1.2.8 Consumer and producer surplus
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
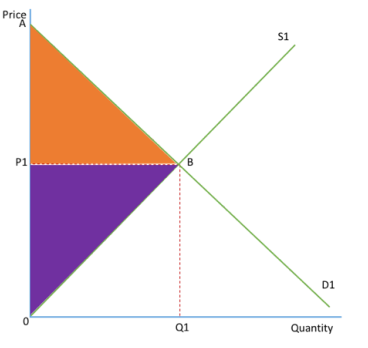
CONSUMER SURPLUS
the difference between the price the consumer is willing to pay and the price they actually pay, set by the price mechanism
This is illustrated by the orange triangle in the diagram, ABP1
The demand curve shows the price consumers are willing to pay, and so the difference between the demand curve and the price shows the consumer surplus
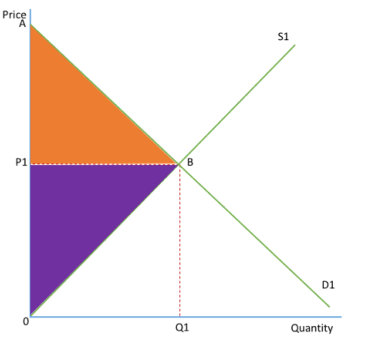
PRODUCER SURPLUS
the difference between the price the supplier is willing to produce their product at and the price they actually produce at, set by the price mechanism
This is illustrated by the purple triangle in the diagram, P1B0
The supply curve shows the price suppliers are willing to sell the good for, and so the difference between the supply curve and the price shows the producer surplus
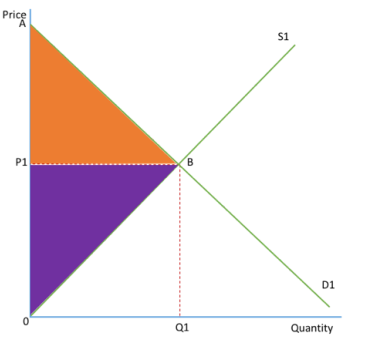
CONSUMER SURPLUS- SHOW
shows the welfare gained by consumers for buying the good
The total satisfaction consumers receive from buying the good is the total area under demand curve: ABQ10
They spend P1BQ10 to gain this satisfaction
Therefore, their net gain is ABP1, the consumer surplus
PRODUCER SURPLUS- SHOW
shows the economic gain for producers by selling the good
PERFECT ELASTIC/INELASTIC DEMAND
Perfectly elastic demand will mean that there is no consumer surplus
perfectly inelastic demand will mean that consumer surplus is infinite
The more inelastic demand= higher consumer surplus is likely to be
When supply is perfectly elastic, producer surplus is 0 and when it is perfectly inelastic, producer surplus is infinite
The more inelastic supply= higher producer surplus is likely to be
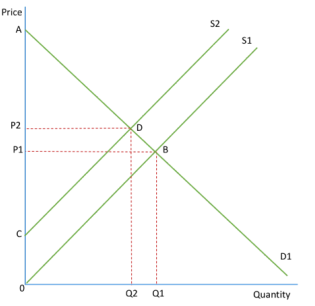
SHIFT IN DEMAND
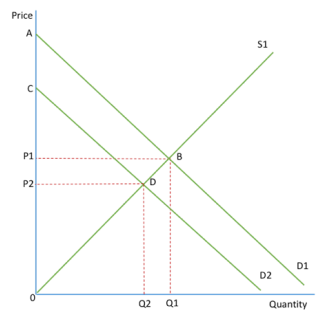
decrease in demand from D1 to D2 will lead to a fall in consumer and producer surplus, as both price and output decrease
Consumer surplus falls from ABP1 to CDP2 and producer surplus falls from P1B0 to P2D0
increase in demand would increase consumer and producer surplus
SHIFT IN SUPPLY
decrease in supply from S1 to S2 will lead to a fall in consumer and producer surplus
Consumer surplus falls from ABP1 to CDP2 and producer surplus falls from P1B0 and P2D0
increase in supply would increase consumer and producer surplus