11 Biology - Receptors
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Rods
Are sensitive to intensity of light, not colour.
Cones
Photoreceptors that respond to colour
Synapses
Junctions between neurons that allow communication through neurotransmitters.
Effectors
Parts of the body that are sent messages in response to the stimuli. These can be either muscles of glands
Image of a Neuron
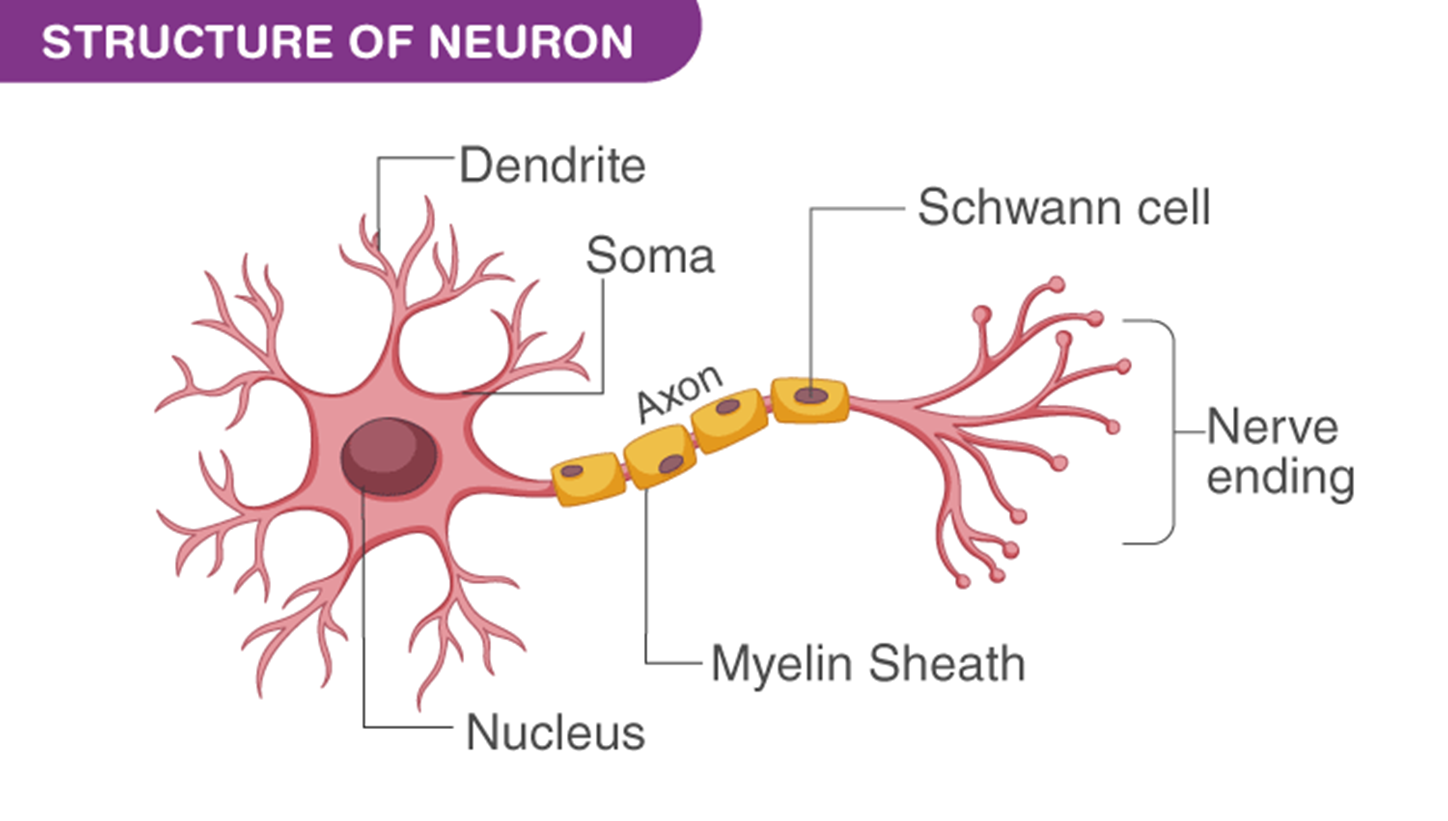
Purpose of the Soma / Neuron cell body
Electrical signals are generated in the soma and sent down the axon to the nerve endings.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical signals use chemicals called neurotransmitters such as dopamine, adrenaline, and serotonin. Neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors to either excite or inhibit them.
CNS (Central Nervous System)
Consists of the Brain and Spinal cord. Processes sensory information and coordinating voluntary and involuntary actions.
PNS (Peripheral Nervous System)
Consists of the cranial and spinal nerves, and the ganglia (cluster of nerve cell bodies located outside the CNS). Activates voluntary movement and regulated involuntary body functions such as heartbeat, digestion, and breathing.
Key Difference between the CNS and PNS
CNS is the main control centre processing information, while the PNS has a task in communication relay between the stimuli and the brain.
Afferent Neurons
Carry signals towards the CNS from sensory receptors in the body.
Efferent Neurons
Carry signals away from the CNS towards the effectors (muslces and glands).
Spinal Cord (Cross-section)
A central H-shaped grey matter (neuron cell bodies) surrounded by white matter (myelinated axons) that transmit sensory and motor signals.
Action Potential