AP Psych 1.6-2.1 Test (STUDY RODS VS. CONES, Parallel Processing vs Sequential)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Bottom Up Processing:
Using features of an object to perceive an image. It requires a high level of perception and no prior knowledge.
Top Down Processing:
Using background knowledge, prior experiences, and memories to fill in gaps in an image. It makes us miss mistakes.
Someone walks into their kitchen at night and expects to see their fridge. Based on prior knowledge, they know where it is.
Gestalt Theory:
Images are perceived as groups, not isolated.
Exs: Proximity, Similarity, Continuity, and Closure (ignoring gaps).
Parallel Processing:
Processing multiple aspects of a stimulus or problem simultaneously. Simple tasks/routines.
Transduction:
Conversion of one form of energy into another. In sensation, the transformation of physical energy, such as sights, sounds, and smells into neural impulses the brain can interpret.
Bipolar Cells (transduction):
Sensory neurons for vision.
Ganglion Cells:
axons make up the optic nerve
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN):
Region of thalamus
David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel
Psychophysics:
The study of the relationship between the physical characteristics of stimuli, such as their intensity and our psychological experience of them.
Absolute Threshold:
The smallest amount of a stimuli that we can detect. Discovered by Gustav Fechner. Ex: minimum amount of volume to hear a song.
Signal Detection Theory:
A theory stating that motivation is the driving force to perceive faint signals. This theory refutes Weber’s claim.
Ex: When there’s a reason to perform better, we often do.
Difference Threshold:
The smallest amount of change in a stimuli required for it to be perceived.
Weber’s Law:
To be perceived as different, two stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage. The Difference Threshold is a constant figure.
Sensory Adaptation:
Neuron’s diminished sensitivity to odors, sights, and sounds due to constant stimulation. Ex: Smelling your friends strong perfume and then you no longer notice it.
Perceptual Adaptation:
The ability to adjust to an artificially displaced or inverted visual field. Your brain can make sense of odd situations.
Ex: The guy attempted a handshake near the guy’s head as he wore the inverted goggles.
Cocktail Party Effect:
People in a noisy environment are still able to focus and have a conversation despite all the noise.
Eye Diagram:
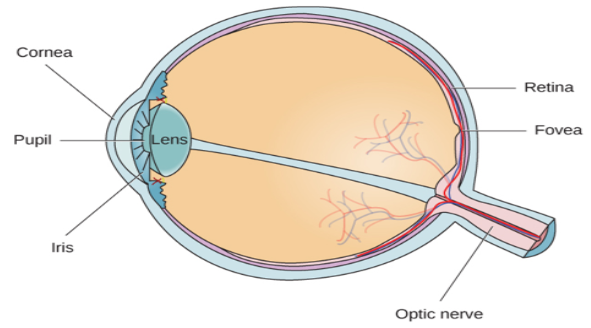
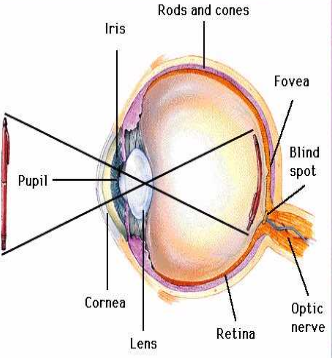
Eye Diagram with Cones/ Rods and Blind Spot:
Cornea (exterior):
Clear outer layer that covers the pupil and iris.
Iris (exterior):
Colored muscle that opens and closes in response to light intensity and controls the size of the pupil opening.
Pupil:
Opening in the center of the eye that lets light pass through.
Lens (exterior):
Transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina. This process is called “Accommodation.”
Retina:
Back of the eye where light receptors are found.
Blind Spot:
Where the optic nerve exits and there are no light receptors.
Fovea:
Cones are highly concentrated.
Rods:
Visual receptors sensitive to violet wavelengths, used for night vision, and receives no color information.
Cones:
Visual receptors that respond during daylight and to color (C=Cones=Color).
Trichromatic Three Color Theory:
3 types of color receptors are sensitive to blue, green, red.
Opponent Process Theory:
3 groups of opposing colors (red-green, blue-yellow, black-white).
Color Blindness (Dichromatism vs. Monochromatism):
Dichromatism: along color pairs.
Monochromatism: black, white, and gray vision.
Sensory Interaction:
The principle that one sense can influence another, as when the smell of food influences its taste.
Embodied Cognition:
The influence of bodily sensations, gestures, and other states on cognitive preferences and judgments.
Selective Attention:
Focusing conscious awareness on a particular stimulus.
We forget the overwhelming majority of stimuli that we encounter in our life.
Inattentional Blindness:
Failing to see visible objects when our attention is focused on something else.
Change Blindness:
Failing to notice changes in the environment. It is a form of inattentional blindness.
Perceptual Set:
A set of mental tendencies and assumptions that make us perceive one thing and not another. Ex: Do you see an old or young woman?

Figure-ground:
The organization of the visual field into objects (the figures/faces) that stand out from their surroundings (The ground).

Grouping:
The tendency to group things into groups.
Depth Perception:
The ability to see objects in three dimensions and judge distance.
Visual Cliff Experiment:
A laboratory device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals. It shows the importance of depth perception in humans.
Experiment: Infants would not crawl into cliff despite the reward.
Stroboscopic Movement:
An illusion of continuous movement when viewing a rapid series of slightly varied images. Ex: Stopmotion films
Phi Phenomenon:
An illusion of movement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and off in quick succession.

Autokinetic Effect:
The illusory movement of a still spot of light in a dark room. (Ex: The optical illusion point when you stare makes it move).
Perceptual Constancy:
Perceiving objects as unchanging (having consistent color, brightness, shape, and size) even as illumination changes. Ex: when a glass of milk still appears white in dim light.
Size Constancy:
This refers to our tendency to perceive objects as unchanging in size, even though our distance from the object may change.
-Relative Height.
Subliminal Perception:
Stimuli below our absolute threshold (that we are not consciously aware of) that impact our behavior.
Pheromones are an example.
Priming:
Images or words that can prepare you for conscious perception and/ or arousal
Monocular Cues:
A depth cue, such as clarity, relative size, texture, interposition or linear perspective available to either eye alone.
Linear Perspective:
Lines meet at a vanishing point to indicate distance. This is a monocular cue.

Texture Gradient:
We can see details close but not far away
Interposition:
If one image covers another, it looks closer and larger.

Relative Clarity:
Objects are more clear when they are closer

Binocular Cues:
A depth cue that depends on the use of two eyes. These are more complex in retinal disparity and convergence.
Retinal Disparity:
The greater the difference between the two images is, the closer the object is. The retinas perceive depth between two near objects and each eye receives different images.
Convergence:
Your eyes must cross to continue focus for near objects. Retinal images are combined by the brain.
Tactile Sensations:
Touch, pressure, temperature, pain, texture.
Proprioception:
Body positioning and movement. Found in joints.
Why do we experience pain?
It warns us of potential dangers, allows body to prepare for fight/flight, and allows for protection of injured body parts.
Where is pain processed physiologically?
It’s processed in the parietal lobe, travels up the spinal cord, and endorphins are released with pain.
Sharp Pain:
Large Myelinated nerve fibers. This is painful and fast.
Throbbing Pain:
Smaller unmyelinated nerve fibers. This is slow and aching.
Where does pain travel and what is released?
It travels up the spinal cord and endorphins are released.
Gate Control Theory:
Neural mechanisms in the Spinal Cord can either open or close to inform the brain of pain signals.
Large nerve fibers can close the “gate”, while small nerve fibers can not
Large nerve fibers can control pain
If you want to stop sharp pain, you need to have…
throbbing pain.
Psychological Factors of Pain:
Cognitive views, emotional state, cultural expectations.
Phantom Limb Syndrome:
When you feel pain in a body part that is no longer there.
Kinesthesis:
Our movement sense; the awareness of our position, and movement of body parts.
Gustatory/ Gustation:
Taste
What are the 6 different gustatory tastes?
Receptors: Taste Buds.
Sweet: energy
Sour: avoid spoiled foods.
Bitter: avoid poisons.
Salt: fuels nerve cells, muscles, and body chemistry.
Umami: savory, tasty, meats and cheeses.
Oleogustus: Fatty detectors.
Olfactory Chemical Sense:
Smell Sense.
Olfactory senses provide information about…
food.
Pheromones:
Odors that communicate sexual messages.
Olfactory pheromones are processed in the…
Olfactory Bulb in the Limbic System; not in the thalamus like the other senses.
The Olfactory Sense is linked to…
memory.
Psychological perceptions:
ratings scale.
Ear Diagram:
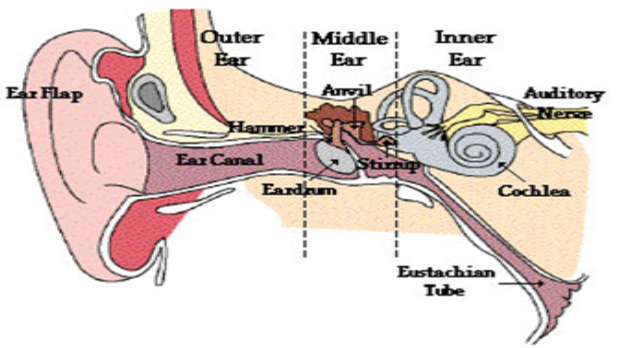
The Outer Ear/ Pinna/ Ear Flap:
It has a funnel like shape to trap incoming sound.
Ear Flap/ Outer Ear/ Pinna
Intensity:
Loudness, measured in decibels.
Frequency:
Amount of times a wave repeats itself.
Pitch (measurement of hearing):
High or low depending on the frequency.
Eardrum (Tympanic Membrane):
Thin piece of skin stretched tightly which vibrates when sound hits it. The eardrum vibrates first when sound waves come in.
Middle Ear Bones:
Bones vibrate and send vibrations to Cochlea.
Oval Window:
Ear bones send vibrations to oval window.
Cochlea:
Bony fluid-filled tube that is shaken by the Oval Window.
The Cochlea’s hair cells are…
bent by the fluids and “tuned” to receive frequencies.
When frequencies are met, the Cochlea hairs…
fire an impulse.
Vestibular Sense/ Semicircular Canals:
This manages balance, coordination, body movement and position.
Ex: Brandon was dizzy and could not stand up after being on a carnival ride that spun in circles. Which of the following physiological structures was most affected by the spinning ride?
Auditory Nerve:
Impulse fired from hair cells in cochlea travels through the auditory nerve to the brain for processing.
Place Theory:
The theory that links pitches to the place where the cochlea’s membrane is stimulated. It explains high pitch sounds but not low pitch.
Frequency Theory:
Rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone. Explains how we hear low pitches.
Volley Theory:
Various nerve impulses fire simultaneously to produce full range of sounds.
Conduction Deafness:
Middle ear damage
Sensorineural Deafness:
Caused by damage to the cochlea’s receptor nerves or auditory nerves.
Cochlear Implants:
Devices that aid in sensorineural deafness.
EBQ:
Use 2 research studies in the EBQ. it is like a dbq essay. Cite sources like (source 1). According to source 1… The ebq will be about pain. Intro will be a thesis that includes pain. Pick one source that supports your claim by using a concept, research. Talk about something from the reading and outside info that supports your thesis in the body paragraphs. You will need 2 pieces of outside information. Underline outside info.
Muller-Lyer Line Illusion:
Cultural Perception makes two lines of the same length appear to be of different lengths.
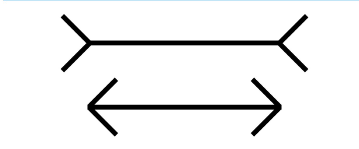
Cultural Perception:
Culture impacts how people think and the way that people understand the stimuli around them.