Monopoly
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is a monopoly?
When there is a single supplier in the market, known as pure monopoly.
What are the characteristics of a monopoly?
Single seller in the market, which is a price maker.
Perfect barriers to entry, imply other firms cannot enter the market.
What happens when a monopolist chooses a high price?
Therefore must accept that it will only sell a certain amount of output.
What happens when a monopolist chooses to seller at a higher output?
To sell all this output then it must sell at a lower price.
What are barriers to entry?
Factors that make it difficult or impossible for firms to enter an industry and compete with existing producers.
What are some barriers to entry in a monopolistic market?
Marketing barriers, can create such a strong brand image that other firms find it impossible to compete
Very high start up costs, setting up a corner shop is a lot cheaper than setting up a nation wide chain of supermarkets.
limit pricing, setting a price high enough to make satisfactory profit but low enough to deter market entry.
What are structural barriers to entry?
The result of the structure of the industry and are not deliberately erected by the firm.
What are behavioural barriers to entry?
The result of direct action by the firm with the intention of preventing market entry.
What does the short run equilibrium look like in a monopoly?
Monopolist has the same demand curve as the market as it is the only firm, MR is below AR, AC and MC are u-shaped due to law of diminishing returns, sells at profit maximising output.
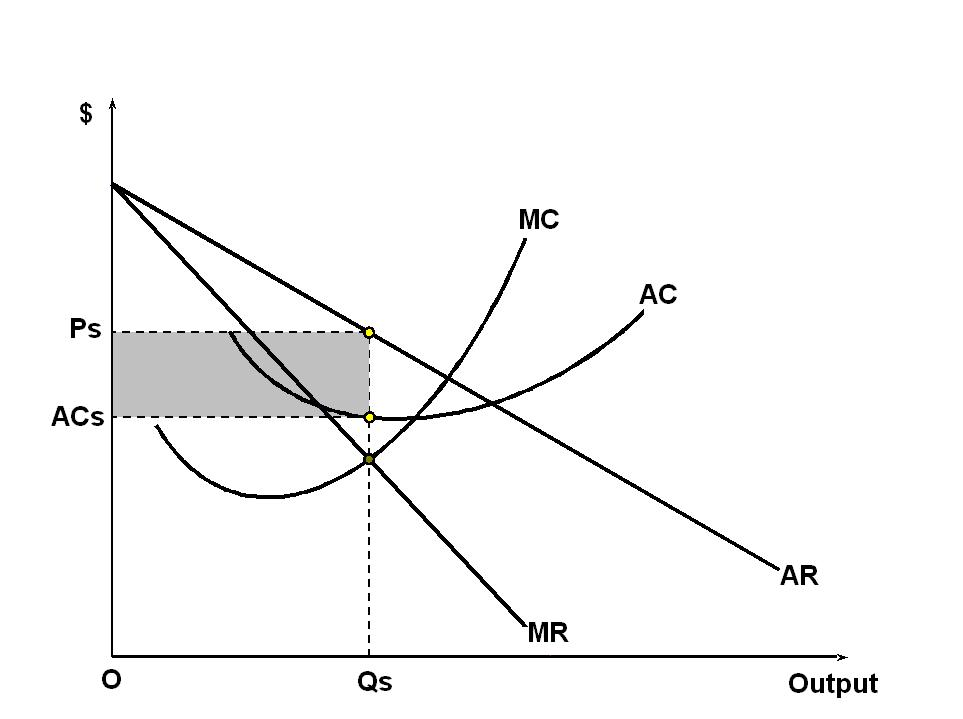
Why does the supernormal profit in the short run not attract firms?
The perfect barriers to entry would stop them from doing so.
What does the long run equilibrium in a monopoly look like?
The LR output, price and profit levels are the same as those in the SR, but could change due to external factors.
Is a monopoly productively and allocatively efficient?
No, because price is above MC and the minimum AC cost.
Why do monopolists not have to attempt to be productively or allocatively efficient?
This is because they don’t have to keep prices competitive and costs low, innovation and efficiency may be poor in the industry.
What happens to cost curves if only FC change?
Only the AC curve will be affected.
What is a natural monopoly?
A market where even if there was just one firm in it, not all the benefits from economies of scale could be achieved.
What are the characteristics of natural monopoly industries?
some kind of distribution network
very high fixed costs
very high minimum efficient scale
What is an example of a natural monopoly?
The rail network