Class 8-1: Animal Nutrients
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is nutrition in animals?
the process of conversion of organic material
where is energy stored?
in fats!
what is the nutrient pathway?
ingestion - food is taken in
digestion - food is broken down
absorption - nutrients absorbed
elimination - waste is removed
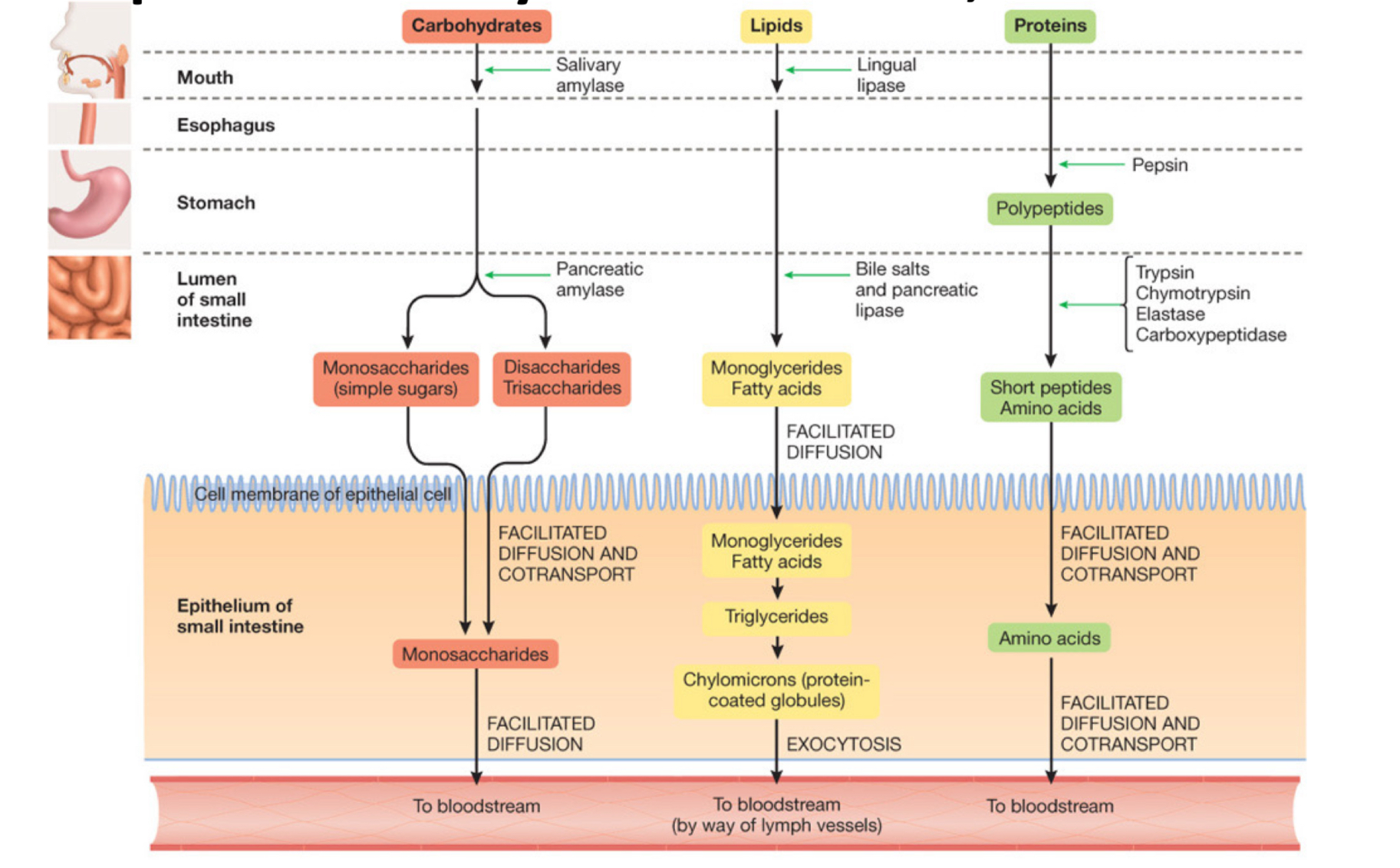
what takes place in the mouth and what enzymes are introduced here?
mechanical & chemical food processing
break down of lipids & carbs
salivary amylase & lipase
what takes place in the esophagus and what enzymes are introduced here?
transport bolus to stomach by peristalsis
no enzymes introduced here
what takes place in the stomach and what enzymes are introduced here?
mechanical & chemical food processing
breaks down proteins to peptides & fats to glycerol + fatty acids (HCl)
pepsin & gastric lipase (+HCl & mucus)
what takes place in the small intestine and what enzymes are introduced here?
digestion & absorption of nutrients
carbs, proteins, fats broken down
pancreatic amylase, lipase, trypsin & intestinal maltase, sucrase, lactase, + peptidases
what takes place in the large intestine and what enzymes are introduced here?
absorbs H2O & compacts waste to feces
holds good gut bacteria
no enzymes secreated
what takes place in the rectum and what enzymes are introduced here?
stores feces & signals to release
spincters used here
no enzymes secreated
after absorbed in the small intestine, what do the nutrients do?
break down to make ATP or stored for energy
used to build molecules for growth and repair
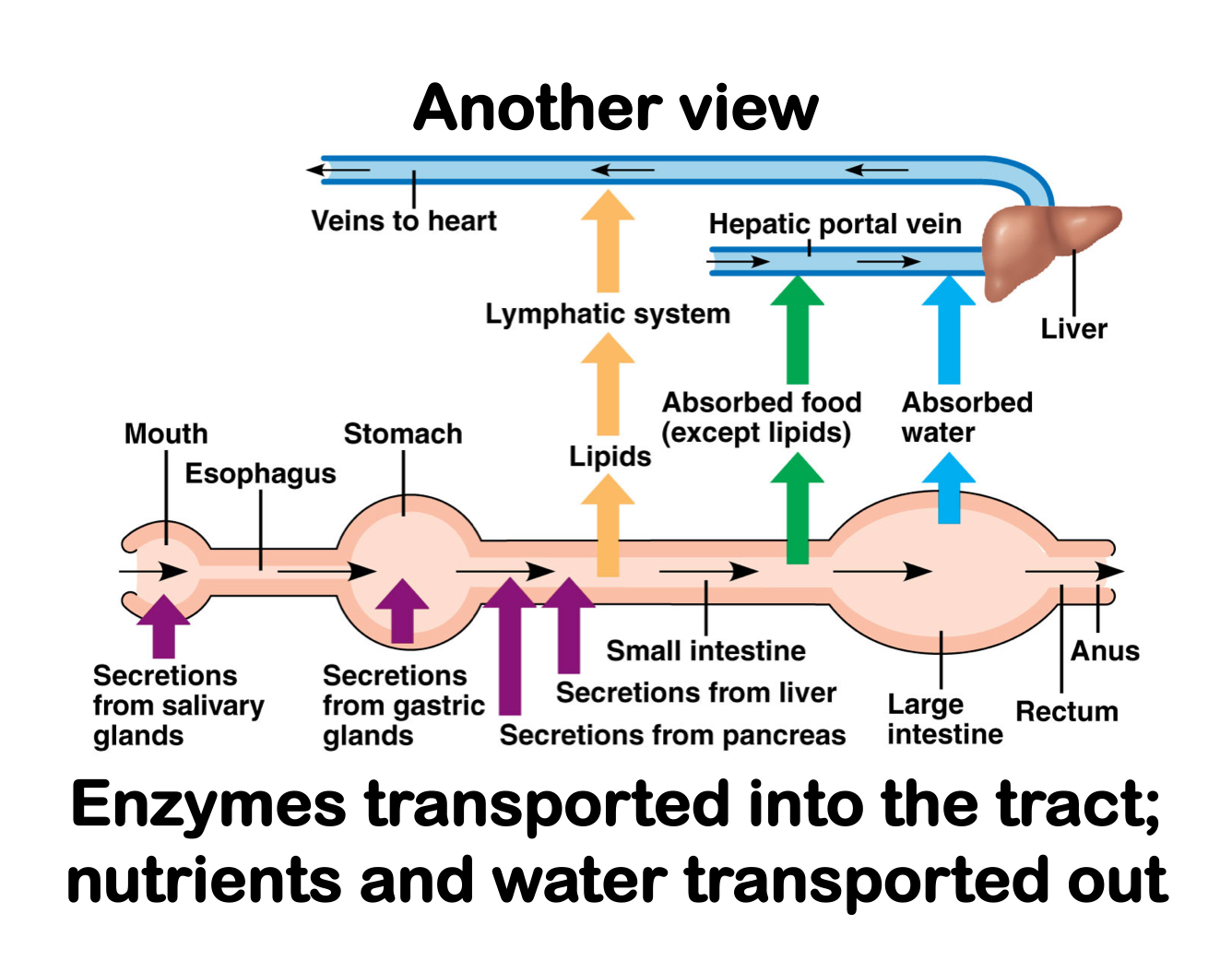
explain what is transported in and out of the tract
4 ways of ingestion (feeders)
fluid
suspension
deposit
mass or bulk

answer!
on the left will be eating smaller fish with multiple small teeth to tear
on the right will be eating algae or plants with large surface teeth to scrape
in mammals where does most of the enzynatic breakdown of macromolecules occur?
small intestine
how does the structure of small intestine support its function of absorbing nutrients?
big surface area (organ - length of small intestines & cell - micro villi)
small diffusion distance between intestine lumen & blood
transport proteins bring nutrients from digestive tract the blood
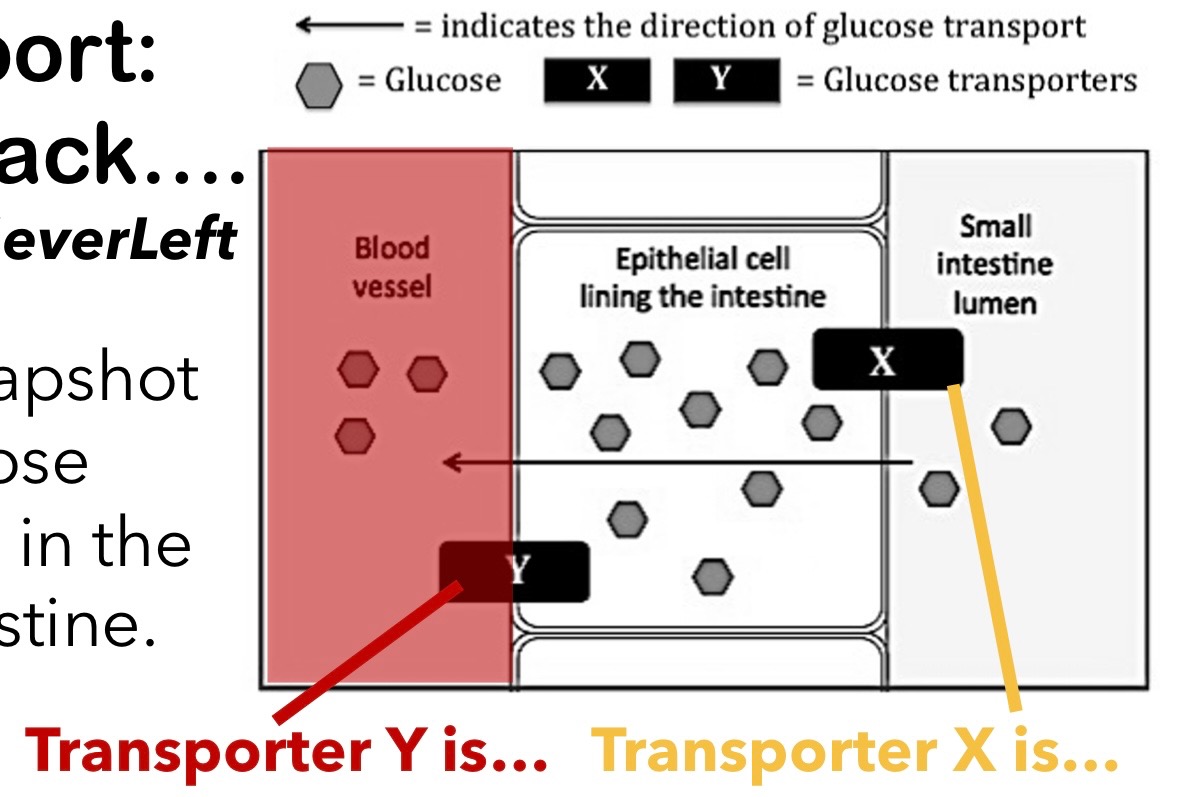
x is active moving the glucose from low [] to high [] (w energy)
y is passive moving glucose from high [] to low []
what does the kidney do?
indirectly involved in food processing
for filtering waste from blood
regulating salt, water, & nitrogen levels
explain the parts of the large intestine
colon: form feces by absorbing addition H2O & compacting remaining wastes
rectum: storage location for feces until eliminated
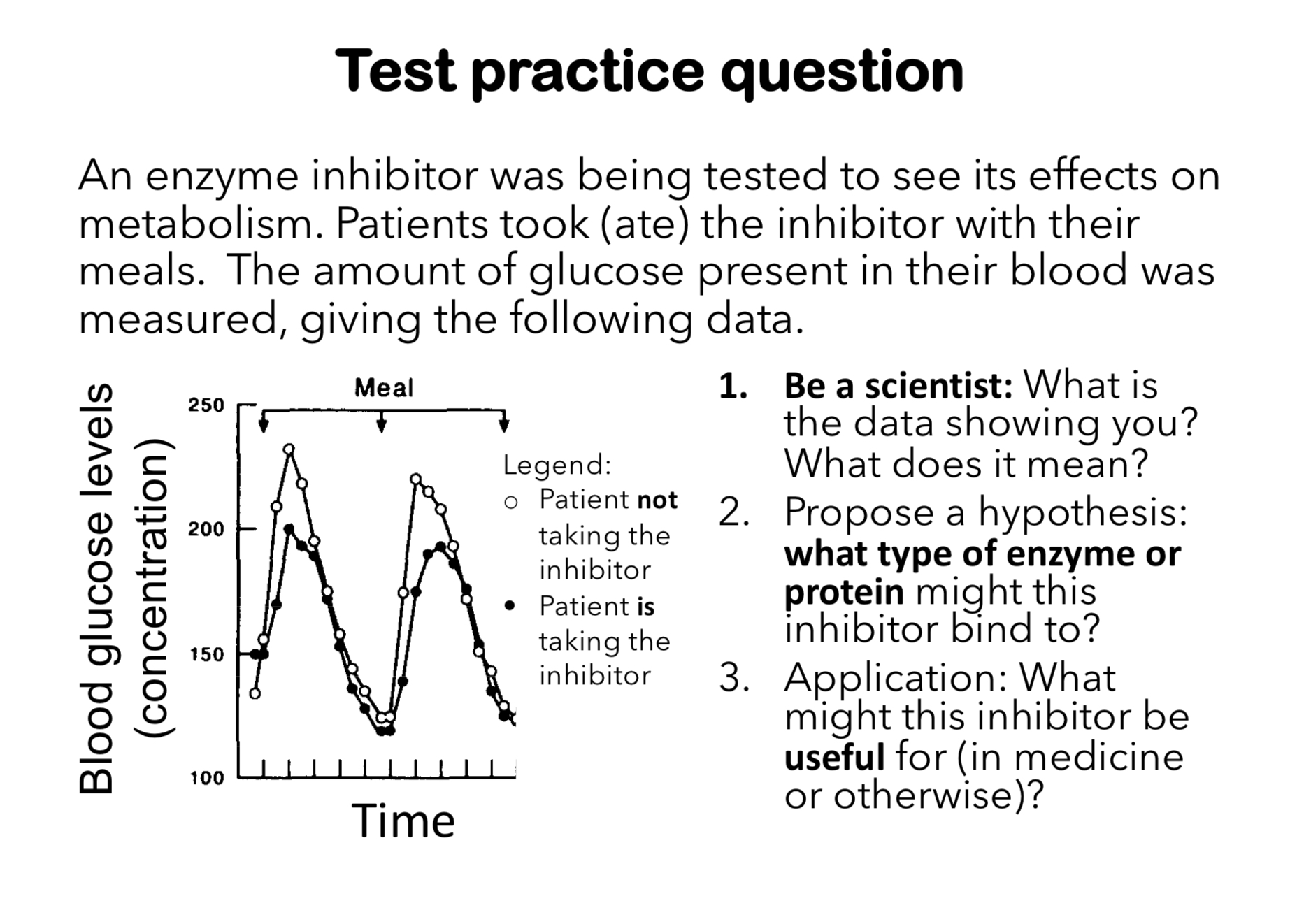
in the 4 steps, what enzymes are active & where?