microscopic anatomy of the periodontium chpt 2
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
what is a cell
the smallest structural unit of living matter capable of functioning independently
group together to make tissues
4 types of tissues
epithelial tissue
nervous tissue
muscle tissue
connective tissue
ectoderm
enamel
mesoderm
connective tissue, muscle, bone, blood
endoderm
bronchi, alveoli, ducts from gallbladder and pancreas
extracellular matrix
a mesh like material that surrounds the cells
structural and biomechanical scaffold for the cells
holds cells together, provides framework for movement and interaction
consists of ground substance and fibers
basal lamina
rigid
ground substance
gel-like and fills space between cells
fibers
are collagen, elastin and reticular fibers
why is the extracellular matrix rigid?
is undergoes mineralization by the deposition of calcium and phosphate
microscopic anatomy on epithelial tissue
makes up the outer surface of the body
skin and mucosa of mouth are made up of stratified squamous epithelium
lines body cavities
composition of epithelial tissue
cells are plentiful
closely packed cells
bound together in sheets
extracellular matrix is sparse and a minor component
basal lamina supports epithelium
what is keratin
a tough fibrous structural protein that occurs in the outer layer of the skin and the oral epithelium
what is keratinization
process by which epithelial cells on the surface of the skin become stronger and water proof
keratinized epithelial cells
have no nuclei
form a rough, resistant layer on the surface of the skin
most heavily keratinized epithelium is on palms of hands and soles of feet
what applies to hands and mouth applies to rest of the body
if white tissues are in mouth, its due to trauma
non-keratinized epithelial cells
have a nuclei
act as a cushion against stress and wear
are softer and more flexible
found in areas such as the mucosal lining of the cheeks
allows for speech, chewing and facial expressions
characteristics of epithelial tissues
they do not have a blood supply, they are avascular
receive oxygen and nourishment from blood vessels in the underlying connective tissue via diffusion
what is connective tissue?
it fills spaces between tissues and organs
it supports and binds other tissues
its cells are separated by abundant extracellular substance
it has sparse cells
it has lots of extracellular matrix
specialized forms of connective tissue
cementum
dentin
alveolar bone
pulp
enamel is not
connective tissue, it is epithelial tissue
cells in connective tissue
fibroblasts
macrophages and neutrophils
lymphocytes
fibroblasts in connective tissue
are the fiber builders
form the extracellular matrix
secrete ECM into the intracellular spaces
macrophages and neutrophils in connective tissue
phagocytes or “cell eaters”
destroy
devour dyign cells and microorganisms that invade body
lymphocytes in connective tissue
play a major role in the immune response
most important cell in connective tissue
fibroblasts
what type of cell makes fibrin, collagen and elastin
fibroblasts (important in aging)
fibroblasts cannot form collagen without
vitamin c
fibroclasts
produce collagenase, which breaks down tissue and bone (breaks down what fibroblasts build)
cycle of fibroblasts
build - destroy - rebuild
basal lamina
thin layer secreted by epithelial cells
not visible under light microscope
can be seen on electron microscope
can be wavy or smooth
aids in attachment of epithelial cells to adjacent structures
if basal lamina is wavy
it has deep extensions of epithelial ridges of epithelium that reach down into connective tissue
if basal lamina is not wavy
can become wavy if bacteria invade
rete pegs
epithelial ridges
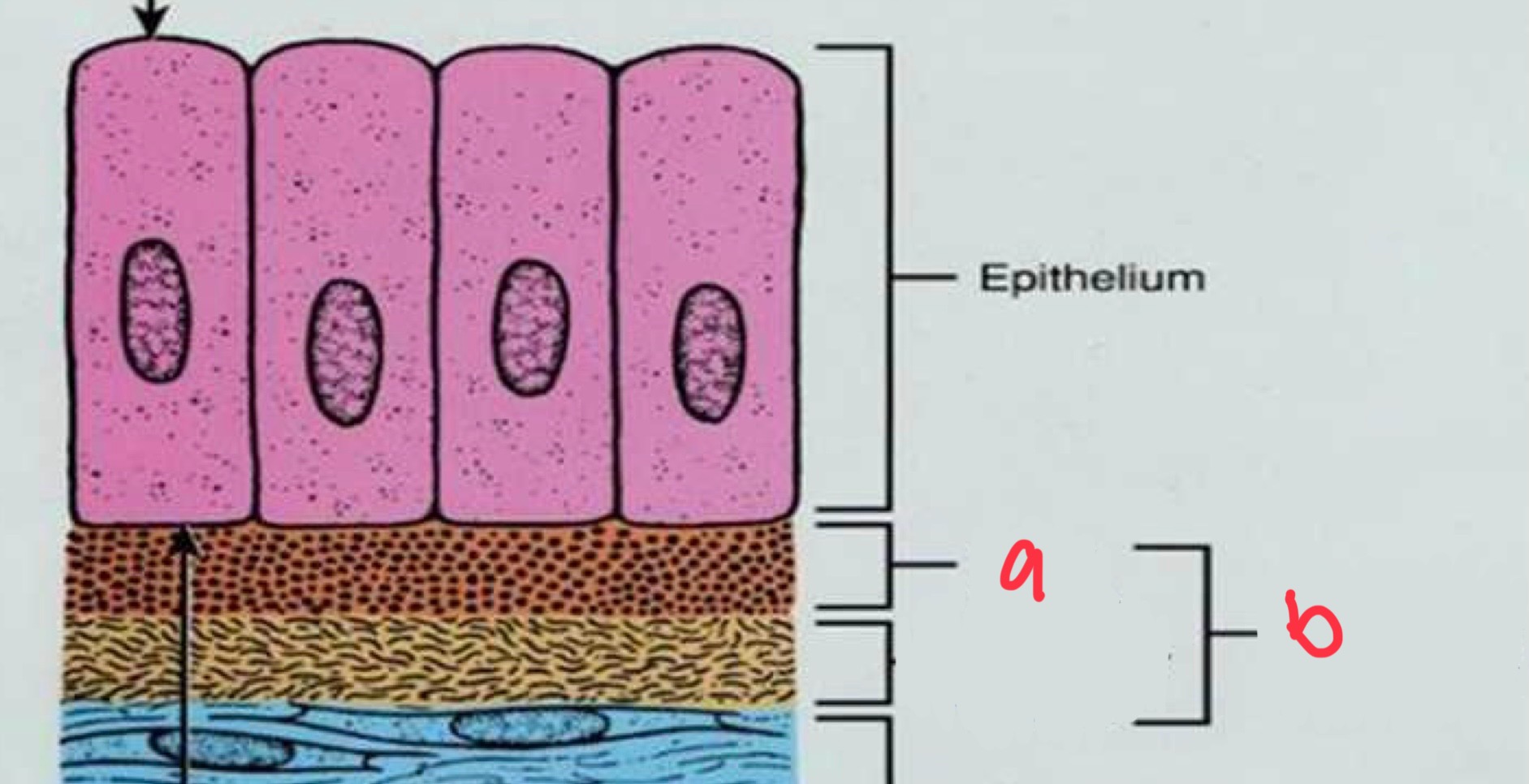
what is a
basal lamina
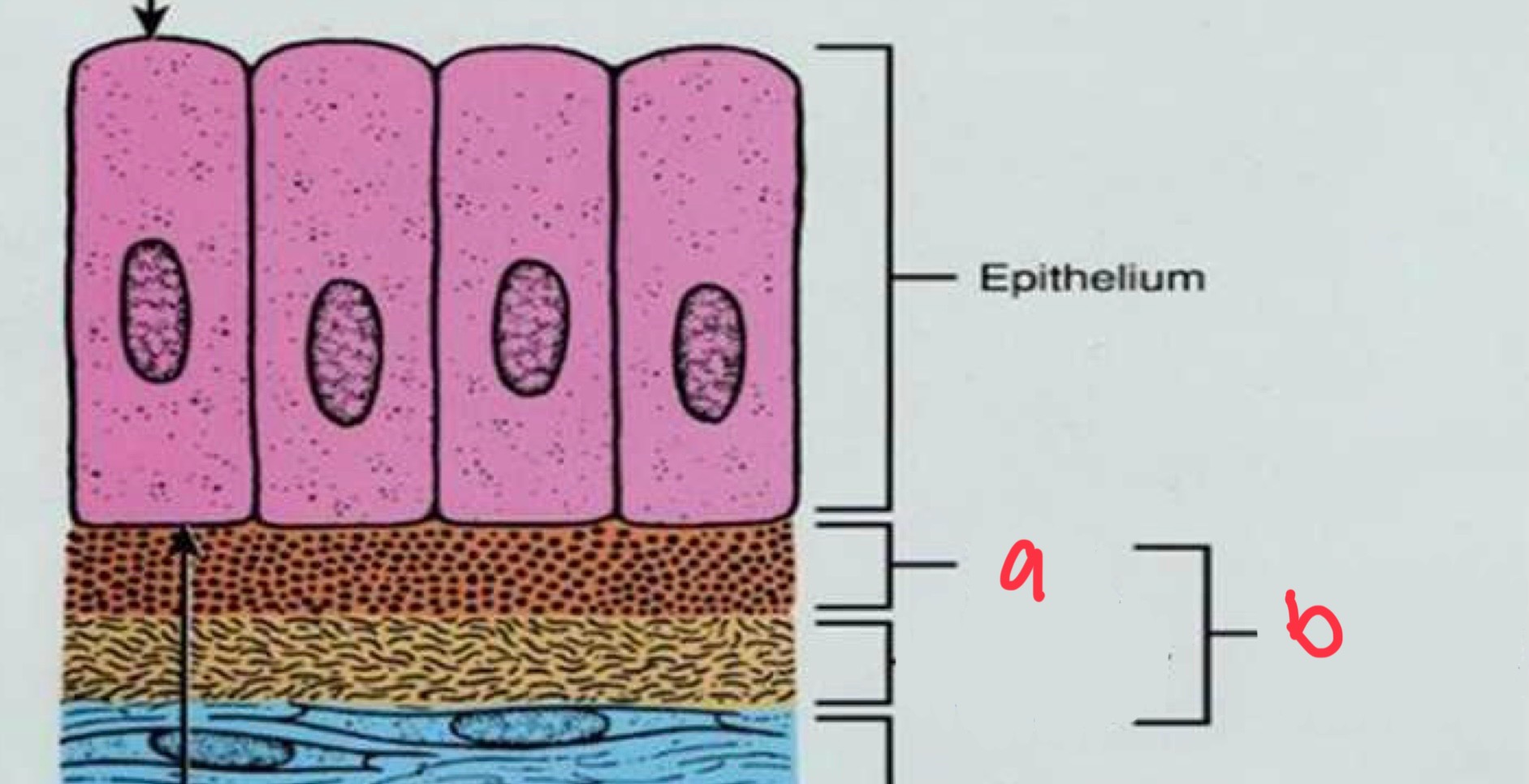
what is b
basement membrane
characteristics of epithelial-connective tissue boundary
wavy, uneven pattern that increases surface area, resists mechanical forces, and increases area to receive nourishment from connective tissue
epithelial ridges at epithelial-connective border
reach down into connective tissue
connective tissue papilla at epithelial-connective border
fingerlike extensions that project up and interlock with epithelium
if tissues in the mouth are sloughing the cause is
loss of hemidesmosomes
squamous cell carcinoma in SITU
did not breach basement membrane
caught before invaded connective tissue and spread
easiest to treat
different from squamous cell which is very invasive
basal cell carcinoma is rarely invasive
what are epithelial cell junctions
cellular structures that mechanically attach a cell and its cytoskeleton to neighboring cells or basal lamina
help withstand mechanical forces and form a protective barrier
2 types of epithelial cell junctions
desmosome
hemodesmosome
hemidesmosomes
connect living to non-living (basal lamina is non-living)
cell - to - basal lamina connection
important form of cell junction found in the gingival epithelium
represents ½ a desmosome
desmosomes
connect living to living (similar to velcro)
cell to cell connection
important form of cell junction found in gingival epithelium
what is gingival epithelium
specialized stratified squamous epithelium
functions well in a wet environment
3 anatomical areas
oral epithelium
sulcular epithelium
junctional epithelium
oral epithelium
covers free and attached gingiva
faces the oral cavity
sulcular epithelium
lines the sulcus
faces the tooth surface without being in contact with the tooth surface
not keratinized
junctional epithelium
base of sulcus
attaches gingiva to tooth or cementum
super thin and easy to break
layers of oral epithelium
basal cell layer
prickle cell layer
granular cell layer
keratinized cell layer
basal cell layer of oral epithelium
cube-shaped cells
prickle cell layer of oral epithelium
spine-like cells with large intracellular spaces
granular cell layer of oral epithelium
flattened cells and increased intracellular keratin
keratinized cell layer of oral epithelium
flattened cells with extensive intracellular keratin
sulcular epithelium - lining of the gingival sulcus
thin, nonkeratinized epithelium
has 3 cellular layers
basal
prickle
superficial
permeable, allowing fluid to flow from gingival connective tissue into the sulcus
fluid is known as gingival crevicular fluid
fluid flow is slight in health and increases in state of disease
sulcular epithelium
junctional epithelium
forms base of sulcus and joins gingiva to tooth surface
surrounds cervix of tooth
easiest point of entry for bacteria
base of sulcus made up of coronal-most cells of junctional epithelium
in health, JE attaches to tooth slightly above CEJ
thin, nonkeratinized
sulcular and junctional areas provide easiest entry for bacteria to inve connective tissue
2 layers
basal
prickle
thicker at coronal zone and thin at apical zone
smooth tissue interface
why is junctional epithelium important?
the teeth create a break in the epithelial covering
this break creates an opening for microorganisms to enter the body
body tries to seal opening by attaching epithelium to the tooth
this junction or “connection” is called the junctional epithelium
JE provides a protective barrier between plaque biofilm and connective tissue
epithelial cells defend periodontium from infection bu signaling the immune response
components of the junctional epithelium
layers of closely packed epithelial cells
desmosomes and hemidesmosomes
sparse ECM
internal basal lamina
thin, between JE and tooth surface
external basal lamina
thin, between JE and gingival connective tissue
hemidesmosomes enable
cells to attach to the internal basal lamina and surface of the tooth
attachment of the hemidesmosomes and the internal basal lamina is not static
cells can move along the tooth surface
components of gingival connective tissue
provides solidity to gingiva
attaches gums to cementum of the root and alveolar bone
few cells
abundance of ECM
3 types of cells
gingival connective tissue has 3 types of cells
fibroblasts (macrophages)
mast cells (neutrophils)
immune cells (lymphocytes)
in the gingival connective tissue the fibroblasts
produce (build) fibers
ECM is composed of
collagen fibers
fibroblasts
vessels
nerves
what is the matrix mainly produced by?
fibroblasts
what cells are embedded in the matrix
connective tissue cells
ECM is essential for
maintenance of normal function of connective tissue
ECM is responsible for
transportation of water, nutrients, metabolites, oxygen, etc.
collagen fibers in ECM form
dense network of strong, rope-like cables that secure and hold connective tissues together
collagen fibers in ECM enable
gingiva to form a rigid cuff around the tooth
monocytes turn into macrophages
once they go into tissue from blood
macrophages eat
bacteria, dead tissue, and spent RNA
longer life expectancy than neutrophils
macrophages
neutrophils
make up 70% of white blood cells
macrophages and neutrophils
neutro. are like EMS 1st responders
macro. follow 2 days later
then neutro. dies and pus is created
what are supragingival fiber bundles
a network of rope-like collagen fiber bundles
supragingival fiber bundles are located
coronal to the crest of the alveolar bone
embedded in the gel-like ECM
supragingival fiber bundles functions
strengthen and reinforce attachment to JE to tooth
brace free gingiva against tooth
provide rigidity to free gingiva needed for chewing
unite free gingiva with cementum and alveolar bone
connect adjacent teeth to one another
fiber bundles are classified
based upon orientation, sites of insertion and structures that they connect
course of gingival fiber bundles
dentogingival
coronal
horizontal
apical
alveologingival
interpapillary
transgingival
circular, semicircular
transseptal
periosteogingival
intercircular
intergingival
principal fiber groups
dentogingival
alveogingival
dentoperiostal
transseptal
secondary fiber groups
periosteogingival
interpapillary
transgingival
intercircular
semicircular
intergingival
alveogingival fiber group
extend from periosteum of alveolar crest into gingival connective tissue
circular fiber group
circle tooth like a ring; not attached to cementum
dentogingival fiber group
embedded in the cementum near CEJ; fan out; attach gingiva to teeth
peristeogingival fiber group
extend from periosteum of alveolar bone; attach gingiva to bone
intergingival fiber group
extend mesiodistally along entire arch and around last molars; link adjacent teeth into a dental arch unit
intercircular fiber group
encircle several teeth; link adjacent teeth in dental arch
interpapillary fiber group
located in papilla above transseptal fiber bundles; connect oral and vestibular interdental papilla
transgingival fiber group
extend from cementum near CEJ; run horizontally between teeth
transseptal fiber group
pass from cementum of 1 tooth, over crest of alveolar bone, cementum of adjacent teeth; secure ligaments of teeth
last to be destroyed
PDL
thin sheet of fibrous connective tissue
surrounds roots of teeth
adjoins the root cementum with the socket wall via bundles of collagen fibers
thickness of space approx. 0.05 - 0.25 mm
thickness depends of age of patient and function of tooth
very sensory, can detect biting on thinnest things
cells in the PDL are mainly
fibroblasts with some cementoblasts and osteoblasts
most important function of the PDL
supportive- to anchor the tooth to the socket and to separate the tooth from the socket wall
sensory function of the PDL
supplied with nerve fibers that transmit pressure and pain
nutritive function of the PDL
supplied with blood vessels that provide nutrients to cementum and bone
formative function of PDL
contains cementoblasts that produce cementum throughout life of tooth; osteoblasts maintain bone of socket
resorptive function of PDL
cells can induce rapid bone resorption in response to severe pressure
5 fiber groups of the PDL
alveolar crest
horizontal
oblique
apical
interradicular
alveolar crest fiber group of PDL
extend for cervical cementum to alveolar crest; run downward; resists horizontal movement of tooth and prevents tooth displacement