Inorganic Chemistry
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is the reason for the first dip in the trend in first ionistation energy of period 3?
Removing an electron from 3p subshell instead of 3s2 subshell which means less energy is needed to remove electron as its furthur from nucleus
What is the reason for the second dip in the trend of first ionisation energy of period 3?
Electron is removed from 3p subshell that has 2 electrons in orbit which leads to electron-electron repulsion making it easier to remove an electron
Explain the trend in first ionisation energy down a group
First ionisation energy decreases down the group as atomic radius increases therefore elctron shielding increases decreasing the attraction between outer electrons and neclus making it easier to remove an electron.
Explain the trend in melting point down group 2
The melting point decreases down the group as positive ions grow larger and further apart weakening the metallic bond between them so does not require a lot of energy to overcome.
What is the trend in the solubility of group 2 hydroxides down the group
The solubility increases
What is the use of calcium hydroxide?
It is used in agricultire to neutralise acids in soil
What is the use of magnesium hydroxide?
It is used as medicine to remove excess stomach acid
What is the trend in Group 2 sulfates down a group?
Solubility decreases
What is the use of barium sulfate and why?
It is ingested and used for x-rays as it does not enter the bloodstream
What is the test for sulfate ions and why must be acidified?
Add acidified barium chloride to sample to form a white precipitate. It must be acidified to prevent barium reacting with anything else
Explain the trend in melting point down group 7.
Melting point increases due to increase in van der waals forces as electron number increases requring more energy to overcome
What is electronegativity?
The ability for an atom to attract a pair of electrons towards itself in a covalent bond
Explain the trend in electronegativity down group 7
As atomic radius increases there is more electron shielding wehich reduced the attraction between nucleus and delocalised electrons, therefore electronegaticity decreases
Explain the oxidising ability down group 7
Oxidising ability decreases down grouo 7 due to increase in atomic radius therefore increase in electron shielding which decreases nucleur attraction between nucleus and free electrons
Explain the reducing ability down group 7
Reducing ability increases down group 7 due to icnrease in atomic radius which results in an increase in electron shielding resulting in weaker attraction between outer electrons and nucleus therefore its easier to lose an electron
What is the reaction of chlorine with cold aqeous water?
Cl2(g) + H20(l) = HCL(aq) + HCLO(aq)
What is the reaction of chlorine with sodium hydroxide?
CL2(g) + 2NAOH(aq) = NaCl(aq) + NaCLO (aq) + H20(l)
What is the test for halides?
Add silver nitrate to sample, chlorine = white ppt, bromine = creamy ppy, iodine = yellow ppt
Test for halides with dilute ammoniaa
chlorine - dissolves bromine - insoluble iodine - dissolves
Test for halides with concentrated ammonia
chlorine - dissolves bromine - dissolves iodine - insoluble
Test for ammonia ions
Add sodium hydroxide to test tube and put red litmus paper in it. Red litmus paper goes blue for true. Mae sure test tube is placed in a beaker full of water on placed over a bunsen burner for gas sodium hydroxide gas to be produced
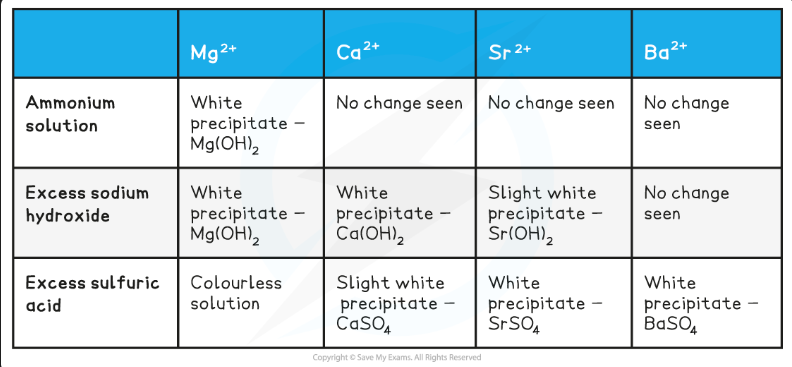
Test for Group 2 ions. Write it down on whiteboard from memory