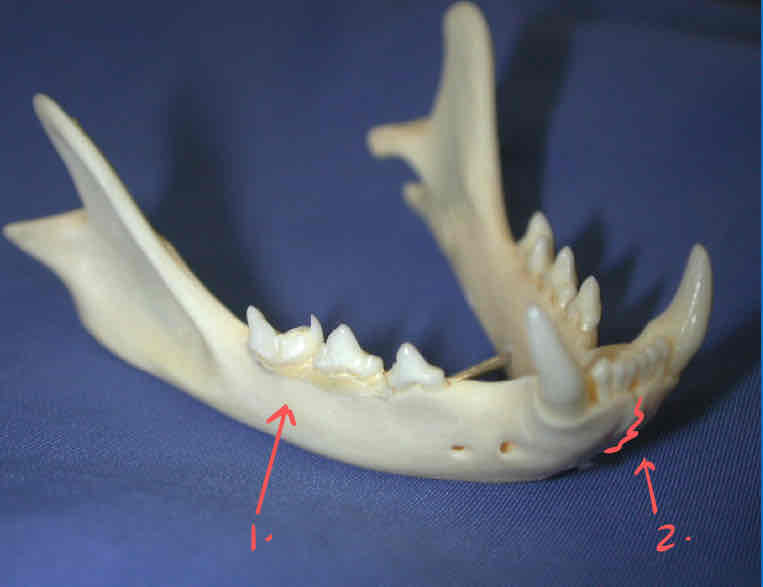
mandible body
intermandibular symphisis: the cranial point on the mandible where each hemimandible articulates
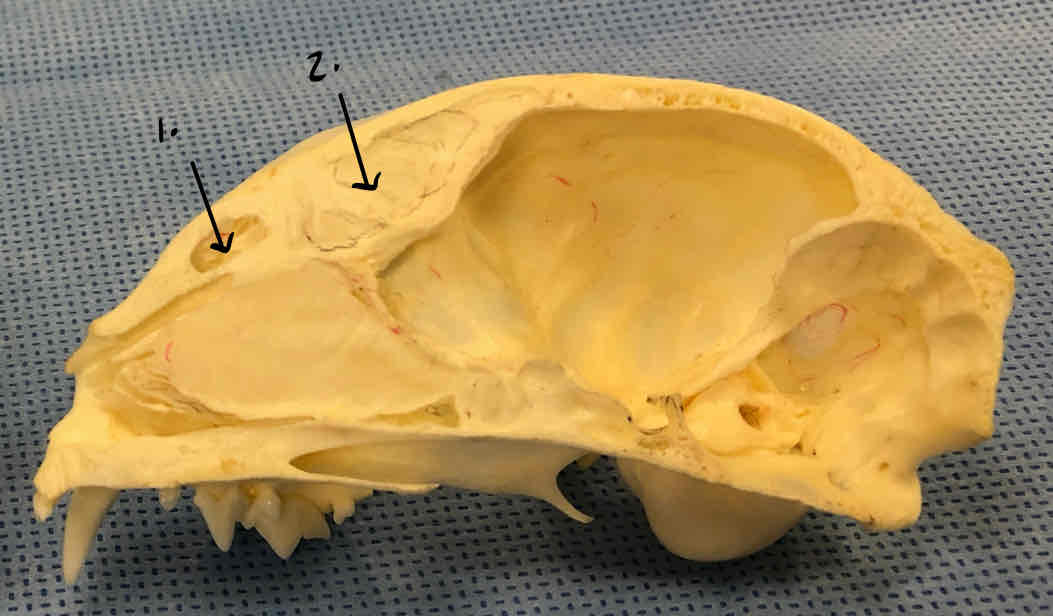
nasal sinus
frontal sinus (obscured)
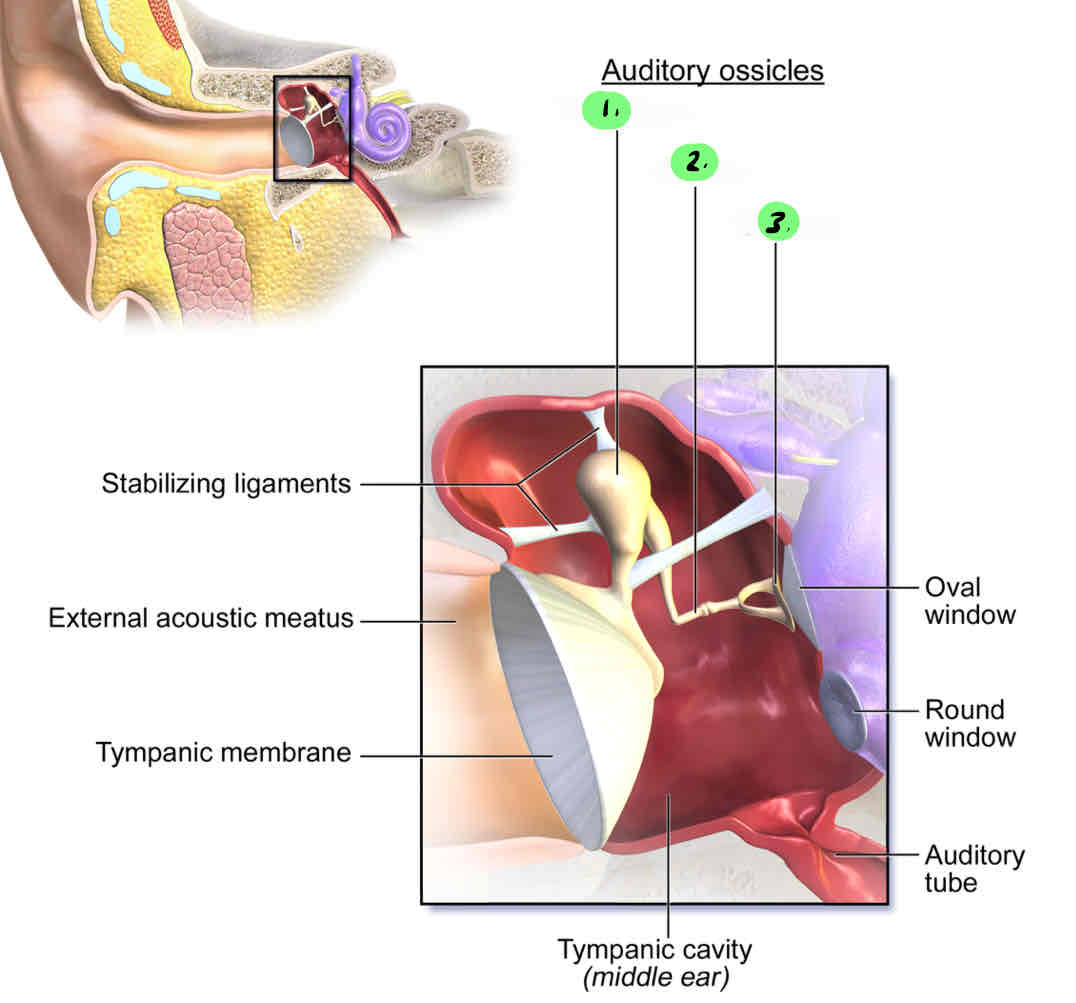
malleus: Sound transmission bone in the middle-ear cavity; evolved from Meckel’s cartilage
incus: Sound transmission bone in the middle-ear cavity; evolved from the quadrate of the first visceral arch
stapes: Bone located in the middle-ear cavity that functions in sound transmission; evolved from the hyomandibula of the second visceral arch
What parts of the cat skull are part of the splanchnocranium?
the three middle ear bones
malleus
incus
stapes
hyoid apparatus
four total structures
What parts of the cat skull are considered chondrocranium?
ethmoid bone
presphenoid
basisphenoid
petrous portion of the temporal bone
occipital bone
The malleus arose from what?
Meckel’s cartilage
The incus arose from what?
The quadrate
The stapes arose from what?
hyomandibular cartilage
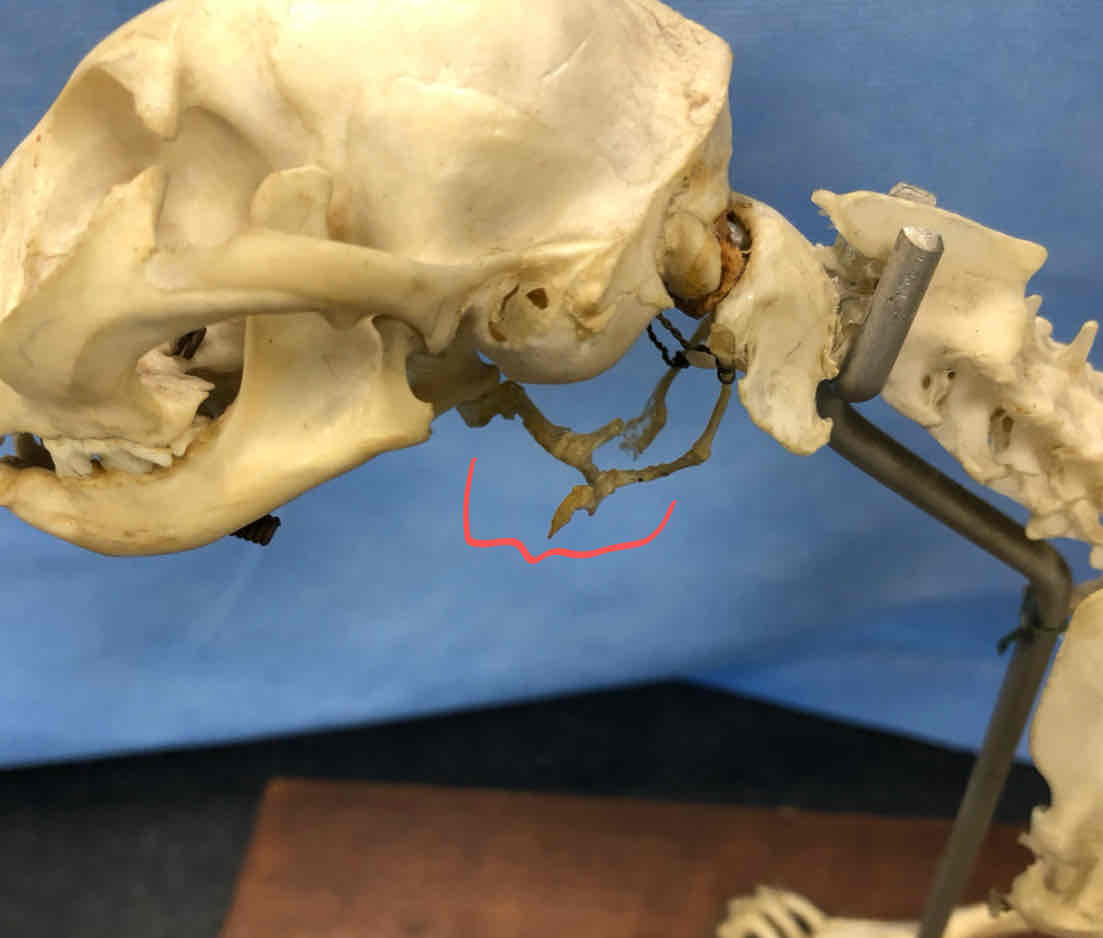
hyoid (splanchnocranium): scaffolding that suports the larynx