Adaptations to Resistance Training
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
muscle strength
maximal force that a muscle group can generate
1-RM
muscular endurance
ability to make repeated contractions agains a sub-maximal load
high vs low resistance training
high: 6-10 reps till fatigue
low: 30-40 reps till fatigue
how does aging generally affect muscle compositions and around what age does this occur
loss of both muscle mass and strength
greatest decline at > age 50
atrophy type II fibers
reduce # of both type I and II fibers
how does resistance training affect muscle composition
changes nervous system and muscle fiber size/function
increase muscle fiber specific tension
increase muscle mass
what is responsible for early gains in strength
neural adaptations - first 2-8 weeks
list the 4 neural adaptations
increase # of motor units
more motor units allow us to send more signals down the T tubules to release calcium
increased firing rate of motor units
more frequency = more power produced
increase motor unit syntonization
motor units fire closer to the same time as one another
improve neural transmission across NMJ
neuron releases acetylcholine, travels across cleft and riches muscle
resistance training increases muscle fiber specific tension in which type of muscle fiber
type 1
due to increase calcium sensitivity - resulting in greater number of cross bridge bound to actin
hyperplasia
increase number of fibers
hypertrophy
increase cross sectional area of muscle fibers
how does training affect muscle protein synthesis
increase
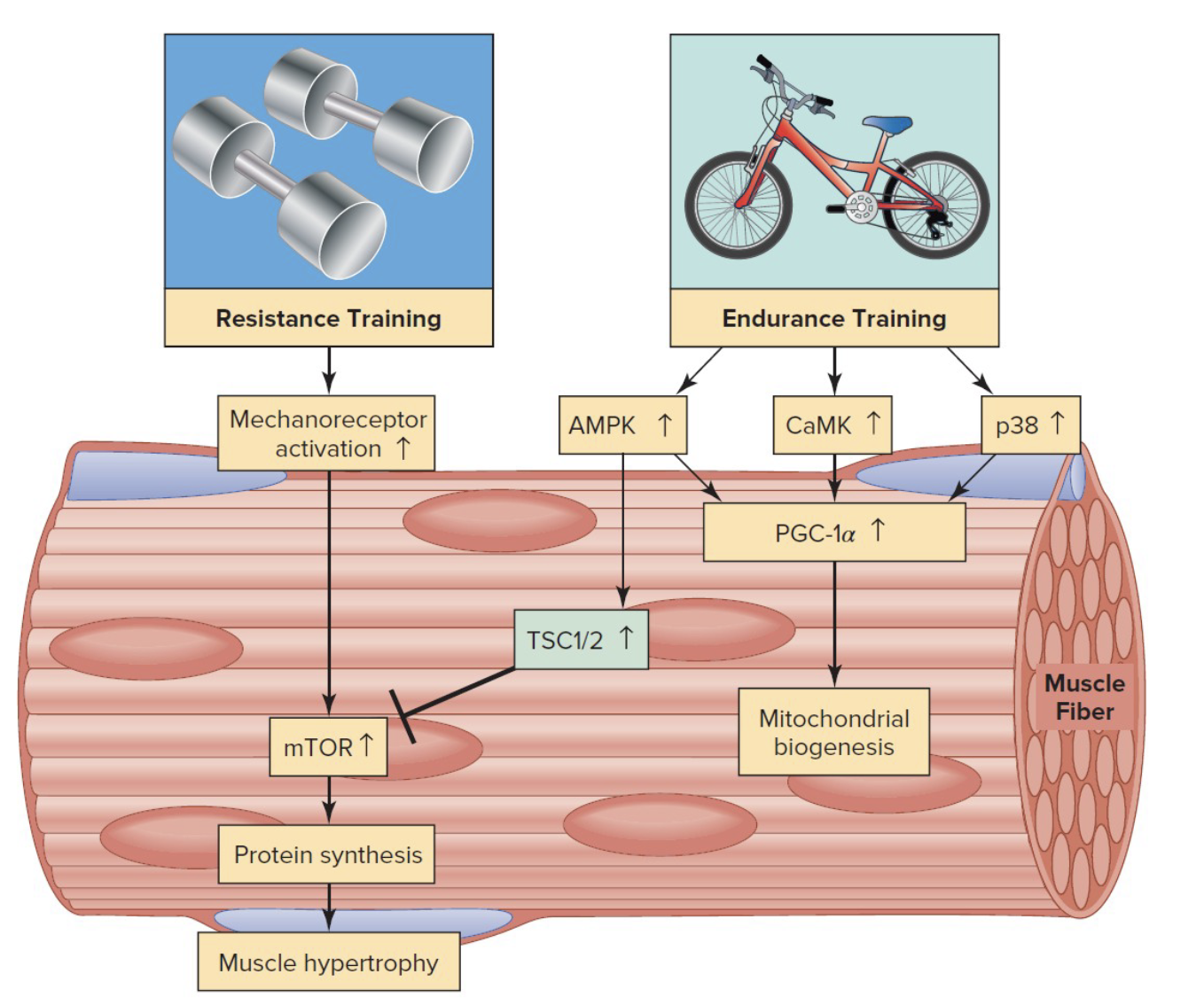
what key factors contribute to resistance training induced increases in muscle protein synthesis
mRNA increase resulting in protein synthesis at ribosome
ribosome increase in number and elevate muscle protein synthesis capacity
activation of mTOR (this is the key factor)
what 2 molecules stimulation mTOR activation for muscle protein synthesis
phosphatidic acid (PA) and Rheb
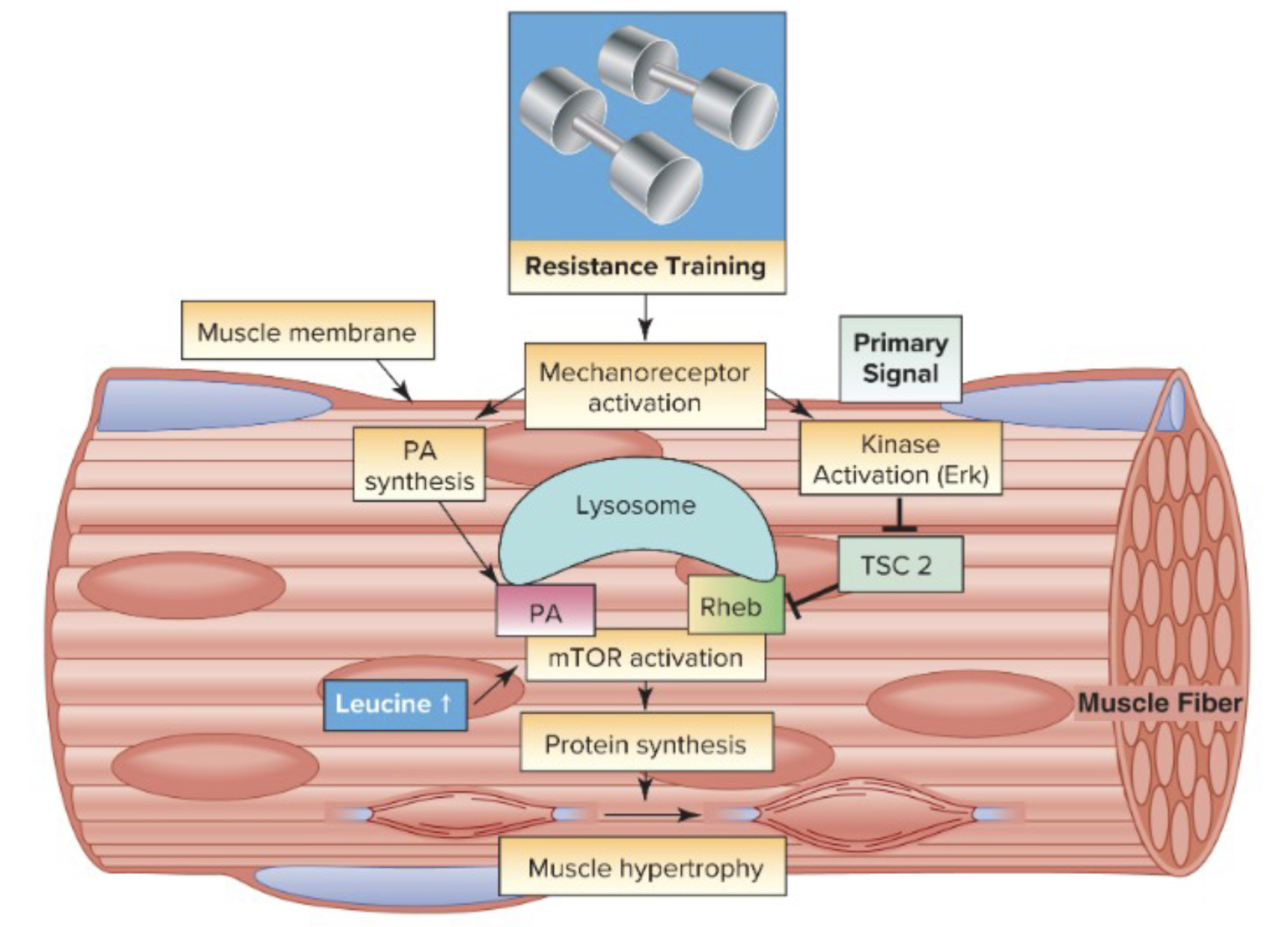
describe the role of TSC 2 in this photo when
At rest, TSC inhibits Rheb so that we do not activate mTOR
when we exercise, ERK inhibits the inhibitor, TSC2 so that we do activate Rheb and mTOR to get protein synthesis
which hormones are linked to mTOR activation and have POTENTIAL to increase muscle protein synthesis (though not absolutely necessary)
insulin like growth factor (IGF-1)
growth hormone
do NSAIDS impact resistance training induced hypertrophy
does not negatively impact, may affect inflammatory response
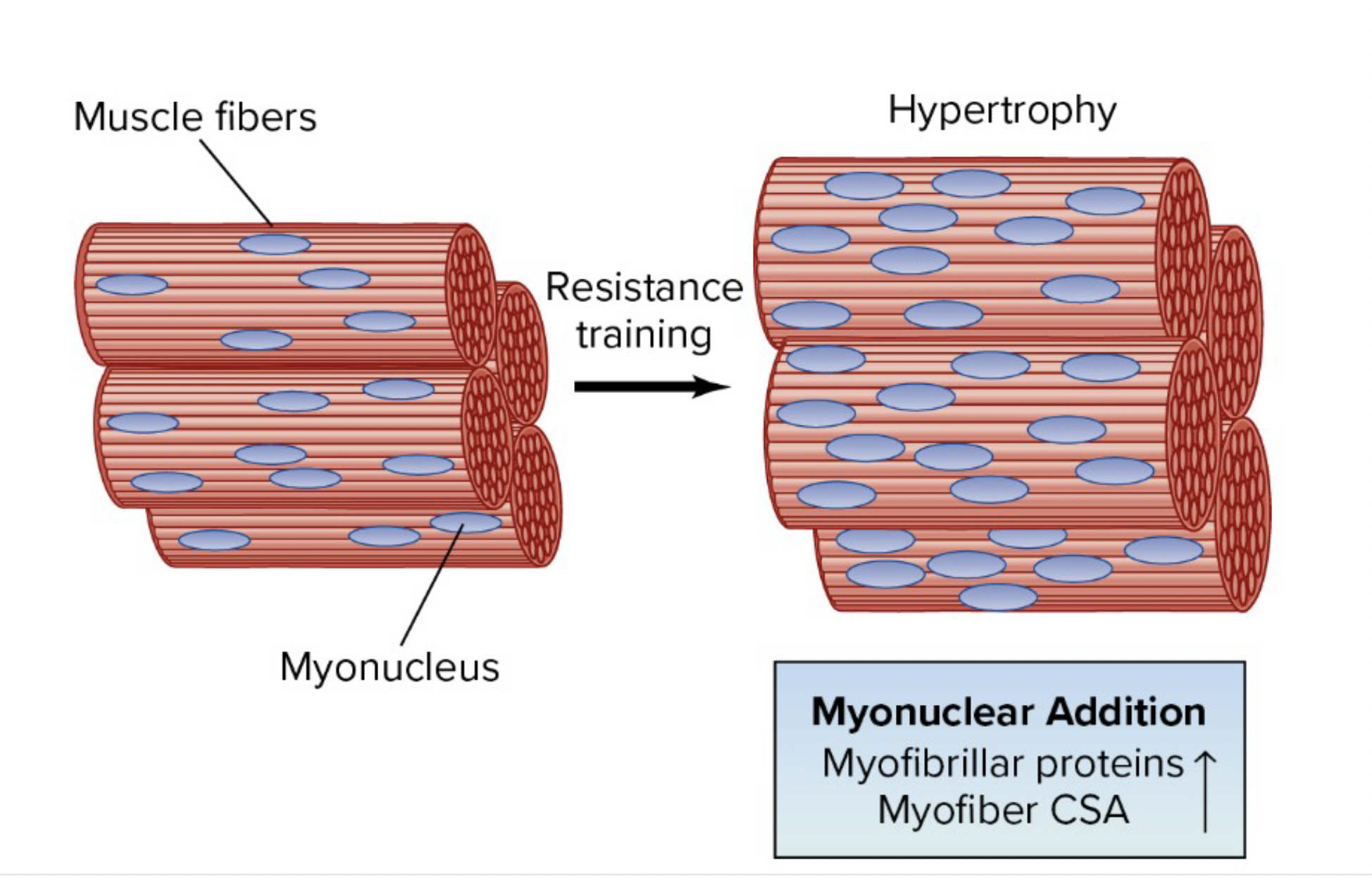
what is the role of satellite cells in resistance training induced hypertrophy
resistance training activates satellite cells to divide and fuse with adjacent fibers to increase myonuclei
additional myonuclei is likely required to support protein synthesis in larger muscle
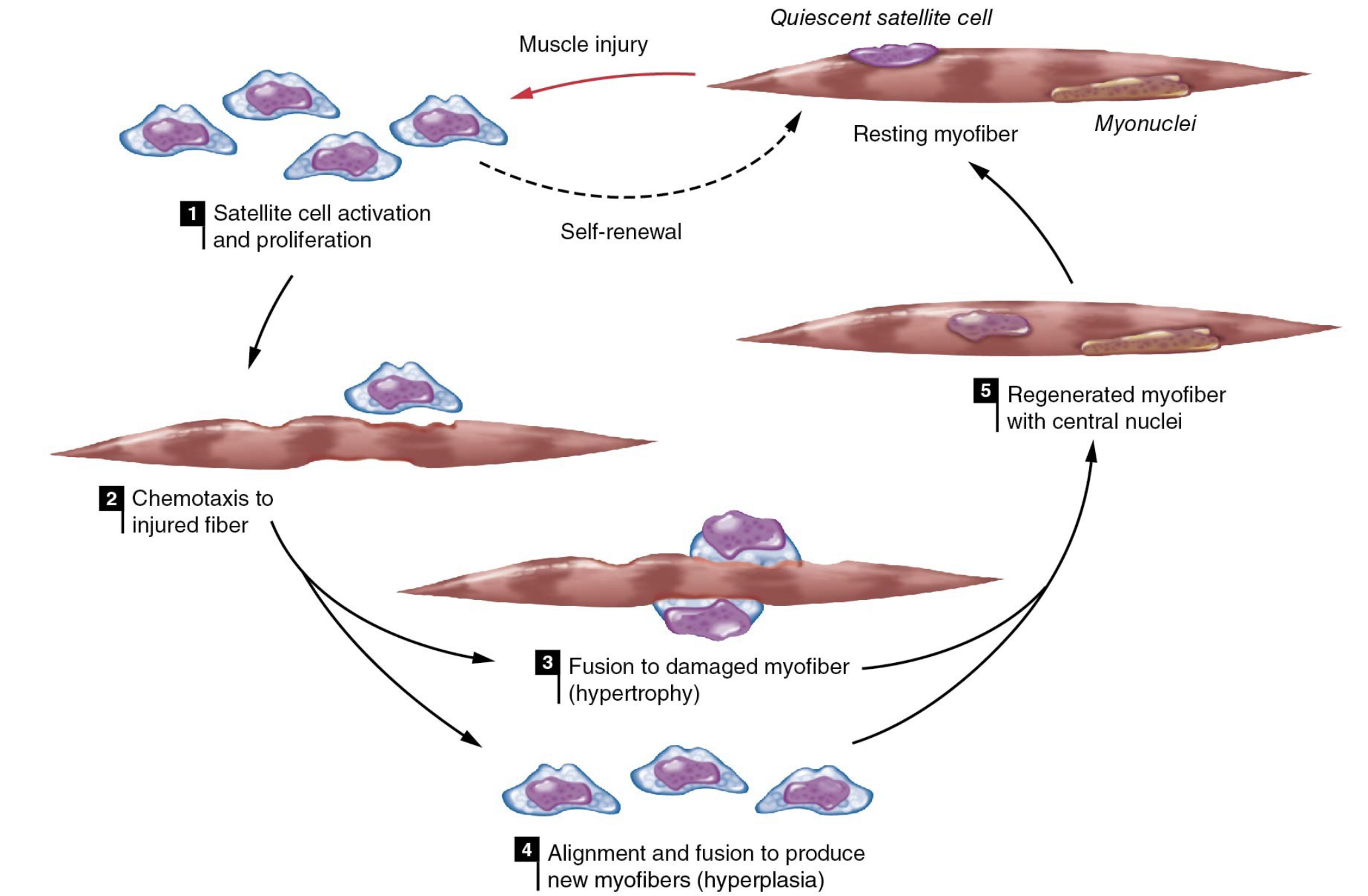
resistance training results in parallel increase in what 2 things
muscle fiber size and number of nuclei
approximately 80% of differences in muscle mass between individuals is due to ___
genetic variation
influences the magnitude of resistance training induced hypertrophy
many hypertrophy linked genes are directly linked to the mTOR path
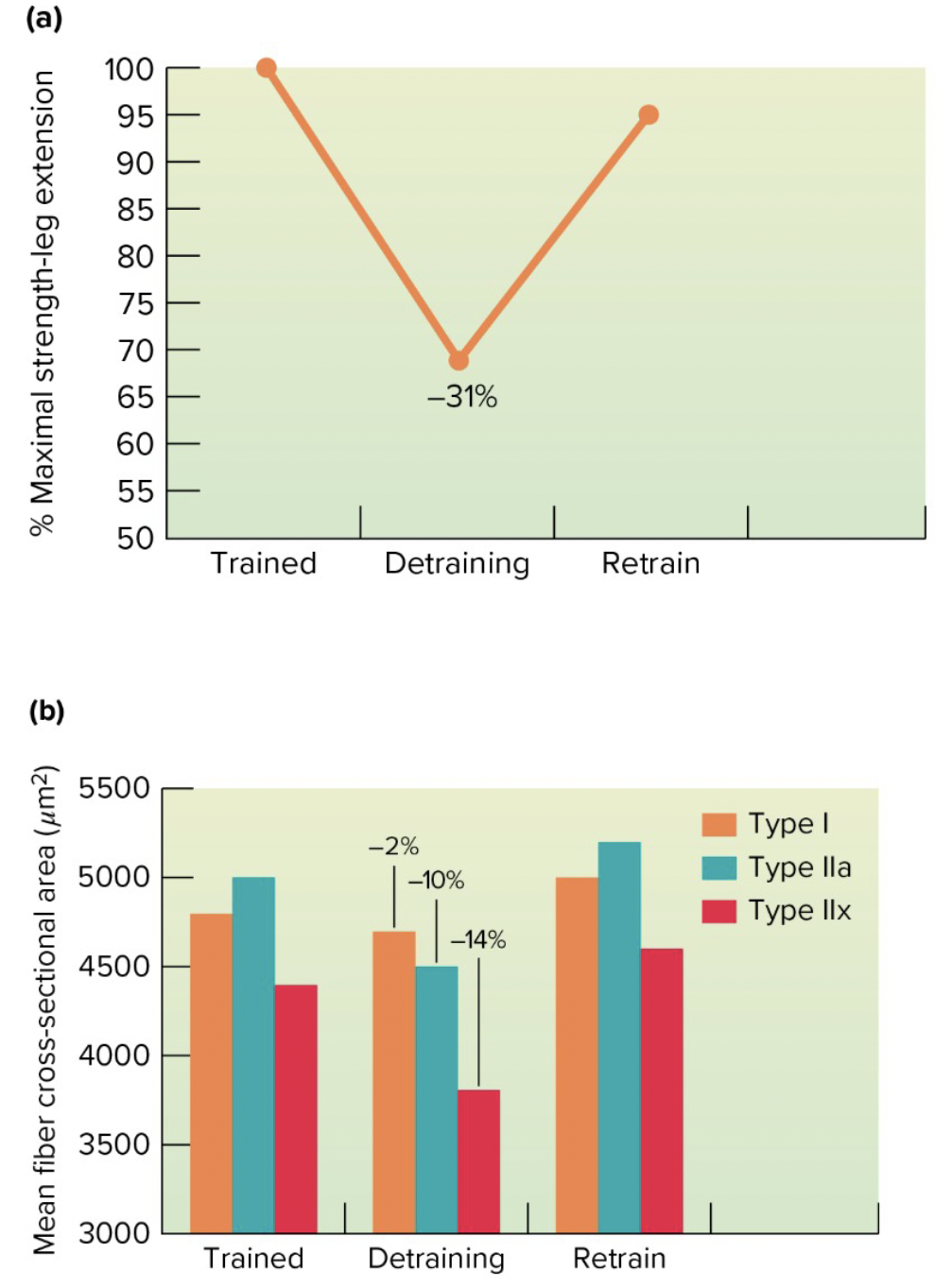
which is fastest to detrain: endurance or strength training
endurance
why do type Iix fibers detrain quickest compared to type I
we always recruit type I first so that will not detrain much unless we are on bedrest
Mechanisms to explain impairment of strength
gains resulting from concurrent training
neural factors
impaired motor recruitment
overtraining
depressed protein synthesis
interference from endurance training