4.4, 4.5, 4.8 atmosphere, wind patterns
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
atmosphere
The mixture of gases that surrounds earth. Broken into 5 distinct layers.
Troposphere
The lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere; where most of earth's weather occurs
Stratosphere
The second-lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere. Contains beneficial ozone (O3) molecules that block UV radiation.
Mesosphere
The 3rd layer of Earth's atmosphere; immediately above the stratosphere
Thermosphere
The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere. It is by far the thickest layer of earth's atmosphere. It blocks harmful X-ray and UV radiation, and the northern lights (aurora borealis) occur in this region
Exosphere
The outer layer of the thermosphere, extending outward into space.
Hadley Cell
Convection Currents that cycle between the equator, 30 degrees North and South. Warm air at equator rises, cools & expands, rains, spreads out, and then sinks back down to earth @ 30 degrees North & South
Coriolis effect
The effect of Earth's rotation on the direction of winds and ocean currents. Deflects winds to the left between 0 and 30 degrees; to the right between 30 and 60 degrees
Trade winds
prevailing winds that blow from east to west between the equator and 30 degrees N & S
Westerlies
prevailing winds that blow from west to east between 30 and 60 degrees N & S
Equator
An imaginary circle at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North Pole and the South Pole; where the suns rays strike earth most directly
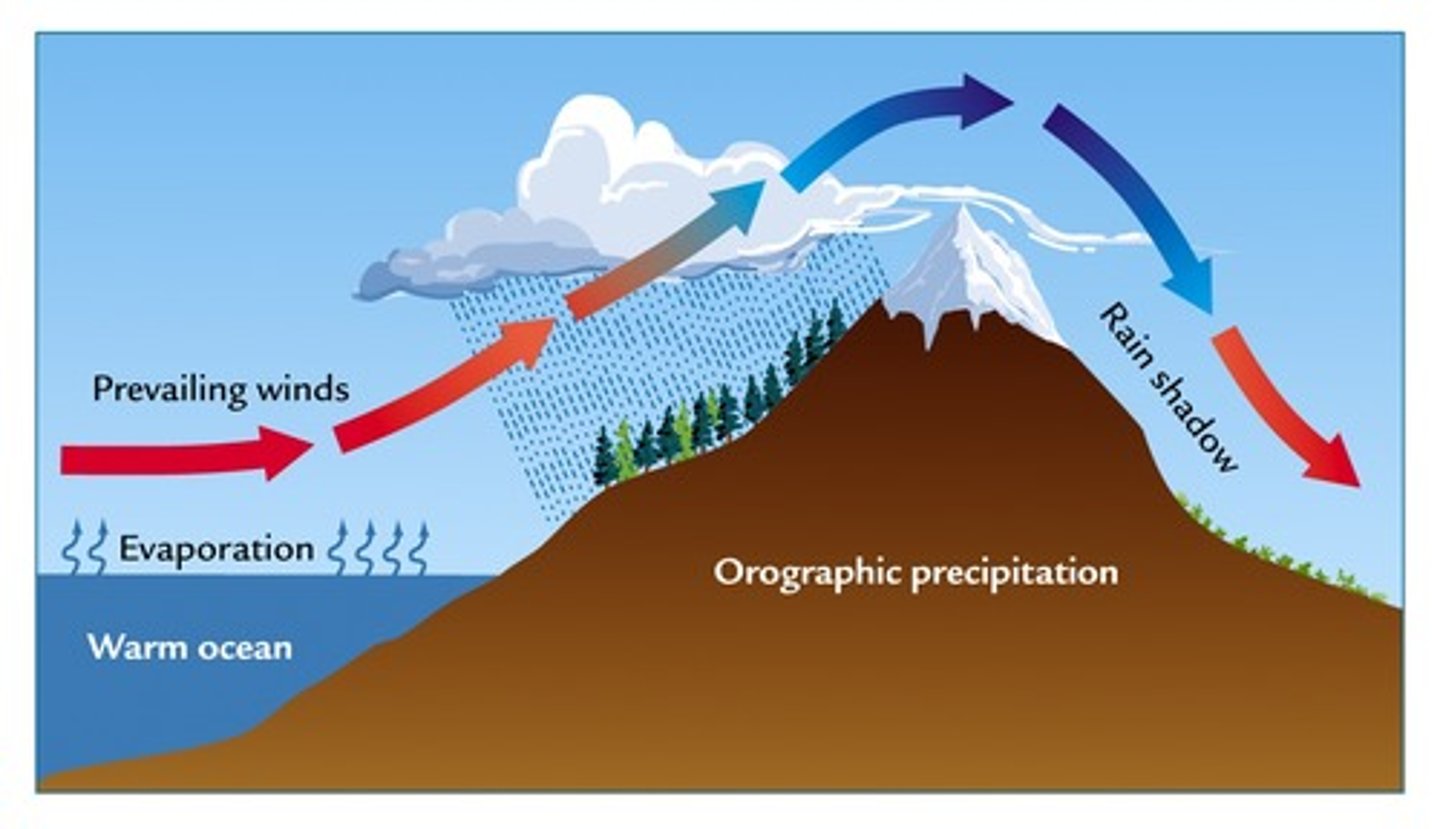
rain shadow effect
High precipitation on the windward side of a mountain range, resulting in lush vegetation & a warm, moist climate on that side, but a desert area on the leeward (opposite from the wind) side.
ITCZ (intertropical convergence zone)
A region of low pressure near the equator where air masses meet. Also known as the doldrums.
Air Property: Moisture
Warm air holds more moisture than cold air
Air Property: Density
Warm air is less dense than cold air, so it rises
Air Property: Pressure
As air rises, it is under less atmospheric pressure, so it expands and cools