Adaptations, interdependence and competition .1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
what is an ecosystem
the interaction between a community of living organisms and their environment.
what is a community
two or more populations of organisms.
what is a population
all the organisms of the same or closely-related species in an area.
Levels of organisation within an ecosystem
Producer
Primary consumer
Secondary consumer
Tertiary consumer
what are the producers
plants + algae which photosynthesise
what are the primary consumers
herbivores which eat producers
what are the secondary consumers
carnivores which eat primary conusmers
what are the tertiary consumers
carnivores that eat secondary consumers
what is the top animal in the feeding relationship called
apex predators
If the population of one organism rises or falls…
then this can affect the rest of the ecosystem
example of a simple food chain
grass → rabbit → fox
if foxes were killed what would happen to the rabbits and grass
population of rabbits would increase bc they are no longer a prey to the foxes
grass would decrease bc increase of rabbits would be eating it
what is interdependence
refers to the fact that all organisms living in an ecosystem depend on each other
competition - plants
all photosynthesising plants and algae in an ecosystem compete for light, space, water and minerals from the soil
competition - animals
compete for food, mates + their territory
what happens to organism that have more resources
tend to grow more healthy and more likely to have off spring
what two things can competition be
interspecific (competition between organisms not in the same species.)
or intraspecific (competition between organisms within the same species.)
what is a stable community
one where the size of the population of all species remains constant over time
what is the number of organisms in an ecosystem and their distribution is affected by
abiotic factors
These are factors that are non-living
what are some examples of abiotic factors (8)
light intensity
temperature
moisture levels
soil pH content
soil mineral content
Wind intensity and direction
Carbon dioxide levels for plants
Oxygen levels for aquatic animals
light intensity
some plants have evolved for optimum growth in bright sunlight (eg. cactus)
whilst other have evolved for optimum growth in shade (eg. many orchids)
if you were to put these two plants in opposite environments they wouldn’t grow very well + eventually die
temperature
both animals and plants have evolved ti grow healthily at their optimum temperatures
eg. polar bears in very cold areas and cactus in hot areas
moisture levels
many houseplants are killed by ppl overwatering/under-watering them
many plants cannot survive in waterlogged soils - roots unable to respire + they rot + plant dies
other plants (eg. pitcher plants) grow best where moisture levels are high
use a soil moisture meter to determine accurately how wet an area is
soil pH content
pH of soils have huge affect on plant grown on them
some plants (eg. azaleas) grow best in acidic soils + will quickly die if placed in alkaline soils
some can grow in both (eg. hydrangea) - flower colour changes in soil
(just like universal indicator paper) hydrangea flowers are blue in acidic soils and pink in alkaline soils.
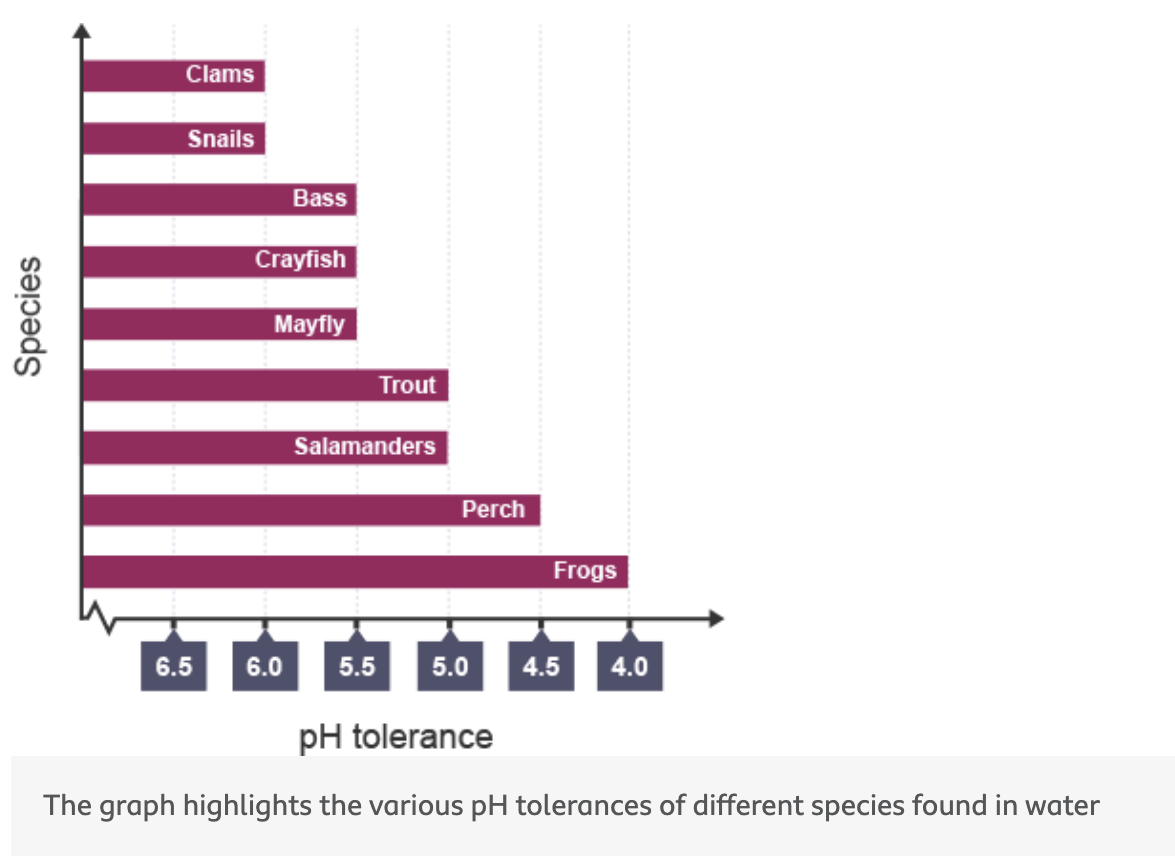
also Different species have evolved to survive at different pH levels found within water.
soil mineral content
many plants require high levels of soil minerals to grow (eg, magnesium required to produce chlorophyll)
plants w unnaturally yellow leaves may have a magnesium deficiency.
Carnivorous plants (eg. pitcher plants) have evolved to catch insects to supplement the low levels of minerals found in the soils in which they grow.
wind intensity and direction
has huge impact on where organisms are found within ecosystems
many organisms prefer more sheltered locations - plant seed more likely to germinate + animals will live close to plants they depend on
strength of the wind can also affect the growth of individual organisms
Carbon dioxide levels for plants
reactant in photosynthesis so plants need it to survive
Areas with higher levels of carbon dioxide are more likely to have healthy plants growing.
Farmers often release carbon dioxide within their greenhouses to maximise their crop yield
Woodlands often have higher carbon dioxide levels than open grassland, so many plants living in open areas have evolved mechanisms to overcome a shortage of carbon dioxide.
Oxygen levels for aquatic animals
Oxygen from the air and oxygen produced by aquatic plants dissolves in water.
Without this, aquatic animals would suffocate and die.
Healthy lakes and rivers = high levels of oxygen
polluted waters = low levels of oxygen
pollution → certain species can survive there such as sludgeworms
what are bioindicator species
their presence or absence informs us about the condition of the habitat.
what is the abundance and distribution of organisms affected by
biotic factors
living factors
examples of biotic factors
Availability of food
New predators
New pathogens
Out-competition
availability of food
major factor in ecosystem - all animals require food
areas like forests have more species of life as its got more rich food supply than deserts/polar regions
new predators
can have a devastating affect
In balanced ecosystems, predators and prey have evolved together.
Predators can catch enough prey to survive, but not so many that they kill all of their food.
Introducing new predators can cause a rapid decline in the numbers of prey, which then reduces the food supply for existing predators.
new pathogens
When organisms inhabit new ecosystems they often bring new pathogens
eg, when europeans visited native americans + introduced viruses meaning lots died
Pathogens have also been introduced on purpose
eg. Myxomatosis(disease affecting rabbits) cause to develop skin tumors + blindness
purposefully released to reduce the population of rabbits + many died
but devlop immunity and population returned to previous levels
Out-competition
introduction of a new species into an ecosystem can result in it out-competing another native species
4 competitions of plants
Light
water from soil
mineral from soil
space
light
plants + algae need light for photosynthesis
competition for light as they grow quickly to reach it + shade other plants
old tree dies in forest there is a rave to fill gap in canopy
water from soil
reactant in photosynthesis so essesential
some fully grown trees eg. oak tree lose 150L of water every day + its used to transport minerals through the plant to leaves
Some plants have roots that are shallow but extend a long way from the tree to maximise the update of water after rainfall
Others have roots that are deep to find stores of underground water
minerals from the soil
require minerals for healthy growth
include nitrate + magnesium
Without sufficient minerals plants suffer deficiency diseases because they cannot grow healthily
space
require space for healthy growth
means their leaves are not shaded which maximises photosynthesis
very close planted = much smaller growth
Competition can be intraspecific, eg. competition between oak trees in a forest, or interspecific such as when another species of tree like birch or yew grew next to oak trees.
when older tree dies, younger trees compete to replace it
species that cannot compete effectively are unlikely to reproduce, and may die - known as survival of the fittest
3 competition in animals
food
mates
territory
food
all need food providing them with energy and raw materials to complete life processes
Because food is so vital, many animals will fight for it.
mates
within a species compete for mates
essential to pass on their genes to their offspring
evolved to have an innate or natural drive to reproduce - often results in fights
these fights competing for mates can often result in serious injury or death, but benefits the population as only the strongest pass on their genes to the next generation
territory
territory contain all of the resources and conditions they need to survive
These include abiotic factors + biotic factors
An example of intraspecific + interspecific competition over territory
intraspecific - be between lions on the grass plains of Africa
interspecific - occur when another predator like leopards lived close to the lions.
what can Plant adaptations be
structural
behavioural
physiological
what do all adaptations mean
make organisms better suited to their ecosystem
provide them with a better chance of survival and reproduction, which are their ultimate aims
what are adaptations that arise from competitions essential for
the process of evolution
survival of the fittest mean the survival of those best adapted
Structural adaptations in plants
these are physical features allowing plants to compete
eg. formation of spines in cacti + roses stop a plant from being eaten by grazing animals
another example, is animals with shallow roots to absorrb lots of water after rain
Behavioural adaptations in plants
these are behaviours which give them an advantage
eg, plant root grow toward light to maximise photosynthesis - ensures they can respond to changes in thier environment
others have evolved structural and behavioural adaptations to catch insects eg. venus fly tap - flytrap itslef is structural and closing of the trap to catch insect is behavioural
Physiological adaptations in plants
are processes which allow them to compete
eg.the formation of poisons for defence - deadly nightshade, are so poisonous they can kill if consumed by humans.
Structural adaptations in animals
physical features which allow them to compete
eg. sharp claws to catch prey, dig burrows or scratch trees to signal territories. The scratching of trees is a behavioural adaptation.
Predators and prey often have similar adaptations :
Both are likely to have good vision and hearing.
Prey often has eyes on the sides of their heads to easily spot predators.
Predators often have their eyes on the front of their heads to judge distance to their prey.
Behavioural adaptations in animals
behaviours which give them an advantage
eg, mating rituals, like a male peacock bird showing his tail feathers to attract a female mate.
eg. working together in packs like wolves to hunt prey
eg. using tools - crocodiles use twigs to lure birds, who would pick them up to build nests.
Physiological adaptations in animals
processes which allow them to compete
eg. production of venom that snakes and spiders have to defend themselves and kill their prey
what is an extremophile
an organism that lives in an extreme environment
The organisms that live in these places have …
highly specialised adaptations
The Polar Regions info
north pole - artic
south pole - antarctic (no polar bear but penguins)
both extremely cold - average : -40 degree celcius
in Northern hemisphere summer the North Pole has has 24 hours of daylight and the South Pole experiences 24 hours of night. This is then reveresed during the Northern hempisphere winter.
north pole animals + adaptations
polar bears have thick white fur for insulations + camouflage
have acute sense of smell + sight to hunt prey
small sa:v ratio to minimise heat loss
thick layer of fat to keep warm
south pole animals + adaptations
male Emperor penguins have evolved to insulate their egg on their feet throughout winter
This is a behavioural adaptation
what are Deep sea volcanic vents
places on the ocean floor where the volcanic gases of underground magma chambers bubble through.
how do species exist in Deep sea volcanic vents
bacteria feed on the chemicals released from the volcanic vents.
Worms feed on the bacteria, and then other species feed on the worms
These ecosystems are unique on Earth.
adaptations of these animals allows them to survive in these conditions