Advanced Viticulture 331
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Ampleography
verification of species based on physical features, observable characteristics of the grapevine
Grafting
attaching the root stock to the scion, creates a bulge near the soil
Mothballing
Keeping the vineyard at a low maintenance level until market recovers and you profit again
Why are cordon and trunks different?
cordons grow new canes every year, while the trunk has gone through bark formation
Root systems function
stabilize, pest management, phytohormone management(synthesize and send them out to the vine to be used), stops leaf from losing more water (drought stress), nutrients, carbohydrate storagem, abscisic acid(promotes leaf detachment, dormancy)
Trunk Function
storage, transport, protection from chemical/phsysical pressures, connects top of the vine with roots
Function of cordons
storage, transportation of nutrients into the canopy
Cane/Shoots function
support leaves, reproduction system is on thesem contain the buds, provide energy(photosynthesis)
Leaf Function
photosynthesis, pull nutrients and redirect them back to the shoot which then reallocates to active growing parts, redirect nutrients for vines to store nutrients over winter, greater surface area for photosynthesis, transpiration(water vapor), tempurature regulation
Three different types of bud
compound dormant bud, lateral/secondary shoots, latent buds(create more shoots if huge frost comes in)
Sessile organisms
plants, an organism that is anchored to a substrate and cannot move freely
Abiotic Stress
high temp, low temp, salinity, toxic elements, drought, pH
Biotic Stress
bacteria, insects, viruses, fungi, herbivores, nematodes
Developmental plasticity
ability to bend organs in order to reach the position most optimal for growth and utilization of light, nutreints and other resources
Plant cells have more membranes and walls true or false
True
Lianas
woody vines, like a grapevine
Perennial
have an annual lifecycle but live for a long period of time - live for more than two years
Polycarpic
will continue to produce fruit many times, over a long period of time - i.e grapevines
Deciduous
shed their leaves when dormant, then regrow them next spring
morphology
form, shape, appearance, external appearance of the vine including clusters, cane, shoot, leaf, root, trunk
Anatomy
the study of internal structure of grapevine organs, usually at the the microscopic or tissue level
Cane is more developed than the shoot T/F
True
Vegetative organs
structural part of the plant - shoot, trunk, tendril, cane, root system
Reproductive organs
flower, cluster, seed
Bud contains both vegetative and reproductive parts
True
What are the permanent parts of a vine
roots, trunk, and cordons
What are the non permanent parts of a vine
shoots/cane, leaves, tendrils, flowers and clusters
How old do canes have to be to grow fruit
one year, produces the best quality
Root tip/apex
critical part of the root responsible of growth and soil penetration
Elongation Zone
cell expansion and differentiation of tissues, as cells elongate it pushes the root forward so they can grow
Meristematic zone
active cell division, have stem cells, helps the root to function(absorption through root hairs
Root cap
protection, facilitate root expansion, gravitropism(growth due to gravity)
VAM
Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrizae - type of endomcycorrizal fungie that form a symbiotic, mutualistic relationship with the roots, providing increases access to water and nutrients(especially phosphorus, zinc and sulfur) in exchange for sugars from the plant
Epidermis
sking around the outermost layer of cell
cortex
body of the root
vascular tissues
phloem(sugar)- to move it back down from the leaves and xylem(water) to transport from roots to the parts of the plant
Root hairs
high turnover rate, as root elongates the maturation zone moves along wiht it, hairs die and then regrows to the new part of the root - only confied to maturation zone
Spur
cane that is cut back, piece of cane from last year
Trunk
permanent stem of the vine, forms a connecting pipeline between roots and arms, the vegetative vigor, fruiting, and life span of the entire vine depends on the health of the trunk
Arms
wood older than 2-3 years that bears the spurs and canes retained at pruning, their sturcture is the same as a shoot, become thicker every year
Axil
Where the petiole of leaf is connected to the shoot, which is on the node
Apical Meristem
Cell division is happening, the main shoot growth length occur here located at the shoot tip
Responsible for organ formation, tissue formation
Three types of buds
Compound Dormant buds - produce primary shoots
Lateral prompt buds - produce lateral shoots
Latent buds - produce water sprouts and suckers
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy.
Every leaf blade consists of
epidermis, a single palisade layer, three layers of spongy mesophyll, few large and several small veins comprising xylem and phloem vessels
Stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move - let CO2 out
Grape flower is a
perfect flower
Pistil
Female: stigma style ovary
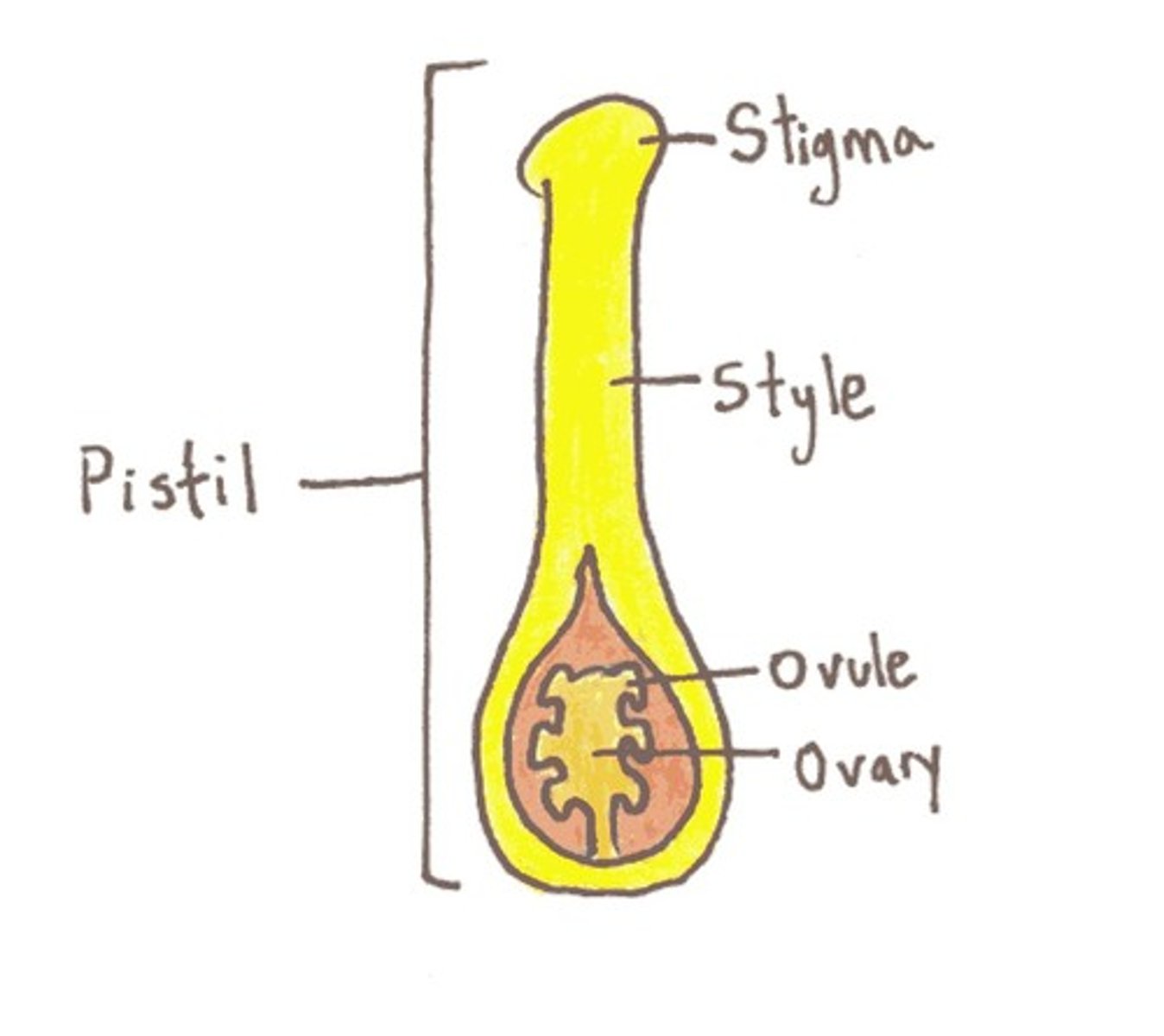
Stamens
Male: anther and filament with pollen sacs
Stage 1 of berry growth
cell division and elongation
Stage 3 of berry growth
via elongation only
Verasion
onset of ripening, occurs between stages 2 and 3
Lignified
convert into woody structure
Lag Phase
berries are not growing in size, seeds are solidifying
xylem function slows down, and stops at stage 3, then its driven by phloem tissue
End of Lag Phase
Berries start to soften and change color, white grapes become translucent
Once ripening has started
berries grow rapidly again, driven entirely by cell expansion rather than divsion
How long have vitis vinifera been cultivated for?
8000 years
What is the origin of vitis vinifera
Vitis sylvestris
Vitis Labrusca
for juice mostly
Taxonomy
The science of classifying organisms
Genus
first part of the name identifies the genus to which the species belong i.e vitis
Species
the second part identifies the species of the genus i.e vinifera
Kingdom --> division --> subdivison --> class --> order --> family --> division
order of identifiying plants
Kingdom
Plants are
1. multicellular - form a tissue, purpose, form organs
2. Eukaryotic - organism composed of cells that have a membrane bound nucleus, membrane bound organelle(mitochondria, chloroplast)
3. Photosynthetic - carbon dioxe and water in presence of sunlight converts to sugar
Division
Tracheophytes = vascular plants
Xylem and phloem ar conducting water and nutrients, grapevines have large xylems
Subdivision
Spermatophytes = plants that produce seeds
Class
Angiosperms: grow their seeds inside an ovary that is embedded in a flower, flowering plants
Order
Rhamnales
Family
vitaceae - characterized by the occorance of tendrils and inflorescence opposite to leaves
How many seeds to grapevines have
2-4 seeds, dicots, if all four get fertilized then you have four seeds
Seed:
A plant organ comprising the embryonic plant and the food storage tissues(endosperm), formed by the maturation of the ovule following fertalization
What are the only two genus referred to as grapevines?
Vitis and Muscadinia
Vitis tendrils
come in pairs, two nodes will have tendrils, and one above and below will not have tendrils, tendrils and clusters are opposite of the leaf on stems
Muscadania
speckles on skin and stems which are the lenticels present on muscadine grape berries, non shredded bark, continous pith
tendrils do not split, on every node
seeds are flatter, ribbed
slip skin
resistant to fungi and phylloxera
Lenticel function
gas exchange, O2, CO2, and water vapor
Vitis
absent of lenticels on the berries, shredded bark, discontinous pith(diaphram)
tendrils split in two, come in pars, one above and one below will not be on the nodes
Seeds: no ribs, ovent
Skin: adheres to pulp
How many species is vitis comprised of
60-70
Eurasian group (around 40)
American Group(around 20)
Riparia(river grape)
not drought resistant, frost resistant because it goes dormant eraly, highly vigorous has acces to a lot of water(river)
Rupestris
red petioles, small leaves compared to riparia, drought tolerant depending on soil characteristics
Berlandieri
highly drought and salt tolerant, perfect flowers, nice clusters, doesnt root well - not used as root stocks
Labrusca
species that brought back to europe that carried phylloxera (used for juice)
Somatic Mutation
natural changes in DNA of a grapevines cells that lead to new varieties, mutations can affect the appearance, flavor, and other traits of the plant
Hermaphroditic flowers
each flower contains both male and female reproductive organs
What is a Cultivar?
international code of nomenclature for cultivated plants - plants that sufficiently distinct, uniform, and stable in its characteristics that when propogated by appropriate means retains those characteristics.
If grapevines have been cloned all over the world why are they different?
Location, environmental factors, spontaneous DNA which causes mutations to cause different characteristics - Somatic mutation: natural changes in DNA of a grapevine cells that lead to new varieties which can affect appearance, flavor, other traits
Allelopathy
reduced growth of neighbouring plants, release of water soluble phenolic compounds
When leaves are shed and plant goes dormant, leaves have chemicals that can surpress growth of other plants.
Stage 1 of berry growth
Berry growth via cell division and elongation
starts immediately after bloom
- berries are firm and green (chlorophyll)
- low sugar content
- organic acids accumulate
- number of cells growing and maximises but volume does not maximize
Flow rate for xylem(water) and phloem(sugar, acids) is high
Stage 2 of berry growth
Lag phase of berry growth
slow growth
organic acid concentration reaches maximum
- berries remain firm but start losing chlorophyll
- seeds start to harden - can feel the seed inside
- number of cells stay constant but volume is increasing by phloem (veraison)
Stage 3 of berry growth
berry growth via elongation only
berry growth restarts after lag phase and ripening
- berries start to soften and lose chlorophyll
- red varieties start accumulating red pigments - ANTHOCYANINS
- sugars accumulate and concentration of organic acids decline
- aroma and flavor components accumulate
- number of cells already maxed, but volume grows until it maxes out
- sugar accumulation: 5mg/day for small berries to over 50mg/day for larger berries
- xylem stops,but phloem brings a lot of sugar at this point into the berry so acid concentration goes down because it is diluted by the sugar
Mature berry composition
70-80% water
20-25% sugar(brix)
TA and pH is inverse relationship
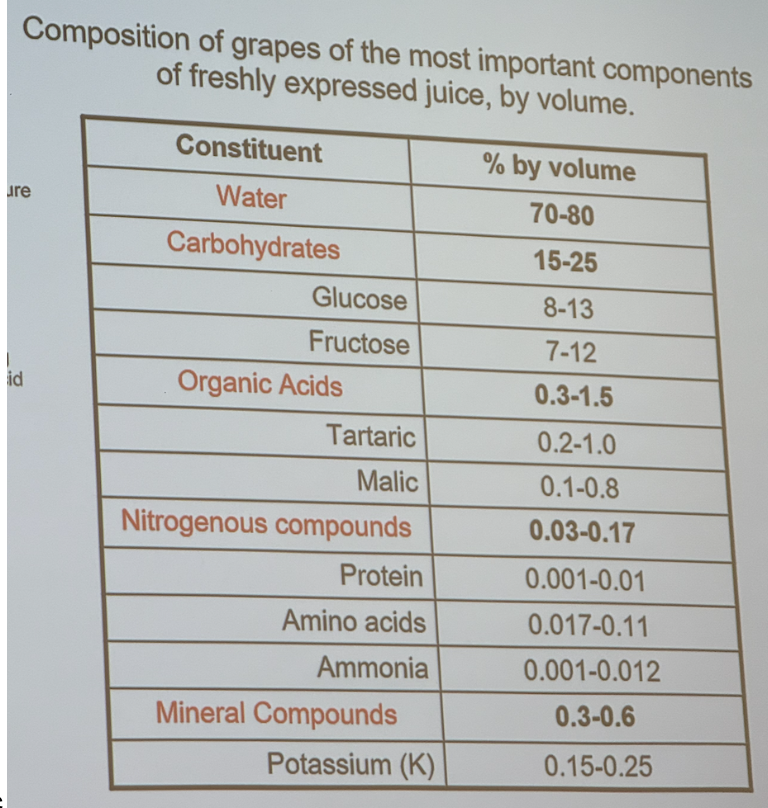
Carbohydrate types in mature berry growth
Glucose 8-13% by volume
Fructose 7-12 % by volume
Organic Acid types in mature berry
Tartaric 0.2-1% by volume
Malic 0.1-.08% by volume
What acids makes up 90% of total fruit acidity?
Tartaric acid and malic acid
Tartaric Acid
stable at high tempurature and resistant to microbial degradation
Malic Acid
hot periods accelerate its degradation (wine with flat taste)
Tool to measure sugars or TSS
Refracto Meter to measure brix(refracting the light) - measure the angle and then convert that into percentage of sugarW
why is sugar measurement so important?
To know how much alcohol there will be, since sugars are converted into alcohol by yeast during fermentation, you can roughly calculate the ABV if you know the sugar concentration
Alcohol % = 0.57 x Brix (the 0.57 can vary)
Factors that influence grape cahracterisitcs of harvest
Variety, temp, light intensity, exposure to light, crop level, nutrient availability
Vine Capacity
total biomass of crop and vegetative growth
Vine Vigor
refers to the rate of growth of a grapevine, essentially how quickly and actively the vine is producing new shoots and leaves
vigor doesn’t mean size9