Exploring Lifespan Development, Berk Chapter 4
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
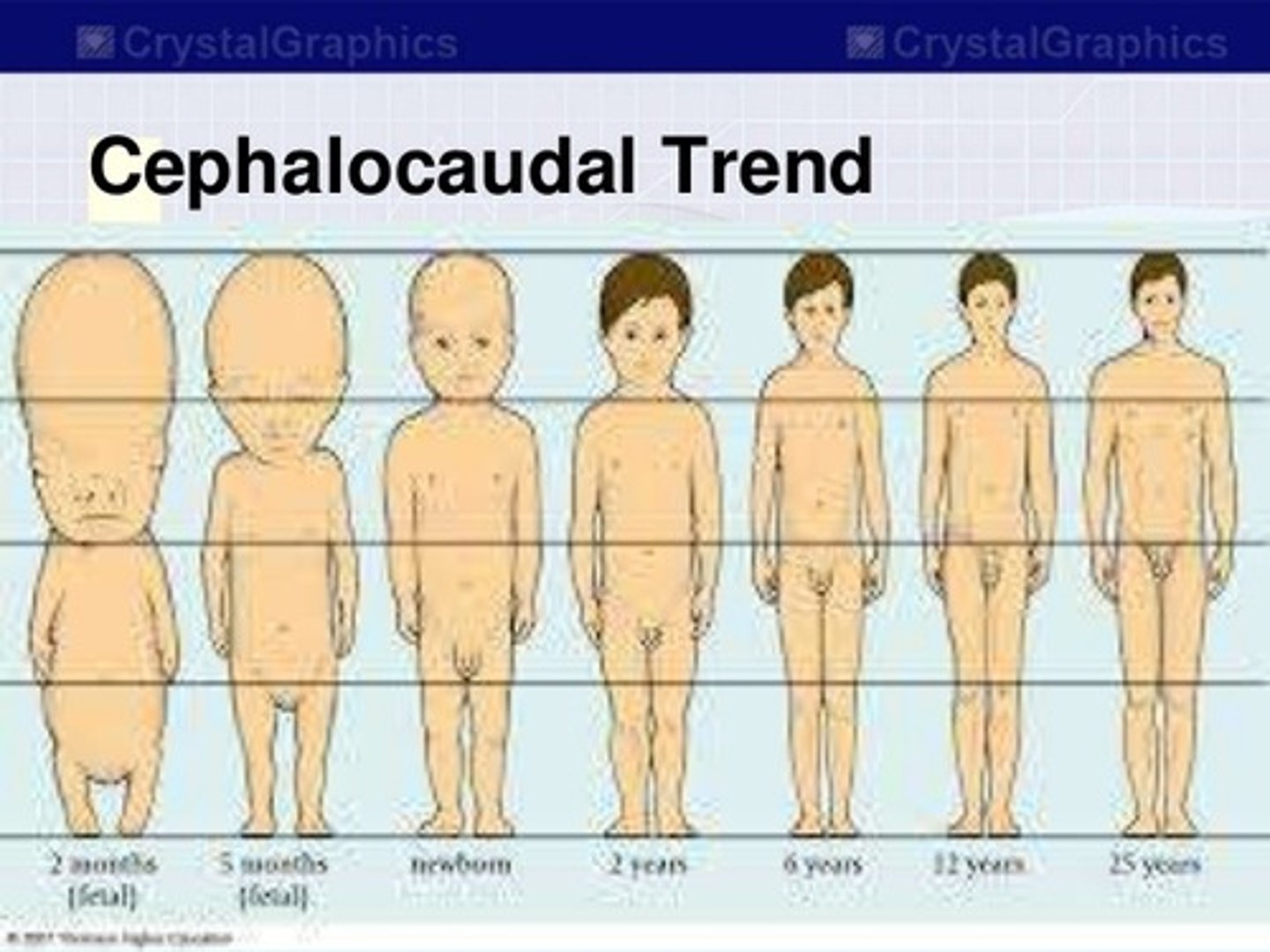
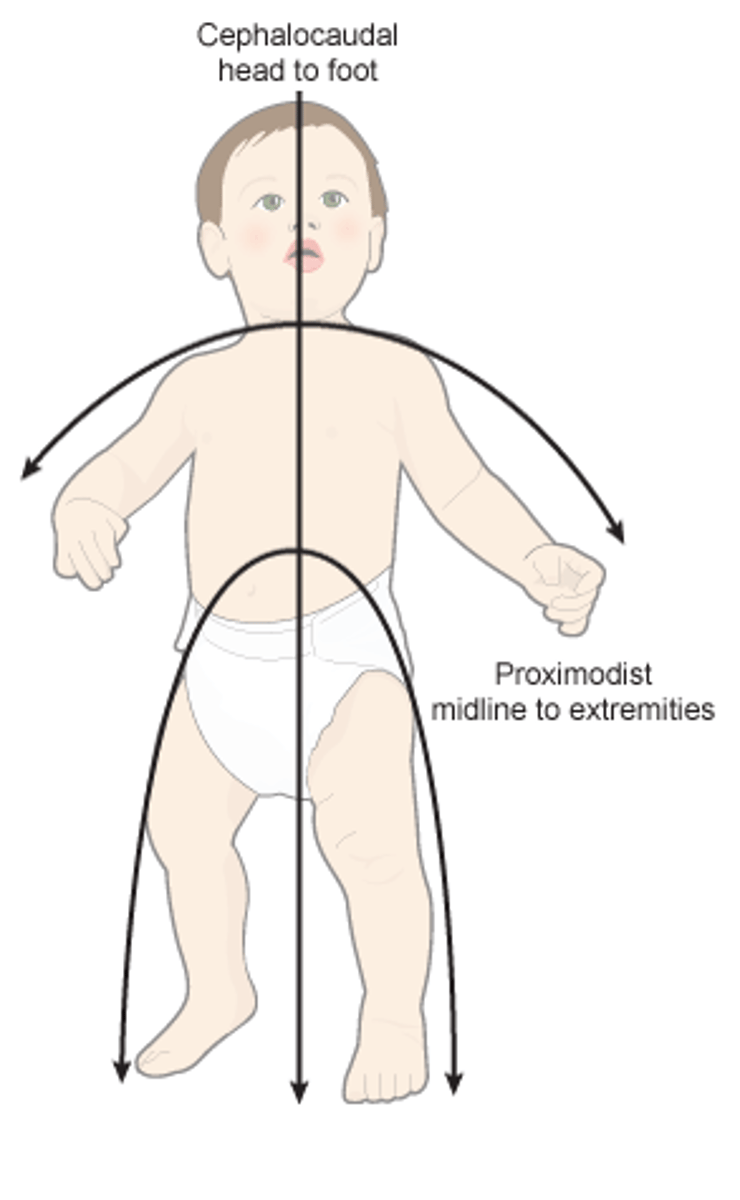
cephalocaudal trend
Latin for "head to tail", a growth pattern where the head develops more rapidly than the lower part of the body
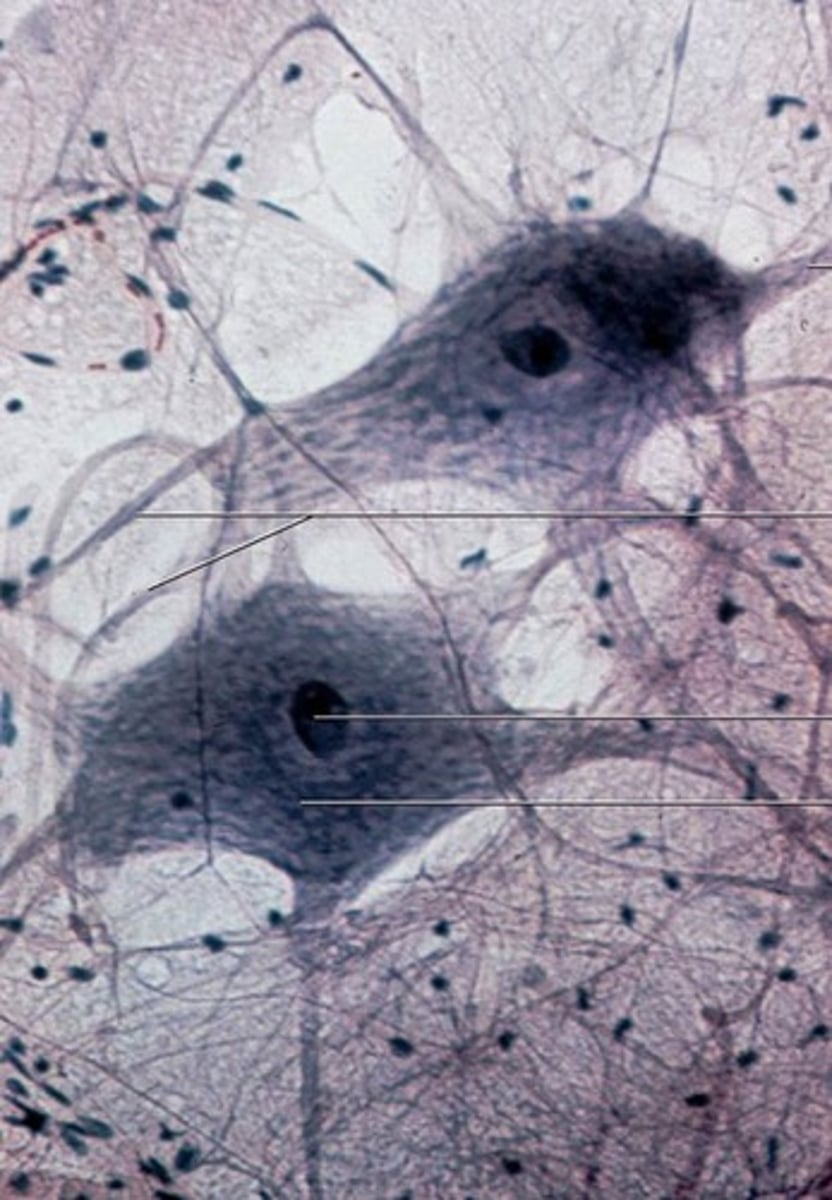
neurons
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
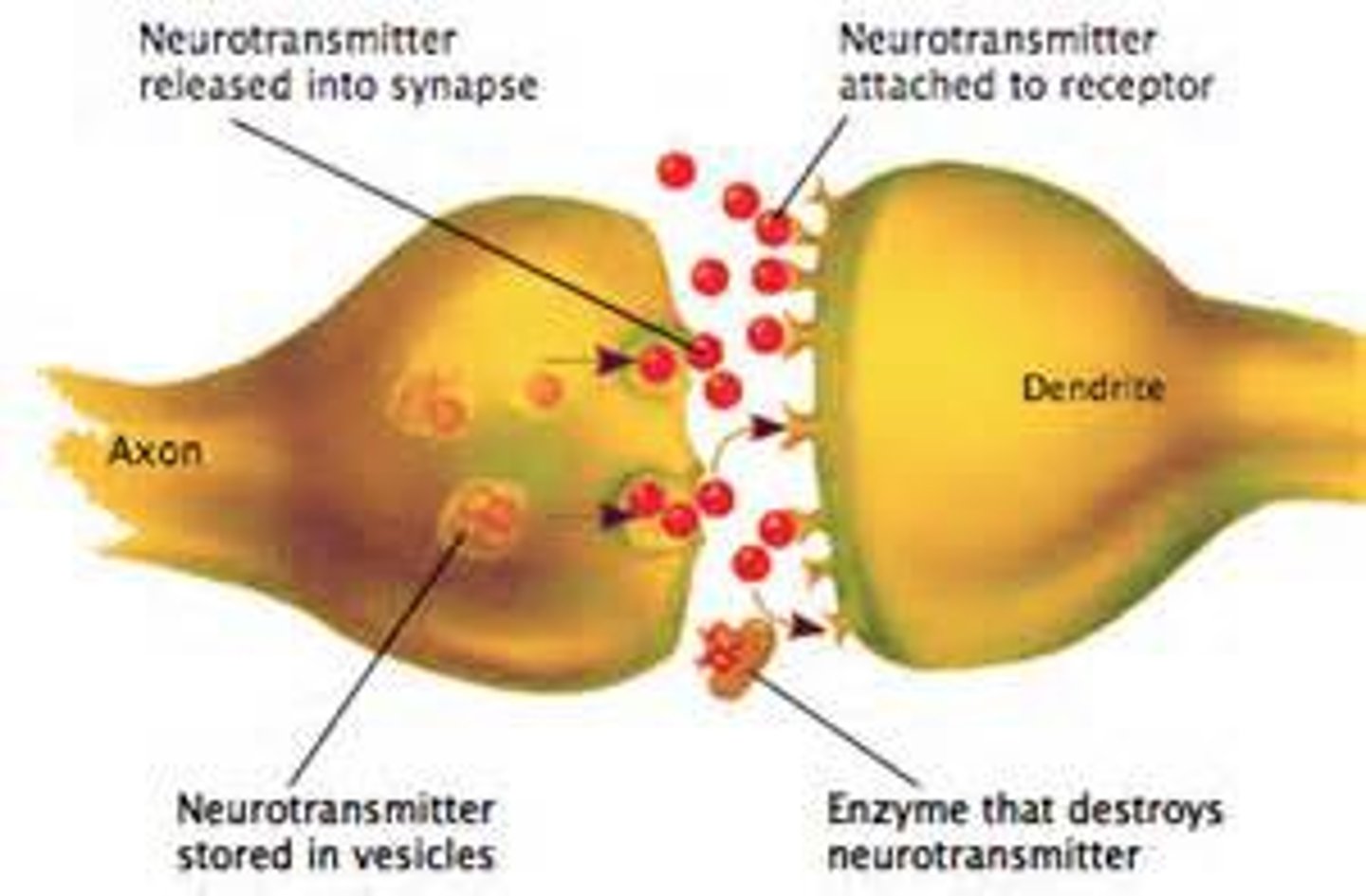
synapses
Tiny spaces between neurons; the gaps between neurons are referred to as synaptic gaps.
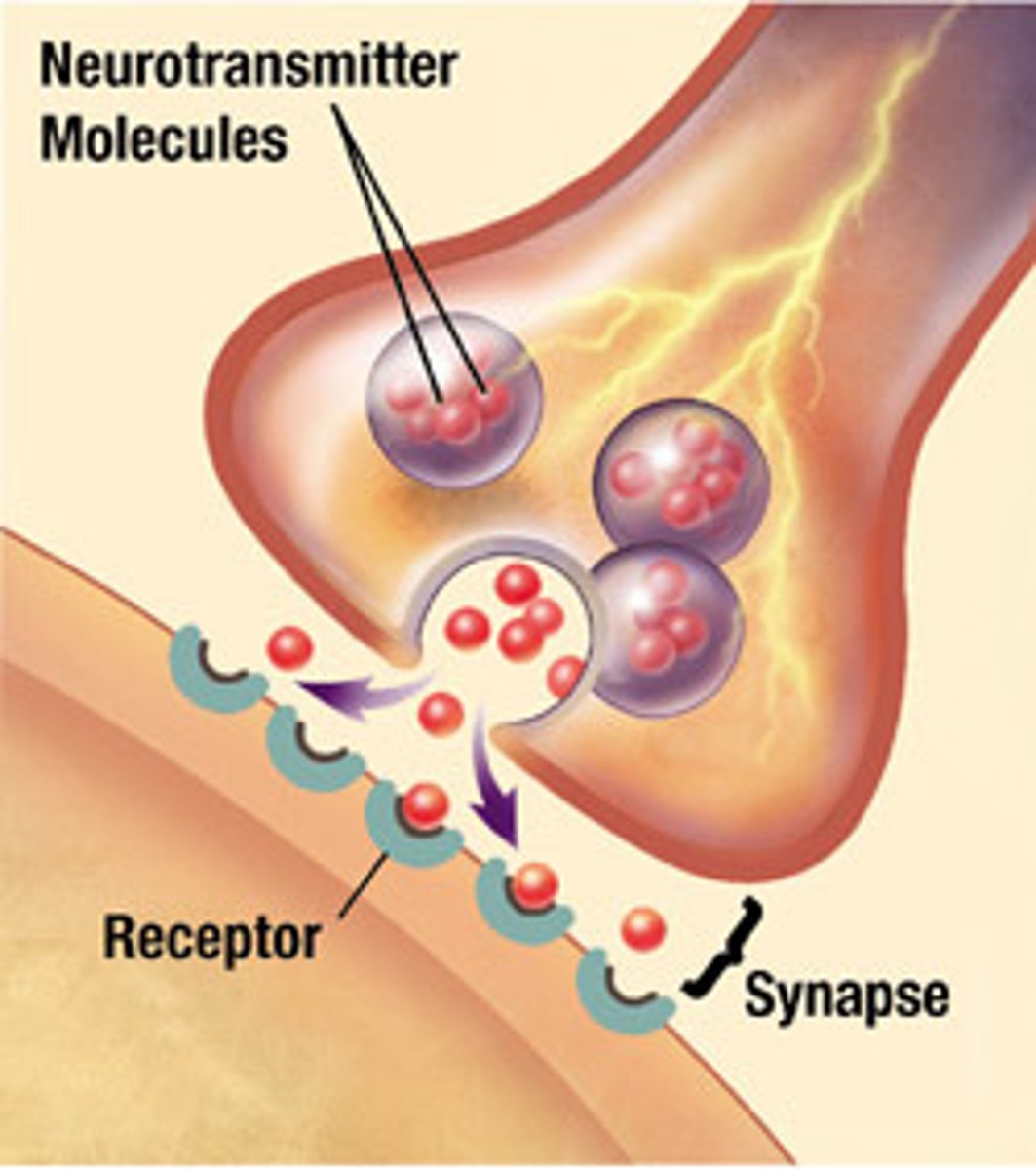
neuro transmitters
chemical messengers in the nervous system
proximodistal trend
growth proceeds literally from "near to far" - from the center of the body outward. Physical growth and motor skills that proceeds from the center of the body outward
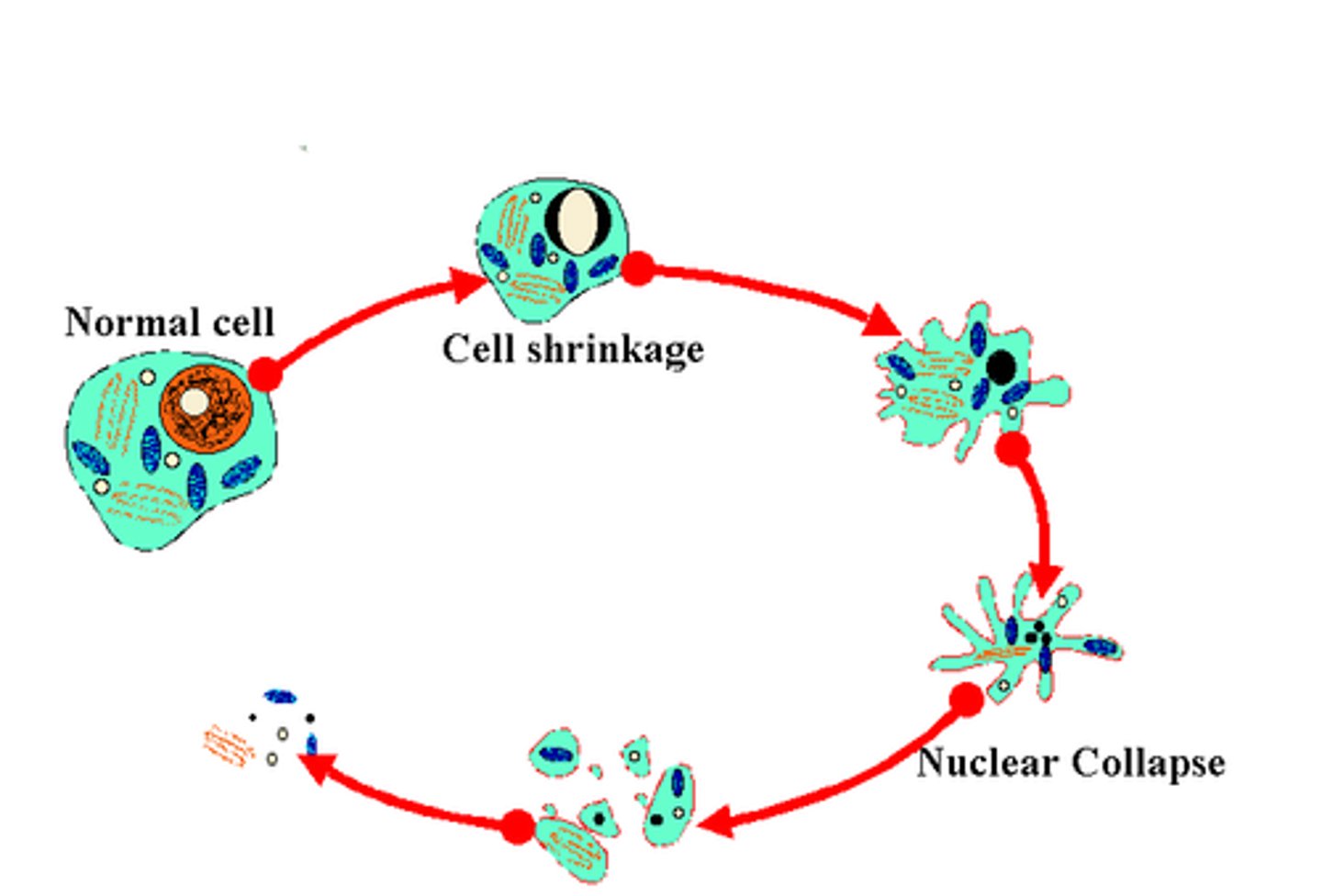
programmed cell death
An induced and ordered process in which the cell actively participates in bringing about its own death.
Apoptosis
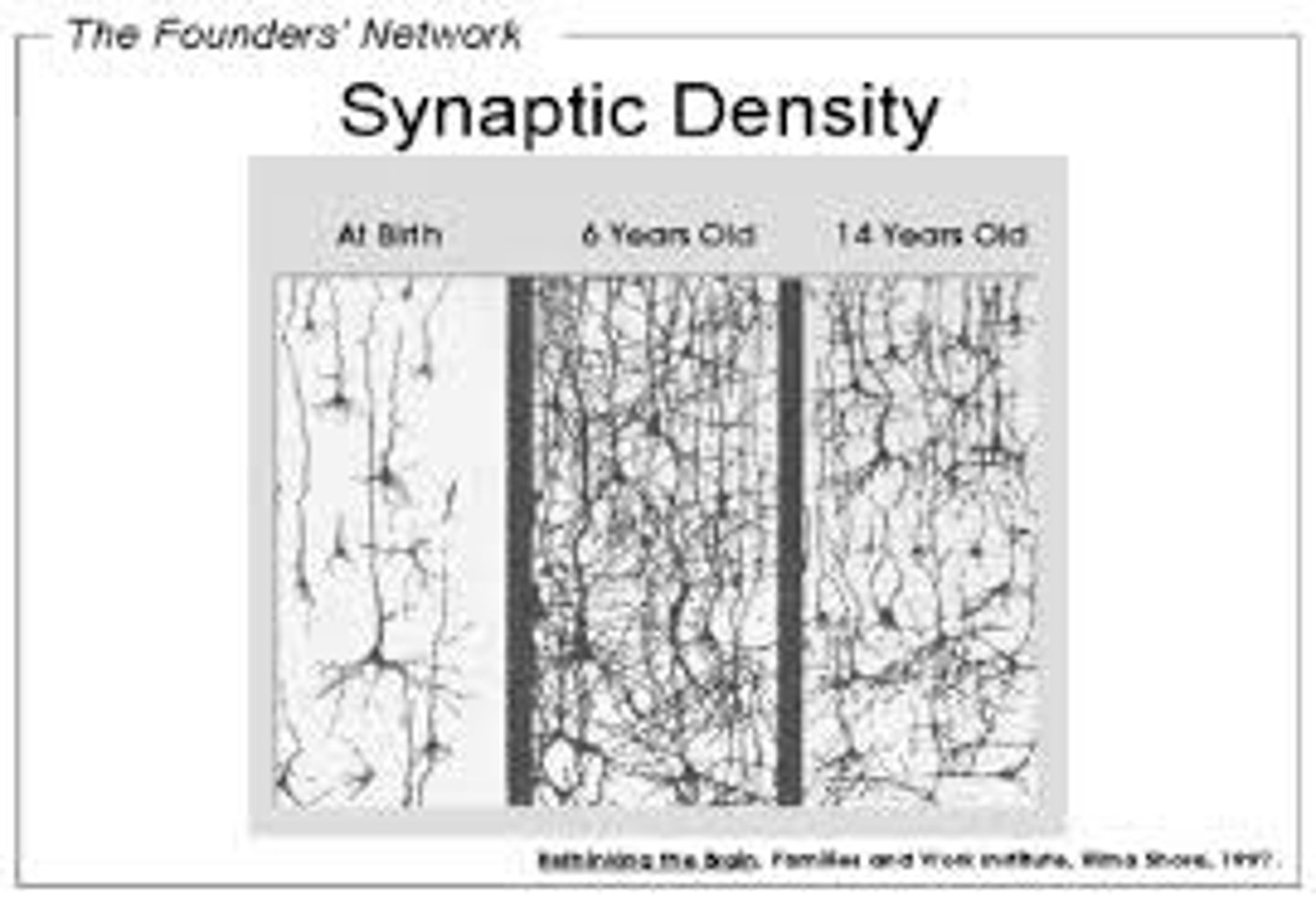
synaptic pruning
A process whereby the synaptic connections in the brain that are frequently used are preserved, and those that are not are lost. Until adolescence
glial cells
Cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
supportive cells of nervous system that guide growth of new neurons; forms myelin sheath; holds neuron in place; provides nourishment and removes waste
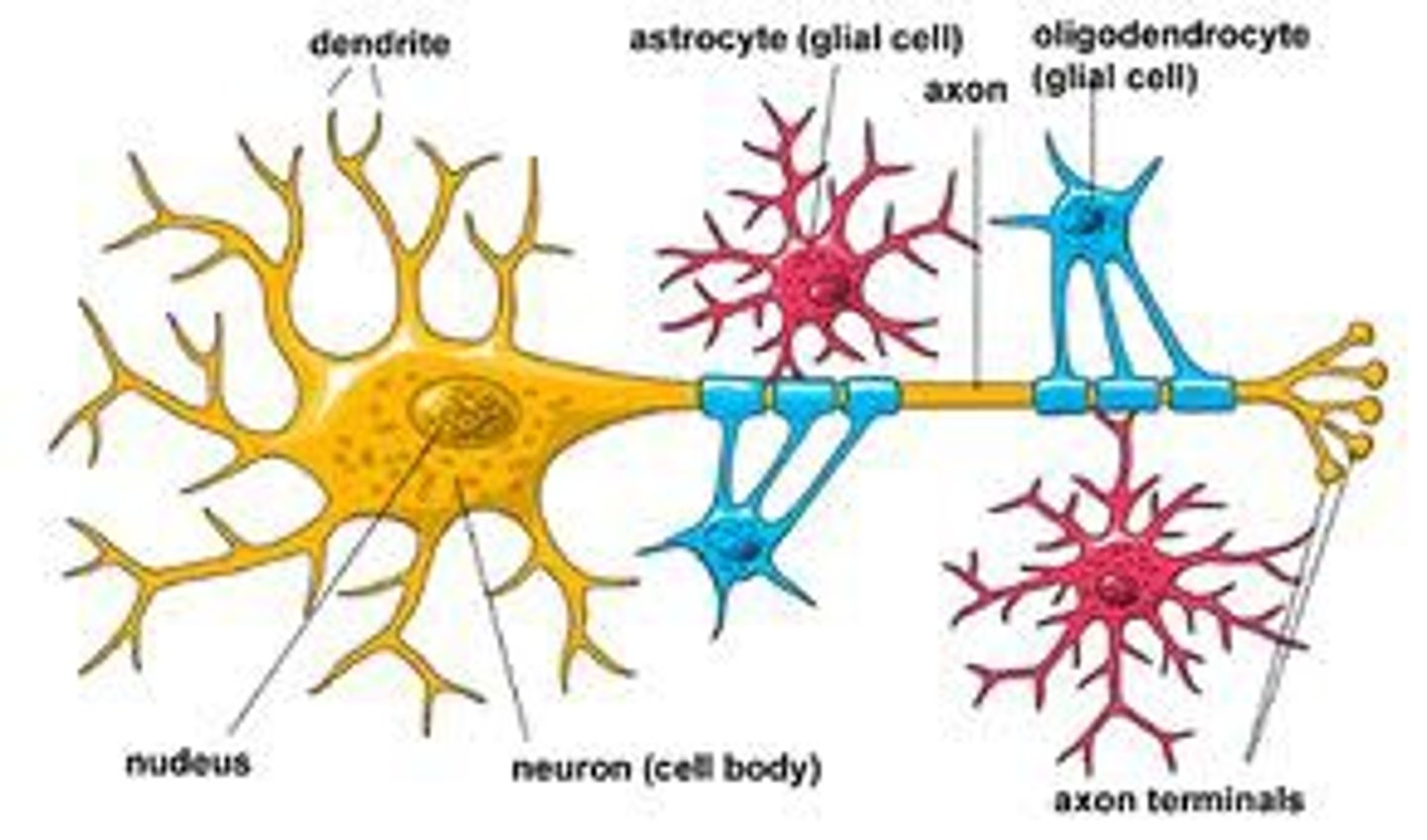
myelination
the process by which axons become coated with myelin, a fatty substance that speeds the transmission of nerve impulses from neuron to neuron
cerebral cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
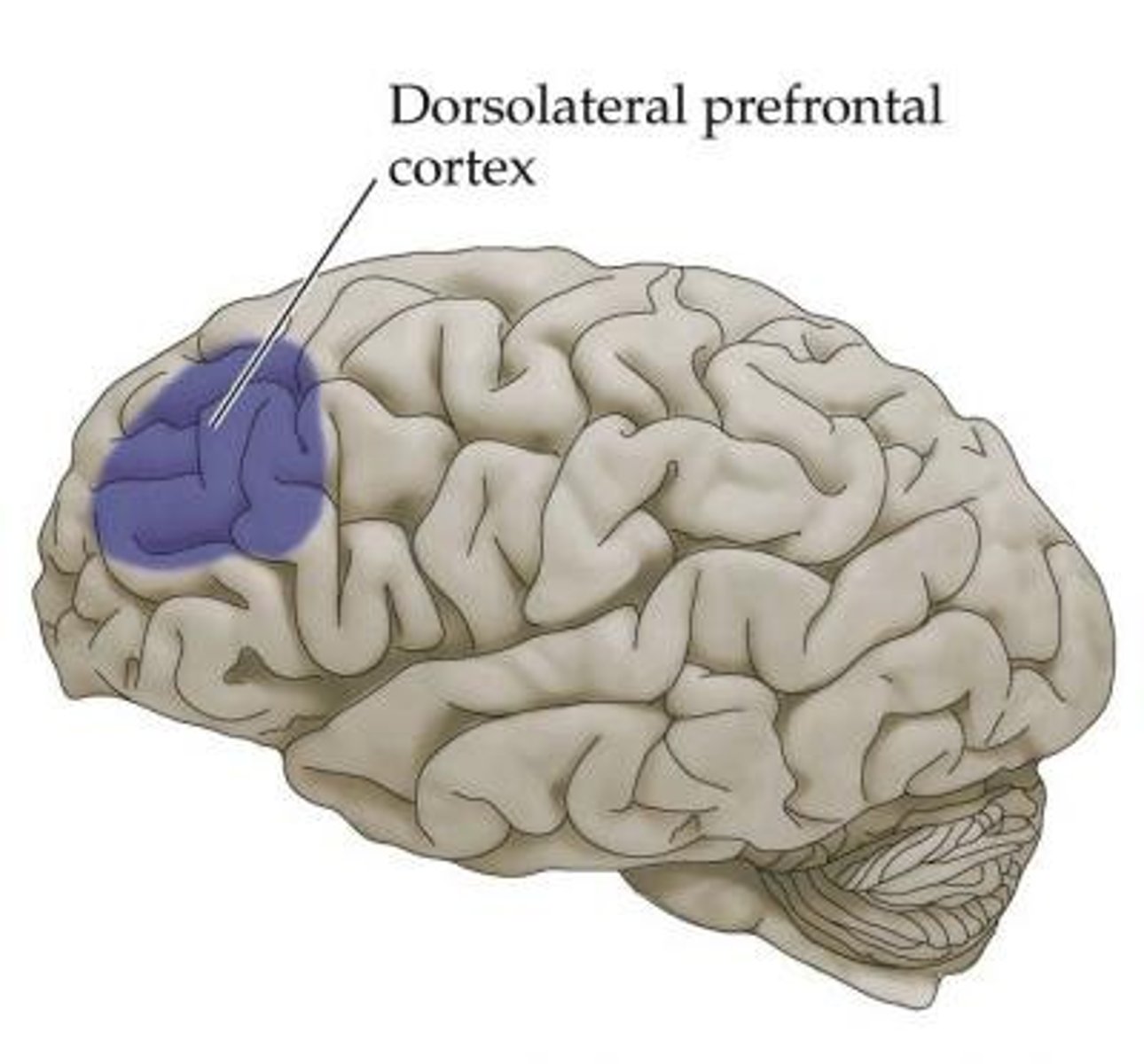
prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
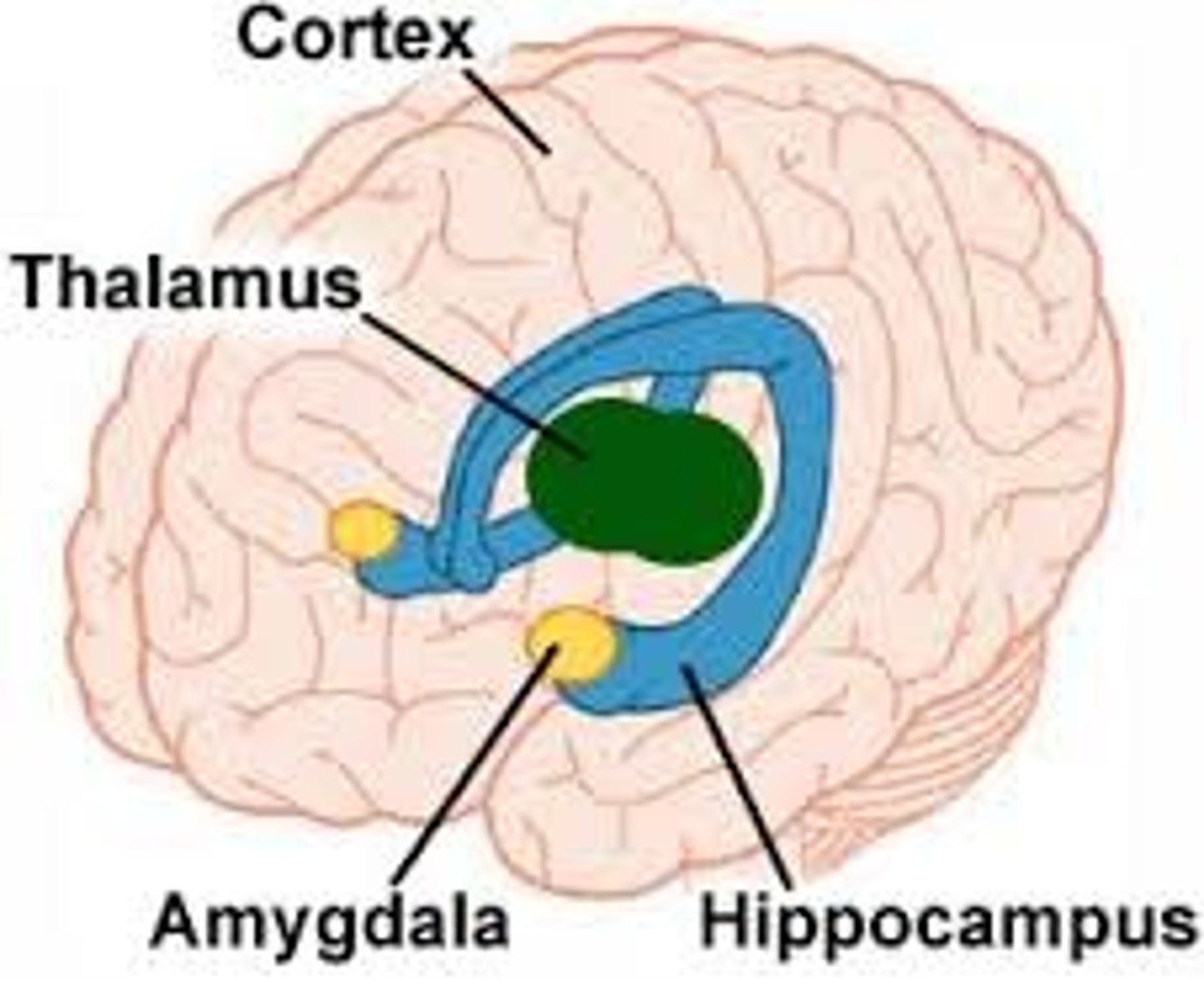
Area of cortex, with reciprocal connections to Amygdala, involved in expressing, inhibiting and reading emotions
lateralization
Cognitive function that relies more on one side of the brain than the other.
Cross hemisphere control of body
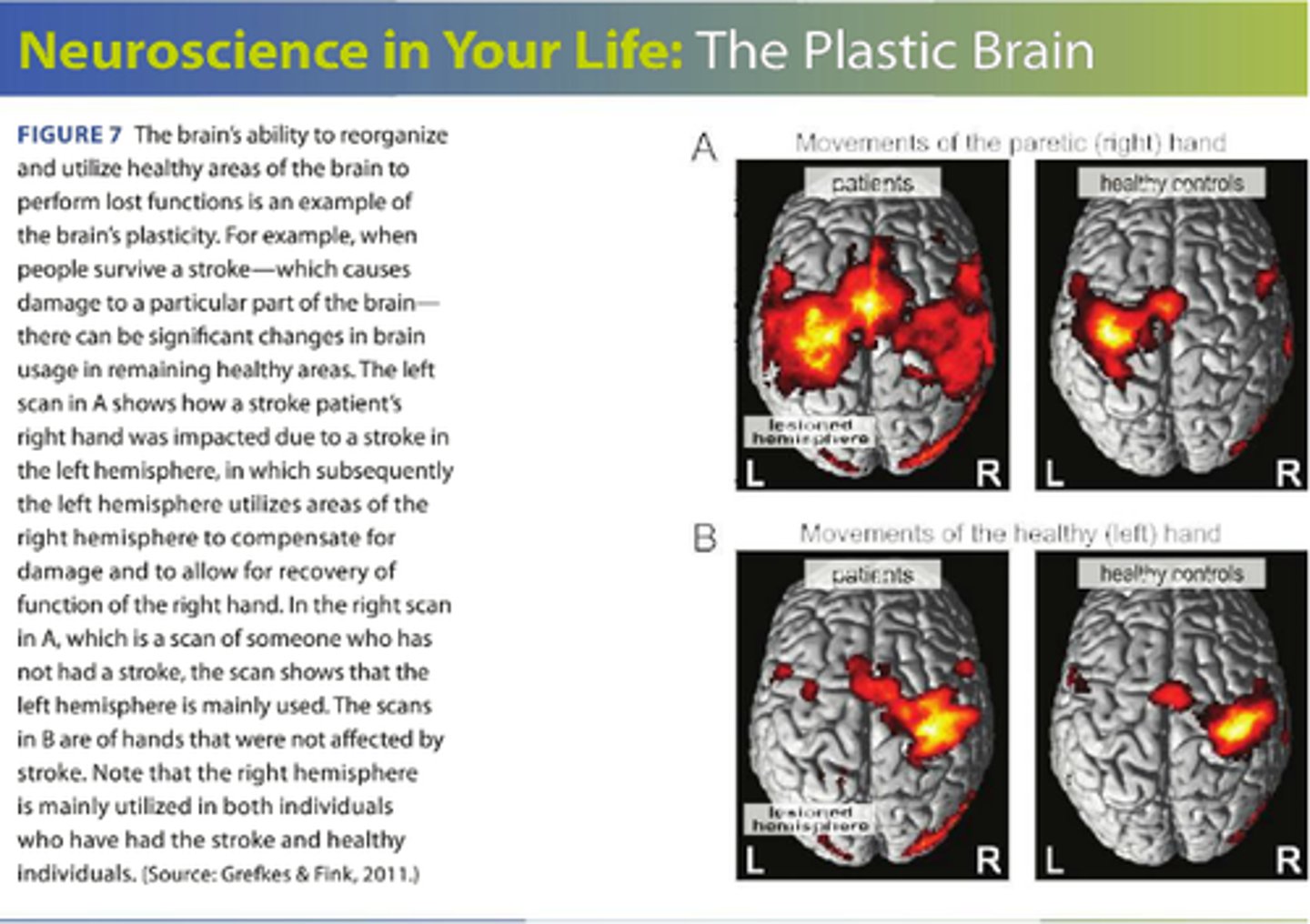
brain plasticity
the ability of other parts of the brain to take over functions of damaged regions. Declines as hemispheres of the cerebral cortex lateralize.
experience-expectant brain growth
brain functions that require certain basic common experiences -which an infant can be expected to have) in order to develop normally.
experience-dependent brain growth
consists of additional growth and refinement of established brain structures as a result of specific learning experiences that occur throughout our lives, varying widely across individuals and cultures.
The mechanism through which the structure of the brain is changed by experience
Marasmus
A childhood disorder characterized by protein and energy malnutrition, resulting in dry skin, loss of adipose tissue from normal areas of fat deposits such as buttocks and thighs, and behavior that is fretful and irritable.

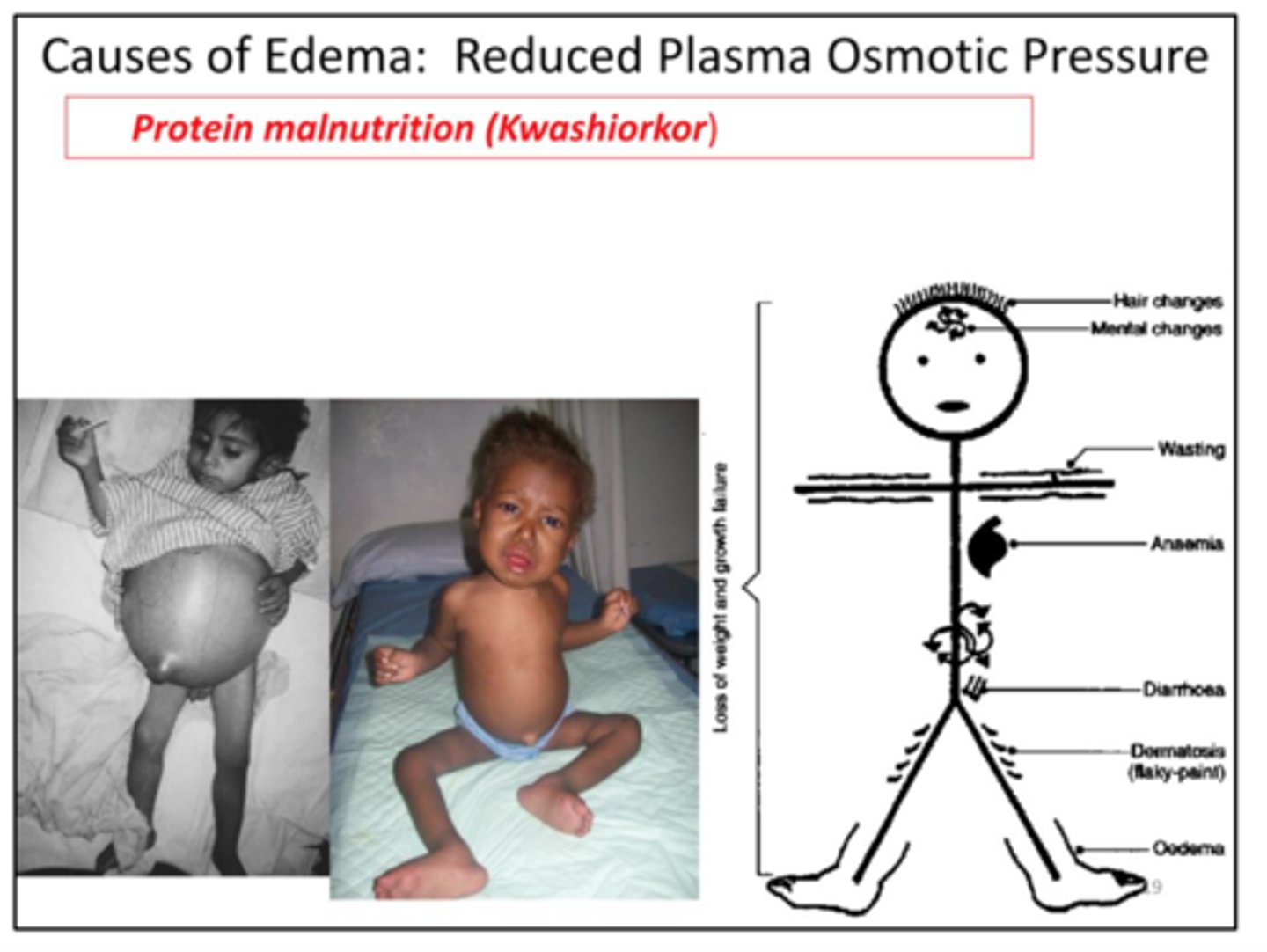
Kwashiorkor
Caused by unbalanced diets lacking protein or essential amino acids-happens when children stop breast-feeding... between 1-3 yrs of age; bloated stomach and physical disabilities.
classical conditioning
A type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events. Ivan Pavlov
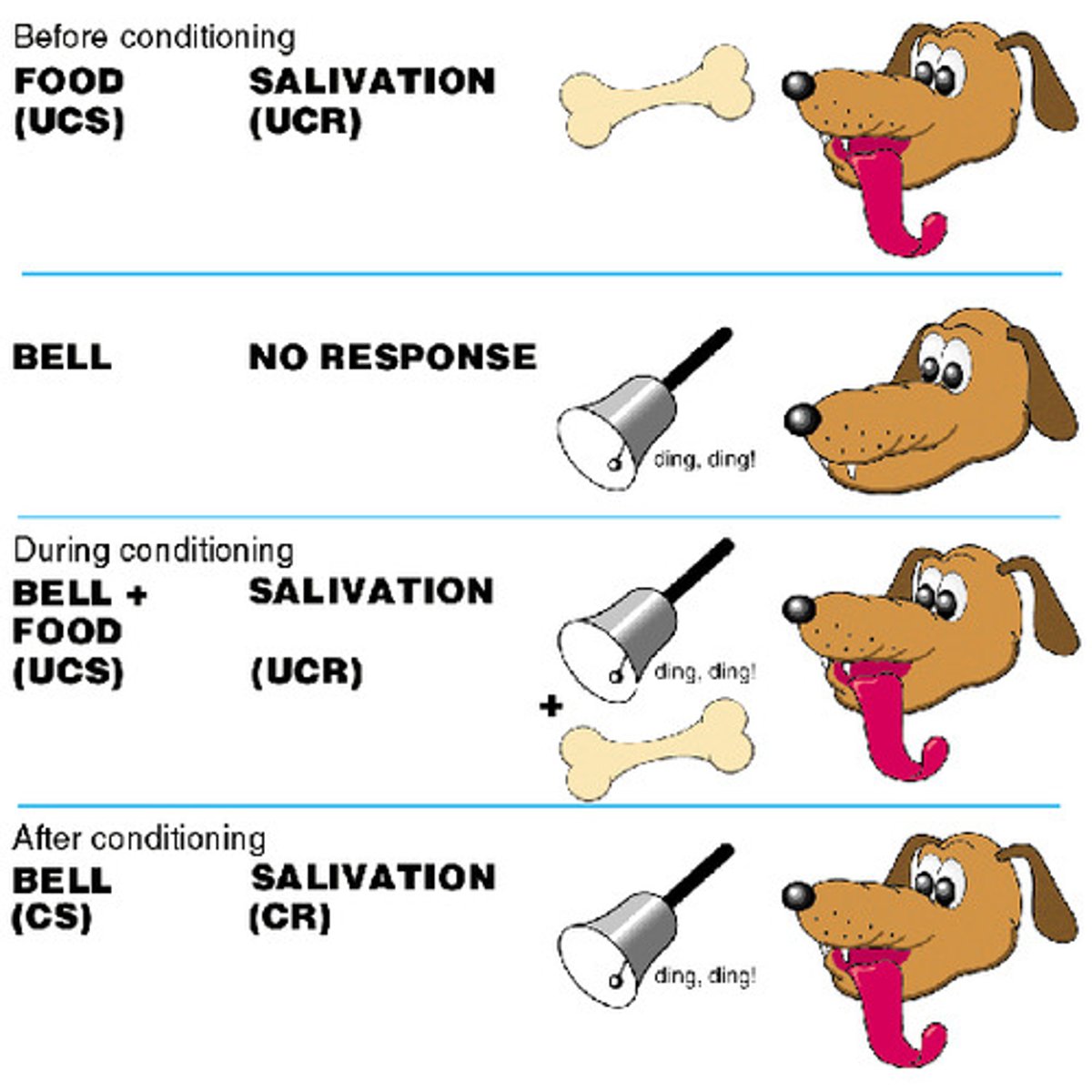
unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
A stimulus that evokes an unconditioned response without previous conditioning

unconditioned response (UCR)
In classical conditioning, the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus (UCS), such as salivation when food is in the mouth.

conditioned stimulus (CS)
In classical conditioning, an originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response
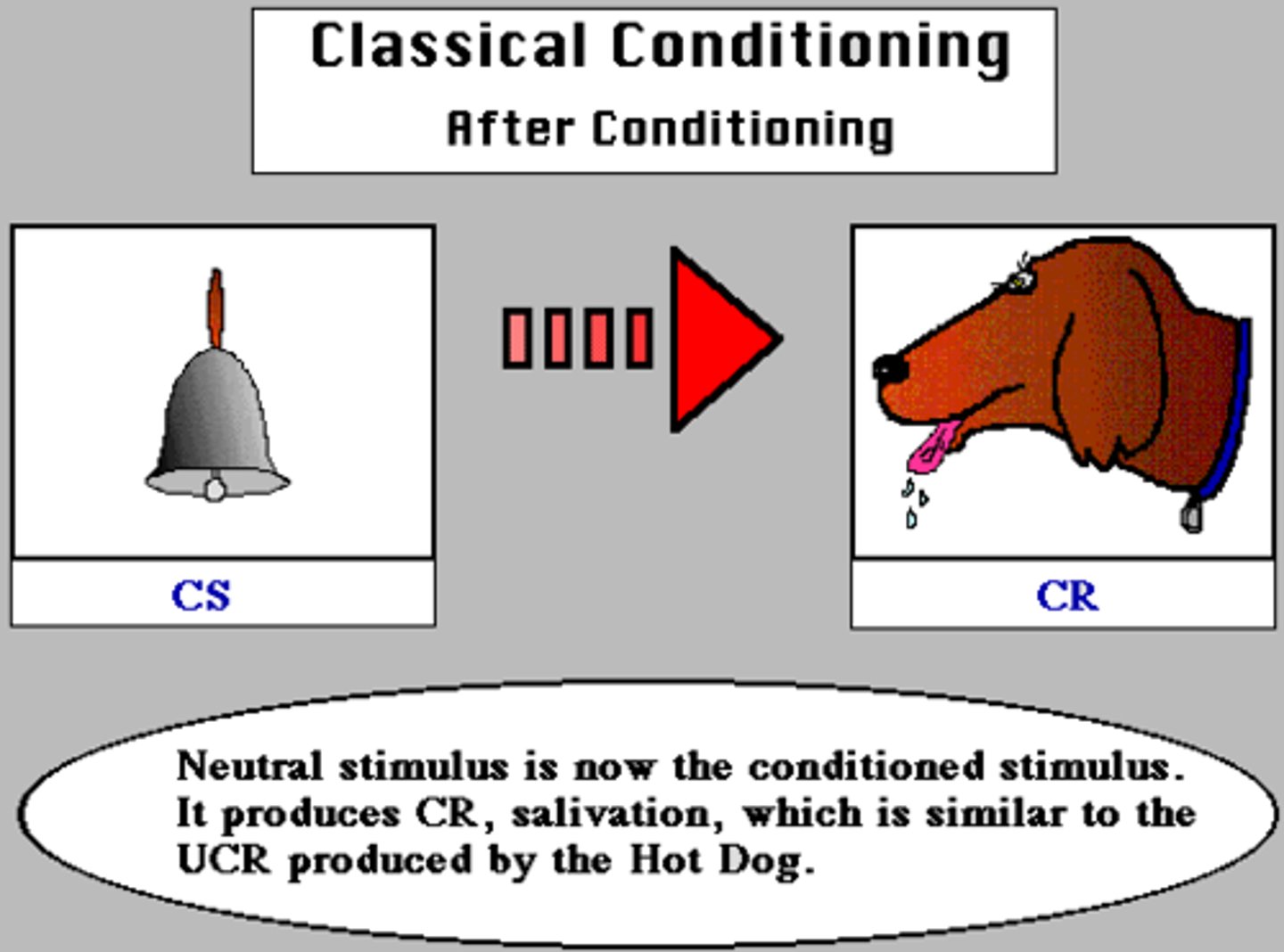
conditioned response (CR)
In classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus (CS).

operant conditioning
A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher.

habituation
An organism's decreasing response to a stimulus with repeated exposure to it
The process of becoming used to a stimulus
reinforcer
a stimulus that increases the occurrence of a response
punishment
removing a desirable stimulus or presenting an unpleasant one to decrease the occurrence of a response
recovery
Following habituation, an increase in responsiveness to a new stimulus.
imitation
Copying -or trying to copy) the actions of someone else
mirror neurons
Frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions or when observing another doing so. The brain's mirroring of another's action may enable imitation, language learning, and empathy.
dynamic systems theory of motor development
a perspective on human development that views the many facets of development as part of a single, dynamic, constantly changing system
statistical learning capacity
analyzing the speech stream for patterns- regularly occurring sequences of sounds-they acquire a stock of speech structures for which they will later learn meanings, long before they start to talk around age 12 months
What feature does the brain specialize in that allows babies to learn language?

contrast sensitivity
the ability to detect differences in light and dark areas in a visual pattern
the ability to detect differences in light and dark areas in a visual pattern. This is poor in infants.
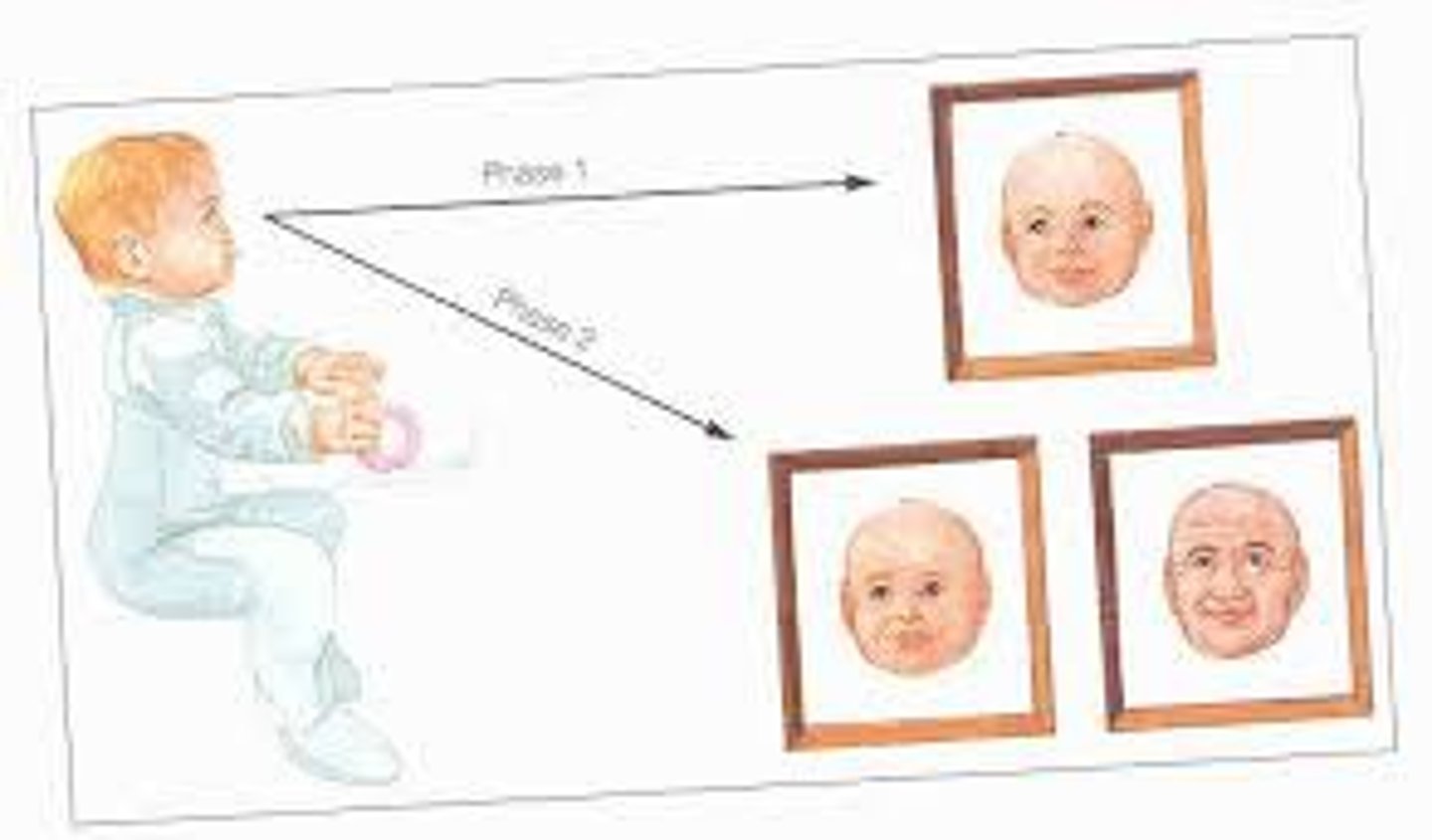
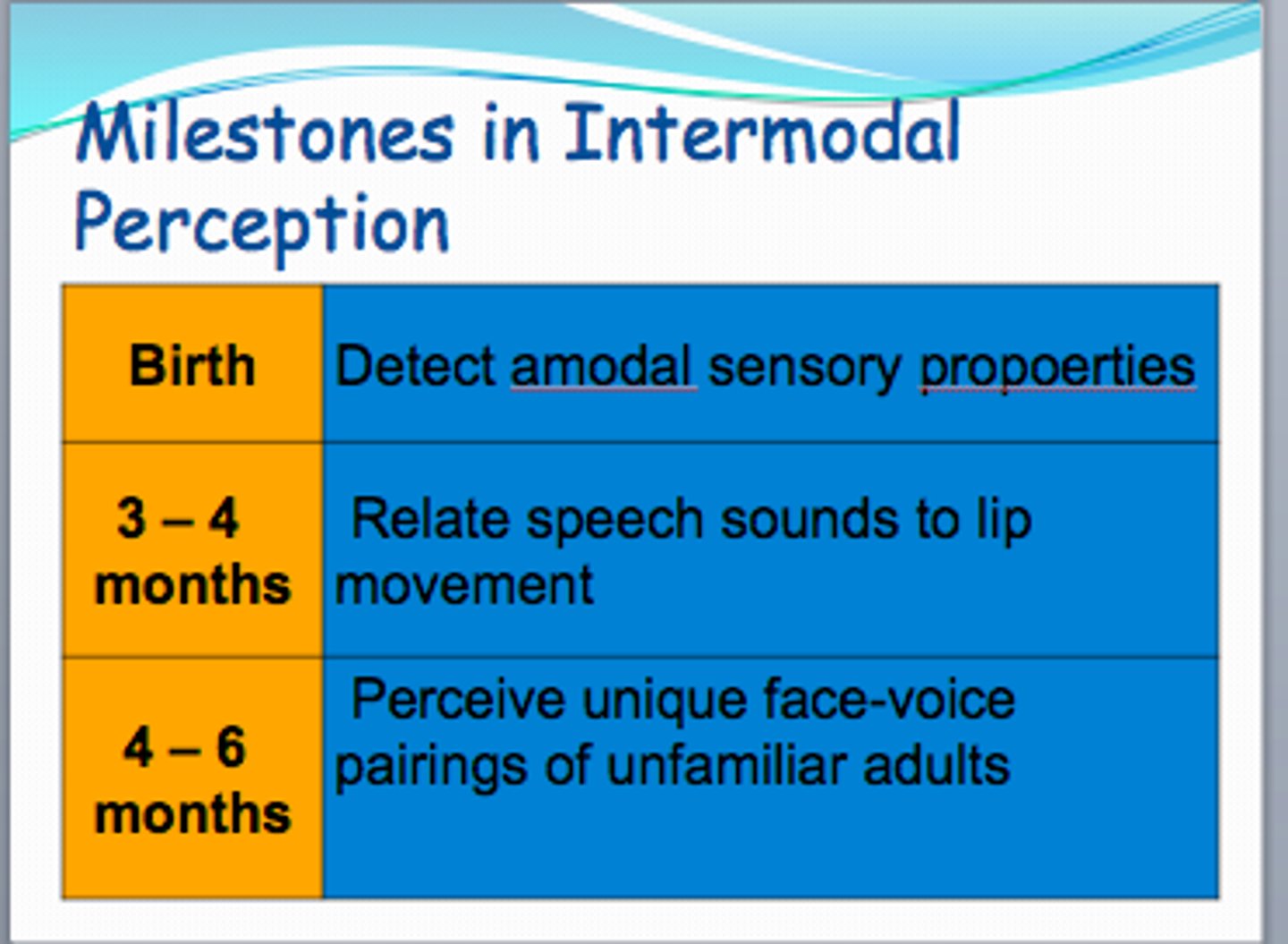
intermodal perception
The ability to relate and integrate information from two or more sensory modalities, such as vision and hearing.
An infant plays with a toy block in the dark, so he cannot see it. Later, he is shown a ball as well as the block. He realizes that it was the block, not the ball that he was playing with in the dark through:
differentiation theory
according to Gibson, infants search for invariant, or unchanging, features of the environment - those that remain stable in a constantly changing world.
Baby: when held upright, holds head erect and steady
Average age achieved: 6 wks
Baby: when prone, lifts self by arms
Average age achieved: 2 months
Baby: rolls from side to back
Average age achieved: 2 months
Baby: grasps cube
Average age achieved: 3m 3w
Baby: rolls from back to side
Average age achieved: 4m 2w
Baby: sits alone
Average age achieved: 7 months
Baby: crawls
Average age achieved: 7 months
Baby: pulls to stand
Average age achieved: 8 months
Baby: plays pat-a-cake
Average age achieved: 9m 3w
Baby: stands alone
Average age achieved: 11 months
Baby: walks alone
Average age achieved: 11 months
Baby: builds tower of two cubes
Average age achieved: 11m 3w
Baby: scribbles vigorously
Average age achieved: 14 months
Baby: walks up stairs with help
Average age achieved: 16 months
Baby: jumps in place
Average age achieved: 23m 2w
Baby: walks on tiptoe
Average age achieved: 25 months
perceptual narrowing effect
perceptual sensitivity that becomes increasingly attuned with age to information most often encountered
depth perception
The ability to judge the distance of objects from one another and from ourselves. It is important for understanding the layout of the environment and for guiding motor activity.
"visual cliff"
Designed by Eleanor Gibson and Richard Walk (1960) and used in the earliest studies of depth perception. It consists of a Plexiglass-covered table with a platform at the center, a 'shallow' side with a checkerboard pattern just under the glass, and a 'deep' side with a checkerboard several feet below the glass. Researchers found that crawling babies readily crossed the shallow side but mostly avoided the deep side. They concluded that around the time infants crawl, most distinguish deep from shallow surfaces.
motion
The first depth cue to which infants are sensitive. Babies 3-4 weeks old blink defensively when an object moves toward their face.
binocular depth cues
Arise because our two eyes have slightly different views of the visual field. Sensitivity to this emerges between 2-3 months and improves rapidly over the first year.
pictorial depth cues
Cues artists use to make a painting look 3D. Babies display sensitivity to this at 3-4 months, and strengthens between 5-7 months. Examples include receding lines that create the illusion of perspective, changes in texture (nearby textures are more detailed than far away ones), and overlapping objects (an object partially hidden by another object is perceived to be more distant).
prereaching age
newborn
ulnar grasp age
3-4 months
age babies transfer object from hand to hand
4-5 months
pincer grasp age
9 months
reason to breastfeed 1: provides the correct balance of fat and protein
Compared with the milk of other mammals, human milk is higher in fat and lower in protein. This balance, as well as the uniques proteins and fats, is ideal for a rapidly myelinating nervous system.
reason to breastfeed 2: ensures nutritional completeness
A mother who breastfeeds need not add other foods to the infant's diet until the baby is 6 months old. The milks is all mammals are low in iron, but the iron contained in human milk is much more easily absorbed by the baby's system. Consequently, formula-fed infants need iron-fortified formula.
reason to breastfeed 3: helps ensure healthy physical growth
1 year old breastfed babies are leaner, a growth pattern that persists through the preschool years and that is associated with a reduction in later weight and obesity.
reason to breastfeed 4: protects against many diseases
Breastfeeding transfers antibodies and other infection-fighting agents from mother to baby and enhances immune system functioning. Breastfed babies have fewer allergic reactions and respiratory and intestinal illnesses. Breast milk also has anti inflammatory effects that reduce illness symptoms. Exclusively breastfeeding in the first four months is linked to lower blood cholesterol levels in adulthood and may help prevent cardiovascular disease.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
Event-related potentials (ERPs)
the EEG waves that regularly accompany certain psychological events (like pictures, music or speech) are recorded in the cerebral cortex. It enables identification of general regions of stimulus- induced activity.
functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
an imaging technique used to examine changes in the activity of the working human brain by measuring changes in the blood's oxygen levels
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
a method of brain imaging that assesses metabolic activity by using a radioactive substance injected into the bloodstream
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS)
infrared light measures blood flow and oxygenation, safe for all ages
pattern perception
ability to discriminate among different figures and shapes. Newborns prefer to look at patterns rather than plain stimuli. But because their vision is poor, very young babies can not resolve the features in complex patterns, so they prefer to look at a checkerboard with large, bold patterns than one with many small squares.