(AnaPhy) Digestive System — Lecture
1/55
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Ingestion
The consumption of solid or liquid food.
Mastication
Chewing, which begins the mechanical breakdown of food, increasing its surface area for enzymatic action.
Propulsion
Moves food along the digestive tract via muscular contractions, primarily peristalsis (wave-like contractions)
Mixing
Involves segmental contractions that churn and mix food with digestive secretions, aiding in digestion and absorption.
Digestion
The mechanical and chemical breakdown of food.
Mechanical digestion
involves physical breakdown (e.g., chewing, churning) that increases surface area.
Chemical digestion
involves enzymatic hydrolysis of large molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) into smaller, absorbable subunits.
Secretion
involves the release of enzymes, acids, buffers, and other substances by digestive glands and cells to aid in digestion.
Absorption
The transport of digested nutrients (monosaccharides, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol, vitamins, minerals) from the digestive tract lumen across the epithelial lining into the blood or lymphatic system.
Elimination
The removal of undigested material, cellular debris, and metabolic waste products as feces through the process of defecation.
Mucosa
The innermost layer, responsible for secretion of mucus, lining the lumen.
Lamina propria
Loose connective tissue containing blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and immune cells (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, or MALT).
Muscularis mucosae
A thin layer of smooth muscle responsible for local movements of the mucosa (e.g., to increase surface area).
Submucosa
A layer of dense irregular connective tissue.
Contains larger blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerve plexuses (submucosal plexus, part of the enteric nervous system) that regulate digestive secretions and blood flow.
May contain glands that secrete substances into the lumen.
Serosa (Visceral peritoneum)
A serous membrane covering the portions of the digestive tract within the abdominal cavity; reduces friction.
Adventitia
Dense fibrous connective tissue that binds portions of the digestive tract outside the abdominal cavity (e.g., esophagus) to surrounding tissues.
Parietal peritoneum
Lines the inner surface of the abdominal wall.
Hard palate
The anterior portion, formed by the maxillae and palatine bones; rigid structure aids in chewing.
Soft palate
The posterior portion, composed of skeletal muscle and connective tissue; closes off the nasopharynx during swallowing.
Uvula
A cone-shaped projection of the soft palate; helps to close off the nasopharynx during swallowing.
Chyme
The semifluid paste of partly digested food and digestive secretions that is formed in the stomach and passed into the small intestine.
32 Teeth
Normal adult mouth has…
Salivary amylase
Chemical in saliva that begins the digestion of carbohydrates.
Lingual lipase
Chemical in saliva that begins the digestion of lipids.
Parotid glands
Large serous glands located anterior to each ear between the masseter muscle and the skin; secrete primarily serous fluid containing amylase; mumps affects these glands.
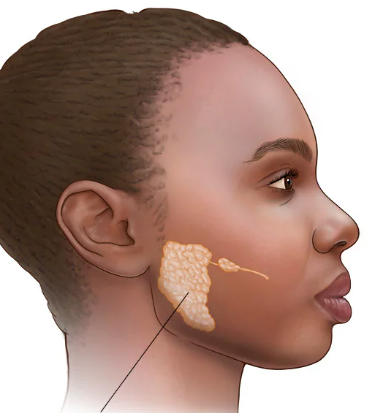
Submandibular glands
Located along the inner surface of the mandible; produce a mixed secretion (more serous than mucous); secrete saliva into the oral cavity via ducts that open on either side of the frenulum of the tongue.
Sublingual gland
Located below the mucous membrane in the floor of the oral cavity, anterior to the submandibular glands; primarily secrete mucous secretions.
Nasopharynx
Posterior to the nasal cavity; serves as an air passageway; contains the pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids).
Opening to the eustachian tube
Oropharynx
Oropharynx: Posterior to the oral cavity; serves as a passageway for both food and air; contains the palatine tonsils.
Laryngopharynx
Inferior to the oropharynx, superior to the larynx; continuous with the esophagus.
Cardial (cardia) / Cardiac orifice
the opening where the esophagus connects to the stomach, specifically the cardia region. Surrounds the cardioesophageal sphincter; receives food from the esophagus.
Mucus
Secreted by mucous cells, protects the stomach lining from the acidic environment.
Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Secreted by parietal cells, activates pepsinogen to pepsin and kills bacteria.
Pepsinogen
Inactive form of pepsin, secreted by chief cells; converted to active pepsin by HCl.
Intrinsic factor
Secreted by parietal cells, essential for the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine.
Gastrin
Hormones released in the stomach, released by enteroendocrine cells
Pyloric sphincter
a muscular ring at the lower end of the stomach, acting as a valve to regulate the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the small intestine (duodenum).
Rugae
Large folds of the mucosa and submucosa in the stomach; allow the stomach to expand when filled with food.
Duodenum
The shortest part of the small intestine (10 inches); receives chyme from the stomach, digestive enzymes from the pancreas, and bile from the liver and gallbladder; most digestion occurs here.
Jejunum
The middle portion of the small intestine (3 feet); most nutrient absorption occurs here.
Ileum
The terminal portion (6 feet); absorbs vitamin B12 and bile salts; empties into the large intestine.
Villi
Fingerlike projections of the mucosa that extend into the intestinal lumen; increase surface area for absorption.
Microvilli
Tiny, hairlike projections of the plasma membrane of the absorptive epithelial cells; form the brush border; greatly increase surface area; contain brush border enzymes that complete the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins.
Large intestine
Absorbs most of the remaining water, ions (e.g., sodium, chloride), and some vitamins from the undigested residue.
Compacts and stores undigested material and waste as feces.
Contains a large population of beneficial bacteria (gut flora) that synthesize some vitamins, ferment indigestible carbohydrates, and inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria.
Appendix
A worm-like appendage that hangs from the cecum; contains lymphoid tissue and may play a role in immunity; prone to inflammation
Cecum
The pouch-like first part of the large intestine; receives chyme from the ileum.
Rectum
Stores feces until defecation.
Pancreatic amylase
Secreted by the pancreas into the small intestine, continues the digestion of starch into disaccharides.
Trypsin
Secreted as trypsinogen (an inactive proenzyme); activated by enteropeptidase (a brush border enzyme); digests proteins into smaller peptides.
Chymotrypsin
Secreted as chymotrypsinogen (an inactive proenzyme); activated by trypsin; digests proteins into smaller peptides.
Carboxypeptidase
Removes amino acids from the carboxyl ends of peptides.
Pancreas
Produces a wide spectrum of digestive enzymes that break down all categories of food
Produces Insulin & Glucagon
Liver
Largest gland in the body
Digestive role is to produce bile
Buccal phase
Voluntary
Occurs in the mouth
Food is formed into a bolus
The bolus is forced into the pharynx by the tongue
Pharyngeal-esophageal phase
Involuntary transport of the bolus by peristalsis
Nasal and respiratory passageways are blocked
Peristalsis moves the bolus toward the stomach
The cardioesophageal sphincter is opened when food presses against it
Type I alveolar cells
are one of the two main types of epithelial cells that line the alveoli in the lungs. They are the predominant cell type, making up about 95% of the alveolar surface area.