Clinical Trials
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
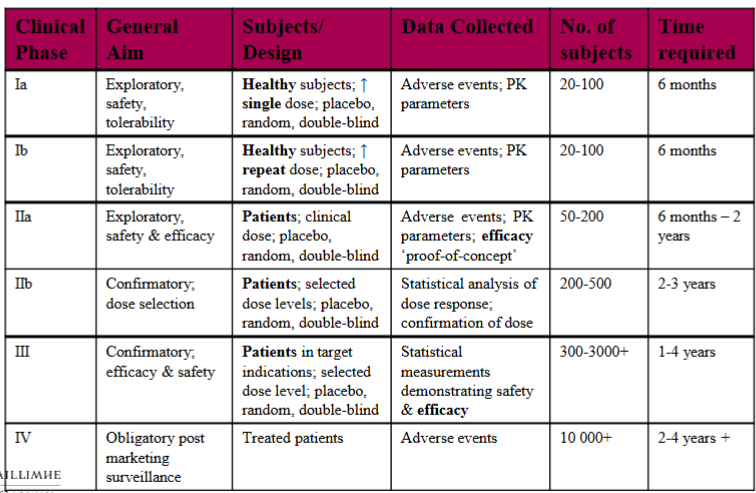
Fill in the phases of clinical development of a drug
Scientific method of clinical trials

What does PICO stand for
Population
Intervention
Control/Comparison
Outcome
What is PICO used for
A framework to formulate specific, answerable clinical or research questions and guide literature searches for evidence-based practice and systematic reviews.
Which of these is not a characteristic of a phase 3 trial
• Randomization to groups
• Placebo controlled
• Compared against current best treatment
• Most funded by pharmaceutical industry
• Well-defined protocol
• Results submitted to Regulatory Authorities
Trick question - they are all characteristics of a phase 3 trial
Name 3 Sources of Funding
Pharmaceutical companies: responsible for organizing the great majority of clinical trials.
National Health Organizations: MRC (UK), NIH (USA): Only justified for trials of major treatment issues.
Locally based trials: No external backing. The best of such studies can provide important source of new therapeutic ideas, but many are poorly organized
IND and NDA are 2 important stages of regulation for new drugs. What do they stand for & what is their purpose
Investigational New Drug (IND) for first in human studies.
New drug Application (NDA) for launching on to the market
What is the regulatory authority in Ireland for new drugs
Health Products Regulatory Authority (HPRA)
What is the regulatory authority in the EU for new drugs
European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA)
What kind of problems can arise with historical trials
Potential incompatibility with patient selection and patient environment
Who is blind in double blind trials
Neither the patient nor those responsible for care and evaluation know which treatment they are receiving
Belmont Report principles
Respect for persons, the requirement to treat individuals as autonomous agents, and the requirement to protect those with diminished autonomy.
Beneficence, maximizing possible benefits and minimizing possible harms.
Justice, as demonstrated by fairness in distribution of the opportunity to participate in research
What are some advantages & disadvantages to multi-centre trials

In a publication of findings (trial report) what steps are missing?
• Title
• Introduction: Why did you start?
• Methods: What did you do?
• Results: What did you find?
• Title
• Summary
• Introduction: Why did you start?
• Methods: What did you do?
• Results: What did you find?
• Discussion: What does it mean?
If a trial has negative results, are they posted
Yes - all results add to medical knowledge
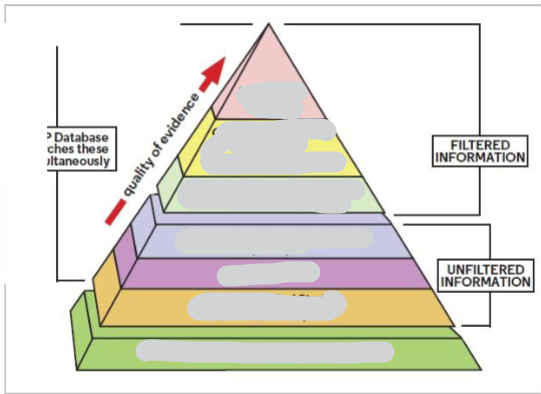
Fill in the Evidence based medicine pyramid
Clinical opinion: based on experience/expertise
Case reports: a finding from a single patient
Case series: a number of cases
Case-control studies: a retrospective study that compares subjects who have a condition (cases) with patients who do not (controls)
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs): prospective investigations of effects where groups are assigned before treatment begins
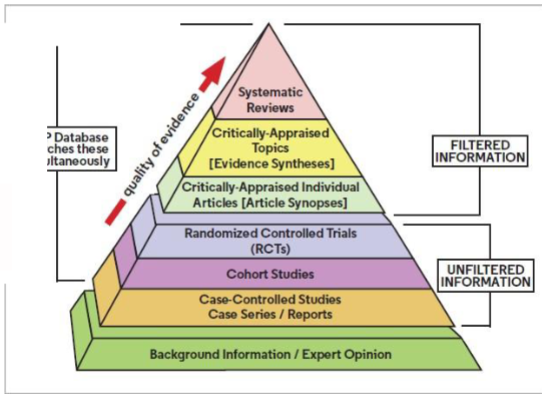
Meta-analysis
A statistical technique that combines numerical data from multiple studies
When are meta-analyses used
It is an optional part of a systematic review.
Used if data from multiple studies are suitable to combine.
(Know difference between this and a systemic review - Systematic Review: A structured, comprehensive review of all relevant studies on a specific research question. Meta-Analysis: A statistical technique that combines numerical data from multiple studies.)
What is a Forest Plot used for
It combines data from systematic reviews and shows their potential to improve healthcare
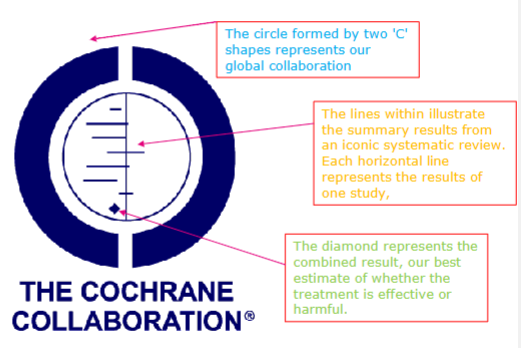
What does each arrow point to in this Forest Plot and Cochrane logo