Honors Bio Notes
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Scientific Method
A systematic approach used by scientists to investigate and understand the natural world. It involves collecting observations, forming hypotheses, making predictions, performing controlled experiments, and forming theories based on the results.
Scientific Method step 1
Collection observations:
The process of gathering information and data about a particular phenomenon or event. It involves asking questions like "what is it?" and "what is happening?" to understand the observations made.
Scientific Method step 2
Forming a hypothesis:
A testable explanation or prediction for a phenomenon or event based on prior knowledge or observations. A good one includes the "if, then, and because" format.
Scientific Method step 3
Making predictions:
The act of forecasting or estimating the outcome or result of a particular experiment or event. It involves using the hypothesis to determine the expected outcomes.
Scientific Method step 4
Verifying predictions:
The process of confirming or validating the predictions made based on the hypothesis. It can involve conducting a literature review, researching books and periodicals, and talking to others in the field.
Scientific Method step 5
Performing Controlled Experiments:
An experiment designed to test the effects of one variable (independent variable) on another variable (dependent variable) while keeping all other factors constant. It involves using control and experimental groups, collecting data, and analyzing the results.
Scientific Method step 6
Forming a Theory:
A well-substantiated explanation or set of principles that explain a wide range of phenomena or events. It is based on extensive analysis of data and observations.
Simple Microscope
A microscope that consists of a single lens, such as a magnifying glass, used to magnify the size of an object.
Magnification
The apparent increase in the size of an object when viewed through a microscope or magnifying lens.
Resolution
The ability of a microscope to distinguish between two closely spaced objects or to reveal fine details of an object.
Compound Microscope
A microscope that uses two lenses, an ocular lens (nearest the eye) and an objective lens (nearest the specimen), to magnify the size of an object.
Ocular Lens
The lens nearest to the eye of the viewer in a compound microscope.
Objective Lens
The lens nearest to the specimen in a compound microscope.
Total Magnification
The overall magnification is achieved by multiplying the magnification of the ocular lens by the magnification of the objective lens. (ocular lens mag. x objective mag)
Binomial Nomenclature
A two-part naming system (Genus, species) used to scientifically name and classify organisms.
Systematics
The study of the evolution of biological diversity, which involves analyzing data from fossil records, comparative homologies, cladistics, comparative sequencing of DNA/RNA, and molecular clocks.
Kingdoms
Bacteria, Archaea, Protista, Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia
Cladogram
A branching diagram that represents the proposed classification (phylogeny) or evolutionary history of organisms based on shared derived characteristics.
Based only on characteristics observable in existing species. The branching patterns in this chart are defined by the presence of unique, evolving innovations (derived characteristics) shared by all members of the group.
Dichotomous Keys
Tools used to identify organisms by presenting pairs of contrasting descriptions and directing the user to another pair or identifying the organism based on the responses.
Characteristics of life 1
Made of one or more cells:
Living things are composed of cells, which are organized into tissues, organs, and systems. Some organisms or unicellular, and some are multicellular
Characteristic of life 8
Adaptations evolve over time:
adaptations are inherited through reproduction
adaptations changing over time is called evolution
natural selection determines which adaptations help organisms survive
Characteristic of life 6
Requires Energy:
some organisms make their own food (autotrophic) (plants)
some organisms eat their food (heterotrophic) (humans)
all the energy and reactions combined are called metabolism
Characteristic of life 7
Maintains Homeostasis:
trying to keep the internal conditions stable
humans sweat and try to maintain 98.6⁰F or 37⁰C
turtles lay in the sun to try and warm up
Characteristic of life 5
Responds to Stimuli:
Organisms can detect and respond to changes in their environment, ensuring their survival.
reacting to internal or external stimuli is called a response
how does your skin respond to sunlight?
how do your eyes respond to darkness?
how does your brain respond to sunlight / darkness?
Characteristic of life 3
Grows and Develops:
Living things undergo growth, increasing in size and complexity, and develop into mature forms.
growth = increase in mass or size
develops = different abilities
Characteristic of life 4
Reproduces:
Living organisms have the ability to produce offspring, ensuring the continuation of their species.
produces offspring with similar traits (heredity)
compound microscopes
Used for magnifying small, transparent specimens
Consists of two or more lenses to enhance image quality
Provides high-resolution, three-dimensional images
Used in various scientific fields, such as biology and medicine
Allows for observation of cellular structures and organisms
stereomicroscopes
A type of microscope that provides a three-dimensional view of small objects. It uses two separate optical paths to capture and combine images, resulting in a magnified and detailed view. Uses two ocular lenses.
phase contrast microscopes
Optical instruments used to enhance contrast in transparent specimens
Utilize a phase plate to convert phase differences into variations in brightness
bends light in a unique way for studying live cells and observing cellular structures
Enables visualization of transparent samples without staining or killing cells
Widely used in biology, medicine, and research for non-invasive imaging
Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM)
This microscope revolutionized our understanding of the microscopic world by using a beam of electrons instead of light to magnify and visualize small samples. It operates on the principles of quantum mechanics and provides high-resolution images with magnifications up to 1 million times. Electron microscopy has been instrumental in various scientific disciplines, uncovering hidden details and intricate structures. The process involves emitting a beam of electrons from a cathode, accelerating them towards the sample, and detecting the signals they create to generate images. Different techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), enhance the imaging capabilities. Electron microscopy is not only used in scientific research but also in industries like quality control and forensic investigations. Advancements in technology continue to improve electron microscopy. However, all samples must be dead and the views are flat and one dimensional
Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM)
Microscope that uses a beam of electrons to create high-resolution images of a sample's surface. Provides detailed information about the sample's topography, composition, and morphology (3D view). Offers higher magnification and resolution compared to optical microscopes. Useful in various fields like materials science, biology, and nanotechnology. However, samples must be dead, but it can magnify items +/- 100,000x.
Characteristic of life 2
Levels of organization
Atoms - Molecules - Cells - Tissues - Organs - Organ Systems - Organisms
Domain Bacteria
One of the three domains of life
Prokaryotic organisms without a nucleus
Found in diverse habitats, including soil, water, and human body
Play vital roles in nutrient cycling and decomposition
Some may cause diseases, while others are beneficial for human health and industry
prokaryotes
cell walls with peptidoglycan
unicellular
auto or heterotrophic
Domain Archaea
EX: Methanopyrus
Prokaryotes
Cell walls without peptidoglycan
unicellular
auto or heterotrophic
One of the 3 domains of life
Kingdom Bacteria
One of the 6 kingdoms of life
Prokaryotic organisms without a nucleus
Found in diverse habitats, including soil, water, and human body
Play vital roles in nutrient cycling and decomposition
Some may cause diseases, while others are beneficial for human health and industry
prokaryotes
cell walls with peptidoglycan
unicellular
auto or heterotrophic
Kingdom Archaea
One of the 6 kingdoms of life
EX: Methan opyrum
Prokaryote
Cell walls without peptidoglycan
unicellular
auto or heterotrophic
Domain Eukarya
One of the 3 domains of life
Contains 4 kingdoms of life
Eukaryotes
Contains multicellular and unicellular organisms
Autotrophic and heterotrophic
Kingdom Protista
One of the 6 kingdoms of life
EX: Paramecium
Eukaryotes
Cell walls have some cellulose
Uni and multicellular organisms
auto or heterotrophic
Kingdom Fungi
one of the 6 kingdoms of life
EX: Mushroom
Eukaryote
Cell walls with chitin
most multicellular
Heterotrophs
Kingdom Plantae
One of the six kingdoms of life
EX: Moss
Eukaryote
cell walls with cellulose
Multicellular
Autotrophs
Kingdom Animalia
one of the six kingdoms of life
EX: Earthworm
Eukaryote
no cell walls
Multicellular
Heterotrophs
Heterotrophs
an organism deriving its nutritional requirements from complex organic substances.
an organism that eats other plants or animals for energy and nutrients. The term stems from the Greek words hetero for “other” and trophe for “nourishment.”
Autotrophs
an organism that is able to form nutritional organic substances from simple inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide.
an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals. Because autotrophs produce their own food, they are sometimes called producers.
Prokaryote
a microscopic single-celled organism that has neither a distinct nucleus with a membrane nor other specialized organelles. This category includes the bacteria and cyanobacteria.
organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles. These organisms are divided into two distinct groups: the bacteria and the archaea, which scientists believe have unique evolutionary lineages.
cells without a nucleus
Eukaryote
Cells with a nucleus
an organism consisting of a cell or cells in which the genetic material is DNA in the form of chromosomes contained within a distinct nucleus. This category includes all living organisms other than the eubacteria and archaebacteria.
an organism whose cells contain a nucleus within a membrane. The genetic material and information of a eukaryote is contained within this nucleus. These organisms vary from single-celled organisms to complex multicellular animals and plants.
Hierarchical Classification
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Does King Philip Come Over For Green Soup
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Clade
groups on a cladogram
one branch of the cladogram
Outgroup
first, most ancestral characters
Characters
traits or characteristics
Ancestral Characters
Found in all descendants
Derived Characters
not found in common ancestors
Phylogenetic trees (Phylogenies)
Represents hypothesized evolutionary relationships among organisms and may include extinct as well as modern species
Jean Baptiste LaMarck Theory
Parents changes passed to offspring:
Ex: Giraffes
Won’t work because then tattoos, built up muscle, scars, etc., would transfer to babies
Charles Darwin Theory
Theory:
Natural Selection (derived around 1857)
Strongest survive
Principles of Natural Selection
Variation, overproduction, heritability, and reproductive advantage
Variation
Individuals differ
Overproduction
populations produce more offspring than can survive
Heritability
variations are inherited from parents
Reproductive advantage
some variations are better than others
Fossils
record of species that lived long ago
Derived traits
Newly evolved
Ex: Feathers
Ancestral traits
Newly evolved
Ex: Feathers
Comparative Anatomy
comparing the anatomy of different organisms
Homologous Structures
Anatomically similar
Inherited from a common ancestor
ex: vertebrae, forelimbs
Vestigial Structures
Reduced form of functional structures
ex: snake pelvis, human appendix
Analogous Structures
Anatomically similar
NOT inherited from a common ancestor
ex: wings of insects & birds
Comparative Embryology
early, pre-birth developmental stages
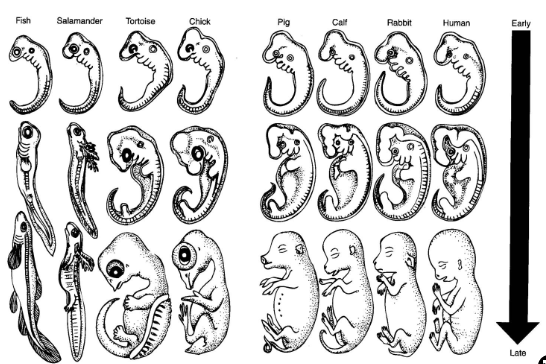
Comparative Biochemistry
Similar chemicals in organisms
ex: cytochrome C (Needed for respiration)
ex: DNA/RNA
Geographic Distribution
Where plants and animals are found
closer geographically usually = closer in similarity
Adaptation
a trait shaped by Natural Selection
Fitness
Measure of relative contribution an individual trait makes to the next generation
Camouflage
blend in with the environment
Mimicry
Resemble another species
ex: monarch (poisonous) & viceroy (harmless) butterflies
Antimicrobial resistance
Bacteria immune to effects of antibiotics
Hardy Weinberg Principle
Populations stay the same unless forced to change
Hardy-Weinberg conditions
1. Large Population
2. No immigration / Emigration
3. Random mating
4. No mutations
5. No natural selection
Hardy-Weinberg Equation
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
Allele + genotype frequencies stay the same unless forced to change
Genetic Drift
change in allele frequency due to chance
Founder effect
Small, separated populations all have characteristics of “founders”
Bottleneck
Population declines to small number + rebounds
Gene pool of rebound population is similar to the small population
Ex. Cheetahs in Africa
Gene flow
genes coming into or leaving a population
Nonrandom Mating
When mates are chosen
Based on some characteristic
Ex. Galapagos iguana’s: females chose bigger males
Mutation
change in genetic material
Natural Selection
Selection of individuals that are best adapted for survival
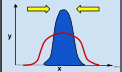
Stabilizing Natural selection
selection against both extremes
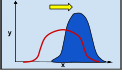
Directional Natural Selection
selection against one extreme
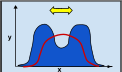
Disruptive Natural Selection
selection against the mean
Sexual Natural Selection
when males & females differ greatly in appearance
Reproductive Isolation
Populations that cannot breed and produce fertile offspring
Prezygotic Isolation
Before fertilization begins
Ex. Meadowlark songs, firefly times
Postzygotic Isolation
After fertilization begins
Ex. Lions + tigers
Speciation
Creation of a new species
Allopatric Speciation
Physical barrier
Ex. Mountains, rivers
Sympatric speciation
No physical barrier
Ex. Apple maggot flies: depends on fruit eaten
Adaptive Radiation/Divergent Evolution
One species gives rise to many others
Ex: Mammals, cichlid fish
Coevolution
Evolution of one species causes evolution of another species because of close relationship
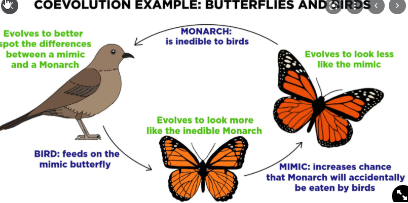
Convergent Evolution
Unrelated species evolve similar traits because of similar ecology / climates in different parts of the world
Ex. Mara and rabbit
Rate of speciation: Gradualism
Evolution happens in small, gradual steps
Ex. Stripes of tiger
Rate of Speciation: Punctuated equilibrium
Abrupt, rapid spurts of change
Ex. snails