chapter 3.2-5 (lecture slides)
1/228
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
229 Terms
Cytoplasm
Includes cytosol and organelles.
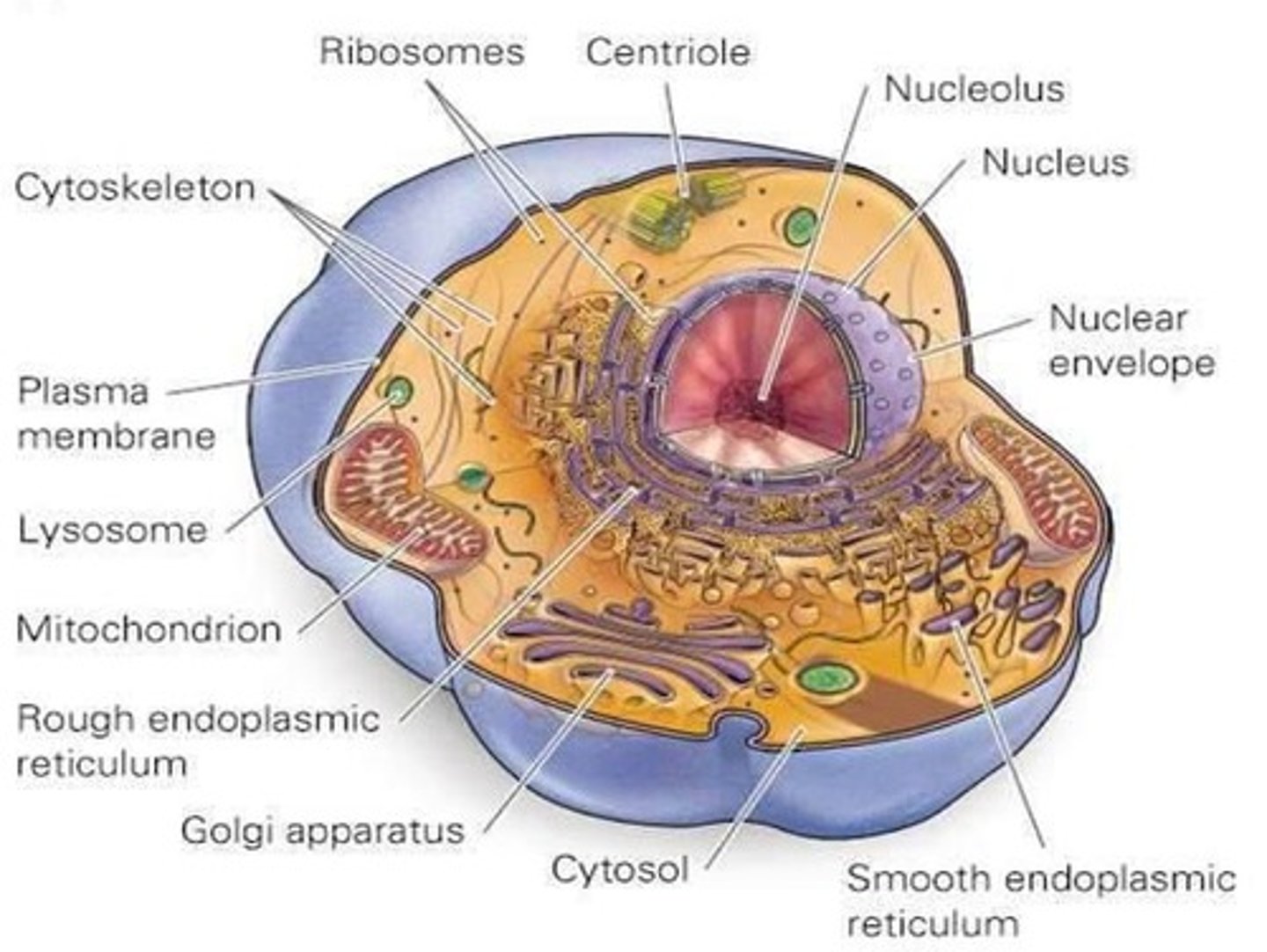
Organelles
Perform specific jobs required by the cell and work with other organelles.
Cytosol
Watery matrix with salts and enzymes; houses the organelles.
Plasma membrane
Encloses all cells and defines the outer boundary of cells.
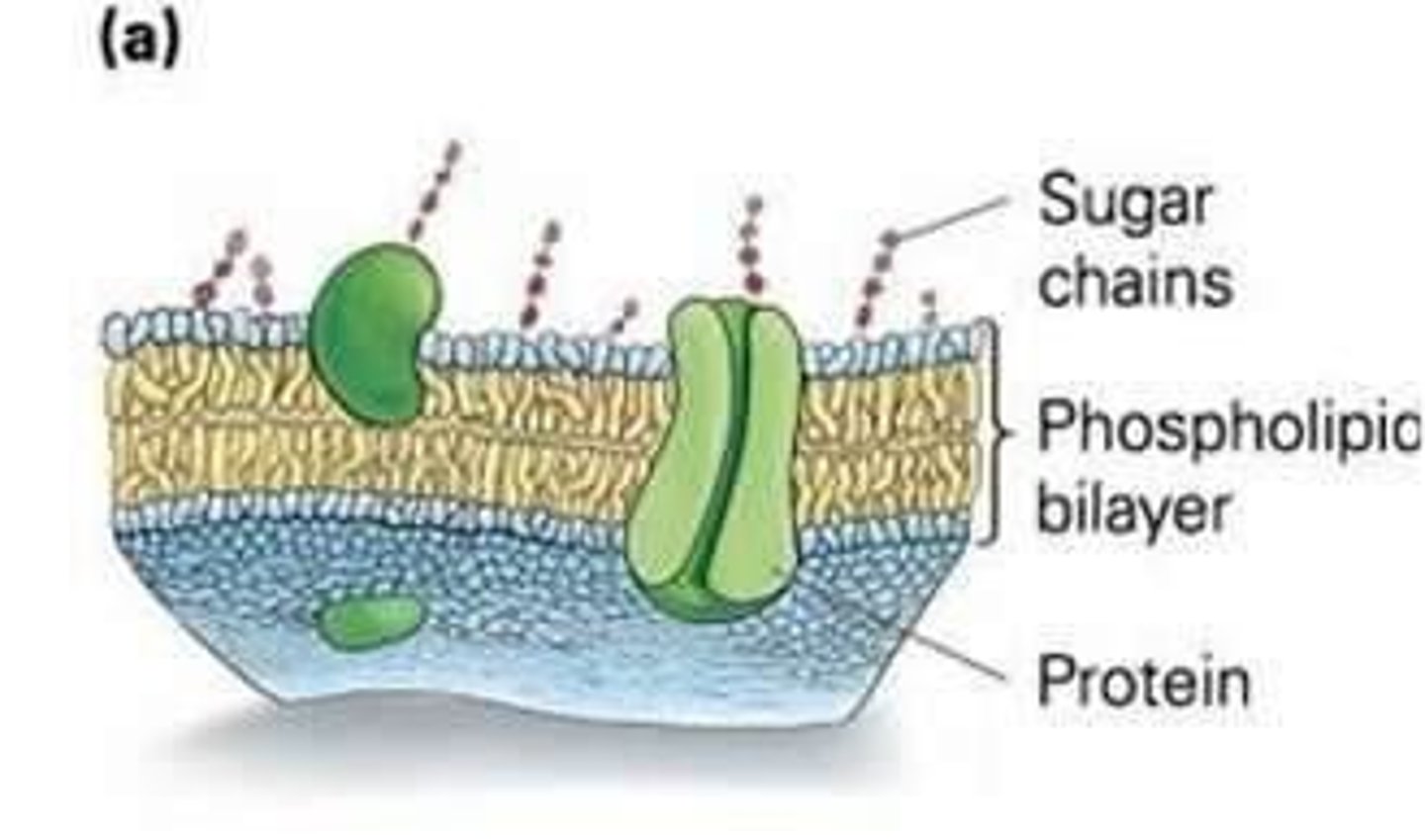
Plasma membrane
Isolates cell contents from the environment.
Plasma membrane
Determines materials to be allowed in or out.
Semipermeable
Some molecules can cross and some are prevented from crossing.
Membrane structure
Fluid properties allow lipids and proteins to slide laterally.
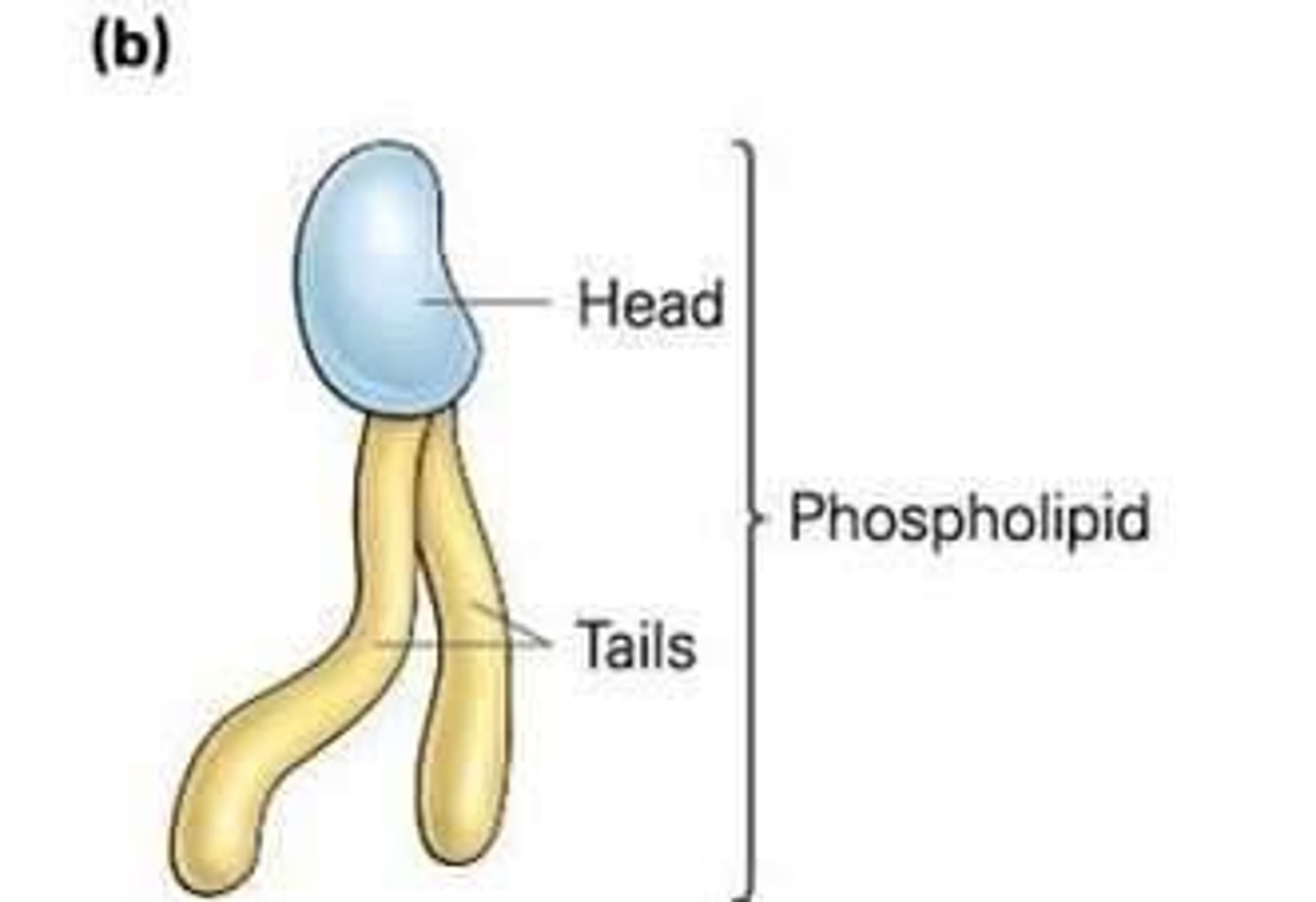
Phospholipid bilayer
Hydrophilic heads maximize exposure to water and hydrophobic tails interact with each other; exclude water.
Embedded proteins
Carry out enzymatic functions, serve as receptors for outside substances, and help transport substances throughout the cell.
Cell wall
Protection outside the plasma membrane for plants, fungi, and bacteria; provides structural support.
Nucleus
Holds chromatin (DNA and proteins) in eukaryotic cells; surrounded by nuclear envelope.
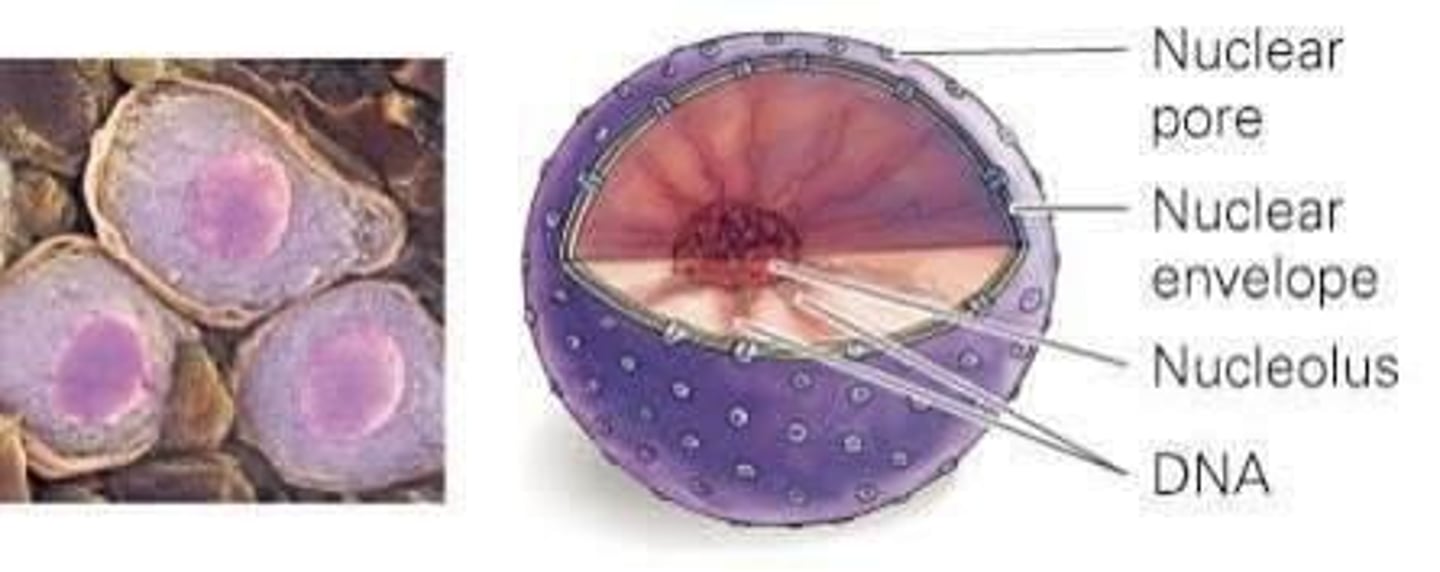
Nucleolus
Synthesizes ribosomes; inside nucleus.
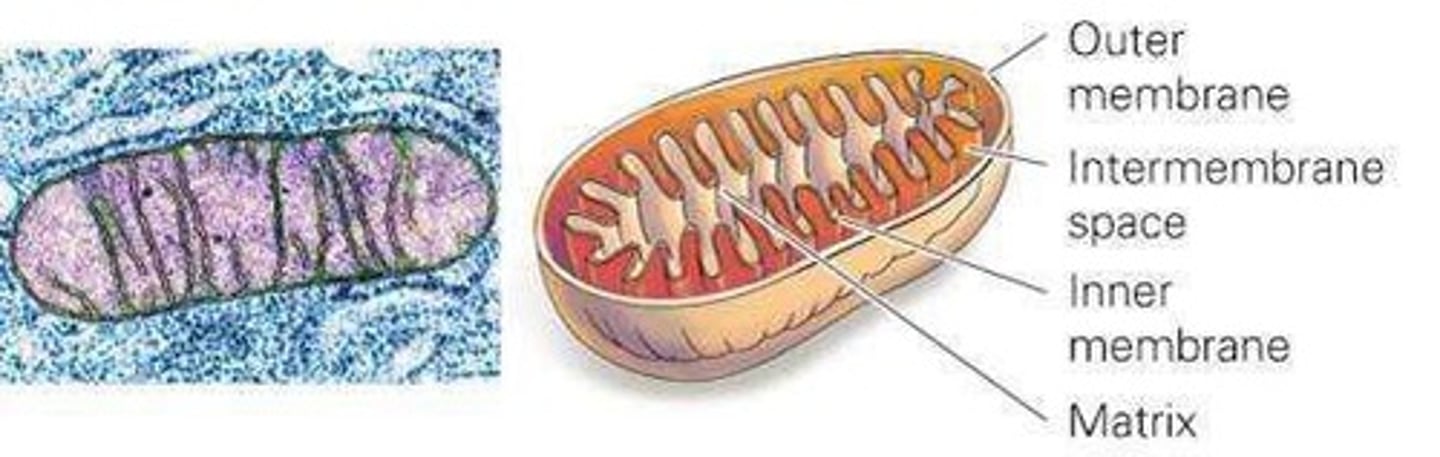
Mitochondrion
Produces energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
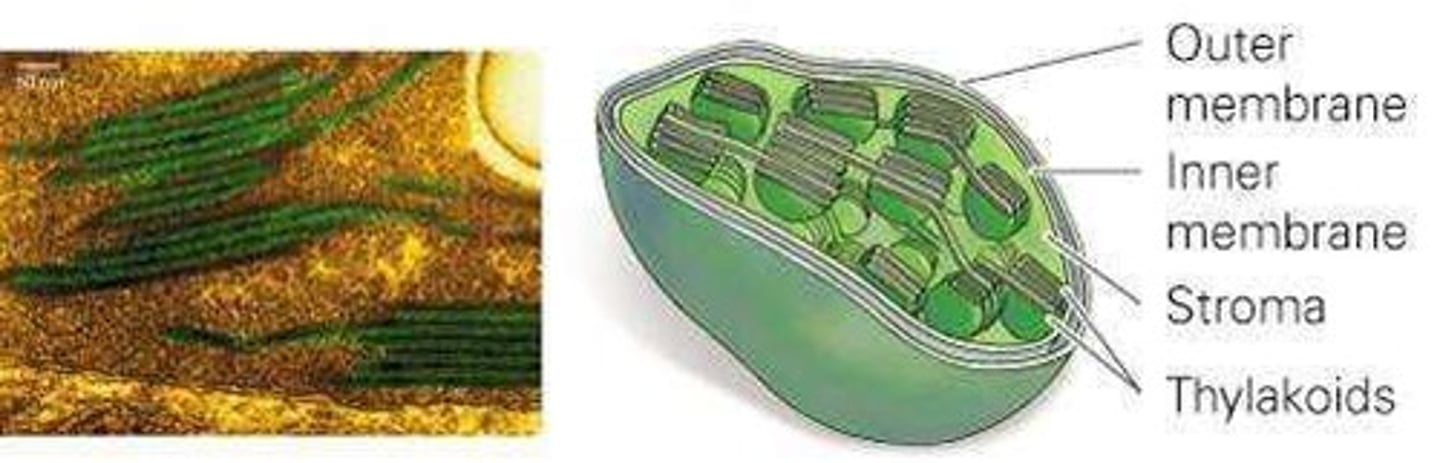
Chloroplast
Produces sugars through photosynthesis in plant cells.
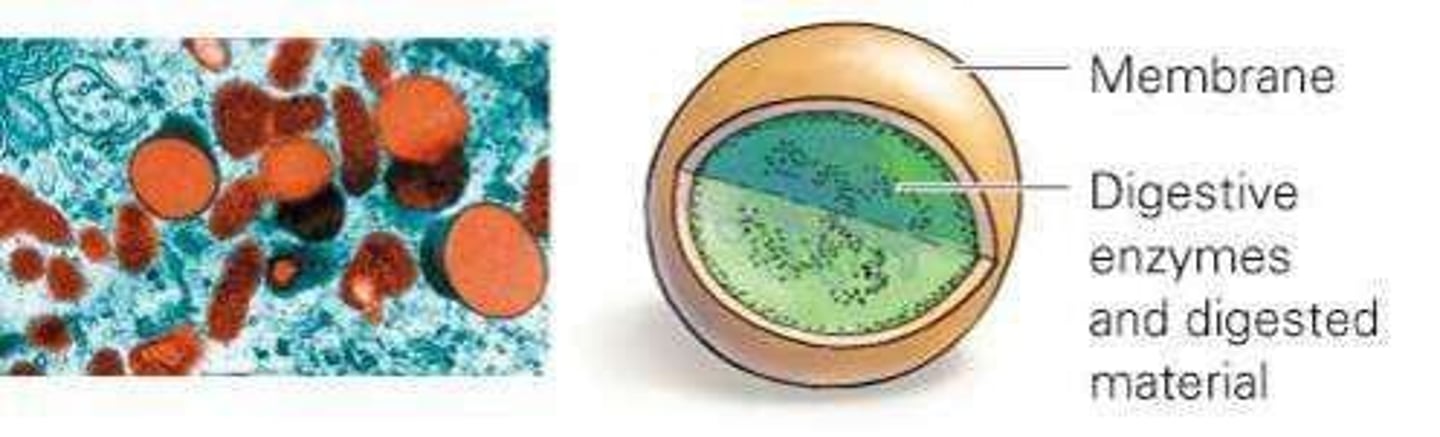
Lysosome
Contains digestive enzymes to recycle molecules.
Ribosomes
Assemble proteins; free floating or attached to ER.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER)
Membrane network with ribosomes attached for protein synthesis.
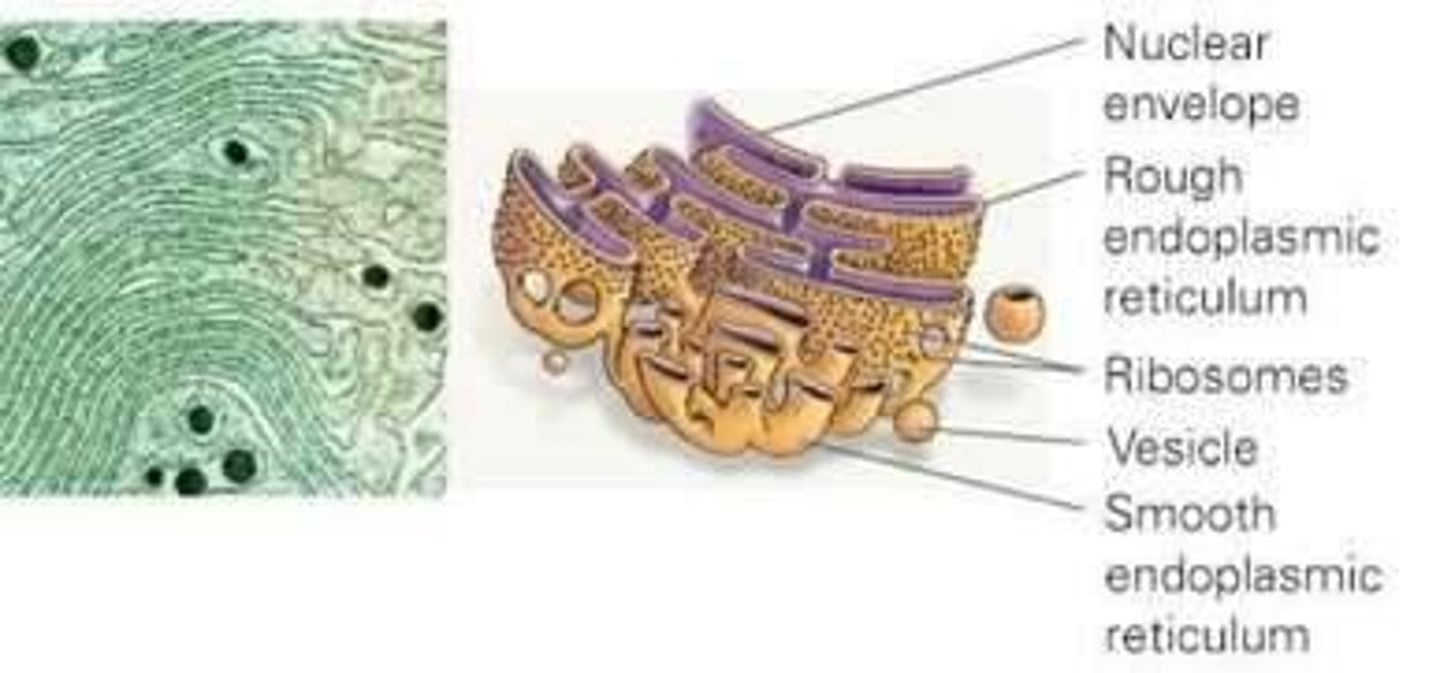
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER)
Involved in lipid synthesis or detoxification; lacks ribosomes.
Golgi apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins.
Centrioles
Move chromosomes during animal cell division.
Cytoskeletal elements
Form cytoskeleton for maintaining shape and structural support.

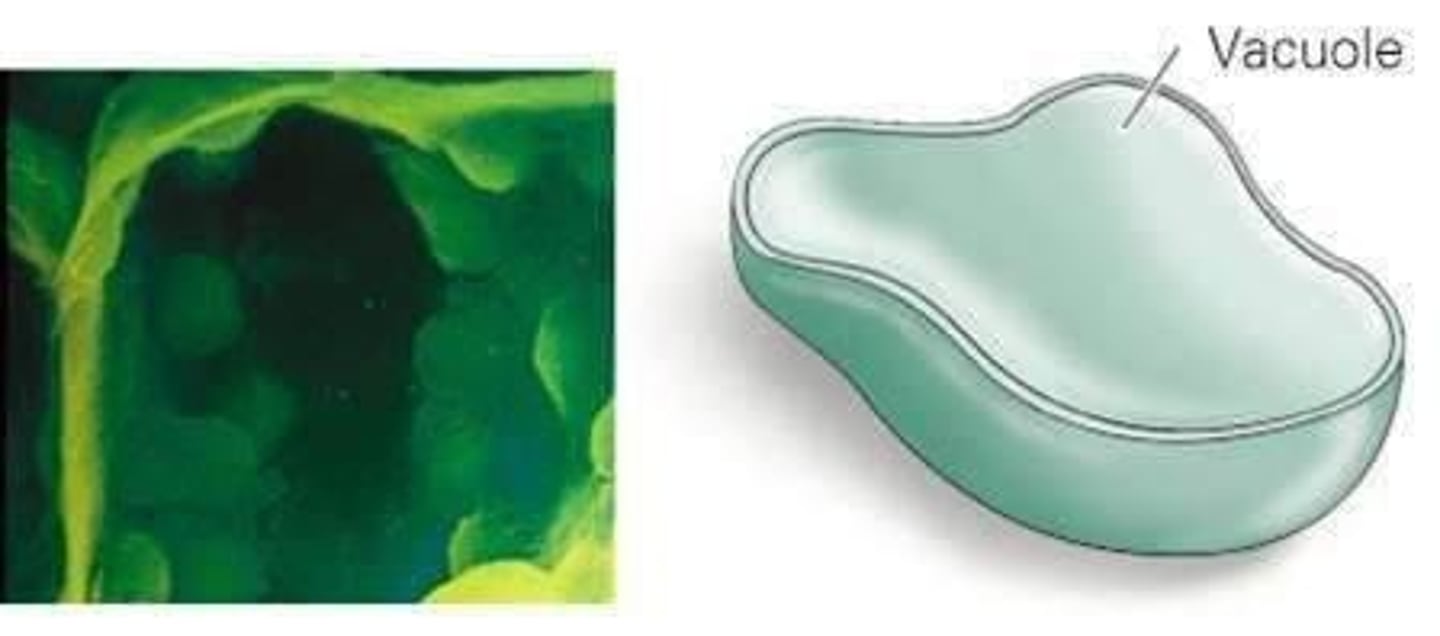
Central vacuole
Stores water, sugars, and pigments in plant cells.
Chlorophyll supplements
Marketed as energizing, detoxifying, and healing wounds; no evidence supports the marketing claims.
Creatine
Used in protein synthesis and cellular respiration; effects of supplementing not well studied.
Liquid supplements
Elite cyclists ingested during a 1-week training camp; one group had only carbohydrates and the other group had protein and carbohydrates.
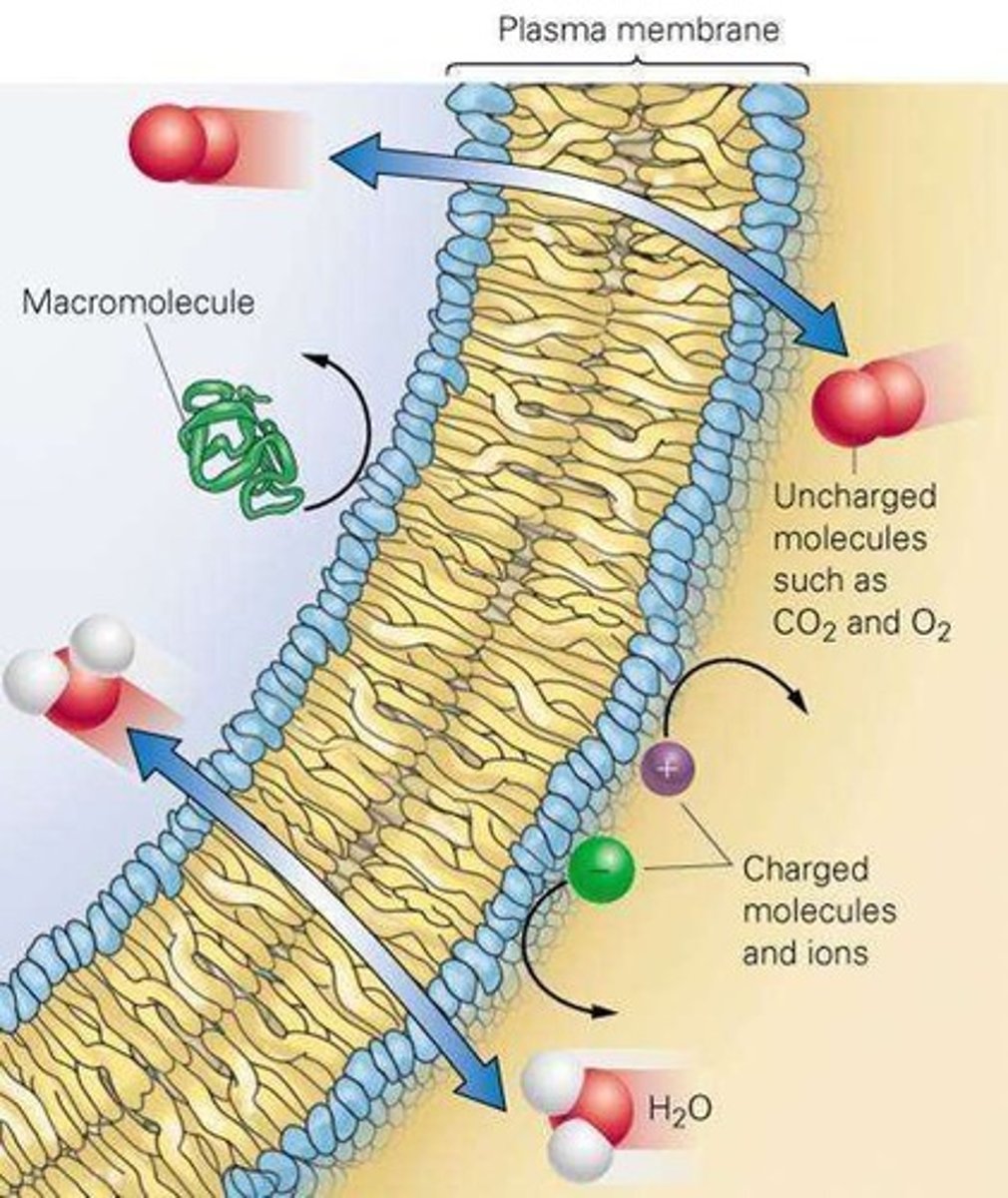
Membrane transport
Substances must travel through the plasma membrane.
Equilibrium
Substances able to cross reach equilibrium - equal concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
Plasma membrane
Phospholipid bilayer that is differentially permeable.
Hydrophobic substances
Pass more easily through the hydrophobic interior of the plasma membrane.
Passive transport
Movement of molecules without energy.
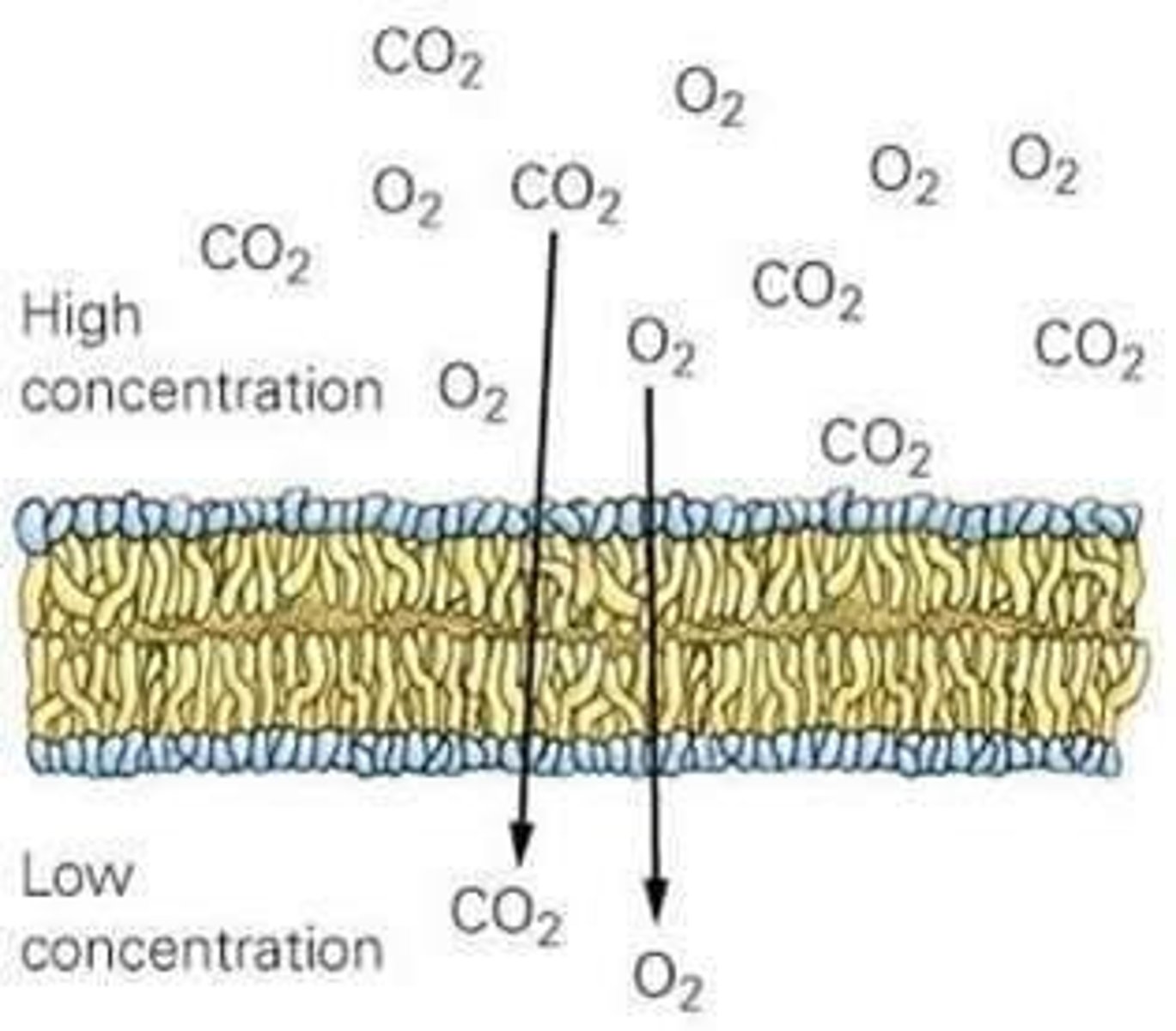
Diffusion
Passive transport from area of high concentration to low concentration.
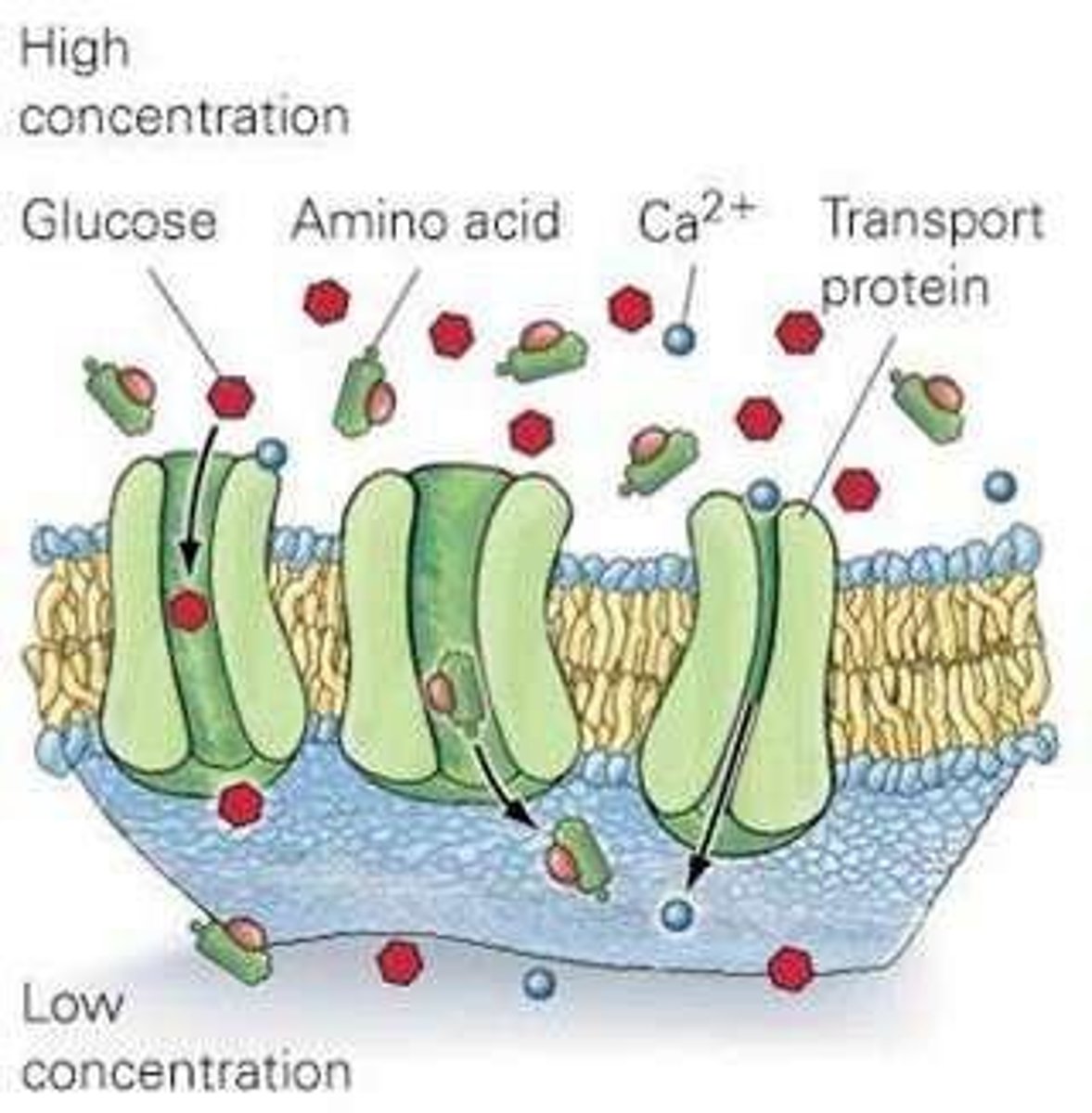
Facilitated diffusion
Transport proteins help move hydrophilic and charged molecules across the membrane from high to low concentration without using energy.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a membrane from high to low concentration.
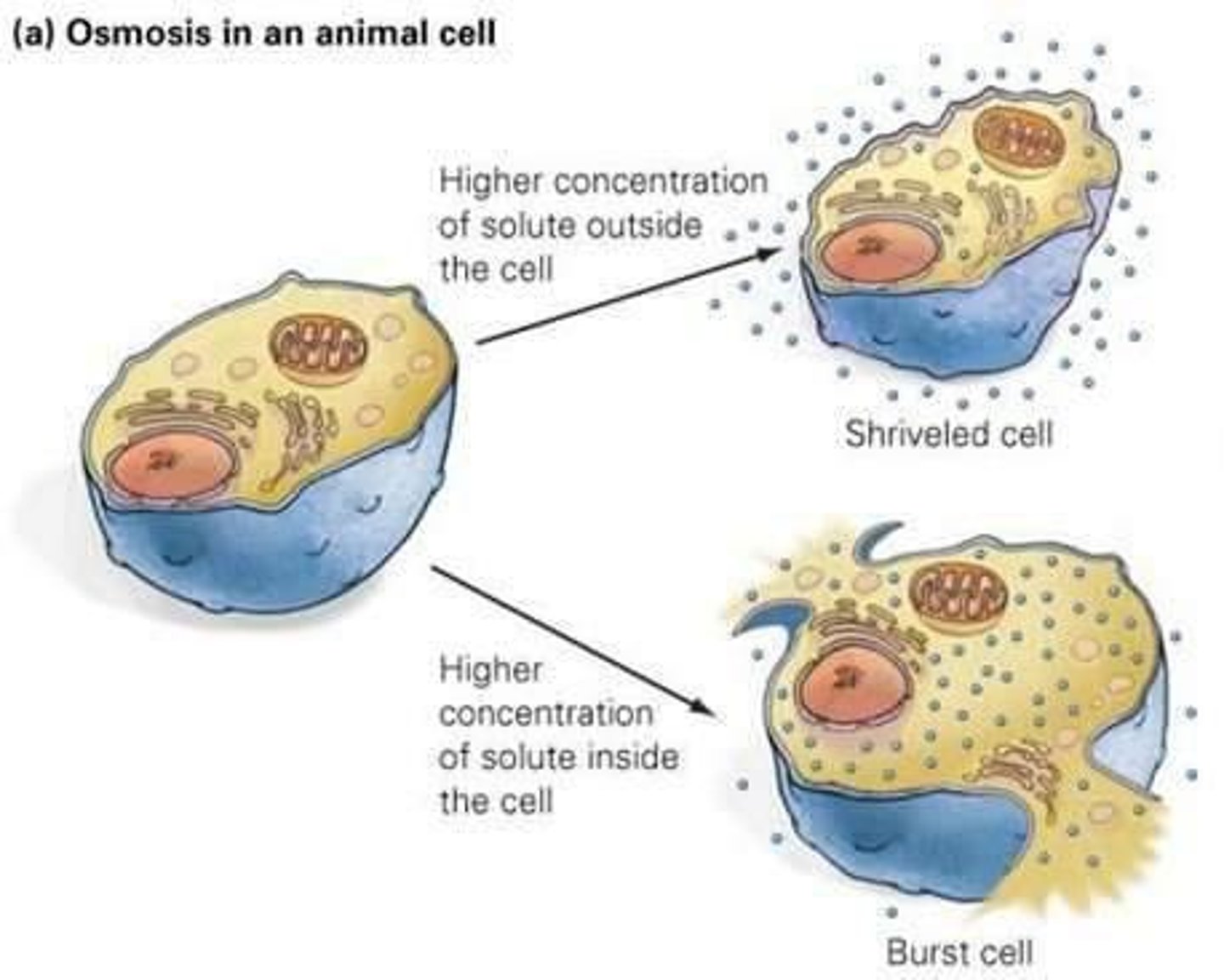
Active transport
Uses proteins to move molecules from low to high concentration, powered by energy from ATP.
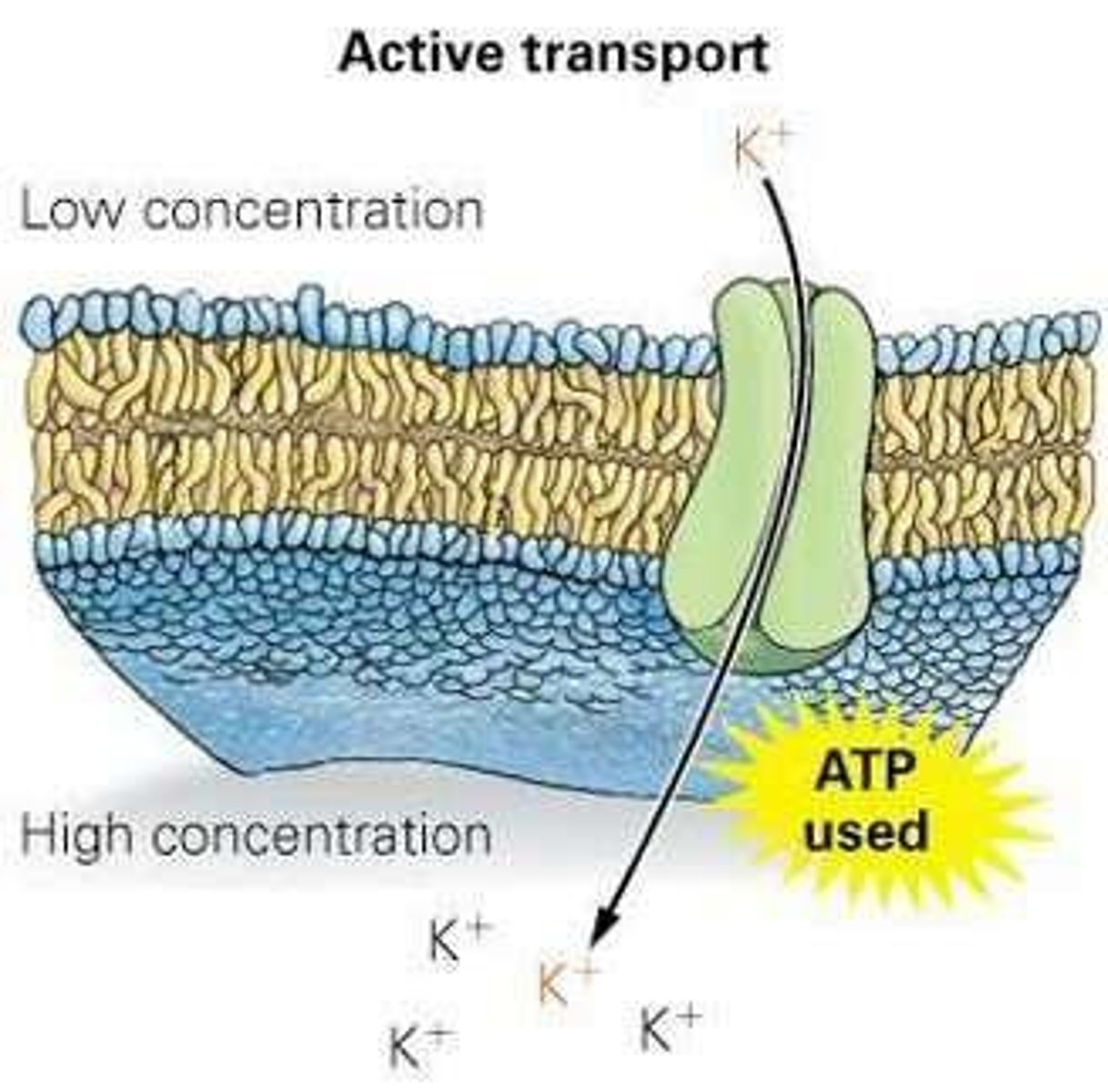
Exocytosis
A membrane-bound vesicle fuses with the membrane and expels the large molecule outside the cell.
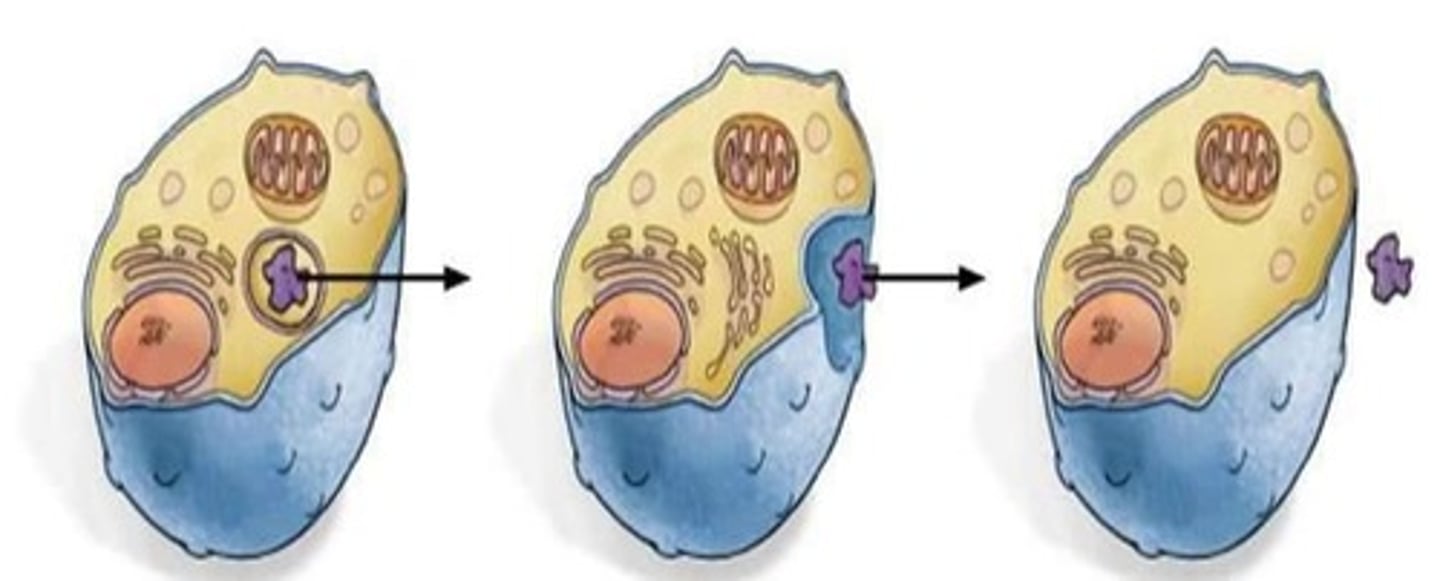
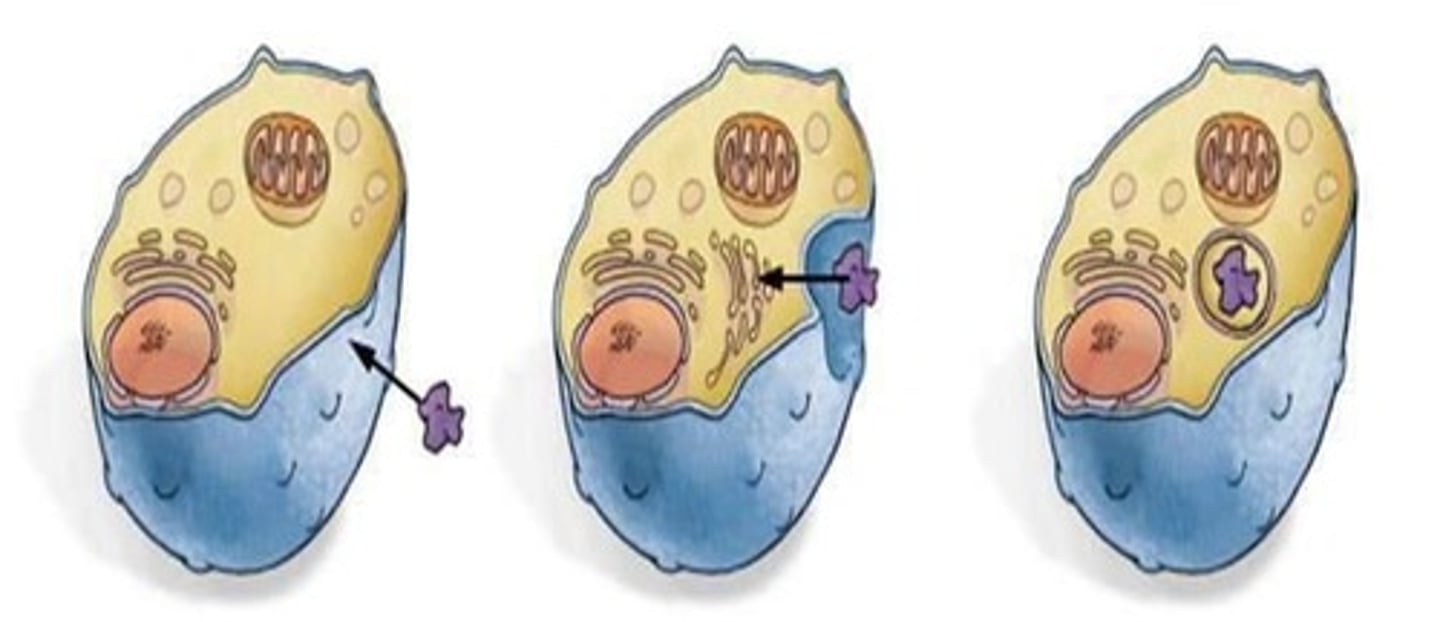
Endocytosis
A vesicle pinches the plasma membrane inward and brings a large molecule into the cell.
Transport proteins
Proteins that assist in moving hydrophilic molecules through the plasma membrane.
Hydrophilic molecules
Molecules that are attracted to water and require transport proteins to cross the plasma membrane.
Concentration gradient
The difference in concentration of a substance across a space.
ATP
A molecule that provides energy for active transport processes.
Saltwater effect on cells
Osmosis will cause water to move out of the cell when placed in saltwater.
Nutrients role in the body
Essential for various bodily functions.
Function of water in the body
Vital for maintaining homeostasis and facilitating biochemical reactions.
Major dietary macronutrients
Include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, each serving distinct functions in the body.
Major dietary micronutrients
Include vitamins and minerals that are crucial for various physiological functions.
Structure and function of the plasma membrane
Composed of a phospholipid bilayer that regulates the entry and exit of substances.
Structure and function of subcellular organelles
Organelles perform specific functions within the cell, contributing to overall cellular operation.
Distinction between passive and active transport
Passive transport does not require energy, while active transport does.
Processes of endocytosis and exocytosis
Endocytosis brings substances into the cell, while exocytosis expels substances out of the cell.
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions occurring in the body
Enzymes
Proteins that catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions
Activation energy
Energy required to start a metabolic reaction
Induced fit model
Substrate: chemical being metabolized; Active site: enzyme region where substrate binds; Enzyme changes shape after substrate binds, stressing the substrate bonds
Enzyme specificity
Each enzyme catalyzes a particular reaction based on enzyme shape and active site shape
Metabolic rates
The measure of a person's energy use, depends on speed and efficiency of different enzymes, and changes according to activity levels
Basal metabolic rate (BMR)
The energy use of a resting wakeful person, average BMR is 70 calories/hour or 1680 calories/day
Factors influencing metabolic rate
Exercise, Biological sex, Genetics
How do enzymes affect metabolic reactions?
Enzymes decrease the activation energy of a reaction
Enzyme naming convention
Enzymes are named for the reaction catalyzed and end in the suffix -ase
Example of an enzyme
Sucrase breaks down sucrose
Unique enzyme shapes
Result from varying sequences of amino acids determined by genes
Relevance of body weight
Discuss the relevance of body weight as a predictor of healthfulness
Anaerobic respiration
Describe how anaerobic respiration differs from aerobic respiration
Cellular respiration process
Describe the process of cellular respiration from the breakdown of glucose through the production of ATP
Proteins and fats breakdown
Explain how proteins and fats are broken down during cellular respiration
Is Being Overweight Unhealthy?
A. Yes; B. No
Metabolic rate
The rate at which metabolism occurs in a living organism, influenced by factors such as exercise, biological sex, and genetics.
Exercise
A factor that increases metabolic rate during and after physical activity.
Biological sex
A factor influencing metabolic rate, with males requiring more calories due to higher muscle mass and testosterone levels.
Testosterone
A hormone that increases the rate of fat breakdown in males.
Genetics
A factor that can lead to lower basal metabolic rates and differences in fat storage and utilization.
Cellular respiration
A series of metabolic reactions converting food energy into a usable form and releasing waste products.
Chemical bonds
Structures that store energy in electrons and produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) when broken.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
A molecule containing adenine, ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups, serving as an energy carrier in cells.
Phosphorylation
The process of transferring a phosphate group from ATP to another molecule, resulting in energy transfer and the production of adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
ATP and cellular work
ATP is used for movement of cells, active transport of substances across membranes, and making complex molecules.
Regenerating ATP
The process where cellular respiration adds a phosphate group to ADP to regenerate ATP.
Complete the Equation for Cellular Respiration
The equation for cellular respiration is glucose + oxygen yields carbon dioxide + water.
Aerobic cellular respiration
A type of cellular respiration that requires oxygen and occurs in three stages, primarily in the mitochondria.
Breathing
The process of inhaling oxygen into the lungs and exhaling carbon dioxide.
Stages of cellular respiration
Cellular respiration occurs in three stages, involving the removal of electrons from glucose and their use to make ATP.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
A coenzyme that acts as a taxicab for electrons during cellular respiration.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
Taxicab for electrons.
Empty taxicab (NAD+)
Picks up electrons and hydrogen ions (H+).
Full taxicab (NADH)
Carries electrons to final destination.
Stages of cellular respiration
Includes Stage 1: Glycolysis, Stage 2: Citric acid cycle, Stage 3: Electron transport chain and ATP synthesis.
Glycolysis
6-carbon glucose molecule broken down into two 3-carbon pyruvic acid molecules; occurs in the cytosol; doesn't require oxygen; produces 2 ATP.
Citric acid cycle
Series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in the mitochondrial matrix that continues the breakdown of glucose fragments, produces 2 ATP, and releases carbon dioxide.
Electron transport chain
Series of embedded mitochondrial proteins that act as a conveyor belt for electrons.
Hydrogen ions (H+)
Concentration decreases in mitochondrial matrix and increases in intermembrane space; charged ions can't diffuse across the membrane and escape through protein channel, ATP synthase.
ATP synthase
Protein channel through which H+ ions pass to synthesize ATP.
Hydroelectric Dam Analogy
Water passes through turbine; mechanical energy converted to electricity, analogous to H+ ions passing through ATP synthase.
ATP production
26 ATP molecules synthesized during the process.
Metabolism of other nutrients
If carbohydrates and fats are unavailable, proteins may be used; amino group is removed and other components enter the citric acid cycle.
Fat metabolism
If carbohydrates are unavailable, fats may be used; glycerol and fatty acids enter the citric acid cycle.
Anaerobic respiration
Metabolic process to generate energy without oxygen, possible in certain cells like muscle cells.
Muscle cells
Usually produce ATP by aerobic respiration; intense exercise depletes oxygen supply, leading to ATP from glycolysis only.
Fermentation
Process that regenerates NAD+ levels during anaerobic conditions.
Pyruvic acid
Product of glycolysis that loses carbon dioxide and is metabolized inside mitochondrion.