Databases Midterm
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Common Uses for Database Systems
Recording or maintaining Inventory
Local Libraries
Transactions
Customer Management
What is a file based system?
Collection of application programs that can perform services for the end users.
Each program defines and manages its own data
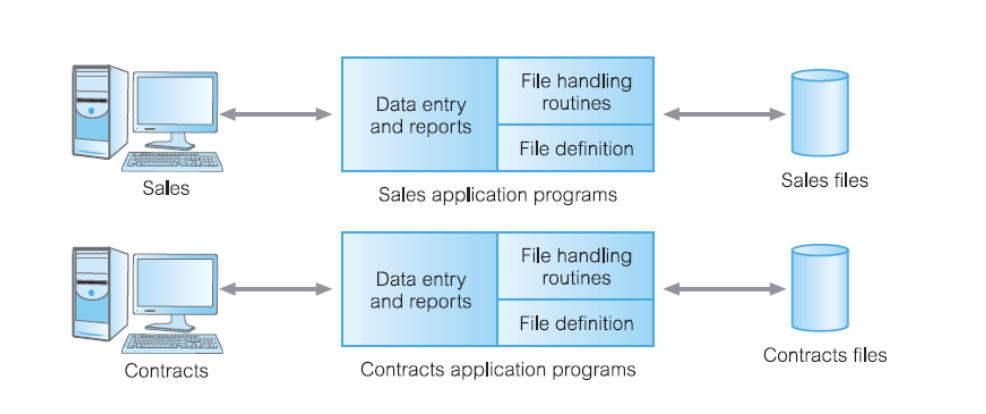
What is this type of processing? Explain the processing
File Based Processing: Each computer program has its own separate data that handles the same information but within its own category (e.g. Sales and Contracts)
What are limitations of File-Based Approach
Separation and Isolation of Data
Duplication of data
Data Dependence
Incompatible file formats
Fixed Queries/Proliferation of application programs
What is DBMS?
Database Management System is a software system that enables users to define, create, maintain, and control access to the database
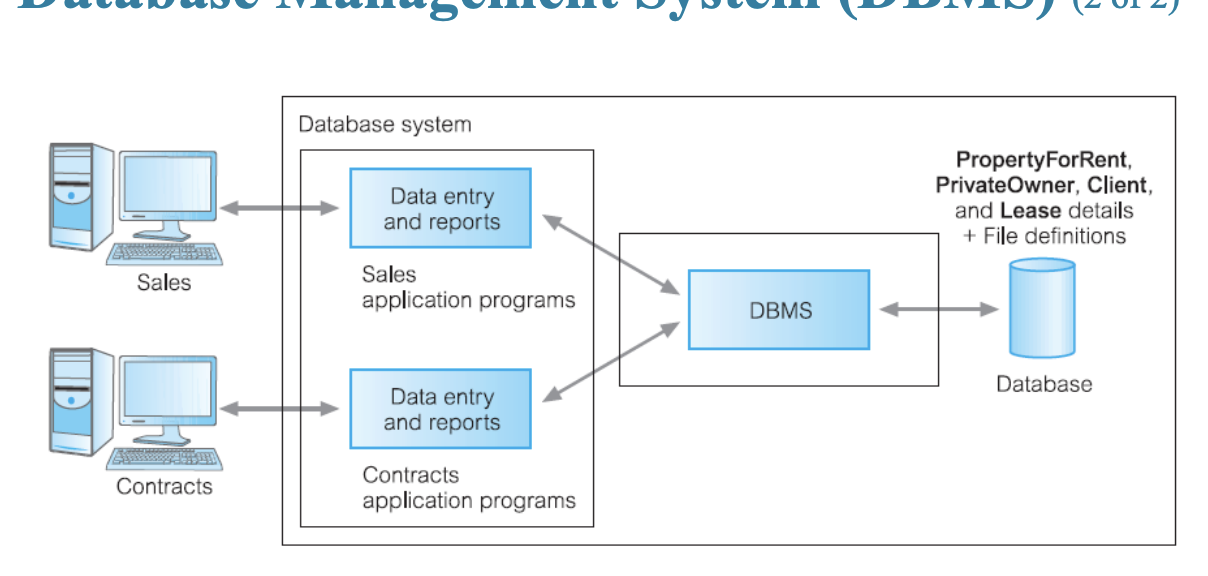
What type of processing is this? Explain the processing
Database Management System: Each computer program is within the same database system, they both use the same database management system that connects the same datatypes, structures and data constraints.
What are a DBMS typical functions?
Data Storage, Retrieval, and Update
USer Accessible Catalog
Transaction Support
Recovery Services
Authorization Services
Support for Data Communication
Integrity Services
Services to Promote Data Independence
Utility Services
Data Definition
The components within a database table that holds its relative ID, the user it belongs to, etc:
Example: Table Employee, Their employee ID, First Name, and Last Name, and the date they were Hired.
Data Storage
storing and organizing data efficiently
Example: Hard drive, Disk, Cloud
Data Retrieval
User Query’s the database to retrieve specific information. DBMS processes the queries and returns the requested data
example:
SELECT country, COUNT(*) AS total_ customers
FROM customers
GROUP BY country
HAVING COUNT (*) > 10;Data manipulation
Updating, inserting, deleting data in the database
Data Security
The DBMS provides mechanisms to control access to the data, ensuring that only authorized users can view and modify it. This includes user authentication, access control lists, and encryption
Data integrity
The DBMS enforces rules to maintain the accuracy and consistency of the data
Example: primary keys, foreign keys, and check constraints
Concurrency Control
Multi user environments, the DBMS manages simultaneous access to the data to prevent conflicts and ensure data consistency
Backup and Recovery
The DBMS provides tools for backing up data and restoring it in case of data loss or failures
Advantages of using DBMS
Balance conflicting requirements
Improved data accessibility and responsiveness
Increased productivity
improved maintenance through data independence
Increased concurrency
Improved backup and recovery services
Disadvantages of using DBMS
SIZE
complexity
cost of DBMS
additional hardware costs
higher impact of a failure
Roles in the Database Environement
Data Administrator
Database Administrator
Database Designers (Logical and Physical)
Application Programmers
End Users (Naive and sophisticated)
Data Administrators responsibilities
defining data elements, data names, and their relationship with the database
Database Administrator Responsibilities
works on creating, maintaining, querying, and tuning the database of the organization. Also maintains security and Integrity
Database Designers (Logical) Responsibilities
identifying the data, the entities and attributes, the relationships between the data, and the constraints, on the data that is to be stored in the database. Needs to have a complete understanding of the organizations data and any constraints on this data
Database Designers (Physical) Responsibilities
decides how to logical database design is to be physically realized: mapping the logical database design into a set of tables and integrity constraints
Selecting specific storage structures and access methods for the data to achieve good performance
Application Programmers Responsibilities
required functionality for the end users must be implemented by the application programmers once the database has been implemented
These developers interact with the database with DML queries that are written in C, C++, Java, and Pascal
End Users (Naive) Responsibilities
Uses existing applications to interact with the database. Ex. online library system, ticket booking system.
End Users (Sophisticated) Responsibilities
familiar with the structure of the database and the facilities offered by the DBMS
3 Objectives of Three-Level Architecture
All users should be able to access the same data
A Users view is immune to changes made in other views
users should not need to know physical database storage details
change database storage structure without affecting users views
Internal structure of database should be unaffected by changes to physical aspects of storage
Change conceptual structure of database without affecting all users
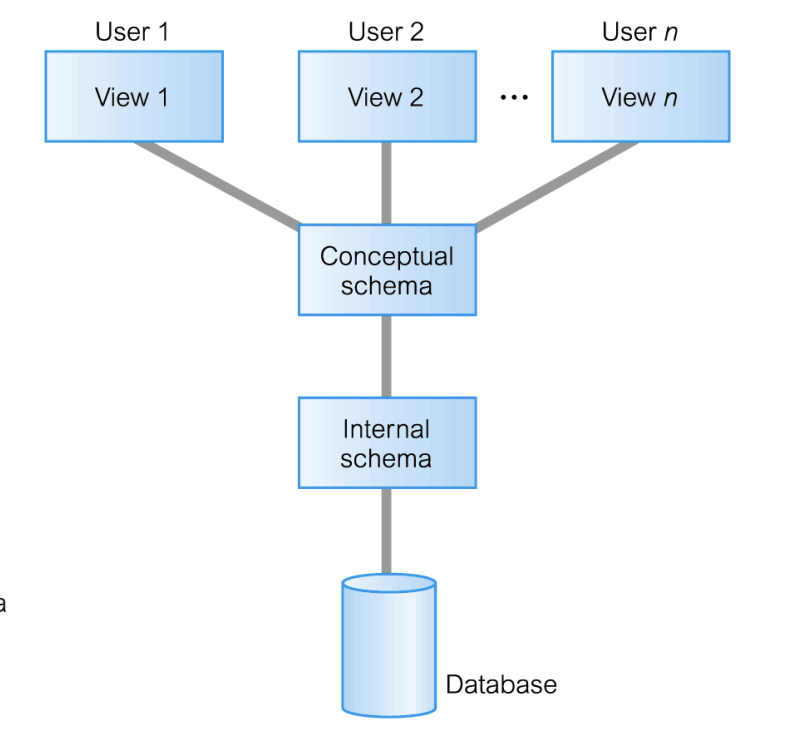
What are the levels of this ANSI-SPARC 3-lvl Architecture (top to bottom)
External level, Conceptual level, Internal Level, Physical Data Organization
What is the External Level in the ANSI-SPARC 3-lvl Architecture
Users view of the database
Describes that part of database that is relevant to a particular user
What is the Conceptual Level in the ANSI-SPARC 3-lvl Architecture
Community view of the database
Describes what data is stored in database and relationships among the data
What is the Internal Level in the ANSI-SPARC 3-lvl Architecture
Physical representation of the database on the computer
Describes how the data is stored in the database
Whaat can the External View contain?
What will the Conceptual level contain?
What will the Internal level contain?
Data Models:
List all the Data Models
Relational Data Model
Network Data Model
Hierarchical Data Model
What Data Model is this?
Relational Data Model
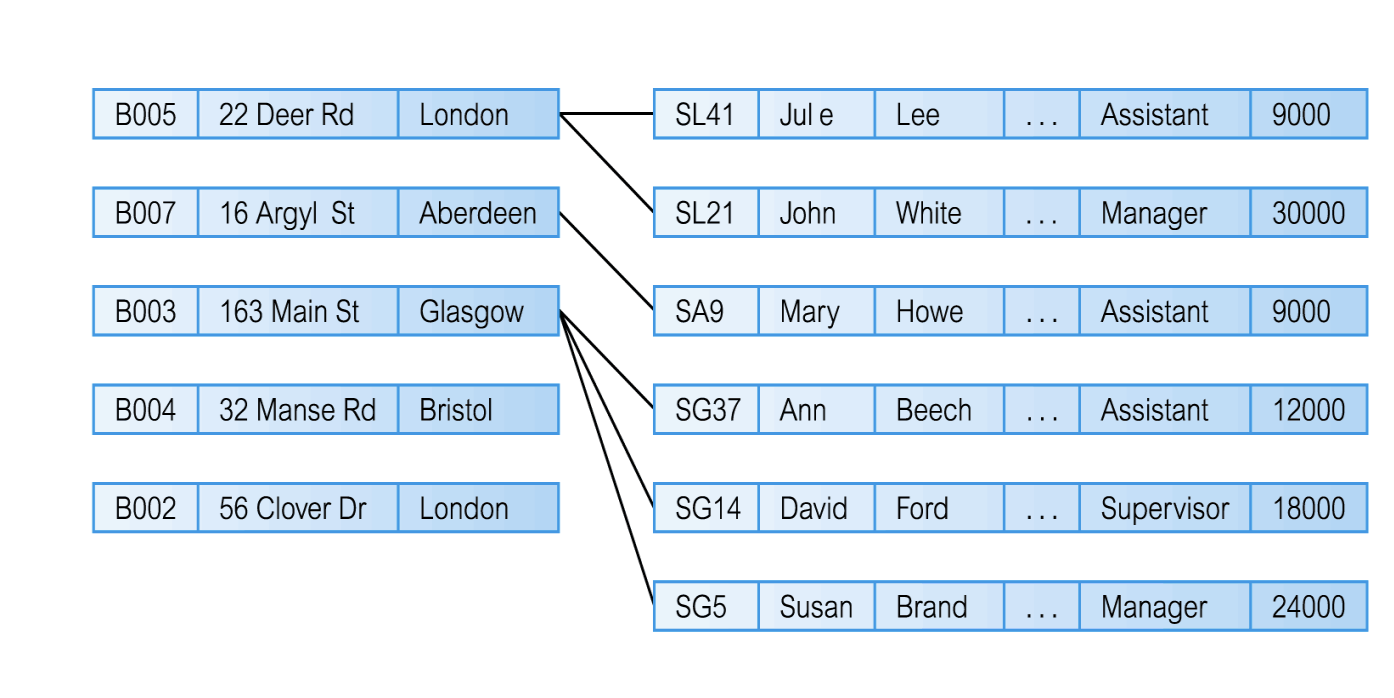
What Data Model is this?
Network Data Model
What Data Model is this? H
Hierarchical Data Model
What is a system catalog?
A fundamental component of DBMS and Repository of Information (metadata) describing the data in the database.
What does a system catalog typically store?
names, types, and sizes of data items; constraints on the data;
names of authorized users;
data items accessible by a user and the type of access;
usage statistics
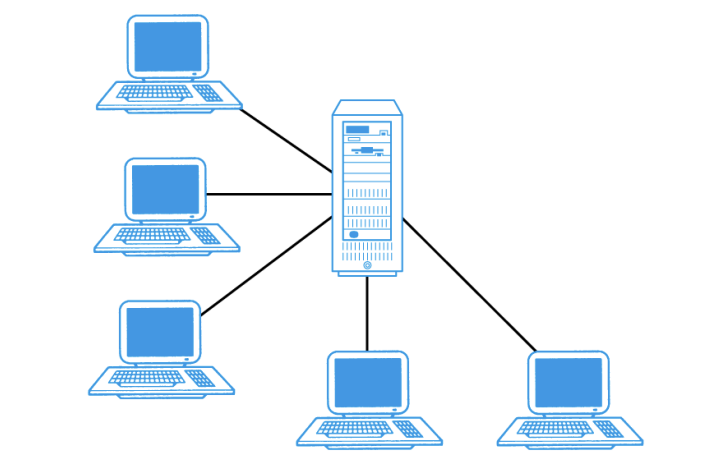
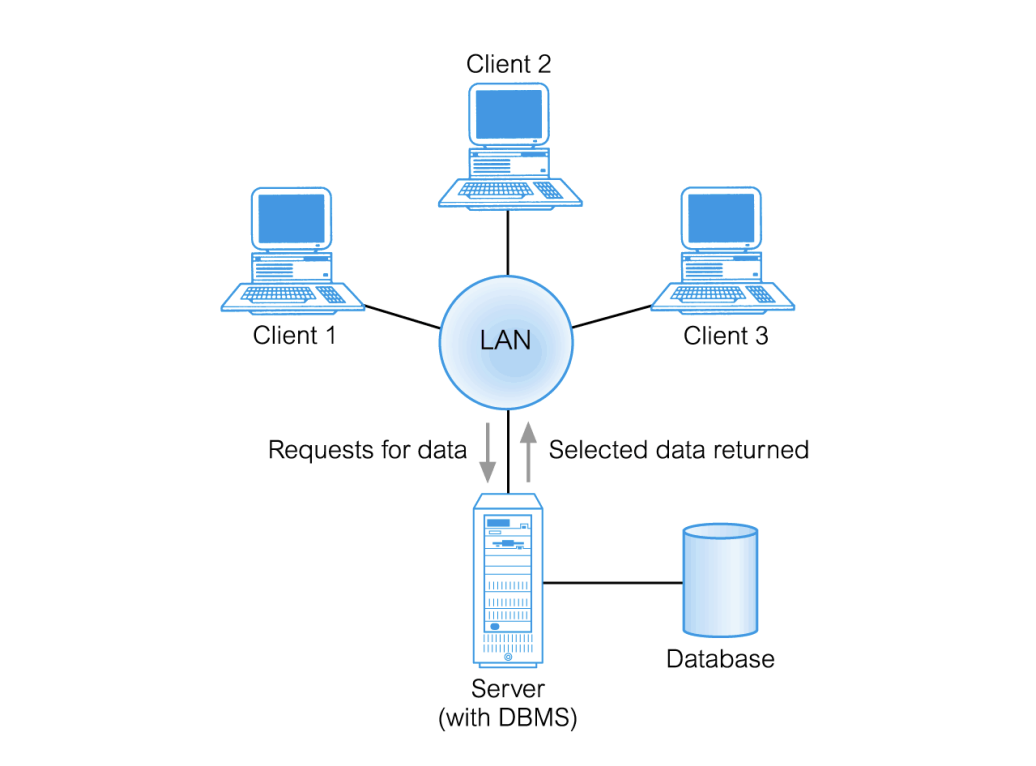
Explain the teleprocessing architecture
Traditional architecture
single mainframe with a number of terminal attached
Trend is now towards downsizing
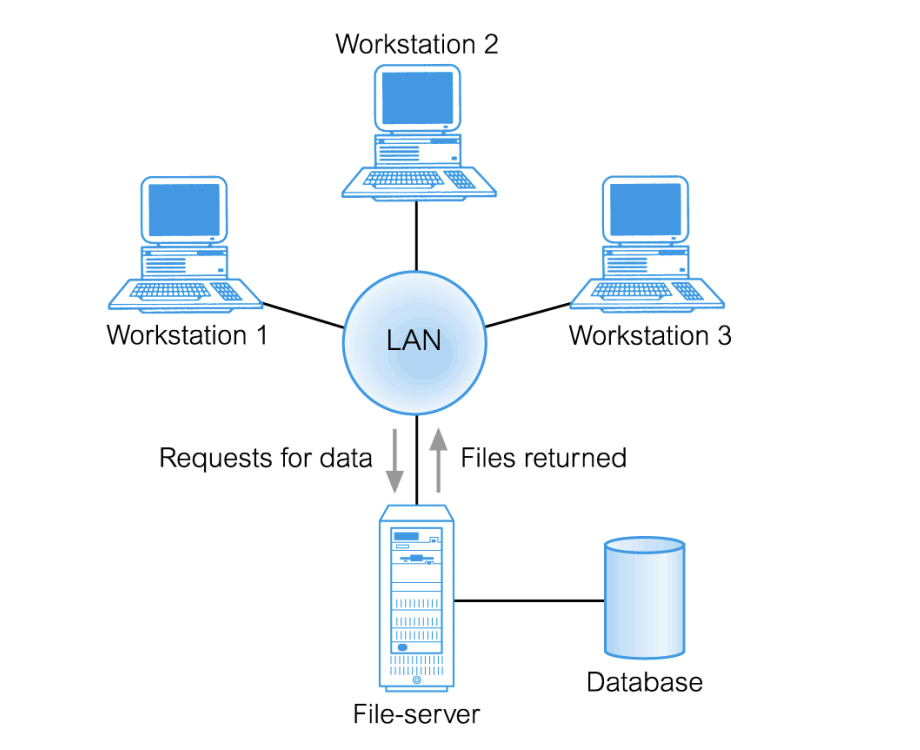
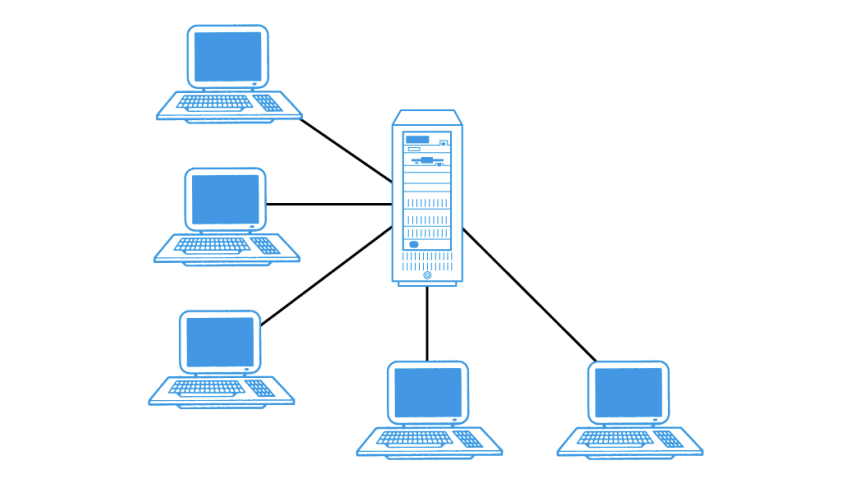
File-Server
connected to several workstations across a network
DB resides on it
DBMS and Applications run on each workstation
File-Server disadvantages
significant network traffic
Copy of DBMS on each workstation
concurrency, recovery, and integrity control more complex
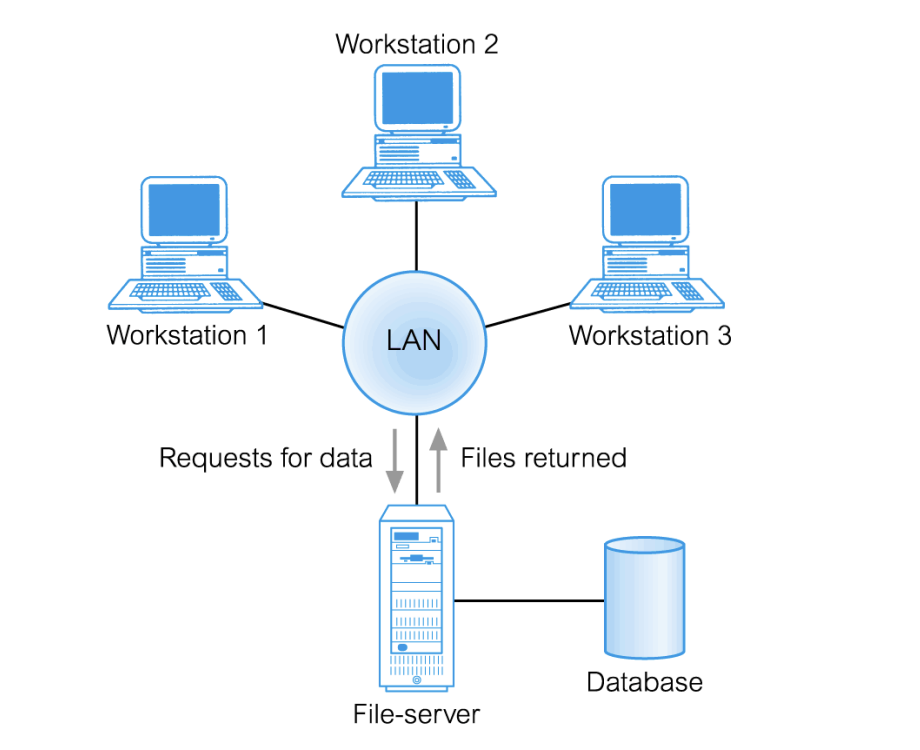
What architecture is this?
File Server architecture
What architecture is this?
Teleprocessing architecture
What architecture is this?
2 tier client server architecture
Traditional Two-Tier Client Server:
Tier 1 Client: Manages user interface and runs application
Tier 2 Server: holds database and DBMS
Traditional Two-Tier Client Server Advantages
wider access to existing databases;
increased performance;
possible reduction in hardware costs;
reduction in communication costs;
increased consistency.
Three- Tier Client Server Advantages
‘Thin’ client, requiring less expensive hardware.
Application maintenance centralized.
Easier to modify or replace one tier without affecting others.
Separating business logic from database functions makes it easier to implement load balancing.
Maps quite naturally to Web environment
What is Transaction Processing Monitors?
program that controls data transfer between clients and servers in order to provide a consistent environment, particularly for online transaction processing (OLTP)
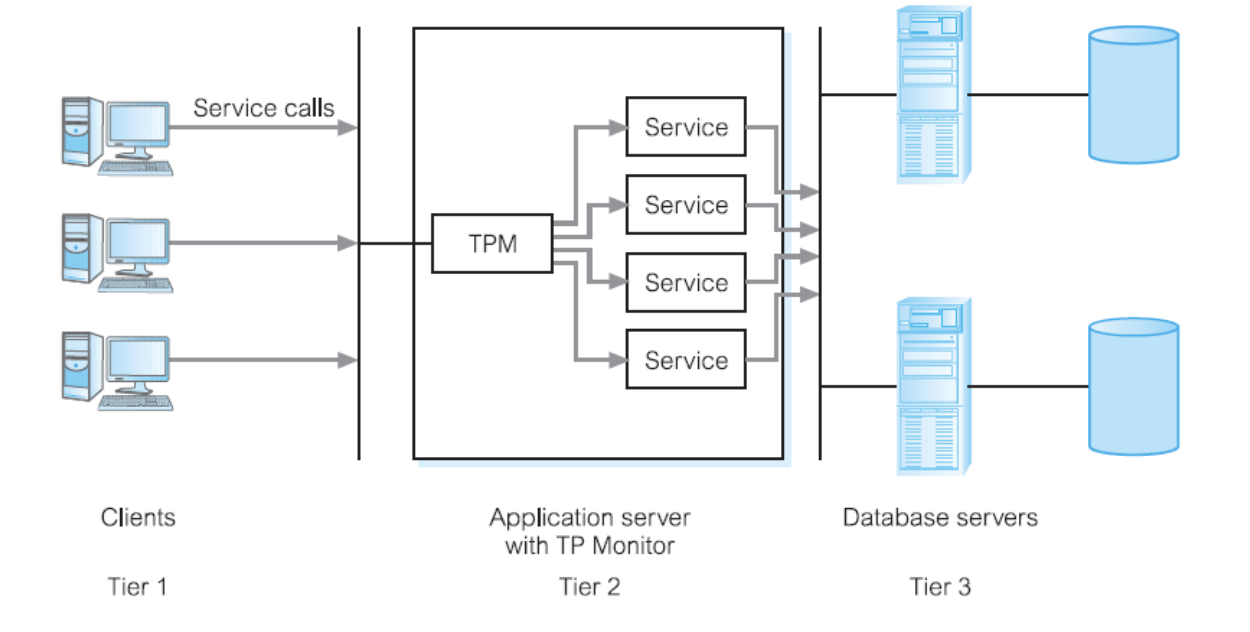
What model is this?
Transaction Processing Monitor as Middle Tier of 3-Tier Client-Server
What is SaaS?
Software as a Service: Software and data hosted on the cloud.
How is SaaS accessed?
thin client interface (web browser)
Rapid elasticity in cloud computing
Providers capacity caters for customers spikes in demand and reduces risk of outages and service interruptions. Capacity can be automated to scale rapidly based on demand
Risks of Cloud Computing
Network Dependency
System Dependency
Cloud Provider Dependency
Lack of control
lack of information on process transparency
What is a relation in the context of the relational model
a table with columns and rows logically
what are a relations key components?
Attributes, Domain, Tuple, Degree, Cardinality
Attribute
named column of a relation
Domain
set of allowable values for one or more attribute
Tuple
row of a relation
Cardinality
number of tuples in a relation
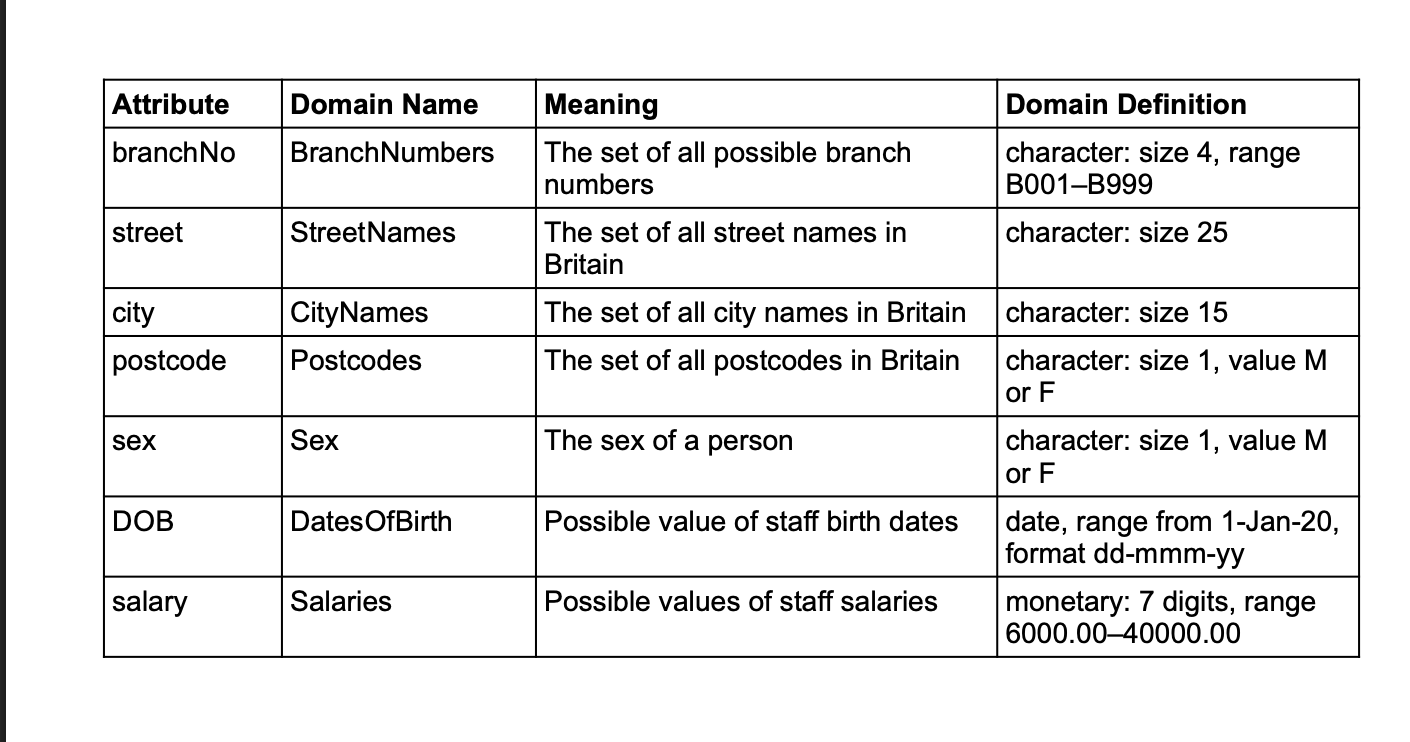
In a relational Database, what is this an example of
Attribute domains
Explain the difference between a primary key, a candidate key, and a foreign key
Primary: identifies unique tuples within relation
Candidate: A table can have multiple candidate keys, but only one is chosen as the primary key.
Foreign: attribute, or set of attribute, within one relation that matches candidate key
What is entity integrity, and why is it mportant in relational databases?
in base relation, no attribute of a primary key can be NULL
What is referential integrity, and why is it mportant in relational databases?
If foreign key exists in a relation, either foreign key value must match a candidate key value of some tuple in its home relation or foreign key value must be wholly null.
What are the primary purposes and advantages of using views in a relational database?
providing powerful and flexible security mechanism by hiding parts of database from certain users. Can simplify complex operations on base relations. Permits users to access data in a customized way so that the same data can be seen by different users in different ways, at the same time
What are five basic operations in relational algebra?
selection
projection
union
set difference
Cartesian product
TRC
Tuple relational Calculus: whole tuples (rows):
|
DRC
Domain Relation calculs: individual fields (columns):
StudentID, Name, Age