Chapter 13- Spinal Cord and Somatic Reflexes
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Spinal Cord Functions
conduction, neural integration, locomotion, reflexes
Central Power Generators
Groups of neurons that coordinate repetitive muscle movements
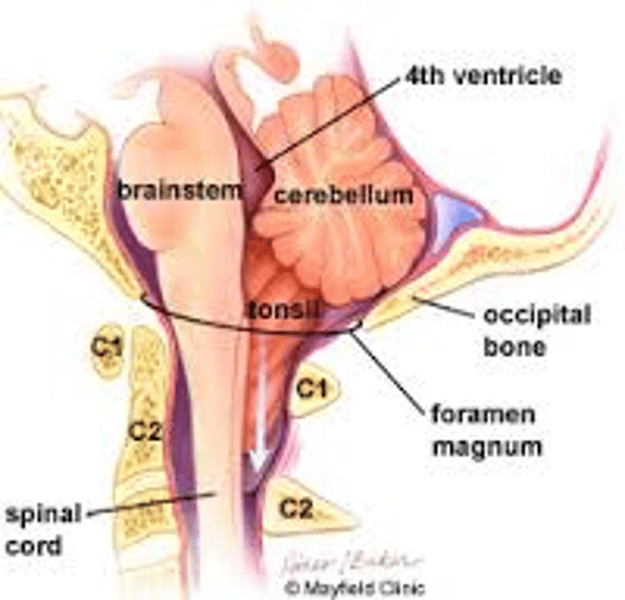
Where does the spinal cord begin?
superiorly at the brain stem (foramen magnum)
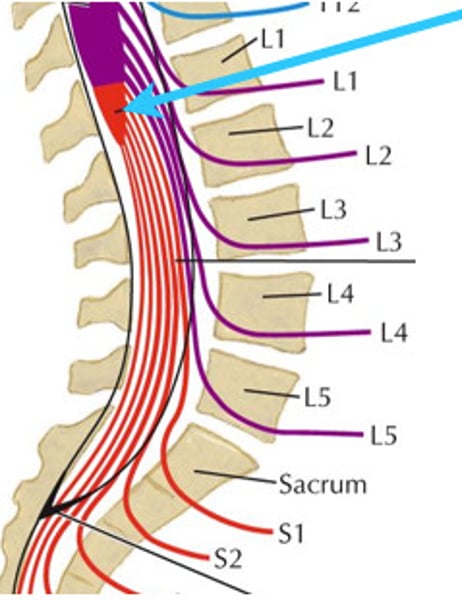
Where does the spinal cord end?
L1-L2
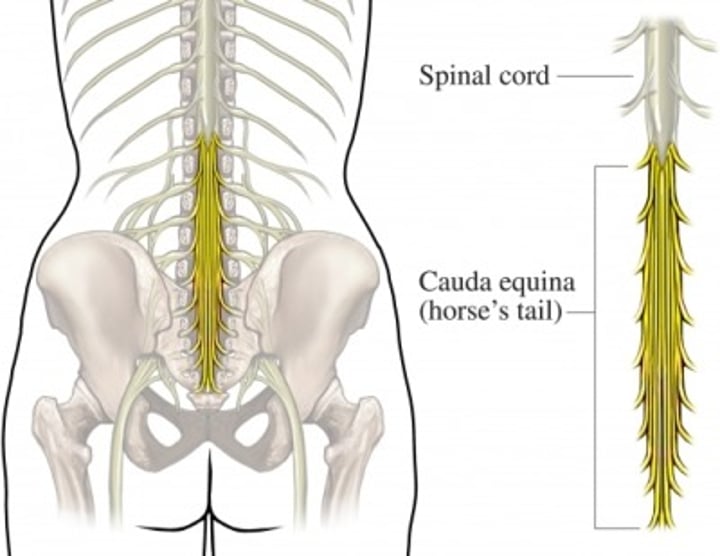
The lower 1/3 of the spinal column is known as what?
cauda equina (L2-S5)
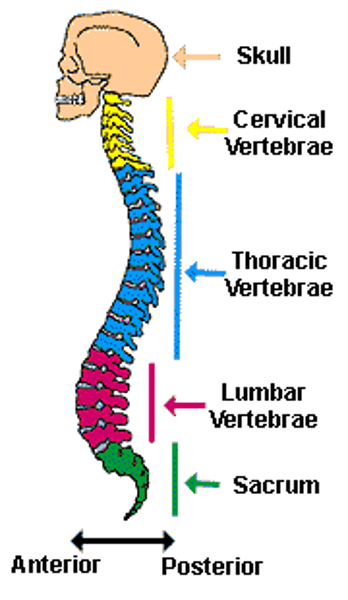
four regions of the spinal cord
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral
How many spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord?
31 pairs
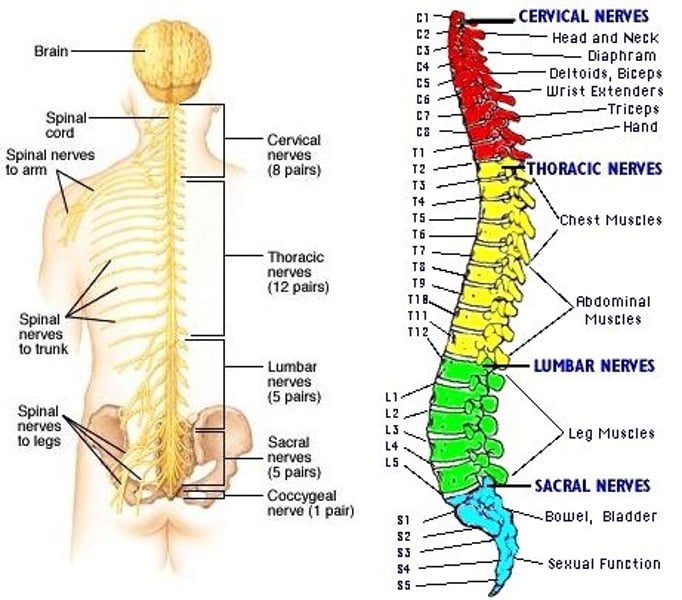
Cervical Enlargement of Spinal Cord
Responsible for supplying nerves to the upper limb
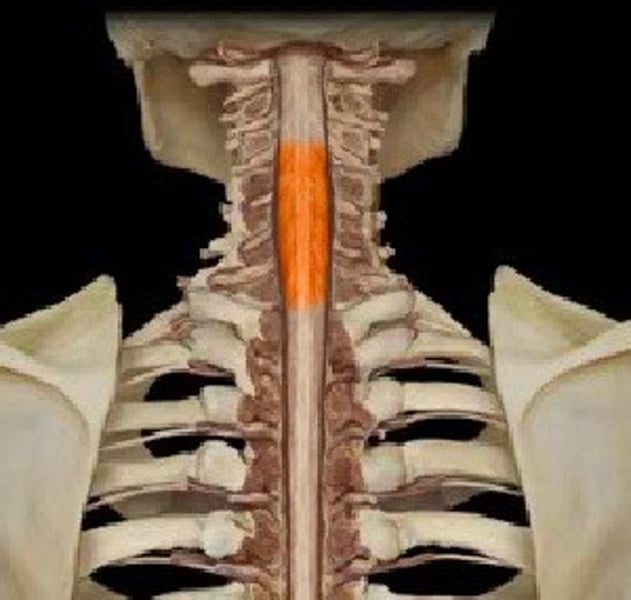
Lumbar Enlargement of Spinal Cord
Responsible for supplying nerves to the lower limb
Protective coverings of spinal cord (superficial to deep)
bone (vertebrae), epidural space, meninges
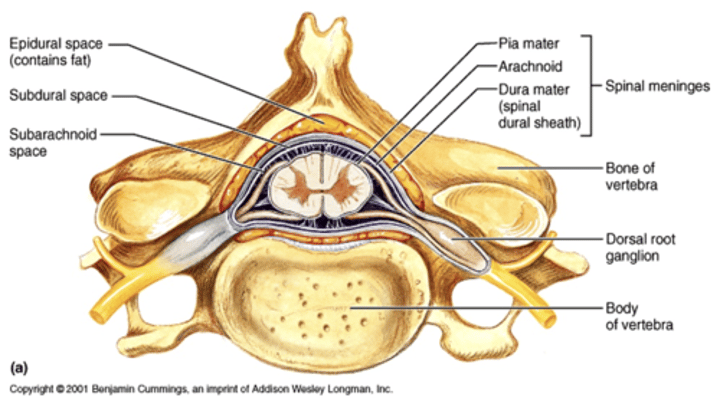
epidural space
fatty space between the vertebrae and dura mater
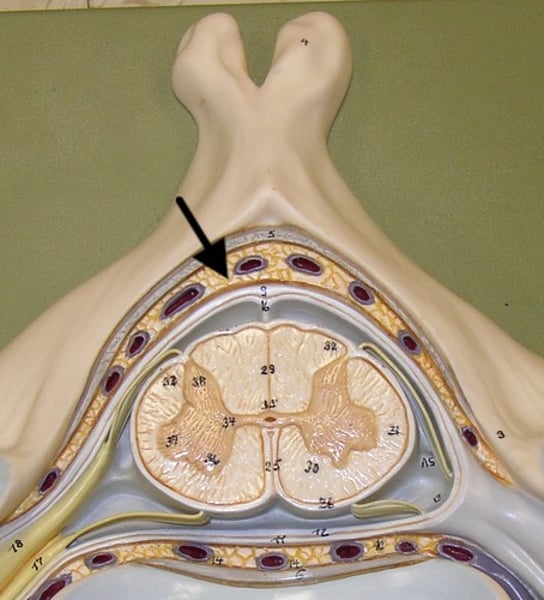
Meninges layers
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
dura mater (dural sheath)
most superficial of the three meninges
arachnoid mater
weblike middle layer of the three meninges
subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
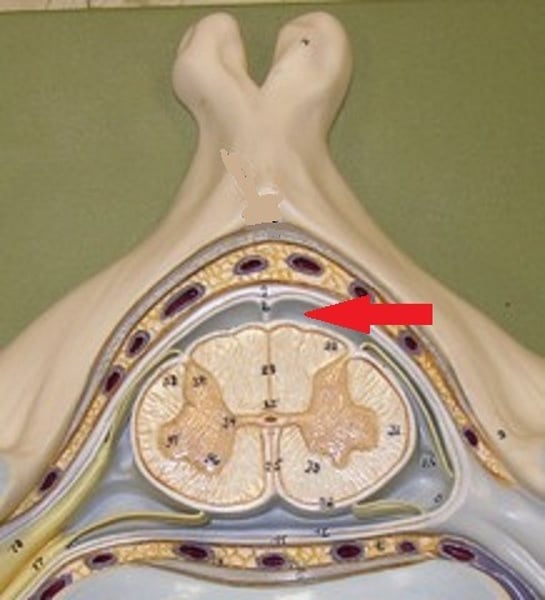
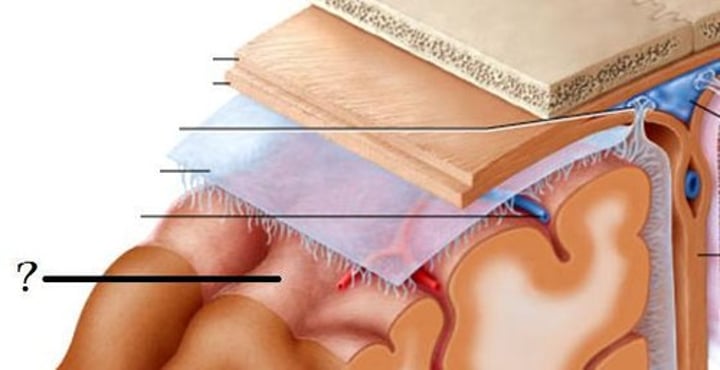
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
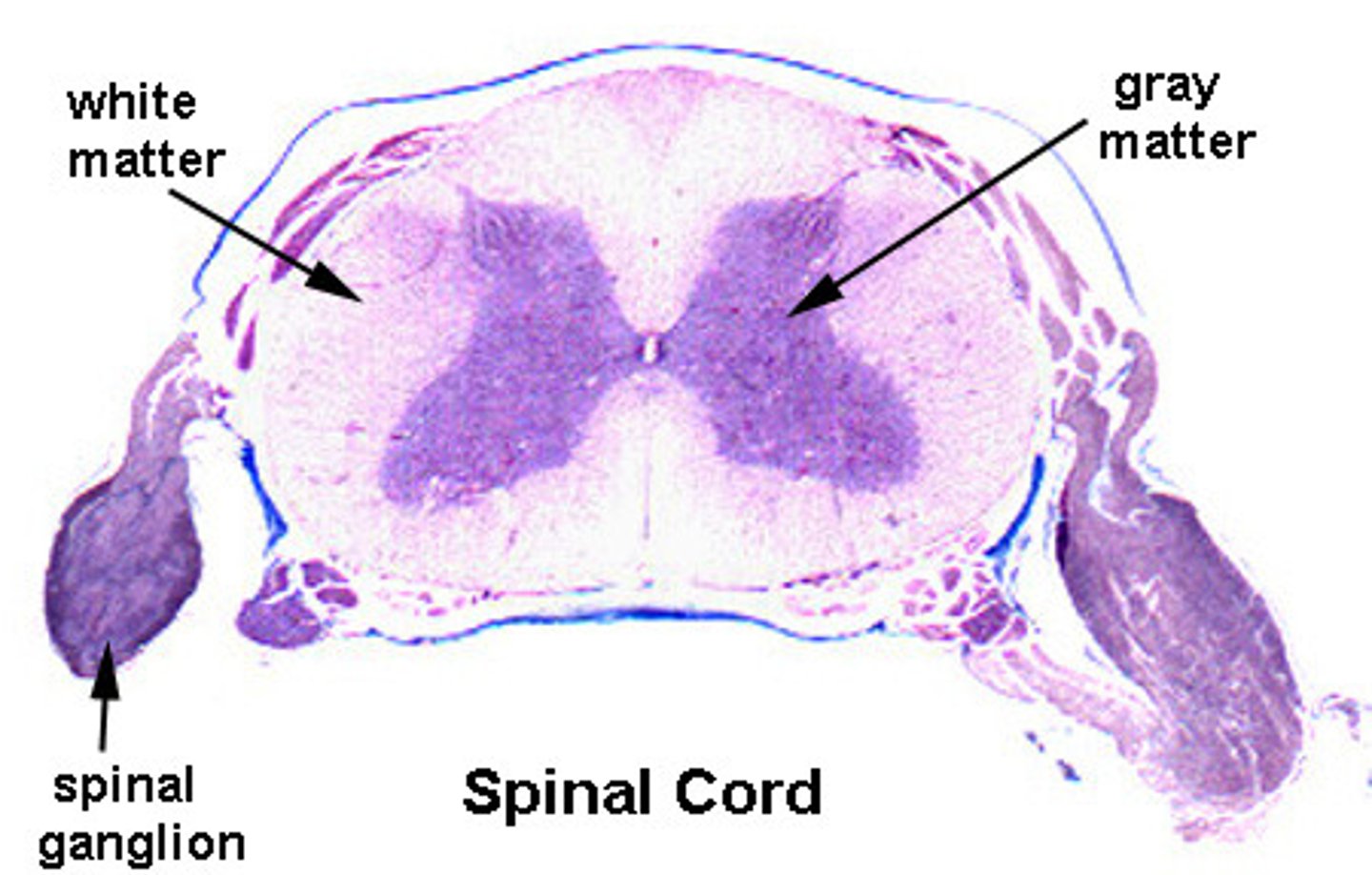
In the spinal cord, gray matter is surrounded by
white matter
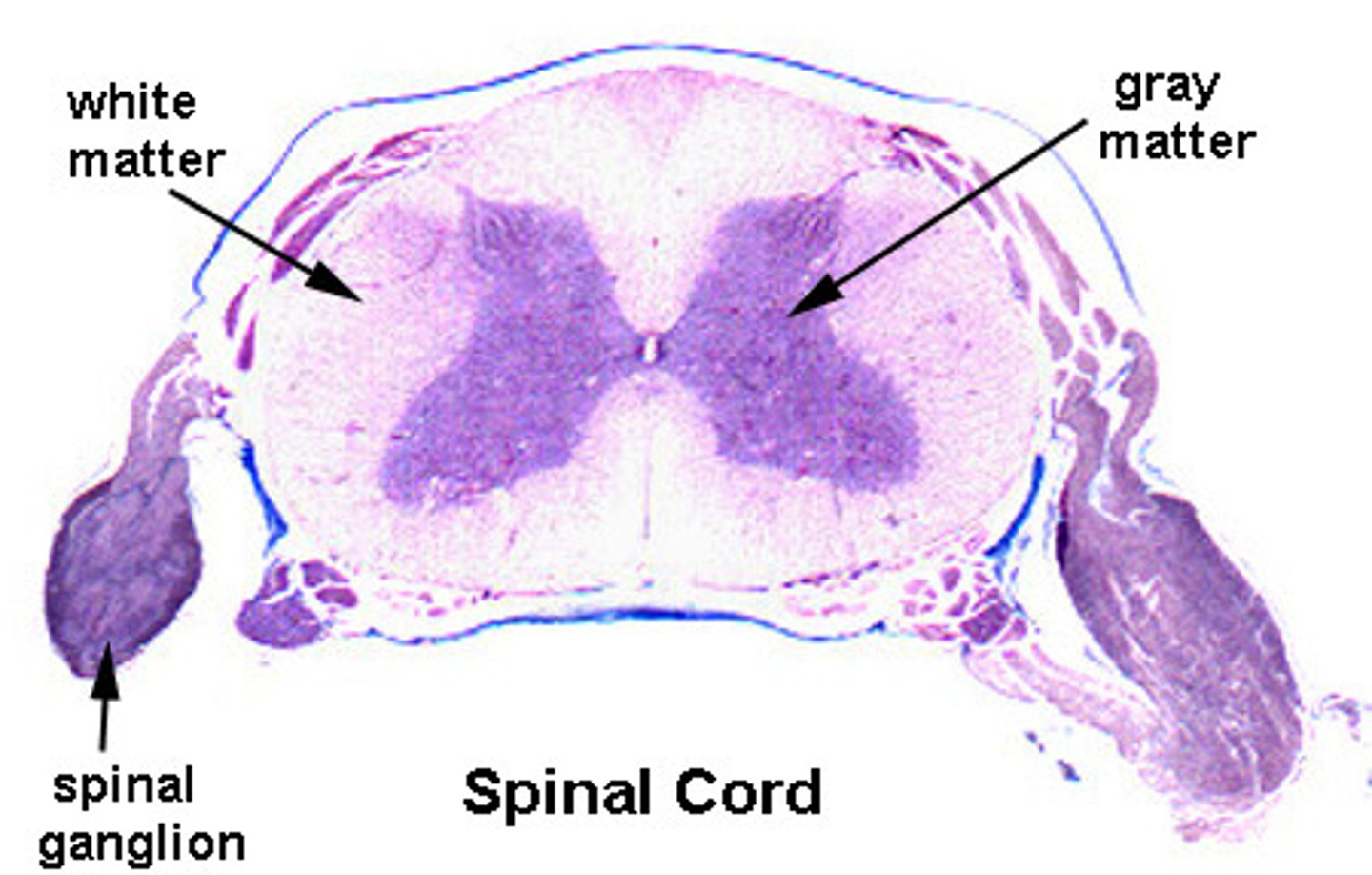
gray matter of spinal cord
-composed of somas, dendrites, and trigger zones
-site of synapses (integraton) for local potentials
white matter of spinal cord
-surrounds gray matter
-myelinated axons bundled together into tracts
-myelination gives white matter its pearly white color
Decussation
The anatomical crossing over of neurons from left to right
Ascending Spinal Tracts
carry sensory information toward the brain
Ascending Tracts usually transverse 3 neurons:
1. First-order neuron
2. Second-order neuron
3. Third-order neuron
First-Order Neuron
sensory neuron that detects stimulus and sends to spinal cord or brain stem
Second-Order Neuron
Interneuron that carries signal to the thalamus
Third-Order Neuron
Interneuron that carries signal from thalamus to the cerebral cortex
What is the thalamus also called?
gateway to cerebral cortex or the "mailroom"
descending tracts
carry motor information down the brainstem and spinal cord to effectors
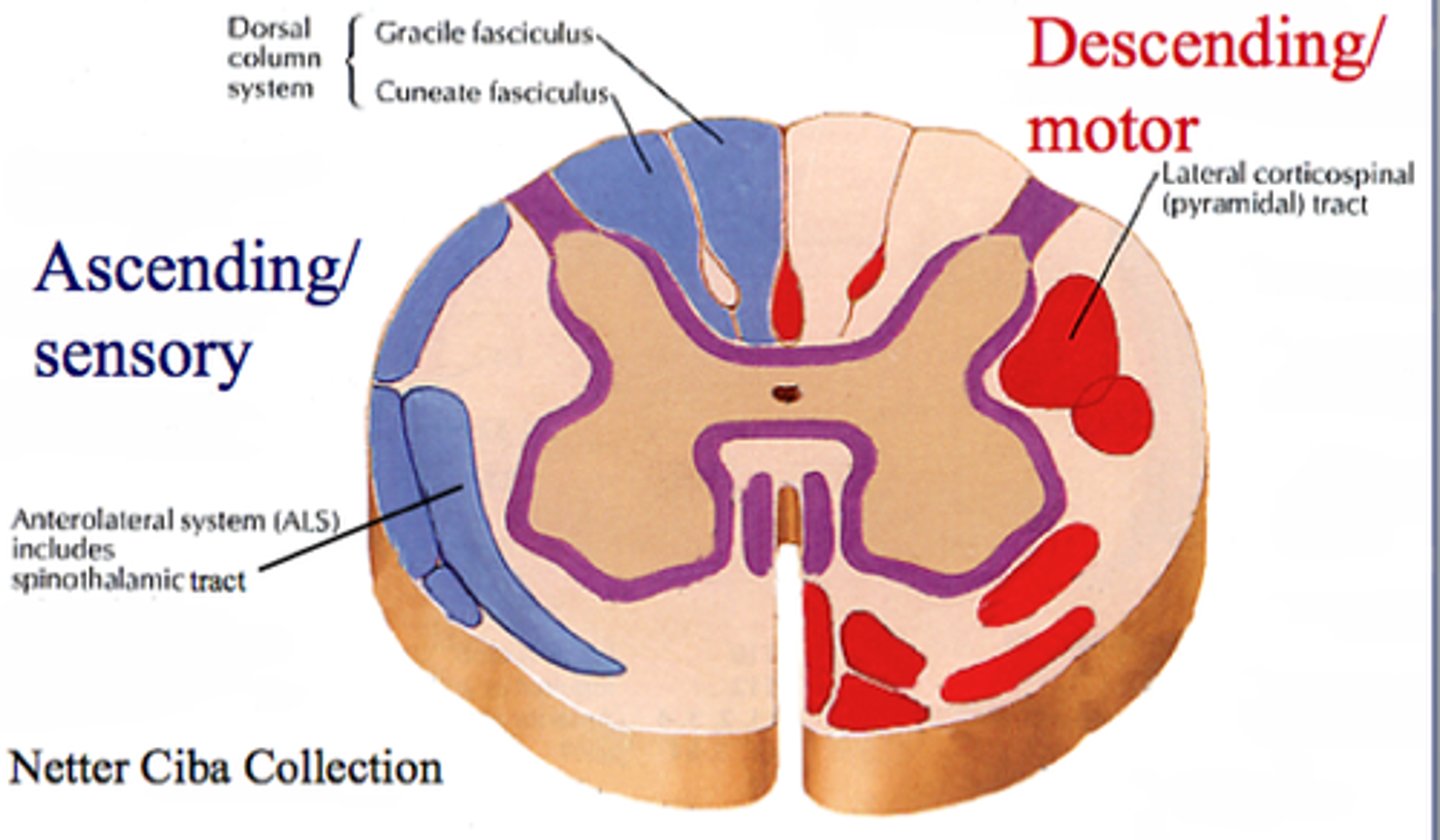
Descending Tracts transverse 2 neurons:
1. Upper Motor Neuron
2. Lower Motor Neuron
Upper Motor Neuron
Soma is in the cerebral cortex (gray matter); its axon synapses with a lower motor neuron
Lower Motor Neuron
carries signal from spinal cord to the effector
Nerves are made up of
bundles of axons
Spinal Nerve Anatomy
endoneurium, perineurium, epineurium
Endoneurium
surrounds nerve fibers
Perineurium
surrounds nerve fiber fascicles
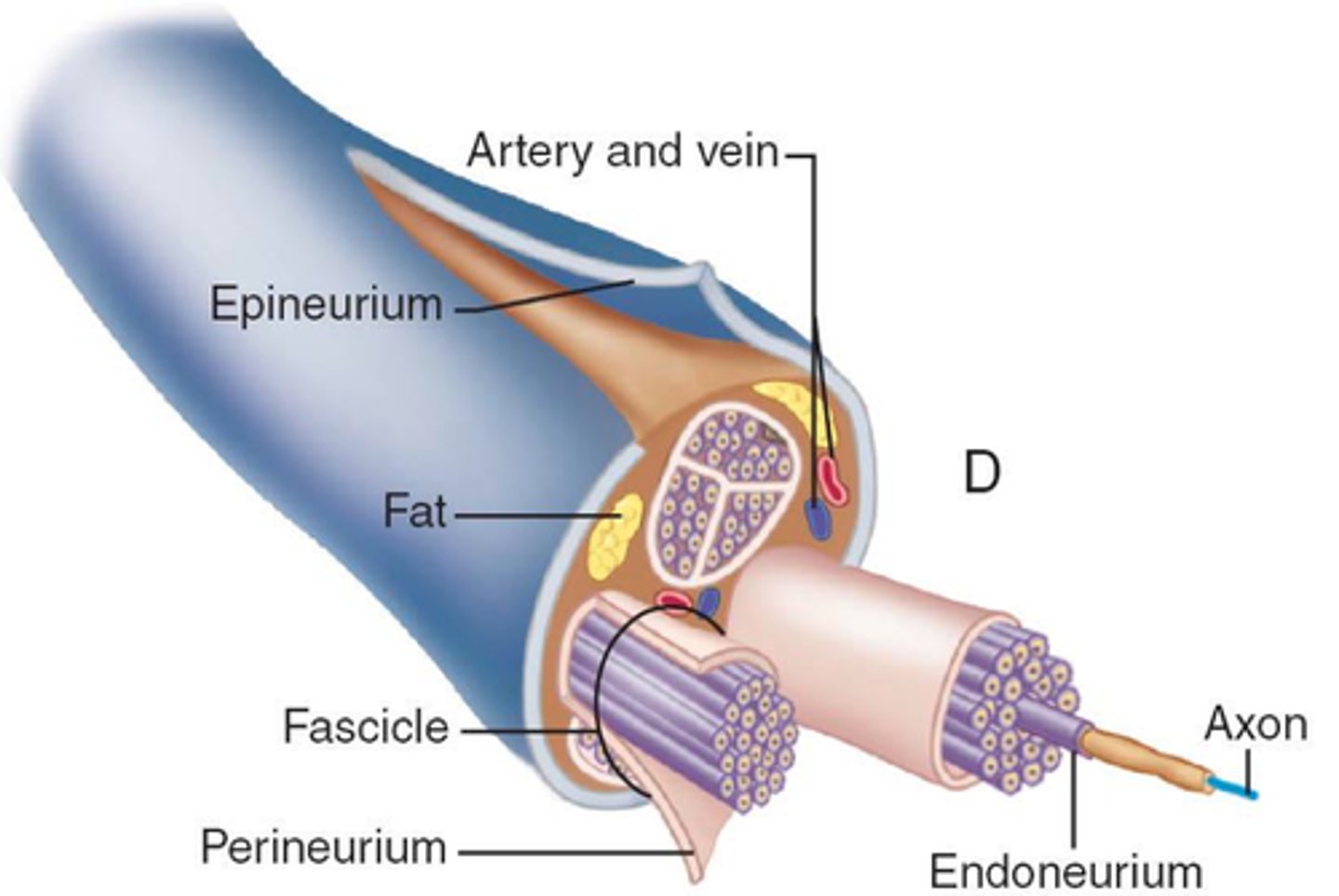
Epineurium
surrounds the entire nerve
The epineurium is important for
preventing the nerve from stretching
Nerves can only be:
sensory, motor, or mixed
nerve FIBERS can be:
afferent, efferent, somatic, visceral, general, or special
Where do spinal nerves arise?
roots proximal to the spinal cord
Spinal Nerve Anatomy:
-sensory input travels through the dorsal root
-motor output travels through the ventral root
-dorsal root ganglia house the soma of sensory neurons
what type of fibers do spinal nerves contain?
afferent and efferent fibers
4 traits of reflexes
1. require stimulation
2. must be quick
3. involuntary
4. stereotyped
somatic reflexes
activate skeletal muscle
visceral reflexes
involuntary muscles and glands
Anatomy of Somatic Reflex
-utilizes a reflex arc
-somatic receptors in skin, muscles, or tendons
-afferent nerve fiber
-integration center
-efferent nerve fiber
-effectors
example of a stretch reflex
patellar (knee-jerk) reflex
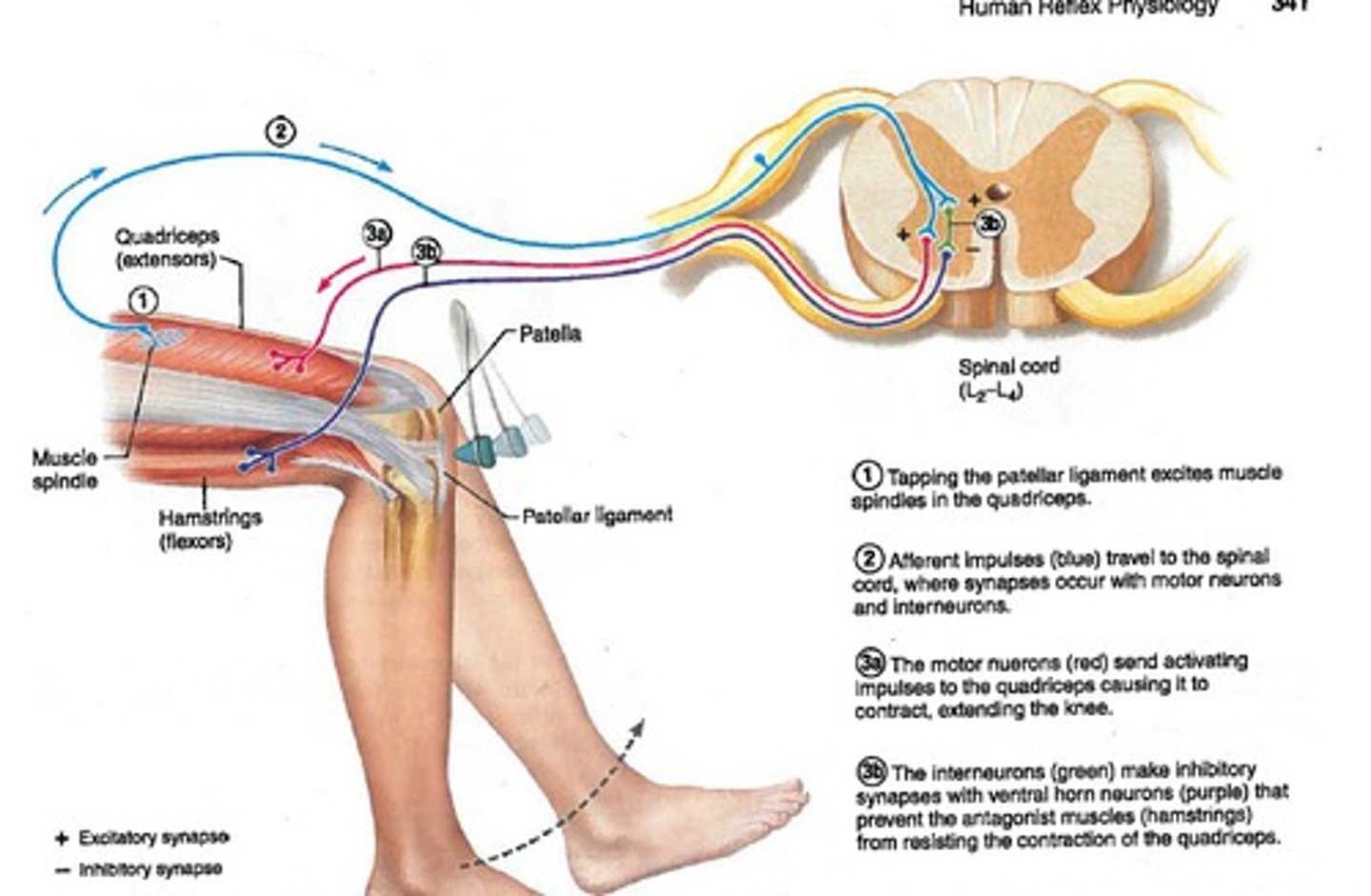
stretch reflex
-brain sets length for a muscle and stretch reflex maintains that length
The stretch reflex is important for
-maintaining muscle tone and adjusting it without consciousness.
-large muscles involved in posture
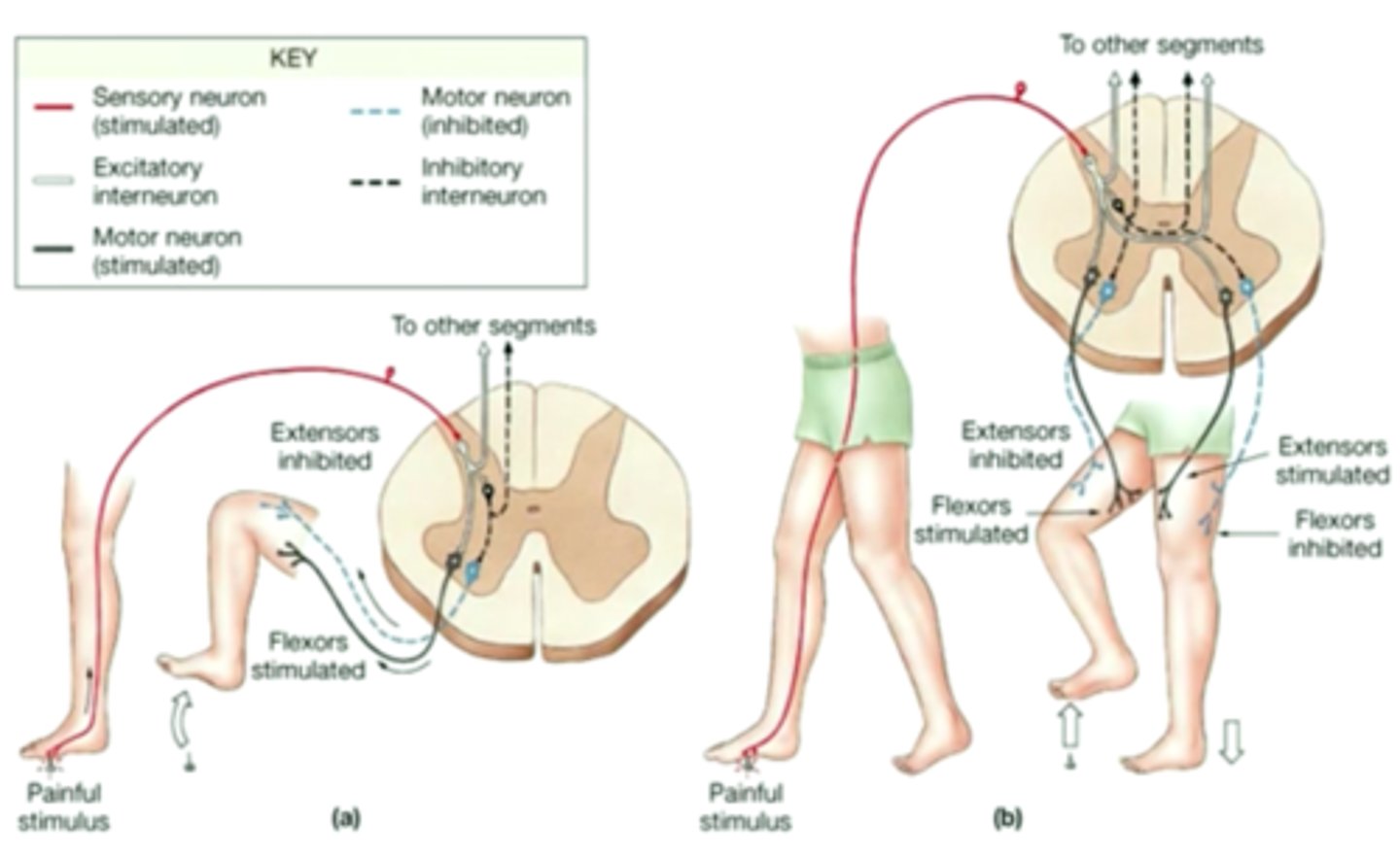
The Flexor (Withdraw) Reflex
-involves 2 reflex arcs simultaneously
-in response to a painful stimulus
-often accompanied by a crossed-extensor reflex
A flexor reflex
withdrawals limb
Crossed-extensor Reflex
stabilizes body during withdrawal
Testing reflexes demonstrates what?
health/integrity of the spinal cord
Plantar Reflex (Babinski)
tests the integrity of the spinal cord from L4 to S2
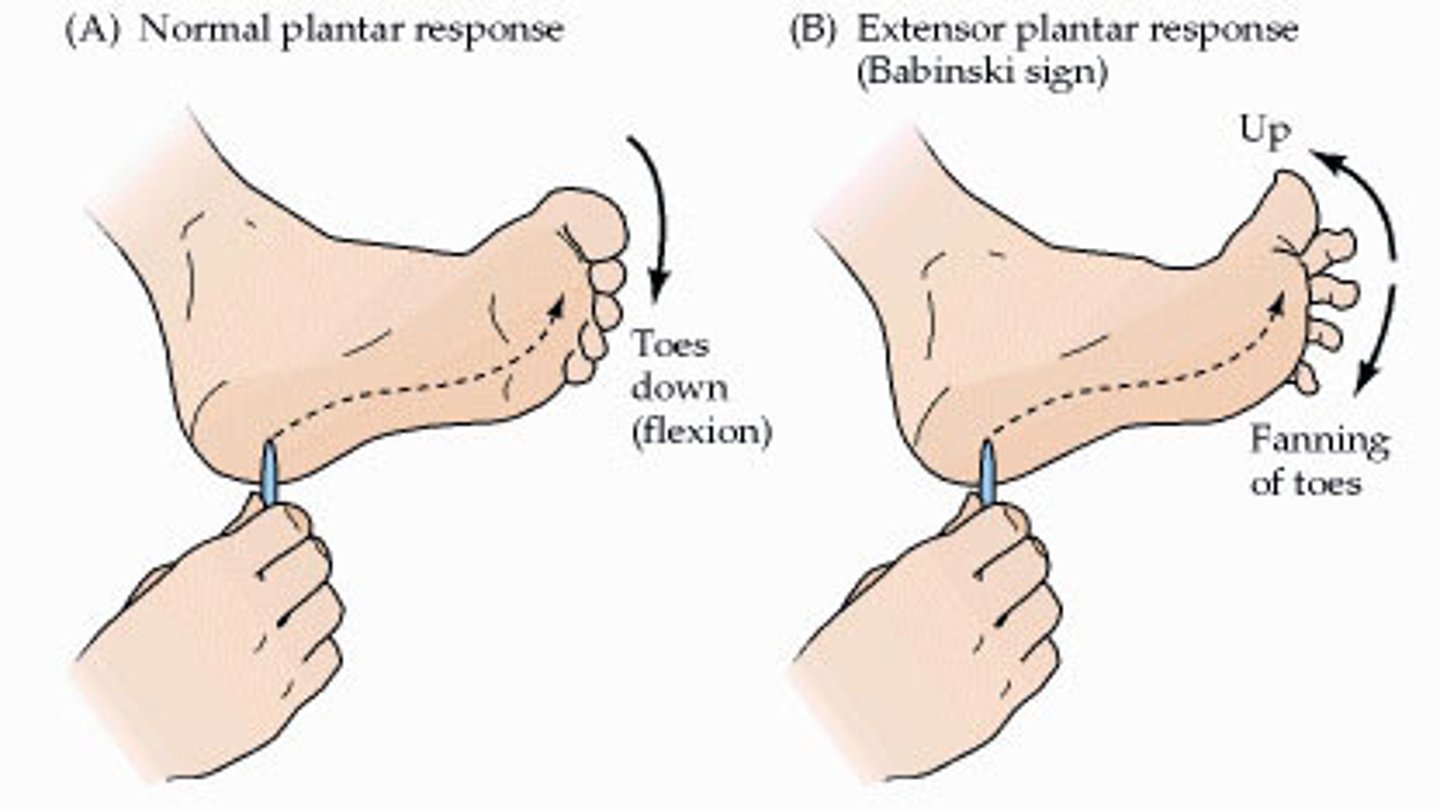
An infant up until age 1 will exhibit the Babinski sign due to
incomplete myelination of their nervous system at birth
The Babinski sign in older individuals indicates?
spinal cord or brain disease
Polio
-Destroys motor neurons in brain stem and spinal cord
-Causes muscle pain, weakness, loss of reflexes, atrophy, and ultimately paralysis
-spread through contaminated water

Lou Gehrig's Disease (ALS)
-degeneration of motor neurons and muscle atrophy
-astrocytes fail to reabsorb glutamate (neurotransmitter) and it accumulates to toxic levels
-cause is unknown

Rabies
-a viral infection from animal bites
-virus replicates in muscle tissue
-spreads via somatic nerve fibers to the CNS and then the autonomic nerve fibers
-causes seizures, coma, and death
-essential a 100% fatality rate if not treated before reaching the CNS
