Architecture History Quiz 3
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
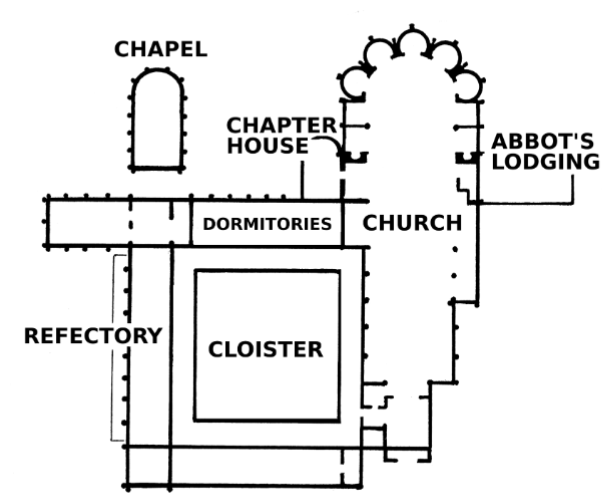
Monastery Layout
Chapter House - Meeting room
Cloister - Courtyard
Refectory - Dining hall
Dormitories - Living space
Chapel - Private religious space
Romanesque architecture traits
Heavy
Rose window
Roman arches
Vault ribbing
West front for entrance
Tympanum over entrance
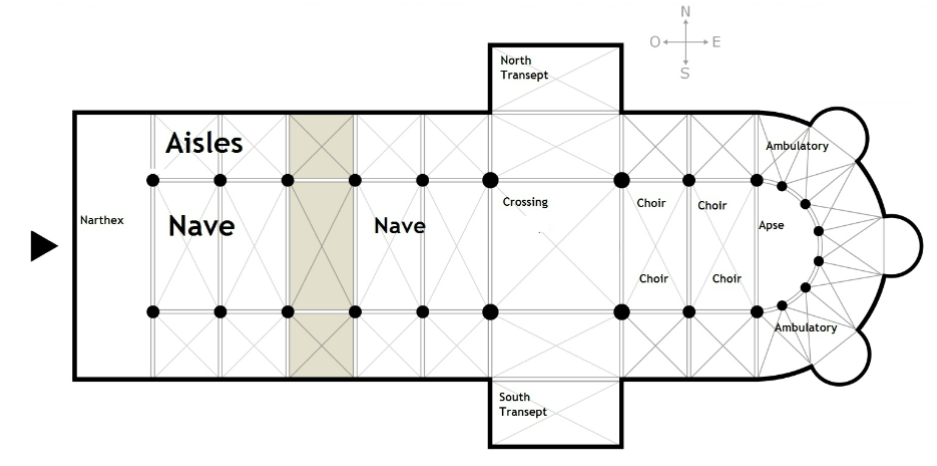
Parts of a church
Aisles
Apse
Choir
Nave
Ambulatory
Transept
Chevettes
Crossing
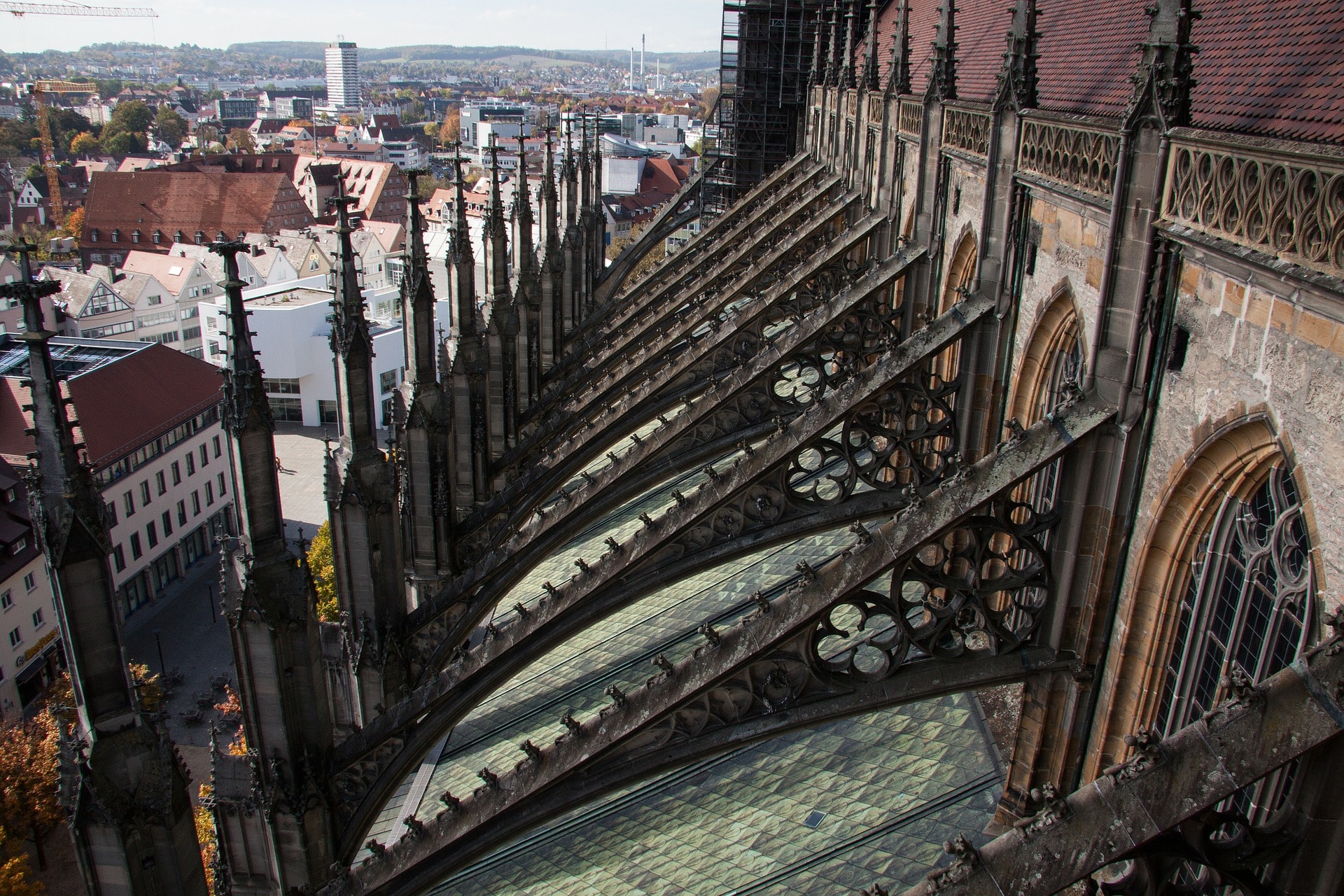
Gothic architecture traits
Gothic Arch
Flying Buttress
Gothic eras
Early Gothic - Plate tracery in windows, no outside windows in triforium
High Gothic - Rayonnant Style, Decorated Style, glazed triforia, bar tracery in windows, band windows
Late Gothic - Flamboyant Style, Perpendicular Style
English Gothic
Square apse
Length over height
Decorative vaults including tierceron
Concealed buttressing
Smaller, square towers
Double trancepts
Less carving on portals
French Gothic
Round apse
Prioritized height
Simple vaulting
Flying buttresses
Tall, thin towers
Single trancepts
Carved portals over west end
German Gothic
Pierced towers and spires
Portal
An opening in a wall of a building, gate or fortification, especially a grand entrance to an important structure occasionally featuring a tympanum over top

Flying buttress
Architectural elements that support the weight of a structure, often supporting a heavy roof or dome and allow more light to be let in

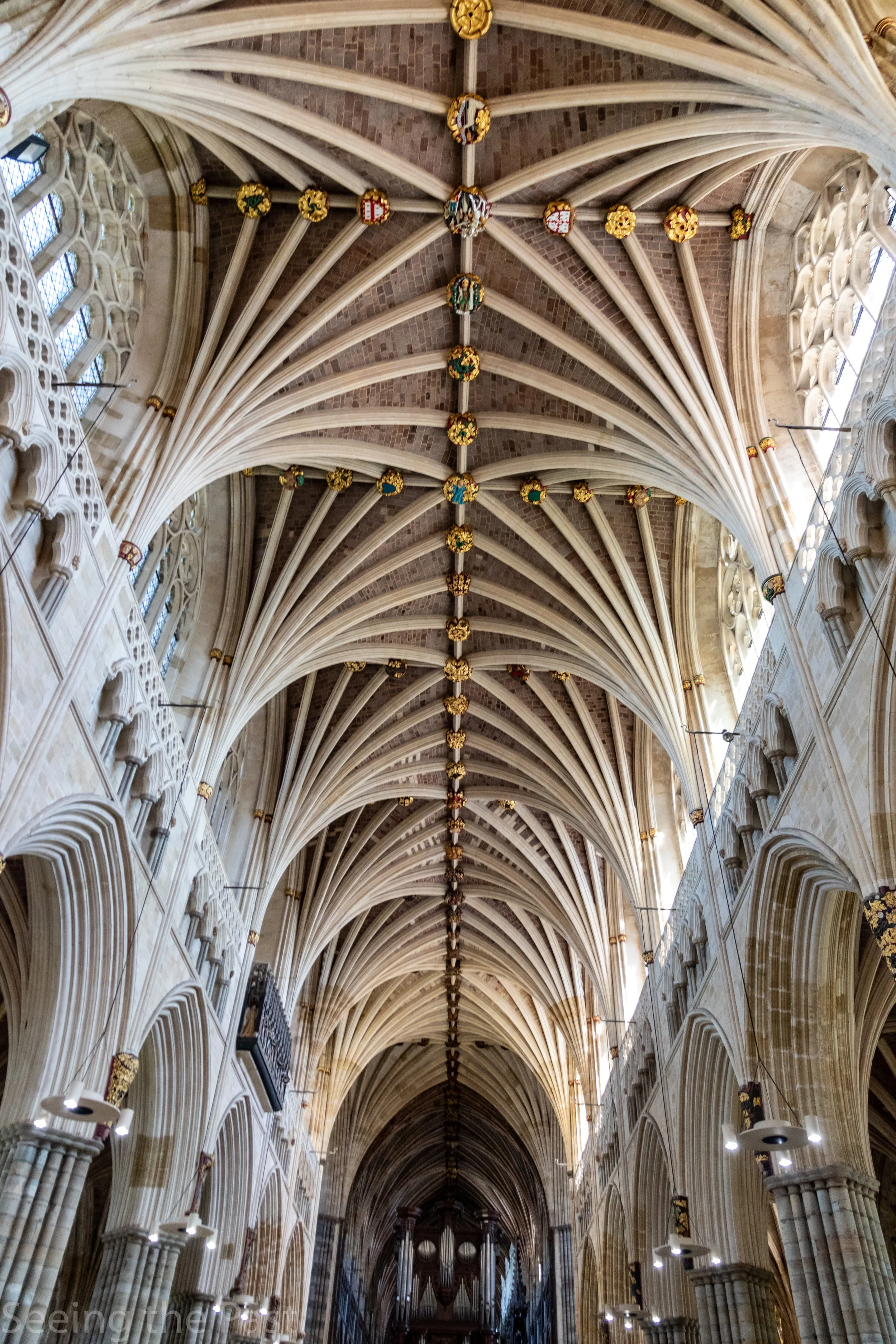
Hammer beam truss
A timber roof system characteristic of English Gothic architecture, featuring short, projecting beams that support the roof rafters

Tiercerons
A type of decorative, branching vault

Gallery vs triforium
Triforium - Within the wall structure and serves primarily aesthetic and structural purposes
Gallery - Projects into the church space and serve practical congregational needs
Piano nobile
Second floor in the US, main floor in Renaissance Europe
Palladio
Wrote influential architectural books, served Venice and the Veneto
Palladianism
A European architectural style that emphasizes symmetry, rational geometric forms, and classical elements
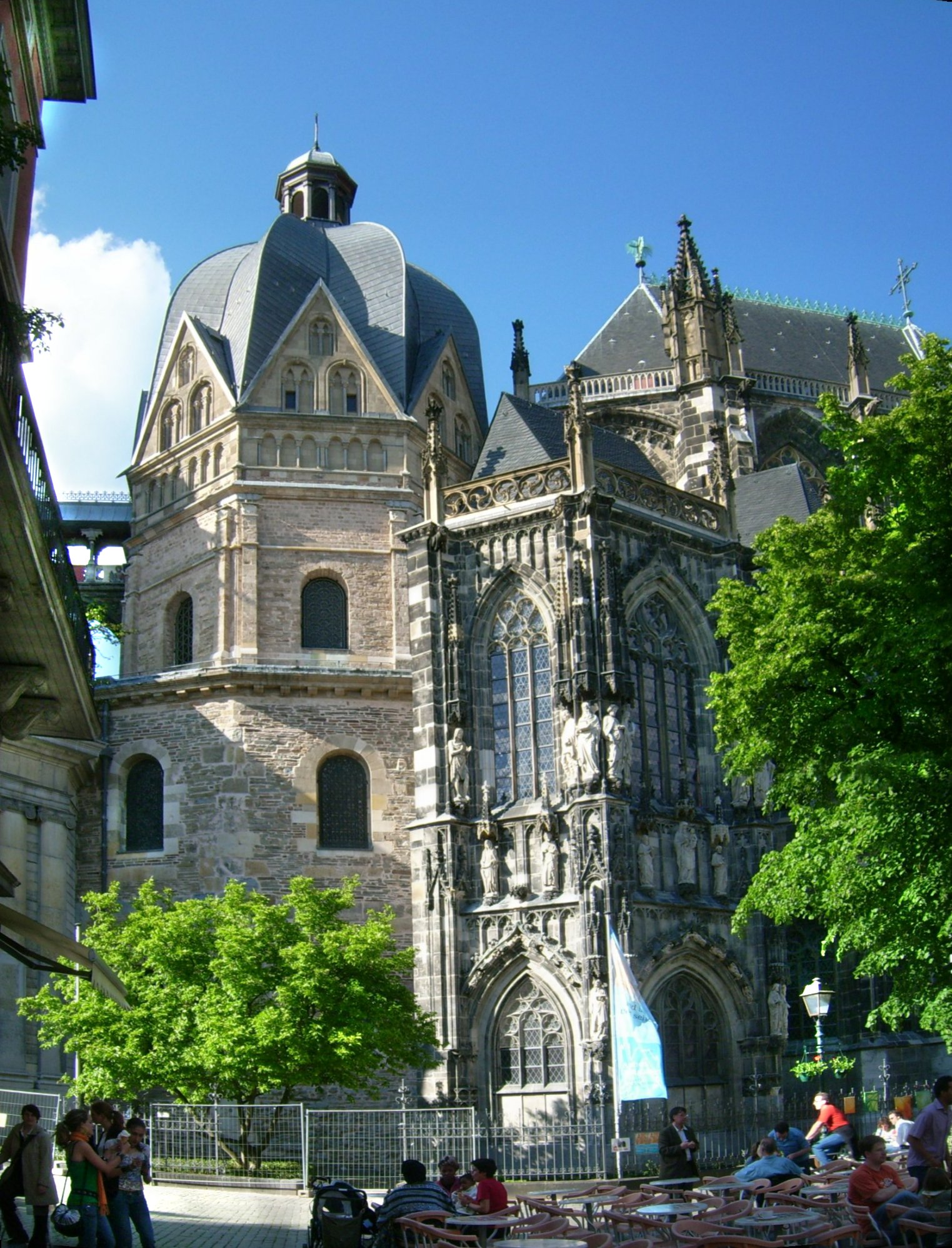
Palatine Chapel
Carolingian

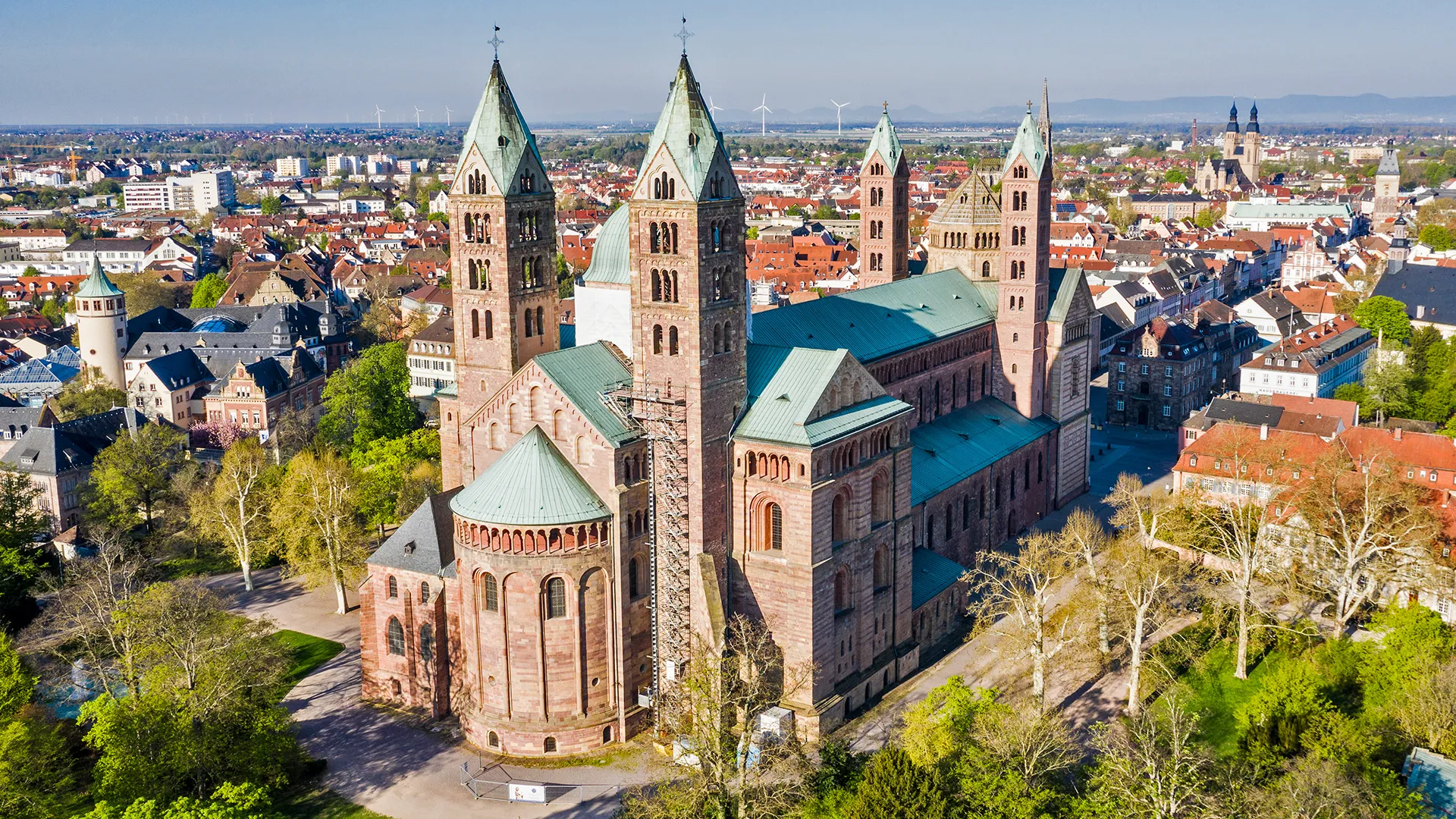
Speyer Cathedral
Romanesque

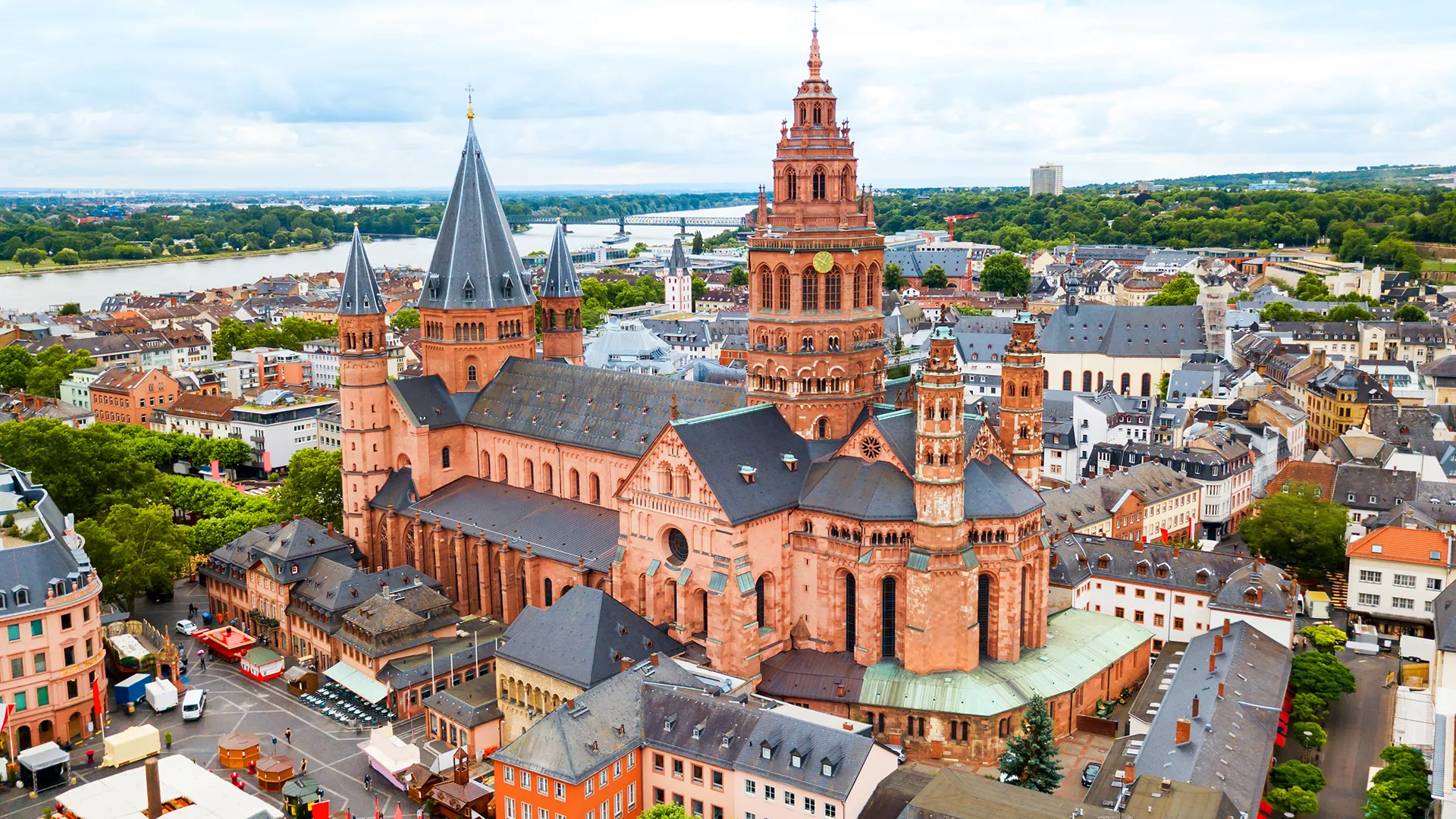
Mainz Cathedral
Romanesque

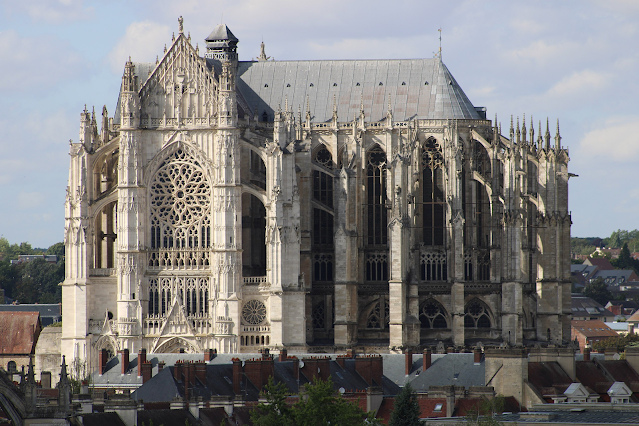
Beauvais Cathedral
Gothic

Notre Dame de Paris Cathedral
Gothic

Chartres Cathedral
Gothic
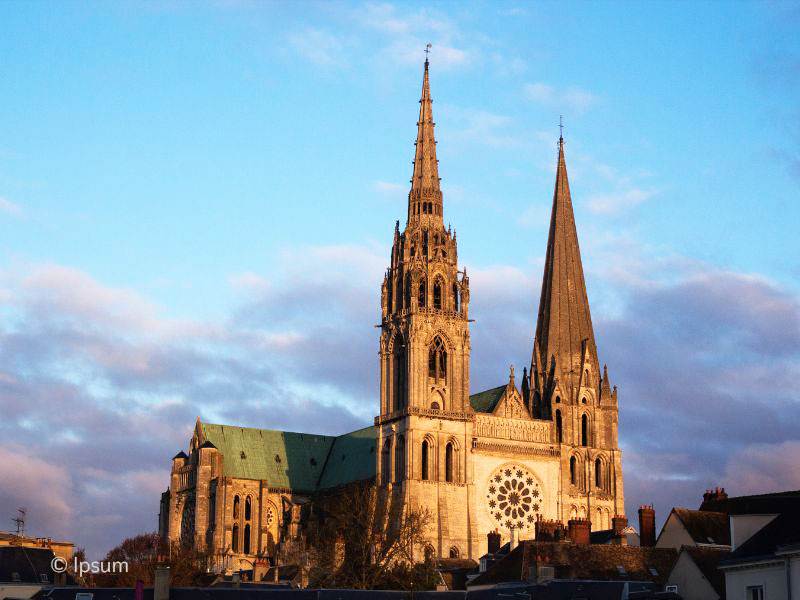

Sainte Chapelle Chapel
Gothic
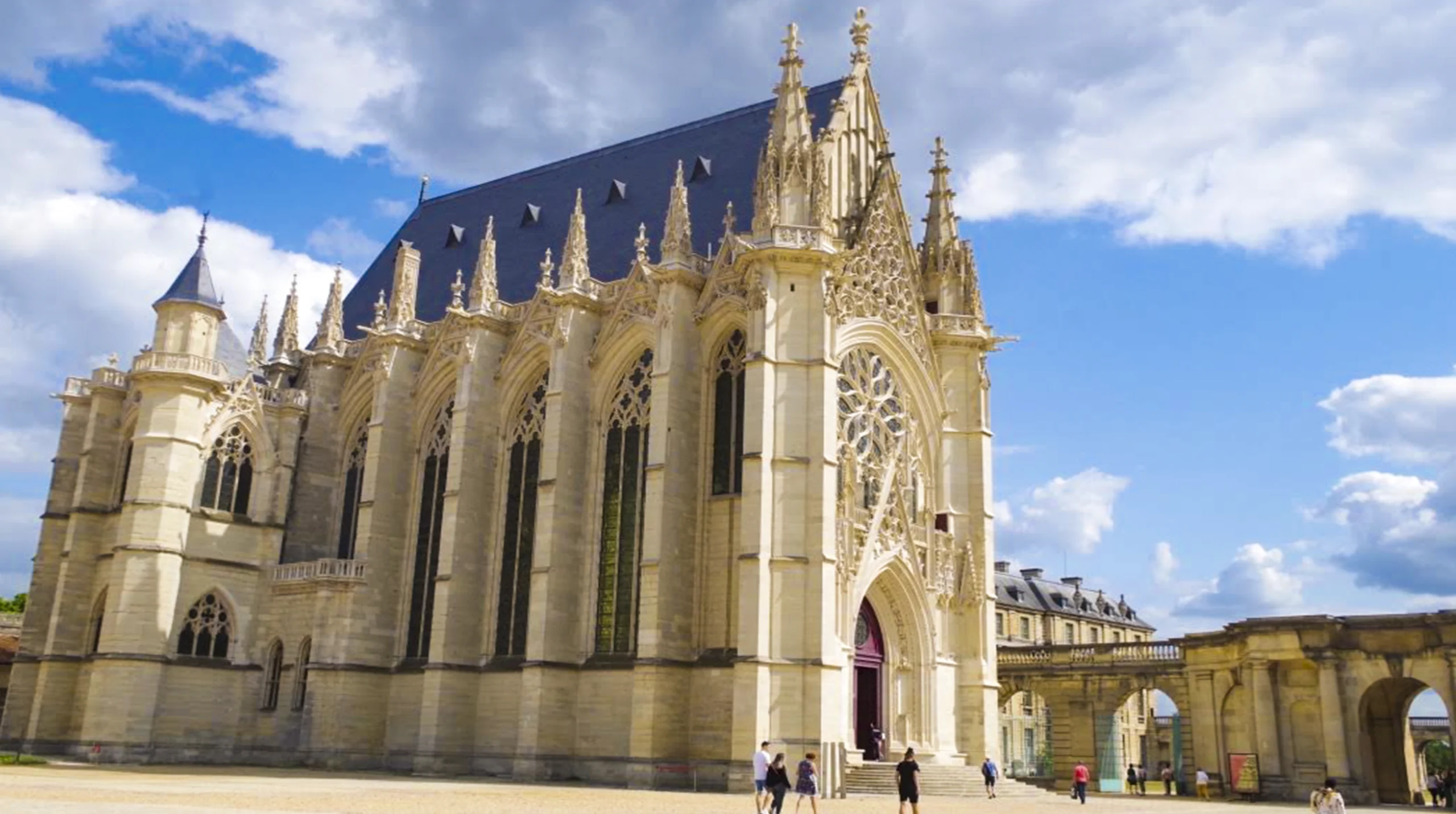

Salisbury Cathedral
Gothic
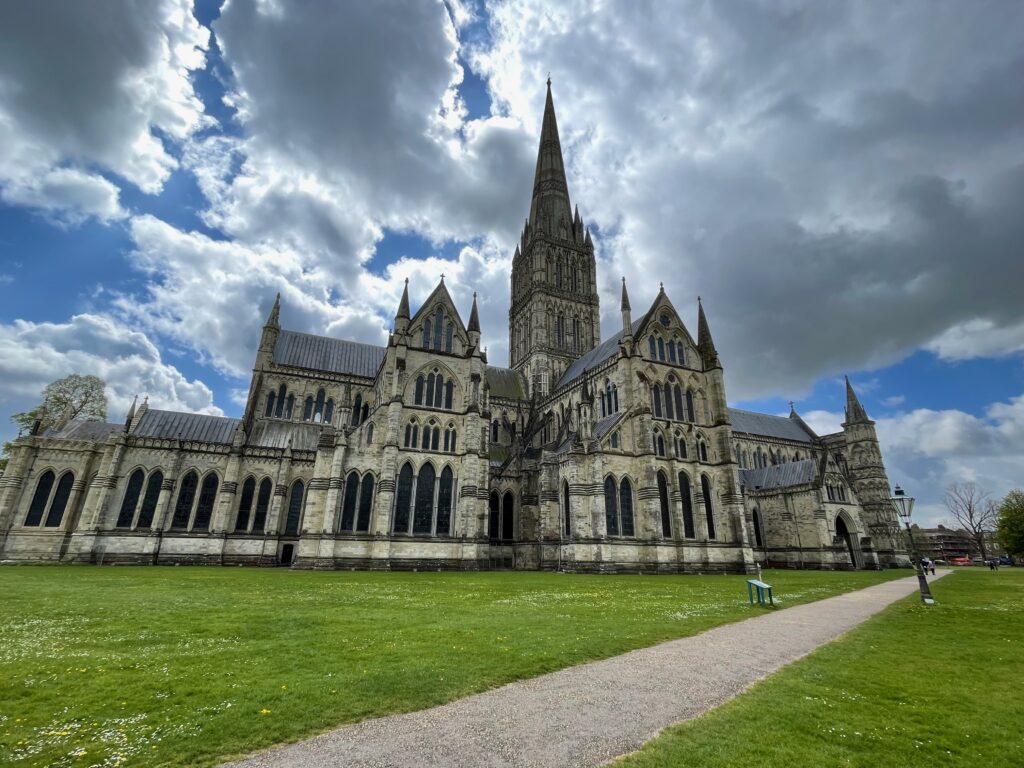

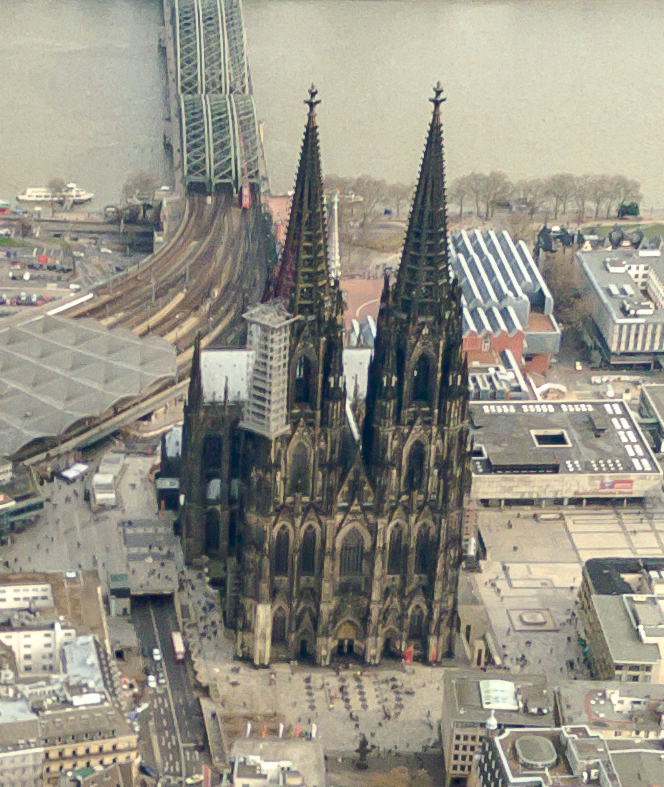
Cologne Cathedral
Gothic

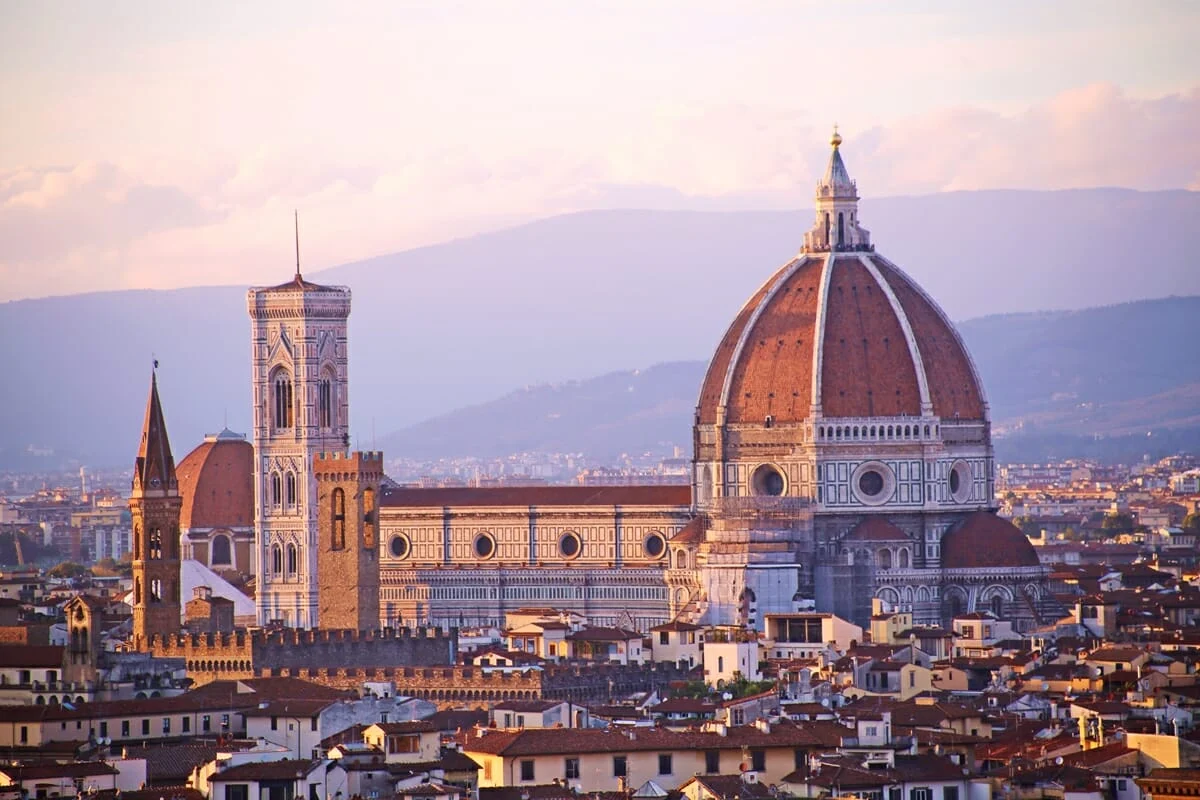
Florence Duomo
Renaissance

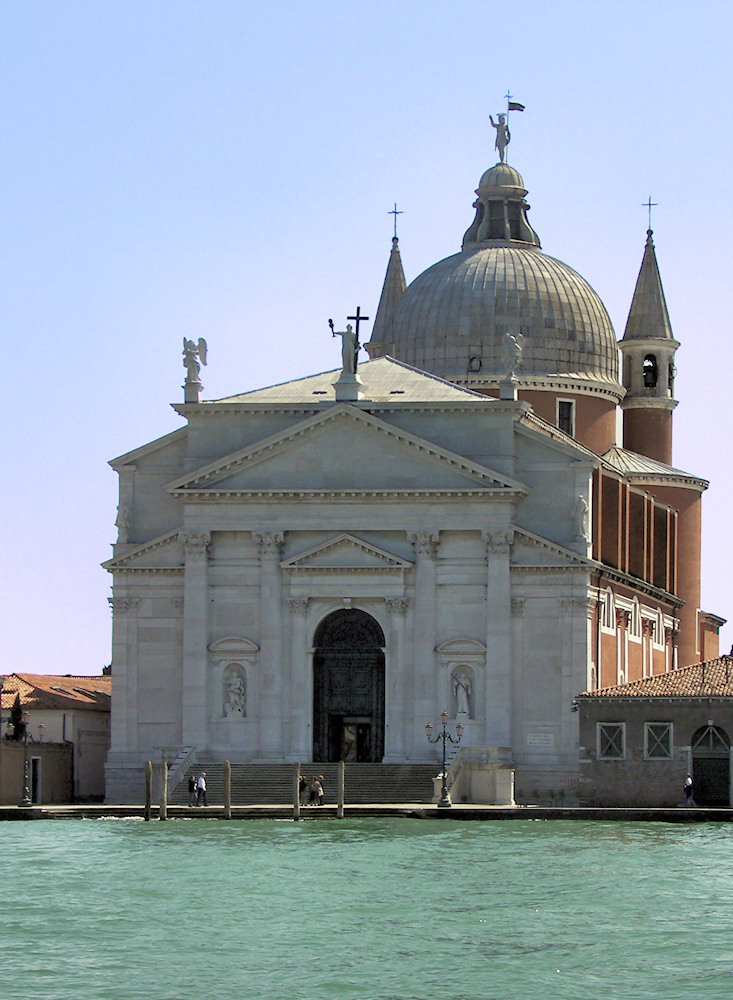
Il Redentore
Renaissance

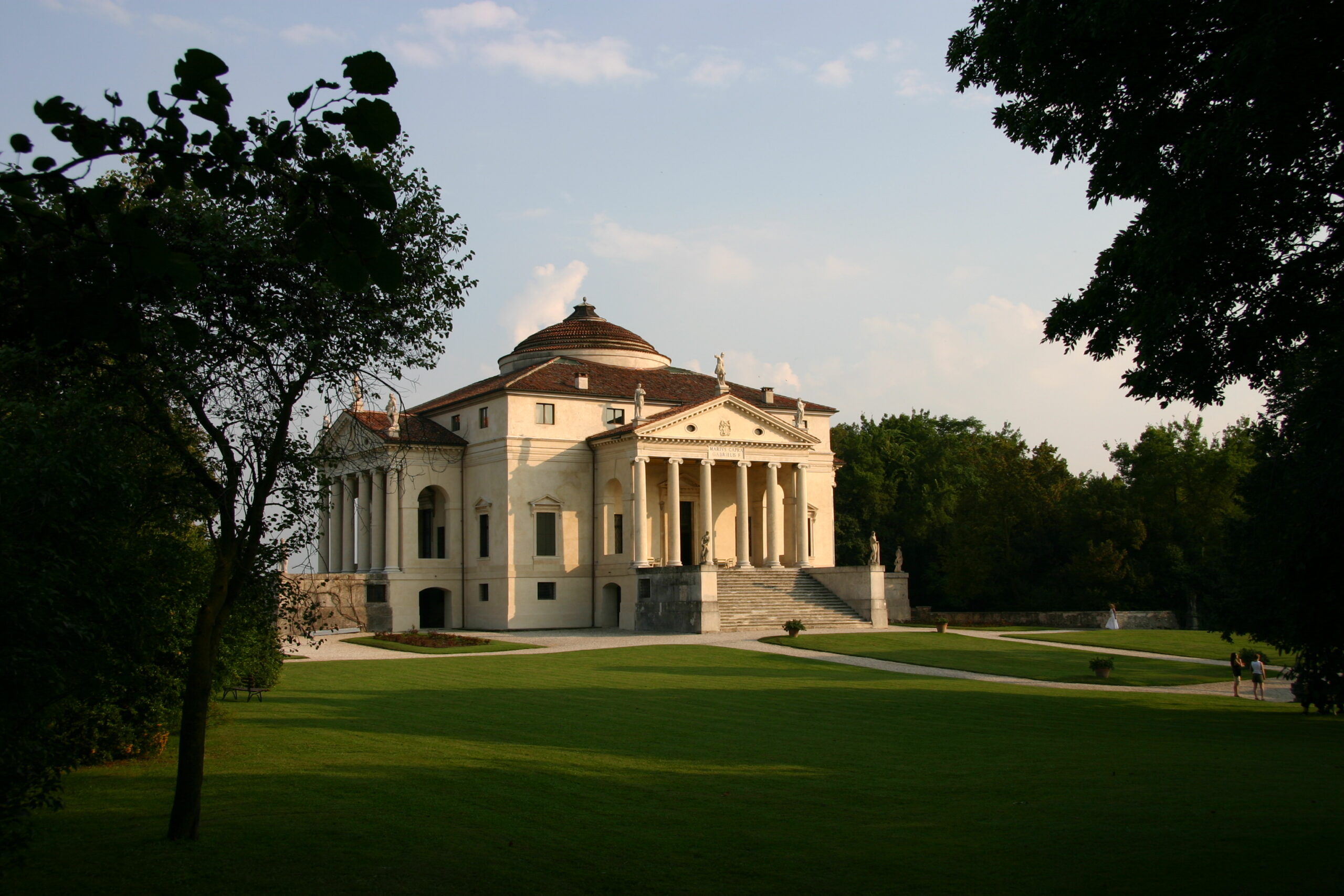
Villa Rotunda
Renaissance

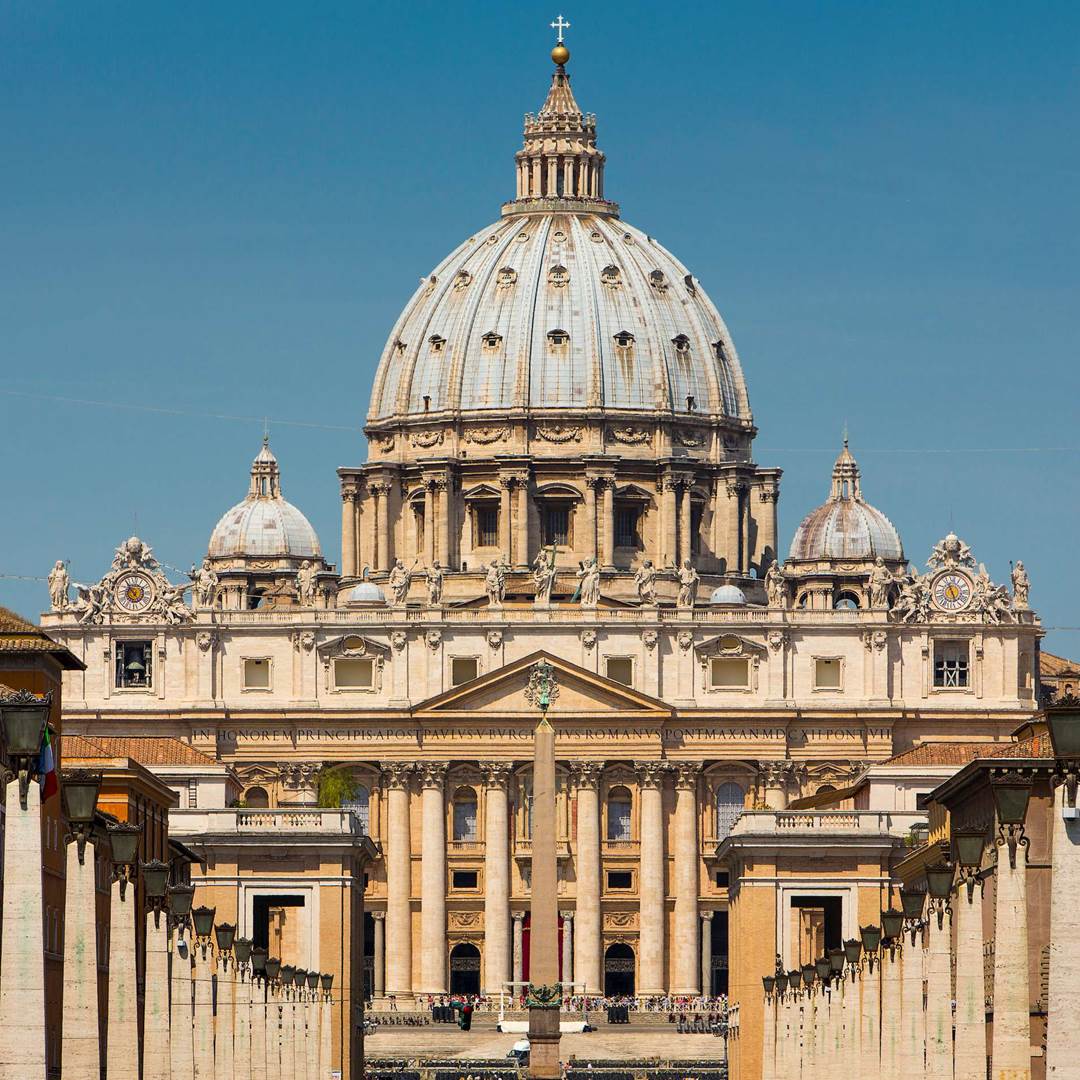
St. Peter’s
Renaissance

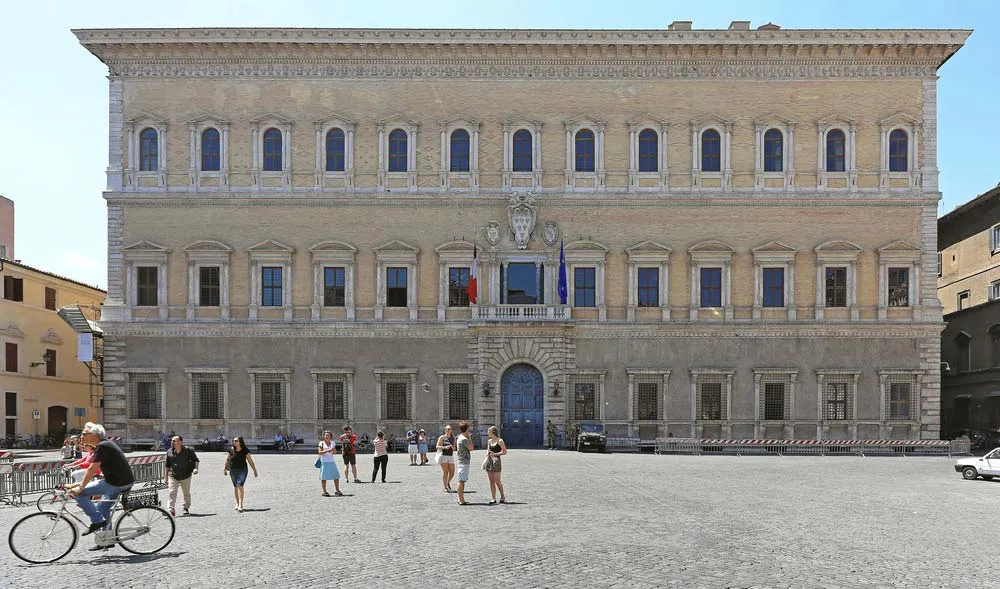
Farnese palace
Renaissance

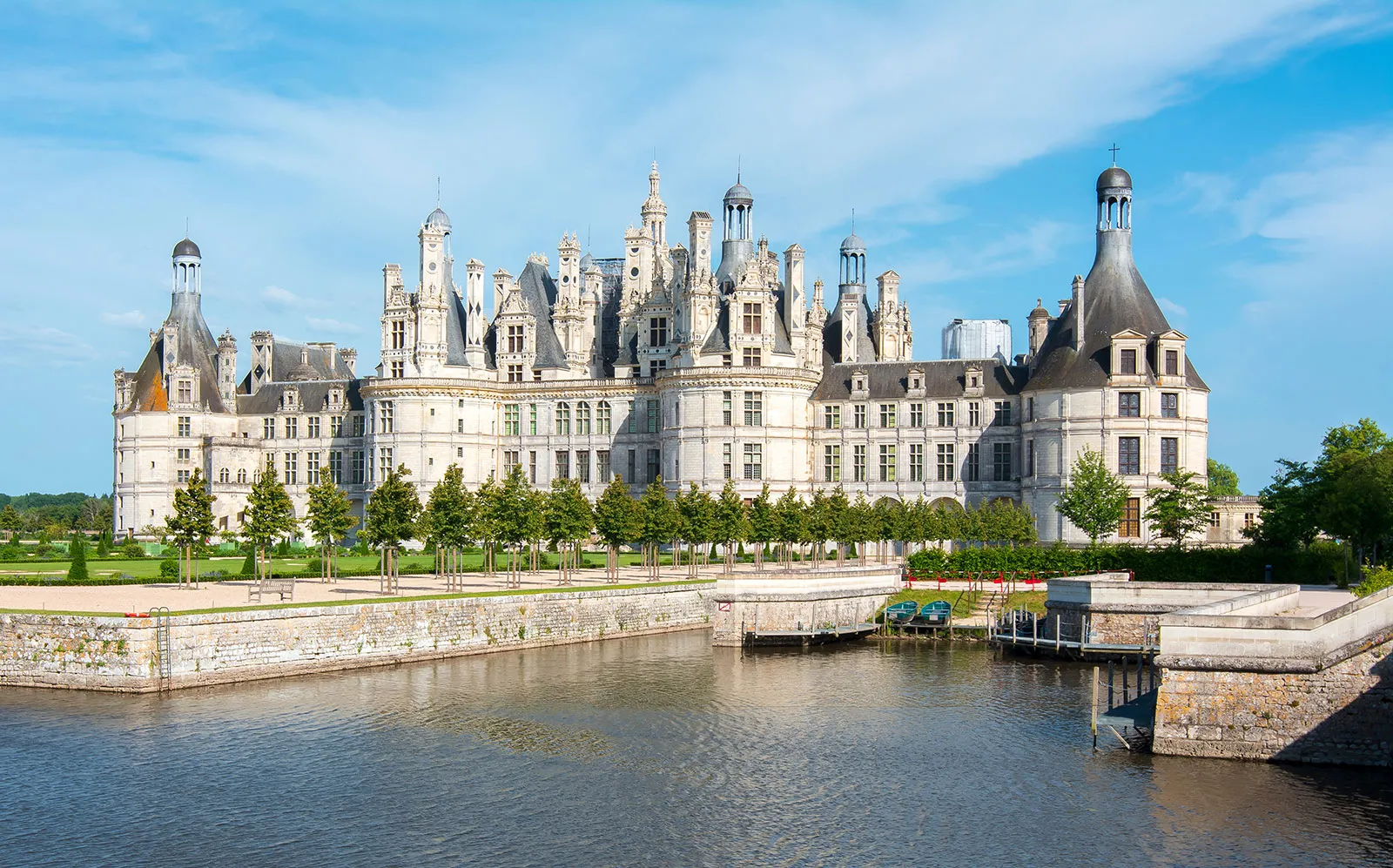
Chateau de Chambord
Renaissance

Brunelleschi
Italian architect, designer, goldsmith and sculptor considered to be a founding father of Renaissance architecture (Florence Duomo, San Lorenzo)
Bramante
Pioneering architect of the High Renaissance style, particularly in Rome, where he introduced new designs and proportions based on classical antiquity (plans for St. Peter's Basilica formed the basis of the design executed by Michelangelo)
Michelangelo
Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance (finished St. Peter’s)
Palladio
Italian Renaissance architect active in the Venetian Republic (Il Redentore, Villa Rotunda)