Animal Evolution
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
cnidaria
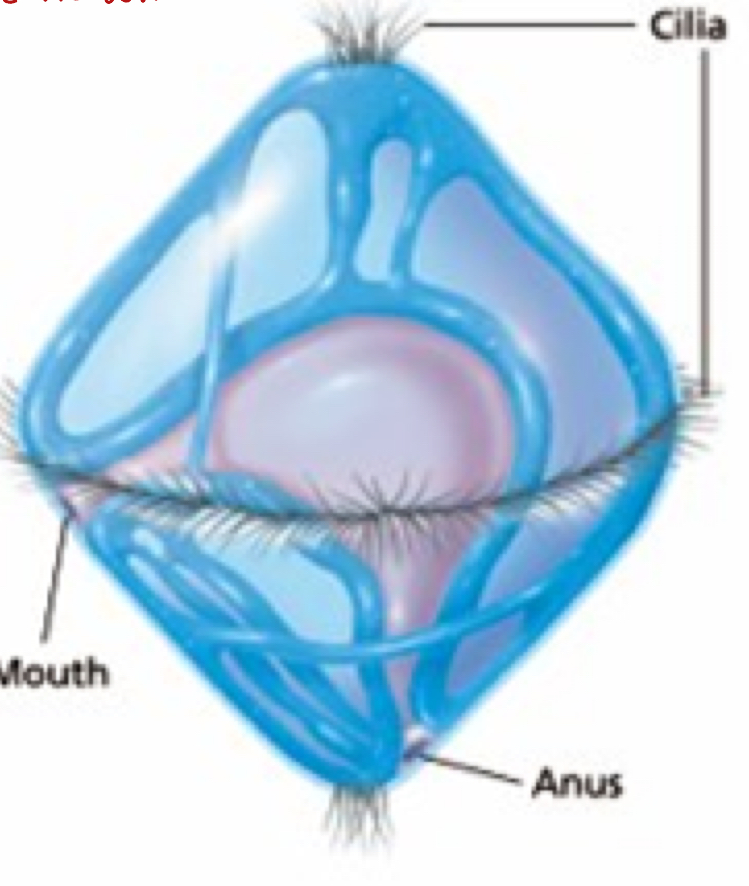
diploblastic with mostly acellular mesoglea; radial symmetry, nerve net, incomplete gut
medusae cnidaria
planktonic, predatory
polyp cnidaria
sessile, asexual
mesoglea
noncellular, gelatinous, structure and buoyancy
cnidocytes
stinging cells used to capture prey by cnidaria; may have toxins and chemicals; shared derived character
planula
free swimming larvae of cnidaria that sexually reproduce
anthozoa
sea anemones, corals
corals
colonies of polyps, calcium carbonate skeleton built by successive generations of anthozoa, basis of diverse communities
zooxanthelle makes anthozoa
autotrophic; symbiotic relationship
medusozoa
dominant stage; painful and toxic poison injections; moon jelly, box jellies, sea nettle; sea turtle resistant
colonies of polyps
Portuguese man-o-war, by the wind sailor
annelidia
homoplasious true segmentation; true worms in sea, freshwater, soil; coelomates, complete gut, chaetae; hermaphrodites (sexual)
chaetae
chitinous bristles
trochophore larva
shared with mollusks
annelida lifetyles
predators, filter feeders, detrivores, parasites, worms; some have parapodia
parapodia
pairs of paddle like appendages used for locomotion, gills
mollusca
marine, freshwater, terrestrial; filter feeders, herbivores, carnivores; coelomates, complete gut, reproduce sexually; gills, need moisture to move/gas exchange
foot (mollusca)
large muscle used for movement
radula (mollusca)
rasping feeding structure made of chitin teeth that scrape surfaces, drill, or harpoon food
mantle
protects internal organs, secretes shell
polyplacophora (mollusca)
chitons; basal taxon; grazing herbivores; distinctive 8 overlapping shell plates
gastropoda (mollusca)
coiled external shell; snails, slugs, nudibranchs; grazing herbivores and predators
gastropoda (mollusca)-nudibranches
eat cnidarians and keep cnidoctyes on back for protection; use mucus to prevent triggering stinging cells
flatworms mimic…
nudibranch toxicity (bastian)
bivalvia- mollusca
clams, oyster, muscle, scallops, filter feeders; two shells, simple eyes, adductor muscles to close shells, no radula (enlarged gills)
adductor muscles
holds bivalvia shells closed
cephalopoda
squid, cuttlefish, octopus, nautilus (basal taxon, external shell only); predators; modified foot and radula, complex eyes, beak
cephalopoda radula
beak like jaws, poisonous saliva
cephalopoda foot
tentacles, siphon (used for jet propulsion)
cephalopoda traits
shell moved inside mantle, gradually lost; chromataphores
chromatophores
specialized cells in skin containing pigments under precise nervous and muscular control; used for camouflage, communication
arthropoda
most diverse animal group; coelomates, sexual reproductions, separate sexes; exoskeleton of chitin; true segmentation; jointed appendages; well developed sensory system
arthropoda cuticle
exoskeleton made of chitin; can be flexible or hard, molt leaves body vulnerable until it hardens; keeps moisture in
true segmentation
jointed appendages lead to specialization of function
tagmosis
fusion of segments into functional units, division of labor between body parts (usually thorax, head, abdomen)
arthropoda: chelicerata
aquatic, terrestrial, predators, parasites; (ex: horseshoe crabs, arachnids); have chelicerae; two body regions cephalothorax and abdomen
cephalothorax
head and thorax together
book lungs
respiratory organs composed of many fine leaves; situated in the abdomen and have openings on the underside
arachnids
chelicerata; 4 pairs of legs, chelicerae, pair of pedipalps; unique web spinning, spinnerets
chelicerae
appendages that serve as pincers or fangs (plus poison glands in spiders)
pedipalps
appendages modified as sensory organs or for feeding (sucking mouthparts in ticks)
spinnertes
used to wrap nuptial gifts to females
arthropodia: crustacea
mainly aquatic; shellfish, pill bugs, barnacles; plankton larvae, filter feeders, scavengers; multiple modified appendages for feeding, respiration (most have gills)
chordata
4 derived characteristics (notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail)
notochord
longitudinal, flexible rod located under nerve cord; (vertebral disk all left in humans), fluid filled cells incased in fibrous tissue
dorsal, hollow nerve cord
develops from ectoderm rolled into tube; brain, spinal cord
pharyngeal slits
series of pouches separated by grooves along sides of pharynx (behind mouth); allows water to enter, exit body without passing through digestive tract; filter feeding and respiration
post-anal tail
tail that extends posterior to anus; used for locomotion in aquatic chordates
chordata: petromyzontida
lampreys; aquatic ectoparasites; sister taxa to mynixi; vertebral column with flexible cartilage sheath (no collagen) with small projections; no jaws, keratin teeth; evolved paired fins, inner ear with semicuricualr canals for balance
codont
extinct early vertebrae with mineralized teeth, suspension feeder
mineralization of endoskeleton began in…
mouth
jaws evolved from…
anterior gill arches (hypothesized)
lateral line system
organs in rows on body sides sensitive to vibrations; do not need to see, can feel instead
chordata: chondrocytes
sharks, skates, rays; mostly cartilaginous skeleton; placoid tooth like scales
sharks
chondrocyte; powerful swimmers, liver oil for buoyancy, sink if stop swimming, can pump water over gills if resting; receptors in head detect electric field, acute olfactory senses; predators (swallow prey whole, take large chunks with rows of teeth)
skates and rays
chondrocyte; dorsoventrally flat, use enlarged pectoral fins to fly underwater; crush prey with jaws, spikes and poisonous barbs on tails for defense
chordata: osteichthytes
bony fish; ray finned fishes (Actinopterygii); lobe finned fishes (Actinistia); lungfishes (Dipnoi); ossified skeleton; operculum; internal or external fertilization, varied parental care
ray finned fishes (Actinopterygii)
(Actinopterygii); bony rays support fins; seahorses, eels, salmon
lobe finned fishes
(Actinistia); rod-shaped bones in fins; coelocanth
lungfishes
(Dipnoi); have lungs, can breathe air
ossified skeletion
skin with bony scales, mucus to reduce drag; mineralized skeleton throughout whole body
operculum
protective bony flap; covers gills
lineages that evolved lungs
bony fish living in oxygen poor shallow estuaries
lungs evolved into the…
swim bladder
swim bladder
air filled sac to control buoyancy
lung-bearing lineages evolved…
lobe fins to ‘walk’ along bottom
tertrapods
animals with 4 limbs and digits
modifications from land…
head separated form body by neck; bones of pelvic girdle fused to backbone (lets them stand against gravity
tiktaalik
oldest known official tetrapod fossil, insight into how ancestor looked
chordata: amphibia
frogs, toads, salamanders, caecilians; carnivores that feed with sticky tongue to catch prey; rely on skin for gas exchange; throat muscles to inflate lungs; some aquatic some terrestrial; camouflage or aposematic coloration; external fertilization, eggs must be wet
toads
leathery skin, live in dry habitats
caecilians
lost legs, nearly blind burrowers
frogs
court females with loud vocalizations
salamanders
long tail