5.1 - Introduction to Soil System
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Soil Systems and Society - 5.1 Introduction to Soil Systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What is soil?
a complex ecosystem that is made up of minerals, organic material, gases and liquids which forms the habitat for many animals and plants. it’s found in layers/horizons
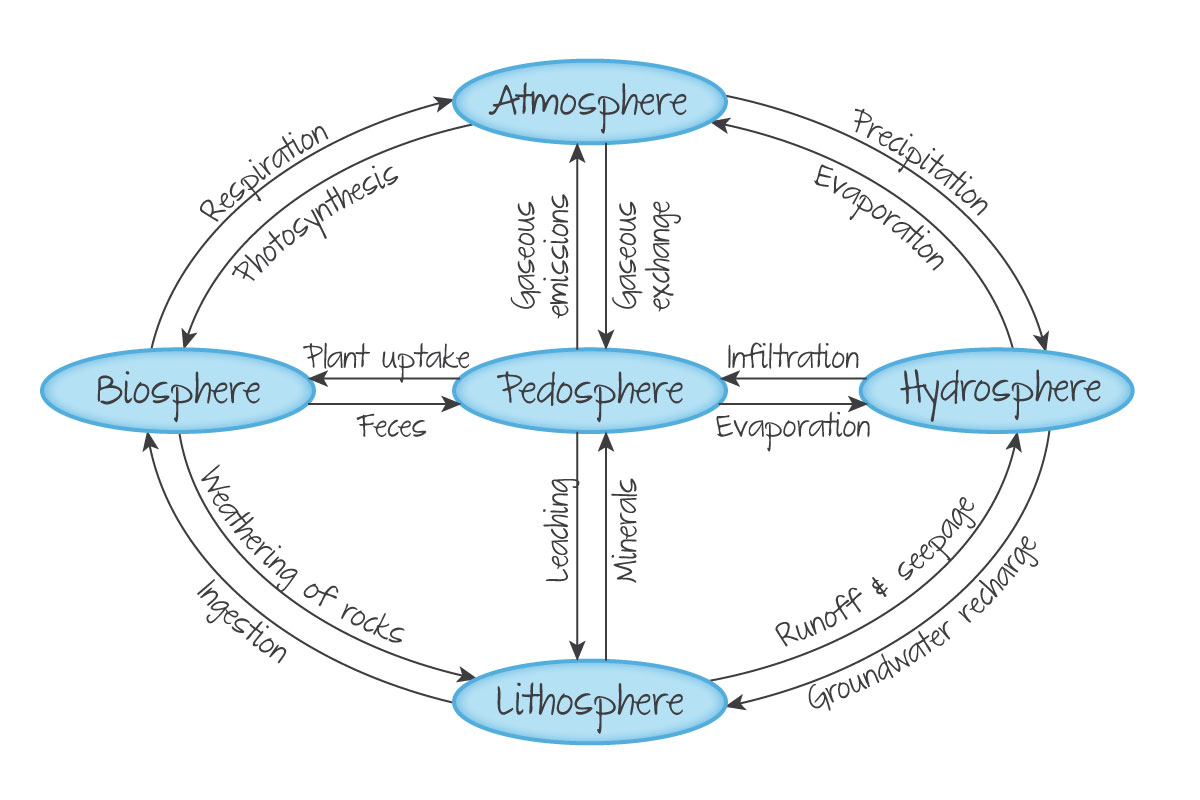
What sphere is the soil a part of?
the pedosphere
Where is the pedosphere?
between the biosphere and lithosphere
What influences the pedosphere?
the atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere
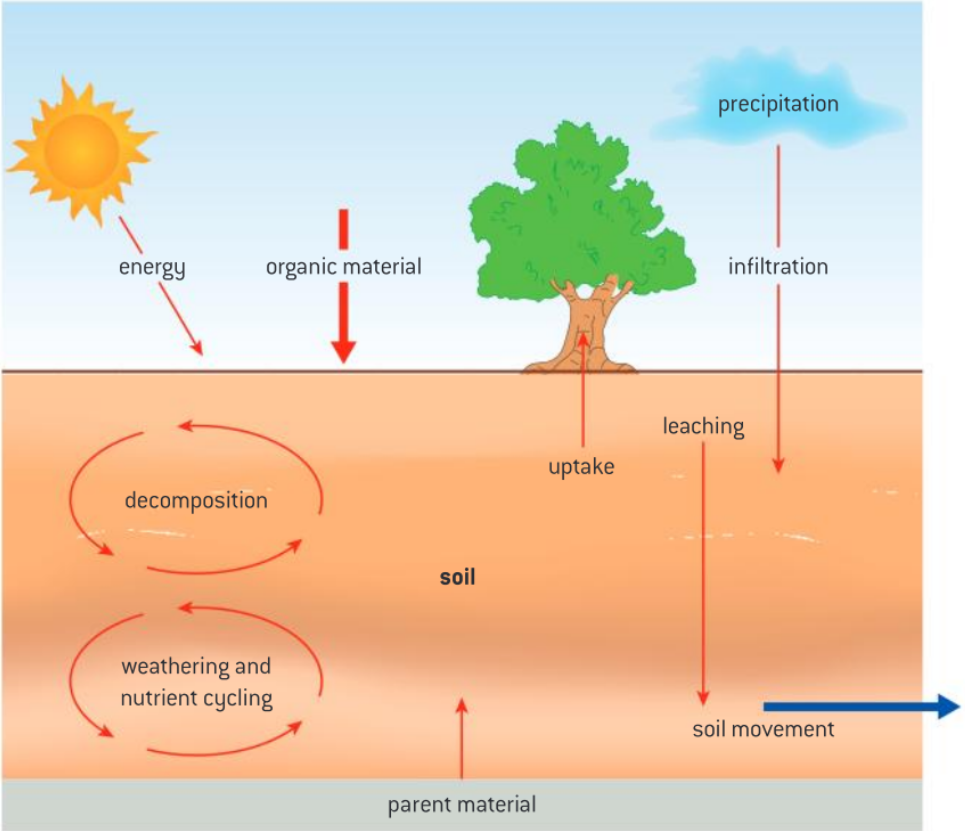
Storages in soil
Organic matter, organisms, nutrients, minerals, air and water
Transfers within soil
Biological mixing, translocation (movement of soil particles in suspension) and leaching (minerals dissolved in water moved through soil)
Inputs
Organic material including leaf litter and inorganic matter from parent material, precipitation and energy
Outputs
Uptake by plants and soil erosion
Transformations
Decomposition, weathering and nutrient cycling
Systems Diagram
Systems Diagram
What makes up rock particles?
Insoluble - gravel, sand, silt, clay, chalk
Soluble - mineral salts, compounds of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sulphur, magnesium
What makes up humus?
Plant and animal matter in the process of decomposition
What makes up water?
Water either seeping down from precipitation or moving up from underground sources by capillary action
What makes up air?
Mainly oxygen and nitrogen
What makes up soil organisms?
Soil invertebrates, microorganisms, and large animals
Function of rock particles
provides the skeleton of the soil
derived from the underlying ___ or from ___ particles transported to the environment (ex. glacial hill)
Function of humus
gives the soil a dark colour
returns mineral nutrients back to the soil
absorbs and holds on to a large amount of water
Function of water
dissolved mineral salts become available to plants
rapid downward movement of ___ causes leaching of minerals
rapid upward movement can cause salination
large volumes of ___ in the soil can cause waterlogging, leading to anoxic conditions and acidification
Function of air
well-aerated soils provide ocygrn for the respiration of soil organisms and plant roots
Function of soil organisms
large particles of dead organic matter are broken down by soil invertebrates like worms, leading to smaller particles
smaller particles are then decomposed by ______________ thus recycling mineral nutrients
larger burrowing soil animals (ex. moles) help mix and aerate the soil
Translocation
involves the movement of soil-forming materials through the developing soil profile
How does translocation occur?
by water running through soil transferring materials from upper to lower portions of the profile.
Salinization
when water is evaporating at the soil surface and water from lower soil layers moves upwards. it dissolves materials and takes them to the surface. happens in hot, dry climates when precipitation < evaporation
Leaching
in colder and wetter climates when water flows down in the soil, dissolving minerals and transporting them downwards. when precipitation > evaporation
The quality of soil influences what?
The primary productivity of an area. The better the quality of soil, the better the productivity
What is soil vital for?
Plant survival
Crop production
Habitat
Water filtration
Foundation
All food we depend on
Stores & transfers heat
Factors that affect soil
underlying rock (parent rock)
climate
topography
biological factors
time
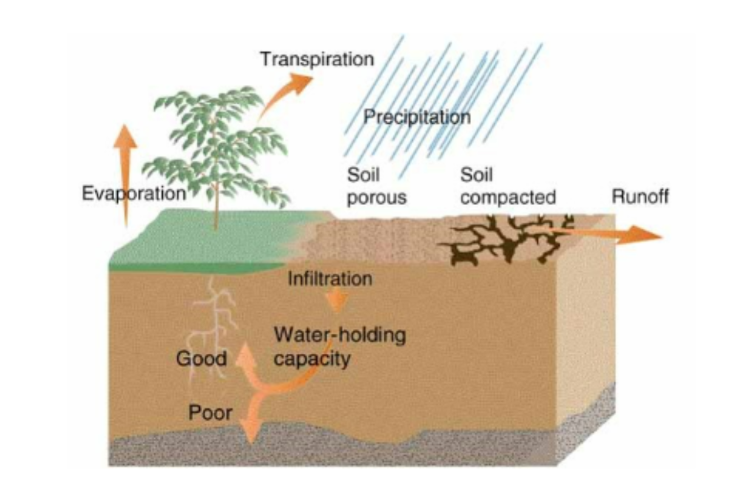
The role of soil in water movement
Precipitation (rain in porous soil then infiltrates the soil and gets to the roots, watering plants) or (rain in compacted soil, leading to runoff)
Evaporation
Transpiration when water from the soil turns into water vapor and moves to the atmosphere
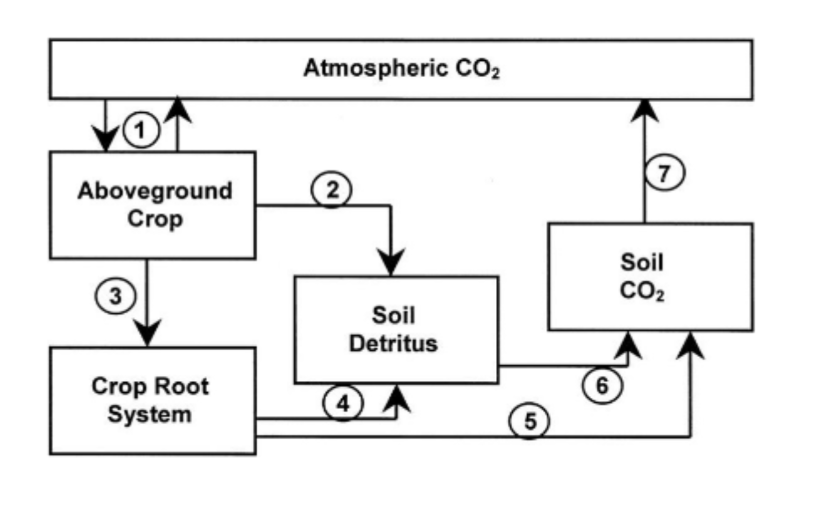
The role of soil in carbon cycling
Atmospheric CO2 → Aboveground Crop → Soil Detritus → Soil CO2 → back to Atmospheric CO2
Atmospheric CO2 → Aboveground Crop → Crop root system → Soil Detritus/Soil Co2 → back to Atmospheric CO2
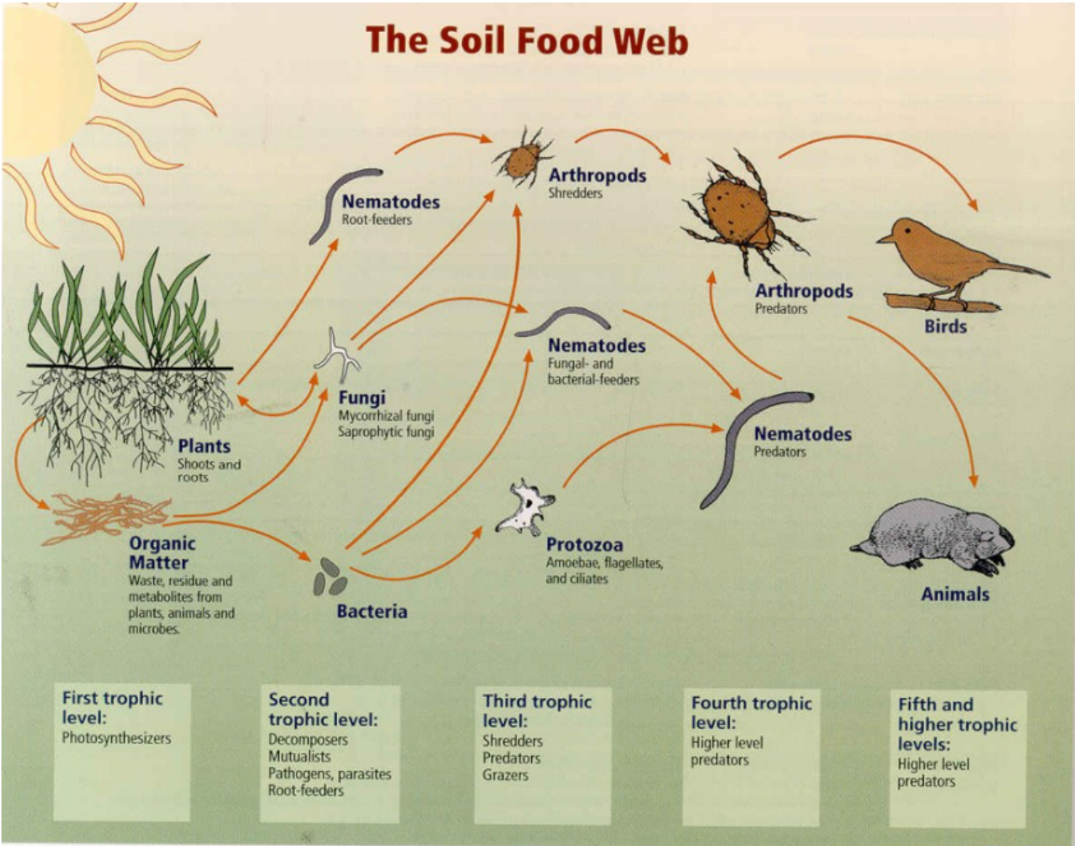
The soil food web
1st trophic level: Photosynthesizers
2nd tropic level: Decomposers, Mutualists, Pathogens, Parasites, Root-feeders
3rd trophic level: Shredders, Predators, Grazers
4th and 5th+ trophic level: Higher level predators
What is biota?
All the plants, animals, algae, fungi and microbes in an ecosystem
Role of biota in soil formation
Plants hold parent material in place
Roots bind soil particles together and increase water filtration into the soils, reducing runoff and erosion
Roots growing in cracks and fissures break apart rocks, speeding up soil formation
Lichens on rocks increase weathering
Vegetation is the initial source of the carbon fixed by photosynthesis that becomes organic matter in the soil
How does vegetation affect microclimates with relation to the role of biota in soil formation?
slowing wind speeds
shading soil surface
retaining snow
resulting in cooler and more moist soil environments
Soil Upper Levels
Have been altered due to the climate or organisms
Soil lower boundary
Hard rock that is devoid of biological activity
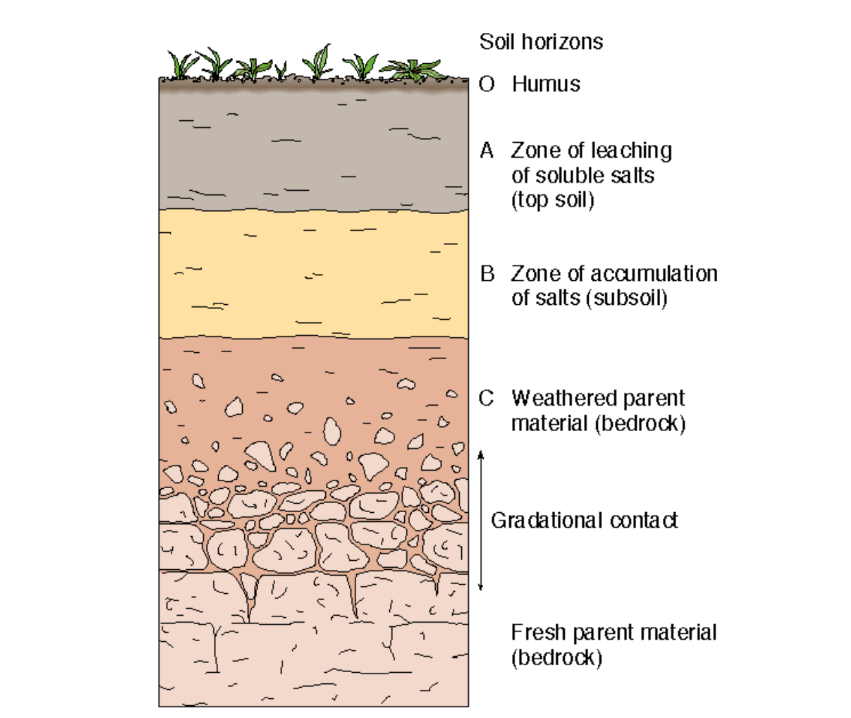
What is included in a soil profile?
O - Humus
A - Zone of leaching of soluble salts (top soil)
B - Zone of accumulation of salts (subsoil)
C - Weathered parent material (bedrock)
Gradational Contact
Fresh parent material (bedrock)
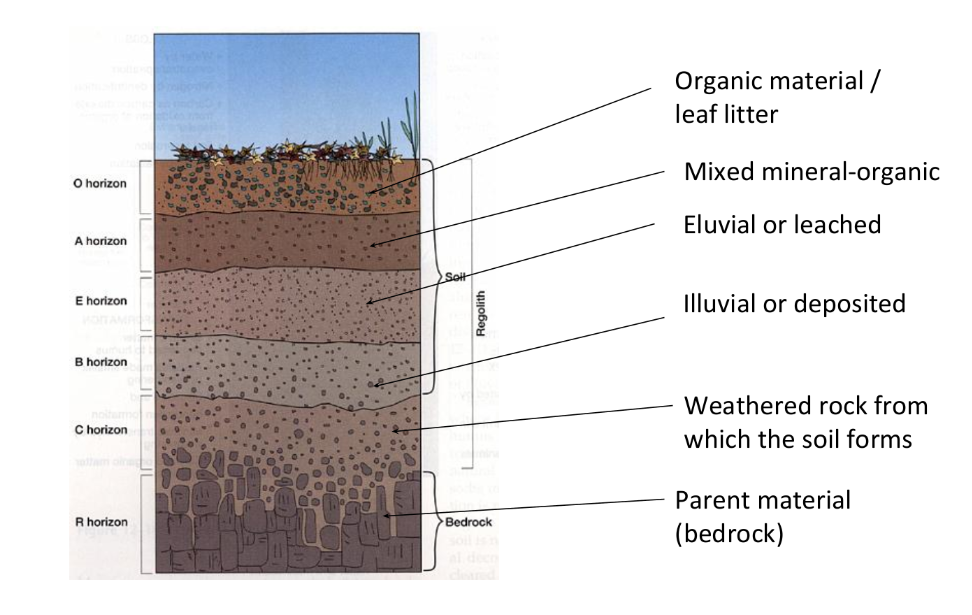
What is included in soil horizons?
O Horizon - Organic material/leaf litter
A Horizon - Mixed mineral-organic (humus layer)
E Horizon - Eluvial or leached
B Horizon - Illuvial or deposited
C Horizon - Weathered rock from which the soil forms
R Horizon - Parent material (bedrock)
The soil system
Soil Structure
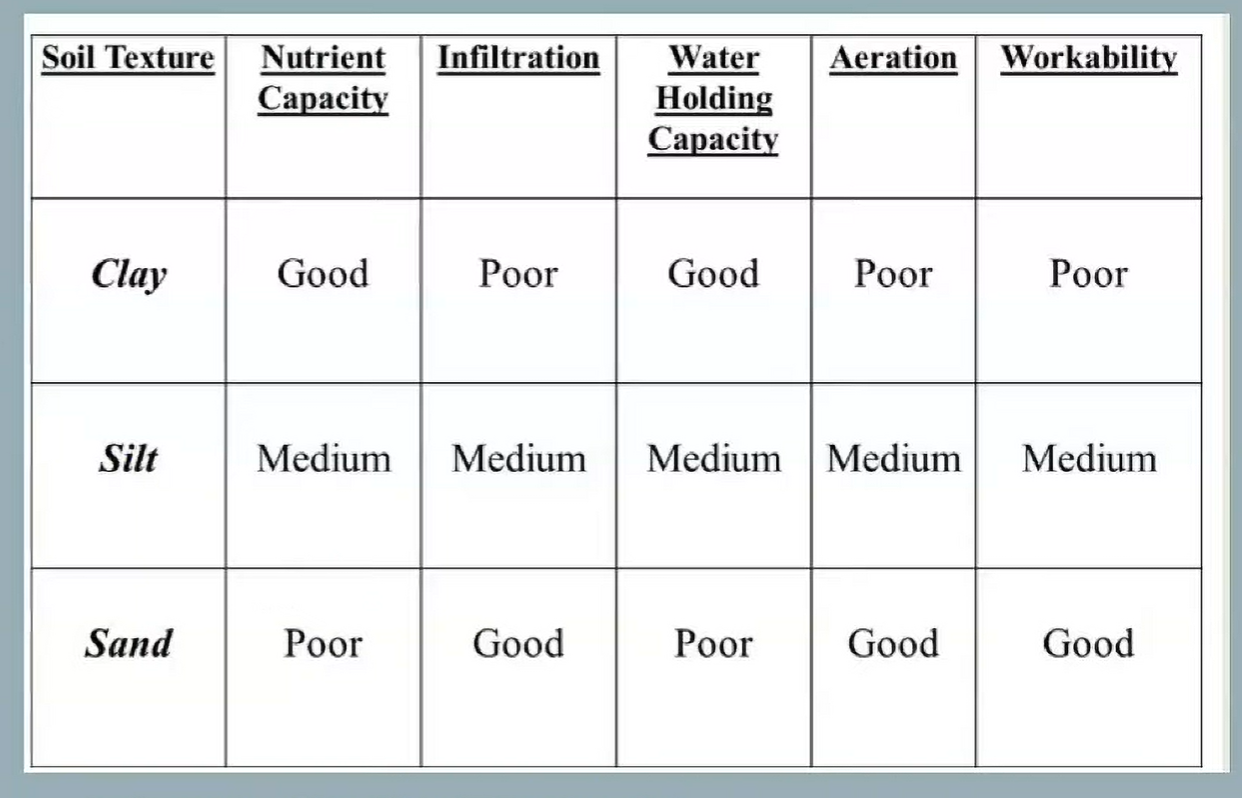
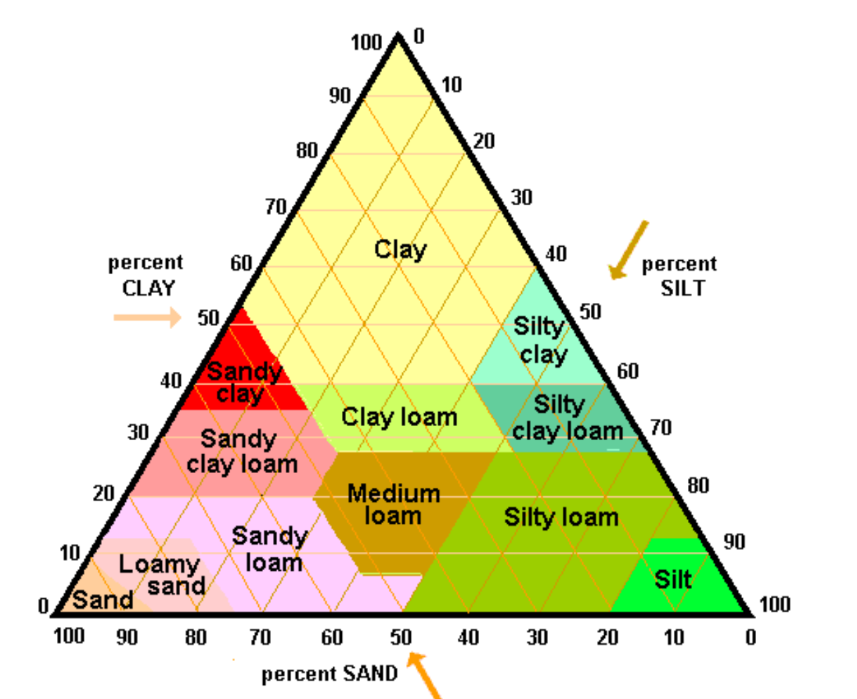
Made up of: Clay, Silt, Sand
Clay Soils are
< 0.002 mm in diameter
consist of very small particles with tiny gaps holding water by surface tension
feel sticky and can be rolled up into a ball easily
rich in nutrients and organic matter
not evenly mixed or easily available to plants
become waterlogged due to poor drainage
poorly aerated
Low primary productivity and low biodiversity
Silty Soils are
0.002 - 0.05 mm in diameter
feel slipper like wet talcum powder and hold together better than sandy soils
Sandy Soils are
0.005 - 2 mm in diameter
gritty and can fall apart easily
have large spaces between large particles (leading to large air spaces) making sandy soil well drained and well aerated
have low nutrient availability to plants because minerals and nutrients are easily washed out (LEACHING)
low biodiversity due to low potential to hold organic matter, low primary productivity and little biota
Loam Soils:
have particles of a variety of sizes
mineral particles are held together by humus which holds water, nutrient ions, and mineral particles
Larger structures made of mineral particles are called “crumbs”
humus contains abundant biota
bacteria and fungi are important in the nitrogen and carbon cycle
soil organisms greatly contribute to soil fertility, removing and digesting detritus from the soil surface and then releasing nutrient ions which roots can take
worm channels improve drainage, help aeration and help root growth
crops grow better in the presence of earth worms
Soil Texture Triangle
Follow the direction of the arrows
Porosity
The amount of space between particles (with relation to a soil’s texture)
Permeability
The ease at which gases and liquids can pass through the soil.
Acidification of soils
Major impact on forestry in Northen Europe where ____ rain cause by industrial pollution has made the soil more ___.
Soil Sustainability
Fertile soil is a non-renewable resource
It is not inert and stable. It develops, evolves, and changes
Soil formation takes 1000s of years
Soil use often exceeds soil formation
Main nutrients in fertile soil
nitrates, phosphates, and potassium. These _____ can be leached out of soil or removed when a crop is harvested
How can nutrients be replaced in agricultural soils?
via chemical fertilizer, growing legumes, crop rotation, or through the application of organicmatter (manure/compost)
O Horizon
Organic material/leaf litter
A Horizon
Mixed mineral-organic (humus layer)
E Horizon
Eluvial or leached
B Horizon
Illuvial or deposited
C Horizon
Weathered rock from which the soil forms
R Horizon
Parent material (bedrock)
Soil pH influences
soil bacteria
nutrient leaching
soil structure
pH in soil
Affects whether the plant can use nutrients or not
Term for low pH soil
Acidic Soil
Term for high pH soil
Alkaline Soil
Compare and Constrast table