Articulation System Framework
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
The skeletal framework of articulation system
I.Upper cervical vertebral column
II.Bones of Facial Skeleton
III.Cranial (Skull ) Bones
Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C7)
The cervical vertebra lies behind the pharynx and forms part of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
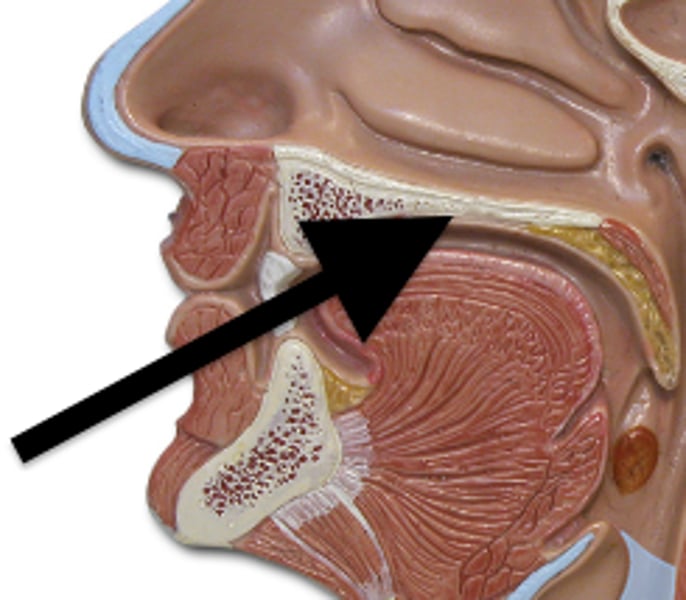
Bones of the facial skeleton that form the articulation framework
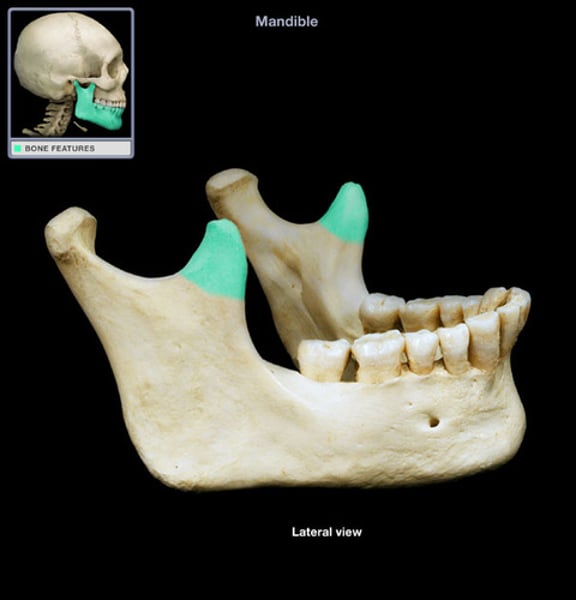
Mandible
Maxilla
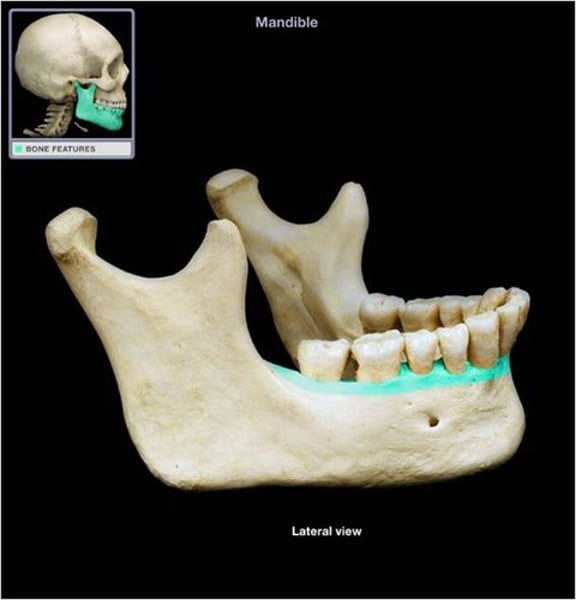
Mandible
Single bone forming the lower jaw
Forms the only movable joint in the skull
It has two projections: condyloid and coronoid processes
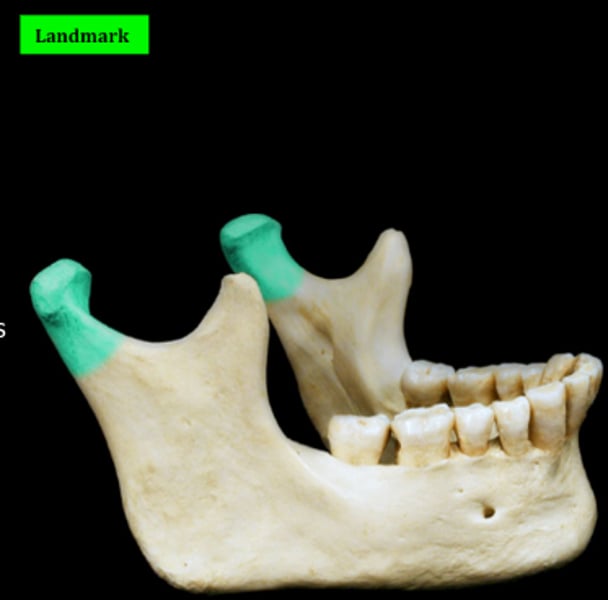
condyloid process of mandible
Articulates with temporal bone by the temporomandibular joint
Coronoid Process of mandible
insertion of temporalis
Prognathic jaw
Class III Malocclusion (underbite)
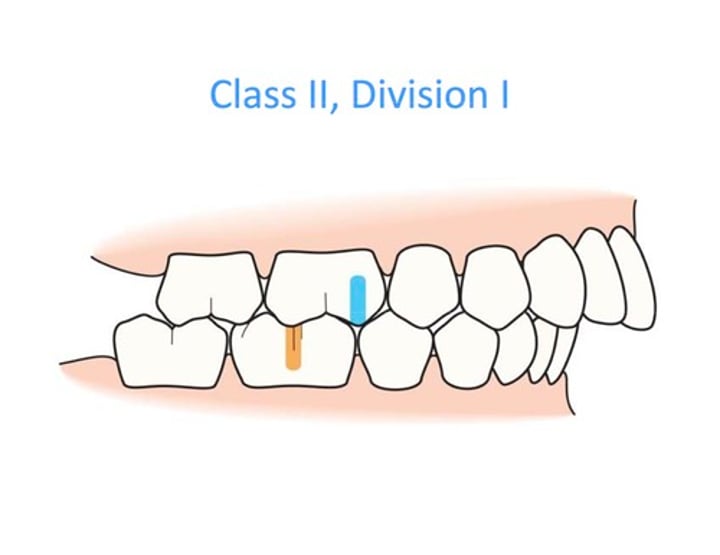
Retrognathic jaw
Class II Malocclusion (overbite)
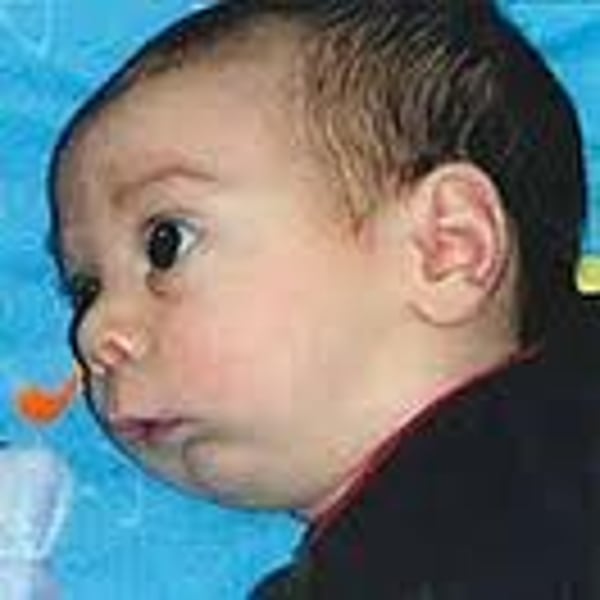
Pierre Robin Sequence (PRS)
An unusually small jaw, which alters tongue position and can induce problems with swallowing

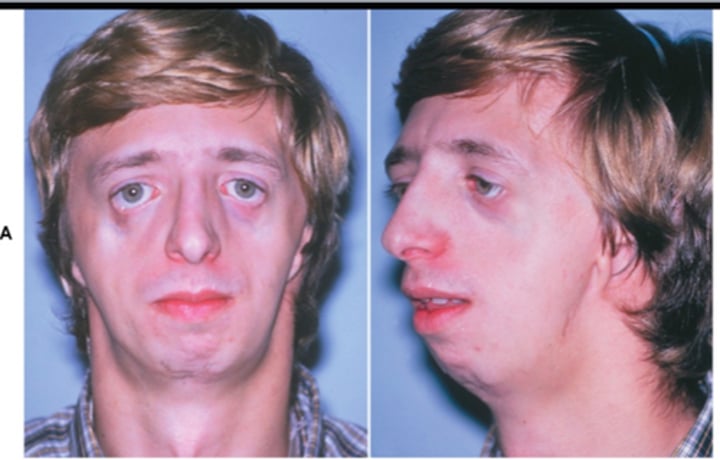
Treacher Collins Syndrome
Variety of facial deformities, including lowered eyes, absent cheekbones, cleft palate
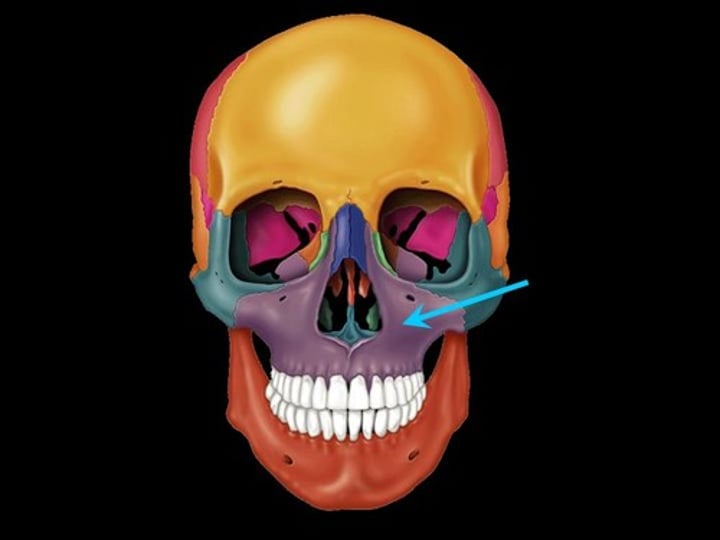
Maxilla
- Upper jaw
-Paired bone forming the nose, upper dental ridge, and most of the hard palate
-Houses upper teeth
-Forms part of orbit of eye (floor)
-Joints w/ all other facial bones except mandible
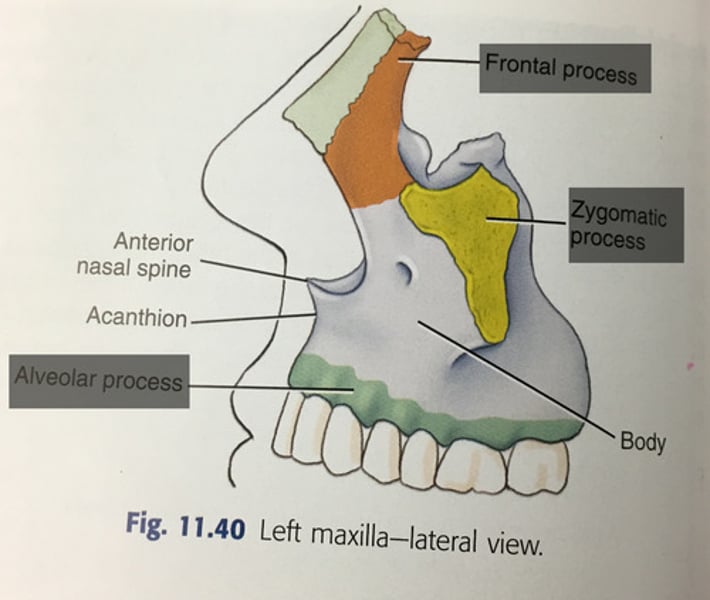
Maxilla has four processes
- Frontal: provides some framework for the nose; articulates with frontal bone
- Zygomatic: articulates with zygomatic bone
- Alveolar: holds the teeth
- Palatine: floor of the nasal cavity, roof of the mouth
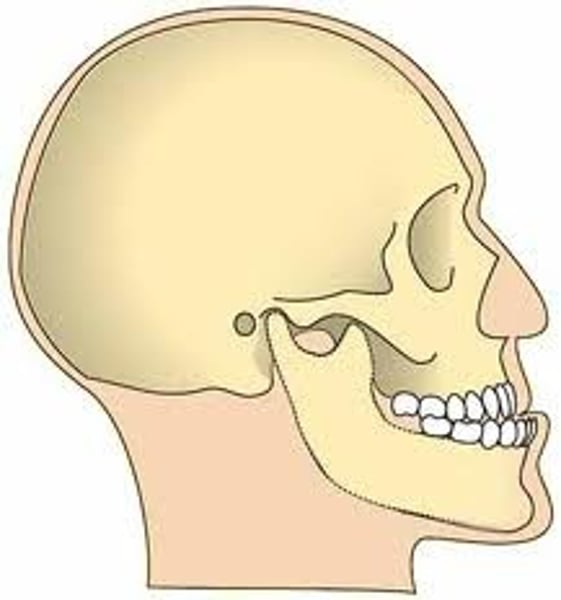
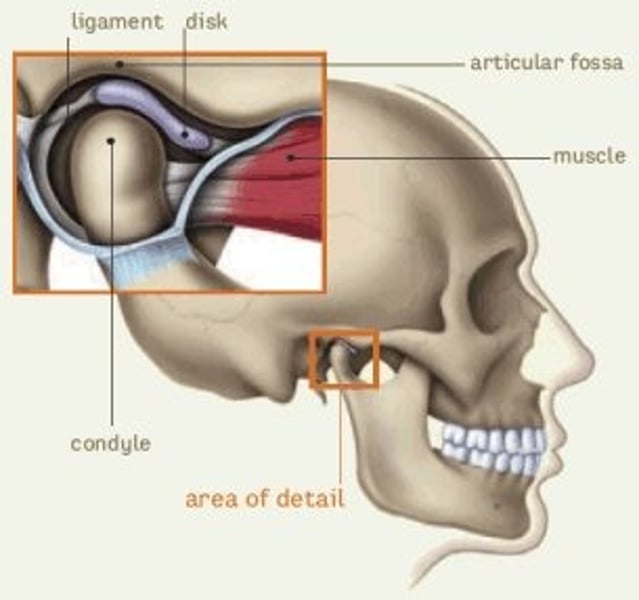
temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
The joint between the temporal bone and the mandible
It is an ellipsoid-condyloid joint (ball and socket).
This joint allows you to hinge and glide (front/back, side/side).
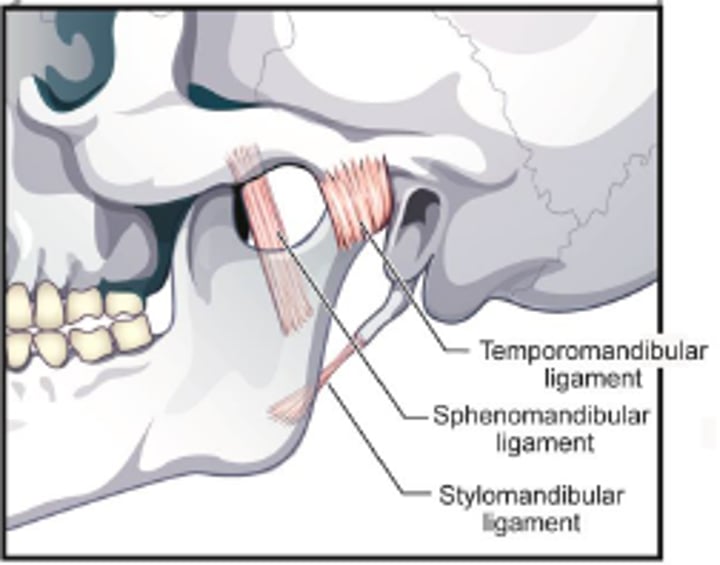
TMJ ligaments
temporomandibular ligament
sphenomandibular ligament
stylomandibular ligament
The mandible can move in three different ways relative to the skull
- Upward and downward
- Forward and backward
- Side to side
What is articulation?
Adjustment of the shape of the vocal tract by movement of articulators
Cavities of the articulatory system
oral, buccal, nasal, pharyngeal
oral cavity
Extends from mouth to the faucial pillars
Size and shape or the oral cavity can be altered by movement of lips, tongue and mandible to make different speech sounds
buccal cavity
Vestibule of the oral cavity; the space between the lips, gums, and teeth.
Oral Cavity Structures
lips, teeth, tongue, palate, tonsils
the function of the lips during articulation
Consonants: /p, b, m, f, v, w/ need lip (labial) involvement
Most back vowels in English require labial movement
Tongue
The most mobile articulator
Consists of four parts:
Dorsum: superior surface
Tip (apex): anterior-most portion
Base: resides in the oropharynx
Root: Inferior
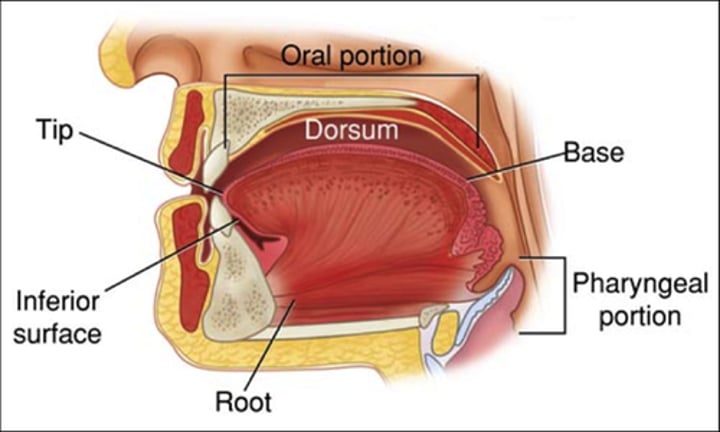
Tongue Portions
Oral/Palatine surface: 2/3--within the oral cavity
Pharyngeal surface: 1/3--within the pharyngeal cavity
Median fibrous septum: divides the tongue into right and left halves (central sulcus)
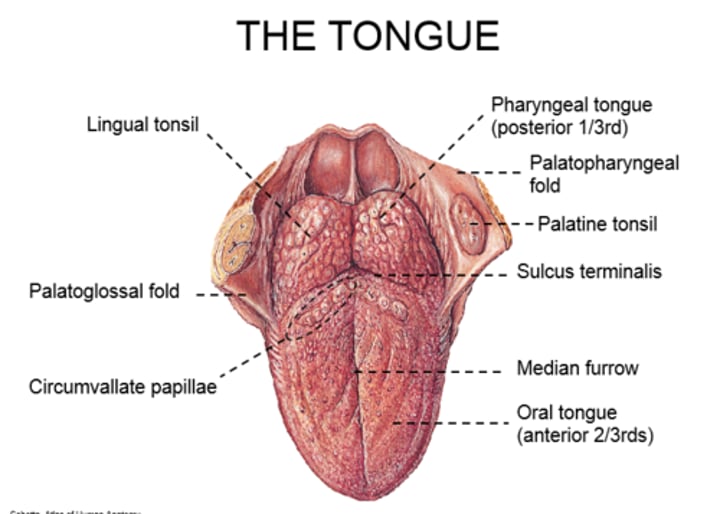
The Palate
Consists of the alveolar arch, hard palate, and soft palate (or velum)